Effect of Additives on Tribological Performance of Magnetorheological Fluids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
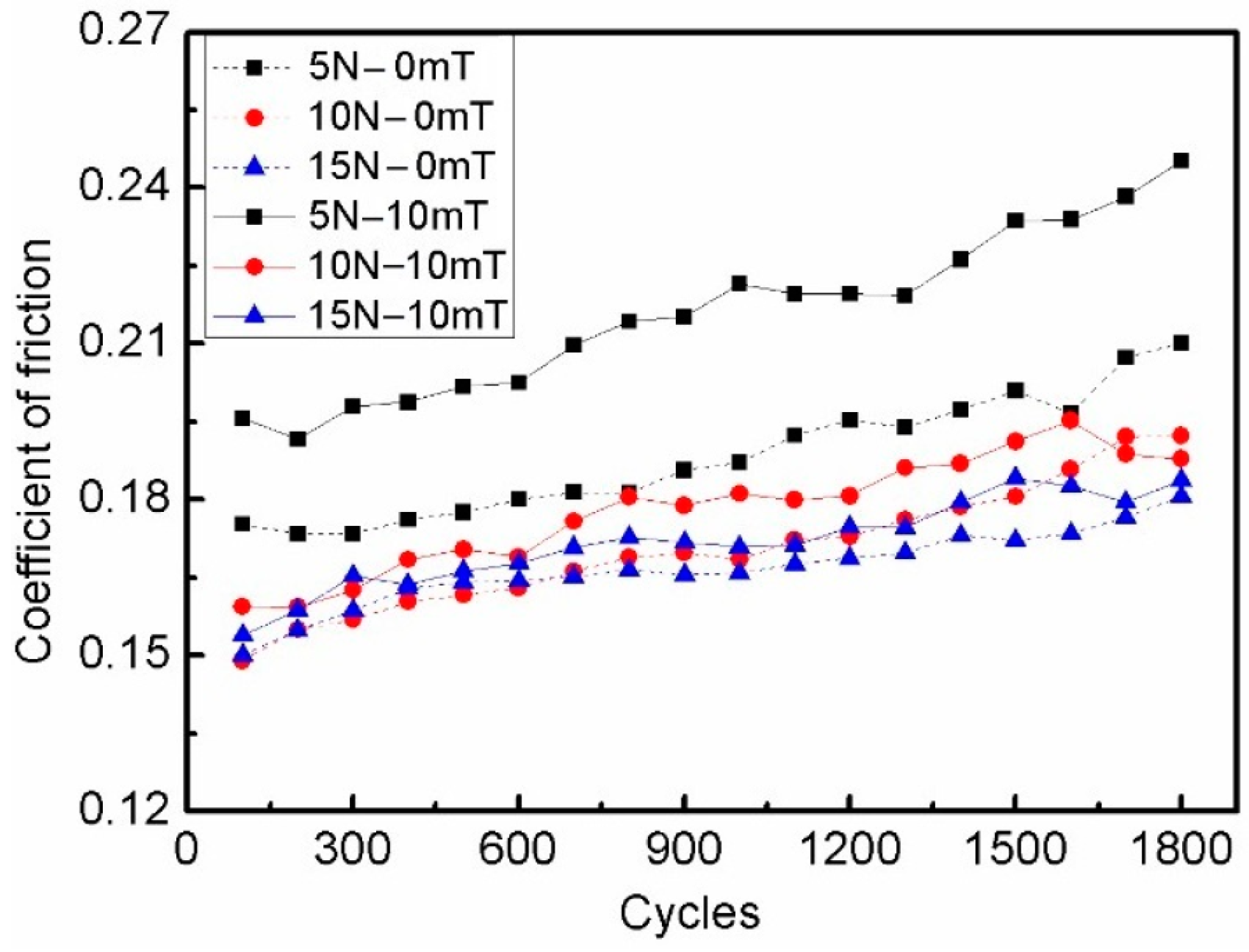
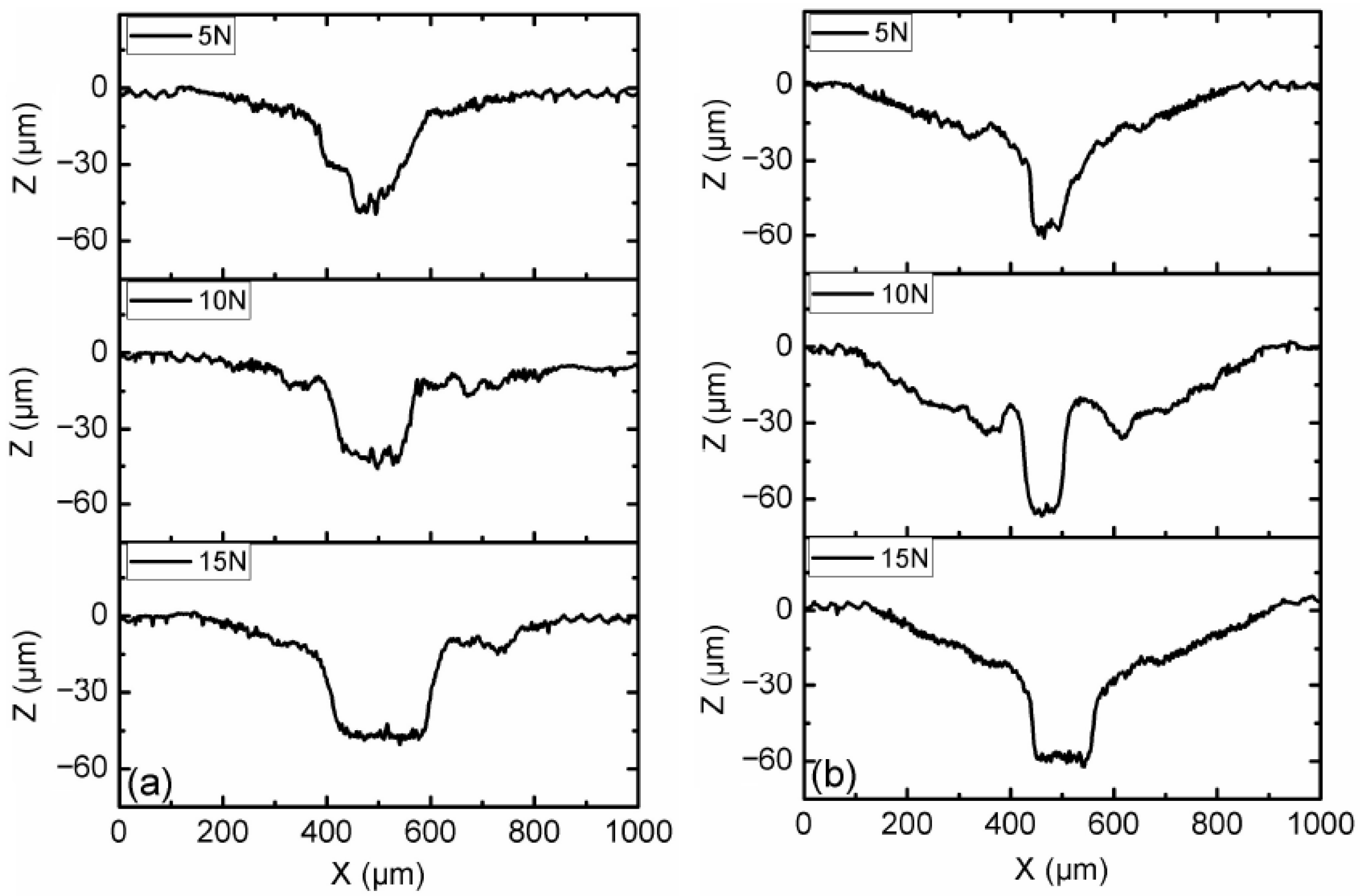
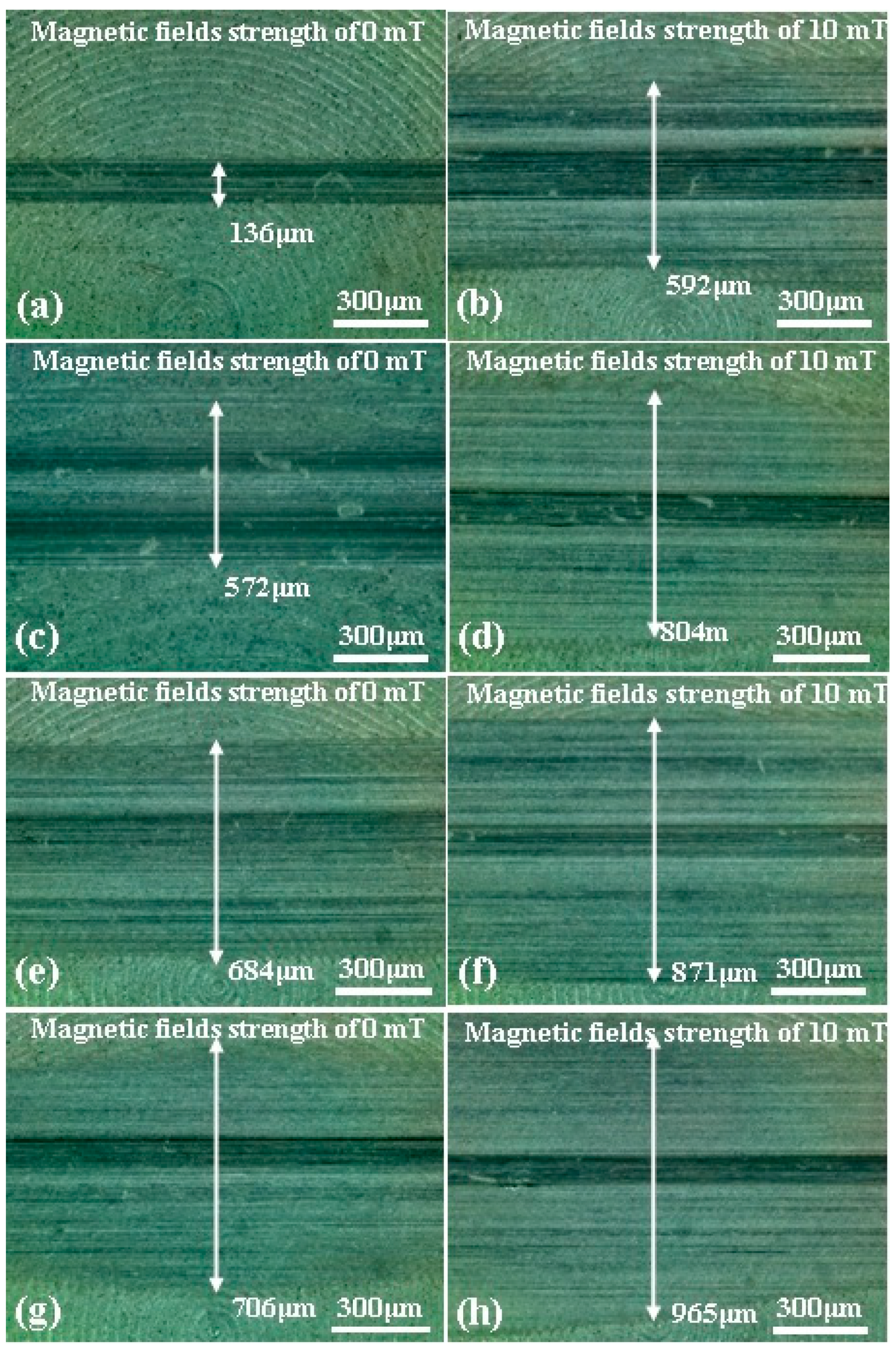
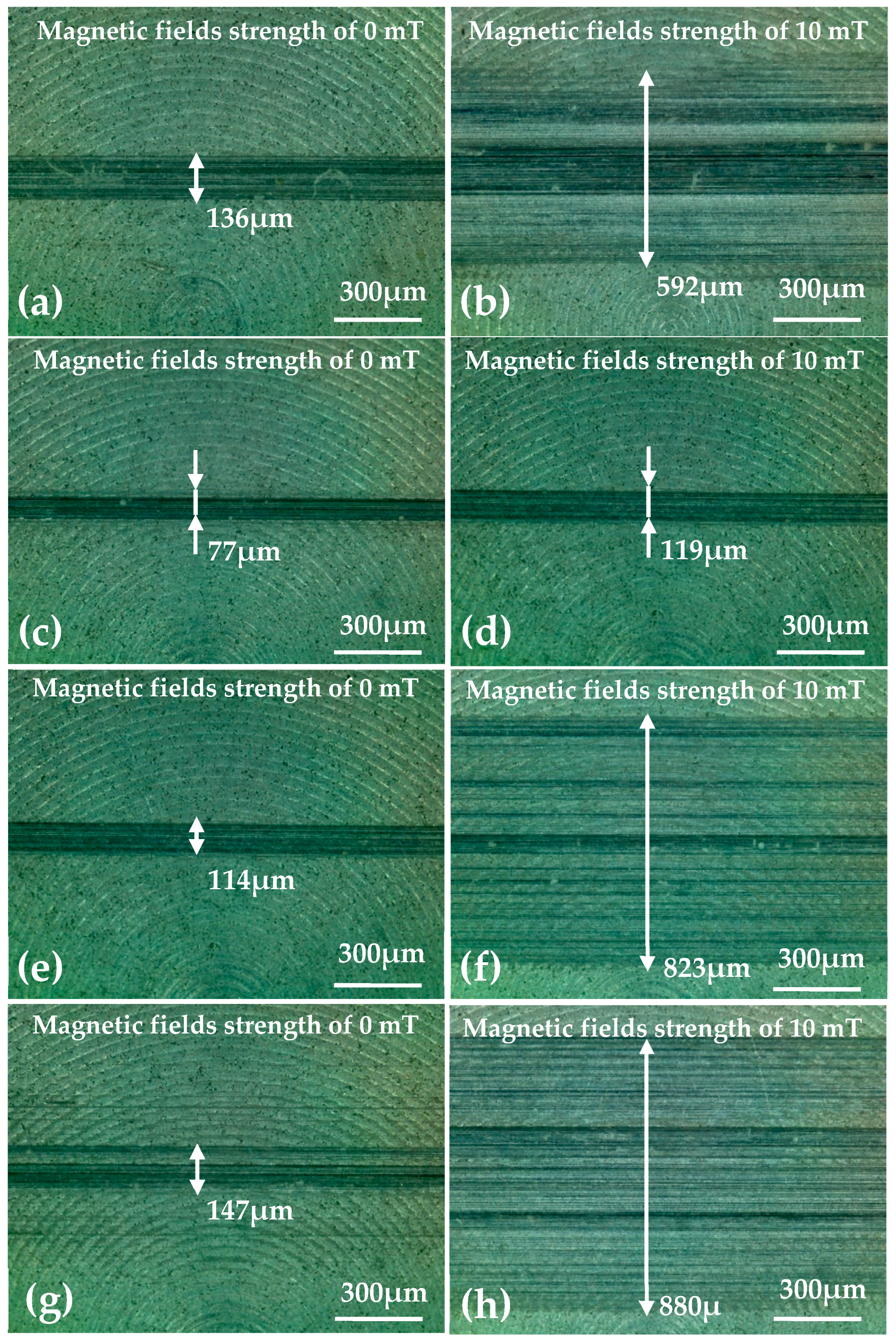
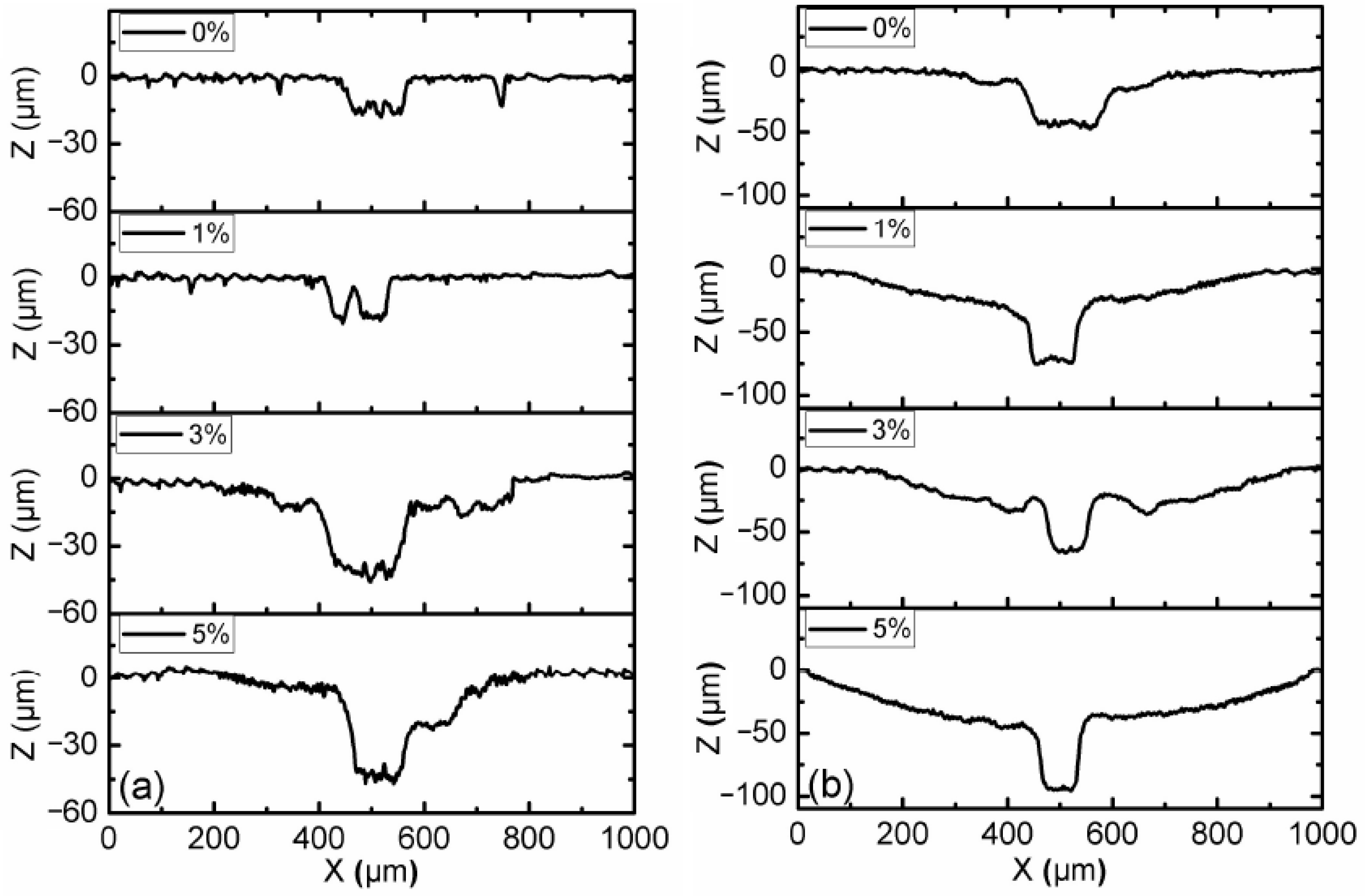
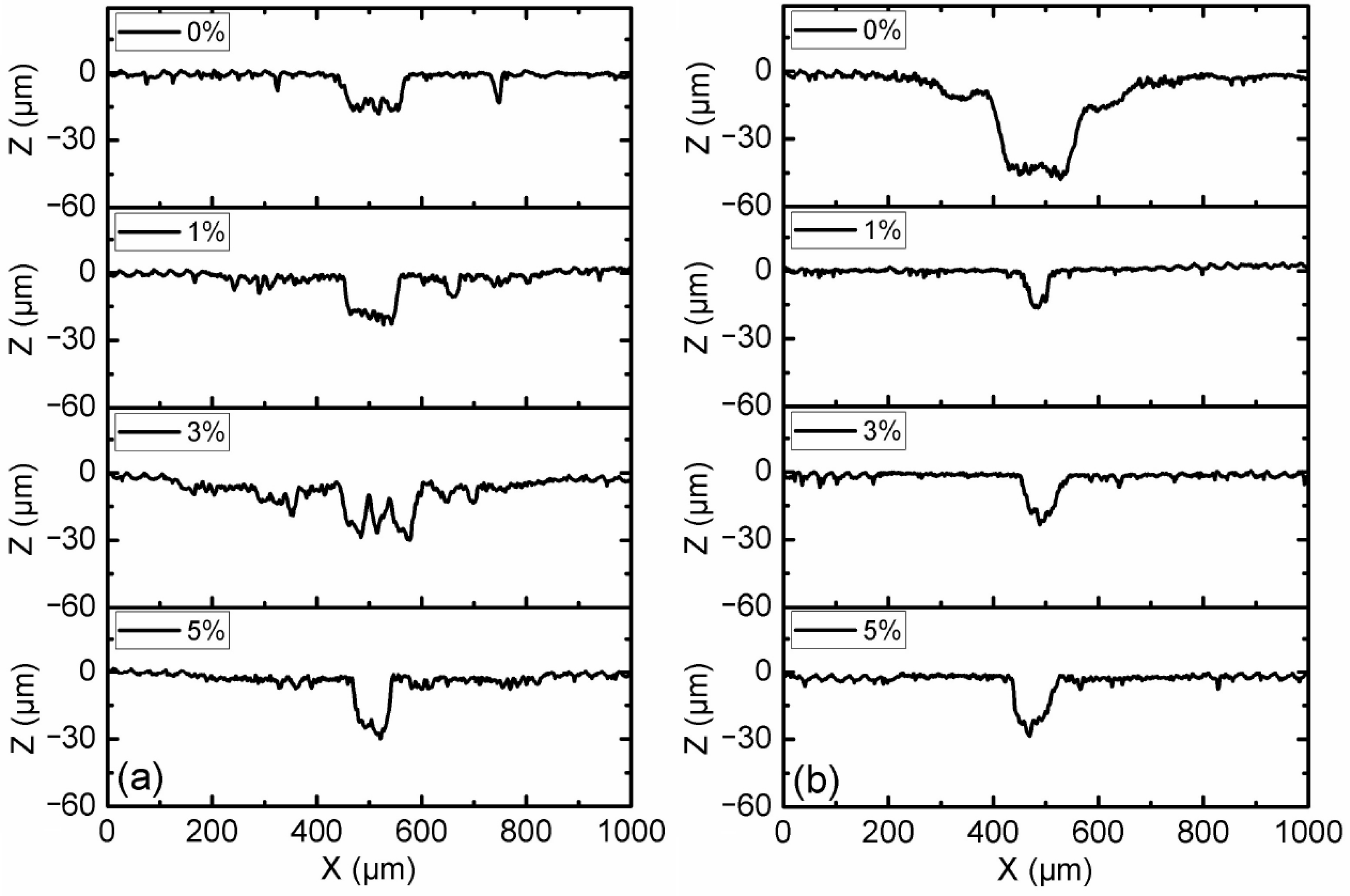
3.1. Effect of Load and Magnetic Field
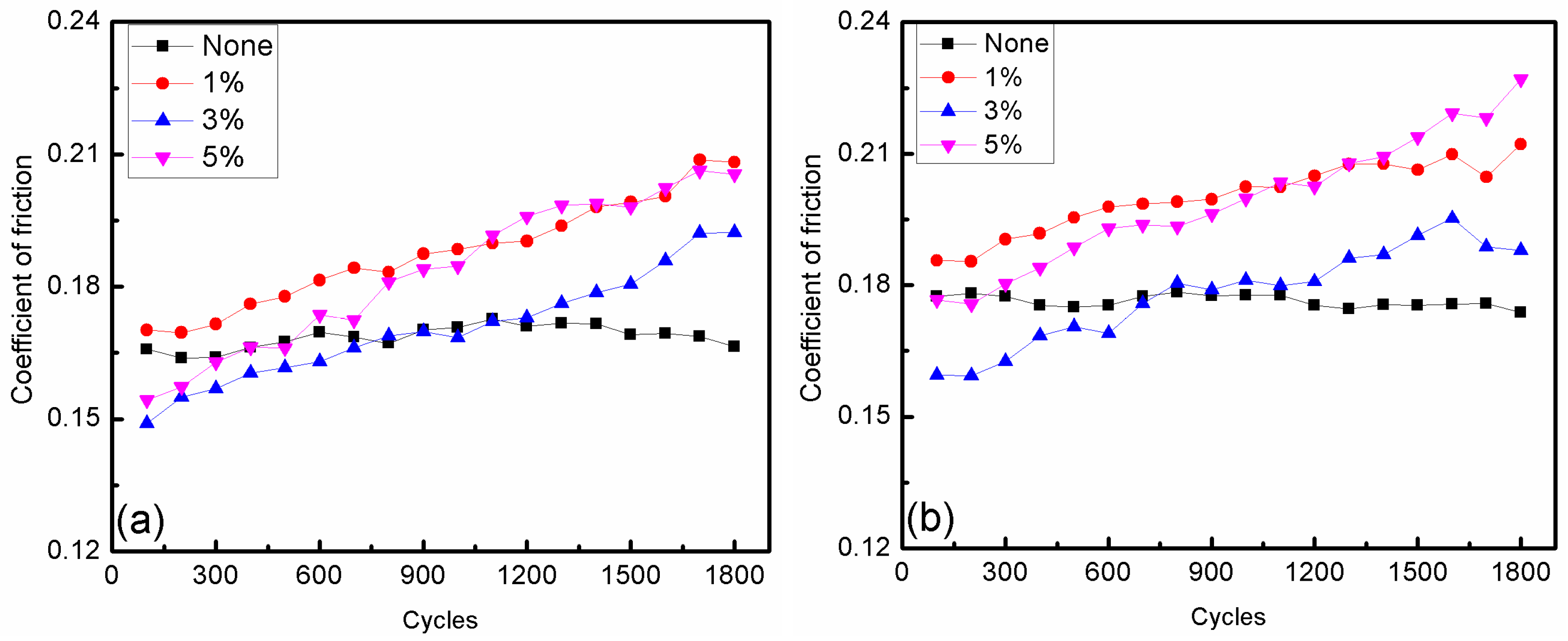
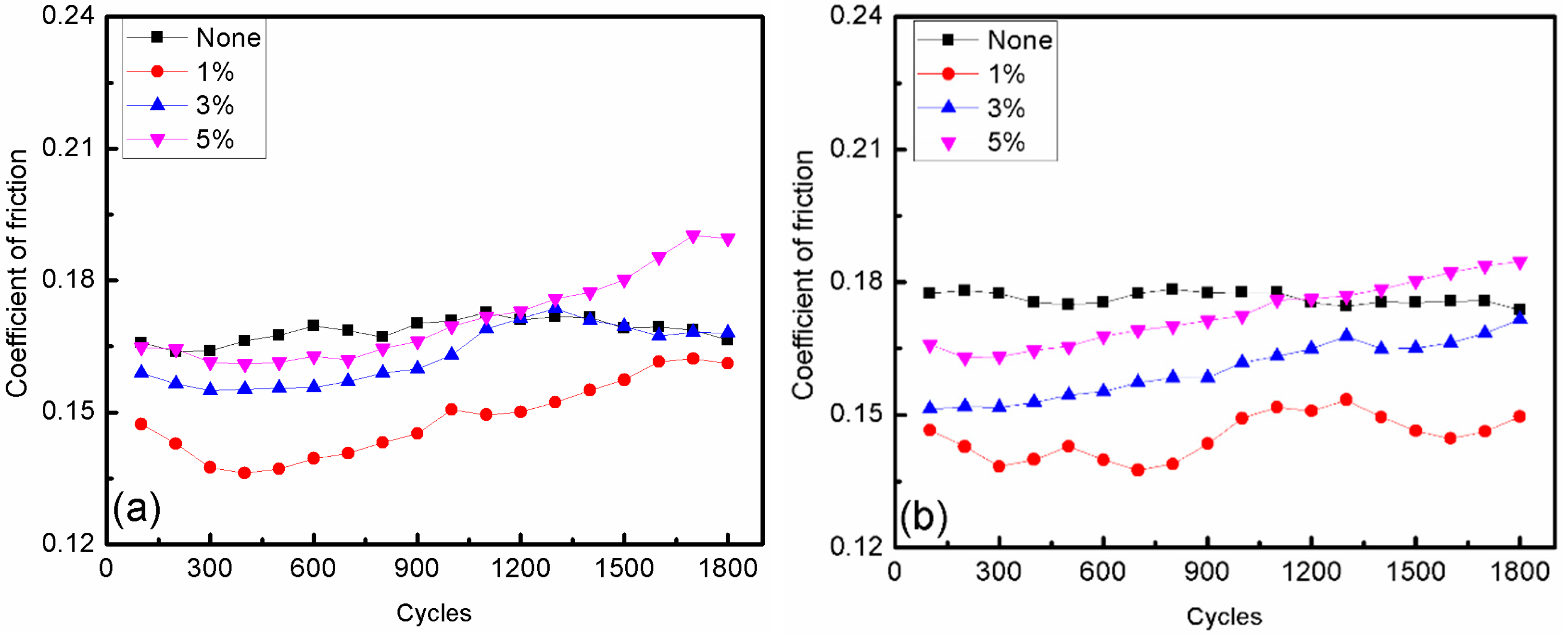
3.2. Effect of Additive Constituents and Contents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ND | Nano-diamond |
| CI | Carbonyl iron |
| MRF | Magnetorheological fluid |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| EDX | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
References
- Ashour, O.; Rogers, C.A.; Kordonsky, W. Magnetorheological Fluids: Materials, Characterization, and Devixces. J. Intel. Mat. Syst. Struct. 1996, 7, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Gordaninejad, F. Flow Analysis of Field-Controllable, Electro- and Magneto-Rheological Fluids Using Herschel-Bulkley Model. J. Intel. Mat. Syst. Struct. 1999, 10, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, M.; Hashemabadi, S.H.; Ghaffari, A. A Review on the Magnetorheological Fluid Preparation and Stabilization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Upadhyay, R.V.; Aswal, V.K. Study of the Magnetorheology of Bimodal Magnetite Suspension. Smart. Mater. Struct. 2012, 1447, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Min, T.H.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, N.H.; Park, K.J.; You, C.Y. Effects of surface treatment on magnetic carbonyl iron/polyaniline microspheres and their magnetorheological study. Coll. Surf. A 2017, 531, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hato, M.J.; Choi, H.J.; Sim, H.H.; Park, B.O.; Ray, S.S. Magnetic carbonyl iron suspension with organoclay additive and its magnetorheological properties. Coll. Surf. A 2011, 377, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.D.; Kang, J.W.; Choi, S.B. Field-dependent characteristics of magnetorheological fluids containing corroded iron particles. Smart. Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 115016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Z.; Piao, S.H.; Zhang, K.; Choi, Y.J. Effect of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles on a carbonyl iron based magnetorheological suspension. Coll. Surf. A 2018, 537, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Liu, Y.D.; Choi, H.J. Physical characteristics of magnetorheological suspensions and their applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.L.; Bullough, W.A.; Feng, C.; Lingard, C. Tribological performance of a magneto-rheological suspension. Wear 2001, 247, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.W.; Lee, S.O.; Jang, K.I.; Min, B.K.; Lee, S.J. Tribological Properties of a Magnetorheological (MR) Fluid in a Finishing Process. Tribol. Trans. 2009, 5, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, C.; Xiu, S.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Liang, D. Experimental study on magnetorheological polishing fluids composition in reciprocating magnetorheological polishing. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2022, 33, 2616–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.L.; Seong, M.S.; Choi, S.B.; Lee, C.H.; Cho, M.W. Tribological characteristics of magneto-rheological fluid for movement sensor application. Smart. Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 017001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, C.H. Reciprocating friction characteristics of magneto-rheological fluid for aluminum under magnetic field. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. 2014, 24, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, D.H.; Song, W.L.; Xiu, S.C.; Meng, X.Z. Effect of surface texture and working gap on the braking performance of the magnetorheological fluid brake. Smart. Mater. Struc. 2016, 25, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.D.; Yan, H.; Qiu, H.Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Q. Friction and wear of magnetorheological fluid under magnetic field. Wear 2012, 278–279, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.J.; Menezes, P.L.; Lovell, M.R.; Jen, T.C. The influence of surface roughness and particulate size on the tribological performance of bio-based multi-functional hybrid lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2015, 88, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Xu, F.; Shen, J.L.; Wang, B.C.; Xu, X.Y.; Shao, J.B. Study on the modification of nanodiamond with DN-10. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2007, 23, 599–603. [Google Scholar]
- Mochalin, V.N.; Shenderova, O.; Ho, D.; Gogotsi, Y. The properties and applications of nanodiamonds. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.X.; Liu, H.L.; Sheldon, B.W.; Webster, T.J.; Yang, S.C.; Yang, H.L.; Yang, L. Surface energy-mediated fibronectin adsorption and osteoblast responses on nanostructured diamond. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolmatov, V.N. Detonation nanodiamonds in oils and lubricants. J. Superhard. Mater. 2010, 32, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Diao, Z.Y.; Peng, Z.; Xue, X.Y.; Zhang, M.; Song, W.L. Influence of Initial Surface Roughness on Tribological Characteristics of Magnetorheological Fluid Based on Damper Design. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2018, 10, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Rostami, M.; Mohammadi, A. Study of Effects of Nano-diamond as an oil additive on engine oil properties and wear rate of the internal parts of agricultural tractors engines. Mech. Eng. 2013, 57, 14443–14447. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.M.; Zi, B.; Zeng, Y.S.; Hou, Y.F.; Meng, Q.R. Temperature-dependent material properties of the components of magnetorheological fluids. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 8459–8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.K.; Sarkar, C. Thermal and Tribological Performance of Graphite Flake-Based Magnetorheological Fluid Under Shear Mode Clutch. J. Tribol. 2021, 143, 121806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


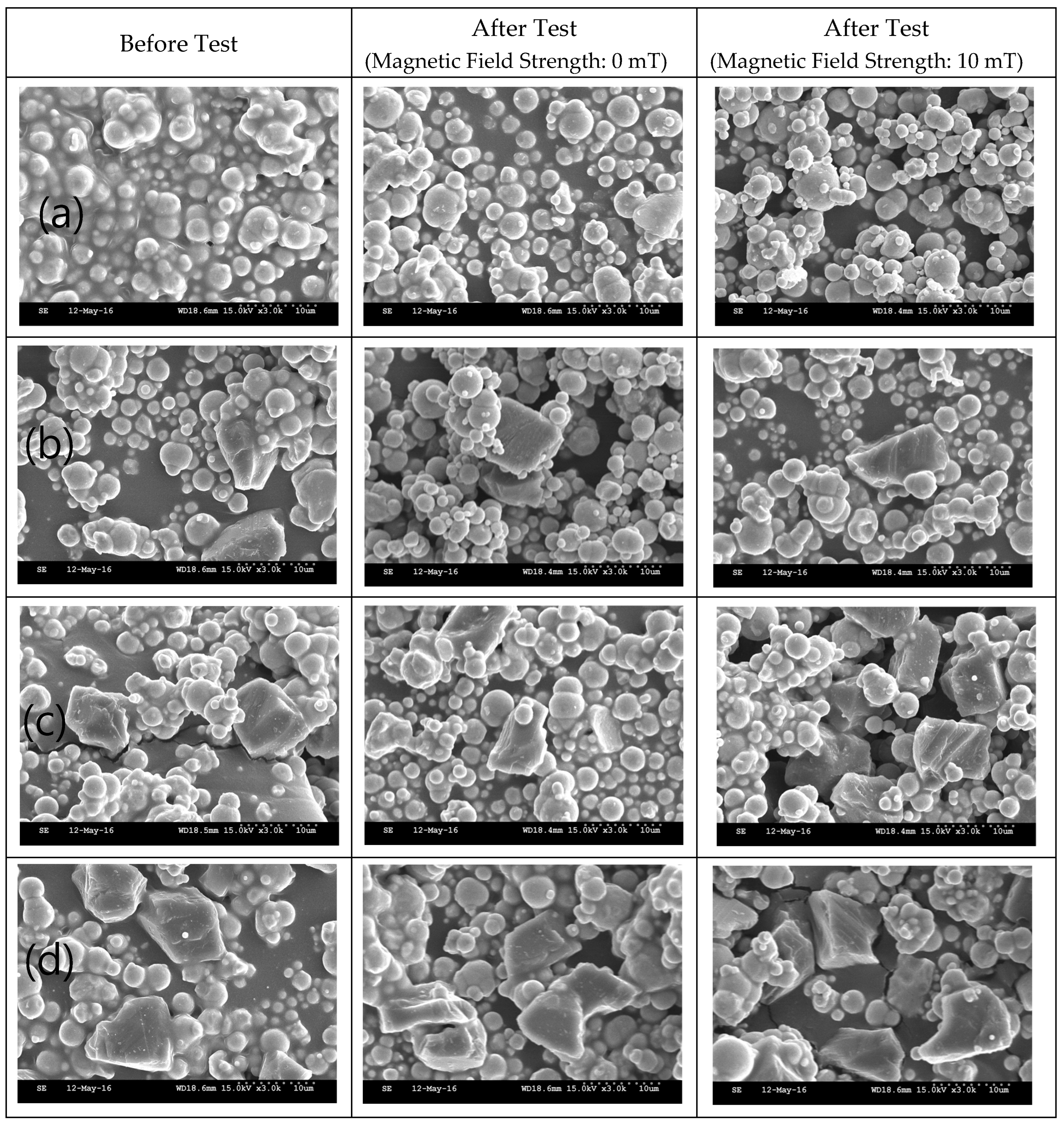
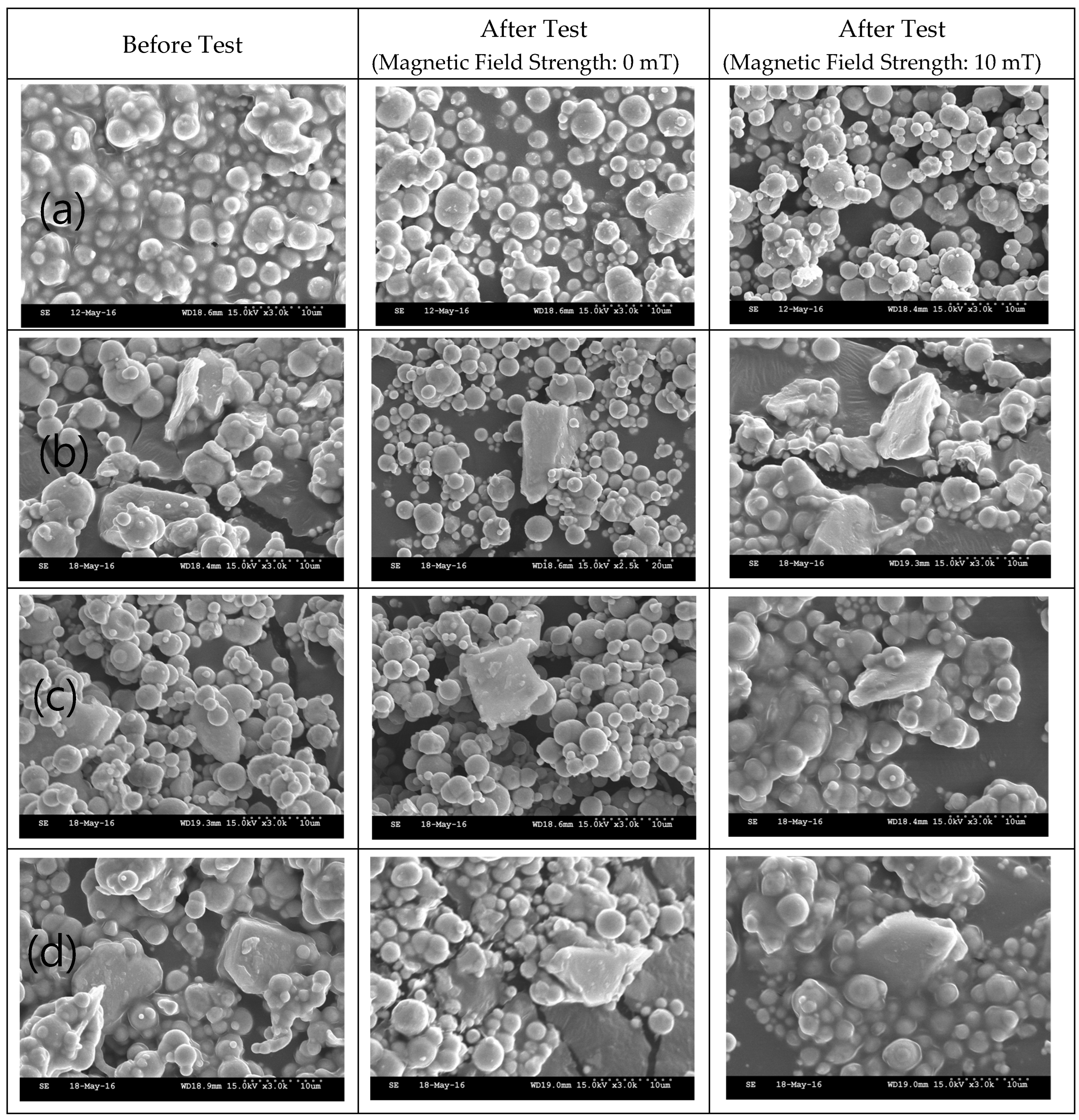
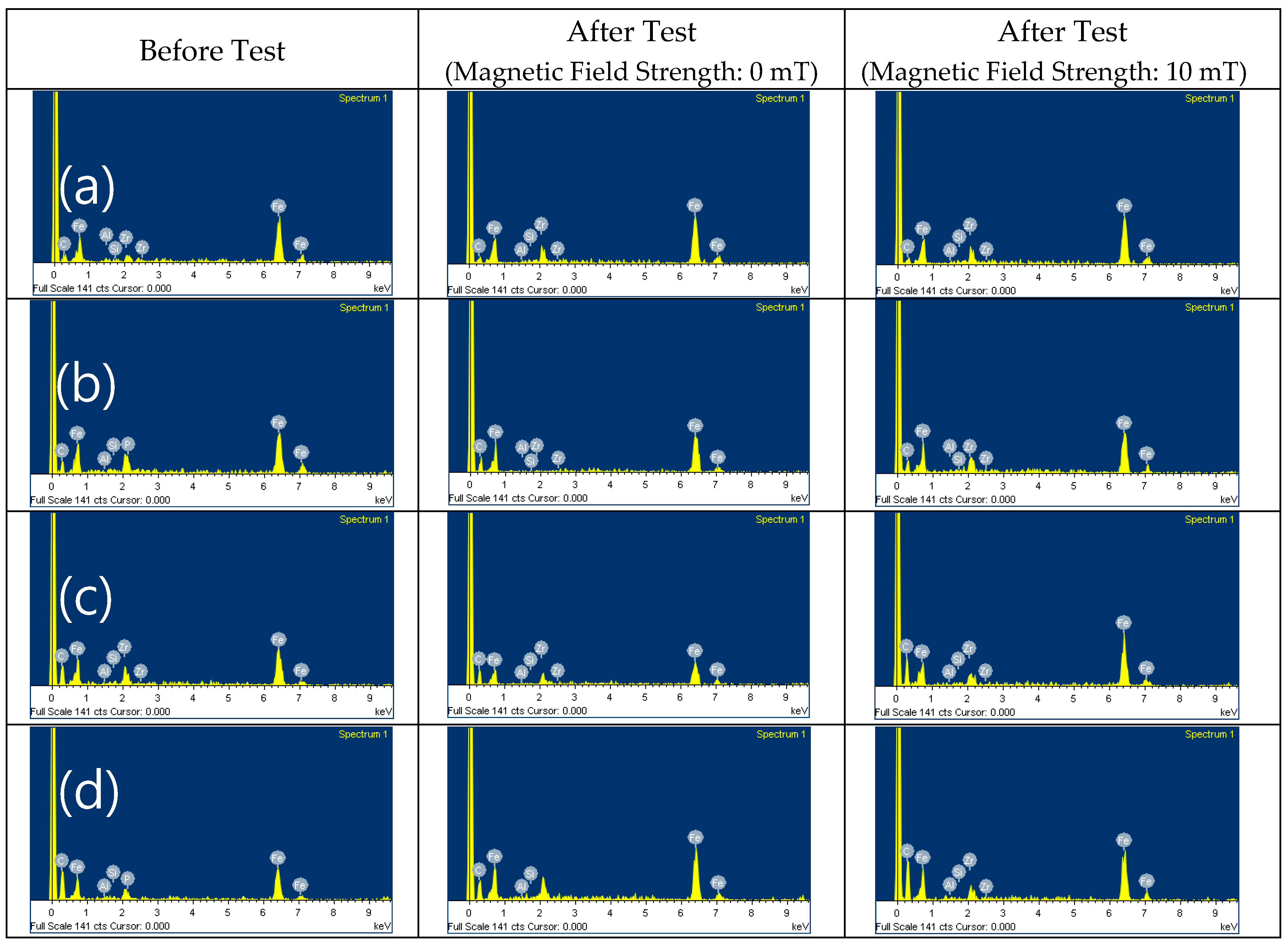
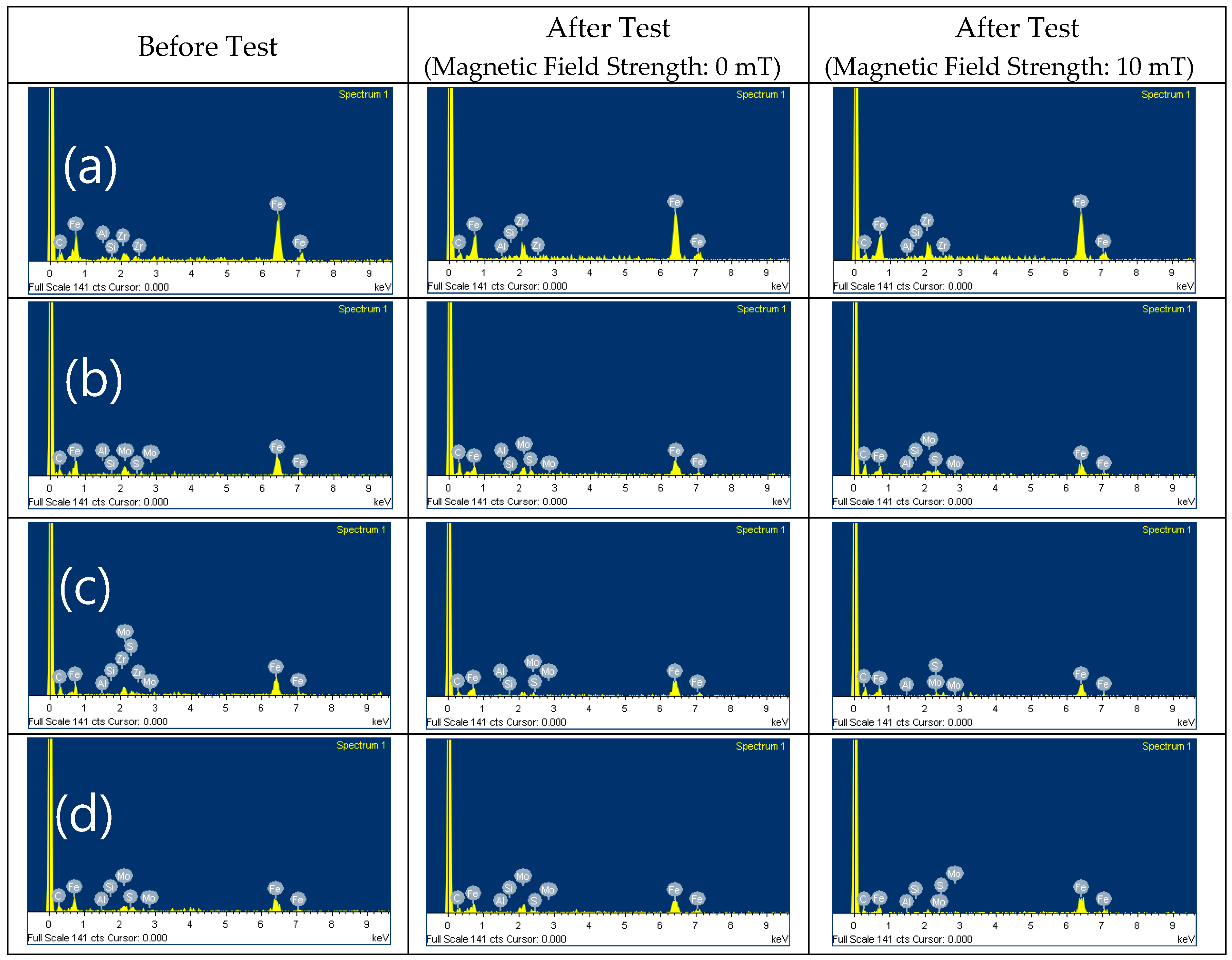
| Parameter | Content of Component (wt.%) |
|---|---|
| Silicone oil | 55–59 |
| CI particles | 35 |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate | 3 |
| Sodium nitrate | 1 |
| Nanodiamond/MoS2 | 1–5 |
| Glycerin | 1 |
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Magnetic field (mT) | 0, 10 |
| Load (N) | 5, 10, 15 |
| Oscillation frequency (Hz) | 1 |
| Reciprocating stroke (mm) | 10 |
| Temperature (°C) | 25 |
| Cycle | 1800 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, S.; Cao, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, P.; Choi, S.-B. Effect of Additives on Tribological Performance of Magnetorheological Fluids. Micromachines 2024, 15, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020270
Zhuang S, Cao Y, Song W, Zhang P, Choi S-B. Effect of Additives on Tribological Performance of Magnetorheological Fluids. Micromachines. 2024; 15(2):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020270
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Songran, Yongbing Cao, Wanli Song, Peng Zhang, and Seung-Bok Choi. 2024. "Effect of Additives on Tribological Performance of Magnetorheological Fluids" Micromachines 15, no. 2: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020270
APA StyleZhuang, S., Cao, Y., Song, W., Zhang, P., & Choi, S.-B. (2024). Effect of Additives on Tribological Performance of Magnetorheological Fluids. Micromachines, 15(2), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020270







