Ultra-Sensitive Impedimetric Immunosensor Using Copper Oxide Quantum Dots Grafted on the Gold Microelectrode for the Detection of Parathion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Methods
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Synthesis of Copper Oxide Quantum Dots
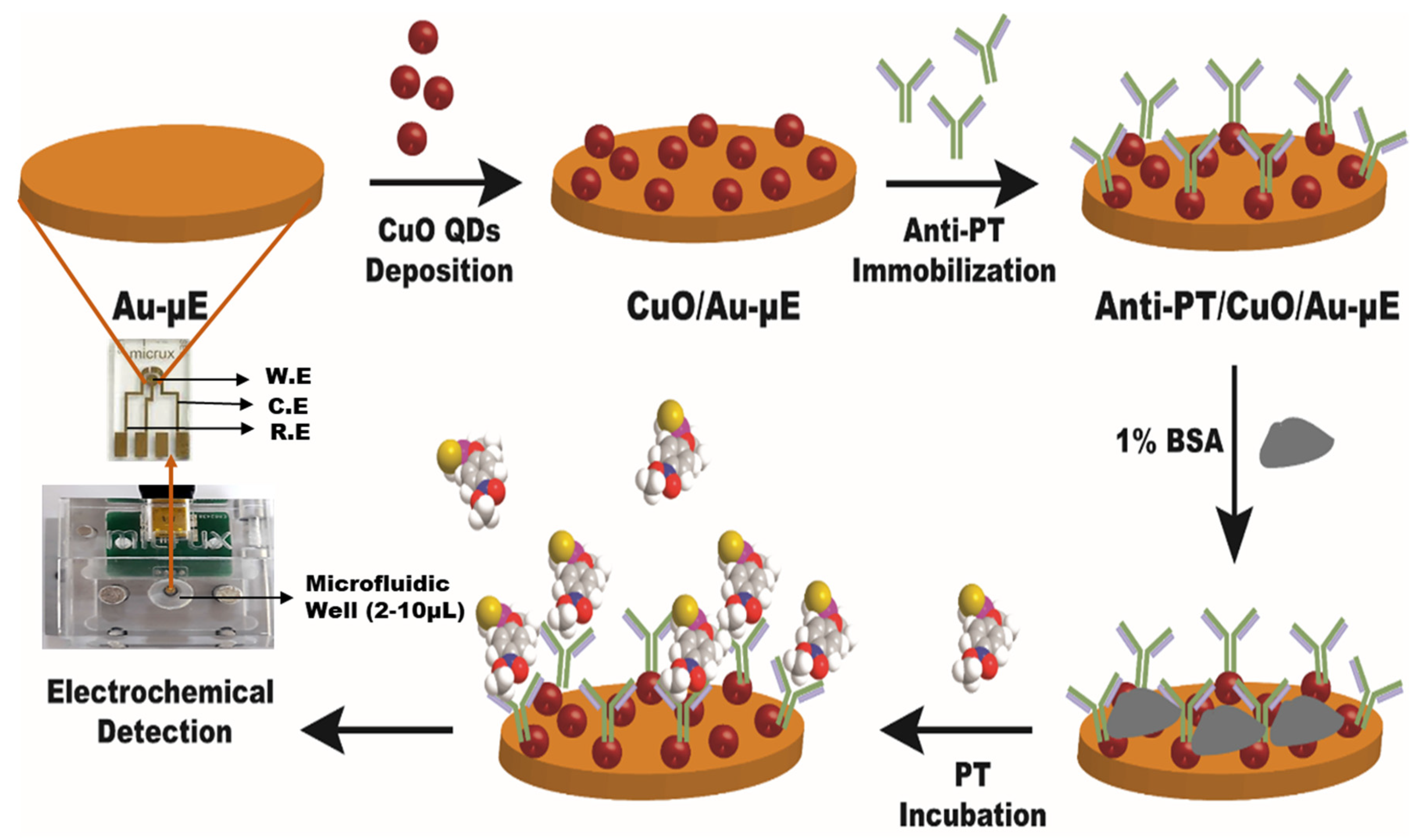
2.4. Development of Anti-PT/CuO/Au-µE
3. Results and Discussion
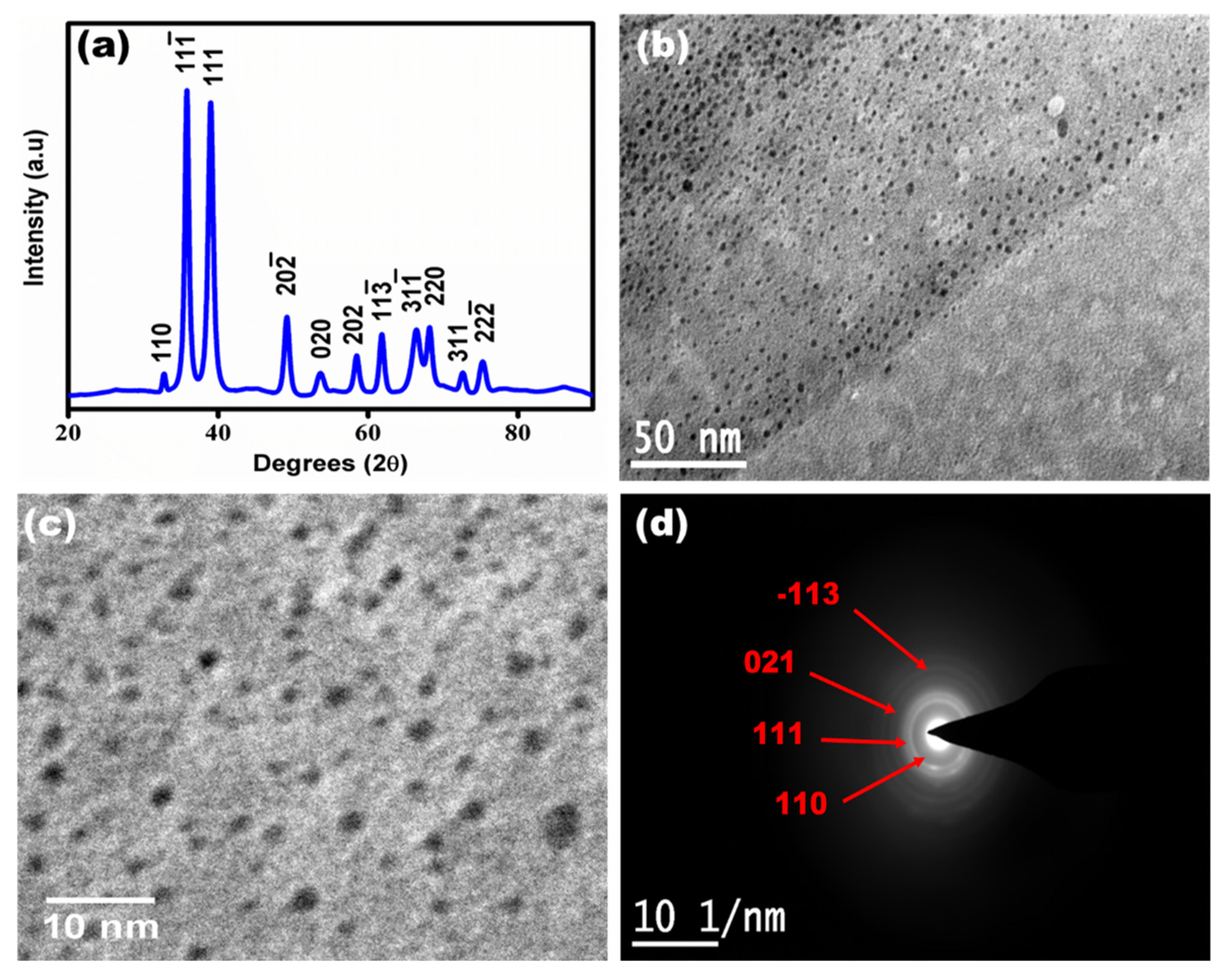
3.1. Characterization of Synthesized Copper Oxide Quantum Dots
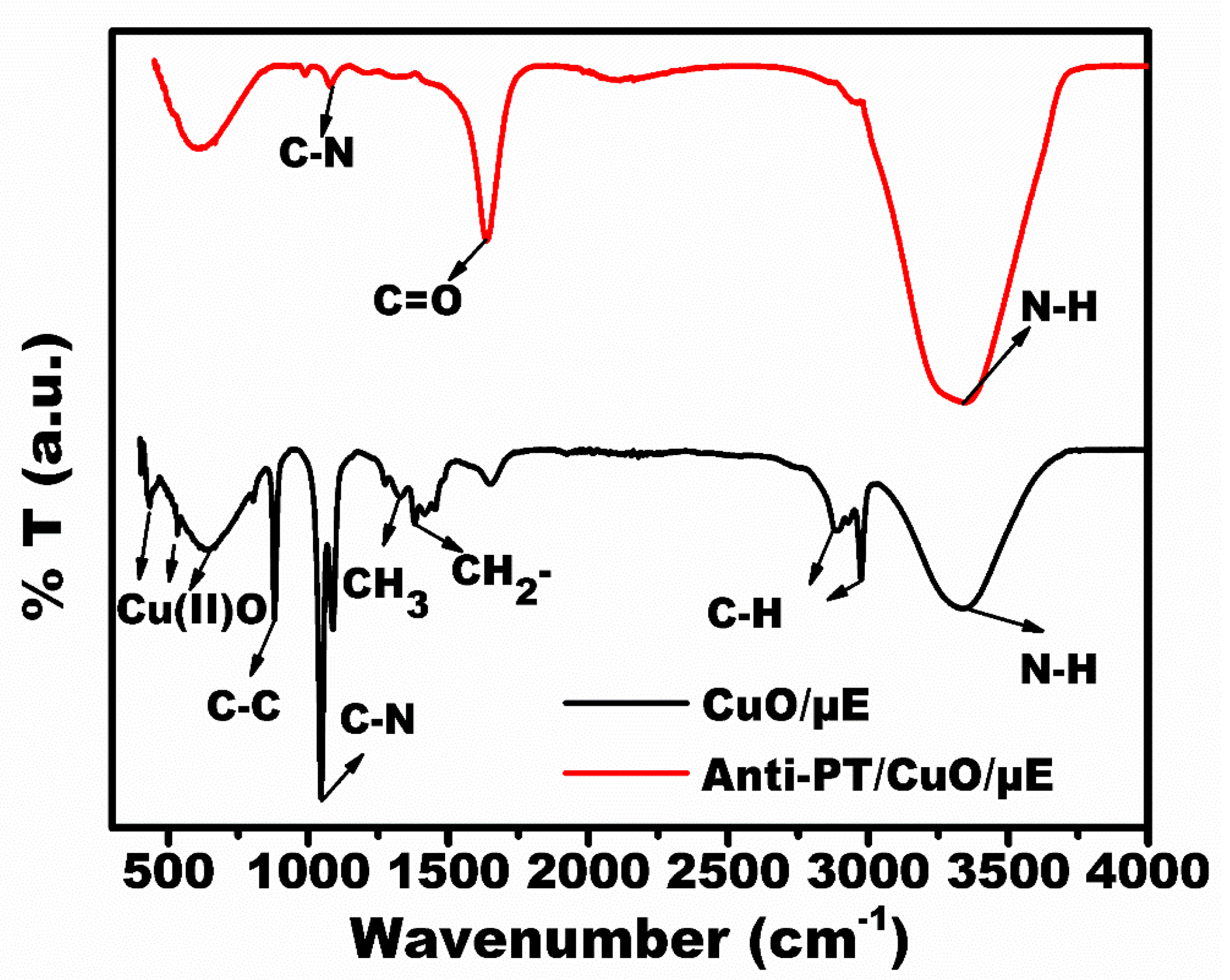
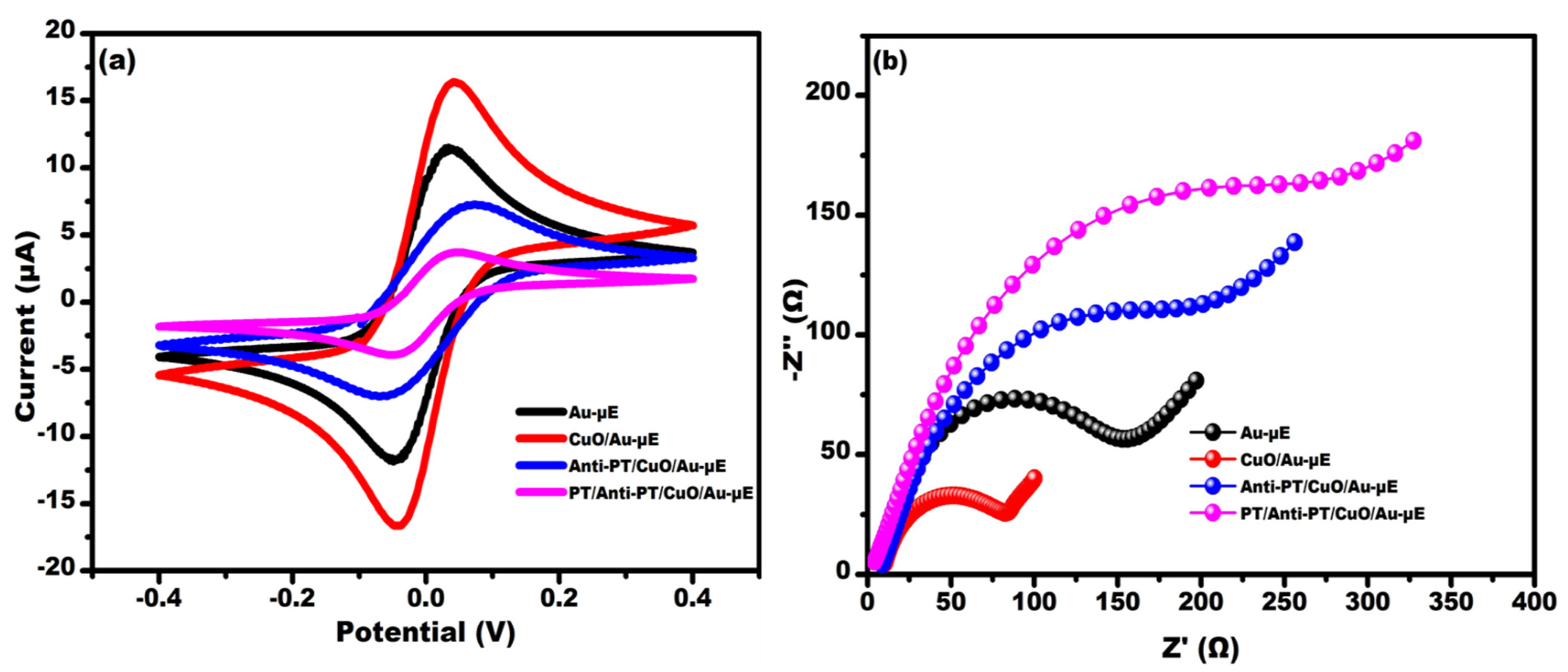
3.2. Characterization of the Developed Immunosensing Platform (Anti-PT/CuO/Au-µE)
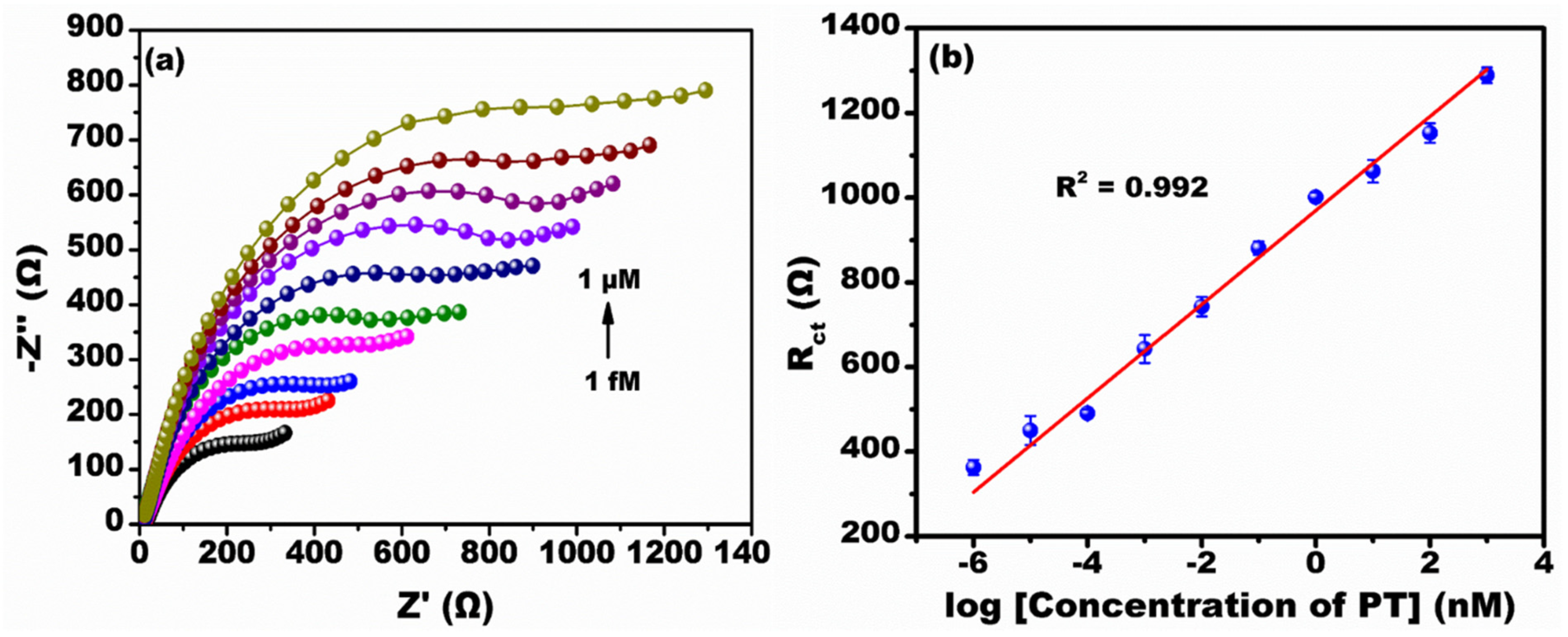
3.3. Impedimetric Detection of Parathion
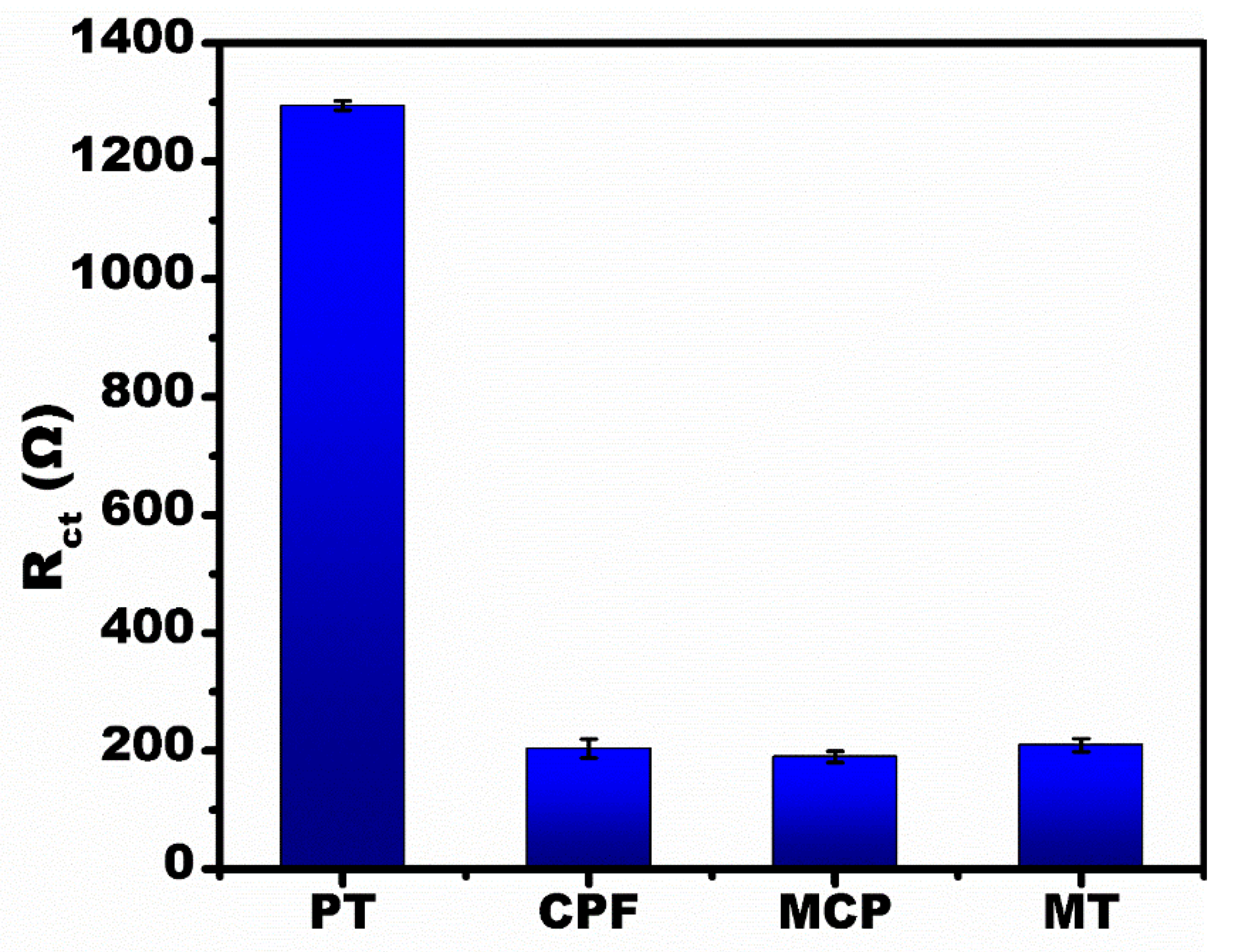
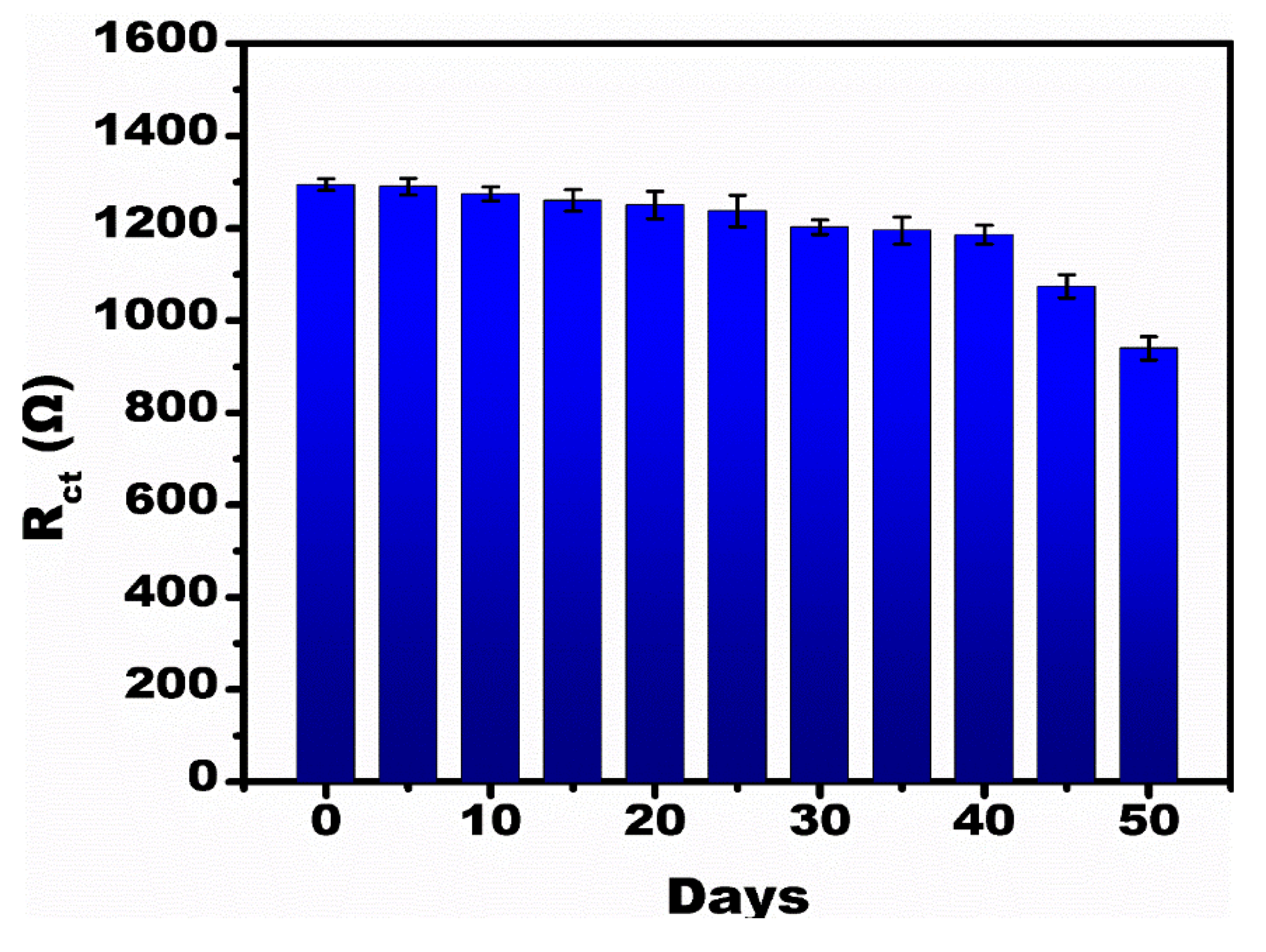
3.4. Selectivity and Stability Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oerke, E.C. Crop losses to pests. J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 144, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Momtaz, S.; Vakhshiteh, F.; Maghsoudi, A.S.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Abdollahi, M. Biosensors and their applications in detection of organophosphorus pesticides in the environment. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Dutta, S. Scenario of Pesticide Pollution and Toxicity in Rajasthan–A Review Article. IJSRD-Int. J. Sci. Res. Dev. 2017, 5, 1578–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Ragnarsdottir, K.V. Environmental fate and toxicology of organophosphate pesticides. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2000, 157, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhananjayan, V.; Ravichandran, B. Occupational health risk of farmers exposed to pesticides in agricultural activities. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 4, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoytcheva, M.; Zlatev, R. Organophosphorus Pesticides Analysis. Pestic. Mod. World-Trends Pestic. Anal. 2011, Chapter–7, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Najeeb, J.; Asim Ali, M.; Farhan Aslam, M.; Raza, A. Biosensors: Their Fundamentals, Designs, Types and Most Recent Impactful Applications: A Review. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, D.; Xu, X.; Ying, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wang, J. Immunosensors for detection of pesticide residues. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helali, S. Impedimetric Immunosensor for Pesticide Detection. State Art Biosens.-Environ. Med. Appl. 2013, Chapter–6, 53751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hara, T.O.; Singh, B. Electrochemical biosensors for detection of pesticides and heavy metal toxicants in water: Recent trends and progress. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Joo, J.; Soon, G.K.; Jang, Y.; Hyeon, T. Synthesis of monodisperse spherical nanocrystals. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4630–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourinia, H.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Amiri, O.; Farangi, M. Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from corn powder and their application as down conversion effect in quantum dot-dye-sensitized solar cell. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 251, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.S.A.; Biju, V. Nanostructured CuO: Facile synthesis, optical absorption and defect dependent electrical conductivity. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 68, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, V. Chemical modifications and bioconjugate reactions of nanomaterials for sensing, imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 744–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talluri, B.; Prasad, E.; Thomas, T. Critical role of surfactants in the formation of digestively-ripened, ultra-small (r <2 nm) copper oxide quantum dots. Superlattices Microstruct. 2018, 116, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talluri, B.; Prasad, E.; Thomas, T. Ultra-small (r < 2 nm), stable (>1 year) copper oxide quantum dots with wide band gap. Superlattices Microstruct. 2018, 113, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ge, J.P.; Li, Y.D. Solvothermal synthesis of monodisperse PbSe nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2497–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimpi, J.R.; Sidhaye, D.S.; Prasad, B.L.V. Digestive Ripening: A Fine Chemical Machining Process on the Nanoscale. Langmuir 2017, 33, 9491–9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagabooshanam, S.; Roy, S.; Mathur, A.; Mukherjee, I.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Bhardwaj, L.M. Electrochemical micro analytical device interfaced with portable potentiostat for rapid detection of chlorpyrifos using acetylcholinesterase conjugated metal organic framework using Internet of things. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseem, M.; Hong, A.R.; Kim, R.T.; Hahn, Y.B. Copper oxide quantum dot ink for inkjet-driven digitally controlled high mobility field effect transistors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 2112–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Regt, J.M.; van Dijk, J.; van der Mullen, J.A.M.; Schram, D.C. Components of continuum radiation in an inductively coupled plasma. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1995, 28, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rathod, K.N.; Savaliya, C.; Babiya, K.R.; Vasvani, S.H.; Ramani, R.V.; Ramani, B.M.; Joshi, A.D.; Pandya, D.; Shah, N.A.; Markna, J.H. Preparation of CuO Quantum Dots by Cost-Effective Ultrasonication Technique. Int. J. Nanosci. 2017, 16, 1750019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhash, P.G.; Nair, S.S. Synthesis of copper quantum dots by chemical reduction method and tailoring of its band gap. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 055003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Zhang, G.M.; Liu, W.M.; Zhang, Q.F.; Wu, Q.D. Quantum yield of photoemission of Ag-BaO thin films for detecting ultrashort infrared laser pulses. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2001, 307, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Tang, J.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, X.Y. Facile synthesis of submicron Cu2O and CuO crystallites from a solid metallorganic molecular precursor. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 294, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgohain, K.; Singh, J. Quantum size effects in CuO nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B-Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2000, 61, 11093–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, A.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Paul, A.K.; Kim, K.H.; Kumar, P. Surface assembly of nano-metal organic framework on amine functionalized indium tin oxide substrate for impedimetric sensing of parathion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.; Willner, I. Probing biomolecular interactions at conductive and semiconductive surfaces by impedance spectroscopy: Routes to impedimetric immunosensors, DNA-sensors, and enzyme biosensors. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 913–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.R.; Hashim, U.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Poopalan, P.; Ramayya, H.R.; Omar, M.I.; Haarindraprasad, R.; Veeradasan, P. A point-of-care immunosensor for human chorionic gonadotropin in clinical urine samples using a cuneated polysilicon nanogap lab-on-chip. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.; Vinayak, P.; Tuteja, S.K.; Chhabra, V.A.; Bhardwaj, N.; Paul, A.K.; Kim, K.H.; Deep, A. Graphene modified screen printed immunosensor for highly sensitive detection of parathion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.; Bhardwaj, N.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Tuteja, S.K.; Vinayak, P.; Paul, A.K.; Kim, K.H.; Deep, A. Graphene quantum dot modified screen printed immunosensor for the determination of parathion. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 523, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Senor | Technique | Linear Range | LoD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Cd(atc)(H2O)2]n/ITO | Impedimetric | 0.1 to 20 ng/mL | 0.1 ng/mL | [27] |
| AntiPT/2ABA/Graphene/SPE | Impedimetric | 0.1 to 1000 ng/L | 52 pg/L (17.8 fM) | [31] |
| GQD/SPE | Impedimetric | 0.01 to 106 ng/L | 46 pg/L (15.8 fM) | [32] |
| Anti-PT/CuO/Au-µE | Impedimetric | 1 fM to 1 µM | 0.69 fM | Present Work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagabooshanam, S.; Talluri, B.; Thomas, T.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Mathur, A. Ultra-Sensitive Impedimetric Immunosensor Using Copper Oxide Quantum Dots Grafted on the Gold Microelectrode for the Detection of Parathion. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091385
Nagabooshanam S, Talluri B, Thomas T, Krishnamurthy S, Mathur A. Ultra-Sensitive Impedimetric Immunosensor Using Copper Oxide Quantum Dots Grafted on the Gold Microelectrode for the Detection of Parathion. Micromachines. 2022; 13(9):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091385
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagabooshanam, Shalini, Bhusankar Talluri, Tiju Thomas, Satheesh Krishnamurthy, and Ashish Mathur. 2022. "Ultra-Sensitive Impedimetric Immunosensor Using Copper Oxide Quantum Dots Grafted on the Gold Microelectrode for the Detection of Parathion" Micromachines 13, no. 9: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091385
APA StyleNagabooshanam, S., Talluri, B., Thomas, T., Krishnamurthy, S., & Mathur, A. (2022). Ultra-Sensitive Impedimetric Immunosensor Using Copper Oxide Quantum Dots Grafted on the Gold Microelectrode for the Detection of Parathion. Micromachines, 13(9), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091385







