Compact Design of a 50° Field of View Collimating Lens for Lightguide-Based Augmented Reality Glasses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Optical Design Method
2.1. Subsection Microdisplay Specifications
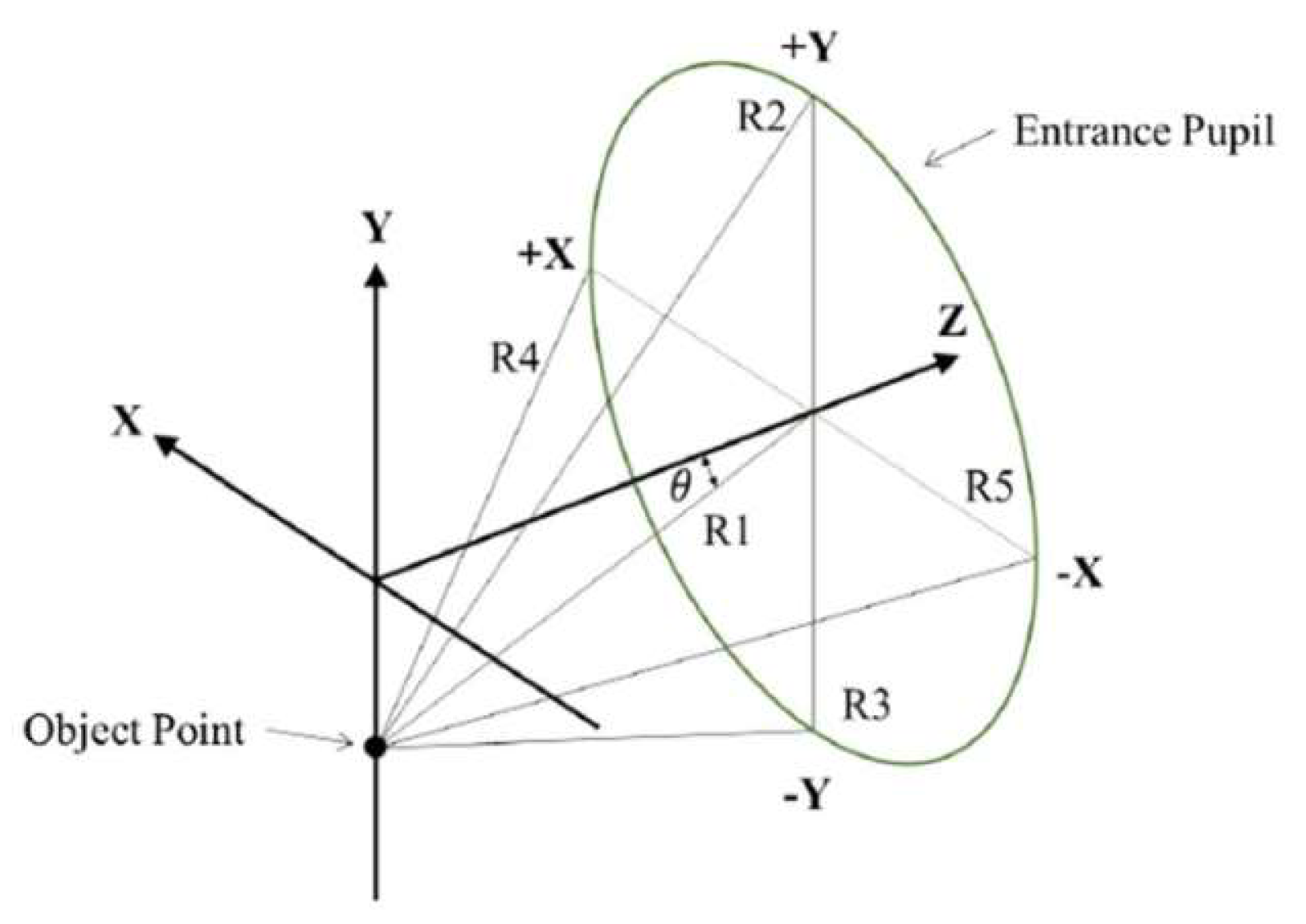
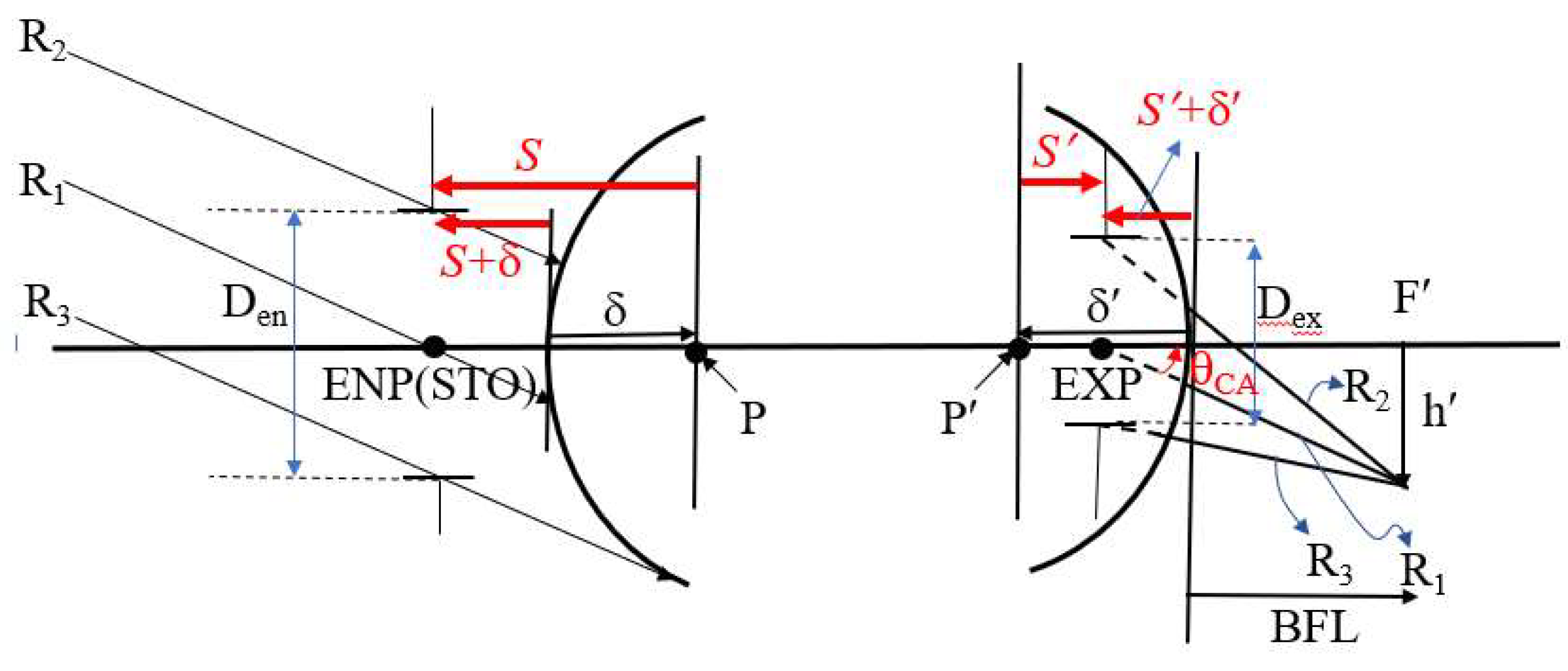
2.2. Five Reference Rays on the Entrance Pupil
2.3. Clear Aperture Calculation of the Lens
2.4. Relationship Among Half FOV, Image Height, Entrance Pupil Diameter, and Effective Focal Length
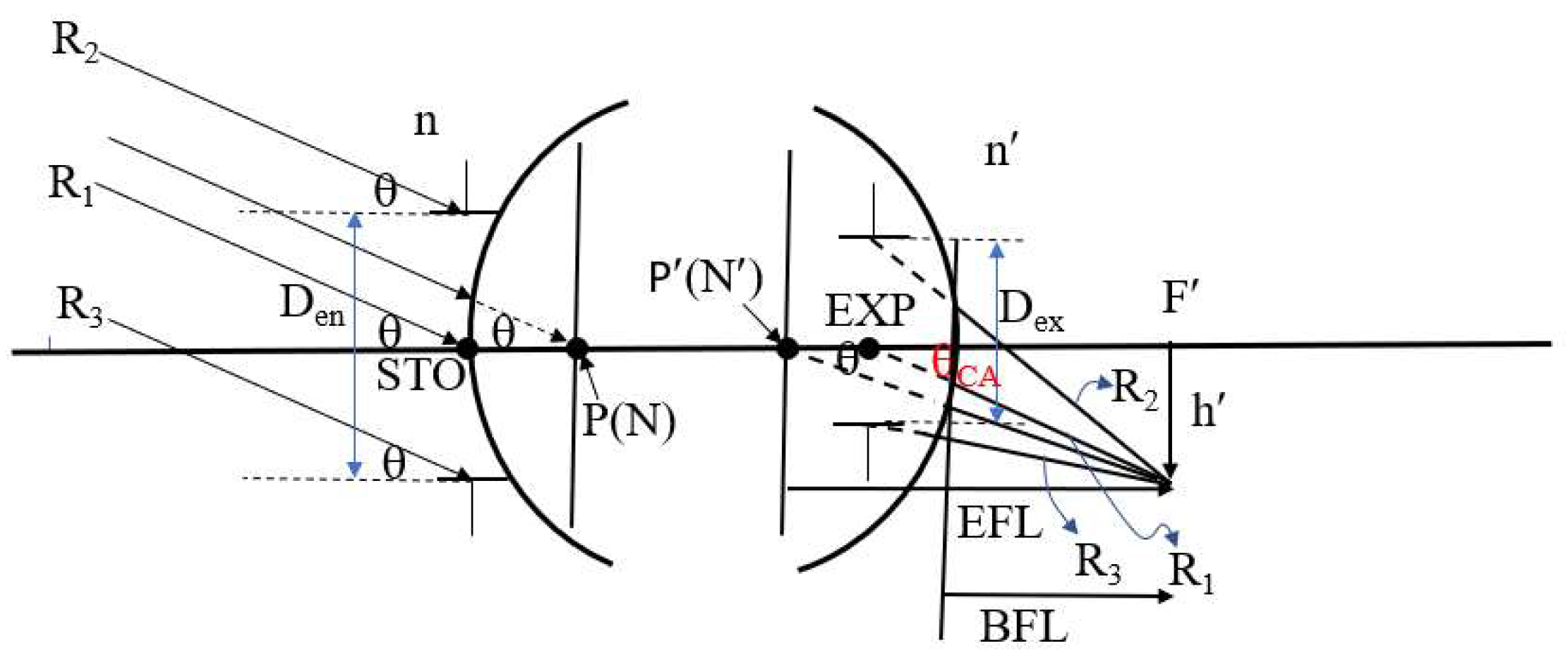
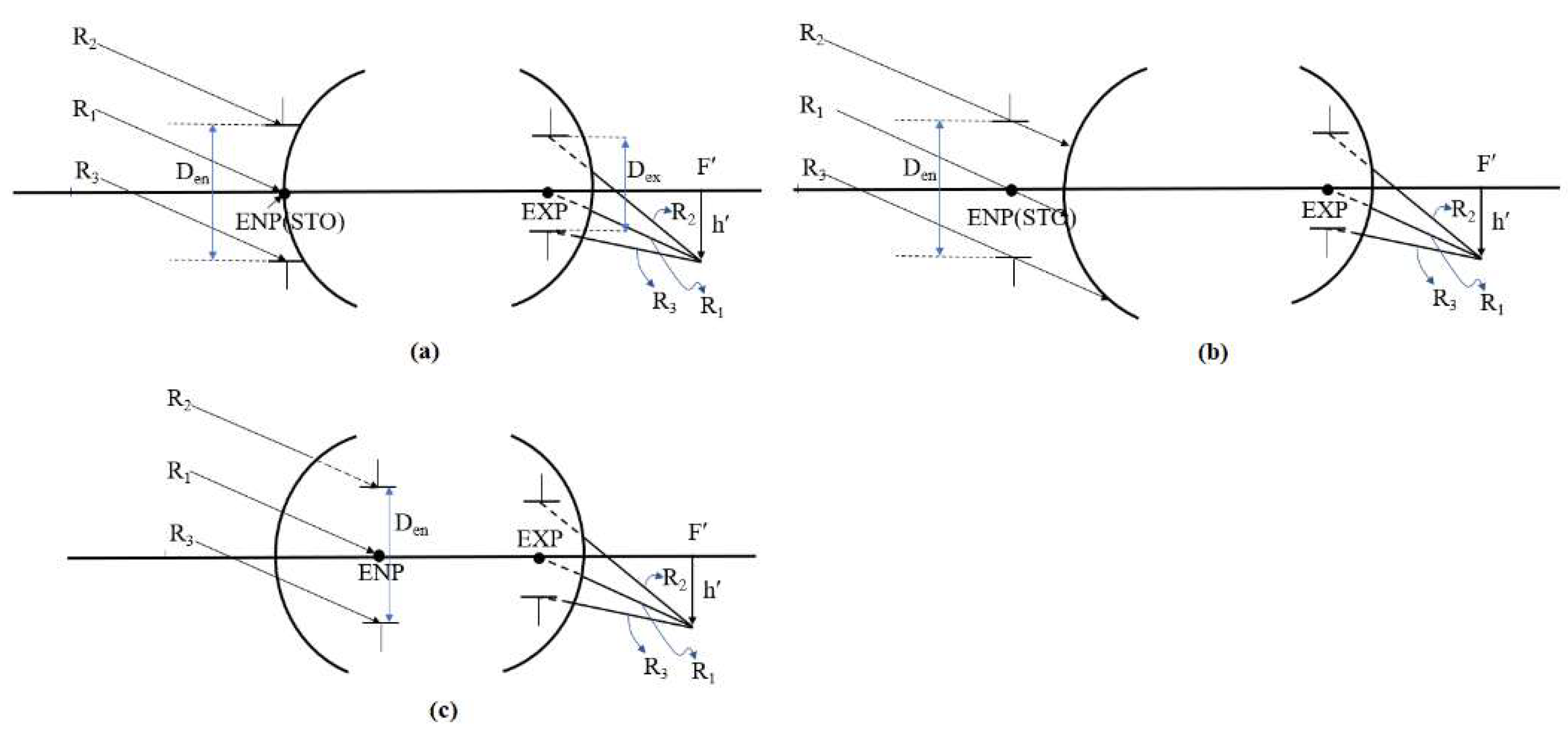
2.5. Entrance Pupil Position and Size
2.6. Exit Pupil Position and Size
2.7. Relationship Between Effective Focal Length and Angular Magnification
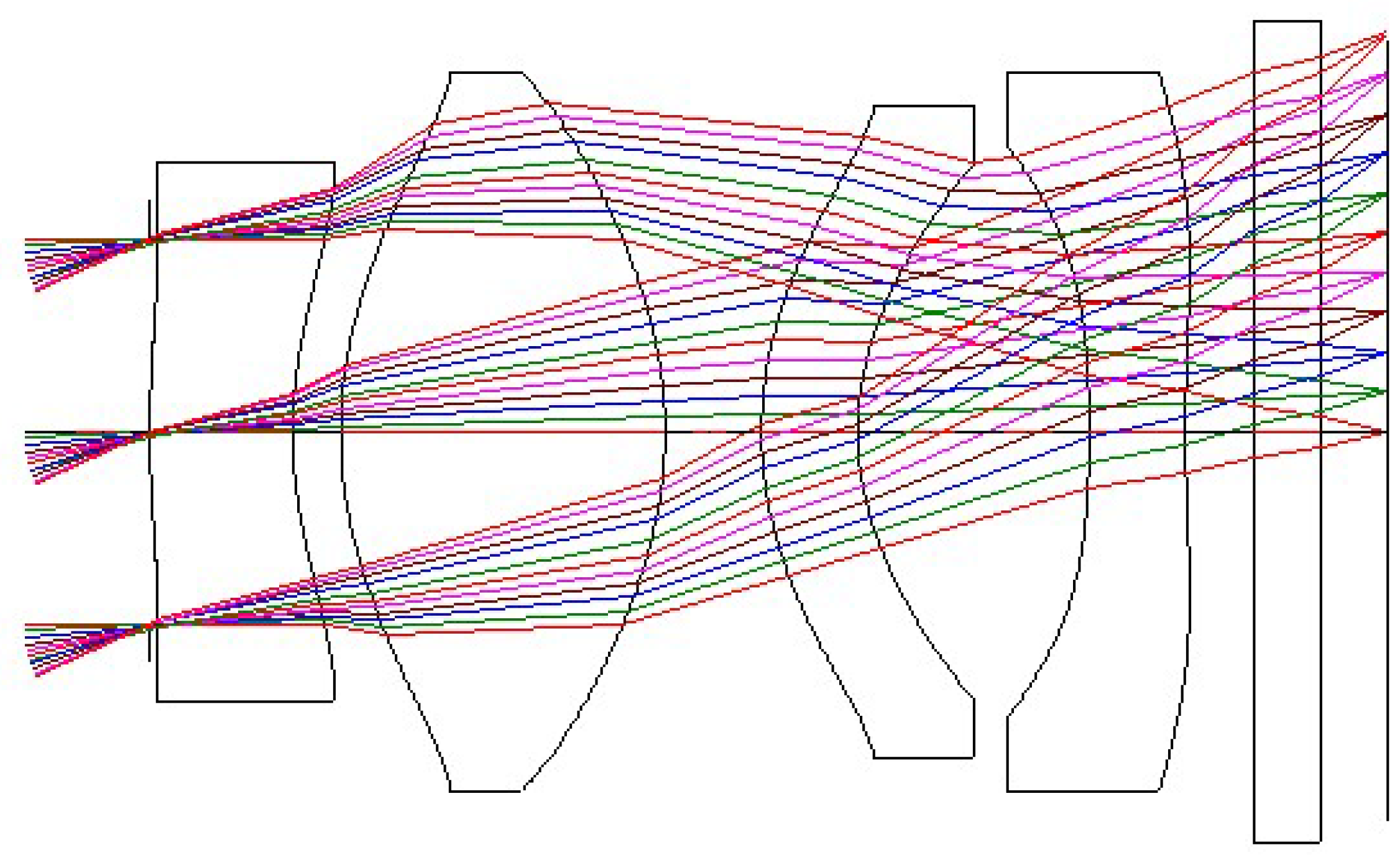
3. Design Result
3.1. Lens Specifications and Lens Data
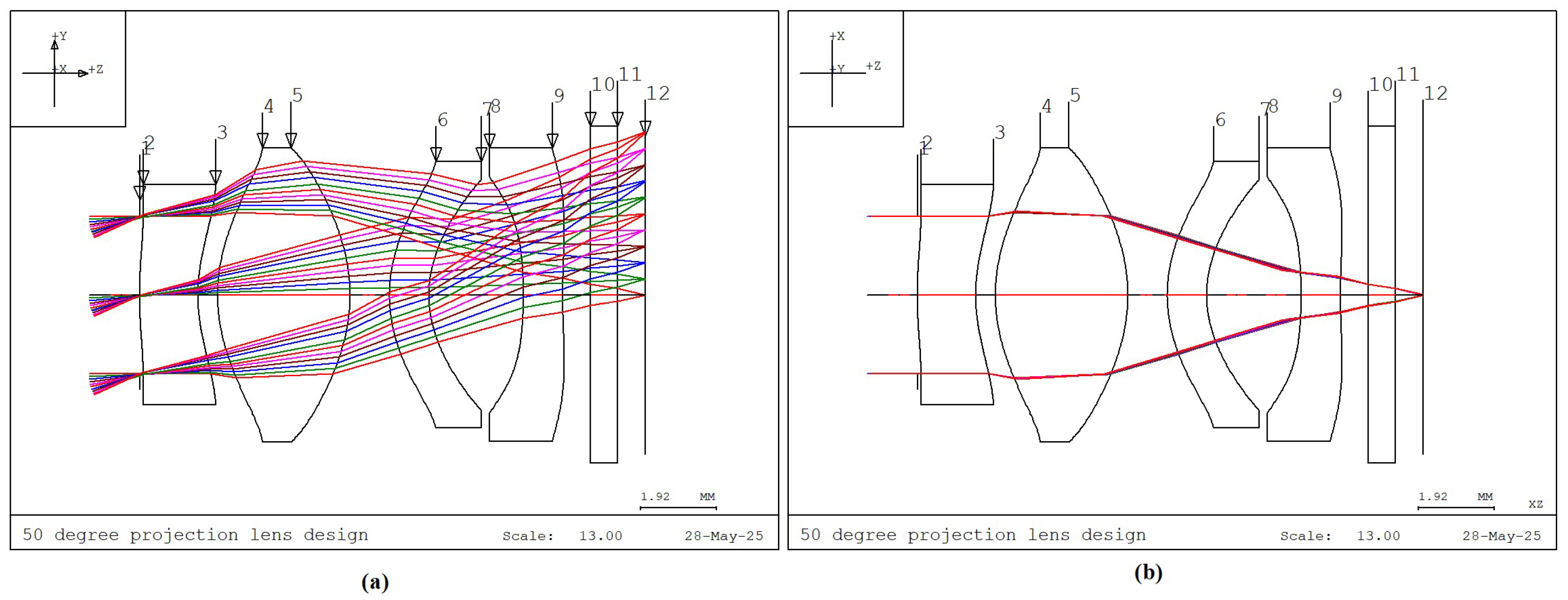
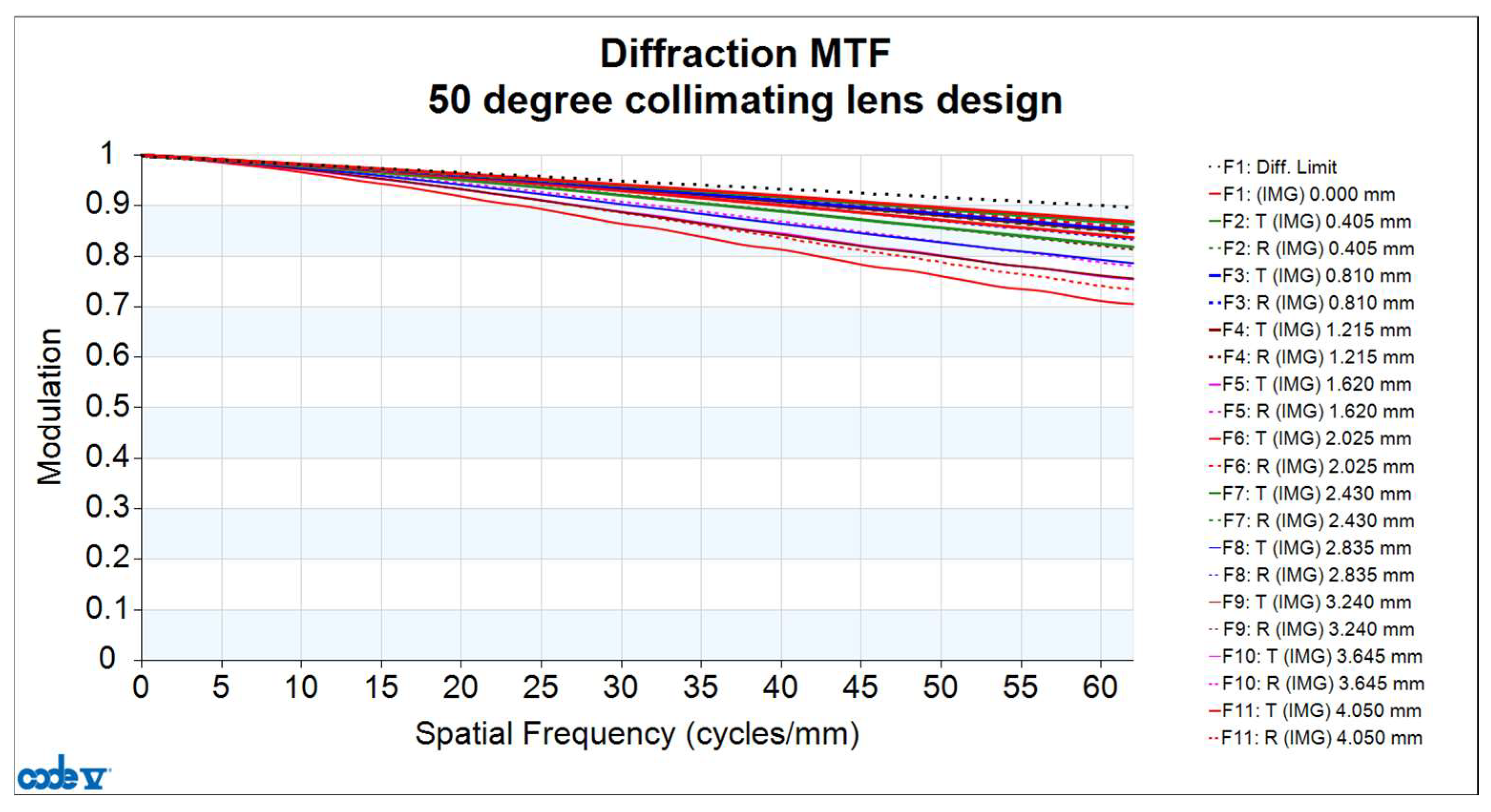
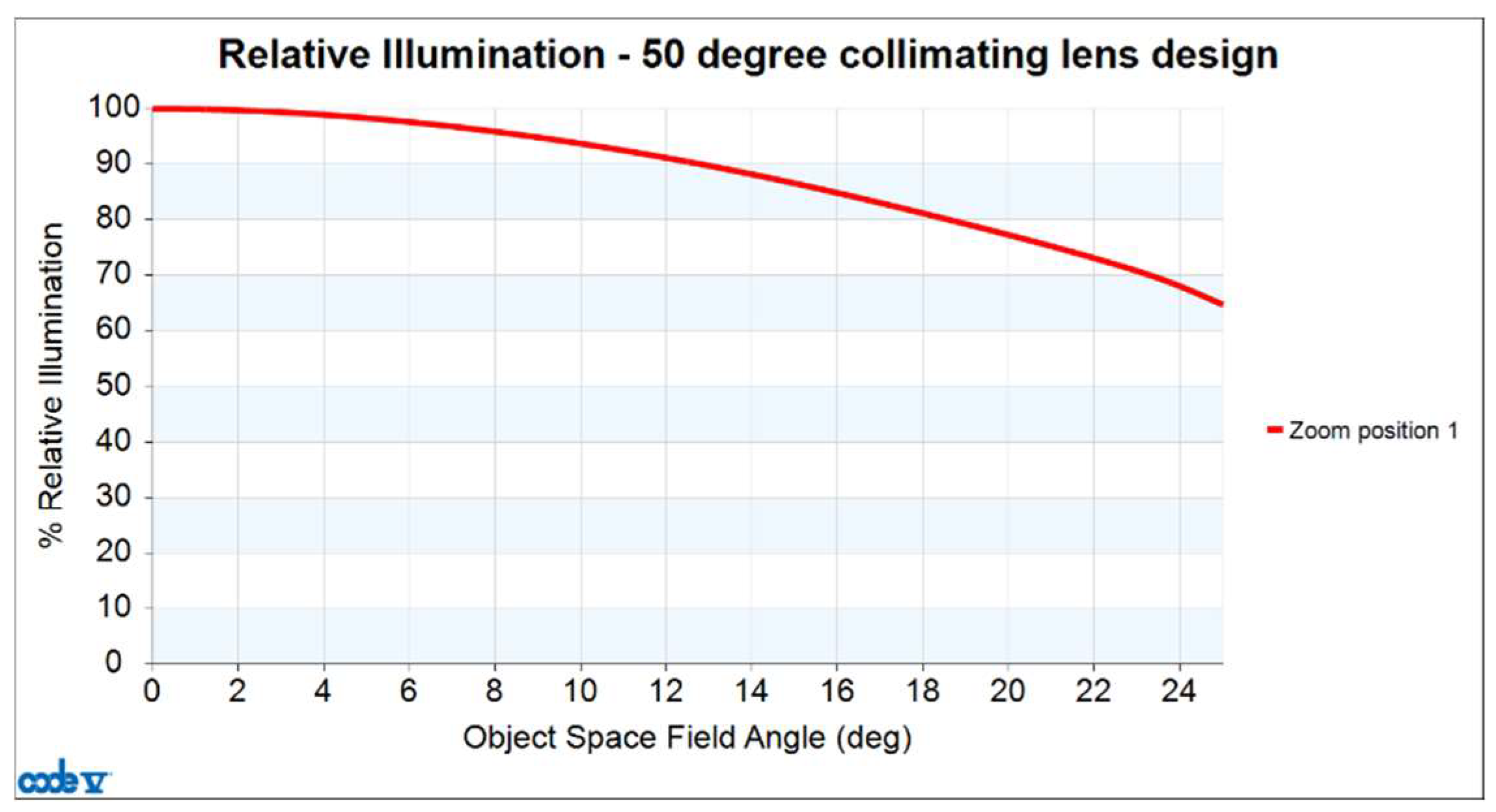
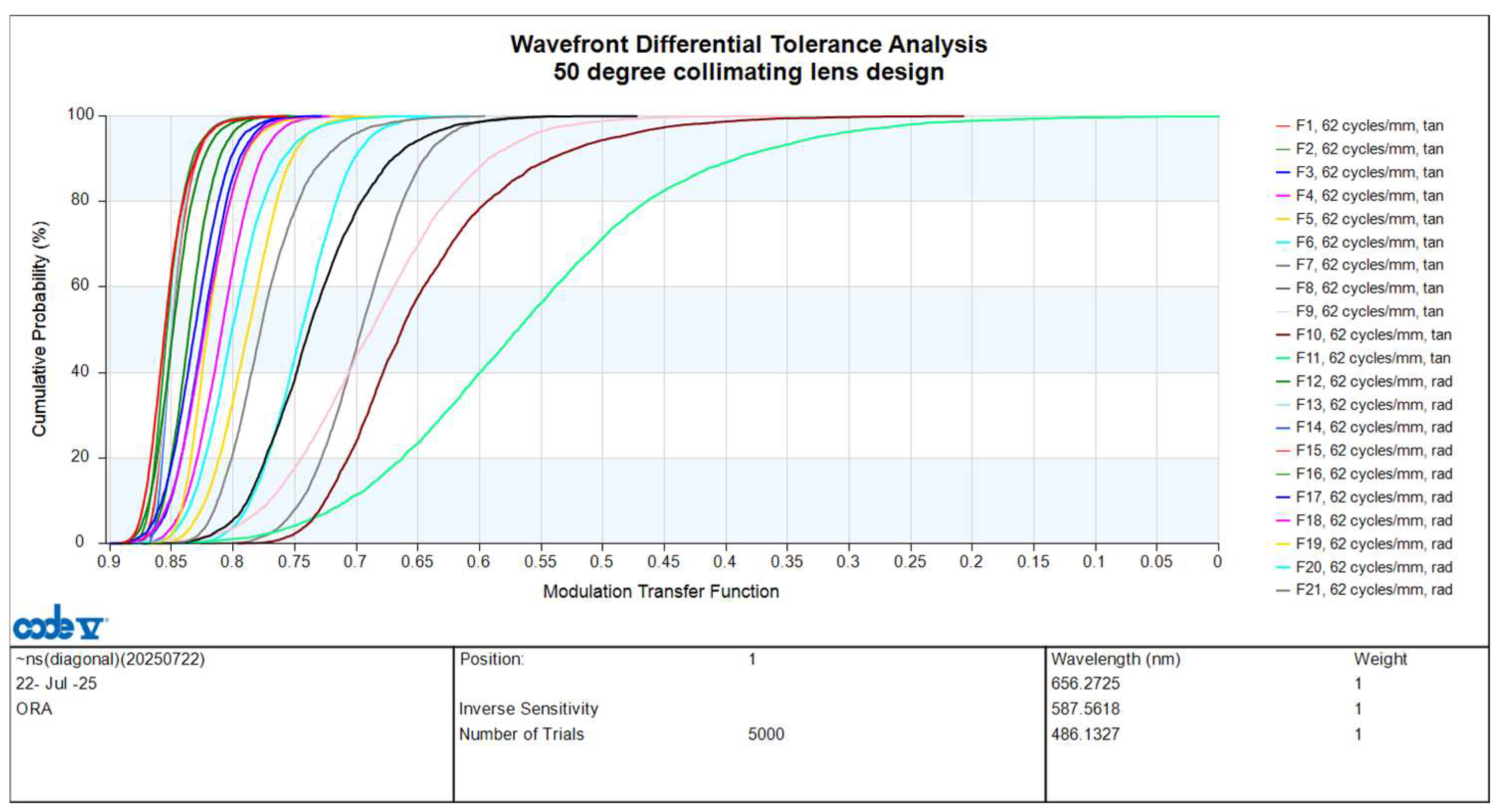
3.2. Analysis of Collimating Lens Image Quality
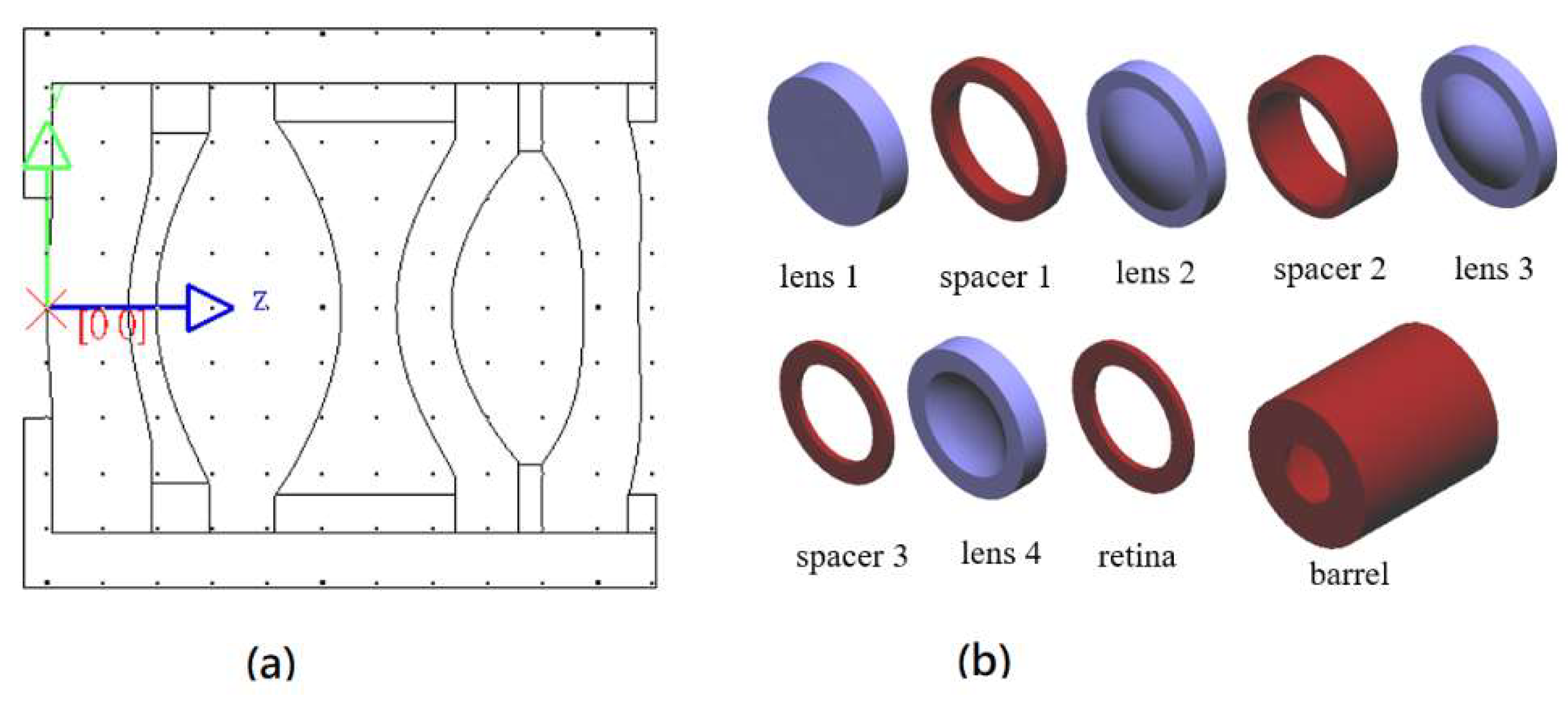
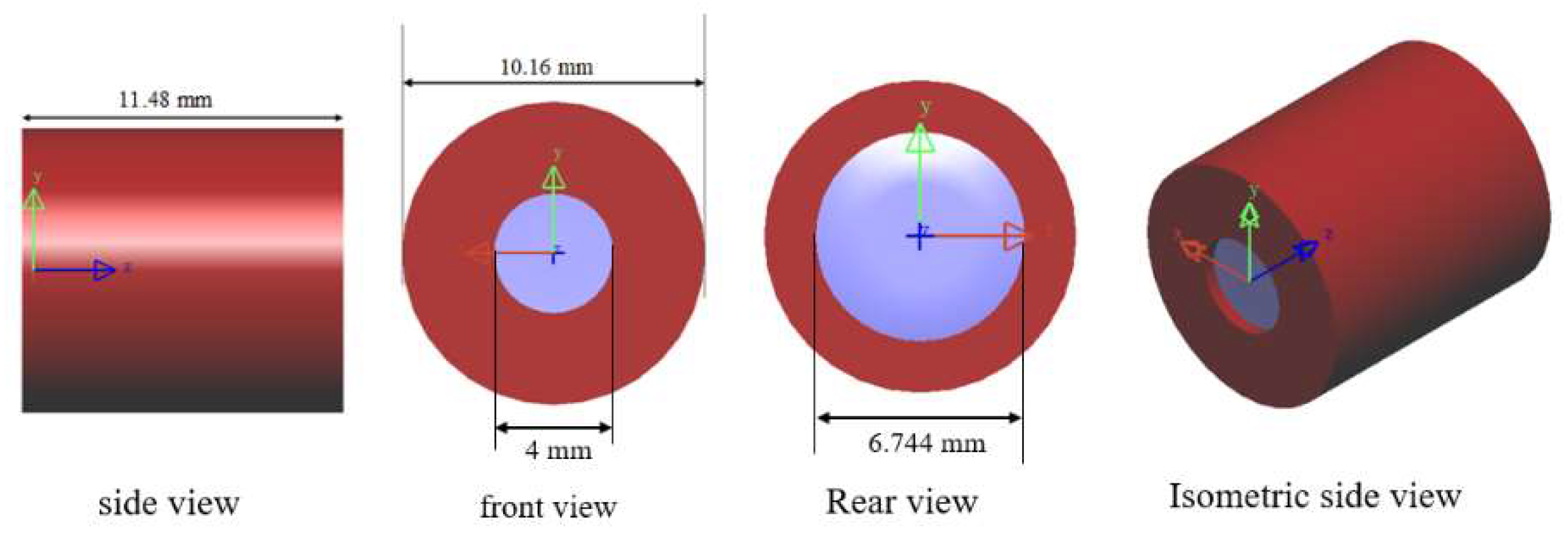
3.3. Lens Manufacturing and Tolerance Analysis
4. Volume and Weight of 50-Degree FOV Collimating Lens
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piao, J.A.; Li, G.; Piao, M.L.; Kim, N. Full color holographic optical element fabrication for waveguide-type head mounted display using photopolymer. Opt. Soc. Korea 2013, 17, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.L.; Kim, N. Achieving high levels of color uniformity and optical efficiency for a wedge-shaped waveguide head-mounted display using a photopolymer. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 2180–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeyama, T. Observation Optical System. U.S. Patent 6,710,902, 23 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, C.P.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, B.; Jin, H. Design of see-through near-eye display for presbyopia. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 8937–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.P.; Tseng, Y.K.; Lee, T.X.; Sun, C.C. Volume holographic waveguide combiner design for AR glasses. Proc. SPIE 2024, 12913, 1291303. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.X.; Tseng, Y.K.; Tsai, W.P.; Lin, W.K.; Zhou, S.K.; Sun, C.; Liang, Y.Y.; Yu, Y.W.; Su, W.C.; Lin, S.H.; et al. Advancing pure ray tracing for the simulation of volume holographic optical elements: Innovations in diffractive waveguide-based augmented reality systems. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 45391–45405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Ha, Y.; Rolland, J.P. Design of an ultralight and compact projection lens. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, H.; Gao, C. Design of a bright polarized head-mounted projection display. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Hua, H. Design of a polarized head-mounted projection display using ferroelectric liquid-crystal-on-silicon microdisplays. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 2888–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.W.; Hung, H.C. Optical design of a compact see-through head mounted display with light guide plate. J. Disp. Technol. 2015, 11, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.M.; Li, J.Y.; Han, P.; Yen, C.T. Design and Evaluation of optical see-through head-mounted display with wide FOV based on dihedral corner reflector array. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 118977–118984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Pan, C.; Gao, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z. Design of ultra-compact augmented reality display based on grating waveguide with curved variable-period grating. Opt. Commun. 2023, 529, 128980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Pei, C.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Wu, R.; Liu, X. Wide-field-of-view and high-resolution waveguide display based on the coupling-collimation system. Appl. Optics 2024, 63, 4543–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.S.; Hsu, Y.S.; Tien, C.L.; Lin, W.K.; Su, Y.L.; Yu, J.Y.; Zhou, S.K.; Liang, Y.Y.; Tsai, W.P.; Sun, C.; et al. Design and Manufacture of 30-degree Projection lens for Augmented Reality Waveguide. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.S.; Hsu, Y.S.; Su, Y.L.; Huang, G.W.; Lin, W.K.; Su, W.C.; Lin, S.H.; Lee, T.X.; Yu, Y.W.; Sun, C.C. Design of a 65-degree Collimating lens for Lightguide-based AR Glasses. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 24861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, V.N. Fundamentals of Geometrical Optics; Chapter 6; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht, E. Optics, Chapter 6, 4th ed.; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Synopsys Inc. Code V Document Library, Version 2023.03; Tolerance Reference Manual. Available online: https://www.synopsys.com/support/licensing-installation-computeplatforms/synopsys-documentation.html (accessed on 26 October 2025).



| Parameters | Specification |
|---|---|
| Pixel number | 800 × 600 |
| Pixel size | 8.1 μm × 8.1 μm |
| Effective area | 6.48 mm × 4.86 mm |
| Diagonal length of the display | 8.1 mm (0.32 inch) |
| Parameters | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Entrance pupil | 4 mm |
| Diagonal FOV | 50° |
| Horizontal FOV | 40.94° |
| Vertical FOV | 31.28° |
| Lens clear aperture maximum | ≤6.8 mm |
| Focal length | 8.68 mm |
| F-number | 2.17 |
| Image height | 4.05 mm |
| Protective glass material | BSC1(HOYA) |
| Protective glass thickness | 0.7 mm |
| MTF (62 cycles/mm) | ≥0.7 |
| Angular resolution (pixel per degree) | 20 PPD |
| Angular magnification | 28.802 |
| Surface Number | Surface Type | Radius (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Glass | Clear Aperture (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Object | Sphere | Infinity | Infinity | ||
| Stop | Sphere | Infinity | 0 | 4.000 | |
| 2 | Asphere | 10.6751 | 1.483 | ‘OKP-1_30’ | 4.083 |
| 3 | Asphere | 4.4966 | 0.500 | 5.085 | |
| 4 | Asphere | 4.3777 | 3.368 | PMMA_SPECAL | 6.378 |
| 5 | Asphere | −4.3101 | 1.000 | 6.798 | |
| 6 | Asphere | 3.8496 | 1.000 | ‘OKP-1_30’ | 6.145 |
| 7 | Asphere | 2.9794 | 2.400 | 5.604 | |
| 8 | Asphere | −13.7379 | 1.000 | ‘OKP-1_30’ | 5.719 |
| 9 | Asphere | 15.2466 | 0.700 | 6.774 | |
| 10 | Sphere | Infinity | 0.700 | BSC1_HOYA | 7.438 |
| 11 | Sphere | Infinity | 0.700 | 7.776 | |
| 12 | Image | Infinity | 0.000 | 8.307 |
| Surface Number | K | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | −120 | 0.335966 × 10−2 | −0.213406 × 10−2 | 0.302968 × 10−3 | −0.192055 × 10−4 |
| 3 | −5.161698 | −0.148158 × 10−2 | −0.606542 × 10−3 | 0.717905 × 10−4 | −0.338550 × 10−5 |
| 4 | −0.800282 | −0.149620 × 10−2 | −0.182126 × 10−3 | 0.211560 × 10−4 | −0.100896 × 10−5 |
| 5 | −4.456061 | −0.298062 × 10−2 | 0.193746 × 10−3 | −0.382837 × 10−5 | −0.339511 × 10−6 |
| 6 | −0.966918 | −0.721381 × 10−3 | −0.108456 × 10−3 | 0.995474 × 10−5 | −0.119197 × 10−5 |
| 7 | −2.644408 | 0.454588 × 10−2 | −0.288402 × 10−3 | 0.113949 × 10−4 | 0.201825 × 10−6 |
| 8 | −74.465683 | −0.133534 × 10−1 | 0.113535 × 10−2 | −0.135322 × 10−3 | 0.838188 × 10−5 |
| 9 | −15.581008 | −0.702624 × 10−2 | 0.481560 × 10−3 | −0.267416 × 10−4 | 0.797422 × 10−6 |
| Type | Minimum | Maximum | Increment |
|---|---|---|---|
| DLF (fringe) | 1 | 5 | 0.5 |
| DLT (mm) | 0.003 | 0.02 | 0.005 |
| DLN | 0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.0001 |
| DLV | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| CYD (fringe) | 1 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| CYN (fringe) | 1 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| TRX (arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 0.1 |
| TRY (arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 0.1 |
| BTY (arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 0.1 |
| BTX (arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 0.1 |
| DSX (mm) | 0.002 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| DSY (mm) | 0.002 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| Field | Spatial Frequency (cycles/mm) | Azimuth | Design MTF | Design Plus Tolerance MTF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 62 | Tangential | 0.8726 | 0.8193 |
| 0.1 | 62 | Tangential | 0.8660 | 0.8293 |
| 0.2 | 62 | Tangential | 0.8490 | 0.7863 |
| 0.3 | 62 | Tangential | 0.8438 | 0.7760 |
| 0.4 | 62 | Tangential | 0.8453 | 0.7801 |
| 0.5 | 62 | Tangential | 0.8333 | 0.7410 |
| 0.6 | 62 | Tangential | 0.8166 | 0.7061 |
| 0.7 | 62 | Tangential | 0.7860 | 0.6409 |
| 0.8 | 62 | Tangential | 0.7495 | 0.5461 |
| 0.9 | 62 | Tangential | 0.7436 | 0.4959 |
| 1.0 | 62 | Tangential | 0.6917 | 0.3023 |
| 0.1 | 62 | Radial | 0.8683 | 0.8220 |
| 0.2 | 62 | Radial | 0.8645 | 0.8212 |
| 0.3 | 62 | Radial | 0.8644 | 0.8223 |
| 0.4 | 62 | Radial | 0.8661 | 0.8205 |
| 0.5 | 62 | Radial | 0.8545 | 0.7996 |
| 0.6 | 62 | Radial | 0.8458 | 0.7804 |
| 0.7 | 62 | Radial | 0.8337 | 0.7616 |
| 0.8 | 62 | Radial | 0.8156 | 0.7341 |
| 0.9 | 62 | Radial | 0.7745 | 0.6793 |
| 1.0 | 62 | Radial | 0.7228 | 0.6173 |
| δ | −2.408 mm | h′ | 4.050 mm |
| δ′ | −7.401 mm | EFL | 8.680 mm |
| S | 2.408 mm | BFL | 1.279 mm |
| S′ | 1.855 mm | θCA | 30.786° |
| S + δ | 0 mm | MT | 0.7828 |
| S′ + δ′ | −5.516 mm | Dex | 3.131 mm |
| Element Name | Material | Specific Gravity (g/cm3) | Volume (cm3) | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lens 1 | OKP-1 | 1.22 | 0.1008 | 0.1230 |
| spacer 1 | Aluminum magnesium alloy | 1.81 | 0.0210 | 0.0568 |
| lens 2 | PMMA | 1.18 | 0.1053 | 0.1242 |
| spacer 1 | Aluminum magnesium alloy | 1.81 | 0.0522 | 0.1410 |
| lens 3 | OKP-1 | 1.22 | 0.0907 | 0.1106 |
| spacer 1 | Aluminum magnesium alloy | 1.81 | 0.0113 | 0.0305 |
| lens 4 | OKP-1 | 1.22 | 0.0659 | 0.0805 |
| retina | PMMA | 1.18 | 0.0079 | 0.0094 |
| barrel | PMMA | 1.18 | 0.03502 | 0.4132 |
| Total | 1.0892 |
| Author /Year | FOV (Degree) | EPD (mm) | F-Number | Lens Number | Microdisplay Size/Resolution | MTF | Distortion (%) | Weight (g) | Volume (cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hua [7]/2003 | 52.4 | 12 | 2.92 | 4 | 1.35 in 640 × 480 | >0.2 at 30 cycles/mm | < 2.5% | 8 | 3.53 |
| Hua [8] /2007 | 56 | 10 | 3.2 | 4 | 1.3 in 640 × 480 | >0.3 at 20 cycles/mm | <3.8% | 6 | 3.15 |
| Zhang [9]/2008 | 55 | 10 | 2.16 | 5 | 0.88 in 1280 × 1024 | >0.4 at 37 cycles/mm | <4.0% | 8.2 | 2.66 |
| Pan [10]/2015 | 30 | 8 | 3.66 | 4 | 0.61 in 800 × 600 | >0.4 at 30 cycles/mm | <2.7% | NR | 12.45 |
| Tsai [11]/2017 | 60 | 6 | 2.57 | 8 | 0.7 in 1920 × 1080 | >0.29 at 62 cycles/mm | <5.0% | NR | 9.76 |
| Sun [14]/2024 | 30 | 14 | 1.17 | 9 | 0.35 in 1280 × 720 | >0.44 at 35 cycles/mm | <2.0% | NR | 25.02 |
| Sun [15]/2025 | 65 | 10 | 2.05 | 7 | 1.03 in 2560 × 2560 | >0.50 at 60 cycles/mm | <0.82% | NR | 22.61 |
| This work | 50 | 4 | 2.17 | 4 | 0.32 in 800 × 600 | >0.23 at 250 cycles/mm | <0.21% | 1.08 | 0.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, W.-S.; Su, Y.-L.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Tien, C.-L.; Cheng, N.-J.; Sun, C.-C. Compact Design of a 50° Field of View Collimating Lens for Lightguide-Based Augmented Reality Glasses. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111234
Sun W-S, Su Y-L, Hsu Y-S, Tien C-L, Cheng N-J, Sun C-C. Compact Design of a 50° Field of View Collimating Lens for Lightguide-Based Augmented Reality Glasses. Micromachines. 2025; 16(11):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111234
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Wen-Shing, Yi-Lun Su, Ying-Shun Hsu, Chuen-Lin Tien, Nai-Jen Cheng, and Ching-Cherng Sun. 2025. "Compact Design of a 50° Field of View Collimating Lens for Lightguide-Based Augmented Reality Glasses" Micromachines 16, no. 11: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111234
APA StyleSun, W.-S., Su, Y.-L., Hsu, Y.-S., Tien, C.-L., Cheng, N.-J., & Sun, C.-C. (2025). Compact Design of a 50° Field of View Collimating Lens for Lightguide-Based Augmented Reality Glasses. Micromachines, 16(11), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111234







