A Wind-Driven Rotating Micro-Hybrid Nanogenerator for Powering Environmental Monitoring Devices
Abstract
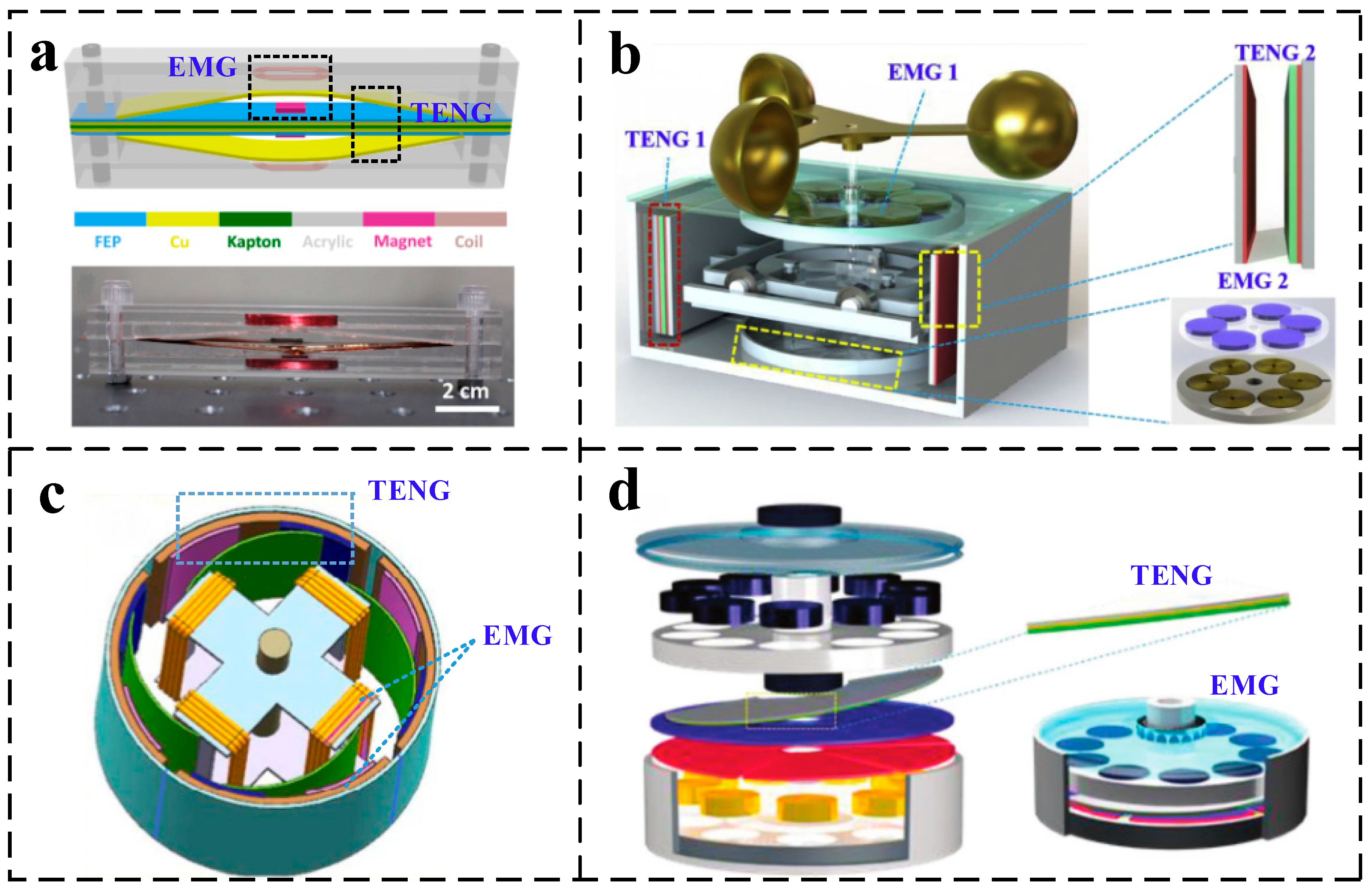
1. Introduction
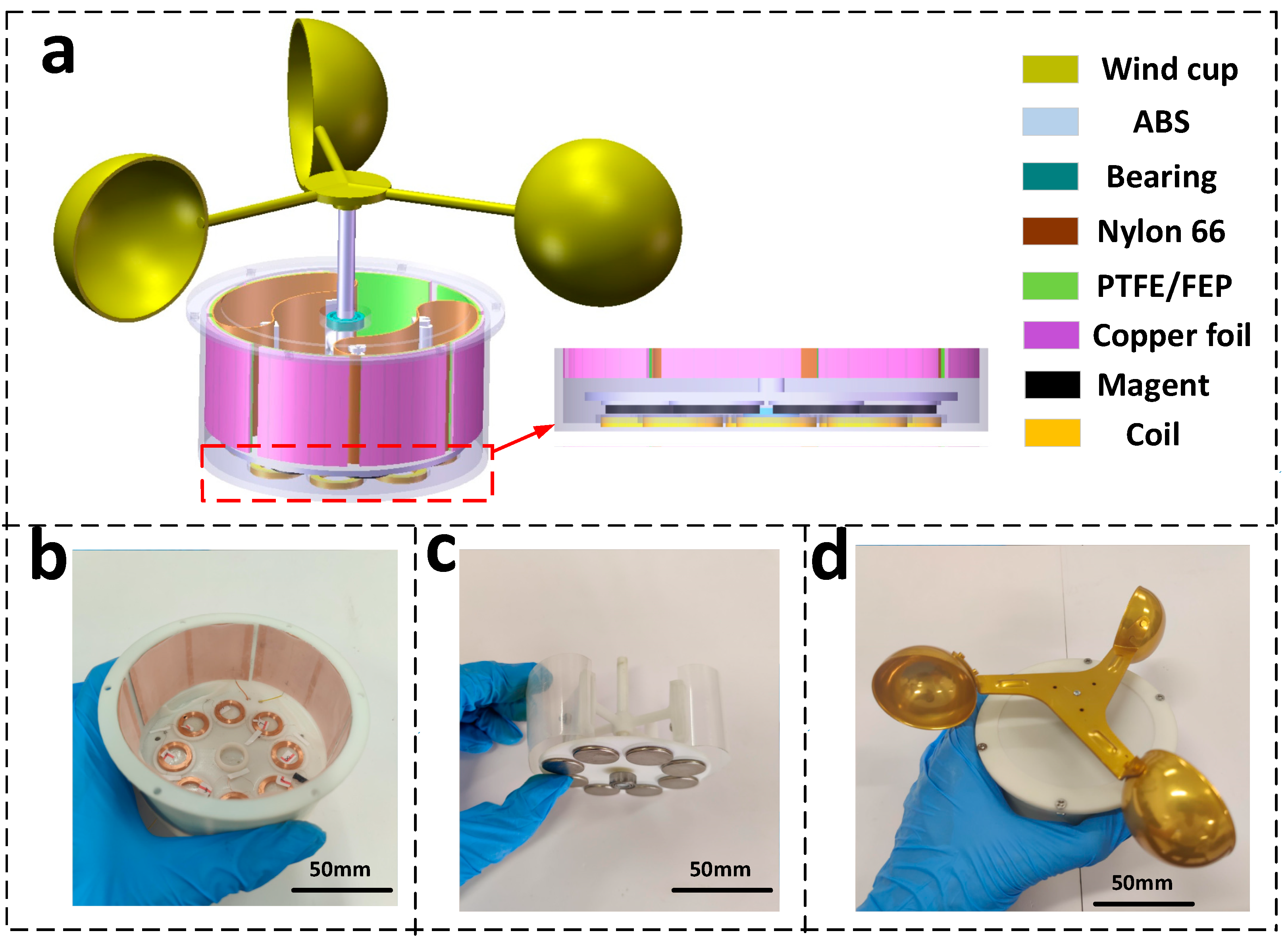
2. Fabrication and Working Principles
2.1. Fabrication
2.2. Working Principle
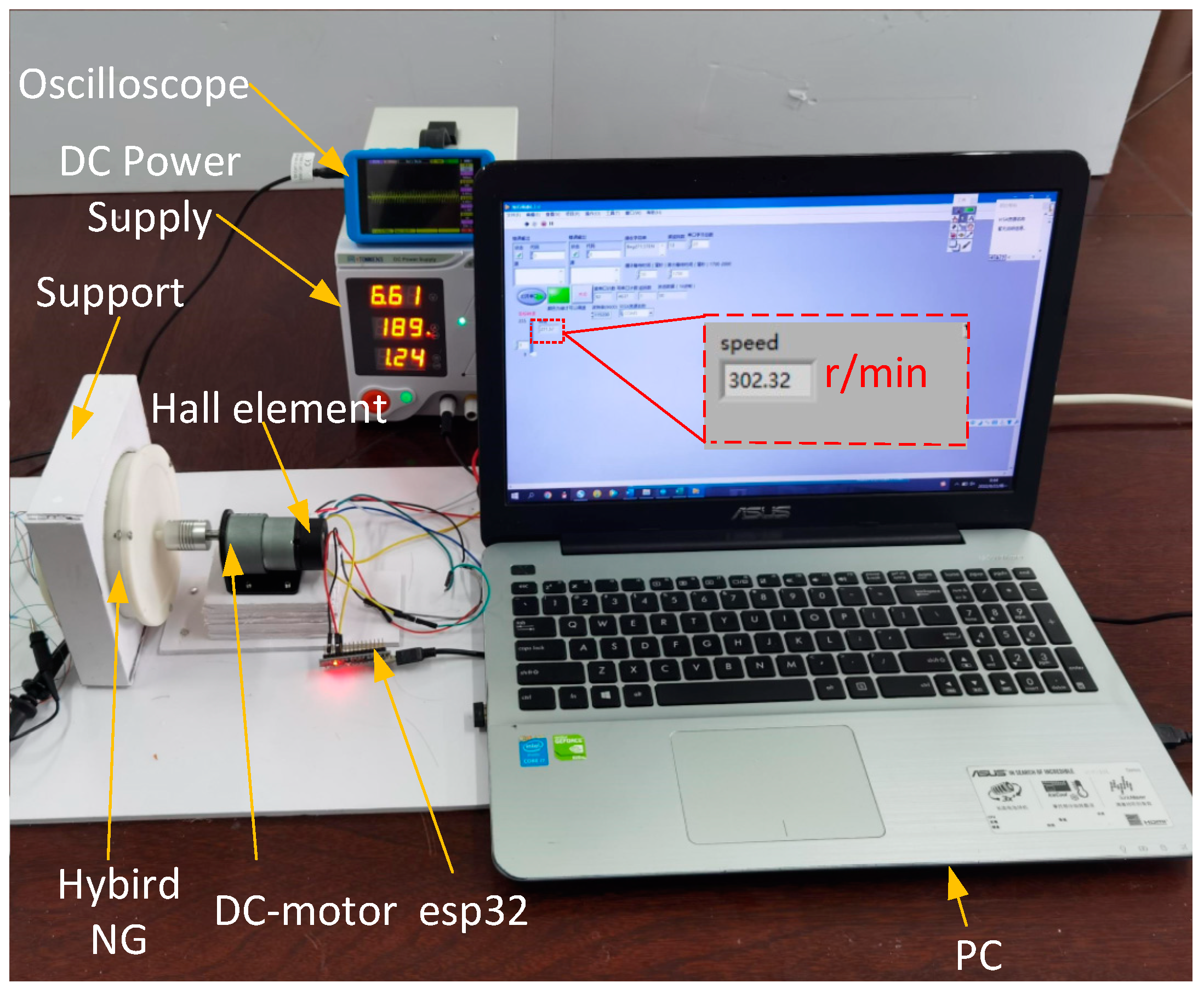
3. Electrical Measurement and Method
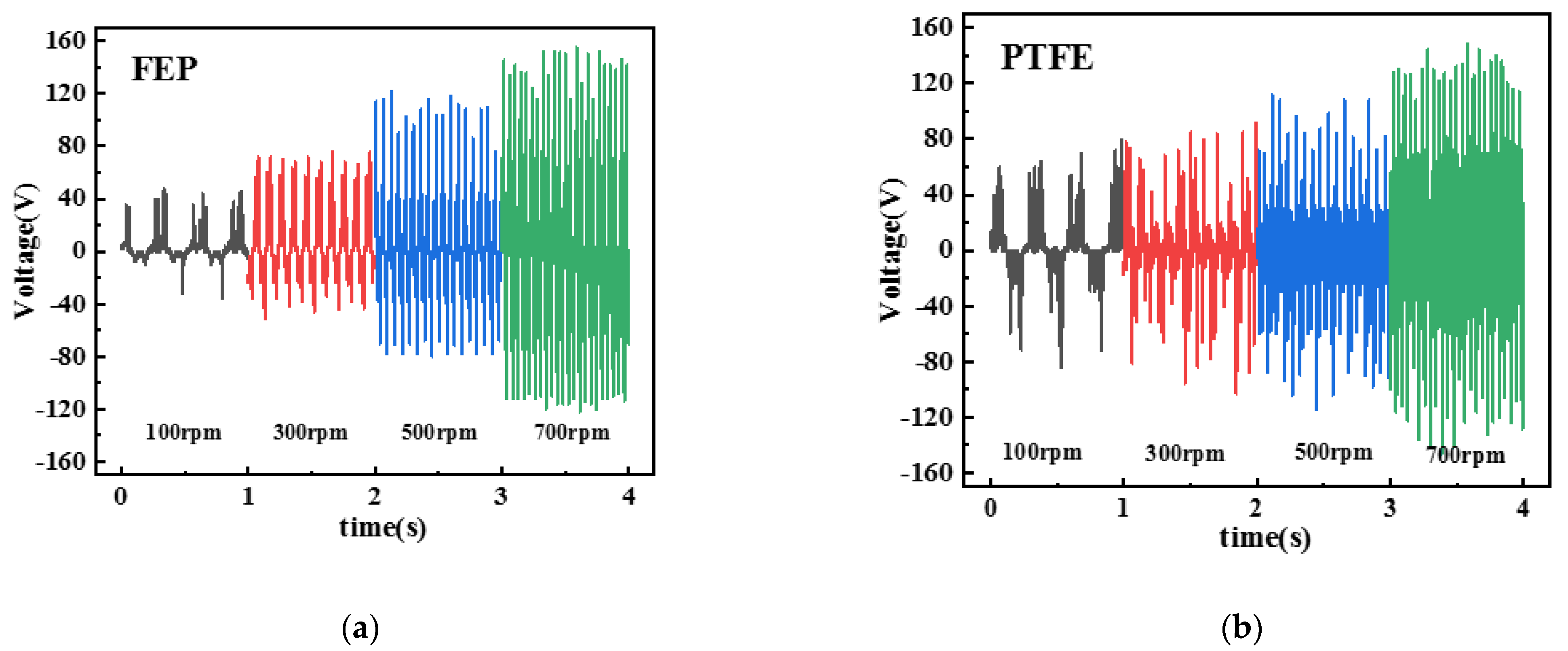
4. Results and Discussion
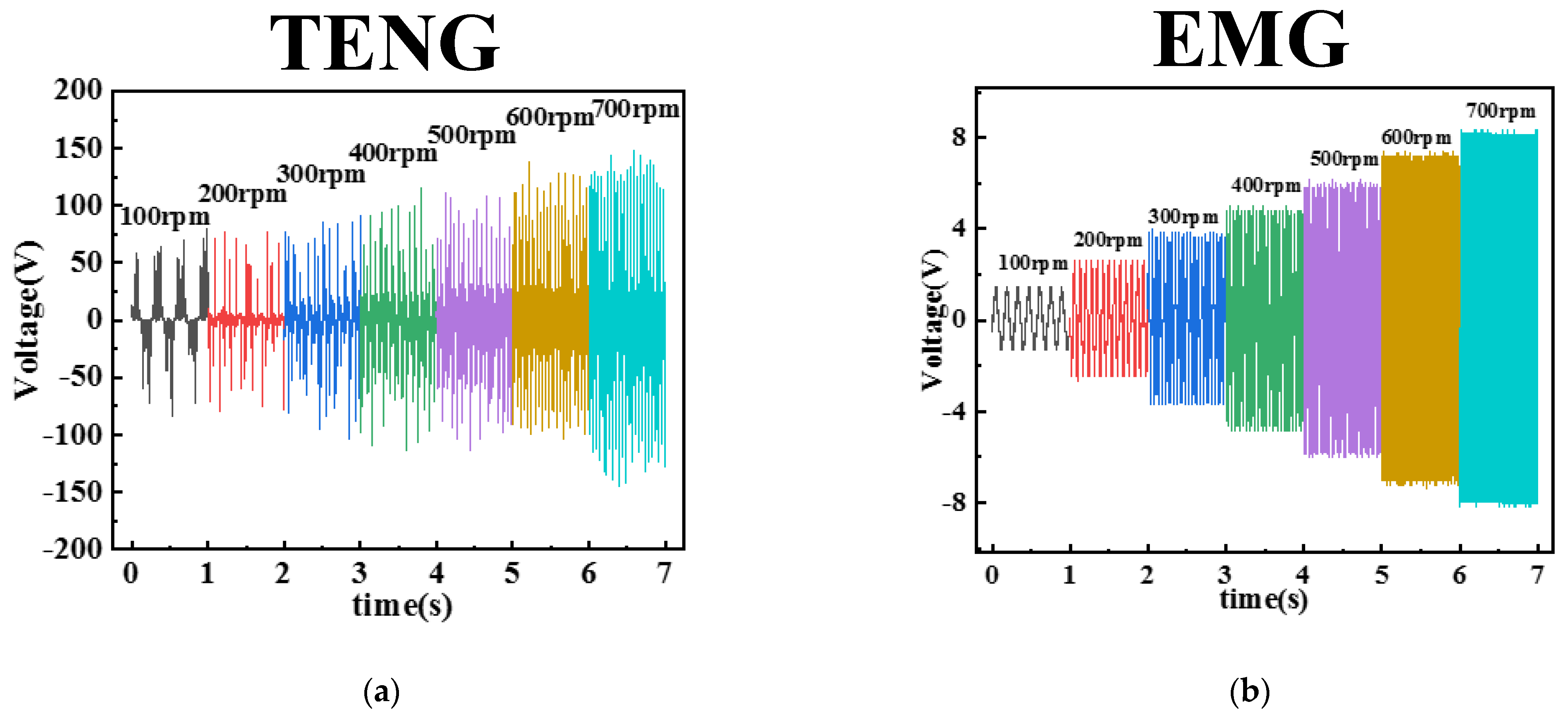
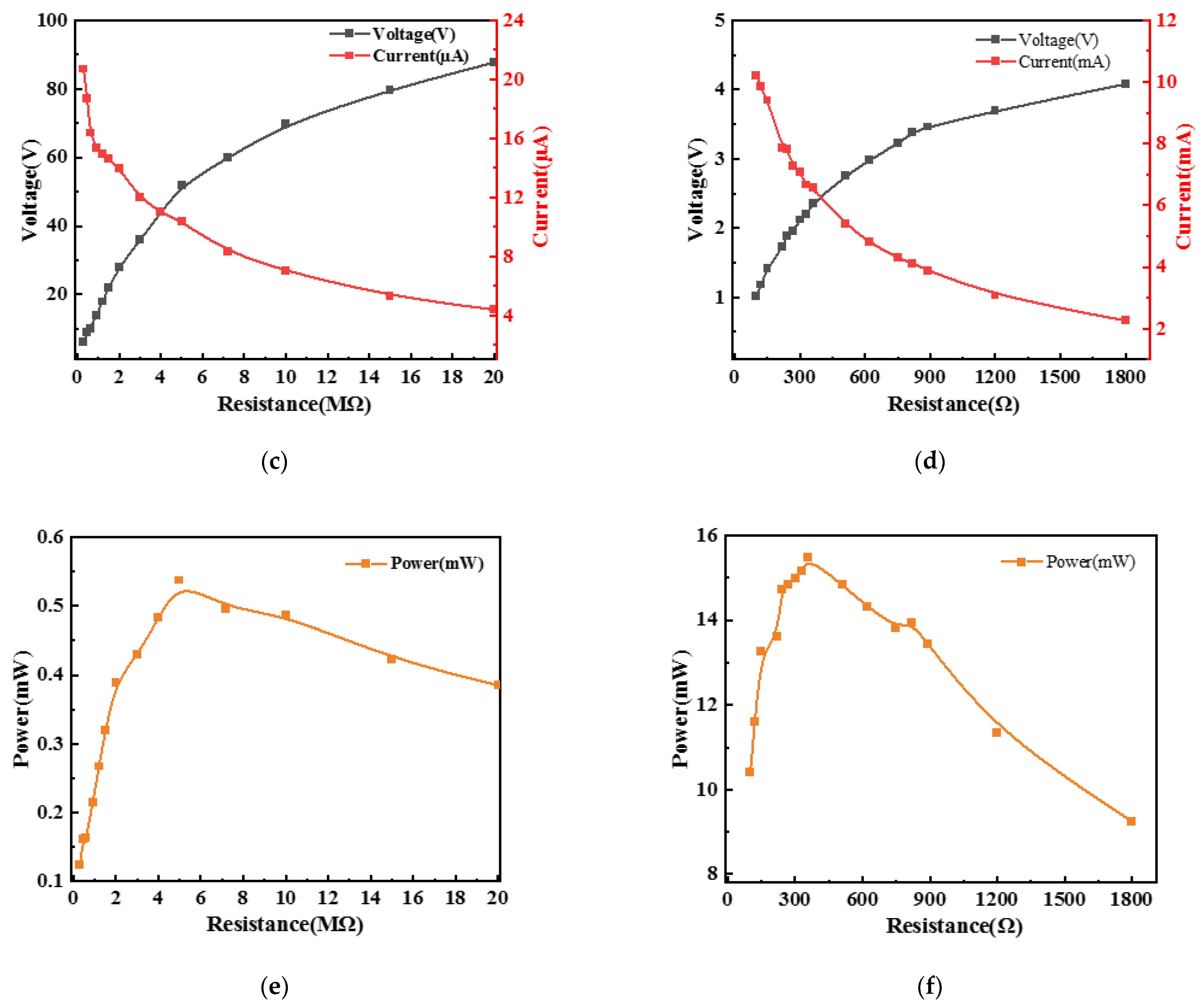
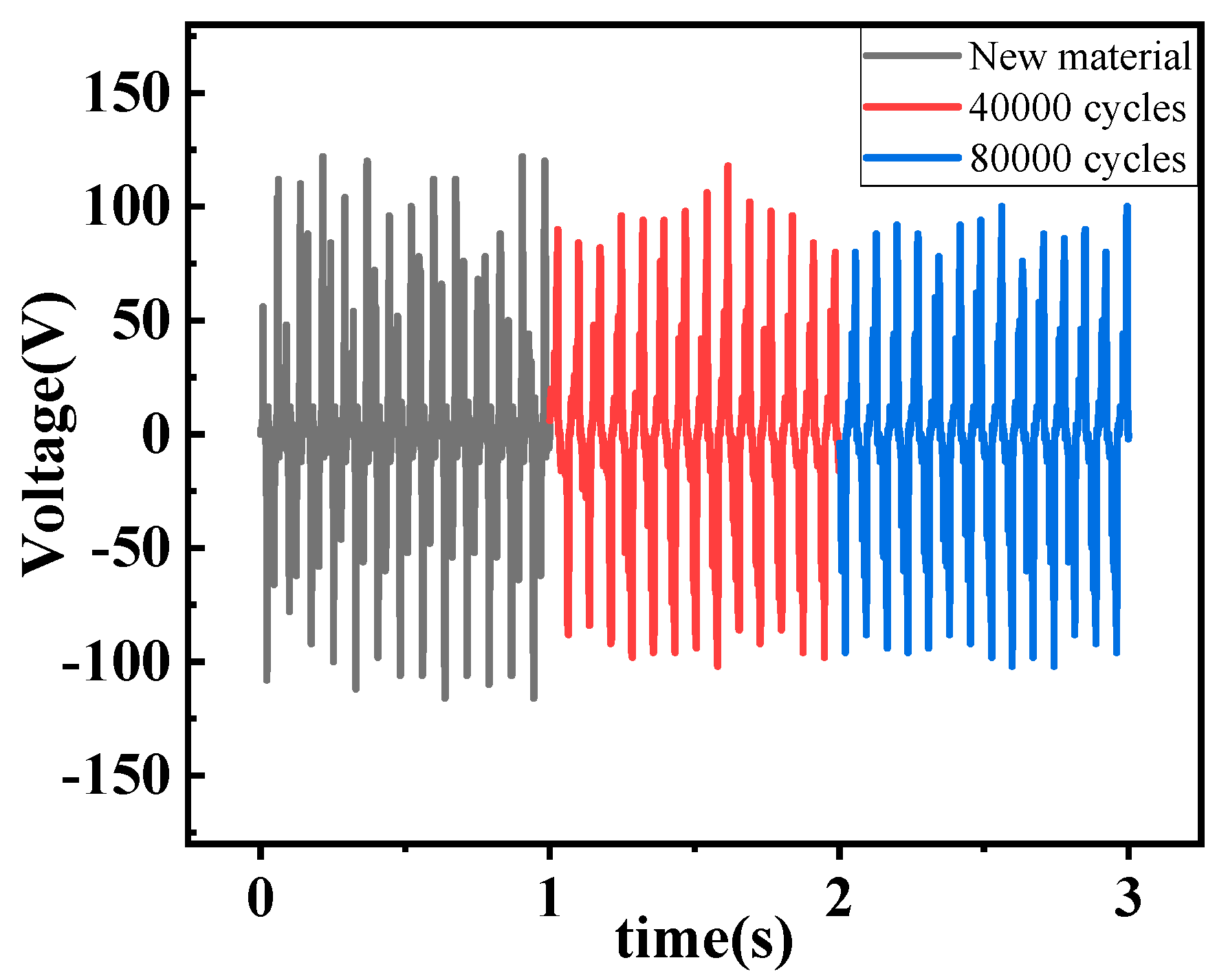
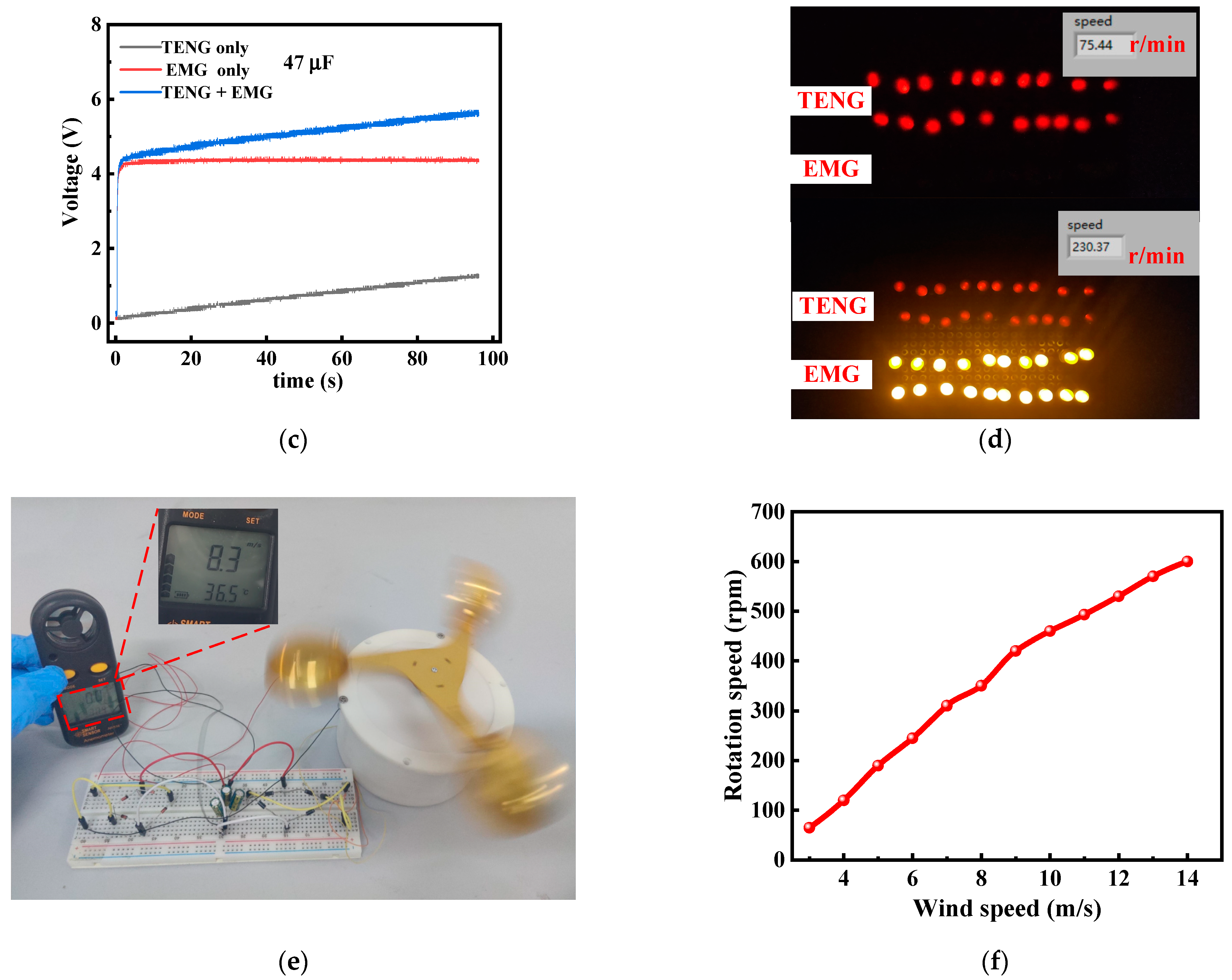
4.1. Output Characterization
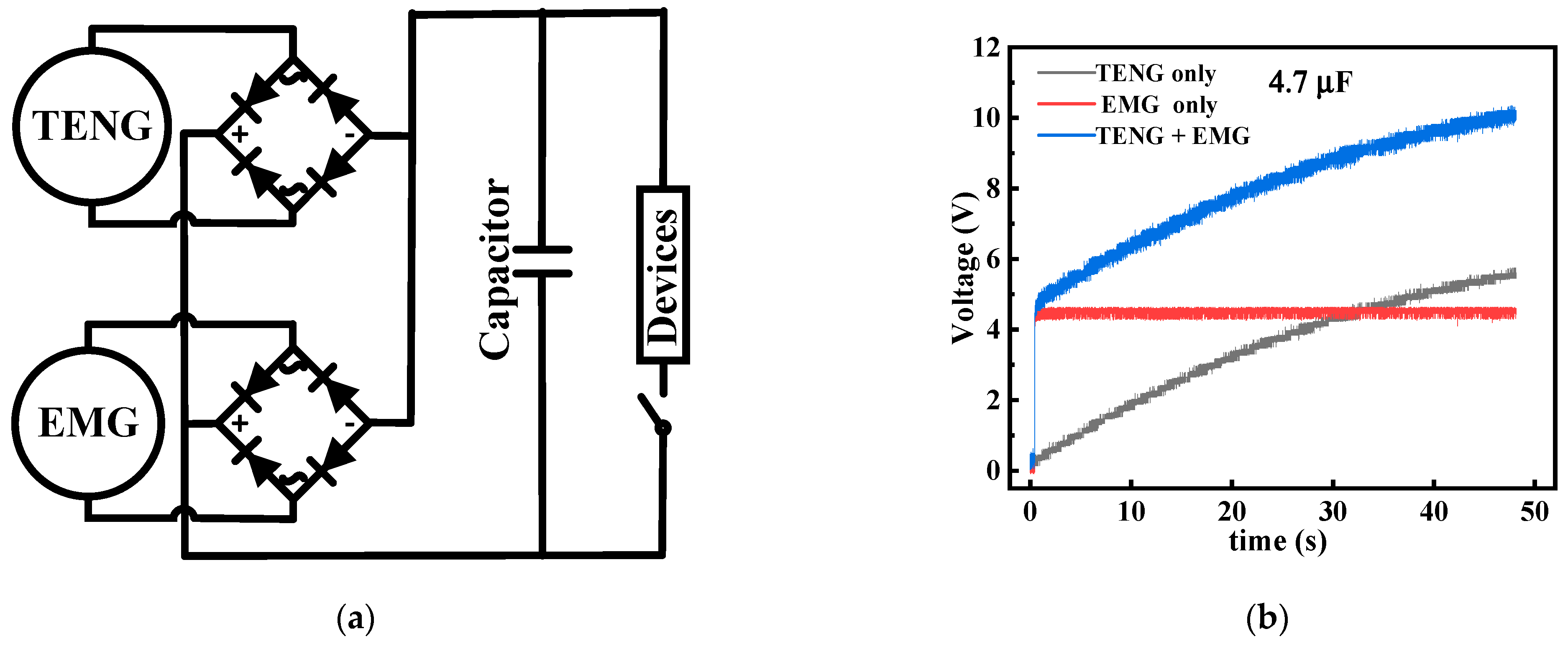
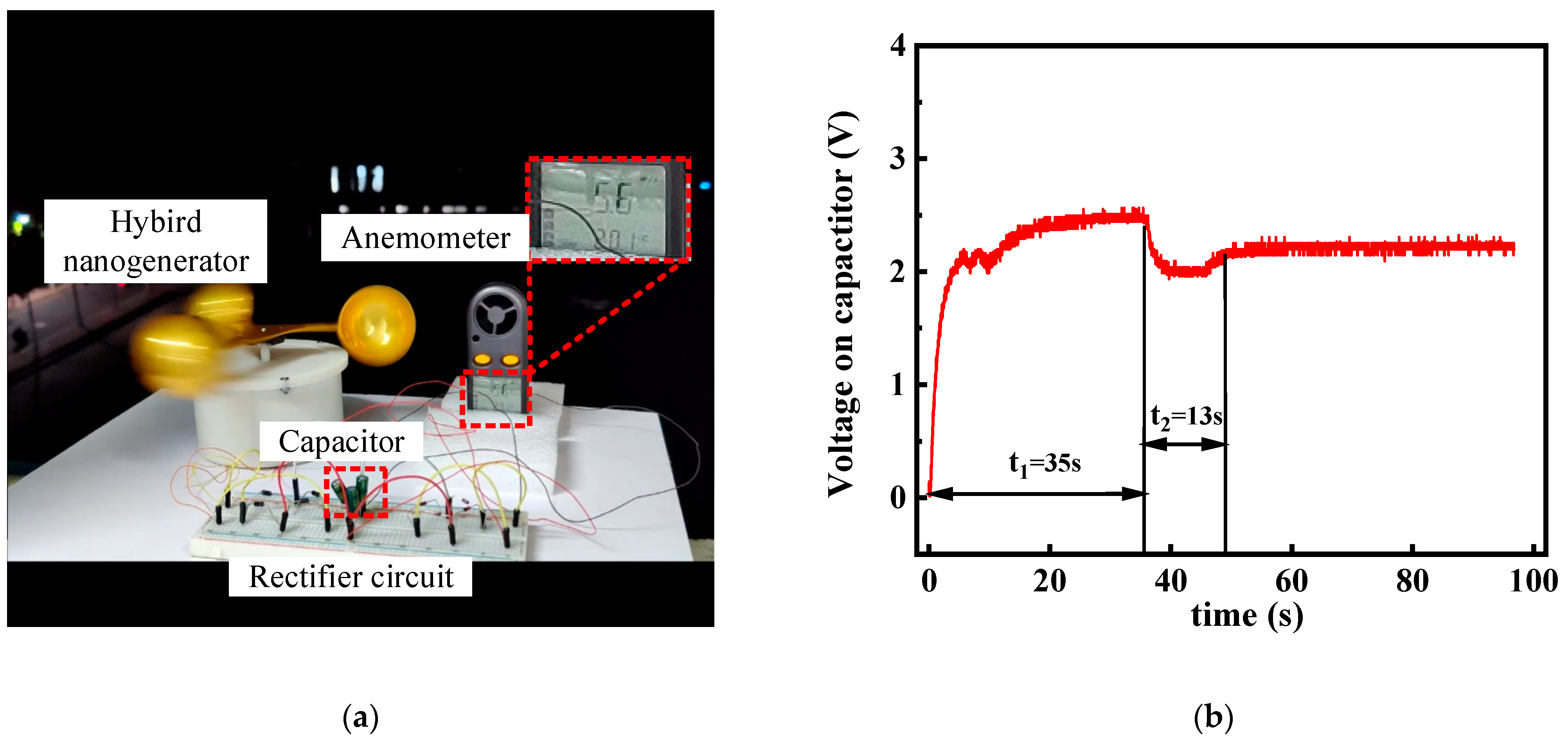
4.2. Demonstration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.H.; Xie, W.B.; Dai, K.J.; Gao, L.X.; Lu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.H.; Mu, X.J. Non-resonant and low-frequency triboelectric-electromagnetic hybridized nanogenerator for vibration energy. Acta Phys. Sin. 2020, 69, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, L.X.; Chen, J.F.; Lu, S.; Zhou, H.; Wang, T.T.; Wang, A.B.; Zhang, Z.F.; Guo, S.F.; Mu, X.J.; et al. A chaotic pendulum triboelectric-electromagnetic hybridized nanogenerator for wave energy scavenging and self-powered wireless sensing system. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xu, L.; He, C.; Zhu, L.P.; Yang, X.D.; Jiang, T.; Nie, J.H.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Z.L. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered, in-situ and real-time water quality mapping. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; Chen, J.; Guo, H.Y. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Harvesting Wind Energy: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Energies 2021, 14, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.C.; Tai, N.L. Review of contribution to frequency control through variable speed wind turbine. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, R.H.; Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, J. Review of Superconducting Generator Topologies for Direct-Drive Wind Turbines. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2013, 23, 5201108. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Li, S.Y.; Dong, S.J.; Nie, J.H.; Iwamoto, M.; Lin, S.Q.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Y.X. Regulating the output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator by using P (VDF-TrFE) Langmuir monolayers. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, H.Q.; Nie, J.H.; Liang, Y.X.; Tao, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.Y.; Fu, E.G.; Wang, Z.L. Manipulating the triboelectric surface charge density of polymers by low-energy helium ion irradiation/implantation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.S.; Bai, P.; Meng, X.S.; Jing, Q.S.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. A Shape-Adaptive Thin-Film-Based Approach for 50% High-Efficiency Energy Generation Through Micro-Grating Sliding Electrification. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3788–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Jiang, T.; Fan, F.R.; Yu, A.F.; Zhang, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Liquid-Metal Electrode for High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator at an Instantaneous Energy Conversion Efficiency of 70.6%. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3718–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.H.; Wang, Z.M.; Ren, Z.W.; Li, S.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Power generation from the interaction of a liquid droplet and a liquid membrane. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Pang, H.; An, J.; Lu, P.J.; Feng, Y.W.; Liang, X.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Z.L. Robust Swing-Structured Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Efficient Blue Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.X.; Hu, D.L.; Qi, M.K.; Gong, J.; Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.F.; Cai, J.; Wu, L.K.; Hu, N.; et al. A double-helix-structured triboelectric nanogenerator enhanced with positive charge traps for self-powered temperature sensing and smart-home control systems. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 19781–19790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.X.; Chen, X.; Lu, S.; Zhou, H.; Xie, W.B.; Chen, J.F.; Qi, M.K.; Yu, H.; Mu, X.J.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Enhancing the Output Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator via Grating-Electrode-Enabled Surface Plasmon Excitation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Hou, C.; Lin, J.H.; Li, Y.F.; Shi, Q.F.; Chen, T.; Sun, L.N.; Lee, C.K. A non-resonant rotational electromagnetic energy harvester for low-frequency and irregular human motion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 203901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukharenko, E.; Beeby, S.P.; Tudor, M.J.; White, N.M.; O’Donnell, T.; Saha, C.; Roy, S.K.S. Microelectromechanical systems vibration powered electromagnetic generator for wireless sensor applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2006, 45, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishchuk, L.P. Electromagnetic Generators and Detectors of Gravitational Waves. Physics 6 2003, 0306013. [Google Scholar]
- Mccloskey, C.A.A. Physical, Electromagnetic generator for harvesting energy from human motion. Sensors 2008, 147, 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Effective energy storage from a hybridized electromagnetic-triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Hybridized Electromagnetic–Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Scavenging Air-Flow Energy to Sustainably Power Temperature Sensors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4553–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.M.; He, J.; Mu, J.L.; Qian, J.C.; Zhang, N.; Yang, C.J.; Hou, X.J.; Geng, W.P.; Chou, X.D. Triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator driven by wind for self-powered wireless transmission in Internet of Things and self-powered wind speed sensor. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.L.; Zou, J.; Song, J.S.; He, J.; Hou, X.J.; Yu, J.B.; Han, X.T.; Feng, C.P.; He, H.C.; Chou, X.J. Hybrid enhancement effect of structural and material properties of the triboelectric generator on its performance in integrated energy harvester. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 254, 115151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Liu, X.; Yue, M.Y.; Yao, H.B.; Tian, H.T.; Sun, X.R.; Wu, Y.H.; Huang, Z.Y.; Ban, D.Y.; Zheng, H.W. Hybridized energy harvesting device based on high-performance triboelectric nanogenerator for smart agriculture applications. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Cao, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Liu, S.M.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, T.H. Optimization strategy of wind energy harvesting via triboelectric-electromagnetic flexible cooperation. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.G.; Jing, X.J. Wind-driven hybridized triboelectric-electromagnetic nanogenerator and solar cell as a sustainable power unit for self-powered natural disaster monitoring sensor networks. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Mu, J.L.; Cui, H.R.; He, W.J.; Zhang, L.; He, J.; Gao, X.; Li, Z.Y.; Hou, X.J.; Chou, X.J. Hybridized Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Harvesting to Realize Real-Time Power Supply of Sensor Nodes. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; Deng, W.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.T.; Zhu, M.H.; Yang, W.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Rotating-Disk-Based Hybridized Electromagnetic-Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Sustainably Powering Wireless Traffic Volume Sensors. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6241–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.H.; Pan, L.; Wang, J.Y.; Xu, M.Y.; Dai, G.Z.; Zou, H.Y.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z.L. An Ultra-Low-Triboelectric Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator for Rotation Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Wind Speed Sensor. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9433–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.P.; Zheng, Y.B.; Feng, Y.G.; Ma, S.C.; Luo, N.; Feng, M.; Chen, S.G.; Wang, D. A triboelectric/electromagnetic hybrid generator for efficient wind energy collection and power supply for electronic devices. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.G.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhang, B.F.; Yang, O.; Yuan, W.; He, L.X.; Wei, X.L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Wind Energy by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for an Intelligent High-Speed Train System. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Yu, X.; Yin, M.F.; Wang, J.L.; Gao, Q.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, T.H.; Wang, Z.L. Gravity triboelectric nanogenerator for the steady harvesting of natural wind energy. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henniker, J. Triboelectricity in Polymers. Nature 1962, 196, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.T.; Wang, P.H.; He, X.; Dai, G.Z.; Zheng, H.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 9461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Zhou, Y.S.; Lin, L.; Xie, Y.N.; Wang, Z.L. Theory of freestanding triboelectric-layer-based nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Xie, Y.N.; Niu, S.M.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding Triboelectric-Layer-Based Nanogenerators for Harvesting Energy from a Moving Object or Human Motion in Contact and Non-contact Modes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.Y.; Wen, Z.; Zi, Y.L.; Yeh, M.H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.P.; Hu, C.G.; Wang, Z.L. A Water-Proof Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator for Energy Harvesting in Harsh Environments. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Structural Parts | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Stator | Outer diameter (mm) | 100 |
| Inner diameter (mm) | 96 | |
| Height (mm) | 55 | |
| FEP/ Copper coil | Length (mm) | 70 |
| Width (mm) | 40 | |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.1 | |
| PTFE | Length (mm) | 70 |
| Width (mm) | 40 | |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.05/0.1/0.2 | |
| Nylon 66 | Width (mm) | 40 |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.3 | |
| Arch outer diameter(mm) | 98 | |
| Wind cup | Diameter (mm) | 200 |
| Magnet (NdFeB-N35) | Diameter (mm) | 20 |
| Thickness (mm) | 2 | |
| Residual magnetic strength (T) | 1.28 | |
| Coil | Outer diameter (mm) | 18.5 |
| Inner diameter (mm) | 12.5 | |
| Number of turns | 480 | |
| Distance between magnet and coil | d(mm) | 0.5 |
| Bearing | Outer diameter (mm) | 13 |
| Inner diameter (mm) | 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, L.; Zhang, P. A Wind-Driven Rotating Micro-Hybrid Nanogenerator for Powering Environmental Monitoring Devices. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122053
Zhu Y, Zhao Y, Hou L, Zhang P. A Wind-Driven Rotating Micro-Hybrid Nanogenerator for Powering Environmental Monitoring Devices. Micromachines. 2022; 13(12):2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122053
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yongqiang, Yu Zhao, Lijun Hou, and Pingxia Zhang. 2022. "A Wind-Driven Rotating Micro-Hybrid Nanogenerator for Powering Environmental Monitoring Devices" Micromachines 13, no. 12: 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122053
APA StyleZhu, Y., Zhao, Y., Hou, L., & Zhang, P. (2022). A Wind-Driven Rotating Micro-Hybrid Nanogenerator for Powering Environmental Monitoring Devices. Micromachines, 13(12), 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122053






