Modeling and Simulation of Tin Sulfide (SnS)-Based Solar Cell Using ZnO as Transparent Conductive Oxide (TCO) and NiO as Hole Transport Layer (HTL)
Abstract
1. Introduction
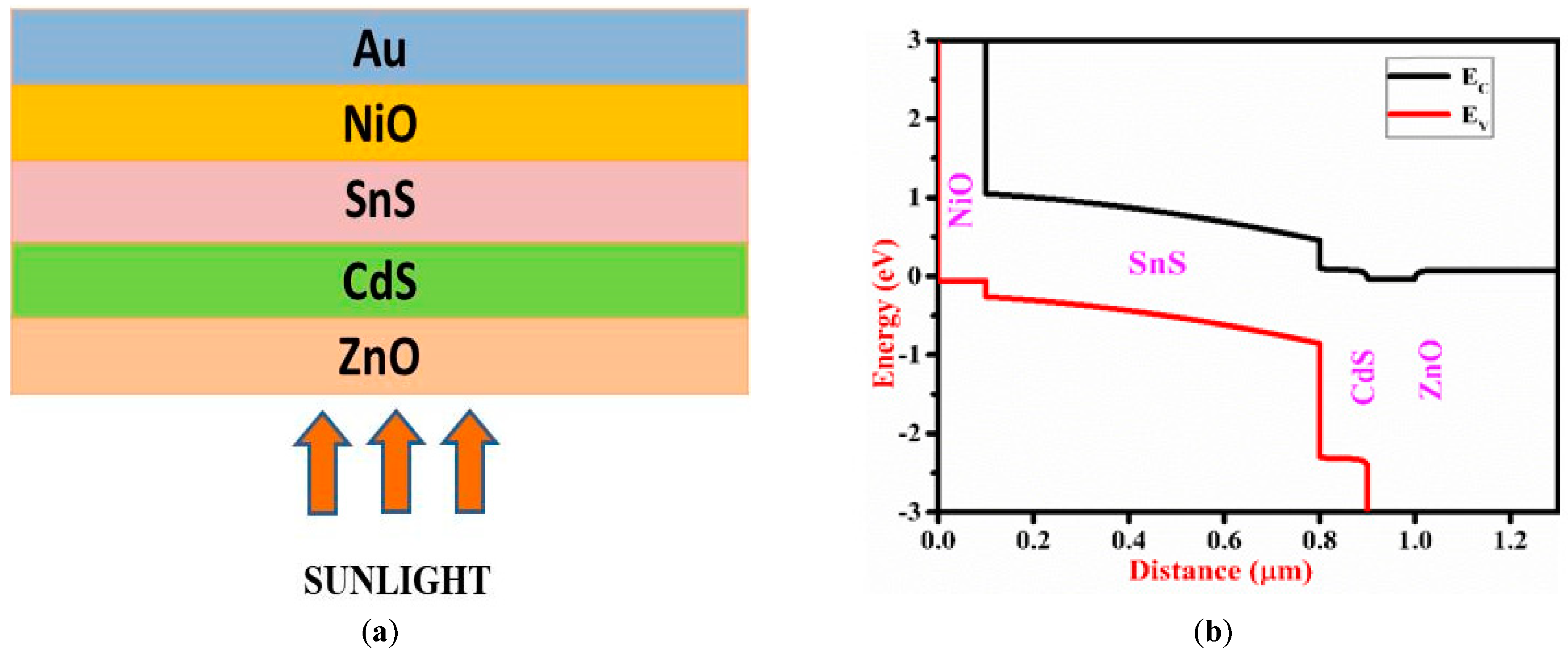
2. Modelling and Simulation
3. Solar Cell Structure and Material Properties
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Impact of Carrier Concentration and Thickness of NiO and ZnO
4.2. Impact of SnS/CdS Interface Defect Density
4.3. Impact of Defect Density and Thickness of Absorber Layer SnS
4.4. Impact of Electron Affinity and Back Contact Metal Work Function of Absorber Layer SnS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrade-Arvizu, J.A.; Courel-Piedrahita, M.; Vigil-Galán, O. SnS-based thin film solar cells: Perspectives over the last 25 years. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 4541–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, G.P.; Pearson, P.J. Challenges of the transition to a low carbon, more electric future: From here to 2050. Energy Policy 2013, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xiang, S.; Yu, J.; Li, C.-Z. Highly efficient prismatic perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 12, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Rahman, S.; Pasanen, H.P.; Tian, J.; Li, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Vivo, P. Hydrogen bonding drives the self-assembling of carbazole-based hole-transport material for enhanced efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy 2022, 101, 107604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, M.; Matta, S.K.; Hiltunen, A.; Deng, Z.; Wang, C.; Dai, Z.; Russo, S.P.; Vivo, P.; Zhang, H. Sulfonated Dopant-Free Hole-Transport Material Promotes Interfacial Charge Transfer Dynamics for Highly Stable Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Mukhopadhyay, I.; Ray, A. Molar optimization of spray pyrolyzed SnS thin films for photoelectrochemical applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 619, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumen-Ulzii, G.; Matsushima, T.; Adachi, C. Mini-Review on Efficiency and Stability of Perovskite Solar Cells with Spiro-OMeTAD Hole Transport Layer: Recent Progress and Perspectives. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 18915–18927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devika, M.; Reddy, N.K.; Ramesh, K.; Patolsky, F.; Gunasekhar, K. Weak rectifying behaviour of p-SnS/n-ITO heterojunctions. Solid-State Electron. 2009, 53, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeganath, K.; Choudhari, N.J.; Pai, G.S.; Rao, A.; Raviprakash, Y. Role of substrate temperature on spray pyrolysed metastable π-SnS thin films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 113, 105050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wang, D.; Jeng, M.; Ho, K.; Wang, D. Stable CdTe thin fi lm solar cells with a MoO x back- contact buffer layer. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2016, 24, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, I.; Lin, H.; Xia, W.; Wu, H.N.; Tang, C.W.; Gao, Y. The effect of MoOx inter-layer on thin film CdTe/CdS solar cell. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 105, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Irfan, H.; Xia, W.; Wu, H.N.; Gao, Y.; Tang, C.W. MoOx back contact for CdS/CdTe thin film solar cells: Preparation, device characteristics, and stability. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 99, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Yang, R.; Wang, D.; Jeng, M.; Chaudhary, S.; Ho, K.; Wang, D. Stable CdTe solar cell with V2O5 as a back contact buffer layer. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 144, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmmed, S.; Aktar, A.; Hossain, J.; Ismail, A.B.M. Enhancing the open circuit voltage of the SnS based heterojunction solar cell using NiO HTL. Sol. Energy 2020, 207, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh, M.; Ranjbar, M.; Kermanpur, A.; Taghaviniaet, N.; Minbashi, M.; Forouzandeh, M.; Ebadi, F. Enhanced performance of planar perovskite solar cells using TiO2/SnO2 and TiO2/WO3 bilayer structures: Roles of the interfacial layers. Sol. Energy 2020, 208, 697–707. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, S.; Rane, R.; Mukherjee, S. ZnO Thin Film Deposition for TCO Application in Solar Cell. Conf. Pap. Energy 2013, 2013, 718692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchuweni, E.; Sathiaraj, T.; Nyakotyo, H. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide thin films for optoelectronic applications. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-C.; Jeng, J.-Y.; Shen, P.-S.; Chang, Y.-C.; Diau, E.W.-G.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chao, T.-Y.; Hsu, H.-C.; Lin, P.-Y.; Chen, P.; et al. p-type Mesoscopic Nickel Oxide/Organometallic Perovskite Heterojunction Solar Cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, M.O.; Barnes, T.M.; Jensen, S.A.; Metzger, W.K. The Roles of Carrier Concentration and Interface, Bulk, and Grain-Boundary Recombination for 25% Efficient CdTe Solar Cells. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 214506. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, P.K.; Mahesh, S.; Snaith, H.J.; Cahen, D. Photovoltaic solar cell technologies: Analysing the state of the art. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, N.; Chandramohan, R.; Valanarasu, S.; Vijayan, T.A.; Rosario, S.R.; Kathalingam, A. Effect of film thickness on the solar cell performance of CBD grown CdS/PbS heterostructure. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 27, 2574–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam Moon, M.; Ali, H.; Rahman, F.; Hossain, J.; Ismail, A.B. Design and Simulation of FeSi2-Based Novel Heterojunction Solar Cells for Harnessing Visible and Near-Infrared Light. Phys. Status solidi 2020, 217, 1900921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Et-Taya, L.; Ouslimane, T.; Benami, A. Numerical analysis of earth-abundant Cu2ZnSn(SxSe1-x)4 solar cells based on Spectroscopic Ellipsometry results by using SCAPS-1D. Sol. Energy 2020, 201, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procel, P.; Xu, H.; Saez, A.; Ruiz-Tobon, C.; Mazzarella, L.; Zhao, Y.; Han, C.; Yang, G.; Zeman, M.; Isabella, O. The role of heterointerfaces and subgap energy states on transport mechanisms in silicon heterojunction solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2020, 28, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabbasa, S.; Rouabaha, Z.; Bouarissab, N.; Chelalia, N. The role of back surface field SnS layer in improvement of efficiency of CdTe thin film solar cells. Optik 2016, 127, 6210–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudour, S.; Bouchama, I.; Hadjab, M.; Laidoudi, S. Optimization of defected ZnO/Si/Cu2O heterostructure solar cell. Opt. Mater. 2019, 98, 109433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykyruy, L.; Yavorskyi, R.; Zapukhlyak, Z.; Wisz, G.; Potera, P. Evaluation of CdS/CdTe thin film solar cells: SCAPS thickness simulation and analysis of optical properties. Opt. Mater. 2019, 92, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Alotaibi, M.F.; Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Srivastava, V.; Arkook, B.; Sadanand, S.; Lohia, P.; Dwivedi, D.K.; Umar, A.; Algadi, H.; et al. Design and Simulation of Efficient SnS-Based Solar Cell Using Spiro-OMeTAD as Hole Transport Layer. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutwade, V.V.; Gattu, K.P.; Sonawane, M.E.; Tonpe, D.A.; Mishra, M.K.; Sharma, R. Contribution in PCE enhancement: Numerical designing and optimization of SnS thin film solar cell. J. Nanopart. Res. 2021, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Jouidri, A.; Koumya, Y.; Rajira, A.; Almaggoussi, A.; Abounadi, A. An output characteristics simulation of SnS based solar cells. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 51, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | ZnO | CdS | SnS | NiO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (nm) | 100 | 100 | 1000 | 250 |
| Bandgap (eV) | 3.37 | 2.4 | 1.31 | 3.8 |
| Electron affinity (eV) | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.3 | 1.46 |
| Dielectric permittivity (relative) | 9 | 10 | 13 | 10 |
| CB effective density of states (cm−3) | 2.2 × 1018 | 2.2 × 1018 | 1.18 × 1018 | 2.8 × 1019 |
| VB effective density of states (cm−3) | 1.8 × 1018 | 1.9 × 1019 | 4.76 × 1018 | 1 × 1018 |
| Electron mobility (cm2/VS) | 100 | 350 | 130 | 12 |
| Hole mobility (cm2/VS) | 25 | 25 | 4.3 | 2.8 |
| Shallow uniform donor density Nd (cm−3) | 1 × 1017 | 1 × 1017 | 1 × 107 | 0 |
| Shallow uniform acceptor density Na (cm−3) | 0 | 0 | 1 × 1015 | 1 × 1021 |
| Electron thermal velocity (cm/s) | 1 × 107 | 1 × 107 | 1 × 107 | 1 × 107 |
| Hole thermal velocity (cm/s) | 1 × 107 | 1 × 107 | 1 × 107 | 1 × 107 |
| Defect density (cm−3) | 1 × 1014 | 1 × 1014 | 1 × 1011 | 1 × 1014 |
| Radiative recombination coefficient (cm3/s) | 2.3 × 10−9 | 2.3 × 10−9 | 2.3 × 10−9 | 2.3 × 10−9 |
| Absorption coefficient (cm−1) | SCAPS | 1 × 105 | 1 × 105 | 1 × 105 |
| Parameters | SnS/CdS Interface [28] |
|---|---|
| Defect type | Neutral |
| Capture cross-section electrons (cm2) | 1 × 10−19 |
| Capture cross-section holes (cm2) | 1 × 10−19 |
| Defect energy level Et | Above the highest Ev |
| Energy with respect to a reference (eV) | 0.06 |
| Total density (cm−2) | 1 × 1010 |
| Structures | VOC V | JSC mA/cm2 | FF % | PCE % | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITO/CeO2/SnS/NiO/Mo (simulated ITO) | 0.890 | 32.67 | 86.19 | 25.06 | [14] |
| ITO/CeO2/SnS/Spiro-OMeTAD (simulated) | 0.887 | 33.74 | 85.61 | 25.65 | [28] |
| p-SnS/CdS/n-Zn MgO (simulated) | ~0.7 | 38.54 | 83 | ~23 | [29] |
| ZnO/CdS/SnS (simulated) | 0.73 | 33.20 | 61.47 | 14.9% | [30] |
| ZnO/CdS/CdTe/SnS/Ni (simulated) | 0.845 | 26.46 | 84.50 | 21.83 | [24] |
| ZnO/CdS/SnS/NiO (simulated) | 0.904 | 34.20 | 86.97 | 26.92 | This paper |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umar, A.; Tiwari, P.; Sadanand; Srivastava, V.; Lohia, P.; Dwivedi, D.K.; Qasem, H.; Akbar, S.; Algadi, H.; Baskoutas, S. Modeling and Simulation of Tin Sulfide (SnS)-Based Solar Cell Using ZnO as Transparent Conductive Oxide (TCO) and NiO as Hole Transport Layer (HTL). Micromachines 2022, 13, 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122073
Umar A, Tiwari P, Sadanand, Srivastava V, Lohia P, Dwivedi DK, Qasem H, Akbar S, Algadi H, Baskoutas S. Modeling and Simulation of Tin Sulfide (SnS)-Based Solar Cell Using ZnO as Transparent Conductive Oxide (TCO) and NiO as Hole Transport Layer (HTL). Micromachines. 2022; 13(12):2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122073
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmar, Ahmad, Pooja Tiwari, Sadanand, Vaibhava Srivastava, Pooja Lohia, Dilip Kumar Dwivedi, Hussam Qasem, Sheikh Akbar, Hassan Algadi, and Sotirios Baskoutas. 2022. "Modeling and Simulation of Tin Sulfide (SnS)-Based Solar Cell Using ZnO as Transparent Conductive Oxide (TCO) and NiO as Hole Transport Layer (HTL)" Micromachines 13, no. 12: 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122073
APA StyleUmar, A., Tiwari, P., Sadanand, Srivastava, V., Lohia, P., Dwivedi, D. K., Qasem, H., Akbar, S., Algadi, H., & Baskoutas, S. (2022). Modeling and Simulation of Tin Sulfide (SnS)-Based Solar Cell Using ZnO as Transparent Conductive Oxide (TCO) and NiO as Hole Transport Layer (HTL). Micromachines, 13(12), 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122073











