An Intelligent Combined Visual Navigation Brain Model/GPS/MEMS–INS/ADSFCF Method to Develop Vehicle Independent Guidance Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Navigation Subsystem Basics and Errors Analysis
2.1. GPS Basics and Error Analysis
2.1.1. Principles of GPS
2.1.2. GPS Impairments
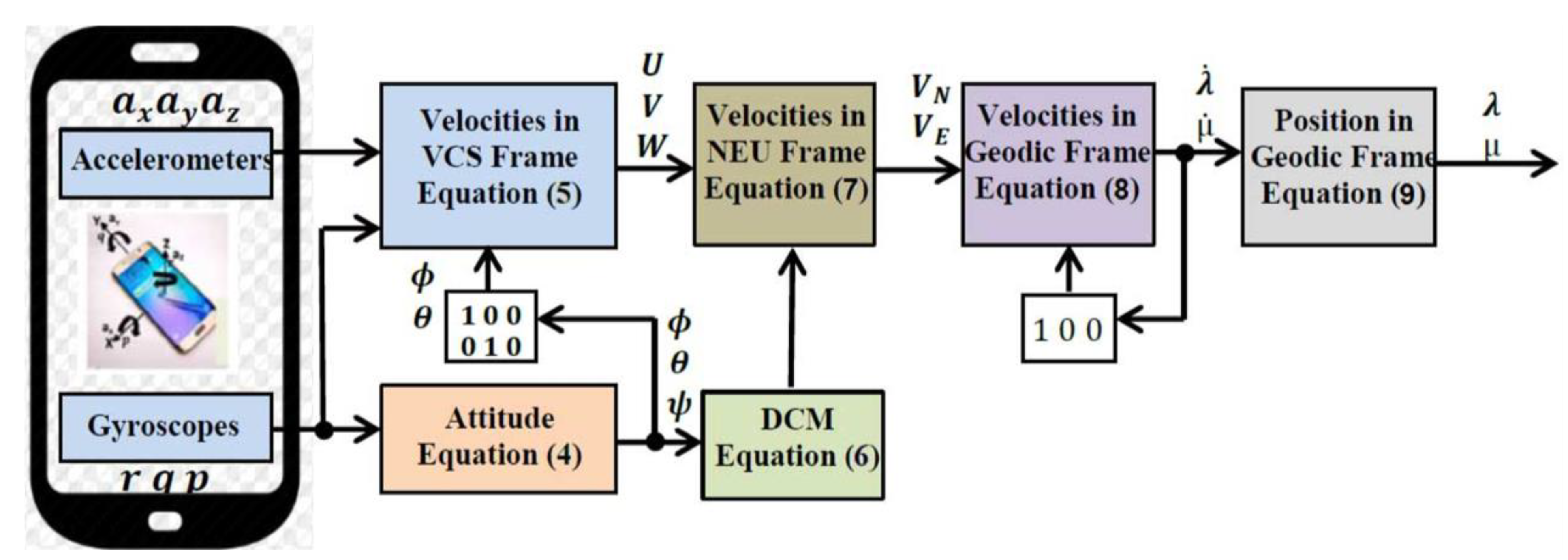
2.2. MEMS–INS Smart-Phone Sensors and Error Analysis
2.2.1. Structure of MEMS–INS
2.2.2. MEMS–INS Analysis Errors
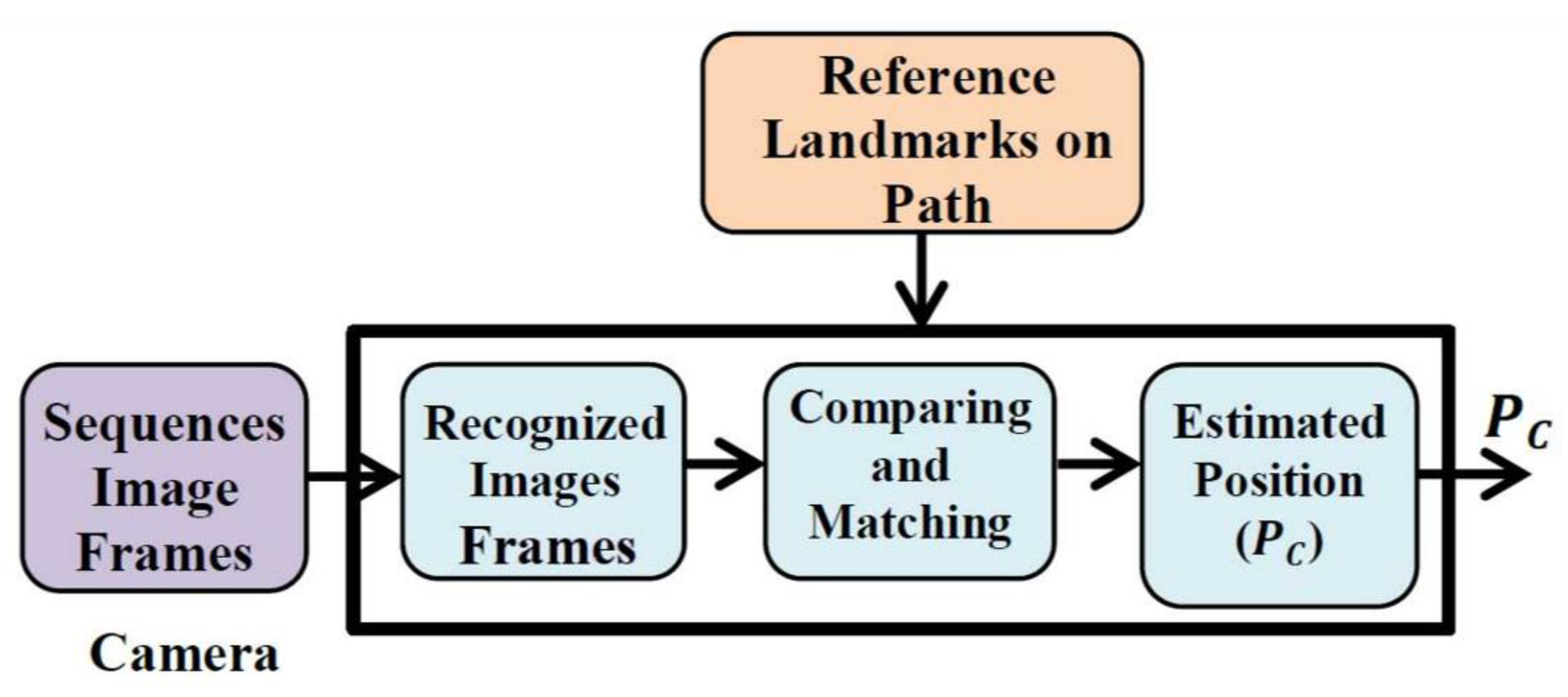
2.3. VNBM and Error Analysis
2.3.1. Principle of VNBM
2.3.2. Error Analysis for VNBM
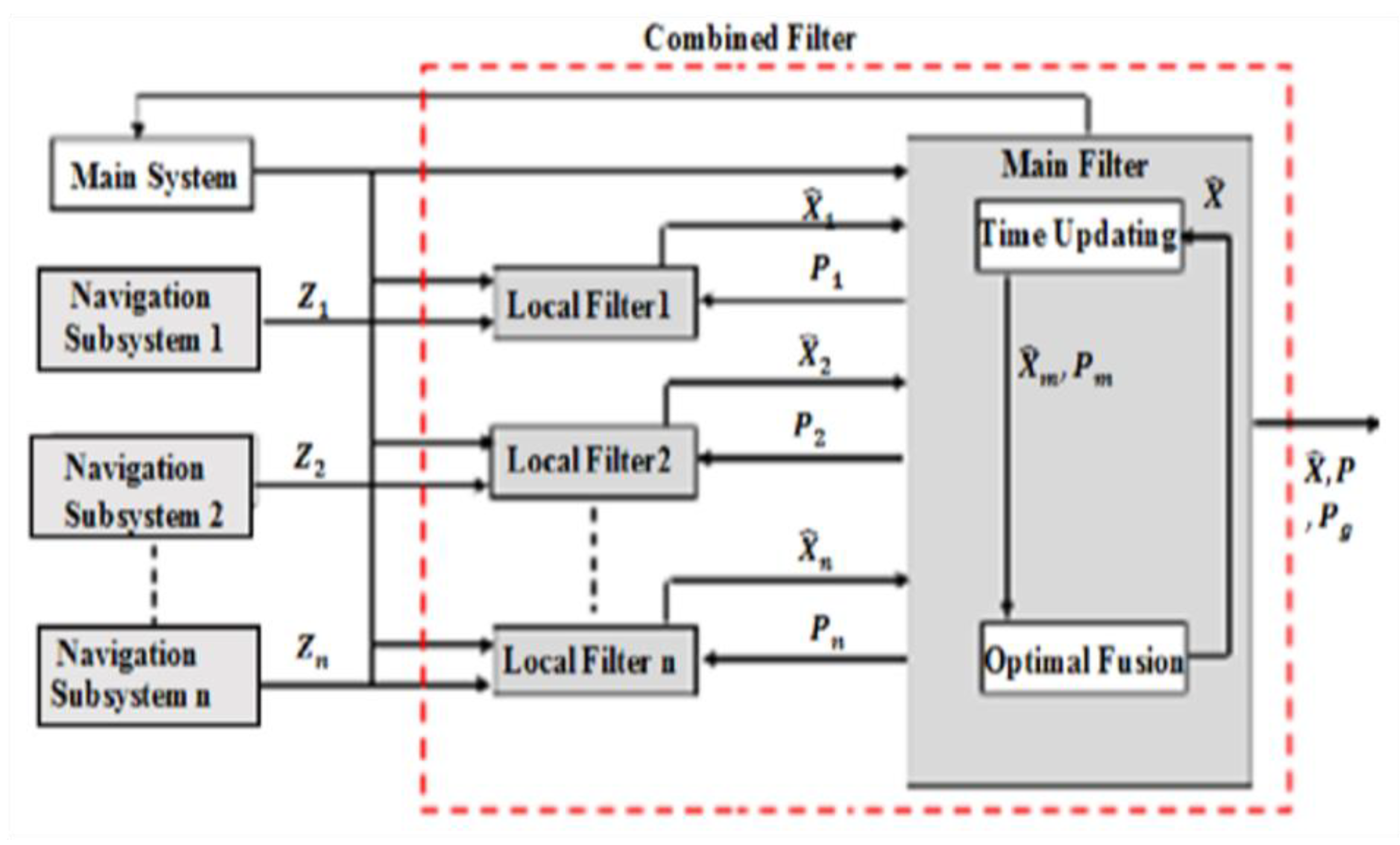
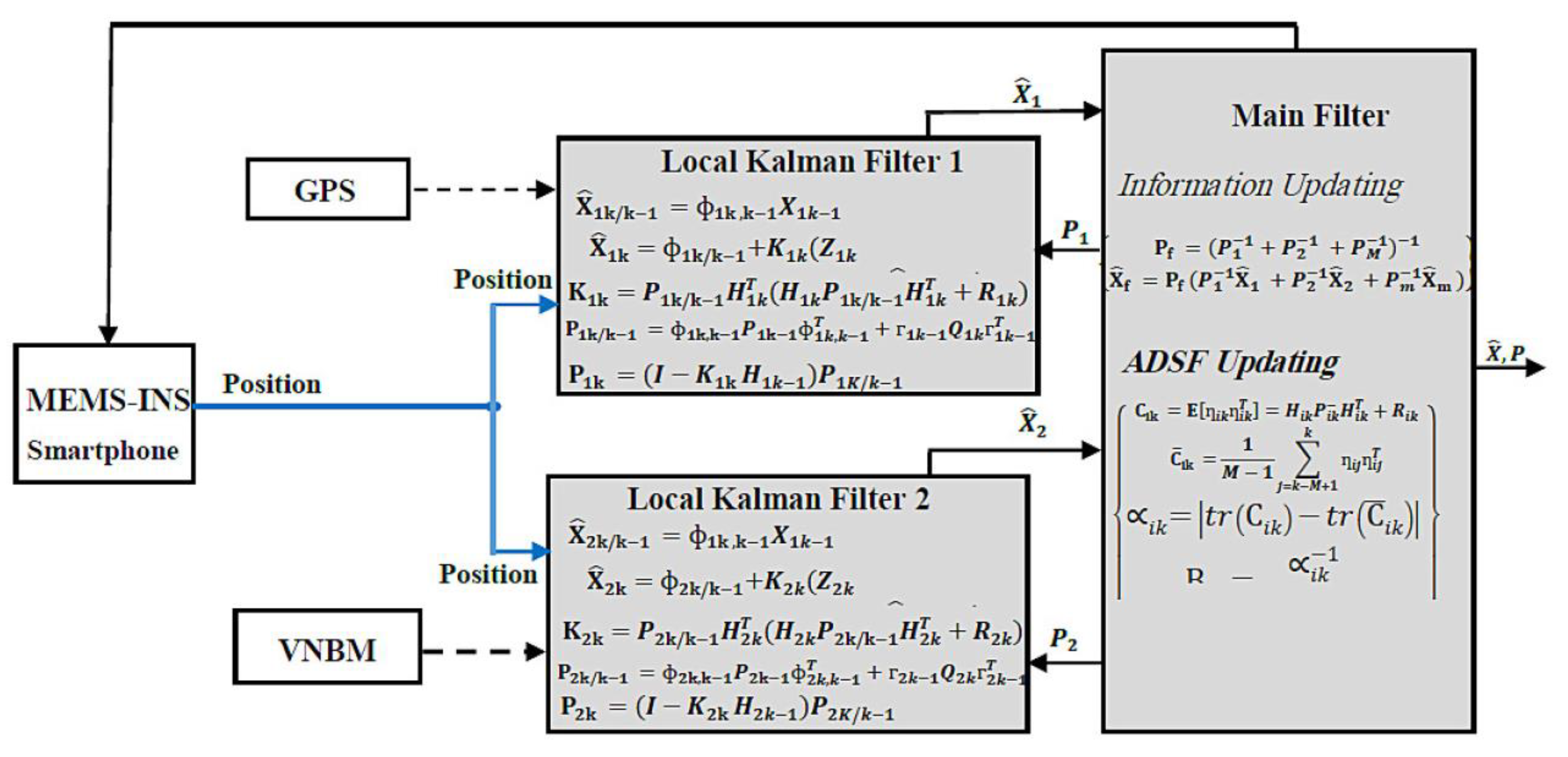
3. Combined Filter Based on Adaptive Data Sharing Factor (ADSF)
3.1. Principle of Combined Filter (CF)
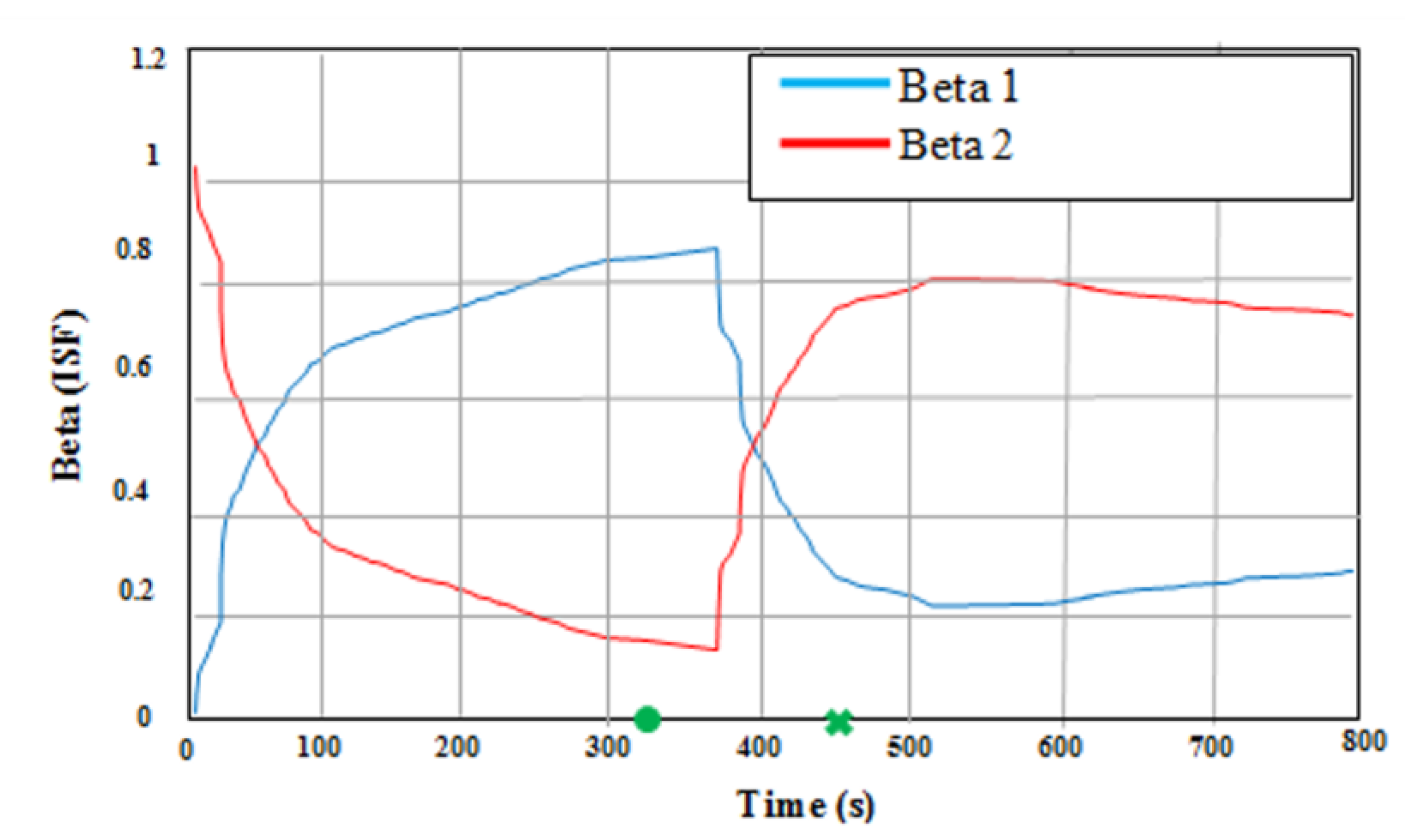
3.2. Adaptive Data Sharing Factor (ADSF) of Combined Filter (CF)
4. Proposed Multi-MEMS Integrated Navigation Method Using the Adaptive DSF Combined Filter
5. Experimental Work and Results
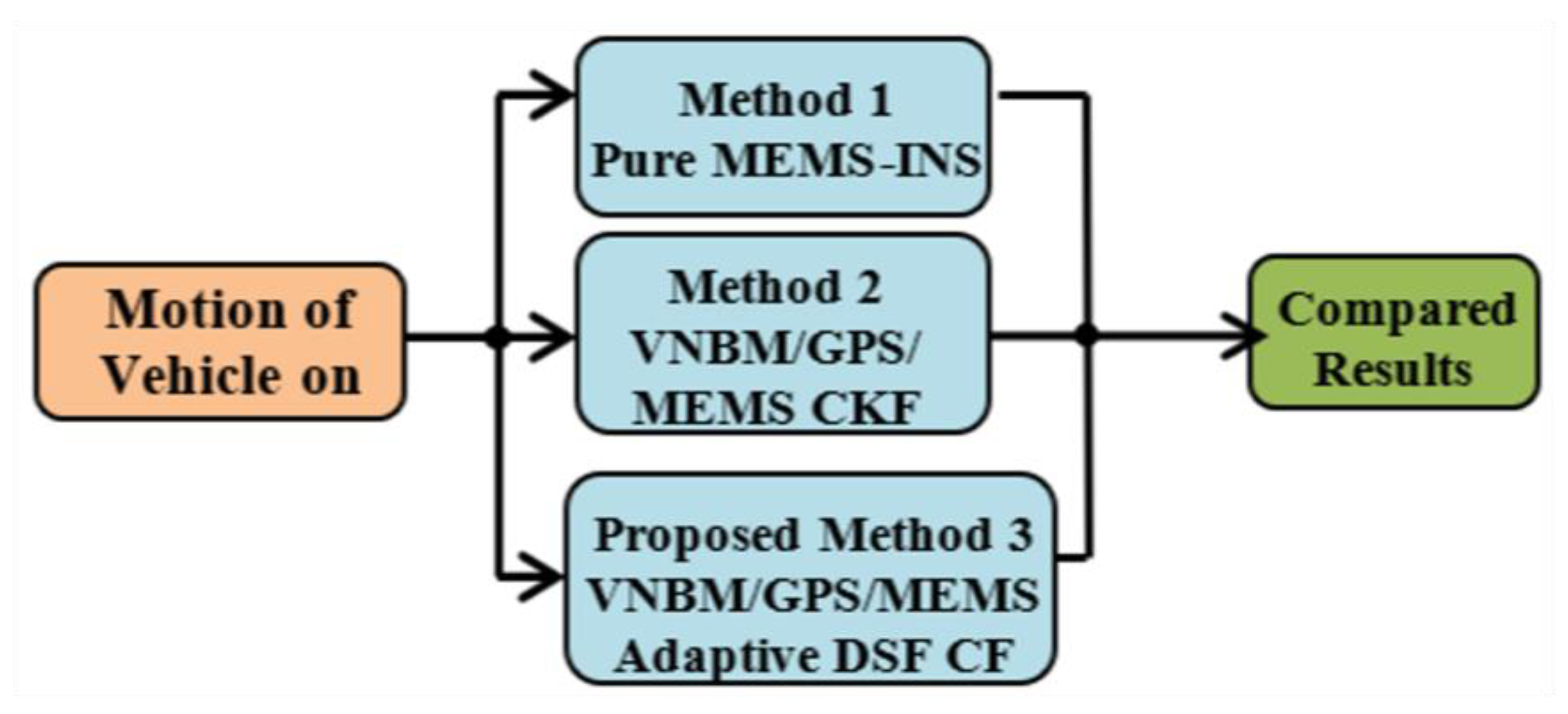
5.1. Integrated Navigation Methods
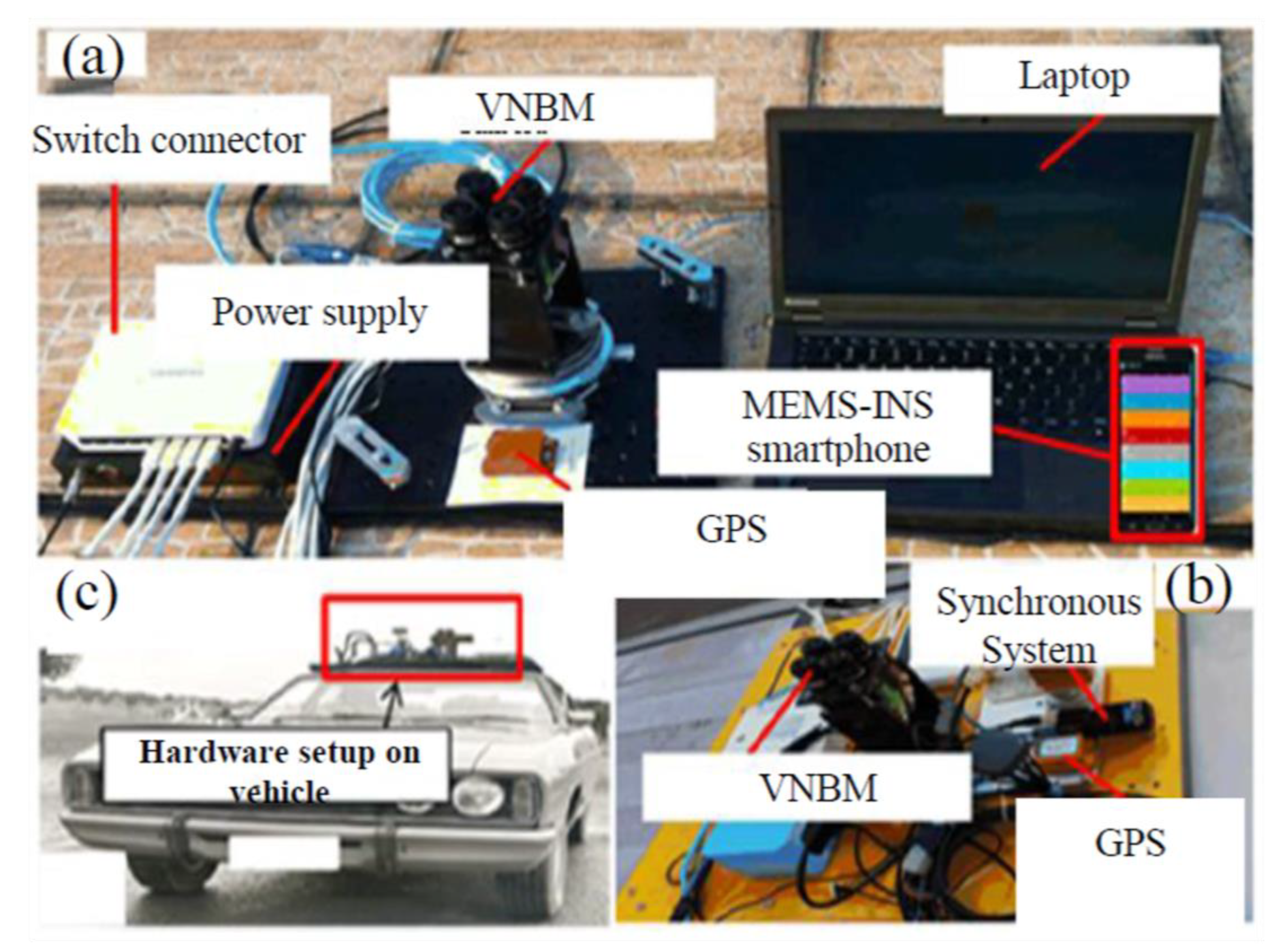
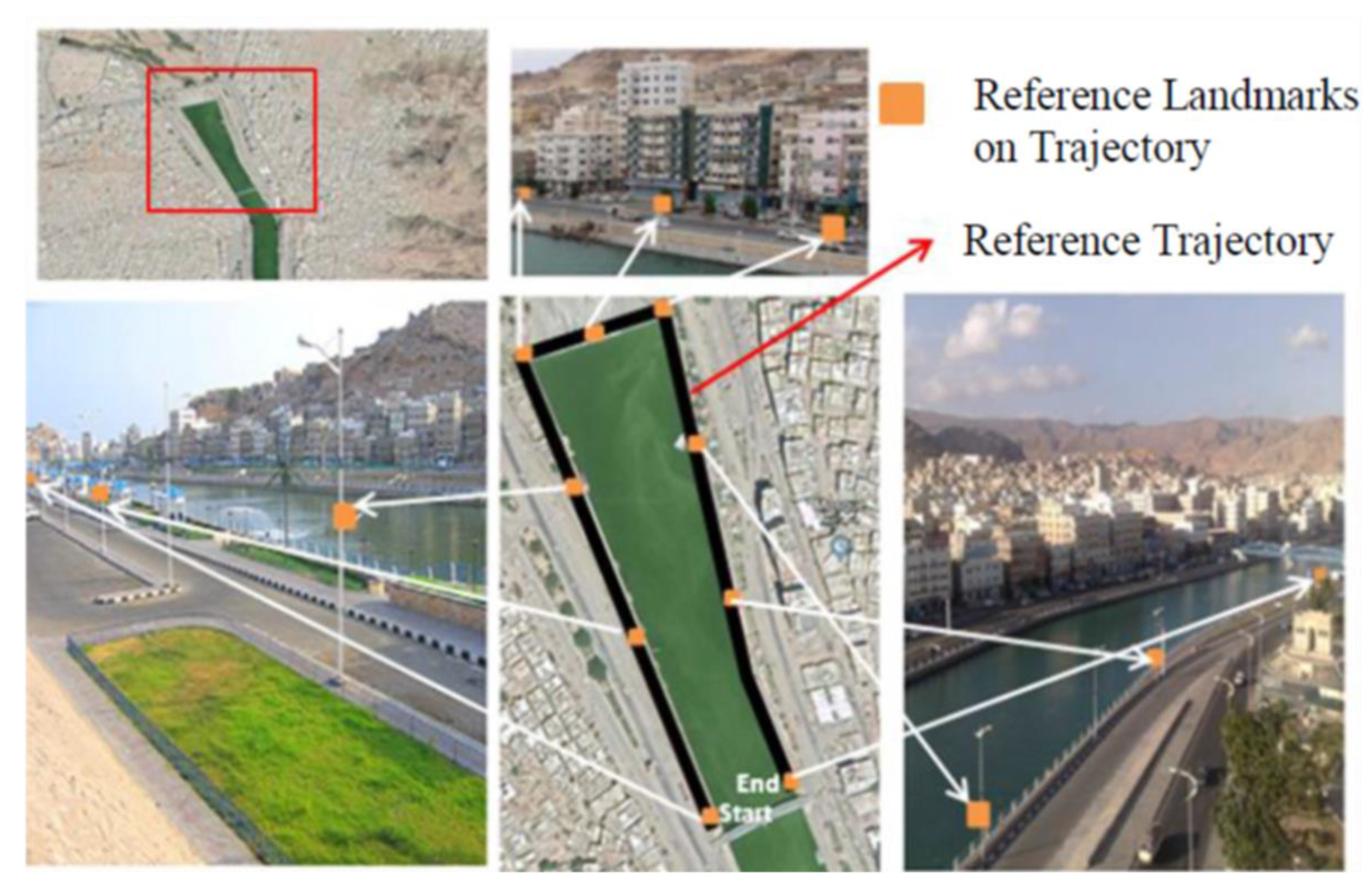
5.2. Hardware and Reference Trajectory
5.3. Parameter Setting of Three Integrated Methods
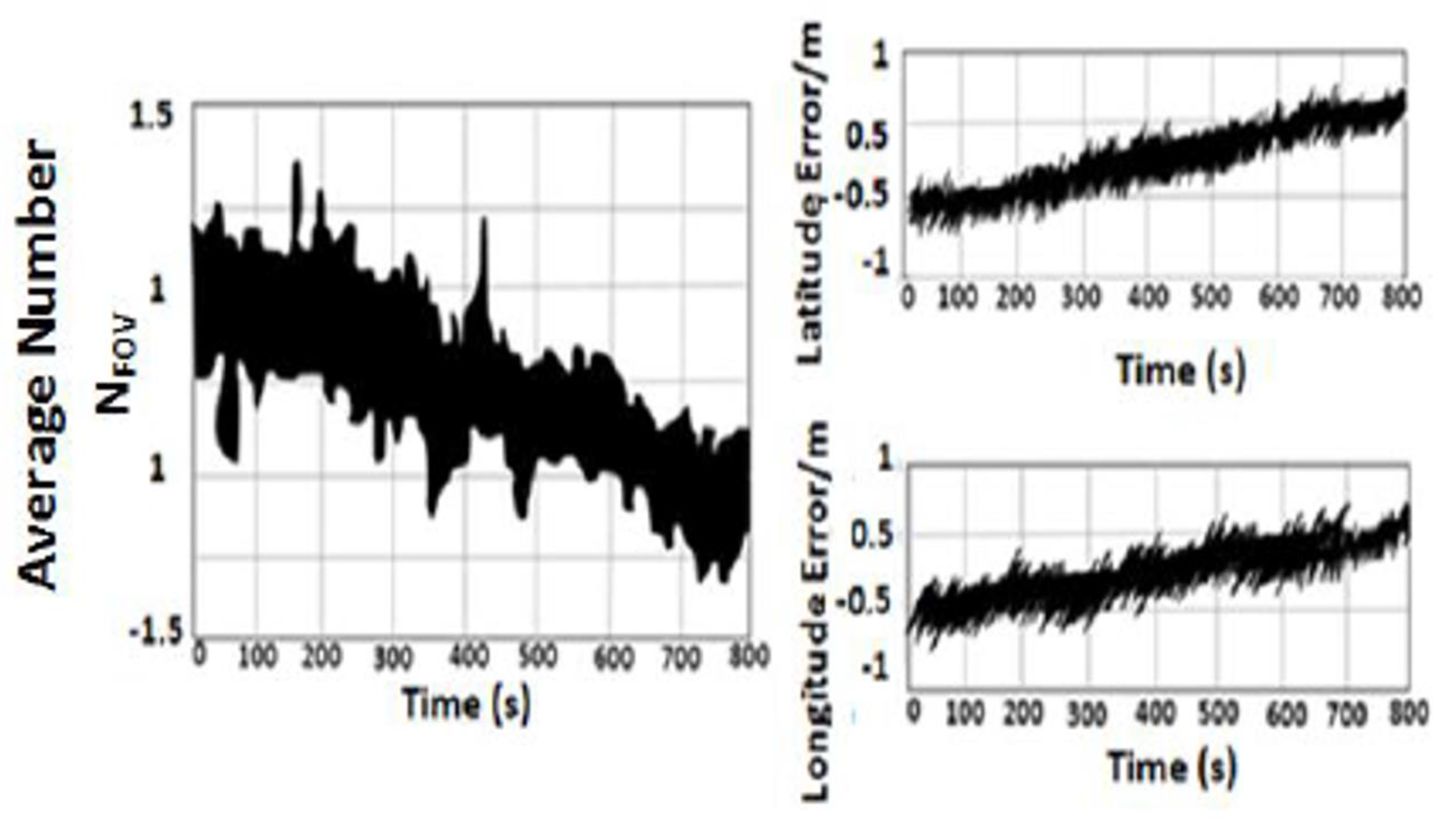
5.4. MEMS–INS, VNBM, and DVL Errors
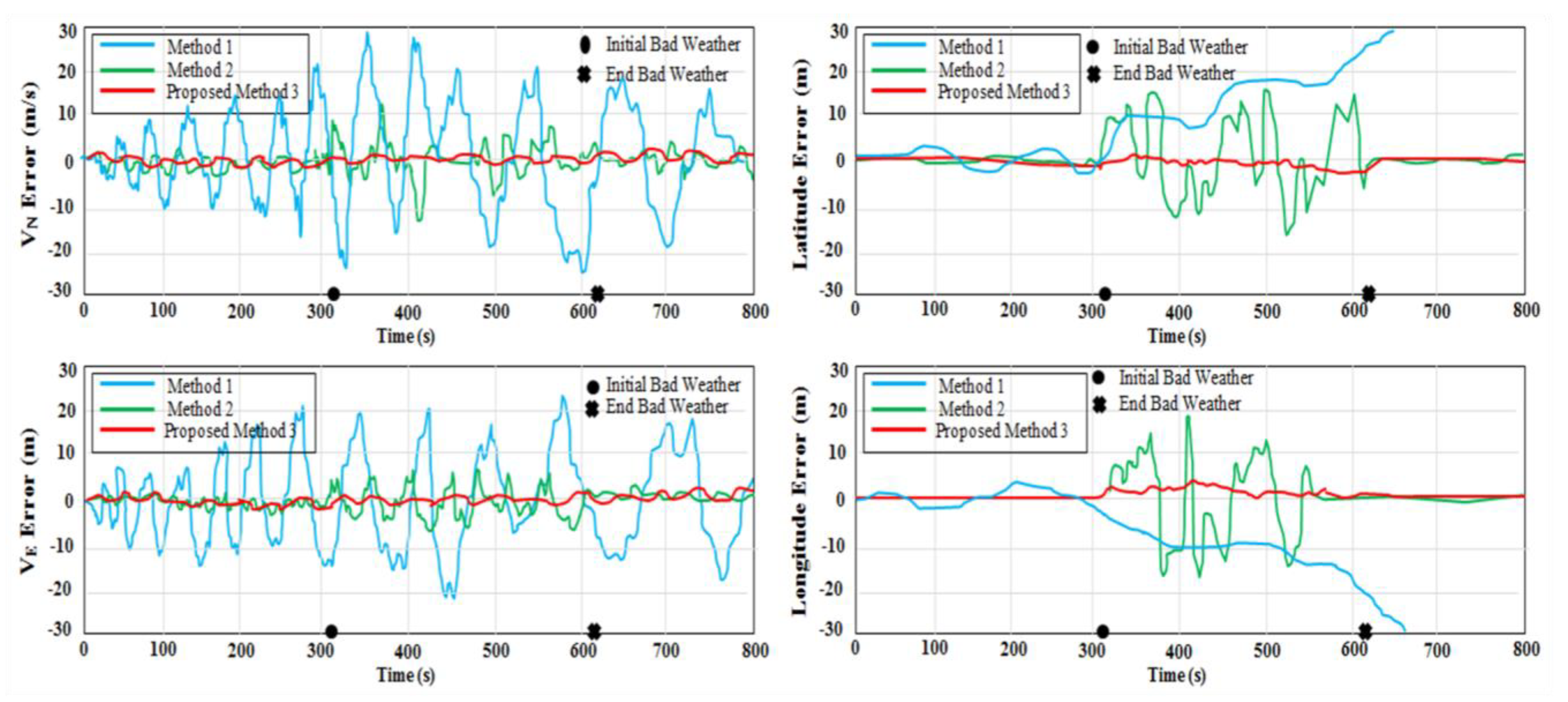
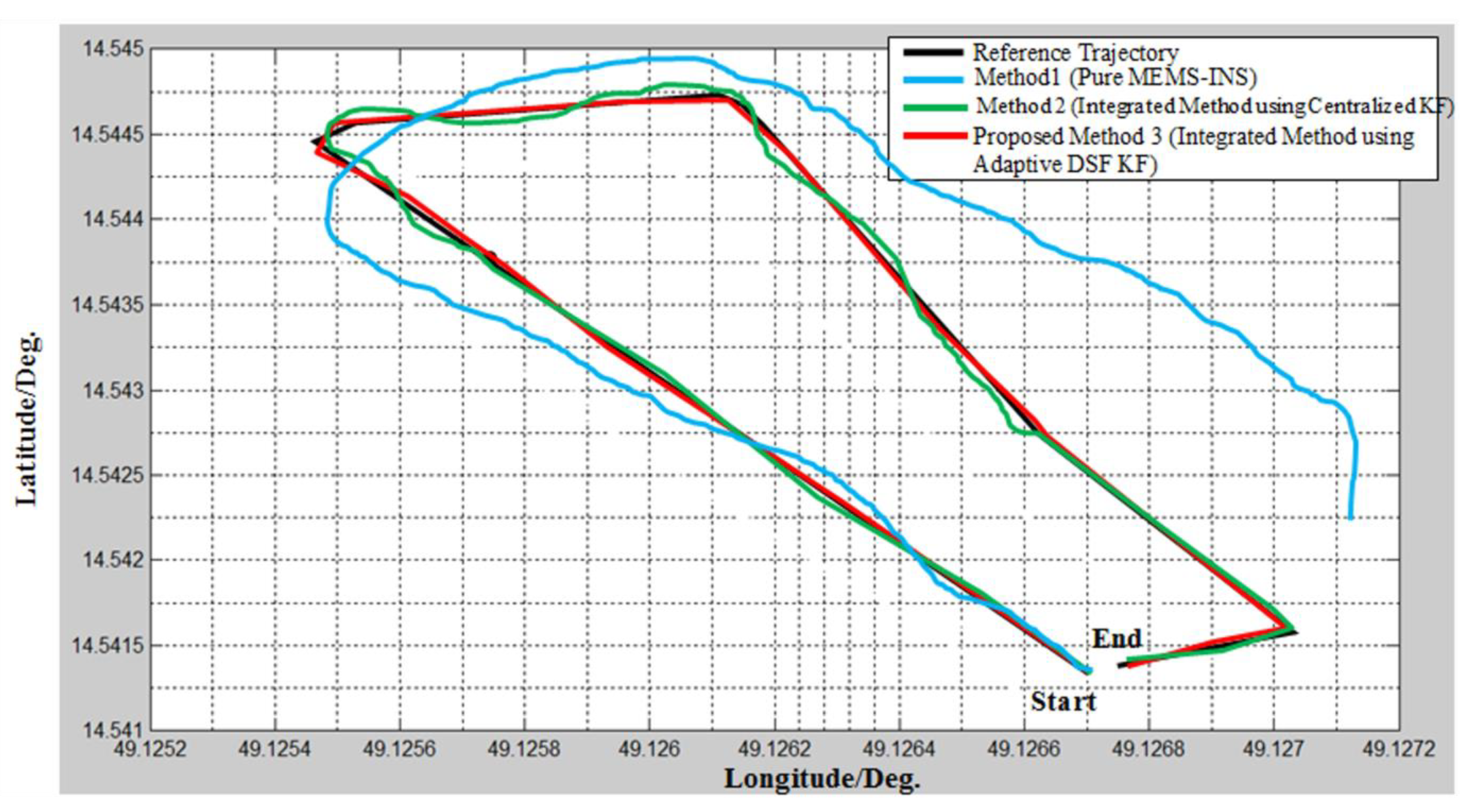
5.5. Comparison Results of USV Navigation Systems
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.; Liao, J.; Xiao, Z.; Li, X.; Havyarimana, V. Online-SVR for vehicular position prediction during GPS outages using low-cost INS. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 26th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Hong Kong, China, 30 August–2 September 2015; pp. 1945–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Lykov, A.; Tarpley, W.; Volkov, A.; Ahn, I.S.; Lu, Y. Gps+ Inertial Sensor Fusion; Bradley University ECE Department: Peoria, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, Y.; Niu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhang, H. Low-end mems imu can contribute in gps/ins deep integration. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium-PLANS 2014, Monterey, CA, USA, 5–8 May 2014; pp. 746–752. [Google Scholar]
- Asada, A.; Ura, T. Three dimensional synthetic and real aperture sonar technologies with Doppler velocity log and small fiber optic gyrocompass for autonomous underwater vehicle. In 2012 Oceans; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Greenvile, SC, USA, 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Münchow, A.; Coughran, C.S.; Hendershott, M.C.; Winant, C.D. Performance and calibration of an acoustic doppler current profiler towed below the surface. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Cong, L.; Sun, X. Accuracy improvement of GPS/MEMS-INS integrated navigation system during GPS signal outage for land vehicle navigation. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2012, 23, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureldin, A.; Karamat, T.B.; Eberts, M.D.; El-Shafie, A. Performance enhancement of mems-based ins/gps integration for low-cost navigation applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 58, 1077–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, J.; Shi, L. A robust astro-inertial integrated navigation algorithm based on star-coordinate matching. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 71, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Kitamura, T.; Yamamoto, J.; Martin, J.; Pignatelli, M.; Kitch, L.J.; Schnitzer, M.J.; Tonegawa, S. Distinct speed dependence of entorhinal island and ocean cells, including respective grid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9466–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiani, C.; Martinelli, A.; Laugier, C.; Scaramuzza, D. Low computational-complexity algorithms for vision-aided inertial navigation of micro aerial vehicles. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 69, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Sun, F.; Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X. Image multi-label annotation based on supervised nonnegative matrix fac-torization with new matching measurement. Neurocomputing 2017, 219, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Ji, R. Robust depth-based object tracking from a moving binocular camera. Signal Process. 2015, 112, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajník, T.; Cristóforis, P.; Kusumam, K.; Neubert, P.; Duckett, T. Image features for visual teach-and-repeat navigation in changing environments. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 88, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Gps/imu Integrated System for Land Vehicle Navigation Based on Mems. Ph.D. Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Khater, H.; Elsayed, A.; El-Shoafy, N. Underwater Navigation System Solution using MEMS-Mobile Sensors during the GPS Outage. J. Commun. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, A.; Michle, A. Using novel technologies in unmanned underwater vehicle. Int. J. Electr. Electron. 2014, 11, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Paull, L.; Saeedi, S.; Seto, M.; Li, H. AUV Navigation and Localization: A Review. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2013, 39, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelb, A. Applied Optimal Estimation; MIT press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaifard, E.; Abbasi, P. Inertial navigation system calibration using GPS based on extended Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2017 Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Tehran, Iran, 2–4 May 2017; pp. 778–782. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, M.G. Global Positioning System (GPS) Error Source Prediction; Air Force Institute of Technology: Dayton, OH, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Noureldin, A.; Karamat, T.B.; Georgy, J. Fundamentals of Inertial Navigation, Satellite-Based Positioning and Their Integration; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Shi, G. High accuracy Navigation System using GPS and INS system integration strategy. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER), Chengdu, China, 19–22 June 2016; pp. 365–369. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.-J.; Li, K.H.H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, W.-T. Real-time precision pedestrian navigation solution using inertial navi-gation system and global positioning system. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, N.Y.; Jeong, S.; Choi, H.T.; Lee, C.M.; Moon, Y.S. Fusion of multiple sensor measurements for navigation of an unmanned marine surface vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2016 16th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Gyeongju, Korea, 16–19 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nister, D.; Naroditsky, O.; Bergen, J. Visual odometry. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2004. CVPR 2004, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-H.; Chiang, K.-W. The Performance Analysis of Stereo Visual Odometry Assisted Low-Cost INS/GPS Integration System. Smart Sci. 2015, 3, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauglitz, S.; Höllerer, T.; Turk, M. Evaluation of Interest Point Detectors and Feature Descriptors for Visual Tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2011, 94, 335–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Chen, Z.; Jacobson, A.; Hu, X.; Milford, M. Biologically inspired visual place recognition with adaptive mul-tiple scales. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 96, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broatch, S.; Henley, A. An integrated navigation system manager using federated Kalman filtering. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE 1991 National Aerospace and Electronics Conference NAECON 1991, Dayton, OH, USA, 20–24 May 1991; pp. 422–426. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, L.; Qin, H.; Tan, Z. Intelligent fault-tolerant algorithm with two-stage and feedback for integrated navigation federated filtering. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2011, 22, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmayer, A.; Miranda, M.; Nebehaj, V. Cooperative federated filtering approach for enhanced position estimation and sensor fault tolerance in ad-hoc vehicle networks. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2010, 4, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Thorp, J.S. Adaptive damping control of inter-area oscillations based on federated Kal-man filter using wide area signals. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 28, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lennox, B.; Goulding, P.R.; Wang, Y. Adaptive information sharing factors in federated kalman filter-ing. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2002, 35, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sang, H.-S.; Shen, X.-B. Adaptive federated kalman filtering attitude estimation algorithm for double-fov star sensor. J. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2010, 6, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar]
- Khater, H.A.; Elsayed, A.; El-Shoafy, N. Improved Navigation and Guidance System of AUV Using Sensors Fusion. J. Commun. 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.Z.; Khater, H.A.; Rizk, M.R.; Bahasan, A.M. GPS/DVL/MEMS-INS smartphone sensors integrated method to enhance USV navigation system based on adaptive DSFCF. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2019, 13, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.Z.; Khater, H.A.; Rizk, M.R.; Bahasan, A.M. A novel GPS/ RAVO/MEMS-INS smartphone-sensor-integrated method to enhance USV navigation systems during GPS outages. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 095103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allotta, B.; Caiti, A.; Chisci, L.; Costanzi, R.; Di Corato, F.; Fantacci, C.; Fenucci, D.; Meli, E.; Ridolfi, A. An unscented Kalman filter based navigation algorithm for autonomous underwater vehicles. Mechatronics 2016, 39, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Index |
|---|---|
| Gyroscopes Dynamic Range | ±100°/s |
| Gyroscopes Bias Stability | ≤100.50° per hour |
| Gyroscopes noise | 0.05° per hour |
| Gyroscopes drift | 0.005° per hour |
| Gyroscopes Nonlinear Degree of Scale Factor | ≤20 ppm |
| Gyroscopes Frequency | 50 Hz |
| Accelerometers Bias Stability | 100 µg |
| Accelerometers Nonlinear Degree of Scale Factor | ≤20 ppm |
| Accelerometers Frequency | 50 Hz |
| GPS Position Error Noise | 0.8 m, 0.8 m, 1 m |
| GPS Velocity Error | 0.1 m/s, 0.1 m/s, 0.1m/s |
| GPS Frequency | 1 Hz |
| Camera FOV | 0.3 m |
| Camera Map Resolution | 648 × 488 |
| Camera Frequency | 10 Hz |
| Methods\Errors | Maximum Latitude Error (m) | Maximum Longitude Error (m) | Latitude RMSE (m) | Longitude RMSE (m) | Position RMSE (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method 1 (Pure MEMS–INS) | 100.98 | 110.23 | 72.543 | 78.32 | 106.75 |
| Method 2 (VNBM/GPS/MEMS–INS/Centralized KF) | 18.53 | 19.47 | 10.43 | 11.67 | 15.65 |
| Method 3 (Proposed VNBM/GPS/MEMS using ADSF Combined filter) | 0.93 | 0.82 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 1.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, H.G.; Khater, H.A.; Moussa, K.H. An Intelligent Combined Visual Navigation Brain Model/GPS/MEMS–INS/ADSFCF Method to Develop Vehicle Independent Guidance Solutions. Micromachines 2021, 12, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060718
Mohamed HG, Khater HA, Moussa KH. An Intelligent Combined Visual Navigation Brain Model/GPS/MEMS–INS/ADSFCF Method to Develop Vehicle Independent Guidance Solutions. Micromachines. 2021; 12(6):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060718
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Heba G., Hatem A. Khater, and Karim H. Moussa. 2021. "An Intelligent Combined Visual Navigation Brain Model/GPS/MEMS–INS/ADSFCF Method to Develop Vehicle Independent Guidance Solutions" Micromachines 12, no. 6: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060718
APA StyleMohamed, H. G., Khater, H. A., & Moussa, K. H. (2021). An Intelligent Combined Visual Navigation Brain Model/GPS/MEMS–INS/ADSFCF Method to Develop Vehicle Independent Guidance Solutions. Micromachines, 12(6), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060718






