A Highly Sensitive Dual-Drive Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Detection of Respiratory Virus Antigens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Analytes
2.3. Conjugation of Fluorescent Microspheres with Antibodies
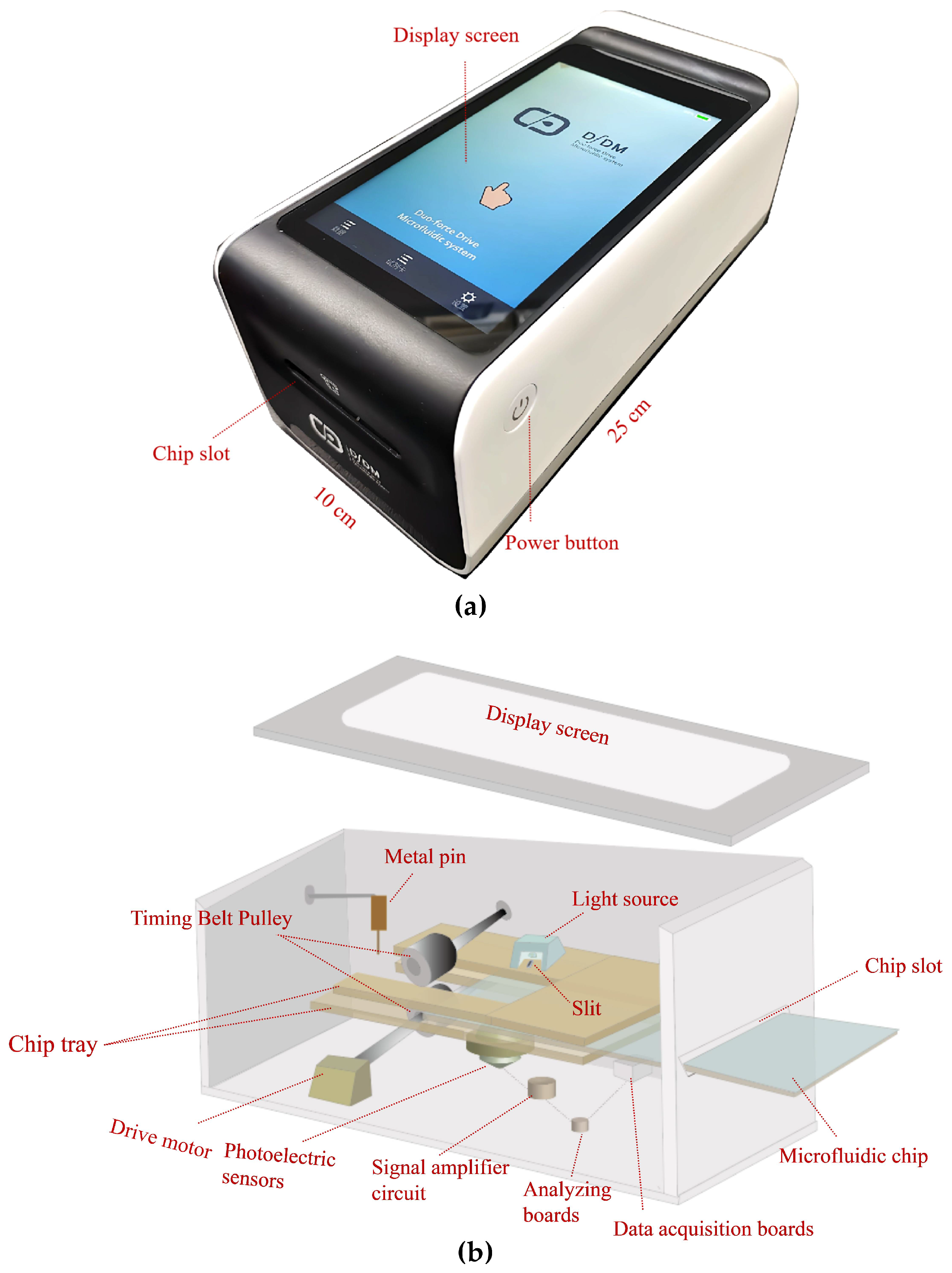
2.4. Description of the Microfluidics Analyzer
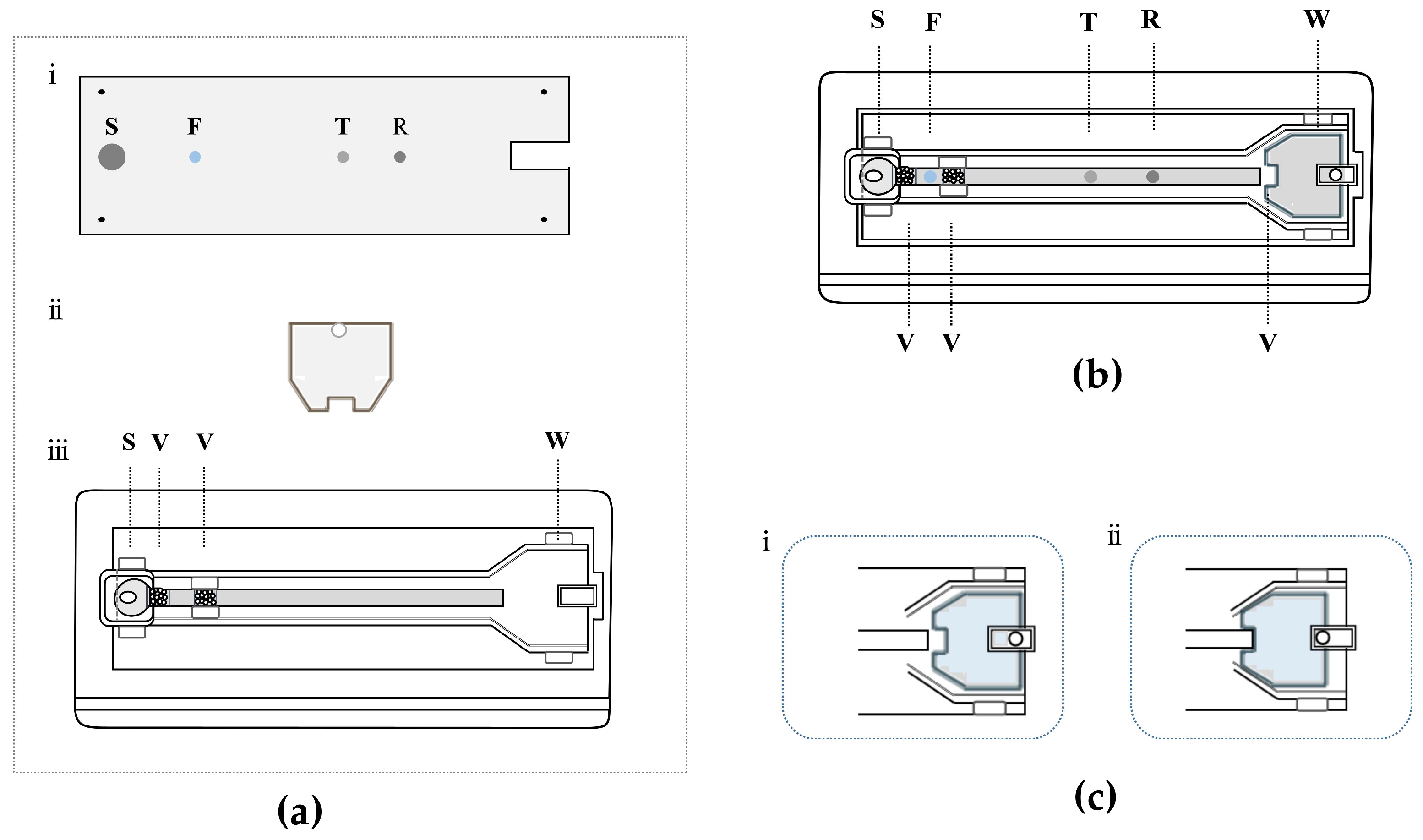
2.5. Dual-Drive Microfluidic Chip Design and Assembly
2.6. Immobilization of Biomolecules on the PMMA Substrate Layer
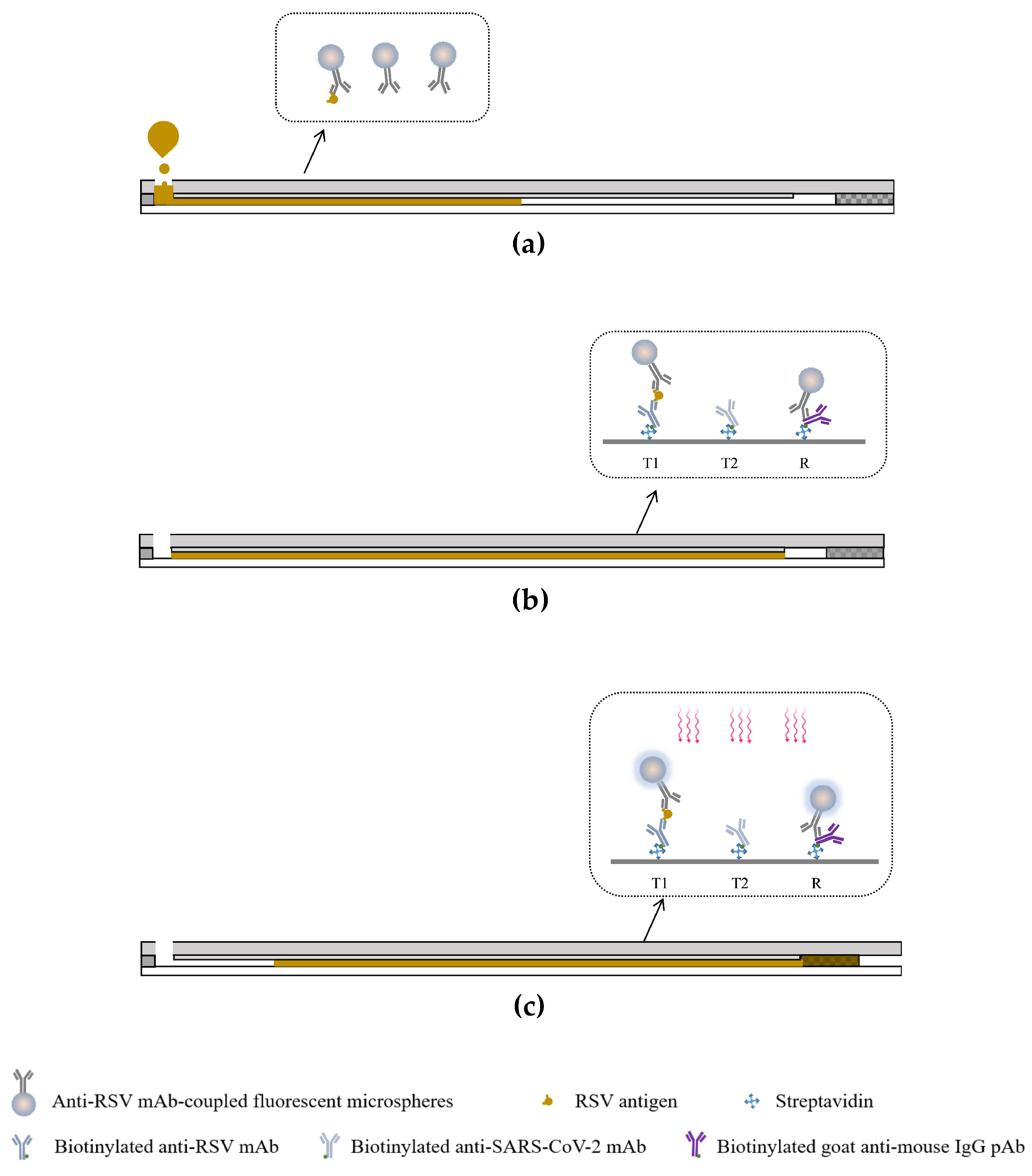
2.7. Working Principle of Dual-Drive Microfluidic Chip
2.8. Validation and Optimization of the Dual-Drive Microfluidic System
3. Results
3.1. Performance of the Microfluidics Analyzer
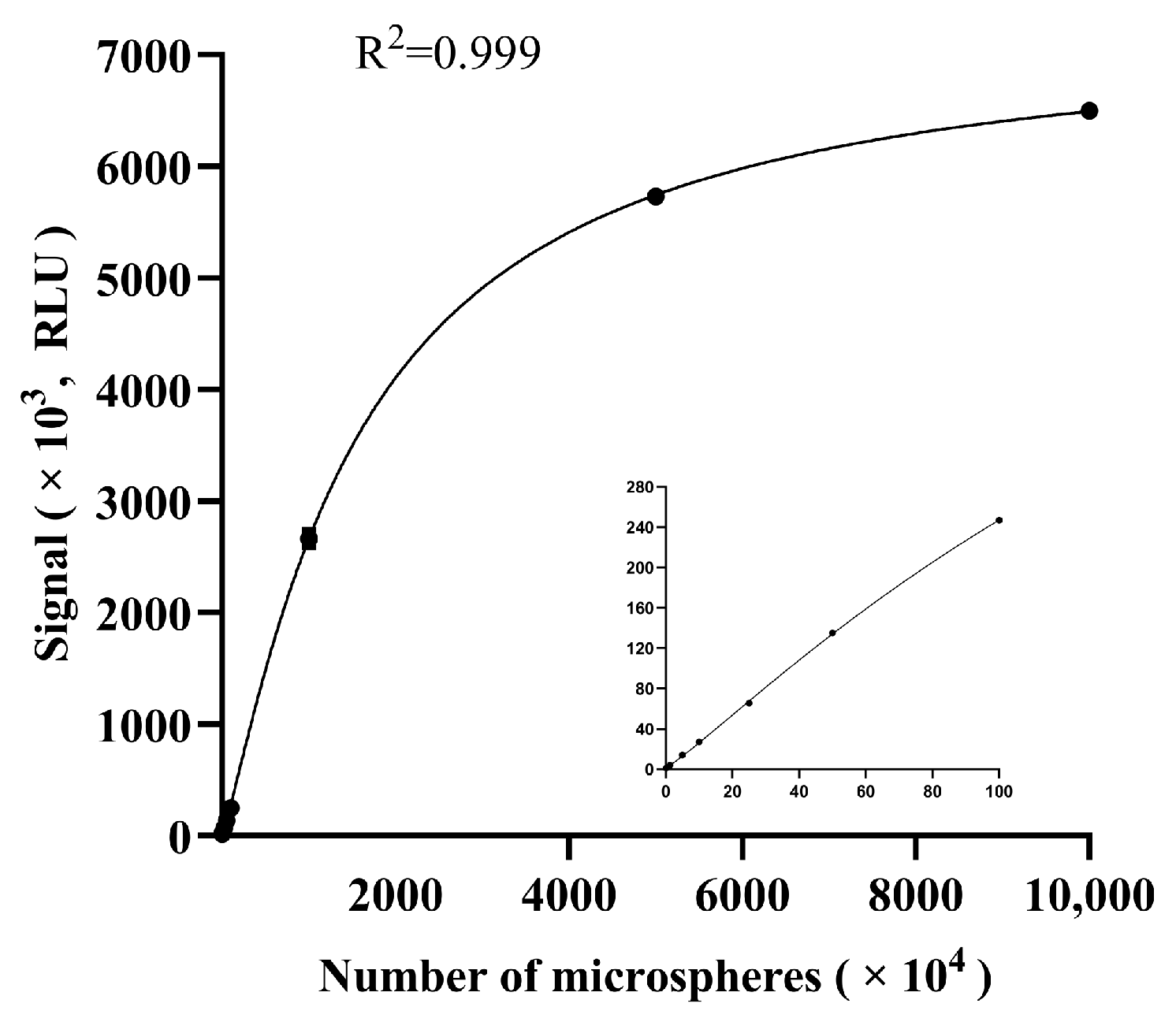
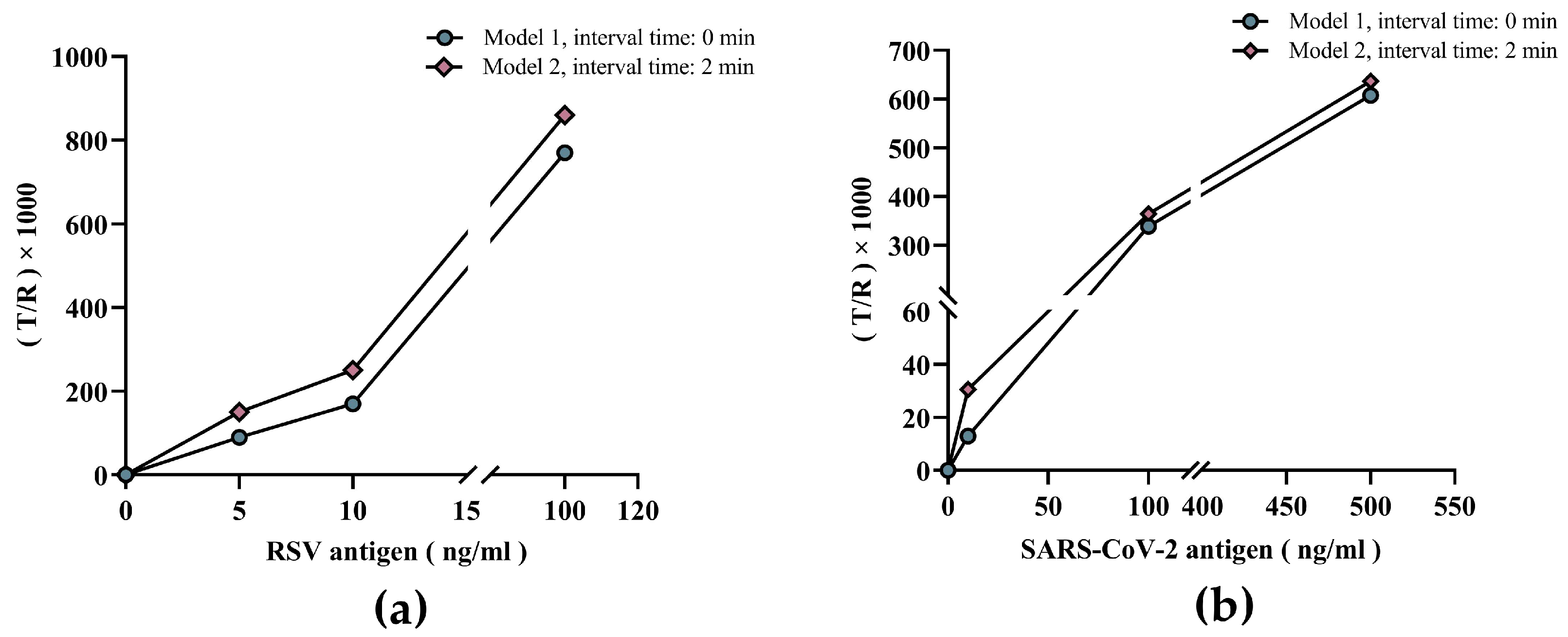
3.2. Validating the Value of the Dual-Drive Microfluidic Chip in Improving Sensitivity
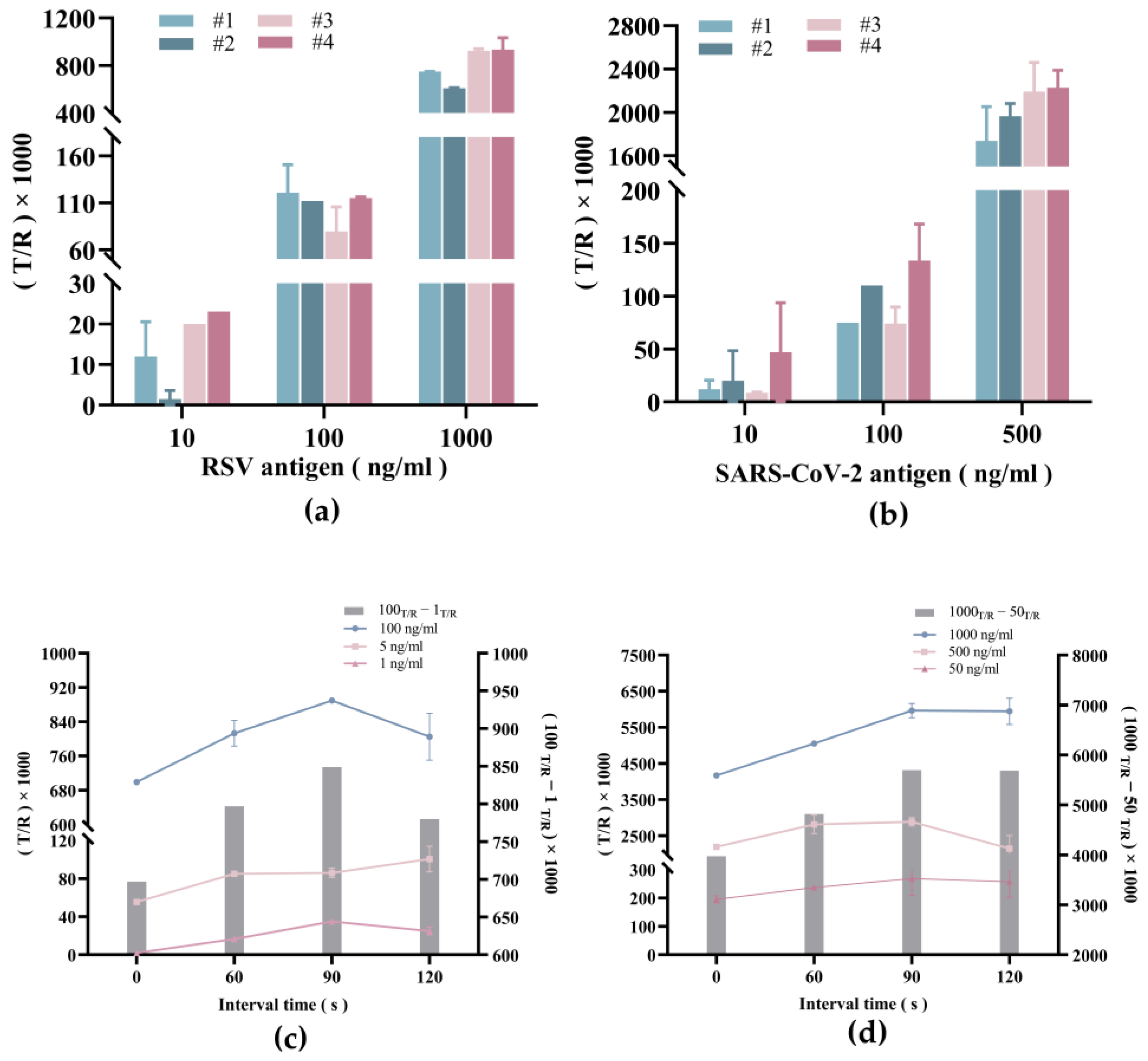
3.3. System Optimization of Dual-Drive Microfluidic Chip
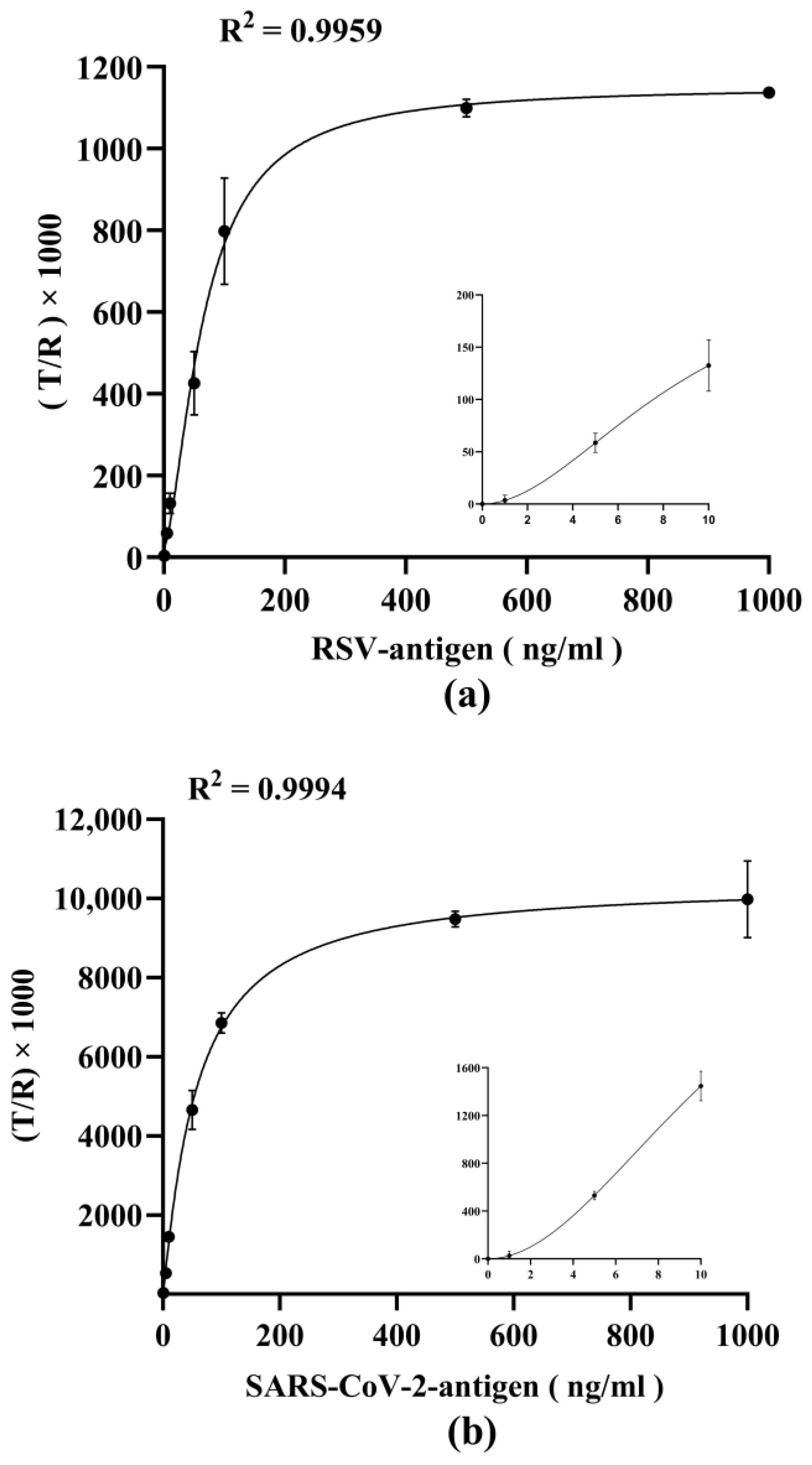
3.4. Detection Capability of Respiratory Virus Antigens by Dual-Drive Microfluidic Chip
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Budd, J.; Miller, B.S.; Manning, E.M.; Lampos, V.; Zhuang, M.; Edelstein, M.; Rees, G.; Emery, V.C.; Stevens, M.M.; Keegan, N.; et al. Digital technologies in the public-health response to COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, X.; Lin, H.; Rodriguez Serrano, A.F.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Hsing, I.M. CRISPR-based one-pot loop-mediated isothermal amplification enables at-home diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA with nearly eliminated contamination utilizing amplicons depletion strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 236, 115402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, E.; Jankelow, A.; Lim, J.; Kindratenko, V.; Ganguli, A.; White, K.; Kumar, J.; Bashir, R. COVID-19 Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Present and Future. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7899–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpaldas, H.; Arumugam, S.; Campillo Rodriguez, C.; Kumar, B.A.; Shi, V.; Sia, S.K. Point-of-care diagnostics: Recent developments in a pandemic age. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 4517–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, P.; Ahmed, R.; Wang, J.; Akin, D.; Soto, F.; Liu, B.F.; Li, P.; Demirci, U. Advanced Point-of-Care Testing Technologies for Human Acute Respiratory Virus Detection. Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, e2103646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lan, T.; Lu, Y. Translating in vitro diagnostics from centralized laboratories to point-of-care locations using commercially-available handheld meters. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2020, 124, 115782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, J.; Luo, Z.; Yang, M.; Yi, C. Virus Detection: From State-of-the-Art Laboratories to Smartphone-Based Point-of-Care Testing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2105904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Han, D.H.; Park, J.K. Towards practical sample preparation in point-of-care testing: User-friendly microfluidic devices. Lab. Chip. 2020, 20, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Nehra, M.; Kumar, R.; Dilbaghi, N.; Hu, T.; Kumar, S.; Kaushik, A.; Li, C.Z. Internet of medical things (IoMT)-integrated biosensors for point-of-care testing of infectious diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Liu, C.; Machain-Williams, C.; Martinez-Acuña, N.; Lozano-Sepulveda, S.; Galan-Huerta, K.; Arellanos-Soto, D.; Meléndez-Villanueva, M.; Ávalos-Nolazco, D.; Pérez-Ibarra, K.; Galindo-Rodríguez, S.; et al. Development of a Rapid Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Detection of Dengue Virus. Biosensors 2022, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, Y.; Mauk, M.G.; Li, R.; Qian, C. Trends of respiratory virus detection in point-of-care testing: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1264, 341283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xu, H.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y. Membrane-based lateral flow immunochromatographic strip with nanoparticles as reporters for detection: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.U.; Tariq, A.; Noreen, Z.; Donia, A.; Zaidi, S.Z.J.; Bokhari, H.; Zhang, X. Capillary-Driven Flow Microfluidics Combined with Smartphone Detection: An Emerging Tool for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Zoëga Andreasen, S.; Wolff, A.; Duong Bang, D. From Lab on a Chip to Point of Care Devices: The Role of Open Source Microcontrollers. Micromachines 2018, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demello, A.J. Control and detection of chemical reactions in microfluidic systems. Nature 2006, 442, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Han, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, P.; Du, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Smartphone-based platforms implementing microfluidic detection with image-based artificial intelligence. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1341–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; He, J.; Huang, L.; Yu, Z.; Su, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhou, J. Microfluidic High-Throughput Platforms for Discovery of Novel Materials. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.S.; Thorsen, T.A.; Babb, J.; Wick, S.T.; Gam, J.J.; Weiss, R.; Carr, P.A. Open-source, community-driven microfluidics with Metafluidics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, A.S.; Price, C.P. Existing and Emerging Technologies for Point-of-Care Testing. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2014, 35, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Haghayegh, F.; Salahandish, R.; Zare, A.; Khalghollah, M.; Sanati-Nezhad, A. Immuno-biosensor on a chip: A self-powered microfluidic-based electrochemical biosensing platform for point-of-care quantification of proteins. Lab Chip 2021, 22, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wang, E.; Chen, P.W.; Tsai, Y.H.; Langouche, L.; Lo, Y.H. A microfluidic design for desalination and selective removal and addition of components in biosamples. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 024109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, P.; Singh, S.K.; Gulati, M.; Vishwas, S.; Kapoor, B.; Chellappan, D.K.; Anand, K.; Gupta, G.; Jha, N.K.; Gupta, P.K.; et al. Microfluidic chips: Recent advances, critical strategies in design, applications and future perspectives. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2021, 25, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Murakami, H.; Kasama, T.; Mitsuzawa, S.; Shinkawa, S.; Miyake, R.; Takai, M. An automatic immuno-microfluidic system integrating electrospun polystyrene microfibrous reactors for rapid detection of salivary cortisol. iScience 2023, 26, 107820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Ye, P.; Yang, K.; Meng, J.; Guo, J.; Pan, Z.; Bayin, Q.; Zhao, W. Application of Microfluidics in Immunoassay: Recent Advancements. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 2959843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, A.; Beaugrand, M.; Yafia, M.; Juncker, D. Capillary microfluidics in microchannels: From microfluidic networks to capillaric circuits. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2323–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, P.; Brack, E.; Alexander, T.; Henry, C.S. Capillary Flow-Driven Microfluidics Combined with a Paper Device for Fast User-Friendly Detection of Heavy Metals in Water. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 5820–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Qiao, X.; Qi, F.; Nishida, N.; Hoshino, T. Analysis of Binding Modes of Antigen-Antibody Complexes by Molecular Mechanics Calculation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverberi, R.; Reverberi, L. Factors affecting the antigen-antibody reaction. Blood. Transfus. 2007, 5, 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, T.C.; Wu, C.C.; Wang, S.C.; Chau, L.K.; Hsieh, W.H. Using a fiber optic particle plasmon resonance biosensor to determine kinetic constants of antigen-antibody binding reaction. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridy, S.; Maged, A.; Baker, A.W.; Shamsuzzaman, M.; Bashir, H.; Xie, M. Monitoring scheme for early detection of coronavirus and other respiratory virus outbreaks. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 156, 107235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Lin, S.; Zhang, H.; Liang, L.; Shen, S. Methods of Respiratory Virus Detection: Advances towards Point-of-Care for Early Intervention. Micromachines 2021, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, L.; Deng, X.; Liang, R.; Su, M.; He, C.; Hu, L.; Su, Y.; Ren, J.; Yu, F.; et al. Recent advances in the detection of respiratory virus infection in humans. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, W.; Pallás-Tamarit, Y.; Juste-Dolz, A.; Sena-Torralba, A.; Gozalbo-Rovira, R.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Navarro, D.; Carrascosa, J.; Gimenez-Romero, D.; Maquieira, Á.; et al. An all-in-one point-of-care testing device for multiplexed detection of respiratory infections. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 213, 114454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Fang, Z.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y. An updated review of SARS-CoV-2 detection methods in the context of a novel coronavirus pandemic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 8, e10356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hong, X.Z.; Li, Y.W.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, B.F. Microfluidics-based strategies for molecular diagnostics of infectious diseases. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Dai, L.; Yang, Y. Microfluidic technology and its application in the point-of-care testing field. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 10, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaaliveetil, S.; Yang, J.; Alssaidy, S.; Li, Z.; Cheng, Y.H.; Menon, N.H.; Chande, C.; Basuray, S. Microfluidic Gas Sensors: Detection Principle and Applications. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd-Moss, M.; Baratchi, S.; Di Venere, M.; Khoshmanesh, K. Self-contained microfluidic systems: A review. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3177–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotoudegan, M.S.; Mohd, O.; Ligler, F.S.; Walker, G.M. Paper-based passive pumps to generate controllable whole blood flow through microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 3787–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanamurthy, V.; Jeroish, Z.E.; Bhuvaneshwari, K.S.; Bayat, P.; Premkumar, R.; Samsuri, F.; Yusoff, M.M. Advances in passively driven microfluidics and lab-on-chip devices: A comprehensive literature review and patent analysis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 11652–11680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Yan, S.; Inglis, D.; Feng, S. A Review of Capillary Pressure Control Valves in Microfluidics. Biosensors 2021, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, D.; Holderby, A.; Dean, J.; Mabbott, S.; Coté, G.L. Paper Microfluidic Device with a Horizontal Motion Valve and a Localized Delay for Automatic Control of a Multistep Assay. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4497–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liu, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; He, J.; Cui, H. High-resolution temporally resolved chemiluminescence based on double-layered 3D microfluidic paper-based device for multiplexed analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Number of Beads | Mean (RLU) | SD (RLU) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 × 107 | 6,501,661 | 170 | 0.003 |
| 1 × 107 | 3,797,041 | 44,224 | 1.165 |
| 2 × 106 | 798,692 | 9422 | 1.180 |
| 4 × 105 | 157,040 | 1745 | 1.111 |
| Detection Items | LoD | LoQ |
|---|---|---|
| RSV | 1.121 | 2.717 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | 0.447 | 0.580 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, J.Z.; Sun, Y.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X. A Highly Sensitive Dual-Drive Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Detection of Respiratory Virus Antigens. Micromachines 2024, 15, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060685
Yang X, Li Y, Lee JZ, Sun Y, Tan X, Liu Y, Yu Y, Li H, Li X. A Highly Sensitive Dual-Drive Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Detection of Respiratory Virus Antigens. Micromachines. 2024; 15(6):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060685
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaohui, Yixian Li, Josh Zixi Lee, Yuanmin Sun, Xin Tan, Yijie Liu, Yang Yu, Huiqiang Li, and Xue Li. 2024. "A Highly Sensitive Dual-Drive Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Detection of Respiratory Virus Antigens" Micromachines 15, no. 6: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060685
APA StyleYang, X., Li, Y., Lee, J. Z., Sun, Y., Tan, X., Liu, Y., Yu, Y., Li, H., & Li, X. (2024). A Highly Sensitive Dual-Drive Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Detection of Respiratory Virus Antigens. Micromachines, 15(6), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060685






