Electrostatic MEMS Two-Dimensional Scanning Micromirrors Integrated with Piezoresistive Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of the Structure for Electrostatic-Driven MEMS Micromirrors
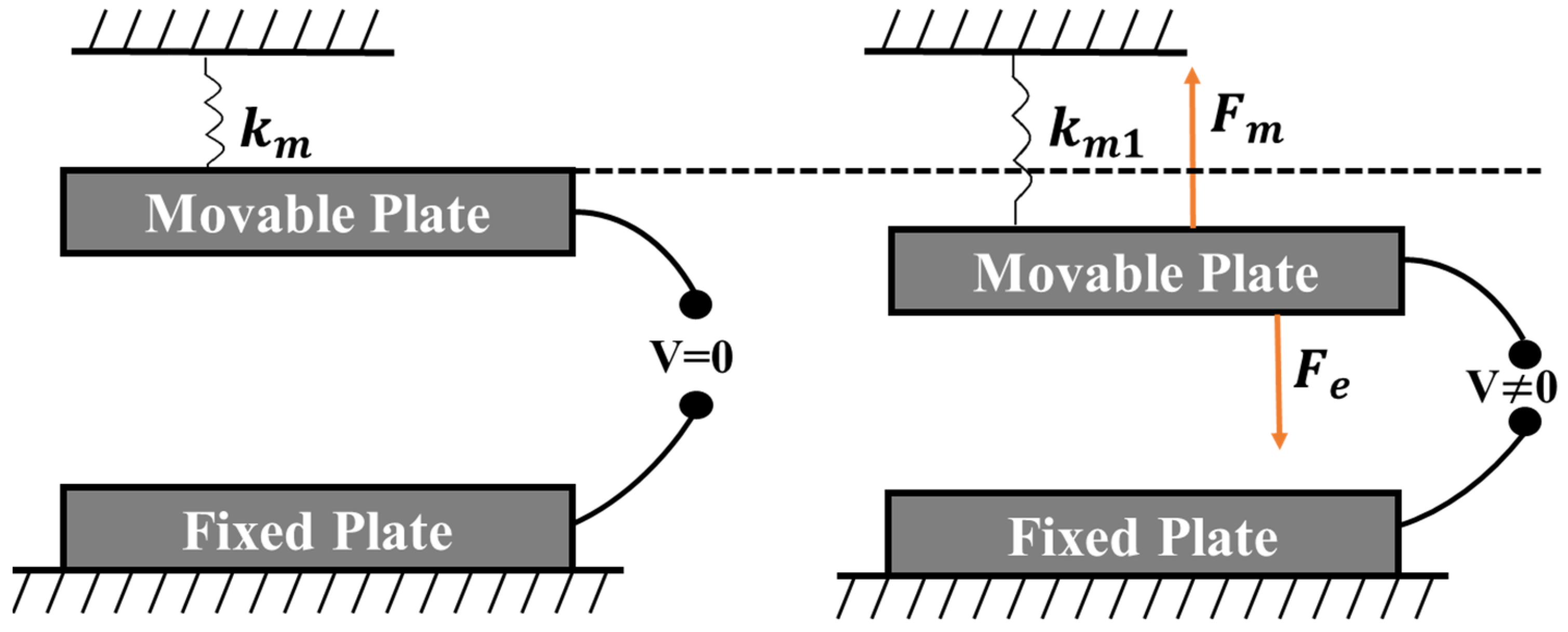
2.1. Principle of Electrostatic Actuation
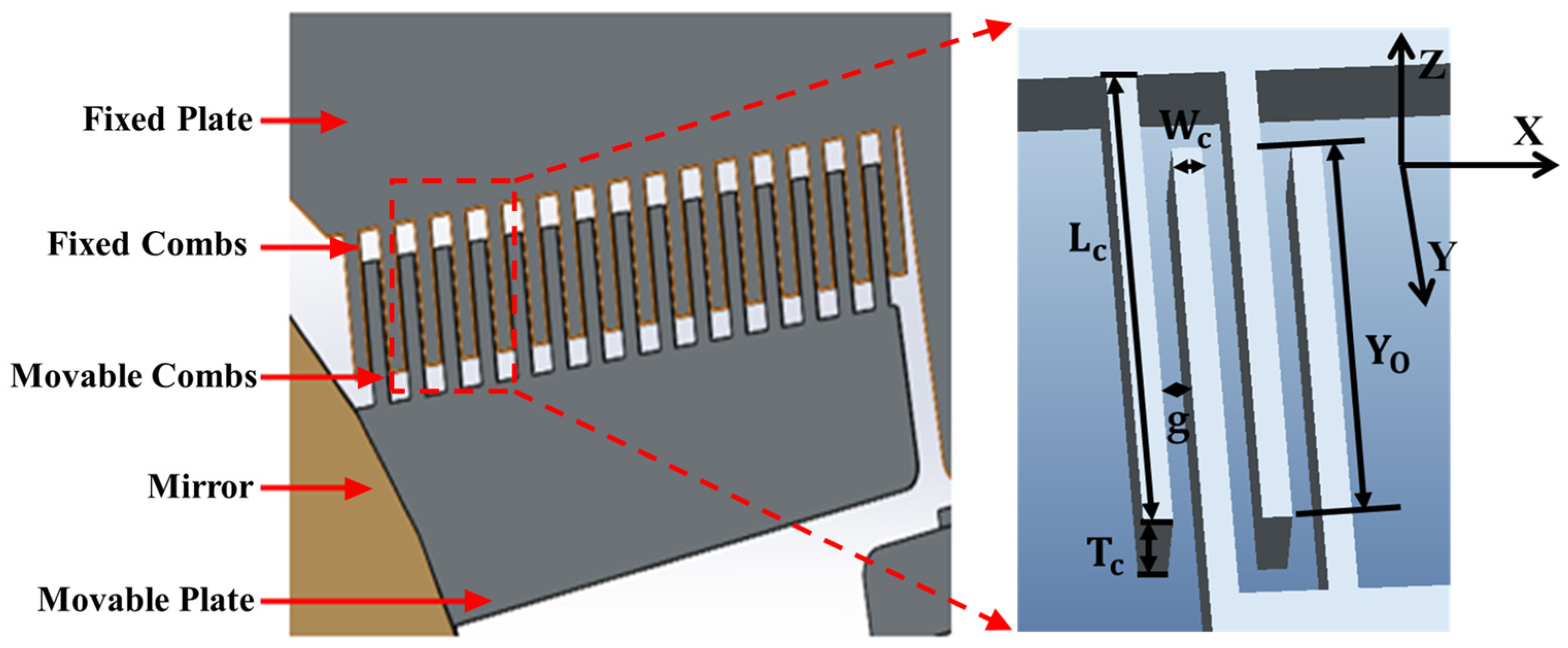
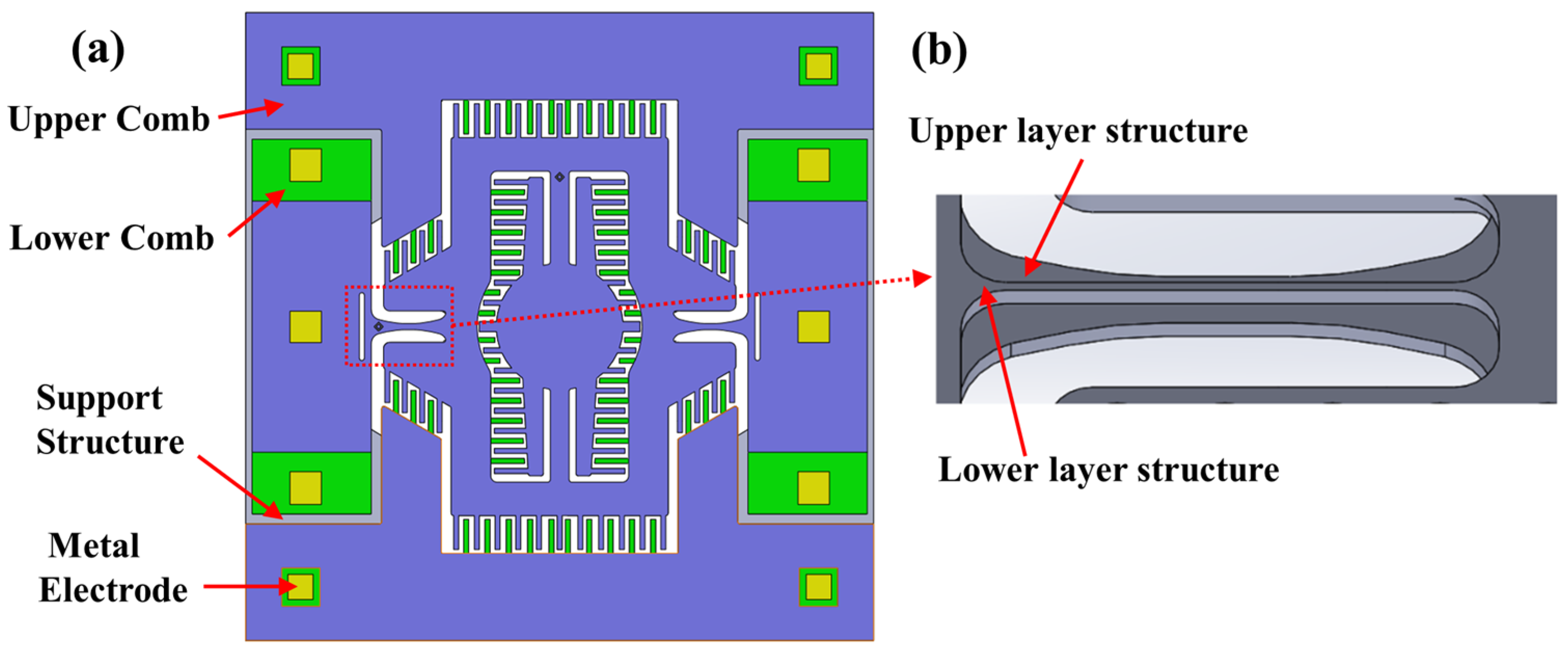
2.2. Design of the Structure for Micromirrors
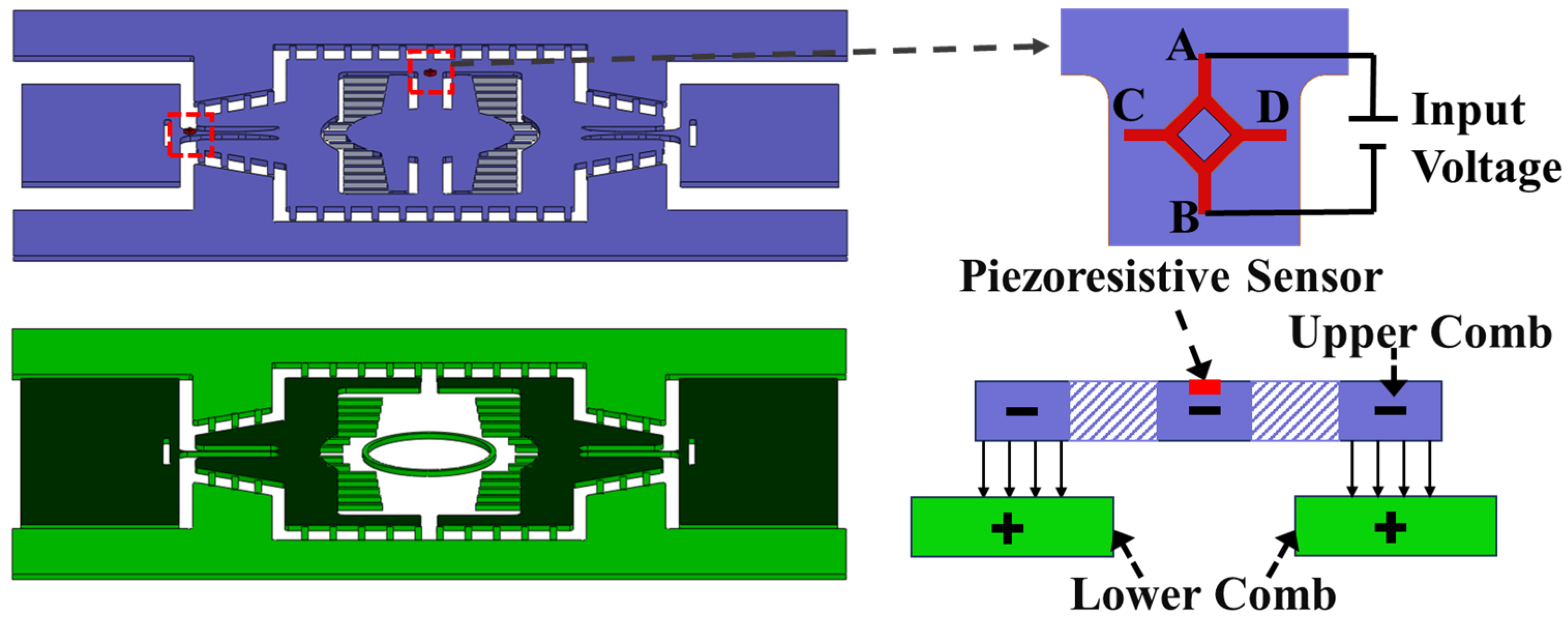
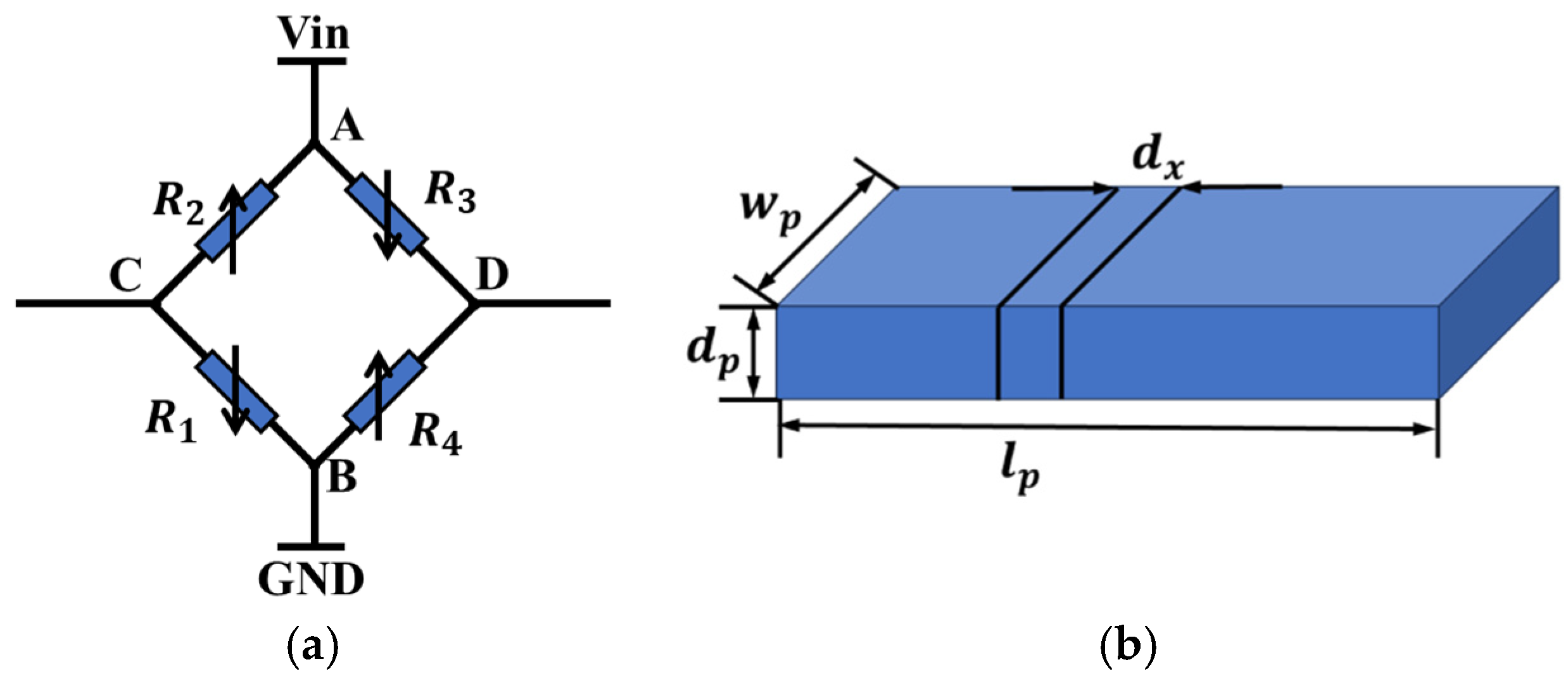
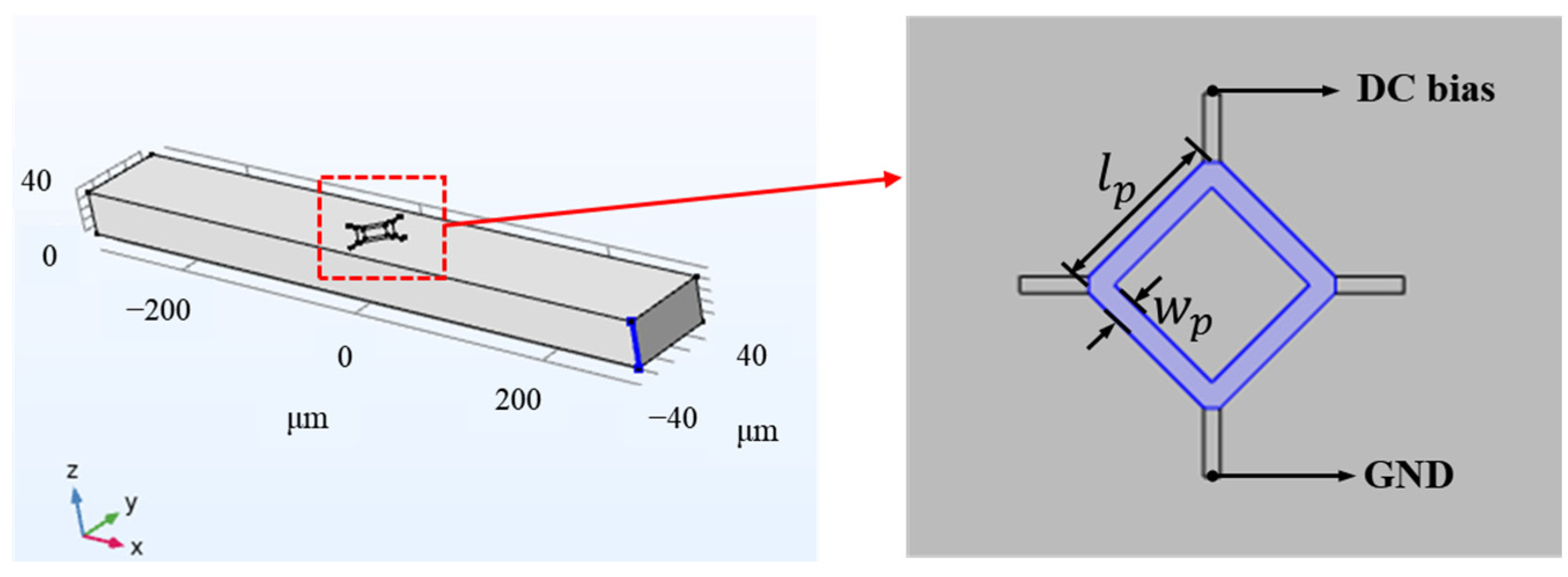
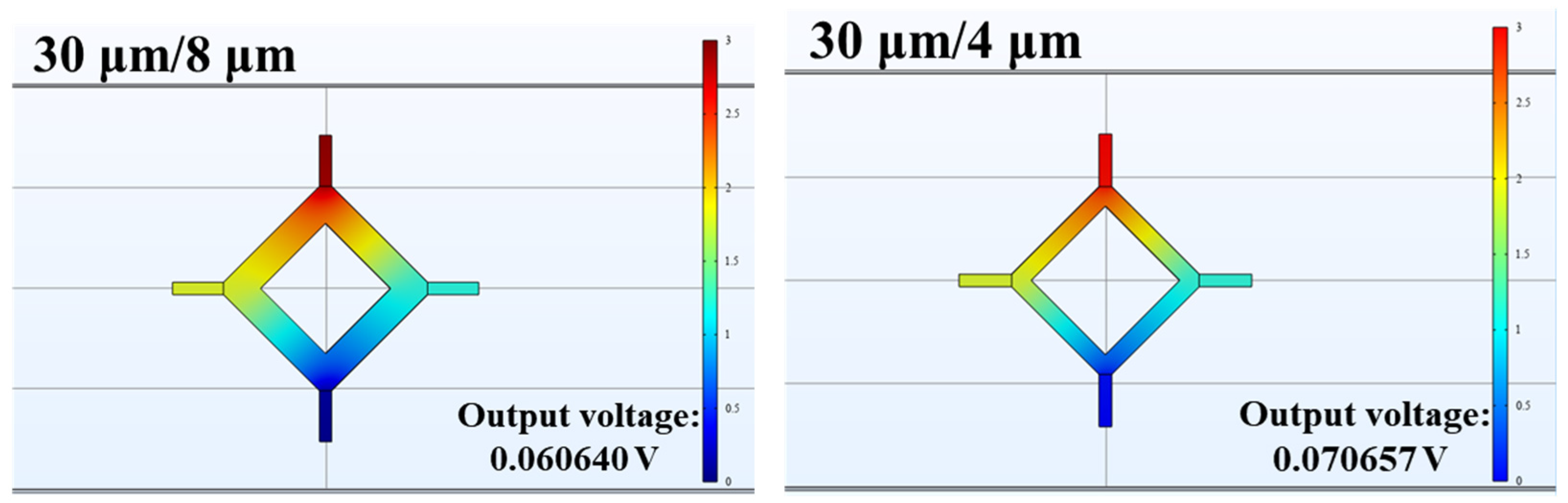
2.3. Design of the Piezoresistive Sensor
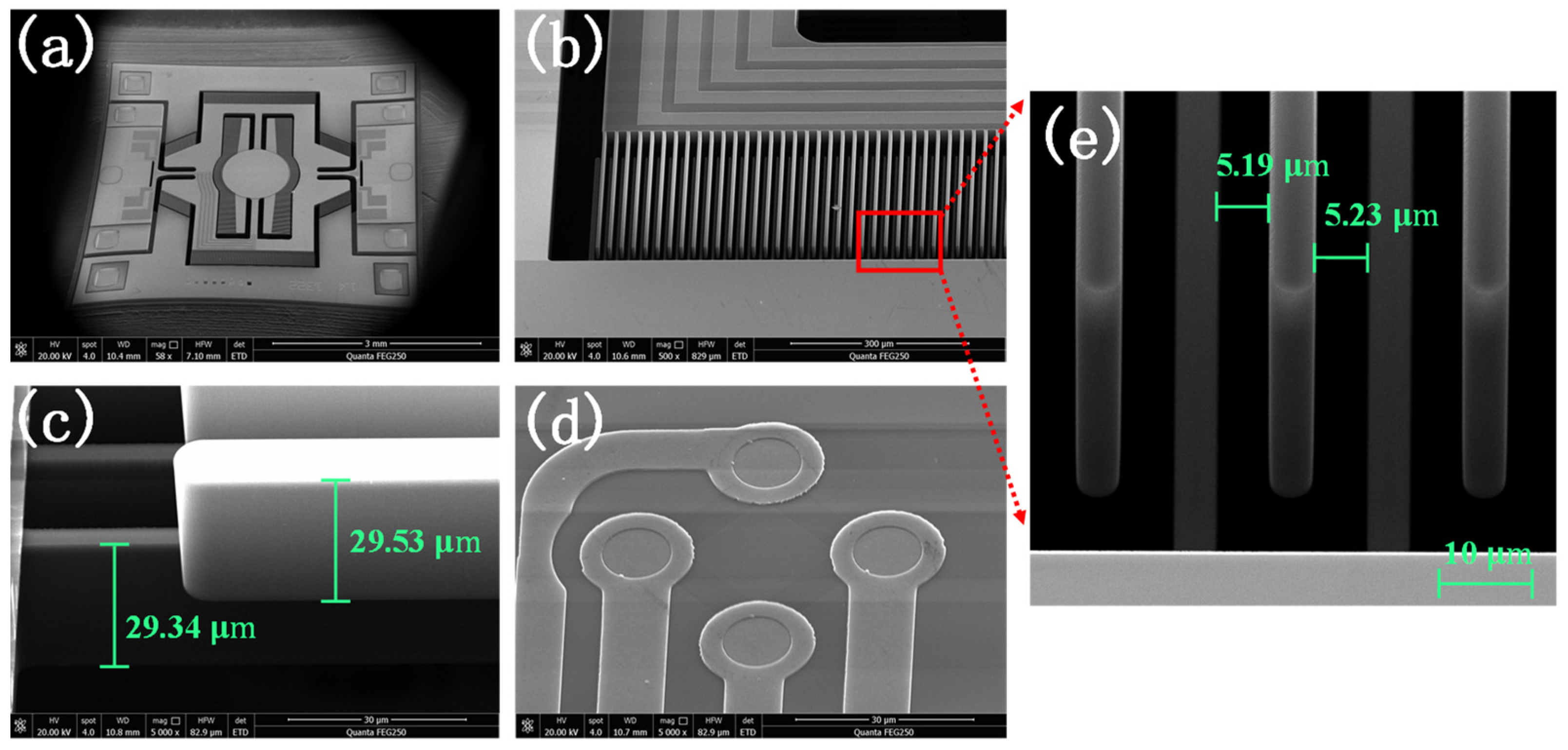
3. Process Flow Design and Fabrication
4. Experiments and Discussion
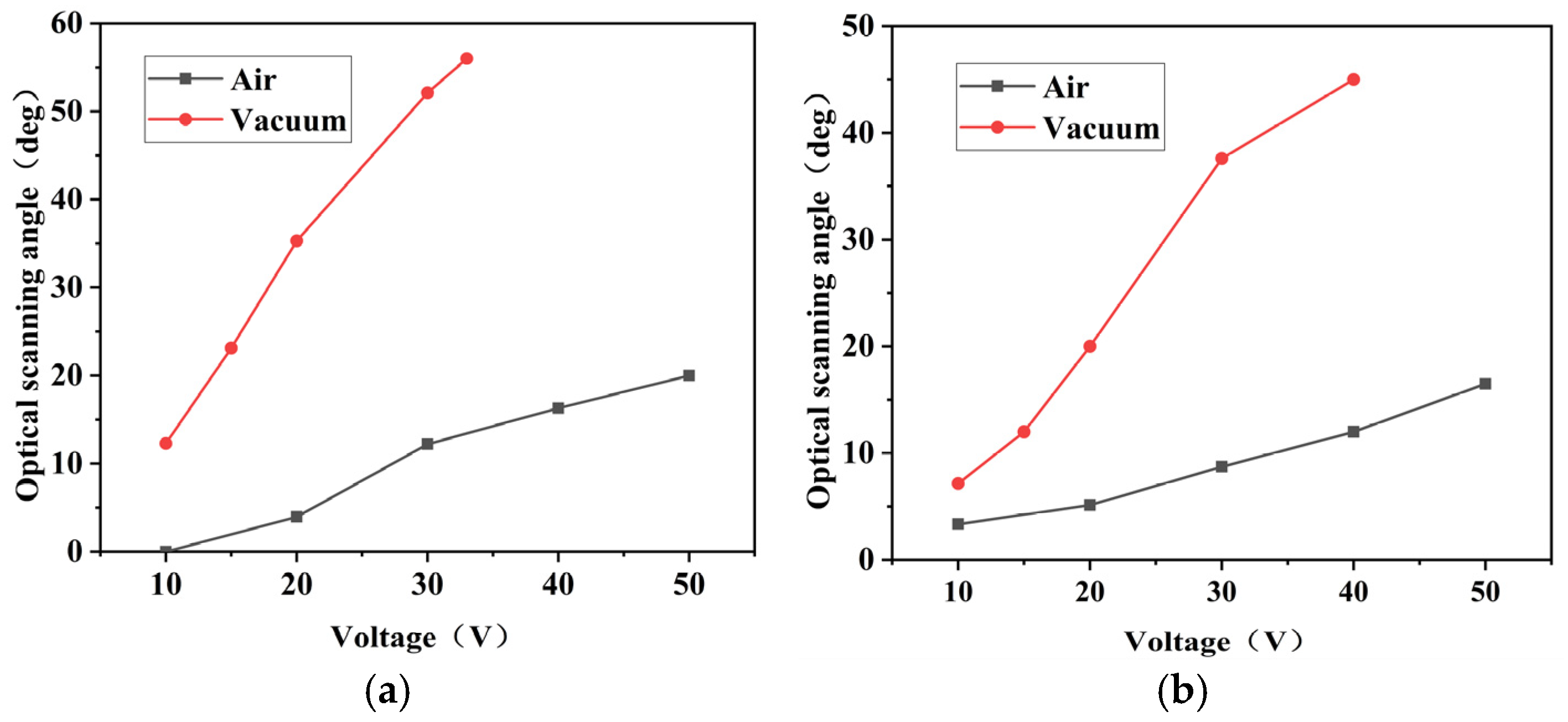
4.1. Testing the Scanning Angles of the Mirror in a Vacuum Environment
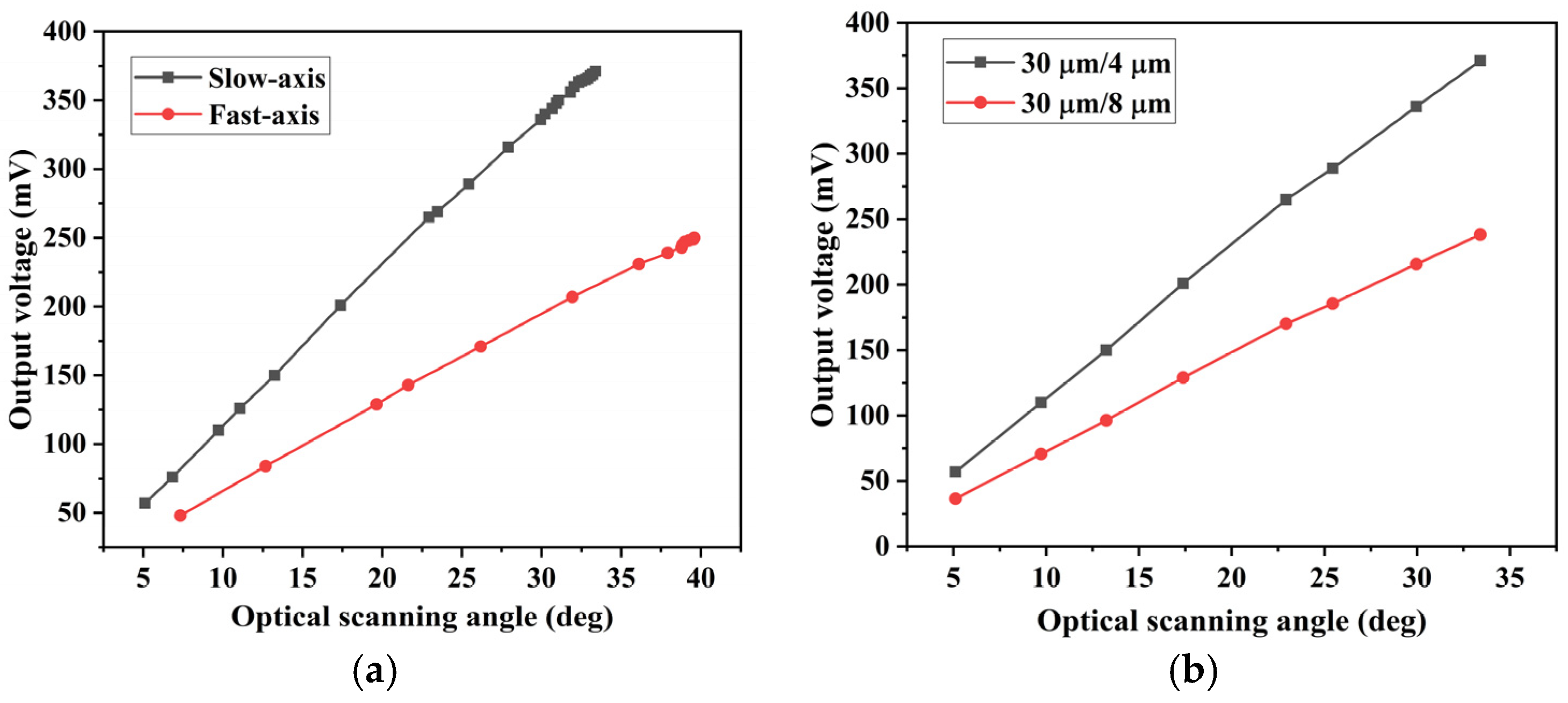
4.2. Testing of the Piezoresistive Sensor
4.3. Testing of the 2D MEMS Scanning Micromirror
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmström, S.T.S.; Baran, U.; Urey, H. MEMS laser scanners: A review. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Senger, F.; Albers, J.; Malaurie, P.; Janicke, C.; Pohl, L.; Heinrich, F.; Kaden, D.; Quenzer, H.-J.; Lofink, F.; et al. Resonant 1D MEMS mirror with a total optical scan angle of 180° for automotive LiDAR. In Proceedings of the MOEMS and Miniaturized Systems XIX, SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–6 February 2020; Volume 11293, pp. 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Watkins, C.; Xie, H. Mems mirrors for lidar: A review. Micromachines 2020, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, A.C.L.; Lai, H.Y.H.; Lin, T.W.; Fu, S.G.; Lu, M.S.C. An electrostatically driven 2D micro-scanning mirror with capacitive sensing for projection display. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 222, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.; Fabre, L.; Conte, F.L.; Kilcher, L.; Kechana, F.; Abelé, N.; Kayal, M. Micro-beamer based on MEMS micro-mirrors and laser light source. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrak, O.; Schwarz, F.; Pohl, L.; Reher, M.; Janicke, C.; Przytarski, J.; Senger, F.; Albers, J.; Giese, T.; Ratzmann, L.; et al. Laser beam scanning based AR-display applying resonant 2D MEMS mirrors. In Proceedings of the Optical Architectures for Displays and Sensing in Augmented, Virtual, and Mixed Reality (AR, VR, MR) II, Online, 28–31 March 2021; Volume 11765, pp. 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Solgaard, O.; Ford, J.E. Optical MEMS for lightwave communication. J. Light. Technol. 2006, 24, 4433–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Qiao, D.; Xia, C. Curved light surface model for calibration of a structured light 3D modeling system based on striped patterns. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 33240–33253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.H.; Hwang, K.; Kim, H.; Jeong, K.H. Scanning MEMS mirror for high definition and high frame rate Lissajous patterns. Micromachines 2019, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Kavehrad, M.; Lou, Y. MEMS-based beam-steerable FSO communications for reconfigurable wireless data center. In Proceedings of the Broadband Access Communication Technologies XI, SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 31 January–1 February 2017; Volume 10128, pp. 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroufi, M.; Fowler, A.G.; Moheimani, S.R. MEMS for nanopositioning: Design and applications. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2017, 26, 469–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroedter, R.; Roth, M.; Janschek, K.; Sandner, T. Flatness-based open-loop and closed-loop control for electrostatic quasi-static microscanners using jerk-limited trajectory design. Mechatronics 2018, 56, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, P.; Molinari, L.; Barbieri, A.; Zamprogno, M.; Mendicino, G.; Boni, N.; Langfelder, G. Nested closed-Loop control of Quasi-Static MEMS scanners with large dynamic range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahmann, J.; Dreyhaupt, A.; Drabe, C.; Schrödter, R.; Kamenz, J.; Sandner, T. MEMS-mirror based trajectory resolution and precision enabled by two different piezoresistive sensor technologies. In Proceedings of the MOEMS and Miniaturized Systems XV, SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–17 February 2016; Volume 9760, pp. 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wantoch, T.V.; Mallas, C.; Hofmann, U.; Janes, J.; Wagner, B.; Benecke, W. Analysis of capacitive sensing for 2D-MEMS scanner laser projection. In Proceedings of the MOEMS and Miniaturized Systems XIII, SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–6 February 2014; Volume 8977, pp. 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H. Integrated optoelectronic position sensor for scanning micromirrors. Sensors 2018, 18, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Maeda, R. Piezoelectric optical micro scanner with built-in torsion sensors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, N.; Okazaki, K.; Kudo, A.; Sawada, R. Stable MEMS electrostatic comb-driven scanning mirror via feedback of comb electrostatic capacitance. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Optical MEMS and Nanophotonics (OMN), Singapore, 31 July–4 August 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 7, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, I.; Sawada, R.; Higurashi, E.; Sanada, S.; Chino, D. Integrated mi-cro-displacement sensor that measures tilting angle and linear movement of an external mirror. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 138, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, K.; Melzer, M.; Stoeckel, C.; Shaporin, A.; Forke, R.; Zimmermann, S.; Kuhn, H. 2D scanning micromirror with large scan angle and monolithically integrated angle sensors based on piezoelectric thin film aluminum nitride. Sensors 2020, 20, 6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. Foundations of MEMS, 2nd ed.; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.C.; Lim, M.G.; Howe, R.T. Electrostatic comb drive levitation and control method. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1992, 1, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadigadapa, S.A.K.M.; Mateti, K. Piezoelectric MEMS sensors: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 092001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourouina, T.; Lebrasseur, E.; Reyne, G.; Debray, A.; Fujita, H.; Ludwig, A.; Asaoka, A. Integration of two degree-of-freedom magnetostrictive actuation and piezoresistive detection: Application to a two-dimensional optical scanner. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2002, 11, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minne, S.C.; Manalis, S.R.; Quate, C.F. Parallel atomic force microscopy using cantilevers with integrated piezoresistive sensors and integrated piezoelectric actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 67, 3918–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, S.; Takigawa, M.; Igarashi, I. Integrated piezoresistive pressure sensor with both voltage and frequency output. Sens. Actuators 1983, 4, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, A.S.; Critello, C.D.; Pullano, S.A. Theory, technology and applications of piezoresistive sensors: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 281, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Goto, H.; Totani, H.; Sakata, M.; Yada, T. Two-dimensional miniature optical-scanning sensor with silicon micromachined scanning mirror. In Proceedings of the Miniaturized Systems with Micro-Optics and Micromechanics II, SPIE, San Jose, CA, USA, 10–12 February 1997; Volume 3008, pp. 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Tabata, M.; Haga, T.; Hane, K. Piezoresistive rotation angle sensor integrated in micromirror. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zuo, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yu, H. High-mode resonant piezoresistive cantilever sensors for tens-femtogram resoluble mass sensing in air. J. Microm. Microeng. 2006, 16, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Shan, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, K.; Yu, H.; Shen, W. Experimental Investigation of Vibration Isolator for Large Aperture Electromagnetic MEMS Micromirror. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Symbol | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| D | Diameter of mirror | 1 mm |
| Length of fast axis | 800 μm | |
| Width of fast axis | 120 μm | |
| Thickness of fast axis | 30 μm | |
| Length of slow axis | 600 μm | |
| Width of upper slow axis | 50 μm | |
| Width of lower slow axis | 10 μm | |
| Thickness of slow axis | 60 μm | |
| Gap between fixed and movable fingers | 5 μm | |
| Width of comb fingers | 5 μm | |
| Length of comb fingers | 280 μm | |
| Thickness of comb fingers | 30 μm | |
| Length of the overlap of the comb finger | 220 μm | |
| Thickness of dielectric layer | 1 μm | |
| Number of comb fingers driving the fast axis | 230 | |
| Number of comb fingers driving the slow axis | 250 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, Y.; Qian, L.; He, K.; Chen, B.; Wang, K.; Li, W.; Shen, W. Electrostatic MEMS Two-Dimensional Scanning Micromirrors Integrated with Piezoresistive Sensors. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121421
Shan Y, Qian L, He K, Chen B, Wang K, Li W, Shen W. Electrostatic MEMS Two-Dimensional Scanning Micromirrors Integrated with Piezoresistive Sensors. Micromachines. 2024; 15(12):1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121421
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Yameng, Lei Qian, Kaixuan He, Bo Chen, Kewei Wang, Wenchao Li, and Wenjiang Shen. 2024. "Electrostatic MEMS Two-Dimensional Scanning Micromirrors Integrated with Piezoresistive Sensors" Micromachines 15, no. 12: 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121421
APA StyleShan, Y., Qian, L., He, K., Chen, B., Wang, K., Li, W., & Shen, W. (2024). Electrostatic MEMS Two-Dimensional Scanning Micromirrors Integrated with Piezoresistive Sensors. Micromachines, 15(12), 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121421






