Simulation and Experimental Study of Ion Concentration Polarization Induced Electroconvective Vortex and Particle Movement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Setup
2.2. Theoretical Model and Simulation
3. Results
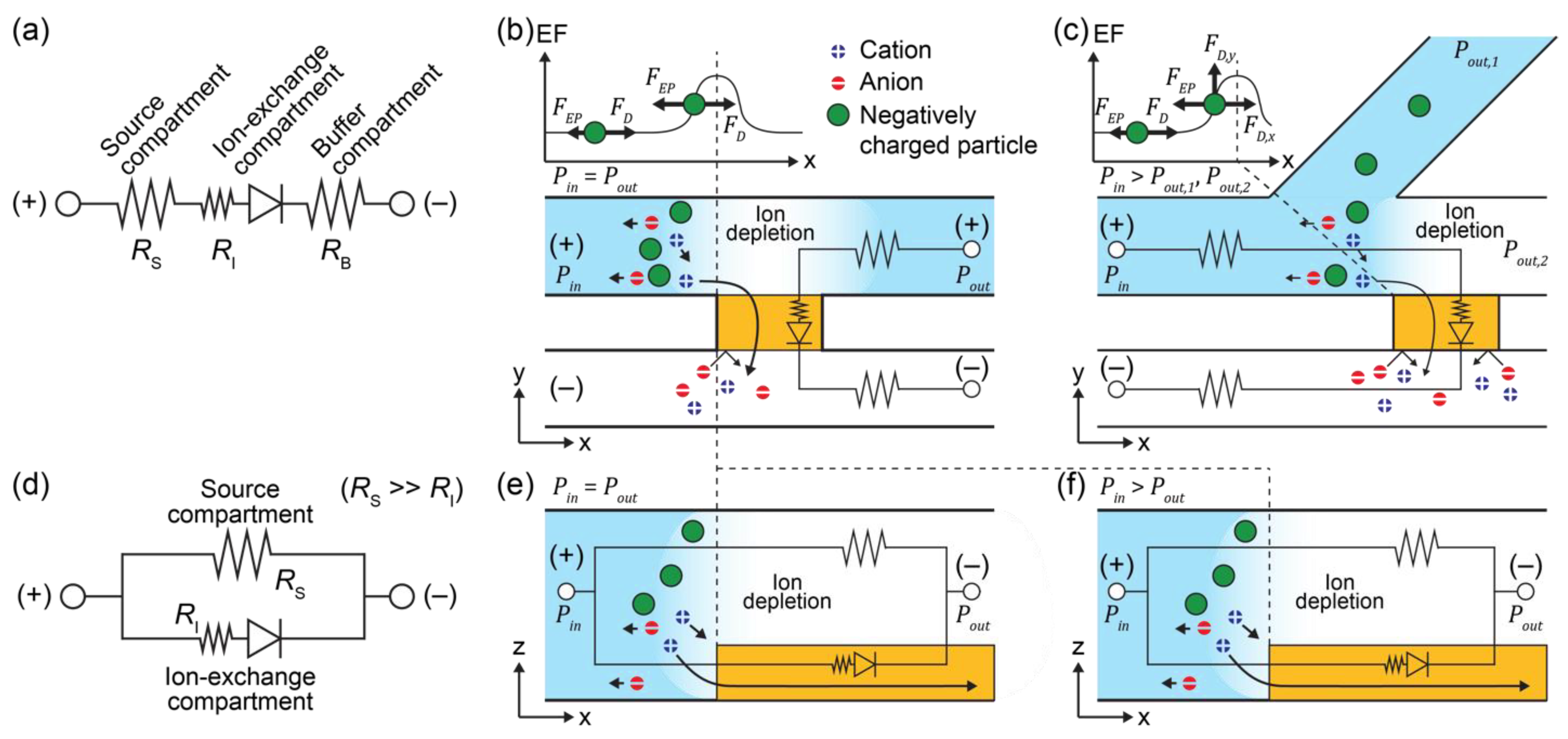
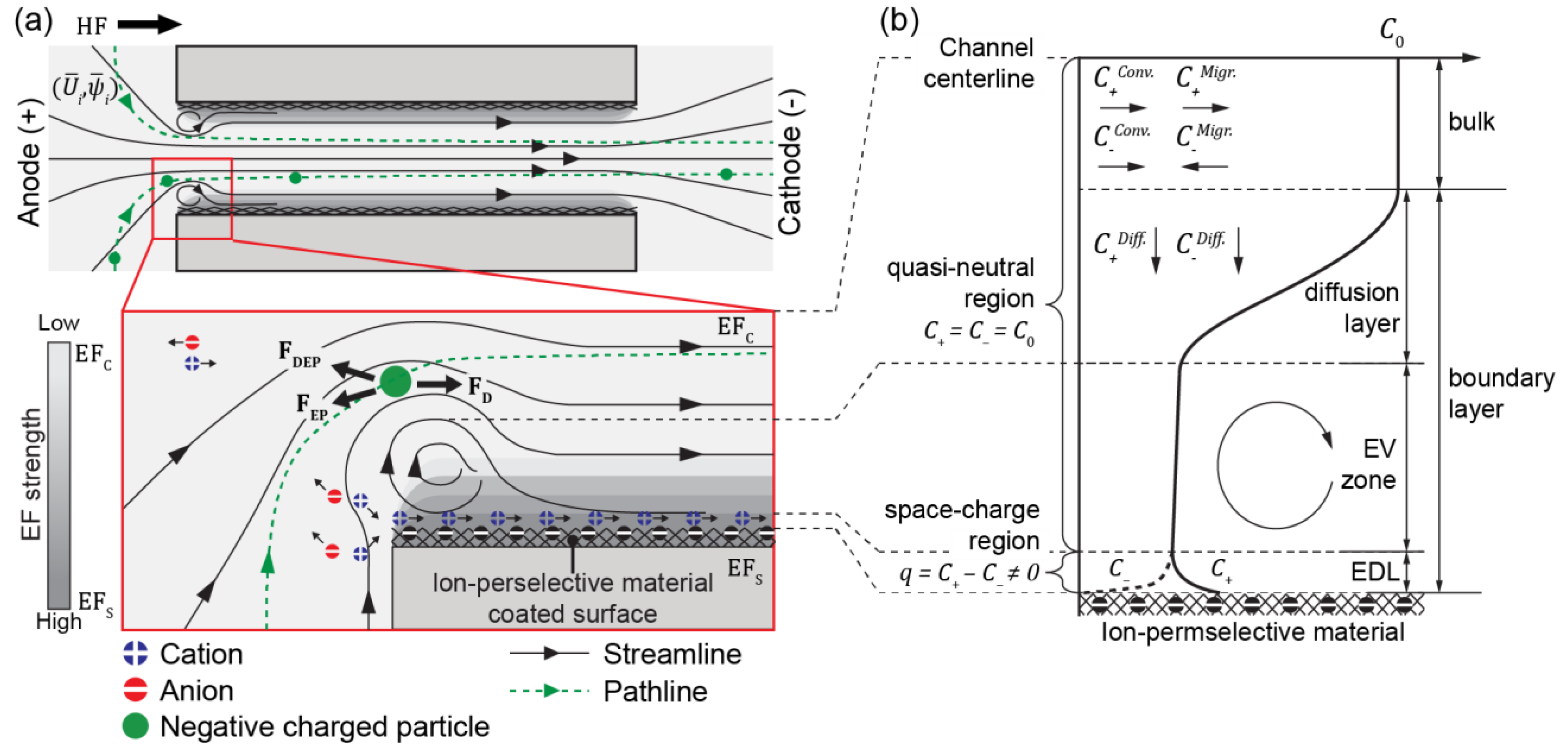
3.1. ICP and Electroconvective Vortex in ICP-2C-EF/HF System
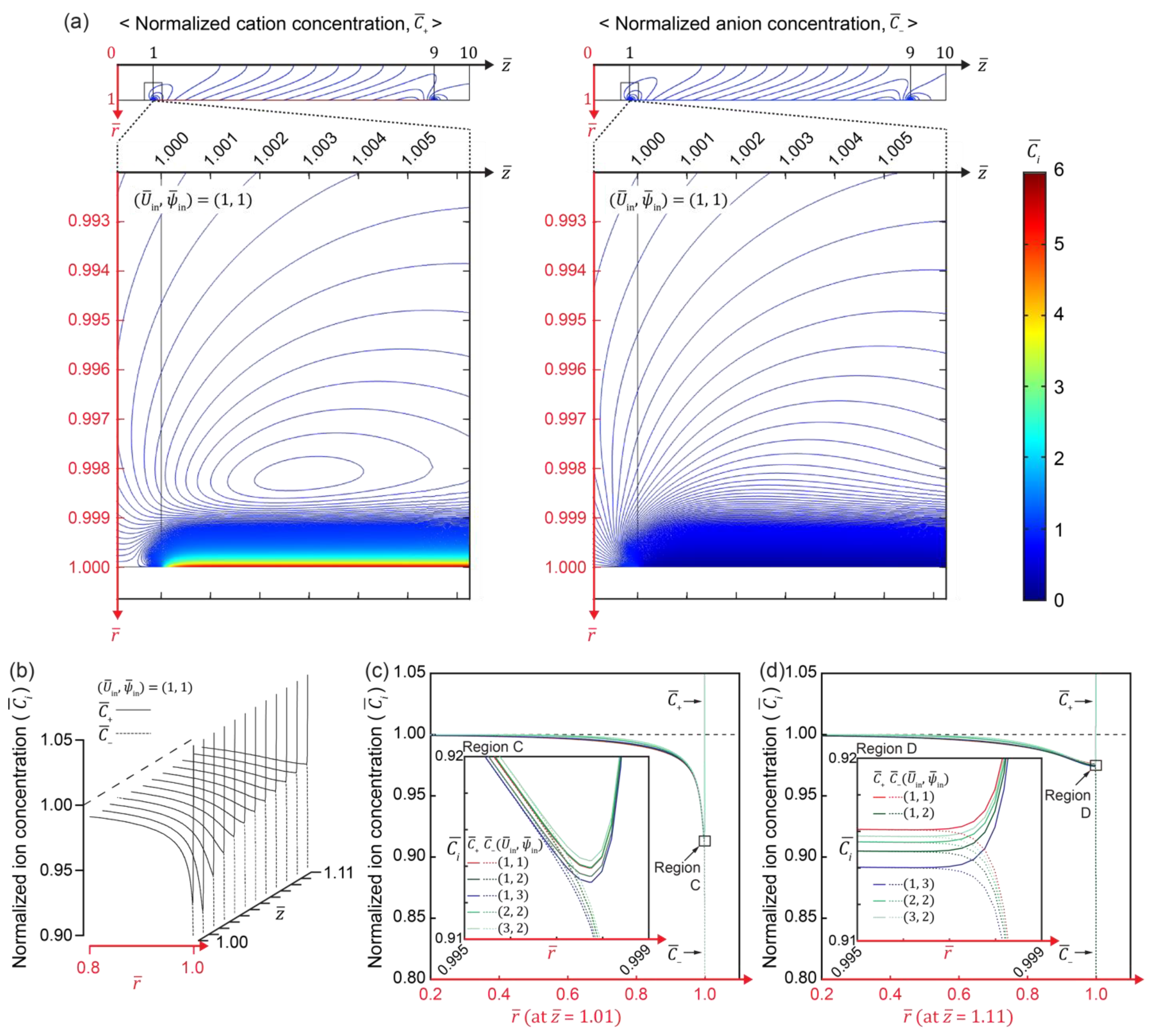
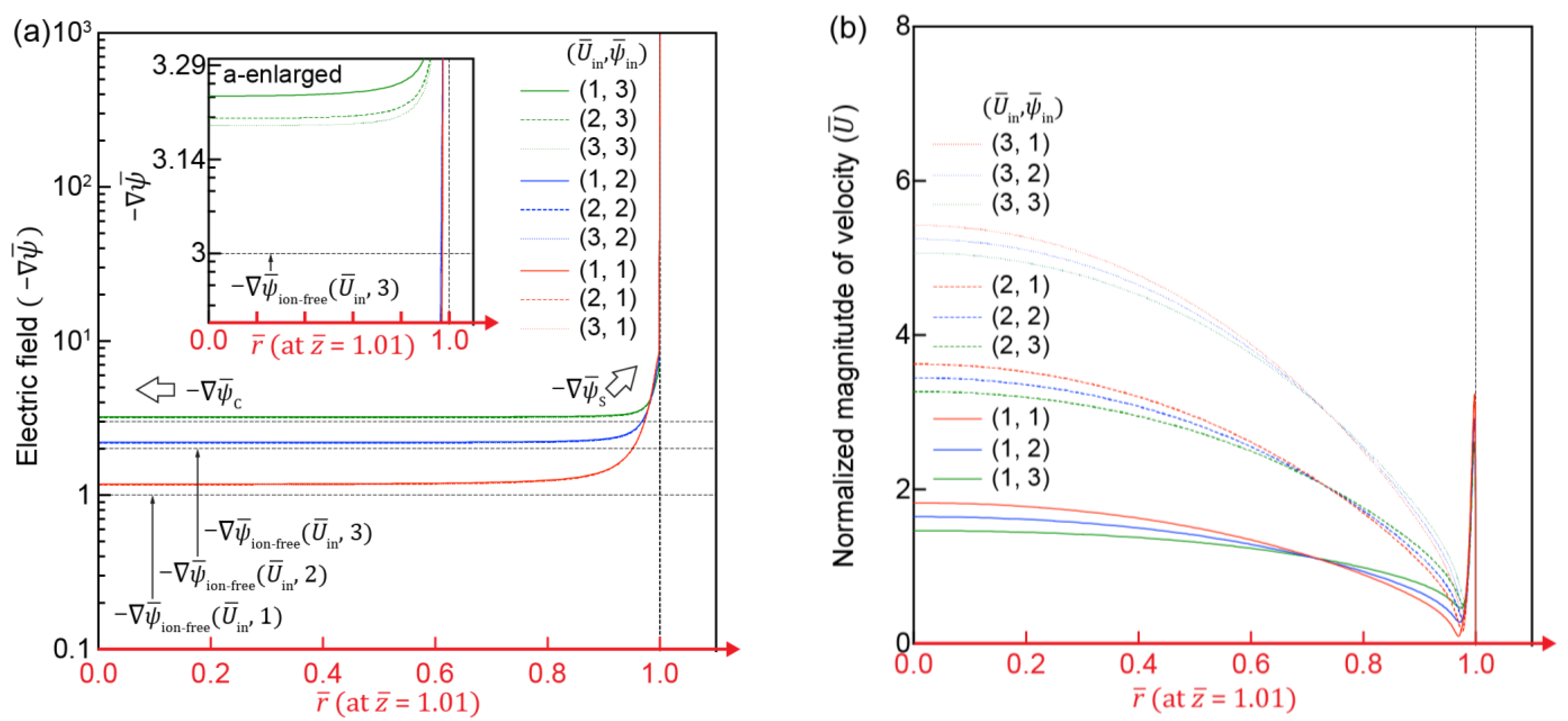
3.2. Effect of Flow and Electric Fields on ICP
3.3. Electric and Flow Field in the IC-Channel
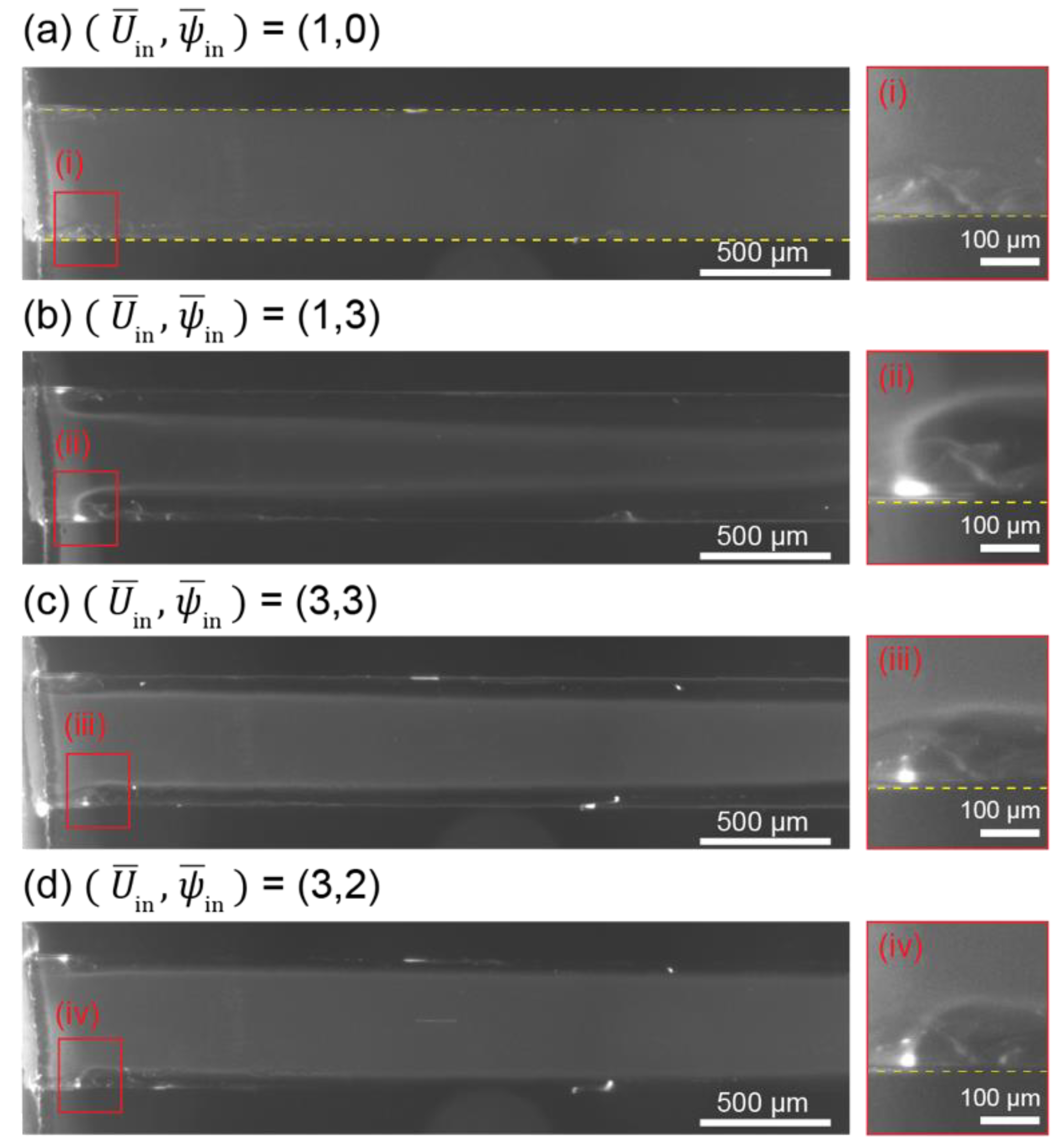
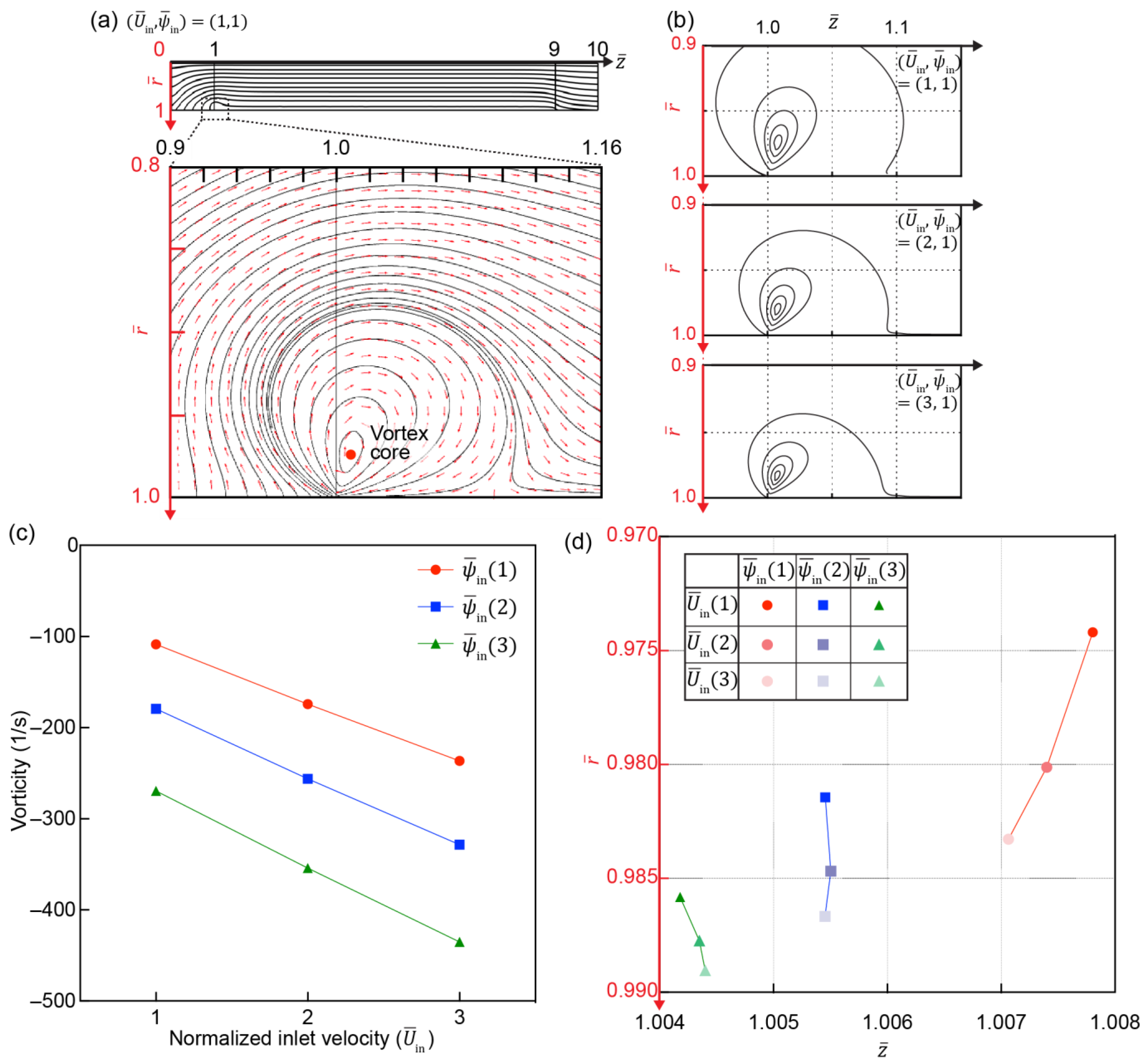
3.4. Development of Electroconvective Vortex
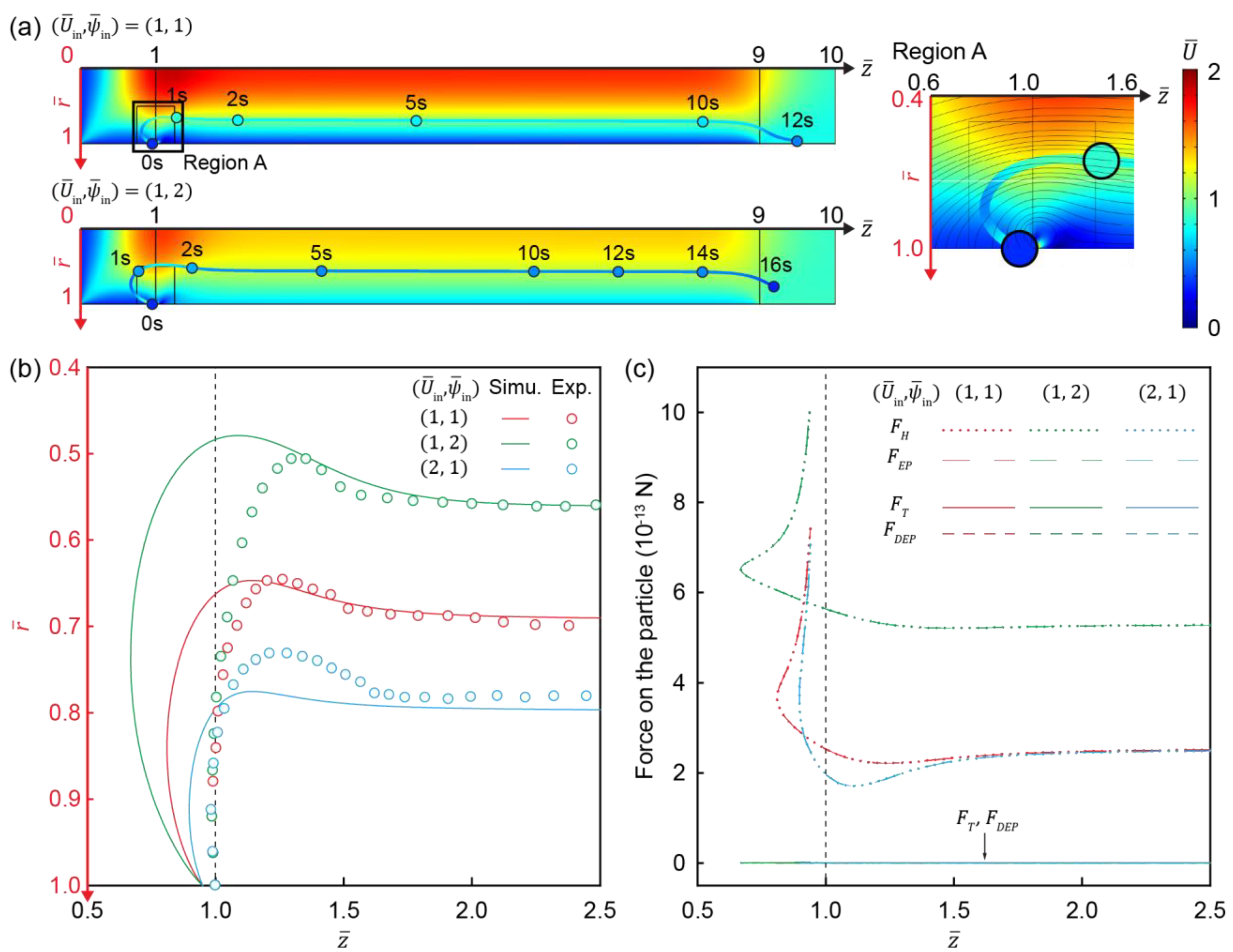
3.5. Movement of Charged Particles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanaka, Y. Concentration polarization in ion exchange membrane electrodialysis. J. Memb. Sci. 1991, 57, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Song, Y.A.; Han, J. Nanofluidic concentration devices for biomolecules utilizing ion concentration polarization: Theory, fabrication, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.; Do, V.Q.; Pham, V.-S.; Han, J. Return flow ion concentration polarization desalination: A new way to enhance electromembrane desalination. Water Res. 2019, 159, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 2010, 264, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Ehara, R.; Itoi, S.; Goto, T. Ion-exchange membrane electrodialytic salt production using brine discharged from a reverse osmosis seawater desalination plant. J. Memb. Sci. 2003, 222, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehayeb, K.M.; Farhat, D.M.; Nayar, K.G.; Lienhard, J.H. Optimal design and operation of electrodialysis for brackish-water desalination and for high-salinity brine concentration. Desalination 2017, 420, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Flavin, M.T.; Han, J. Current efficiency and selectivity reduction caused by co-ion leakage in electromembrane processes. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Song, Y.A.; Han, J. Multiplexed proteomic sample preconcentration device using surface-patterned ion-selective membrane. Lab. Chip 2008, 8, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, S.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, M.W.; Han, J.; Kamm, R.D. Non-lithographic wrinkle nanochannels for protein preconcentration. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3011–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Lee, H.; Kang, K.H.; Lim, G. Ion concentration polarization-based continuous separation device using electrical repulsion in the depletion region. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Cho, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, S. Tunable sheathless microfluidic focusing using ion concentration polarization. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Raj, A.; Zhu, L.; Masel, R.I.; Shannon, M.A. Non-equilibrium electrokinetic micro/nano fluidic mixer. Lab. Chip 2008, 8, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Han, J. Universal amplification-free molecular diagnostics by billion-fold hierarchical nanofluidic concentration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16240–16249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwak, R.; Kim, S.J.; Han, J. Continuous-Flow biomolecule and cell concentrator by ion concentration polarization. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7348–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Ko, S.H.; Kang, K.H.; Han, J. Direct seawater desalination by ion concentration polarization. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dydek, E.V.; Zaltzman, B.; Rubinstein, I.; Deng, D.S.; Mani, A.; Bazant, M.Z. Overlimiting current in a microchannel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 118301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.H.; Song, Y.A.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.; Han, J.; Kang, K.H. Nanofluidic preconcentration device in a straight microchannel using ion concentration polarization. Lab. Chip 2012, 12, 4472–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Jia, M.; Kim, T. Ion concentration polarization in a single and open microchannel induced by a surface-patterned perm-selective film. Analyst 2013, 138, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.; Cho, Y.; Han, S.; Lim, C.S.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, S. Microfluidic in-reservoir pre-concentration using a buffer drain technique. Lab. Chip 2014, 14, 2778–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, H.; Han, J. Concentration polarization and nonlinear electrokinetic flow near a nanofluidic channel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 44501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.H.; Sarkar, A.; Song, Y.A.; Miller, M.A.; Kim, S.J.; Griffith, L.G.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Han, J. Enhancing protease activity assay in droplet-based microfluidics using a biomolecule concentrator. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10368–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yao, S. An on-demand nanofluidic concentrator. Lab. Chip 2015, 15, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.I.; Yoo, Y.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Lee, K.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, H.; Yoon, D.S.; Hwang, K.S.; Kwak, R.; et al. High-ionic-strength pre-concentration via ion concentration polarization for blood-based biofluids. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 268, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knust, K.N.; Hlushkou, D.; Anand, R.K.; Tallarek, U.; Crooks, R.M. Electrochemically mediated seawater desalination. Angew. Chemie 2013, 125, 8265–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, B.D.; Gong, M.M.; Zhang, P.; Sinton, D. Out-of-plane ion concentration polarization for scalable water desalination. Lab. Chip 2014, 14, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.; Sung, G.Y.; Kim, S.J. Overlimiting current through ion concentration polarization layer: Hydrodynamic convection effects. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4620–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Chun, Y.; Nguyen, N.T. A continuous-flow droplet-based concentrator using ion concentration polarization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 44336–44341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.; Yoon, J.; Lim, D.W.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, S. Ion concentration polarization for pre-concentration of biological samples without pH change. Analyst 2016, 141, 6510–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, D.T.; Shaegh, S.A.M.; Yang, C.; Nguyen, N.T. Sample concentration in a microfluidic paper-based analytical device using ion concentration polarization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.; Yang, H.; Sivagnanam, V.; Gijs, M.A.M. Microfluidic protein preconcentrator using a microchannel-integrated nafion strip: Experiment and modeling. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9989–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Kim, T. Multiphysics simulation of ion concentration polarization induced by nanoporous membranes in dual channel devices. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7360–7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Gong, L.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Han, J. Accurate multi-physics numerical analysis of particle preconcentration based on ion concentration polarization. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2017, 9, 1750107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Ye, X.; Li, Z.; Han, J. Deciphering ion concentration polarization-based electrokinetic molecular concentration at the micro-nanofluidic interface: Theoretical limits and scaling laws. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15187–15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Cho, I.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.J. Ion concentration polarization by bifurcated current path. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.; Li, Z.; Han, J. Numerical simulation of continuous extraction of highly concentrated Li+ from high Mg2+/Li+ ratio brines in an ion concentration polarization-based microfluidic system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 217, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanella, J.J.; McLin, M.G.; Wintersgill, M.C.; Calame, J.P.; Greenbaum, S.G. Electrical impedance studies of acid form NAFION® membranes. Solid State Ion. 1993, 66, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, R.; Pham, V.S.; Lim, K.M.; Han, J. Shear flow of an electrically charged fluid by ion concentration polarization: Scaling laws for electroconvective vortices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 114501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, R.; Guan, G.; Peng, W.K.; Han, J. Microscale electrodialysis: Concentration profiling and vortex visualization. Desalination 2013, 308, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, Y.; Yossifon, G. Effects of three-dimensional geometric field focusing on concentration polarization in a heterogeneous permselective system. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Type | Force Field | Ion-Exchange Compartment | Application | Sample | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICP-3C | EF | Nano-channel | ICP layer analysis | Fluorescence | [20] |
| Wrinkled nano-channel | Concentration | β-phycoerythrin | [9] | ||
| Patterned nafion | Concentration | β-phycoerythrin | [8] | ||
| Patterned nafion | Concentration | Enzyme | [21] | ||
| Cracked nano-channnel | Concentration | Bovine serum albumin | [22] | ||
| Patterned nafion | Concentration | Albumin | [23] | ||
| Patterned nafion | Concentration | DNA | [13] | ||
| EF/HF | Patterned nafion | Separation | Red blood cell, E. coli | [14] | |
| Patterned nafion | Separation | Micro- and nano-sized particle | [10] | ||
| Patterned nafion | Desalination, separation | Seawater, white blood cell | [15] | ||
| Bipolar electrode | Desalination | Seawater | [24] | ||
| Patterned nafion | Desalination | Salt solution | [25] | ||
| Nafion nanojunction | ICP layer analysis | Potassium chloride | [26] | ||
| Patterned nafion | Concentration | Fluorescence | [27] | ||
| Nafion membrane | Concentration | Hemagglutinin | [28] | ||
| ICP-2C | EF | Patterned nafion | Concentration | C-reactive protein | [17] |
| Patterned nafion | Concentration | Bacteria | [18] | ||
| Nafion membrane | Concentration | Fluorescence | [29] | ||
| EF/HF | Nano-channel | Flow mixing | Fluorescence | [12] | |
| Patterned nafion | Concentration | Hemagglutinin | [19] | ||
| Patterned nafion | Focusing | Micro- and nano-sized particle | [11] |
| Type | Force Field | Boundary Condition for Ion-Exchange Compartment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICP-3C | EF | Fixed volumetric charge | [30] |
| Fixed volumetric charge | [31] | ||
| Fixed surface charge and electric potential | [32,33] | ||
| EF/HF | Fixed surface charge | [22] | |
| Fixed volumetric charge | [34] | ||
| Fixed surface charge and fixed electric potential | [35] | ||
| ICP-2C | EF | Fixed volumetric charge | [31] |
| EF/HF | Fixed surface charge | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, J.; Cho, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Na, K.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, S. Simulation and Experimental Study of Ion Concentration Polarization Induced Electroconvective Vortex and Particle Movement. Micromachines 2021, 12, 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080903
Yoon J, Cho Y, Kim J, Kim H, Na K, Lee JH, Chung S. Simulation and Experimental Study of Ion Concentration Polarization Induced Electroconvective Vortex and Particle Movement. Micromachines. 2021; 12(8):903. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080903
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Junghyo, Youngkyu Cho, Jaehoon Kim, Hyunho Kim, Kyuhwan Na, Jeong Hoon Lee, and Seok Chung. 2021. "Simulation and Experimental Study of Ion Concentration Polarization Induced Electroconvective Vortex and Particle Movement" Micromachines 12, no. 8: 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080903
APA StyleYoon, J., Cho, Y., Kim, J., Kim, H., Na, K., Lee, J. H., & Chung, S. (2021). Simulation and Experimental Study of Ion Concentration Polarization Induced Electroconvective Vortex and Particle Movement. Micromachines, 12(8), 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080903







