Recent Advances and Applications of Passive Harmonic RFID Systems: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
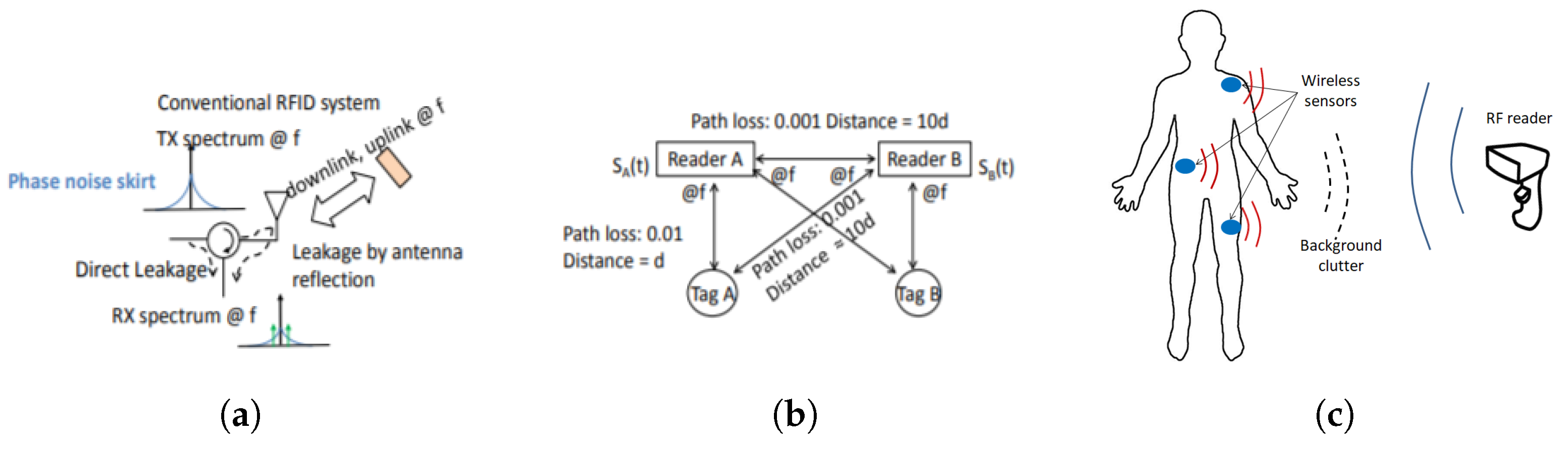
2. Drawback of Conventional RFID
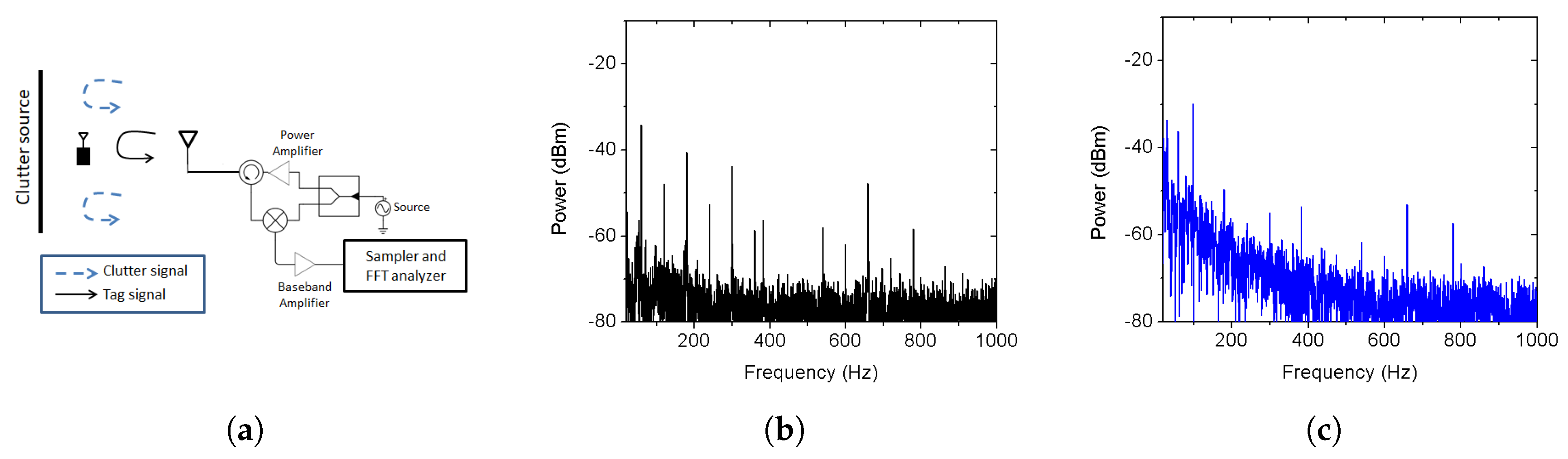
2.1. Clutter
2.2. Localization
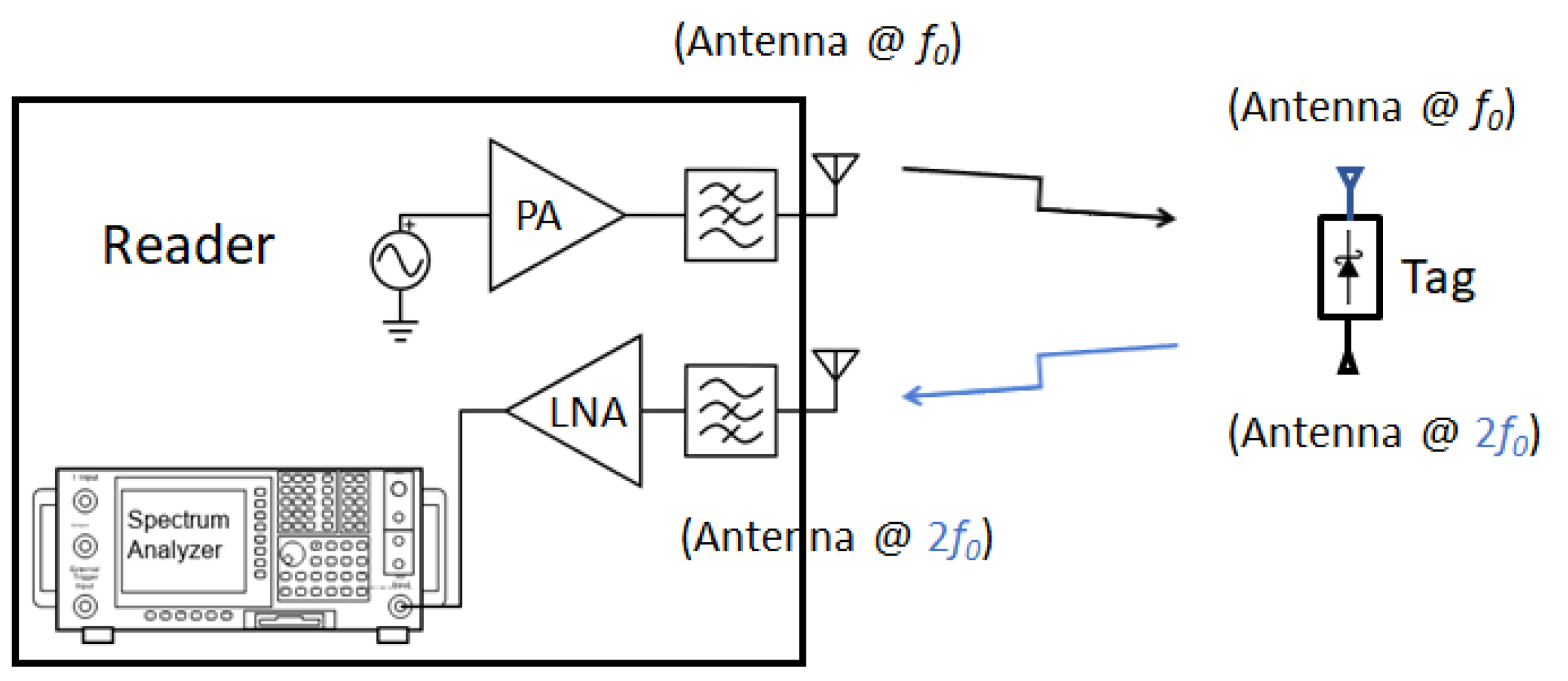
2.3. Harmonic RFID as a Solution
3. Harmonic Generation
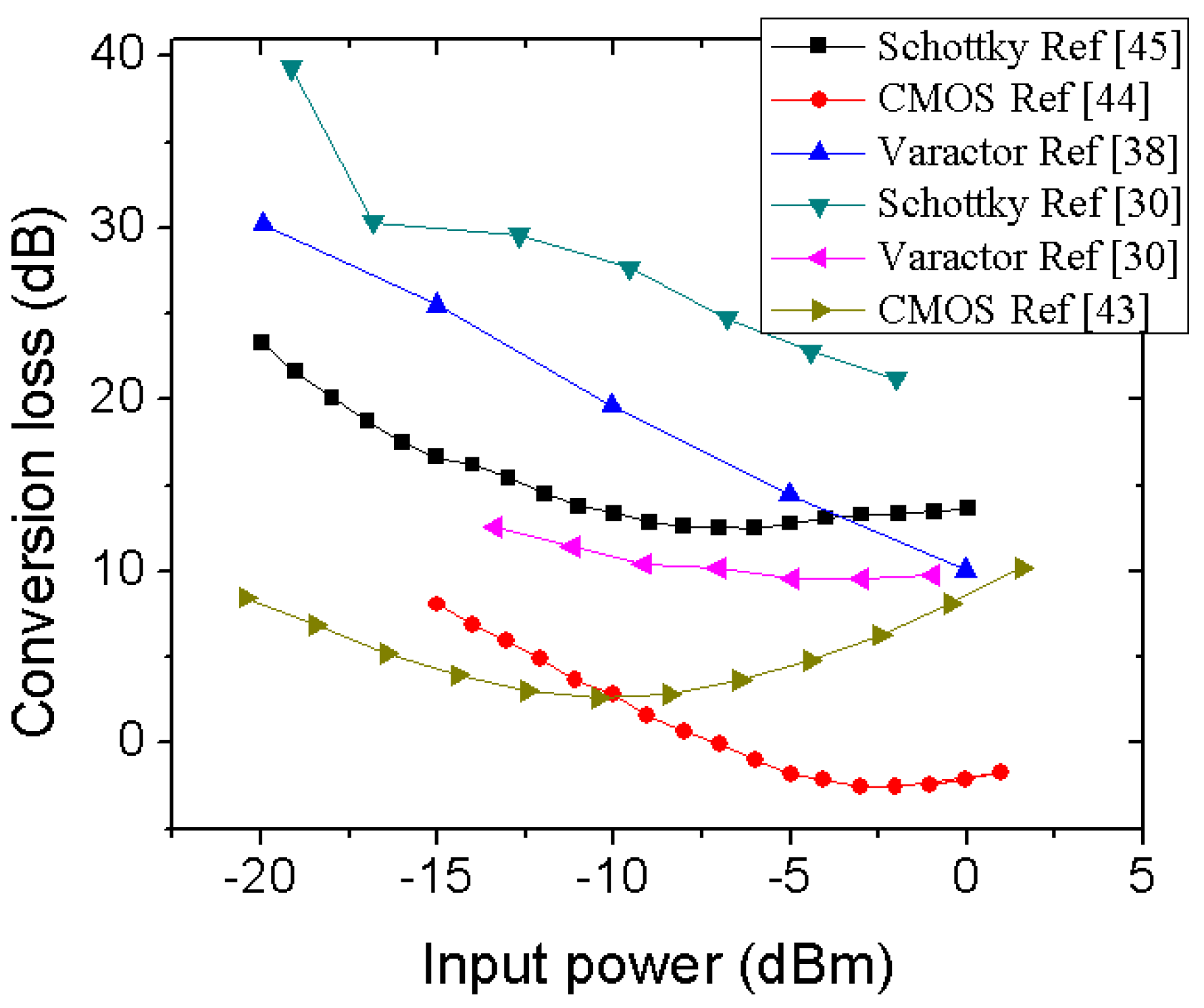
3.1. Conversion Gain
3.1.1. Transistor-Based Harmonic Generator
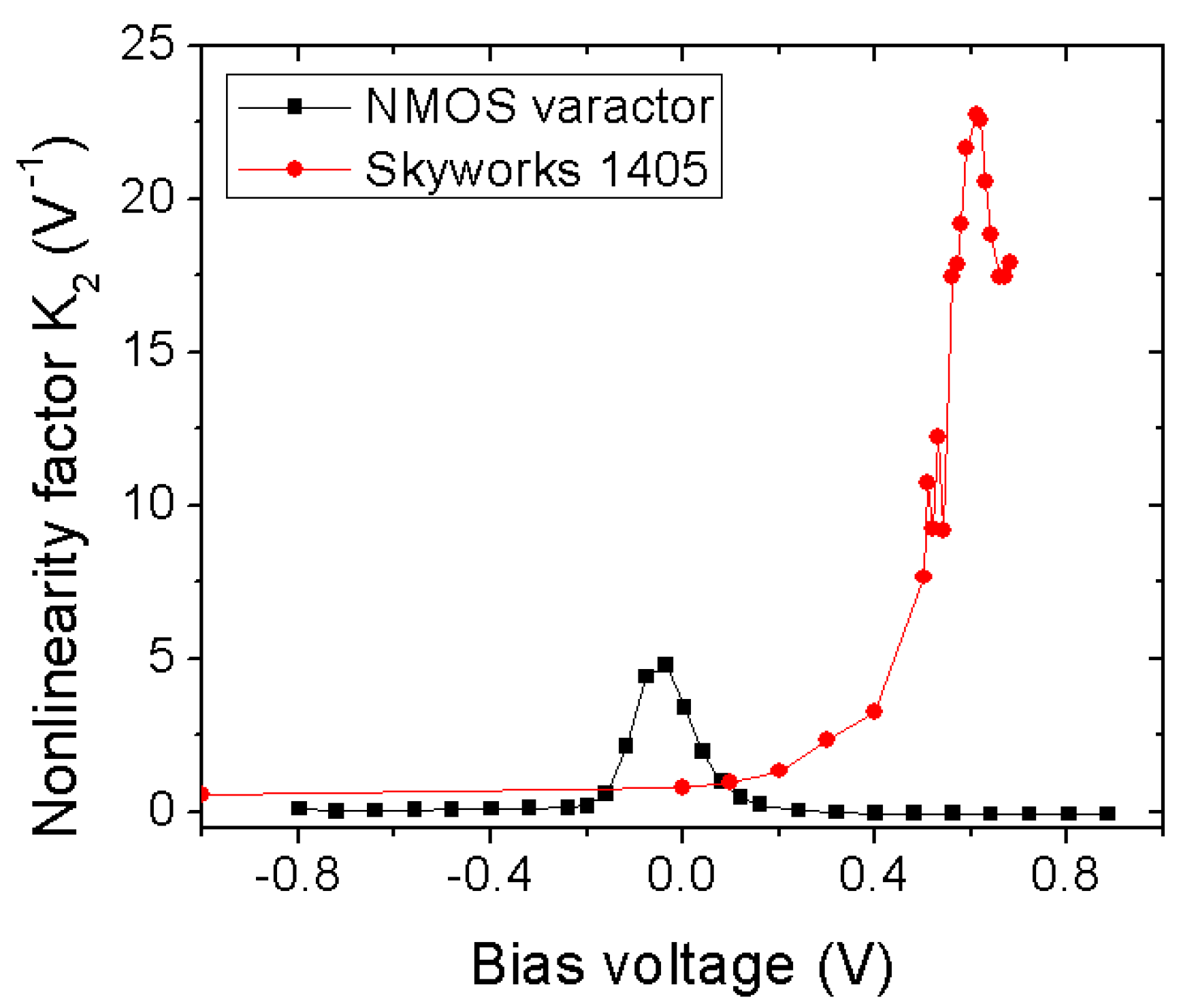
3.1.2. Diode-Based Harmonic Generator
3.2. Power Consumption
3.3. Cut-Off Frequency
3.4. Switching Control
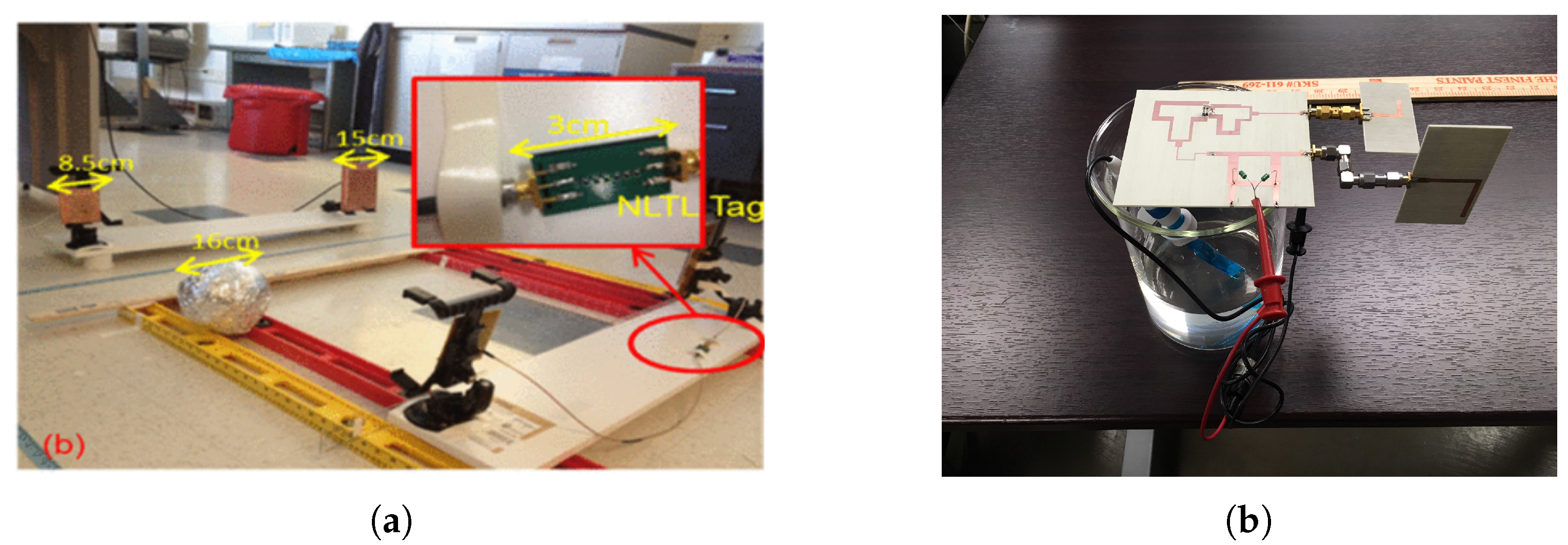
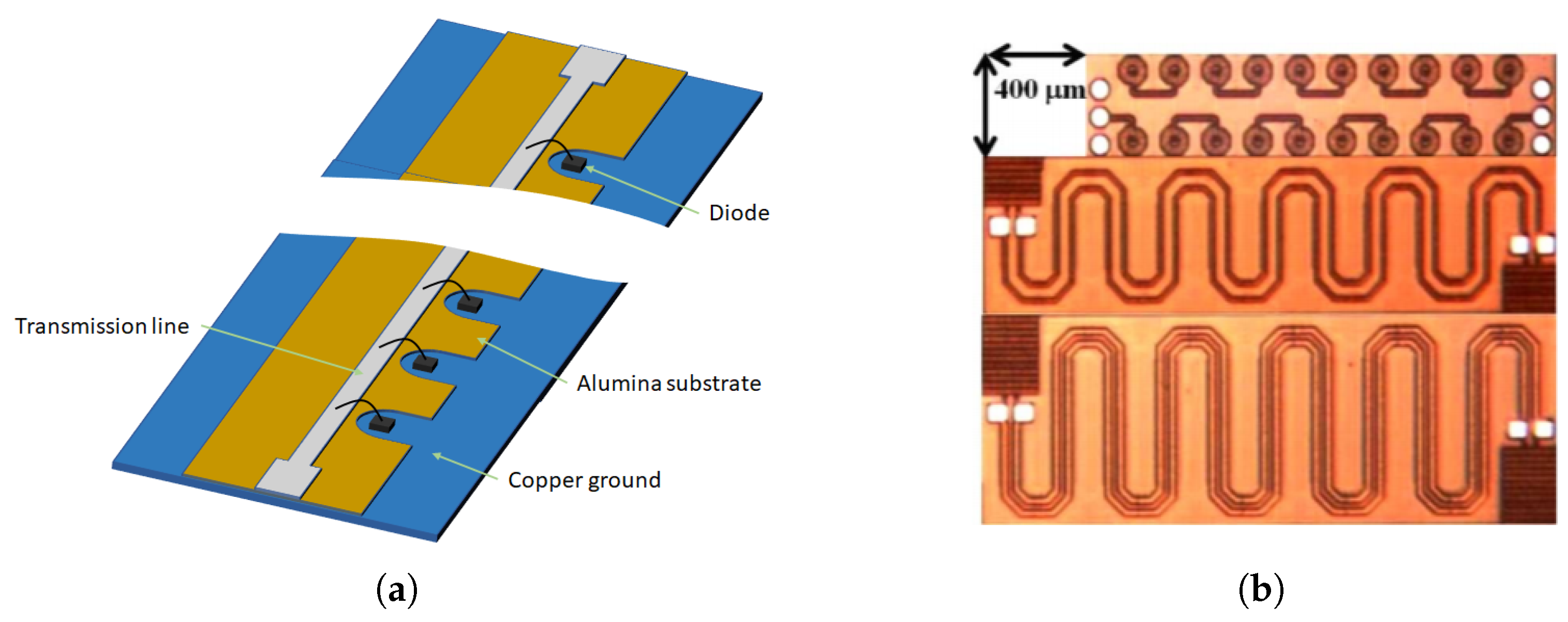
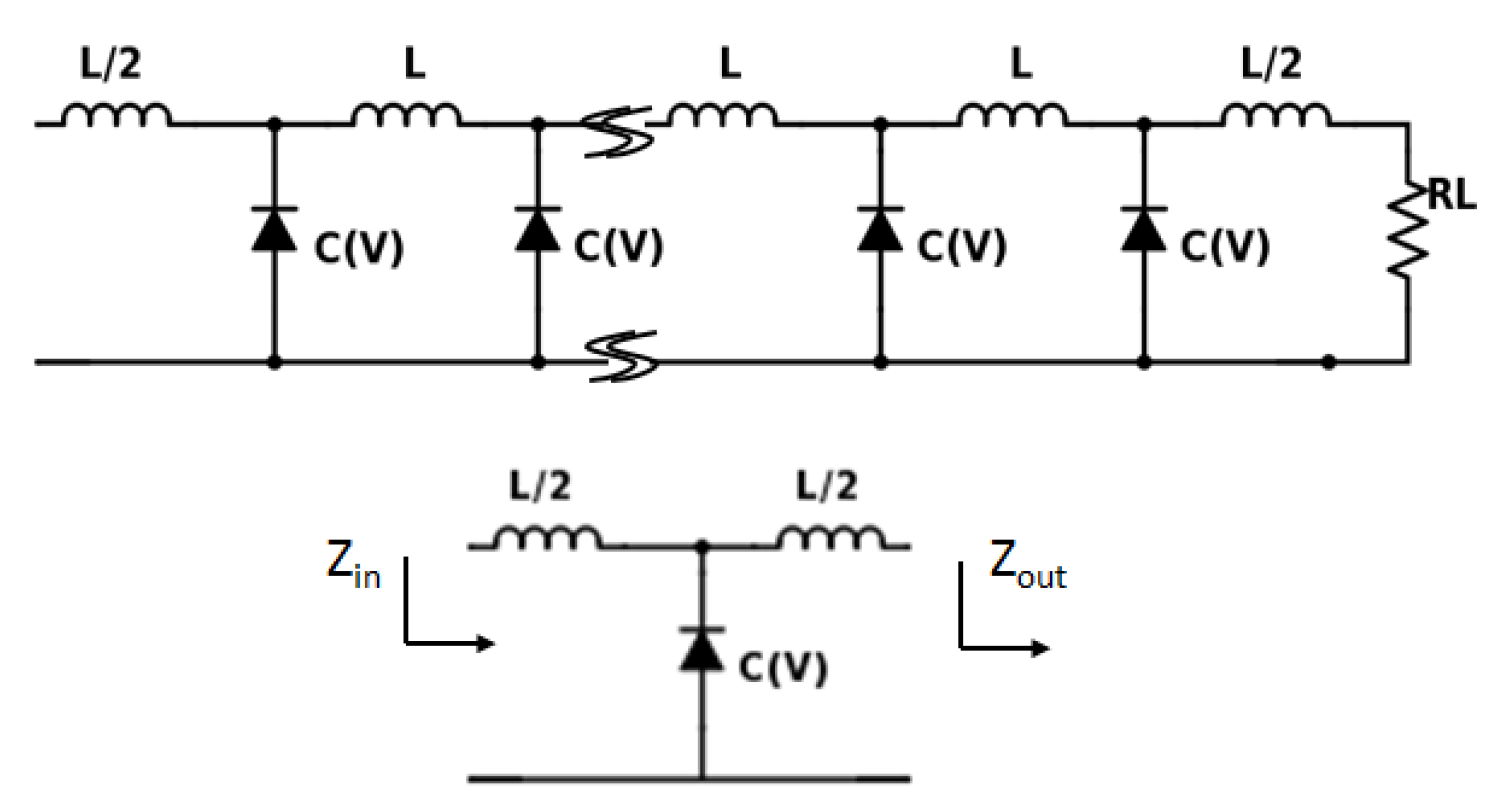
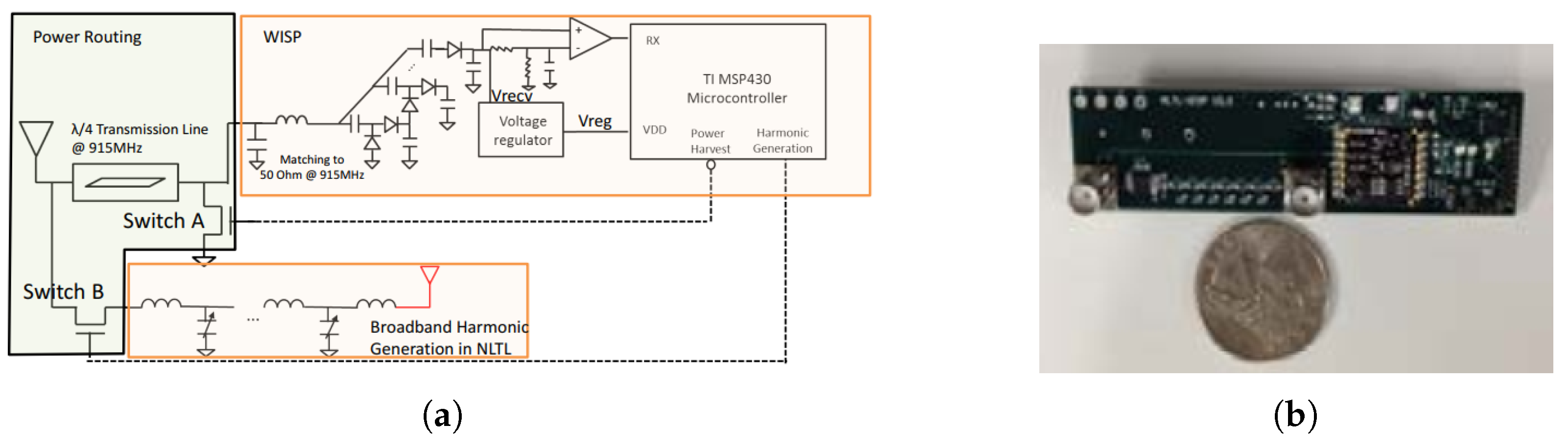
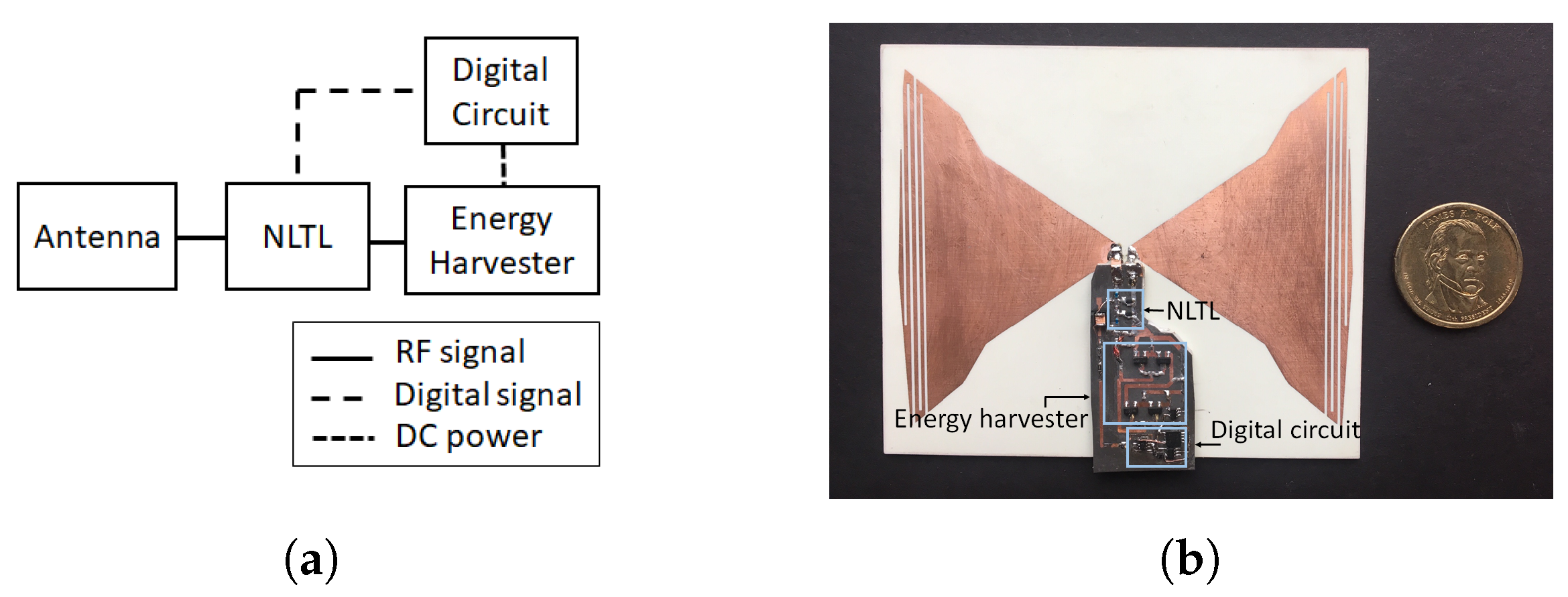
4. Enhanced Harmonic Generation: NLTL
Design Principle
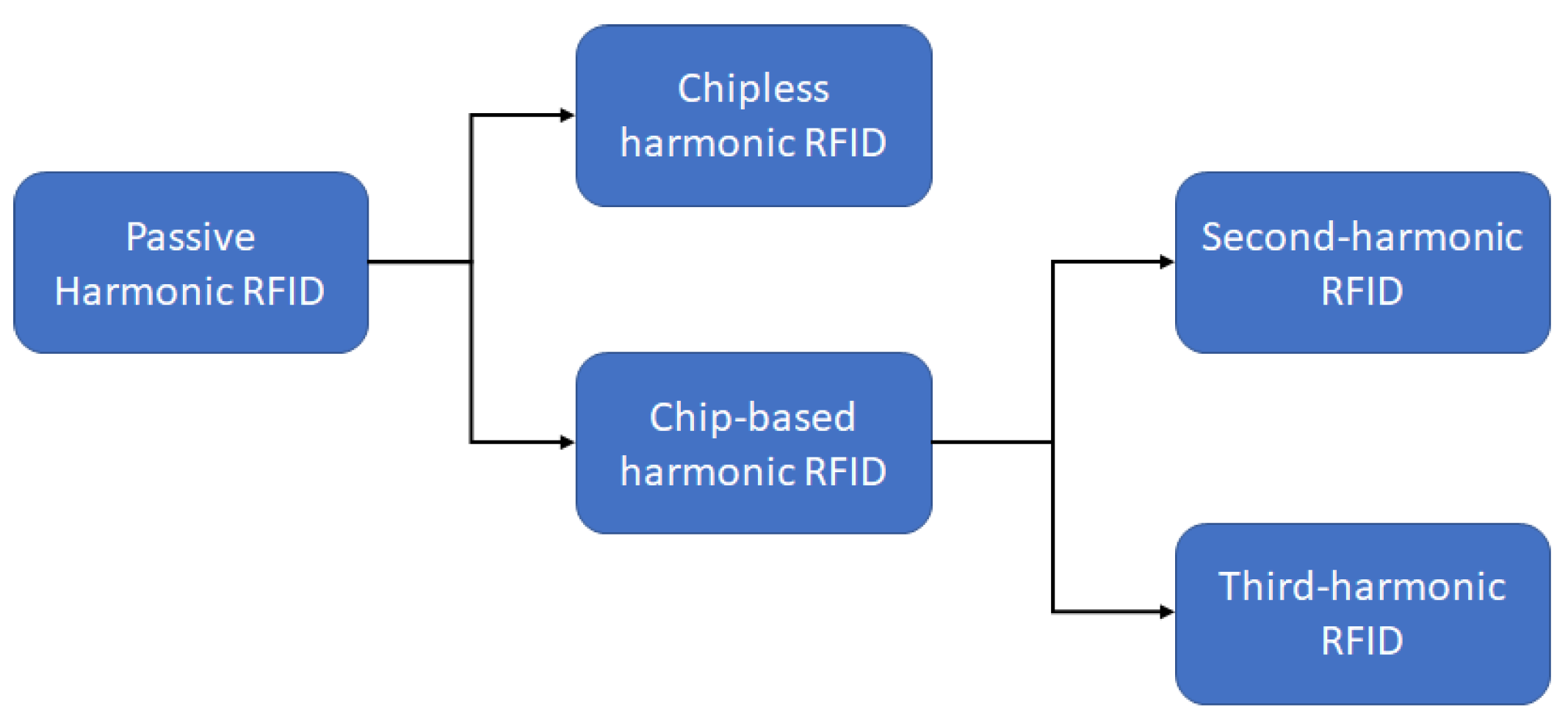
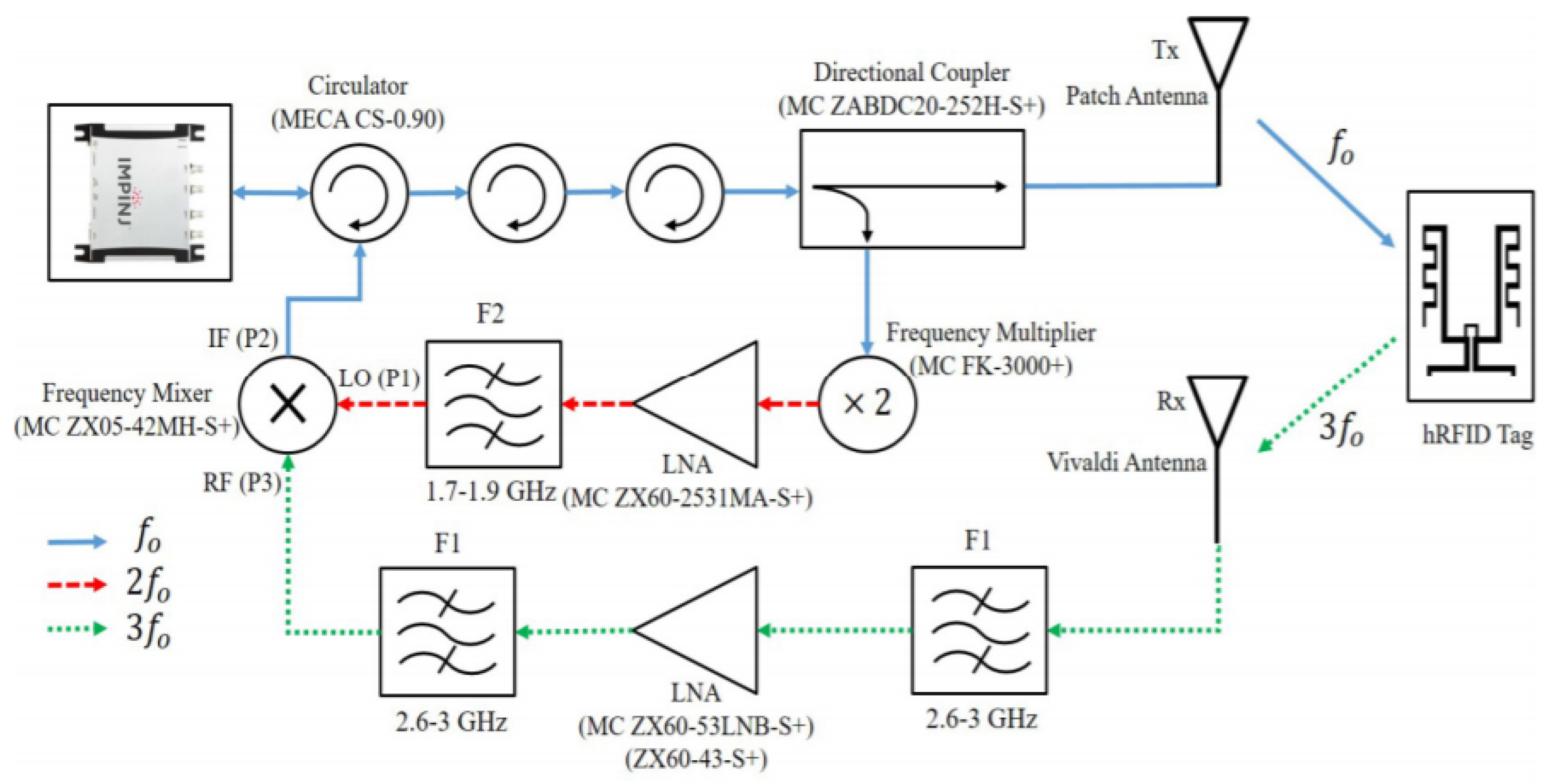
5. Harmonic RFID
5.1. Chipless Harmonic RFID
5.2. Chip-Based Harmonic RFID
5.2.1. Second Harmonic RFID
5.2.2. Harmonic Exploitation of Conventional RFID
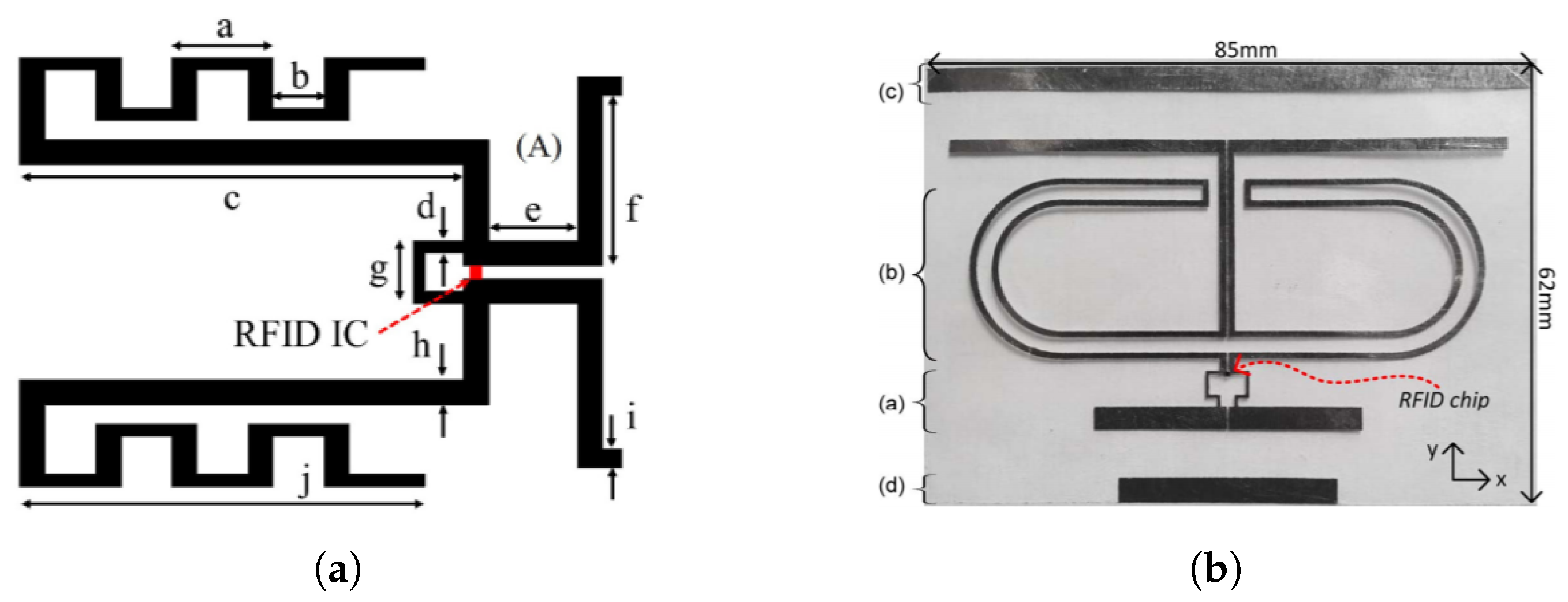
5.3. Antenna Design for Harmonic RFID
6. Applications
- High resolution ranging and vital monitoring,
- Tagging and physical parameter sensing,
- Harmonic radar.
6.1. High Resolution Ranging and Vital Monitoring
6.2. Tagging and Physical Parameters Sensing
6.3. Harmonic Radar
7. Trends and Challenges in Harmonic RFID
7.1. Security
7.2. Miniaturization
7.3. Frequency Bands
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahuja, S.; Potti, P. An introduction to RFID technology. Commun. Netw. 2010, 2, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.; Smith, A.; Reynolds, D.; Edwards, A.; Osborne, J.; Williams, I.; Carreck, N.; Poppy, G. Tracking bees with harmonic radar. Nature 1996, 379, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, L.T.; Chen, M.; Zhao, S.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Y. Real-time locating systems using active RFID for Internet of Things. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 10, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Lunadei, L. The role of RFID in agriculture: Applications, limitations and challenges. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 79, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamba, S.F.; Anand, A.; Carter, L. A literature review of RFID-enabled healthcare applications and issues. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2013, 33, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, A.; Dabo, A.A.A. A review of RFID in supply chain management: 2000–2015. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2016, 17, 189–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.Y.; Sun, C. Active RFID tag, application system and method thereof. U.S. Patent Application 13/482,734, 20 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Lau, Y.C.; Patil, A.P. LANDMARC: Indoor location sensing using active RFID. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, 2003. (PerCom 2003), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 26 March 2003; pp. 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Lavric, A.; Popa, V. A LoRaWAN: Long range wide area networks study. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electromechanical and Power Systems (SIELMEN), Iasi, Romania, 11–13 October 2017; pp. 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitin, P.V.; Rao, K. Performance limitations of passive UHF RFID systems. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 9–14 July 2006; pp. 1011–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Tedjini, S.; Karmakar, N.; Perret, E.; Vena, A.; Koswatta, R.; E-Azim, R. Hold the chips: Chipless technology, an alternative technique for RFID. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2013, 14, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potyrailo, R.A.; Nagraj, N.; Tang, Z.; Mondello, F.J.; Surman, C.; Morris, W. Battery-free radio frequency identification (RFID) sensors for food quality and safety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8535–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, E.; Zampolli, S.; Marco, S.; Scorzoni, A.; Mazzolai, B.; Juarros, A.; Gómez, D.; Elmi, I.; Cardinali, G.C.; Gómez, J.M.; et al. Flexible tag microlab development: Gas sensors integration in RFID flexible tags for food logistic. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 127, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, D.; Chi, S.; Park, M.W. UAV-RFID Integration for Construction Resource Localization. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wu, W.; Moniri, M.; Chibelushi, C.C. Efficient object localization using sparsely distributed passive RFID tags. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 5914–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin-Simard, D.; Bouchard, K.; Gaboury, S.; Bouchard, B.; Bouzouane, A. Accurate passive RFID localization system for smart homes. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Networked Embedded Systems for Every Application (NESEA), Liverpool, UK, 13–14 December 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Buffi, A.; Motroni, A.; Nepa, P.; Tellini, B.; Cioni, R. A SAR-based measurement method for passive-tag positioning with a flying UHF-RFID reader. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 68, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffi, A.; Nepa, P.; Cioni, R. SARFID on drone: Drone-based UHF-RFID tag localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on RFID Technology & Application (RFID-TA), Warsaw, Poland, 20–22 September 2017; pp. 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, A.X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y. STPP: Spatial-temporal phase profiling-based method for relative RFID tag localization. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2016, 25, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lyu, Y.; Patton, J.; Periaswamy, S.C.; Roppel, T. BFVP: A probabilistic UHF RFID tag localization algorithm using Bayesian filter and a variable power RFID model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 8250–8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y. Direction Finding for UWB RFID System in Dense Cluttered Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gravelle, K.; Landt, J.; Lunsford, P.W. System and method for microwave ranging to a target in presence of clutter and multi-path effects. U.S. Patent 8,786,488, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzi, V.; Alimenti, F.; Virili, M.; Mariotti, C.; Orecchini, G.; Mezzanotte, P.; Roselli, L. A novel compact harmonic RFID sensor in paper substrate based on a variable attenuator and nested antennas. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–27 May 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.; Chahal, P. A passive harmonic RFID tag and interrogator development. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2019, 3, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hui, X.; Kan, E.C. Harmonic-WISP: A passive broadband harmonic RFID platform. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–27 May 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.Y.; Yoon, H.G.; Jang, B.J.; Yook, J.G. Effects of reader-to-reader interference on the UHF RFID interrogation range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.; Karuppuswami, S.; Kumar, D.; Chahal, P. Scope and application of harmonic RFID for implanted body area network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on RFID (RFID), Orlando, FL, USA, 28 September–16 October 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, X.; Kan, E.C. Monitoring vital signs over multiplexed radio by near-field coherent sensing. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, M.I.M.; Karuppuswami, S.; Chahal, P. Embedded passive RF tags towards intrinsically locatable buried plastic materials. In Proceedings of the IEEE 66th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 May–3 June 2016; pp. 2575–2580. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.; Kumar, D.; Ghazali, M.I.; Chahal, P.; Udpa, L.; Deng, Y. Monitoring and localization of buried plastic natural gas pipes using passive RF tags. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1949, 020020. [Google Scholar]
- Breitbarth, J. Design and Characterization of Low Phase Noise Microwave Circuits. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Colorado at Boulder, Boulder, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Tao, B.; Gong, Z.; Yin, Z.; Ding, H. A fast UHF RFID localization method using unwrapped phase-position model. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, K. Fusion of RSS and phase shift using the Kalman filter for RFID tracking. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3551–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.M.; Zhang, D.; Souryal, M.R. RFID-based localization and tracking technologies. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2011, 18, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Kan, E.C. Accurate indoor ranging by broadband harmonic generation in passive NLTL backscatter tags. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2014, 62, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Kumar, D.; Chahal, P. A wireless passive pH sensor with clutter rejection scheme. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 3399–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Kan, E.C. Radio ranging with ultrahigh resolution using a harmonic radio-frequency identification system. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Lyon, K.G.; Kan, E.C. A novel passive RFID transponder using harmonic generation of nonlinear transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 58, 4121–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hsu, A.; Kim, K.K.; Kong, J.; Palacios, T. Gigahertz ambipolar frequency multiplier based on CVD graphene. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–8 December 2010; pp. 23.6.1–23.6.4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Karasiewicz, D.; Cifctioglu, B.; Wu, H. A 1.6-to-3.2/4.8 GHz dual-modulus injection-locked frequency multiplier in 0.18 μm digital CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–17 June 2008; pp. 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Oh, H.S.; Yang, J.; Yoon, E.; Hong, S. A 2.4-GHz sub-mW frequency source with current-reused frequency multiplier. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium, 2006, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–13 June 2006; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.C.; Tseng, Y.L.; She, H.C.; Hu, R. A 1.2 GHz programmable DLL-based frequency multiplier for wireless applications. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2004, 12, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, Q.; Suh, Y.J.; Shibata, T.; Yoshimasu, T. A 22-30GHz balanced SiGe BiCMOS frequency doubler with 47dBc suppression and low input drive power. In Proceedings of the 2009 Asia Pacific Microwave Conference, Singapore, 7–10 December 2009; pp. 2260–2263. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K. A 1.8-V operation 5-GHz-band CMOS frequency doubler using current-reuse circuit design technique. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2005, 40, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, V.; Alimenti, F.; Mezzanotte, P.; Virili, M.; Mariotti, C.; Orecchini, G.; Roselli, L. Low-power frequency doubler in cellulose-based materials for harmonic RFID applications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2014, 24, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, P.; Saeed, M.; Hamed, A.; Negra, R. Compact and Wireless 2.5–5 GHz Frequency Doubler for Harmonic RFID Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 12th German Microwave Conference (GeMiC), Stuttgart, Germany, 25–27 March 2019; pp. 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.; Jang, J.; Kim, C.Y.; Hong, S. A W-band high-efficiency CMOS differential current-reused frequency doubler. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2015, 25, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, P.; Morris, F.; Frazier, G. Zero bias resonant tunnel Schottky contact diode for wide-band direct detection. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2005, 26, 894–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champlin, K.S.; Singh, D. Small-signal second-harmonic generation by a nonlinear transmission line (short paper). IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1986, 34, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Viegas, C.; Powell, J.; Sanghera, H.; Whimster, A.; Wang, H.; He, W.; Donaldson, C.; Huggard, P.G.; Alderman, B. A high-power Schottky diode frequency multiplier chain at 360 GHz for Gyro-TWA applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 10th UK-Europe-China Workshop on Millimetre Waves and Terahertz Technologies (UCMMT), Liverpool, UK, 11–13 September 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Maiwald, F.; Lewen, F.; Vowinkel, B.; Jabs, W.; Paveljev, D.; Winnewisser, M.; Winnewisser, G. Planar Schottky diode frequency multiplier for molecular spectroscopy up to 1.3 THz. IEEE Microw. Guid. Wave Lett. 1999, 9, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Afshari, E. Efficient microwave and millimeter-wave frequency multipliers using nonlinear transmission lines in CMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 2889–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Standaert, A.; Reynaert, P. A 525–556-GHz radiating source with a dielectric lens antenna in 28-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodwell, M.J.W. Picosecond Electrical Wavefront Generation and Picosecond Optoelectronic Instrumentation. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell, M.J.; Kamegawa, M.; Yu, R.; Case, M.; Carman, E.; Giboney, K.S. GaAs nonlinear transmission lines for picosecond pulse generation and millimeter-wave sampling. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1991, 39, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Ghazali, M.I.M.; Karuppuswami, S.; Kaur, A.; Chahal, P. A nonlinear transmission line based harmonic RF tag. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 67th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Orlando, FL, USA, 30 May–2 June 2017; pp. 2237–2242. [Google Scholar]
- Callegari, F.; Boggio, J.C.; Fragnito, H.; Arradi, R. Mixing of signals in two-pump fiber optic parametric amplifiers and wavelength converters. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference. Optical Society of America, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 22 February 2004; p. MF18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Snyder, A.W. Four-photon parametric mixing in optical fibers: Effect of pump depletion. Opt. Lett. 1989, 14, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, V.; Mariotti, C.; Alimenti, F.; Virili, M.; Orecchini, G.; Mezzanotte, P.; Roselli, L. Demonstration of a chipless harmonic tag working as crack sensor for electronic sealing applications. Wirel. Power Transf. 2015, 2, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppuswami, S.; Ghazali, M.I.M.; Kaur, A.; Chahal, P. Multi-band harmonic RF tags for barcode applications in a cluttered environment. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 67th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Orlando, FL, USA, 30 May–2 June 2017; pp. 1861–1867. [Google Scholar]
- Alimenti, F.; Roselli, L. Theory of zero-power RFID sensors based on harmonic generation and orthogonally polarized antennas. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 134, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardari, D. Detection and accurate localization of harmonic chipless tags. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2015, 2015, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnour, A.; Lazaro, A.; Villarino, R.; Kaddour, D.; Tedjini, S.; Girbau, D. Passive harmonic RFID system for buried assets localization. Sensors 2018, 18, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Kumar, D.; Chahal, P. A continuous-mode single-antenna harmonic RFID tag. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2020, 30, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Karuppuswami, S.; Kumar, D.; Kaur, A.; Chahal, P. A miniaturized dual band antenna for harmonic RFID tag. In Proceedings of the 51th International Symposium on Microelectronics, Pasadena, CA, USA, 9–11 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, X.; Kan, E.C. Collaborative reader code division multiple access in the harmonic RFID system. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2018, 2, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, P.V.; Rao, K. Harmonic scattering from passive UHF RFID tags. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, North Charleston, SC, USA, 1–5 June 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, G.A.; Duroc, Y.; Tedjini, S. RFID test platform: Nonlinear characterization. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 2299–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, G.A.; Duroc, Y.; Tedjini, S. Analysis of harmonics in UHF RFID signals. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, G.A.; Duroc, Y.; Tedjini, S. Tag-to-reader harmonic link in passive UHF RFID. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS2014), Tampa, FL, USA, 1–6 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, G.A.; Nawale, S.D.; Duroc, Y.; Tedjini, S. Read range enhancement by harmonic energy harvesting in passive UHF RFID. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2015, 25, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allane, D.; Vera, G.A.; Duroc, Y.; Touhami, R.; Tedjini, S. Harmonic power harvesting system for passive RFID sensor tags. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Mondal, S.; Karuppuswami, S.; Deng, Y.; Chahal, P. Harmonic RFID communication using conventional UHF system. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2019, 3, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, G.A.; Duroc, Y.; Tedjini, S. Third harmonic exploitation in passive UHF RFID. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 2991–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, V.; Mezzanotte, P.; Roselli, L. Design of a novel antenna system intended for harmonic RFID tags in paper substrate. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Wireless Power Transfer Conference (WPTC), Boulder, CO, USA, 13–15 May 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Rong, H.; Kan, E.C. Millimeter accuracy passive tag ranging via second harmonics RF backscattering against body movement interference. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 8–12 December 2014; pp. 448–454. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Kan, E.C. Sleep scoring with a UHF RFID tag by near field coherent sensing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium-IMS, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–15 June 2018; pp. 1419–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Baccarelli, R.; Orecchini, G.; Alimenti, F.; Roselli, L. Feasibility study of a fully organic, CNT based, harmonic RFID gas sensor. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on RFID-Technologies and Applications (RFID-TA), Nice, France, 5–7 November 2012; pp. 419–422. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; An, Z.; Yang, L.; Yang, P.; Lin, Q. RFID harmonic for vibration sensing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 20, 1614–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, A.; Villarino, R.; Girbau, D. A passive harmonic tag for humidity sensing. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2014, 670345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubina, B.; Romeu, J.; Mandel, C.; Schüßler, M.; Jakoby, R. Quasi-chipless wireless temperature sensor based on harmonic radar. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Mondal, S.; Deng, Y.; Chahal, P. Wireless battery-free harmonic communication system for pressure sensing. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Kumar, D.; Karuppuswami, S.; Chahal, P. A harmonic RF phase-shifter based wireless pH sensor. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 68th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), San Diego, CA, USA, 29 May–1 June 2018; pp. 796–801. [Google Scholar]
- Psychoudakis, D.; Moulder, W.; Chen, C.C.; Zhu, H.; Volakis, J.L. A portable low-power harmonic radar system and conformal tag for insect tracking. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2008, 7, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrenko, A.; Litchfield, B.; Woodward, G.; Pawson, S. Design and evaluation of a compact harmonic transponder for insect tracking. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2020, 30, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpitts, B.G.; Boiteau, G. Harmonic radar transceiver design: Miniature tags for insect tracking. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2004, 52, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes-Silva, P.; Hrncir, M.; Guimarães, J.; Arruda, H.; Costa, L.; Pessin, G.; Siqueira, J.; De Souza, P.; Imperatriz-Fonseca, V. Applications of RFID technology on the study of bees. Insectes Sociaux 2019, 66, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enander, B.; Fuks, P.; Larsson, G. Transponder for use in locating avalanche victims. U.S. Patent 4,331,957, 25 May 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson, J.; Forssén, T.; Hendeby, G.; Skog, I.; Gustafsson, F. UAS-supported digitalized search-And-rescue using harmonic radar reflection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 7–14 March 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Martone, A.F.; McNamara, D.M. Detection of RF electronics by multitone harmonic radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Jia, Y.L.; Zhang, R. A lightweight RFID security protocol based on elliptic curve crytography. IJ Netw. Secur. 2016, 18, 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- Khattab, A.; Jeddi, Z.; Amini, E.; Bayoumi, M. RFID security threats and basic solutions. In RFID Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Halak, B.; Zwolinski, M.; Mispan, M.S. Overview of PUF-based hardware security solutions for the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 59th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gassend, B.; Clarke, D.; Van Dijk, M.; Devadas, S. Silicon physical random functions. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Washington, DC, USA, 18–22 November 2002; pp. 148–160. [Google Scholar]
- Gope, P.; Lee, J.; Quek, T.Q. Lightweight and practical anonymous authentication protocol for RFID systems using physically unclonable functions. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 2831–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotnyy, L.; Robins, G. Physically unclonable function-based security and privacy in RFID systems. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom’07), White Plains, NY, USA, 19–23 March 2007; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Chahal, P.J.; Mondal, S. Harmonic RFID tag-reader system for long range sensing identification and security. U.S. Patent 10,929,620, 23 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chahal, P.; Kumar, D.; Mondal, S.; Karuppuswami, S. Systems and methods for a multiband sensing platform. U.S. Patent Application 16/695,758, 28 May 2020. [Google Scholar]

| Ref. | Device Type | Output Frequency | Multiplication Factor | Power Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [40] | CMOS | 3.2 or 4.8 GHz | 2× or 3× | 3.7 mW @ 1 V for 2× |
| [41] | CMOS | 2.4 GHz | 2× | 245 uW @ 0.7 V |
| [43] | SiGe BiCMOS | 22–30 GHz | 2× | 65 mW |
| [44] | CMOS | 5.2 GHz | 2× | 9 mW @ 1.8 V and −4 dBm i/p power |
| [39] | CMOS logic gate | 1.2 GHz | 8× to 10× | 52.5 mW @ 2.5 V |
| [42] | Graphene based FET | 1.4 GHz | 2× | NA |
| [23] | Schottky diode | 2.4 GHz | 2× | no external bias |
| [29] | Schottky diode | 5 GHz | 2× | no external bias |
| [45] | Schottky diode | 2 GHz | 2× | no external bias |
| [38] | CMOS varactor diode | Up to 25 GHz | 2× and 3× | negligible power |
| [24] | Varactor diode | 868 MHz | 2× | 20 uW @ 0.6 V and −4 dBm i/p power |
| Architecture | Conversion Efficiency | Power Consumption | Cut-Off Frequency | Switching Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transistor | Very good | High | High (using small process node) | Easy |
| Schottky diode | Good (at high input power) | Zero | Very high | Difficult |
| Varactor diode | Good | Zero or negligible | Moderate | Easy |
| Reference | Power Consumption | Conversion Efficiency | Switching Control | Potential Passive Harmonic RFID Candidate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMOS [40] | High | Good | Good | Weak (due to high power consumption) |
| CMOS [41] | Medium | Good | Good | Moderate (due to medium power consumption and good efficiency and control) |
| BiCMOS [43] | High | Good | Good | Weak (due to high power consumption) |
| CMOS [44] | High | Good | Good | Weak (due to high power consumption) |
| CMOS logic [39] | High | Good | Good | Weak (due to high power consumption) |
| FET [42] | High | Good | Good | Weak (due to high power consumption) |
| Schottky [23] | Low | Bad | Bad | Moderate (due to complicated switching control) |
| Schottky [29] | Low | Bad | Bad | Moderate (due to complicated switching control) |
| Schottky [45] | Low | Bad | Bad | Moderate (due to complicated switching control) |
| CMOS varactor [38] | Low | Medium | Good | Strong (due to all advantages) |
| Varactor [24] | Low | Medium | Good | Strong (due to all advantages) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mondal, S.; Kumar, D.; Chahal, P. Recent Advances and Applications of Passive Harmonic RFID Systems: A Review. Micromachines 2021, 12, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040420
Mondal S, Kumar D, Chahal P. Recent Advances and Applications of Passive Harmonic RFID Systems: A Review. Micromachines. 2021; 12(4):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040420
Chicago/Turabian StyleMondal, Saikat, Deepak Kumar, and Premjeet Chahal. 2021. "Recent Advances and Applications of Passive Harmonic RFID Systems: A Review" Micromachines 12, no. 4: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040420
APA StyleMondal, S., Kumar, D., & Chahal, P. (2021). Recent Advances and Applications of Passive Harmonic RFID Systems: A Review. Micromachines, 12(4), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040420






