Electroosmotic Mixing of Non-Newtonian Fluid in a Microchannel with Obstacles and Zeta Potential Heterogeneity
Abstract
1. Introduction
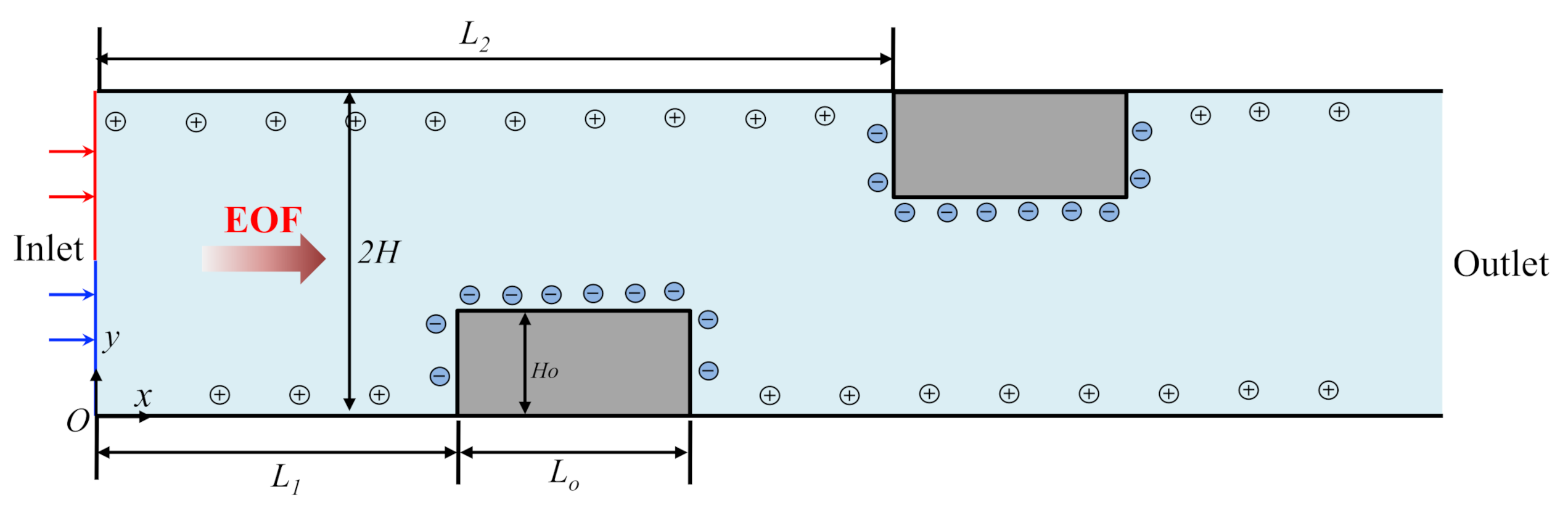
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. Dimensionless Equations
2.3. Boundary Conditions
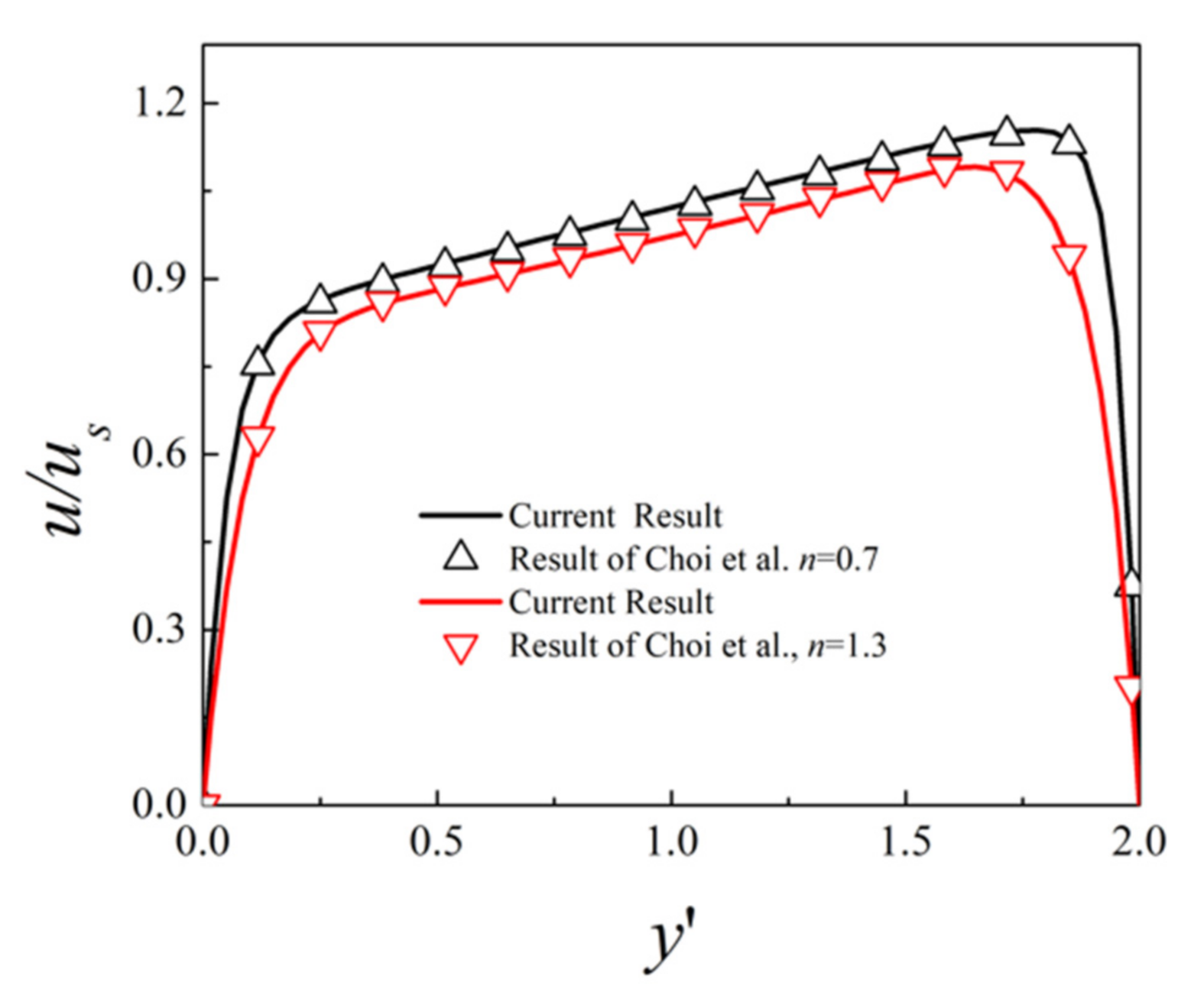
3. Numerical Method and Validation
4. Results and Discussion
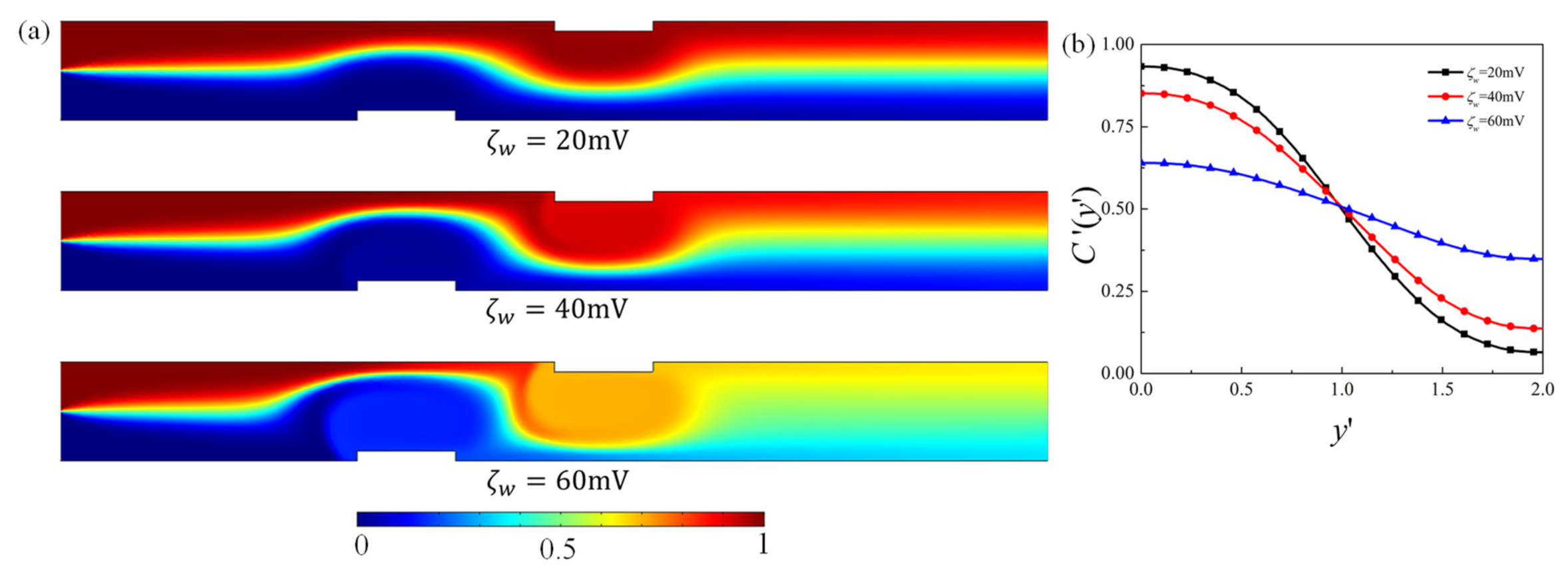
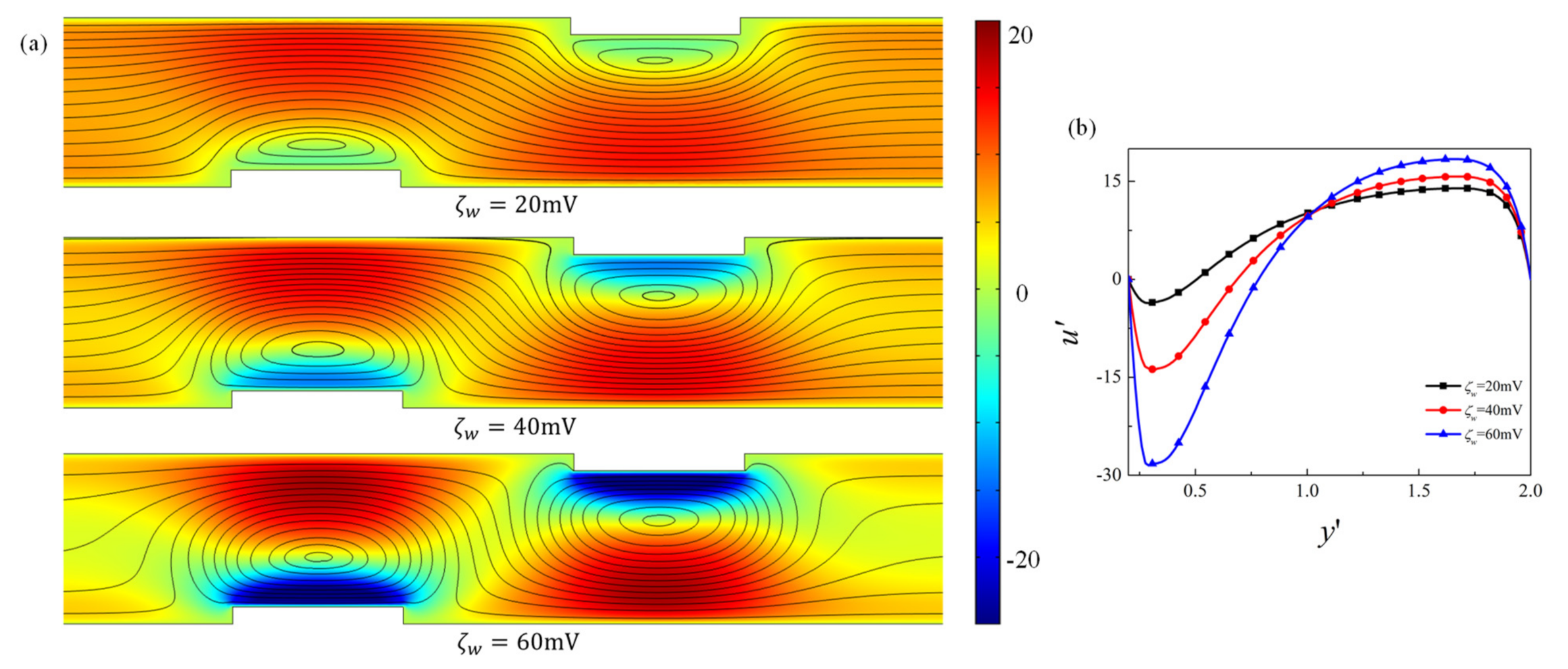
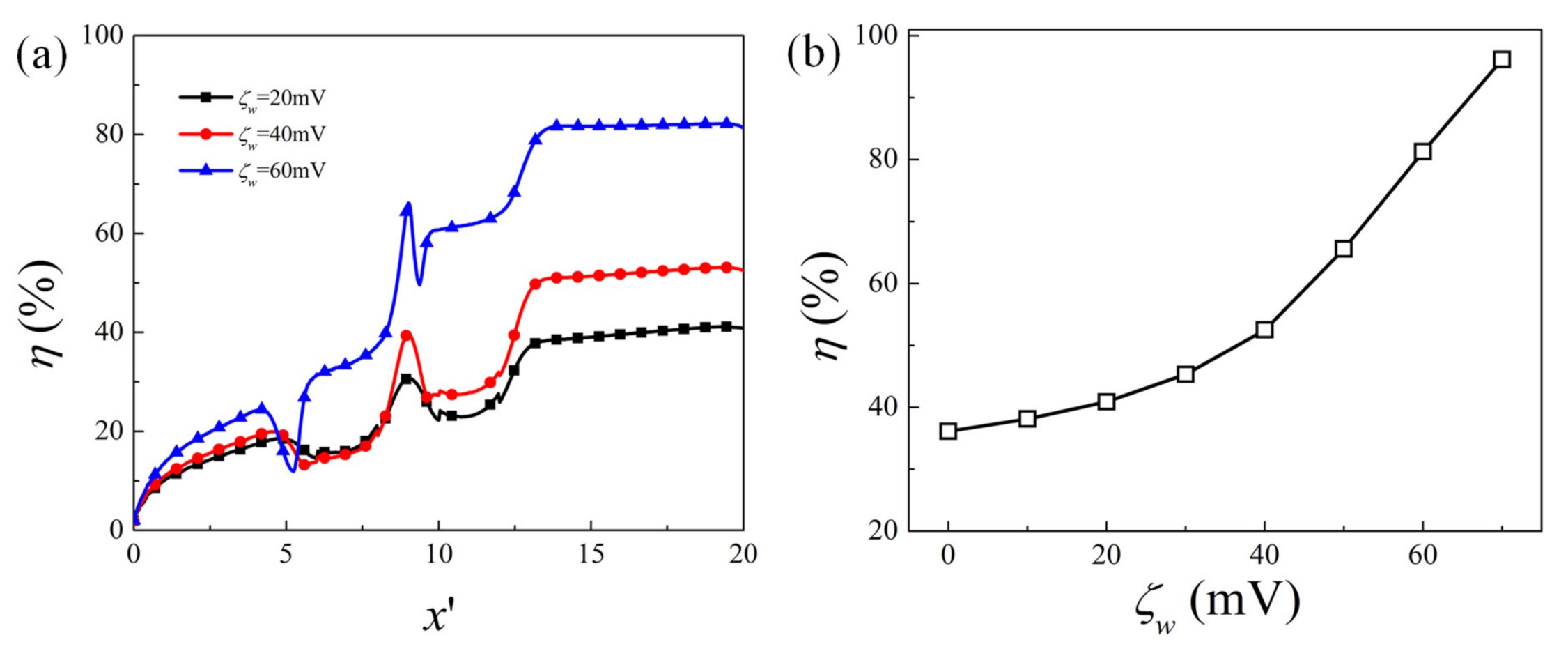
4.1. Effect of Obstacle Surface Zeta Potential
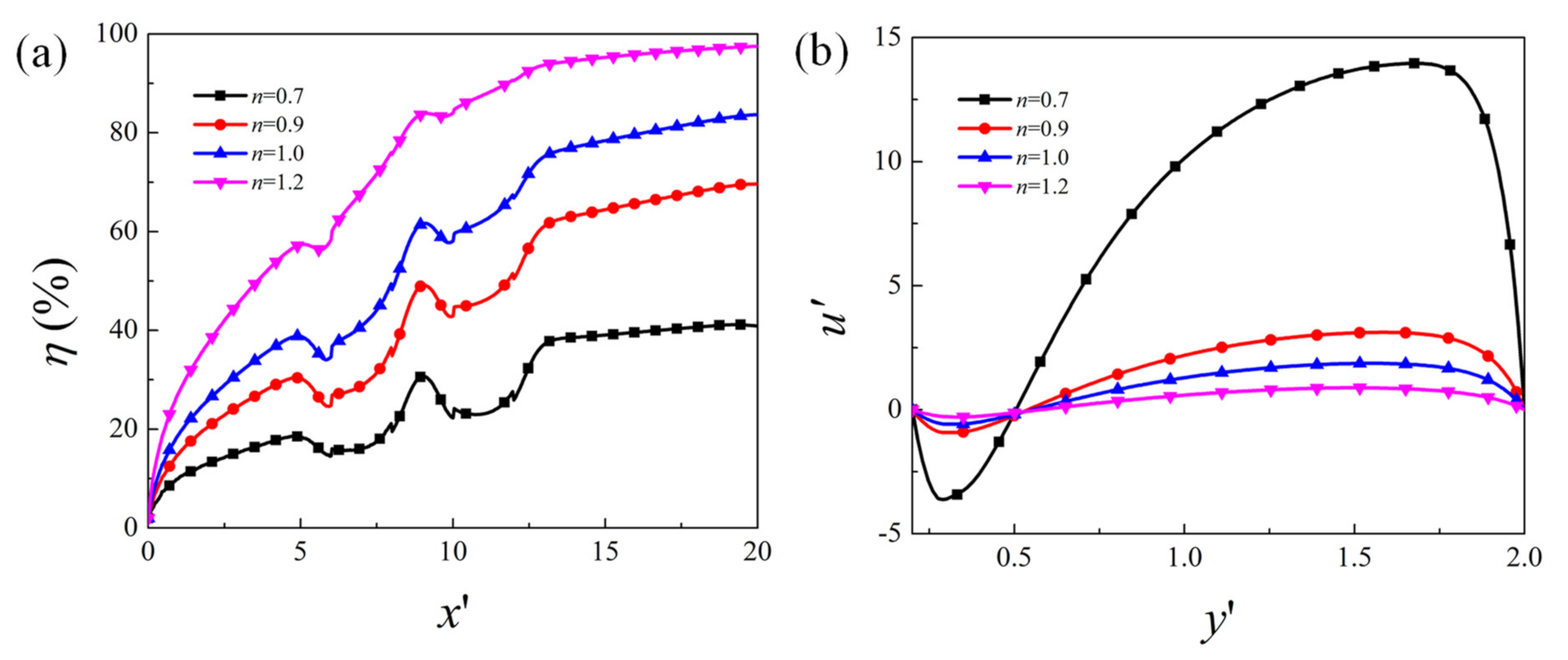
4.2. Effect of Flow Behavior Index
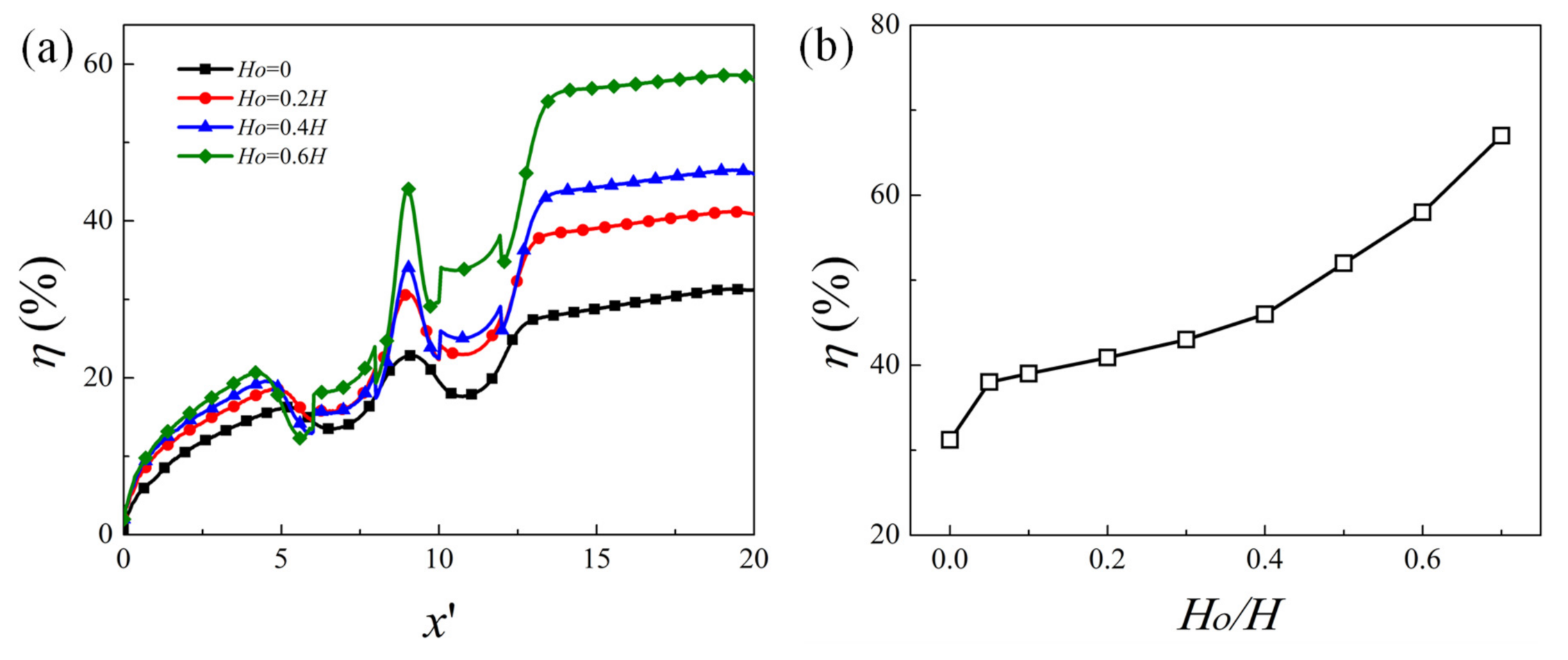
4.3. Effect of Obstacle Height
4.4. Effect of EDL Thickness
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karniadakis, G.; Beskok, A.; Aluru, N. Microflows and Nanoflows: Fundamentals and Simulation; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Daiguji, H. Manipulation of Protein Translocation through Nanopores by Flow Field Control and Application to Nanopore Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9251–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yao, Z.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y. Applications and theory of electrokinetic enrichment in micro-nanofluidic chips. Biomed. Microdevices 2017, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, Y.K.; Kang, S. A Review on Mixing in Microfluidics. Micromachines 2010, 1, 82–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Yang, R.-J. Electrokinetic mixing in microfluidic systems. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2007, 3, 501–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, S.; Bafekr, H.; Valipour, M.S.; Esfahani, J.A. A review on the application, simulation, and experiment of the electrokinetic mixers. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2018, 126, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Ross, A.D.; Locascio, L.E. Rapid Microfluidic Mixing. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasgow, I.; Aubry, N. Enhancement of microfluidic mixing using time pulsing. Lab Chip 2003, 3, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Huang, X.; Yang, C. Vortex generation and control in a microfluidic chamber with actuations. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghighi, Y.; Li, D. Numerical study of a novel induced-charge electrokinetic micro-mixer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 763, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Bau, H.H. Magneto-hydrodynamics based microfluidics. Mech. Res. Commun. 2009, 36, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Lin, J. A Review on Micromixers. Micromachines 2017, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A. Analysis of mixing for electroosmotic flow in micro/nano channels with heterogeneous surface potential. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 75, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-Y.; Liu, C.-H. A novel electrokinetic micromixer. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 118, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Khan, A.I.; Dutta, P. Time-Periodic Electro-Osmotic Flow with Nonuniform Surface Charges. J. Fluids Eng. 2019, 141, 081201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Werner, C.; Li, D. Influence of the three-dimensional heterogeneous roughness on electrokinetic transport in microchannels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, D. Mixing and flow regulating by induced-charge electrokinetic flow in a microchannel with a pair of conducting triangle hurdles. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2007, 5, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basati, Y.; Mohammadipour, O.R.; Niazmand, H. Numerical investigation and simultaneous optimization of geometry and zeta-potential in electroosmotic mixing flows. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 133, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Bera, S. Combined electroosmosis-pressure driven flow and mixing in a microchannel with surface heterogeneity. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 4337–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, Y.; Pan, X. Electrokinetic-vortex formation near a two-part cylinder with same-sign zeta potentials in a straight microchannel. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, T.; Pan, H.; Liu, Z. A Novel Electroosmotic Micromixer with Asymmetric Lateral Structures and DC Electrode Arrays. Micromachines 2017, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-J. A study on the mixing characteristics in a hybrid type microchannel with various obstacle configurations. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 2948–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.; Li, D.; Malekanfard, A.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.; Xuan, X. Electroosmotic flow of non-Newtonian fluids in a constriction microchannel. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Chen, C.-K. Mixing enhancement of electrokinetically-driven non-Newtonian fluids in microchannel with patterned blocks. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 191, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, B.; Bandopadhyay, A. Electroosmosis of a viscoelastic fluid over non-uniformly charged surfaces: Effect of fluid relaxation and retardation time. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 032005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Yin, Z.; Jian, Y.-J.; Chang, L.; Su, J.; Liu, Q.-S. Transient electro-osmotic flow of generalized Maxwell fluids through a microchannel. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2012, 187–188, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zholkovskij, E.; Masliyah, J.H.; Yang, C. Analysis of electroosmotic flow of power-law fluids in a slit microchannel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 326, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Deng, S.; Chen, Y. Periodical pressure-driven electrokinetic flow of power-law fluids through a rectangular microchannel. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2014, 203, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.-O.; Qi, C. Electroosmotic flow of a power-law fluid in a non-uniform microchannel. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2014, 208–209, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailaja, A.; Srinivas, B.; Sreedhar, I. Electroviscous Effect of Power Law Fluids in a Slit Microchannel with Asymmetric Wall Zeta Potentials. J. Mech. 2019, 35, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masliyah, J.H.; Bhattacharjee, S. Electrokinetic and Colloid Transport Phenomena; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Craven, T.J.; Rees, J.M.; Zimmerman, W.B. On slip velocity boundary conditions for electroosmotic flow near sharp corners. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 43603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, T. Comparison of the Nernst–Planck model and the Poisson–Boltzmann model for electroosmotic flows in microchannels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 315, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Nayak, A.K.; Weigand, B. A Comparative Analysis of Mixing Performance of Power-Law Fluid in Cylindrical Microchannels with Sudden Contraction/Expansion. J. Fluids Eng. 2020, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Nayak, A. Influence of varying zeta potential on non-Newtonian flow mixing in a wavy patterned microchannel. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2019, 269, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Zhang, H.; Meng, H.; Qian, S. Electroosmotic Flow of Viscoelastic Fluid in a Nanoslit. Micromachines 2018, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, C. Electrokinetics of non-Newtonian fluids: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 201–202, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.-S.; Yun, S.; Choi, W. An Exact Solution for Power-Law Fluids in a Slit Microchannel with Different Zeta Potentials under Electroosmotic Forces. Micromachines 2018, 9, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Chou, T.H.; Cheng, Y.S.; Huang, M.J.; Yeh, L.H.; Qian, S. Electrophoresis of pH-regulated nanoparticles: Impact of the Stern layer. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 9927–9934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, L.; Cui, D.; Shen, J.; Dutta, D.; Brown, W.; Zhang, L.; Dabipi, I.K. Electroosmotic Mixing of Non-Newtonian Fluid in a Microchannel with Obstacles and Zeta Potential Heterogeneity. Micromachines 2021, 12, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040431
Mei L, Cui D, Shen J, Dutta D, Brown W, Zhang L, Dabipi IK. Electroosmotic Mixing of Non-Newtonian Fluid in a Microchannel with Obstacles and Zeta Potential Heterogeneity. Micromachines. 2021; 12(4):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040431
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Lanju, Defu Cui, Jiayue Shen, Diganta Dutta, Willie Brown, Lei Zhang, and Ibibia K. Dabipi. 2021. "Electroosmotic Mixing of Non-Newtonian Fluid in a Microchannel with Obstacles and Zeta Potential Heterogeneity" Micromachines 12, no. 4: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040431
APA StyleMei, L., Cui, D., Shen, J., Dutta, D., Brown, W., Zhang, L., & Dabipi, I. K. (2021). Electroosmotic Mixing of Non-Newtonian Fluid in a Microchannel with Obstacles and Zeta Potential Heterogeneity. Micromachines, 12(4), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040431






