2D Magnetic Manipulation of a Micro-Robot in Glycerin Using Six Pairs of Magnetic Coils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Electromagnetic Coil Structure and Model
2.1. Electromagnetic Coil Structure
2.2. Electromagnetic Coil Model
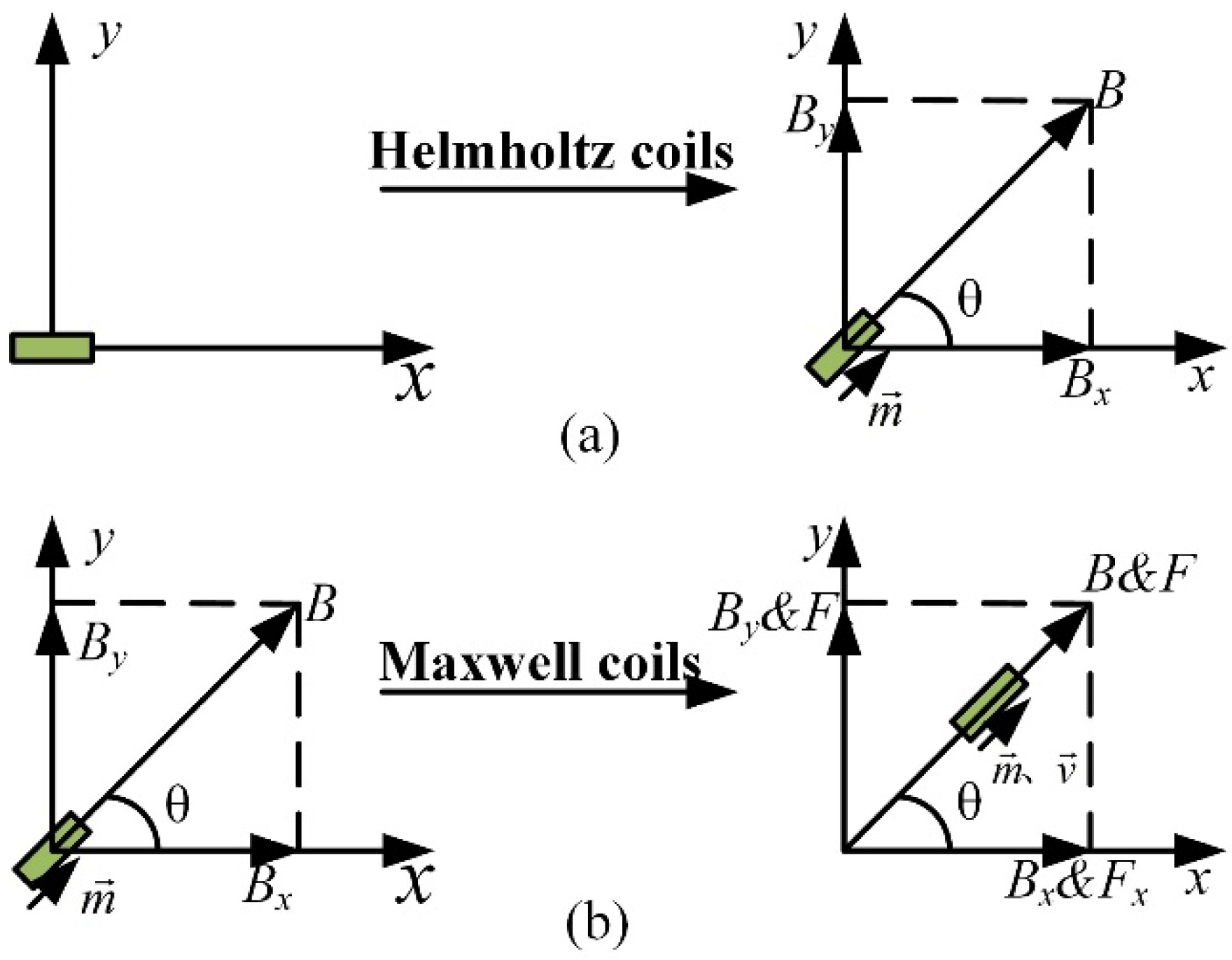
2.3. Dynamic Model of the Micro-Robot
3. Optimal Control of Magnetic Field Drive
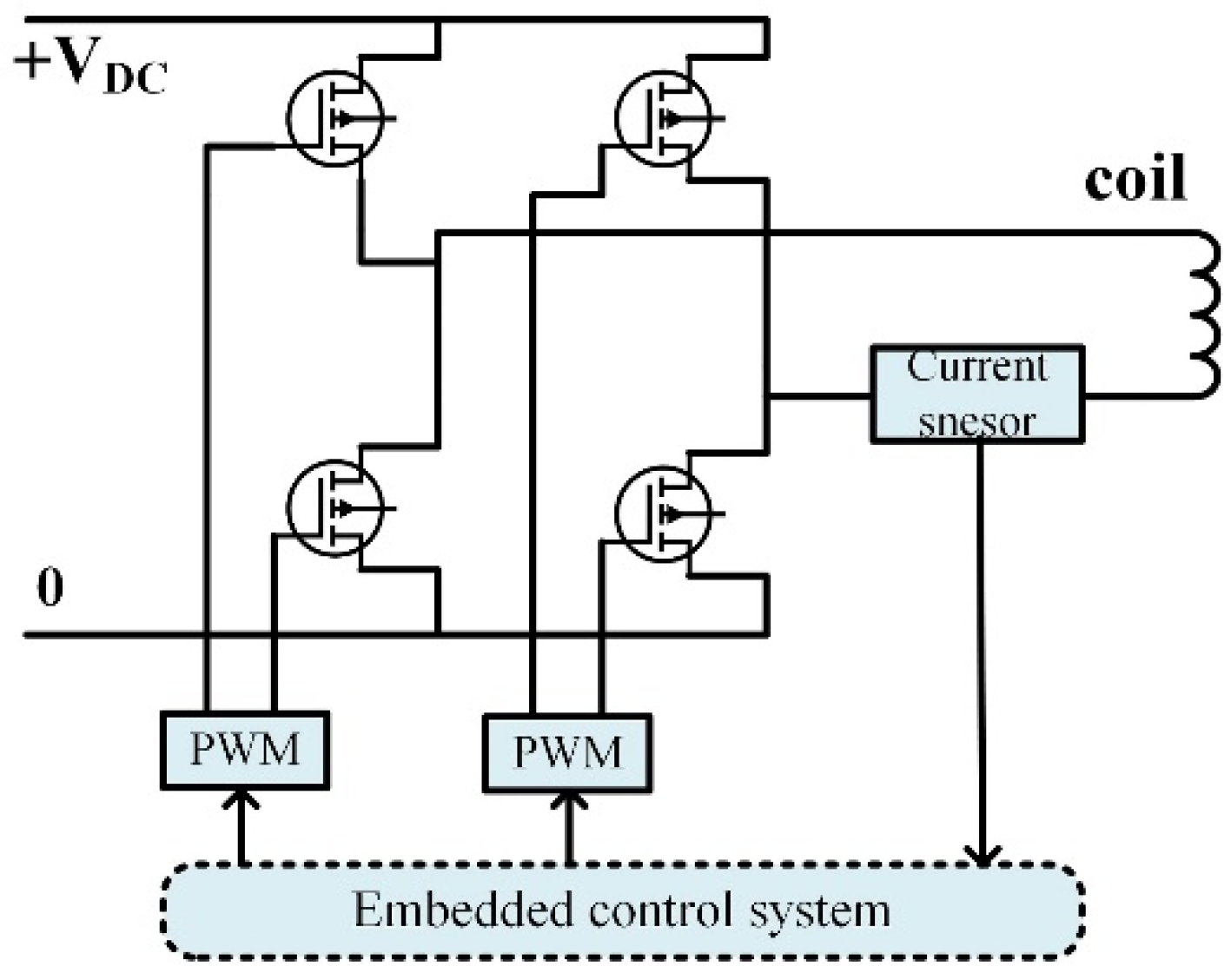
3.1. Design of Driving Circuit
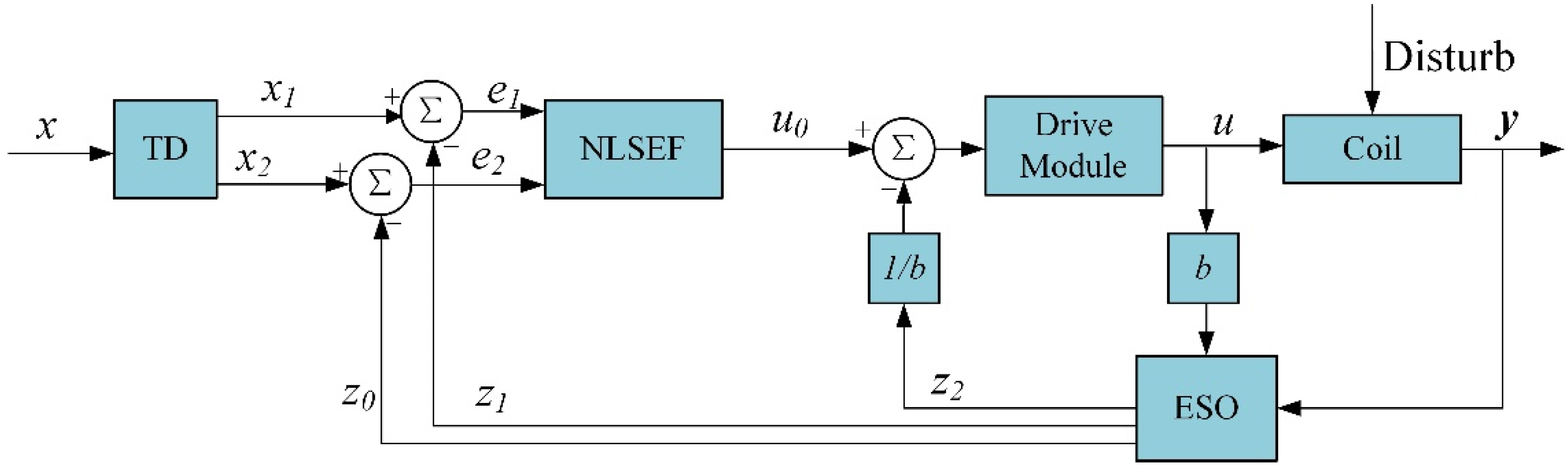
3.2. Design of Auto Disturbance Rejection Controller
4. Closed-Loop Control System
Location Prediction
5. Simulation and Experiments
5.1. Simulation
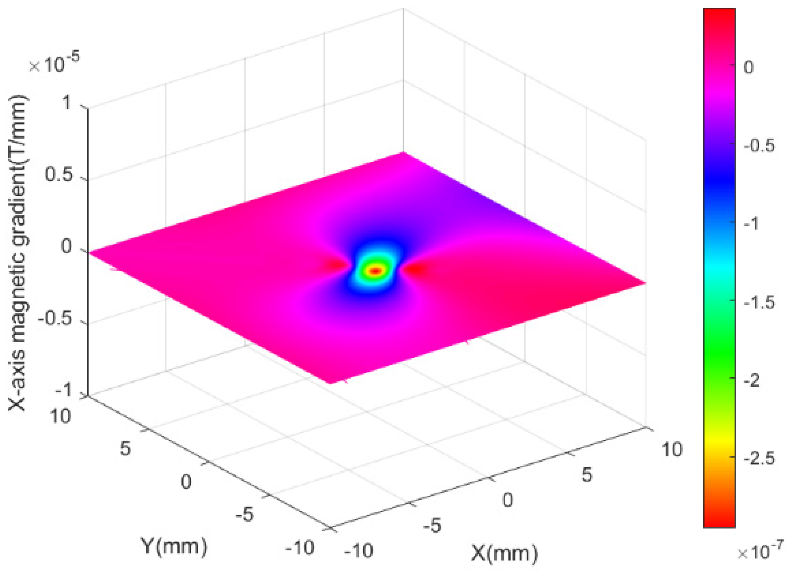
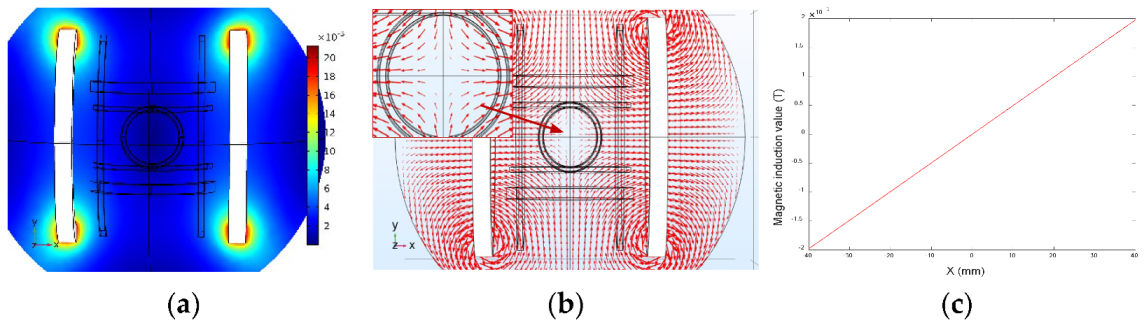
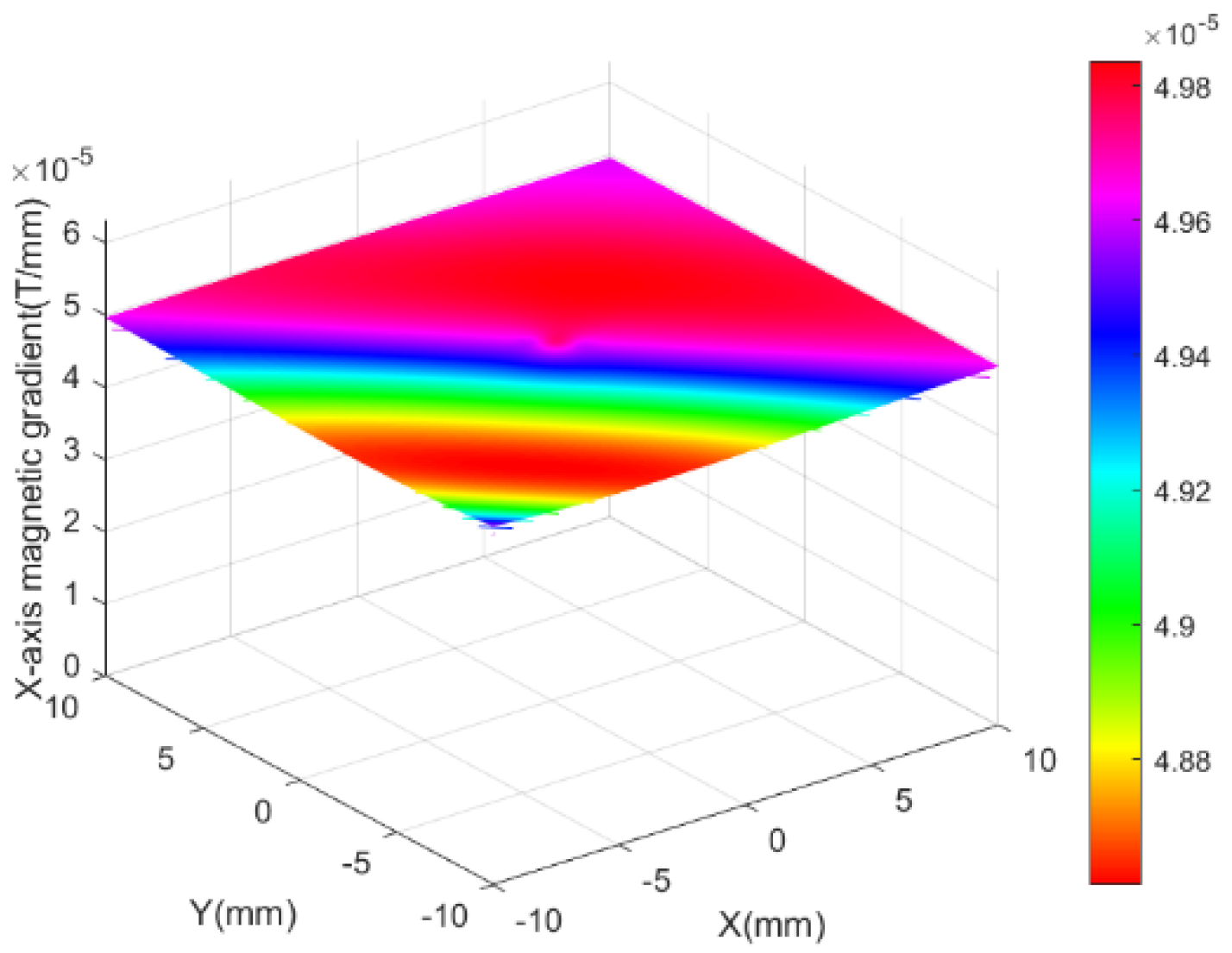
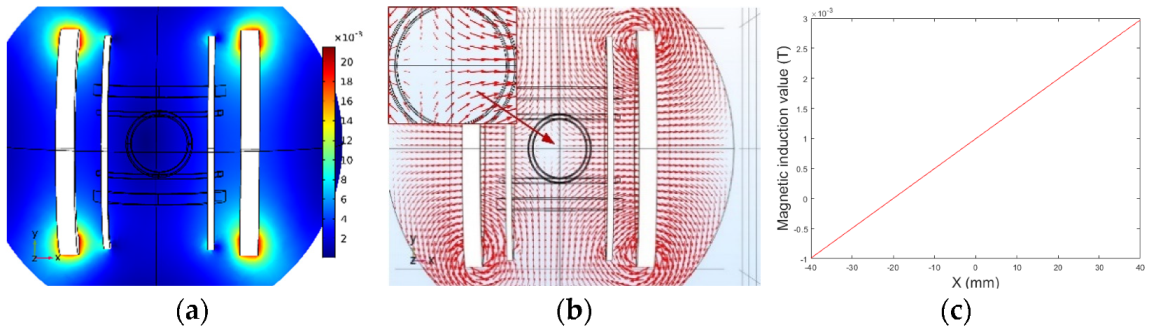
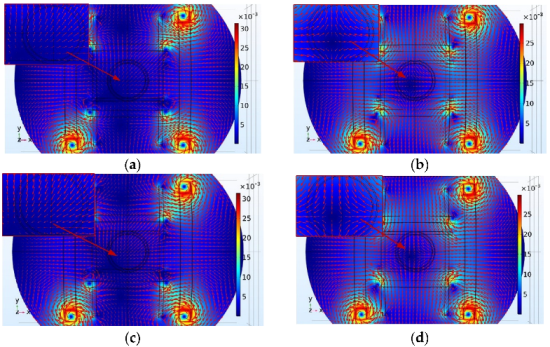
5.1.1. Magnetic Field of Combined Coils
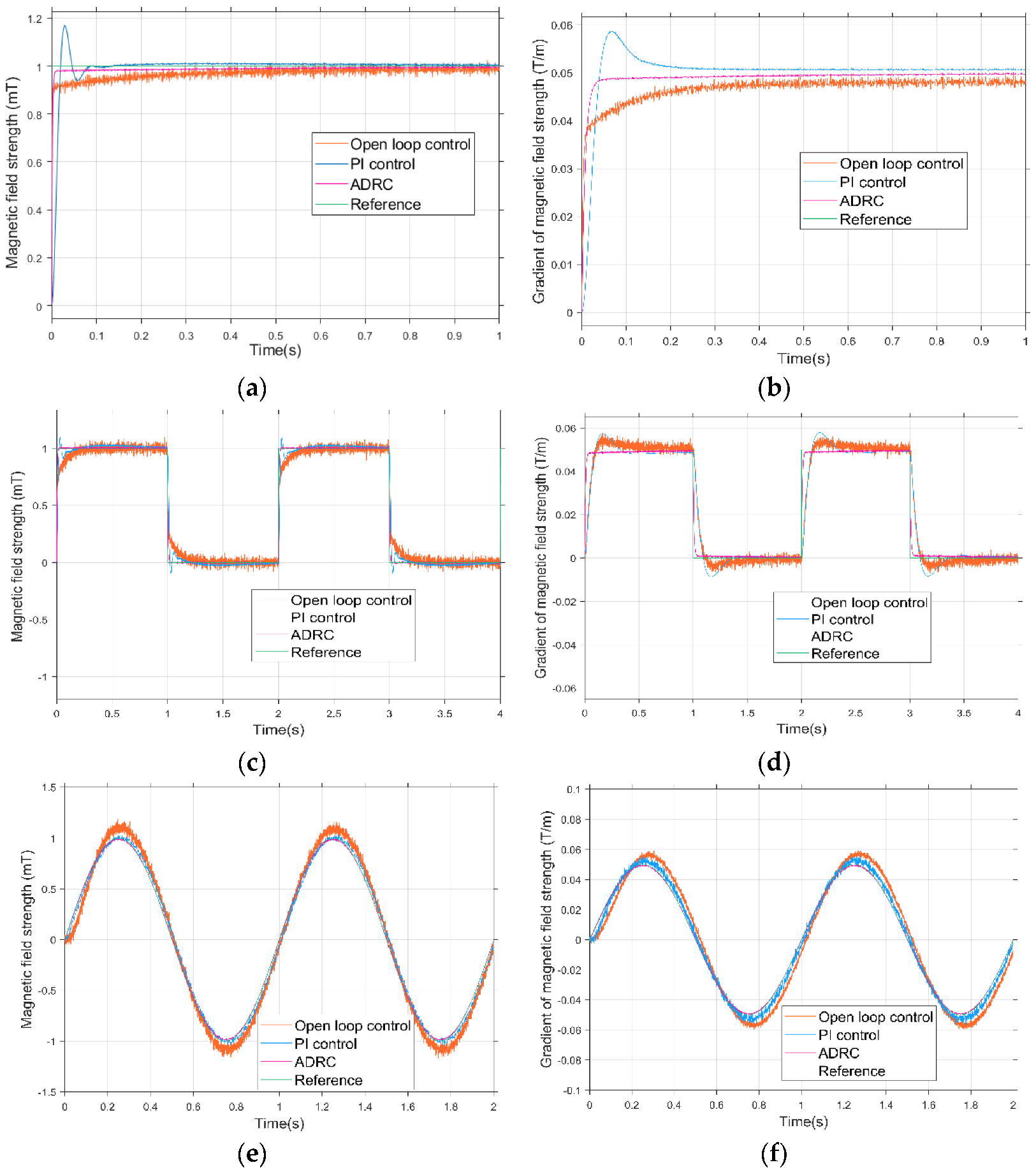
5.1.2. Combined Coil Drive Based on ADRC
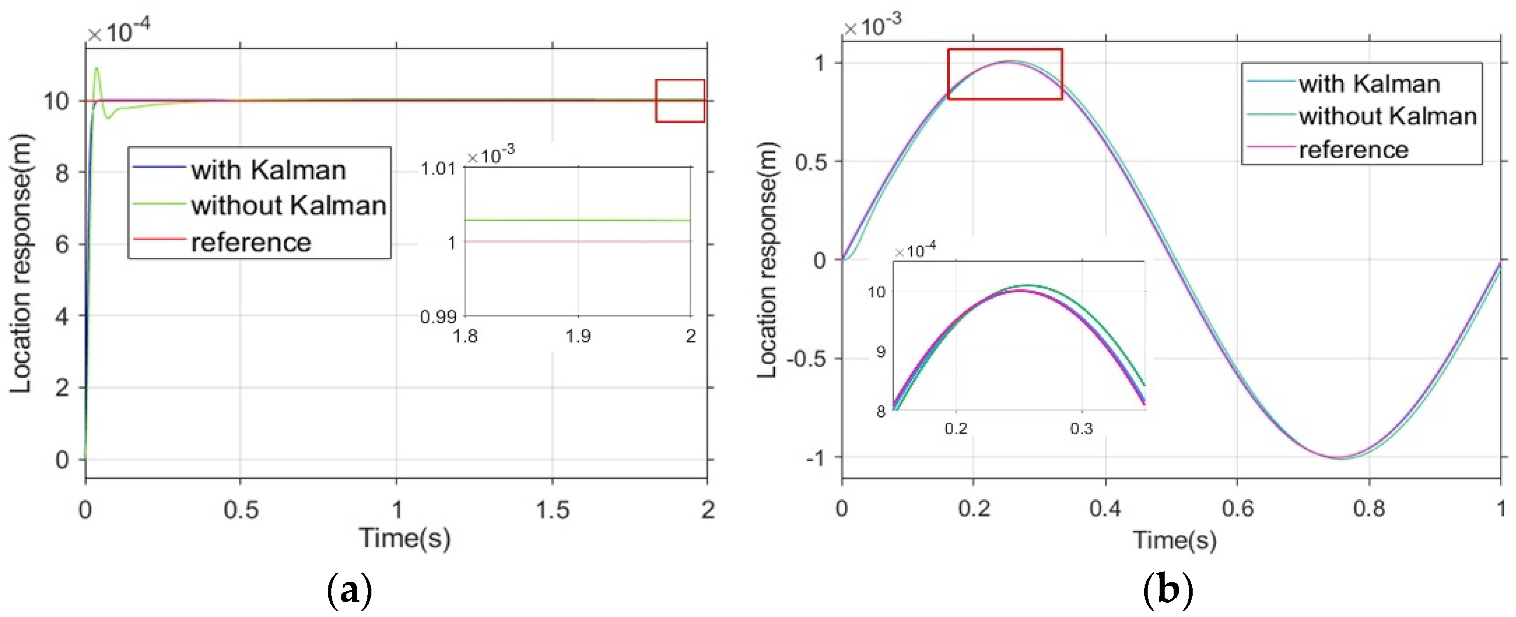
5.1.3. Closed-Loop Control System
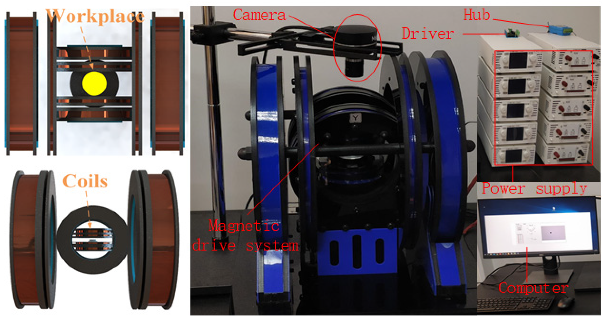
5.2. Experiments
5.2.1. Combined Coils Drive Based on ADRC
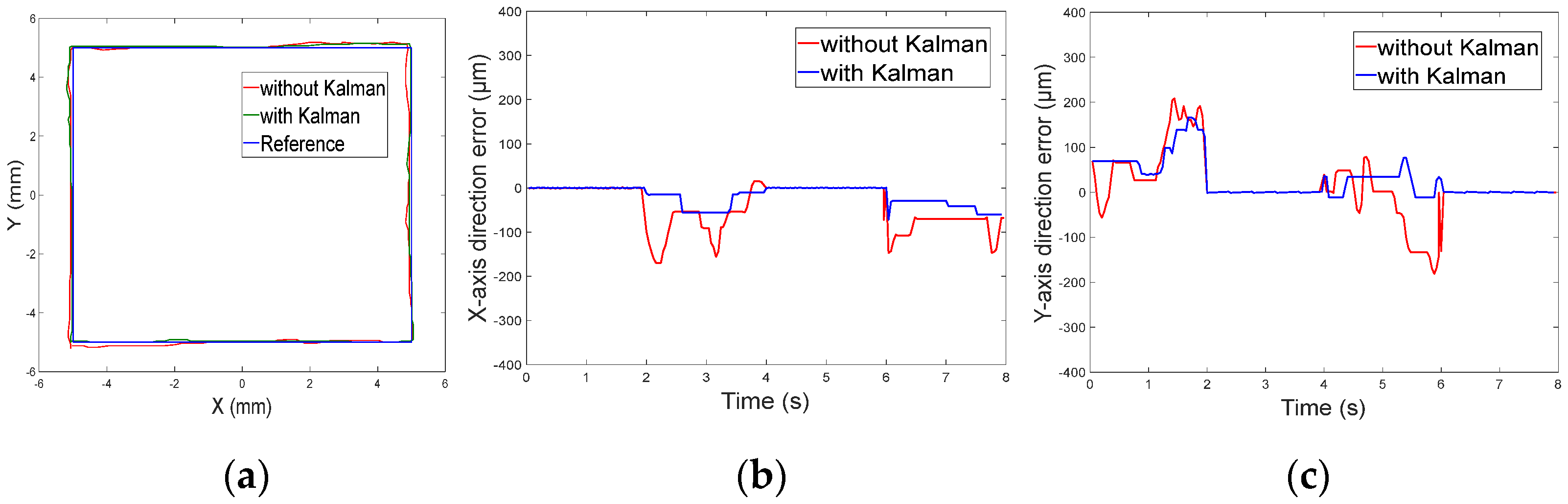
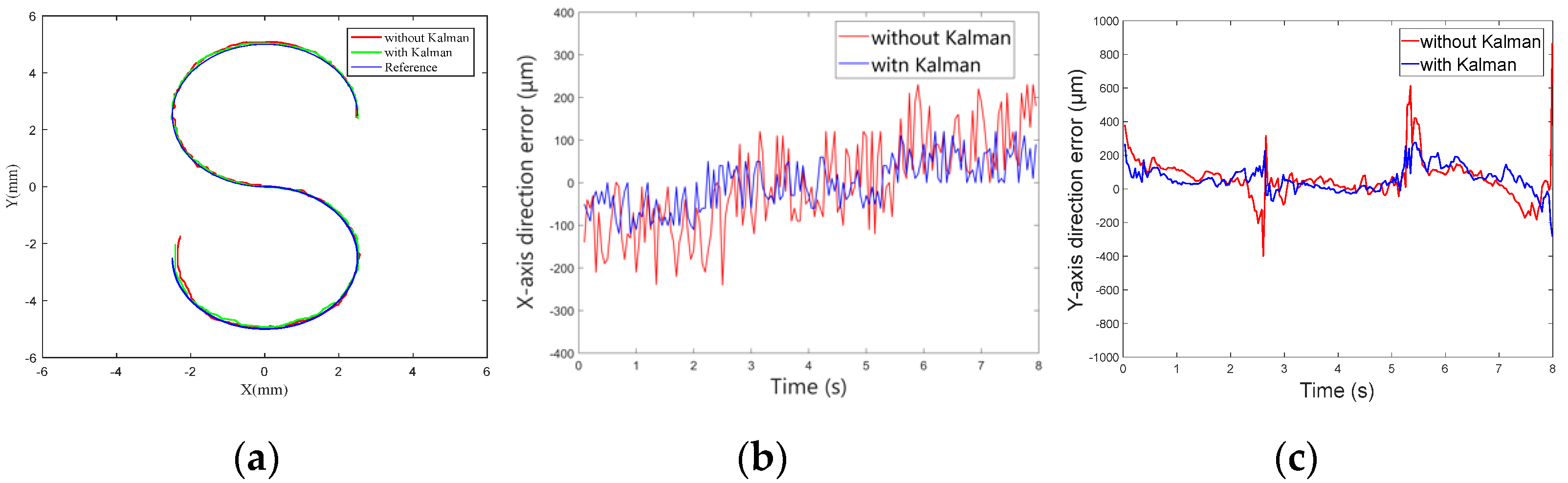
5.2.2. Closed-Loop Motion Control
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, Y.-K.; Li, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.-T.; Li, C.-J. Corrosion resistant nickel coating with strong adhesion on AZ31B magnesium alloy prepared by an in-situ shot-peening-assisted cold spray. Corros. Sci. 2018, 138, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakadate, R.; Iwasa, T.; Onogi, S.; Arata, J.; Oguri, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Akahoshi, T.; Eto, M.; Hashizume, M. Surgical Robot for Intraluminal Access: An Ex Vivo Feasibility Study. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolopion, A.; Xie, H.; Haliyo, D.S.; Regnier, S. Haptic Teleoperation for 3-D Microassembly of Spherical Objects. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2010, 17, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Qiu, F.; Kim, S.; Ghanbari, A.; Moon, C.; Zhang, L.; Nelson, B.J.; Choi, H. Fabrication and characterization of magnetic microrobots for three dimensional cell culture and targeted transportation. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5863–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitti, M.; Ceylan, H.; Hu, W.; Giltinan, J.; Turan, M.; Yim, S.; Diller, E. Biomedical Applications of Untethered Mobile Milli/Microrobots. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, B. Self-Cognizant Bionic Liquid Sensor for Pathogen Diagnosis. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, M.; Zhang, L.; Siringil, E.C.; Peters, C.; Luehmann, T.; Ergeneman, O.; Peyer, K.E.; Nelson, B.J.; Hierold, C. Superparamagnetic microrobots: Fabrication by two-photon polymerization and biocompatibility. Biomed. Microdevices 2013, 15, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kye, H.G.; Park, B.S.; Lee, J.M.; Song, M.G.; Song, H.G.; Ahrberg, C.D.; Chung, B.G. Dual-neodymium magnet-based microfluidic separation device. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.A.; Jones, T.H.; Moss, S.M.; Mishra, S.; Kaul, K.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Ferree, J.; Kumar, P.; Subramaniam, D.; Ganju, R.K.; et al. Electromagnetic fields alter the motility of metastatic breast cancer cells. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-P.; Ge, X.-H.; Xu, J.-H.; Luo, G.-S. Controlled formation and coalescence of paramagnetic ionic liquid droplets under magnetic field in coaxial microfluidic devices. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 152, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, A.W.; Abbott, J.J. Five-degree-of-freedom manipulation of an untethered magnetic device in fluid using a single permanent magnet with application in stomach capsule endoscopy. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 35, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchida, K. Robotic Surgery in Gastrointestinal Surgery. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2020, 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, B.E.; Kummer, M.P.; Abbott, J.J.; Borer, R.; Ergeneman, O.; Nelson, B.J. OctoMag: An electromagnetic system for 5-DOF wireless micromanipulation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2010, 26, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Heunis, C.; Sikorski, J.; Misra, S. Flexible Instruments for Endovascular Interventions: Improved Magnetic Steering, Actuation, and Image-Guided Surgical Instruments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2018, 25, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Togo, S.; Yokoi, H.; Jiang, y. Survey on Main Drive Methods Used in Humanoid Robotic Upper Limbs. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2021, 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharboutly, M.; Gauthier, M.; Chaillet, N. Modeling the trajectory of a microparticle in a dielectrophoresis device. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 114312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosa, G.; Shoham, M.; Zaaroor, M. Propulsion Method for Swimming Microrobots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2007, 23, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, L.-A.; Bright, V.; Dunn, M.; Daily, J.; Raj, R. Development of SiCN Ceramic Thermal Actuators; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, G.; Braive, R.; Couraud, L.; Cavanna, A.; Abdelkarim, O.; Robert-Philip, I.; Beveratos, A.; Sagnes, I.; Haliyo, S.; Régnier, S. Electro-osmotic propulsion of helical nanobelt swimmers. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2011, 30, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chow, Y.T.; Chen, S.; Ma, D.; Luo, T.; Tan, Y.; Sun, D. Magnetic Force-Driven in Situ Selective Intracellular Delivery. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, S.; Felfoul, O.; Mathieu, J.-B.; Chanu, A.; Tamaz, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Mankiewicz, M.; Tabatabaei, N. MRI-based Medical Nanorobotic Platform for the Control of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Flagellated Bacteria for Target Interventions in Human Capillaries. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2009, 28, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Pei, A.; Wang, J. Water-Driven Micromotors. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8432–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongaro, F.; Pane, S.; Scheggi, S.; Misra, S. Design of an Electromagnetic Setup for Independent Three-Dimensional Control of Pairs of Identical and Nonidentical Microrobots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 35, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Gao, W.; Xu, L.-P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Fuel-Free Synthetic Micro-/Nanomachines. Adv. Mater. 2016, 29, 1603250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrni, F.; Prins, M.W.J.; van Ijzendoorn, L.J. Micro-fluidic actuation using magnetic artificial cilia. Lab a Chip 2009, 9, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpi, F.; Pappone, C. Stereotaxis Niobe® magnetic navigation system for endocardial catheter ablation and gastrointestinal capsule endoscopy. Expert Rev. Med Devices 2009, 6, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, M.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Johnson, W.; Sun, Y. A Three-Dimensional Magnetic Tweezer System for Intraembryonic Navigation and Measurement. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 34, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulmas, A.; Andreff, N.; Regnier, S. Closed-Loop 3D Path Following of Scaled-Up Helical Microswimmers; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Li, J.; Ma, W.; Yang, J.; Sun, D. Development of an Enhanced Electromagnetic Actuation System with Enlarged Workspace. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2017, 22, 2265–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Chowdhury, S.; Cappelleri, D. Magnetic mobile microrobots for mechanobiology and automated biomanipulation. In Microbiorobotics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 197–219. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, A.; Samsonas, D.; Leong, F.; Tan, Y.; Thiruchelvam, D.; Valdastri, P.; Oetomo, D. Modeling and control of local electromagnetic actuation for robotic-assisted surgical devices. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, M.; Firouzeh, A.; Paik, J. A low profile electromagnetic actuator design and model for an origami parallel platform. J. Mech. Robot. 2017, 9, 041005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, G.; Gu, Y.; Wang, C.; Huang, S. Realizing Controllable Physical Interaction Based on an Electromagnetic Variable Stiffness Joint. J. Mech. Robot. 2019, 11, 054501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamato, G.; Chiaradia, D.; Solazzi, M.; Frisoli, A. A Lightweight Robotic Device Based on a Micro-Macro Actuation Concept for the Inspection of Railway Pantograph. J. Mech. Robot. 2020, 12, 061002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Self-Assembly of DNA Molecules: Towards DNA Nanorobots for Biomedical Applications. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2021, 2021, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Lam, W.S.; Sun, D. Electromagnetic Actuation of Microrobots in a Simulated Vascular Structure with a Position Estimator Based Motion Controller. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6255–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Choi, H.; Cha, K.; Li, J.; Park, J.-O.; Park, S. Enhanced locomotive and drilling microrobot using precessional and gradient magnetic field. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2011, 171, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Pishkenari, H.N.; Zohoor, H. Position control of a wheel-based miniature magnetic robot using neuro-fuzzy network. Robotica 2022, 40, 3895–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chan, K.-F.; Zhang, L. Automated Control of Magnetic Spore-Based Microrobot Using Fluorescence Imaging for Targeted Delivery with Cellular Resolution. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcese, L.; Fruchard, M.; Ferreira, A. Adaptive Controller and Observer for a Magnetic Microrobot. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 29, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.; Nam, J.; Lee, W.; Jang, G. A Crawling Magnetic Robot Actuated and Steered via Oscillatory Rotating External Magnetic Fields in Tubular Environments. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2017, 22, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Mann, I.S.; Su, H.-J. A Novel Variable Stiffness Compliant Robotic Gripper Based on Layer Jamming. J. Mech. Robot. 2020, 12, 051013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J. From PID to Active Disturbance Rejection Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.J.; Kaliakatsos, I.K.; Abbott, J.J. Microrobots for Minimally Invasive Medicine. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 12, 55–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diller, E.; Sitti, M. Micro-scale mobile robotics. Found. Trends Robot. 2013, 2, 143–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.; Choi, J.; Jeong, S.; Cha, K.; Park, J.-O.; Park, S. Novel electromagnetic actuation system for three-dimensional locomotion and drilling of intravascular microrobot. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2010, 161, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheang, U.K.; Kim, M.J. Self-assembly of robotic micro- and nanoswimmers using magnetic nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Song, S.; Meng, M.Q.H. Electromagnetic Actuation System Using Stationary Six-Pair Coils for Three-Dimensional Wireless Locomotive Microrobot; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Niu, F.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Sun, D. Gradient-Enhanced Electromagnetic Actuation System with a New Core Shape Design for Microrobot Manipulation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 4700–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | HX | MX | HY | MY | HZ | MZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| resistance (Ω) | 2.3 | 11.5 | 1.3 | 3.0 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| Inductance (mH) | 4.397 | 207.2 | 1.514 | 14.82 | 0.1208 | 0.511 |
| Coil average distance (mm) | 170 | 294 | 100 | 173 | 50 | 87 |
| Equivalent radius (mm) | 170 | 170 | 100 | 100 | 50 | 50 |
| Coil outer diameter (mm) | 400 | 400 | 230 | 230 | 120 | 120 |
| Coil inner diameter (mm) | 248 | 248 | 151 | 151 | 66 | 66 |
| Number of turns | 52 | 449 | 31 | 156 | 14 | 39 |
| Single copper wire diameter (mm) | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Q.; Lu, J.; Jia, J.; Qu, J. 2D Magnetic Manipulation of a Micro-Robot in Glycerin Using Six Pairs of Magnetic Coils. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122144
Fan Q, Lu J, Jia J, Qu J. 2D Magnetic Manipulation of a Micro-Robot in Glycerin Using Six Pairs of Magnetic Coils. Micromachines. 2022; 13(12):2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122144
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Qigao, Jiawei Lu, Jie Jia, and Juntian Qu. 2022. "2D Magnetic Manipulation of a Micro-Robot in Glycerin Using Six Pairs of Magnetic Coils" Micromachines 13, no. 12: 2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122144
APA StyleFan, Q., Lu, J., Jia, J., & Qu, J. (2022). 2D Magnetic Manipulation of a Micro-Robot in Glycerin Using Six Pairs of Magnetic Coils. Micromachines, 13(12), 2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122144








