Numerical Scrutinization of Darcy-Forchheimer Relation in Convective Magnetohydrodynamic Nanofluid Flow Bounded by Nonlinear Stretching Surface in the Perspective of Heat and Mass Transfer
Abstract
1. Introduction
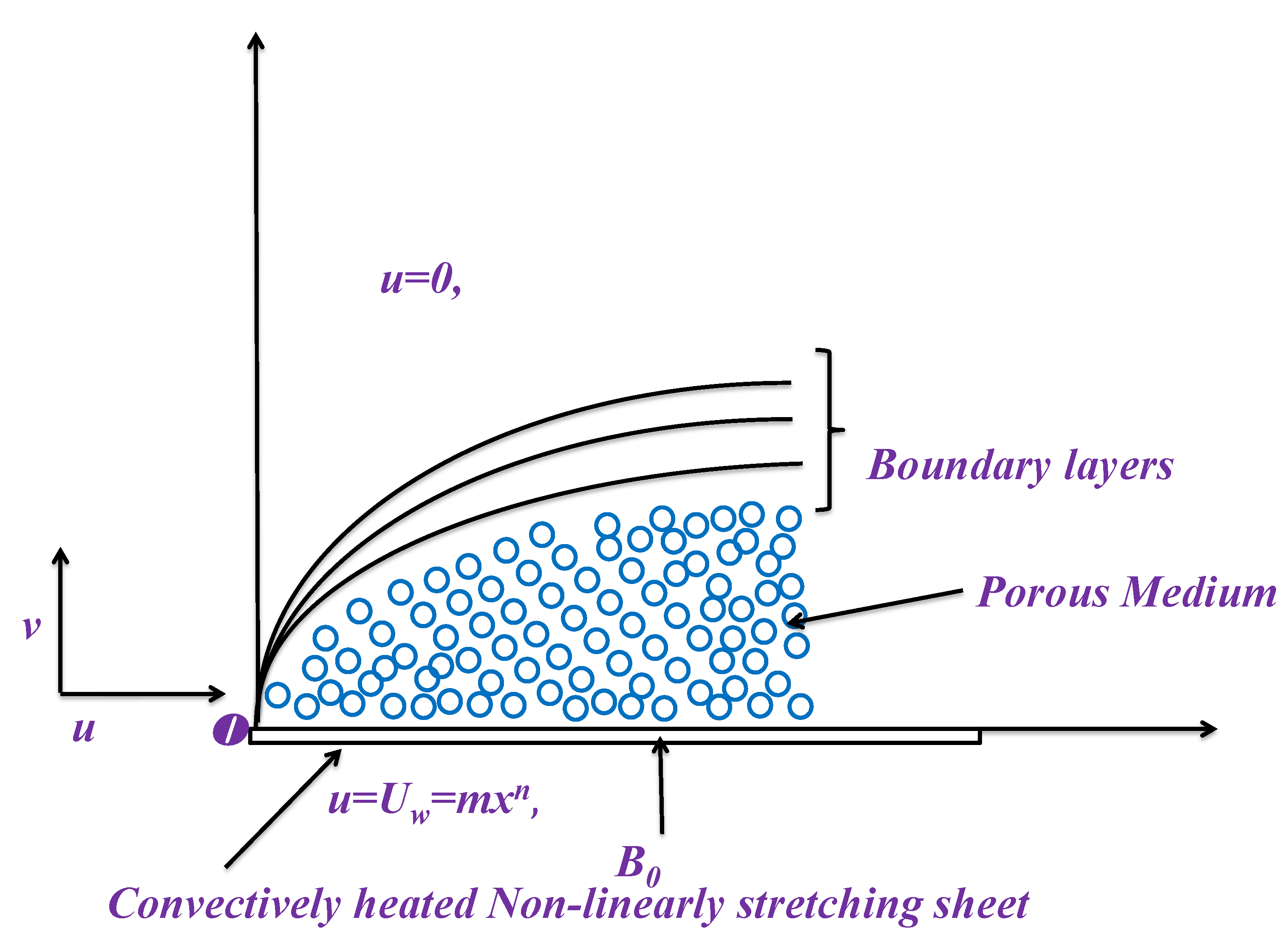
2. Problem Formulation
3. Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
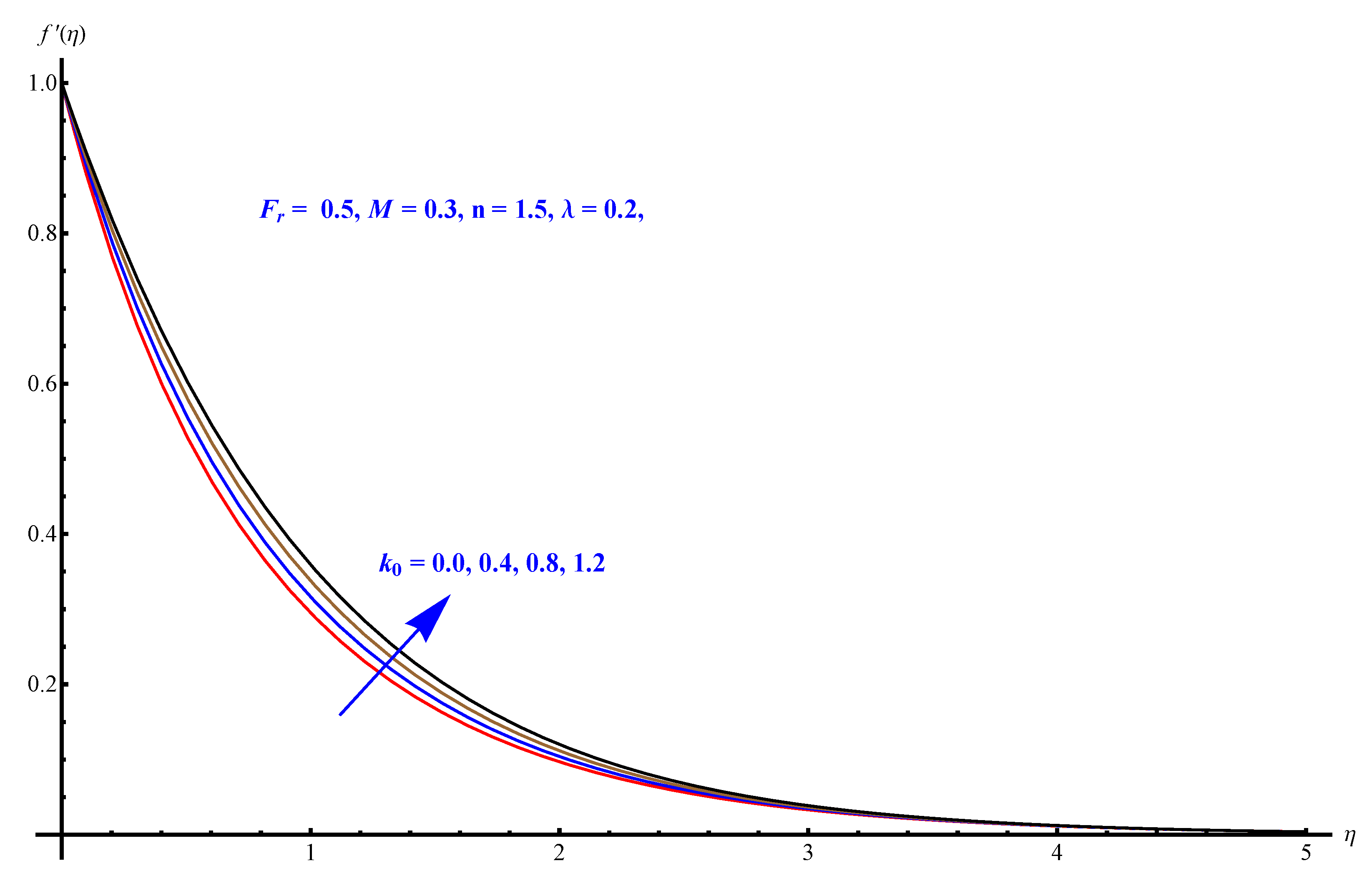
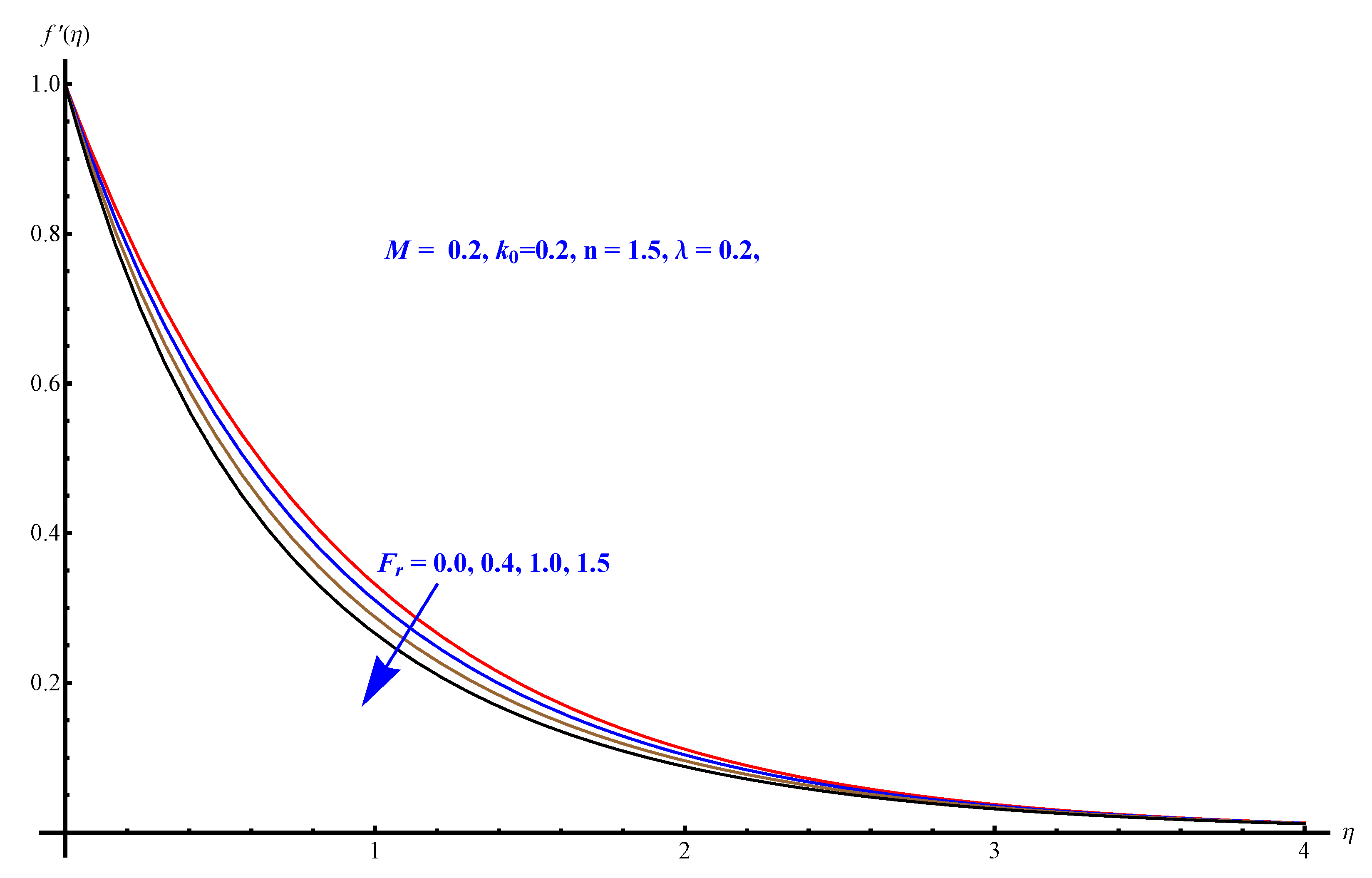
- A decreasing trend in velocity profile is noted for a stronger effect of Forchheimer number .
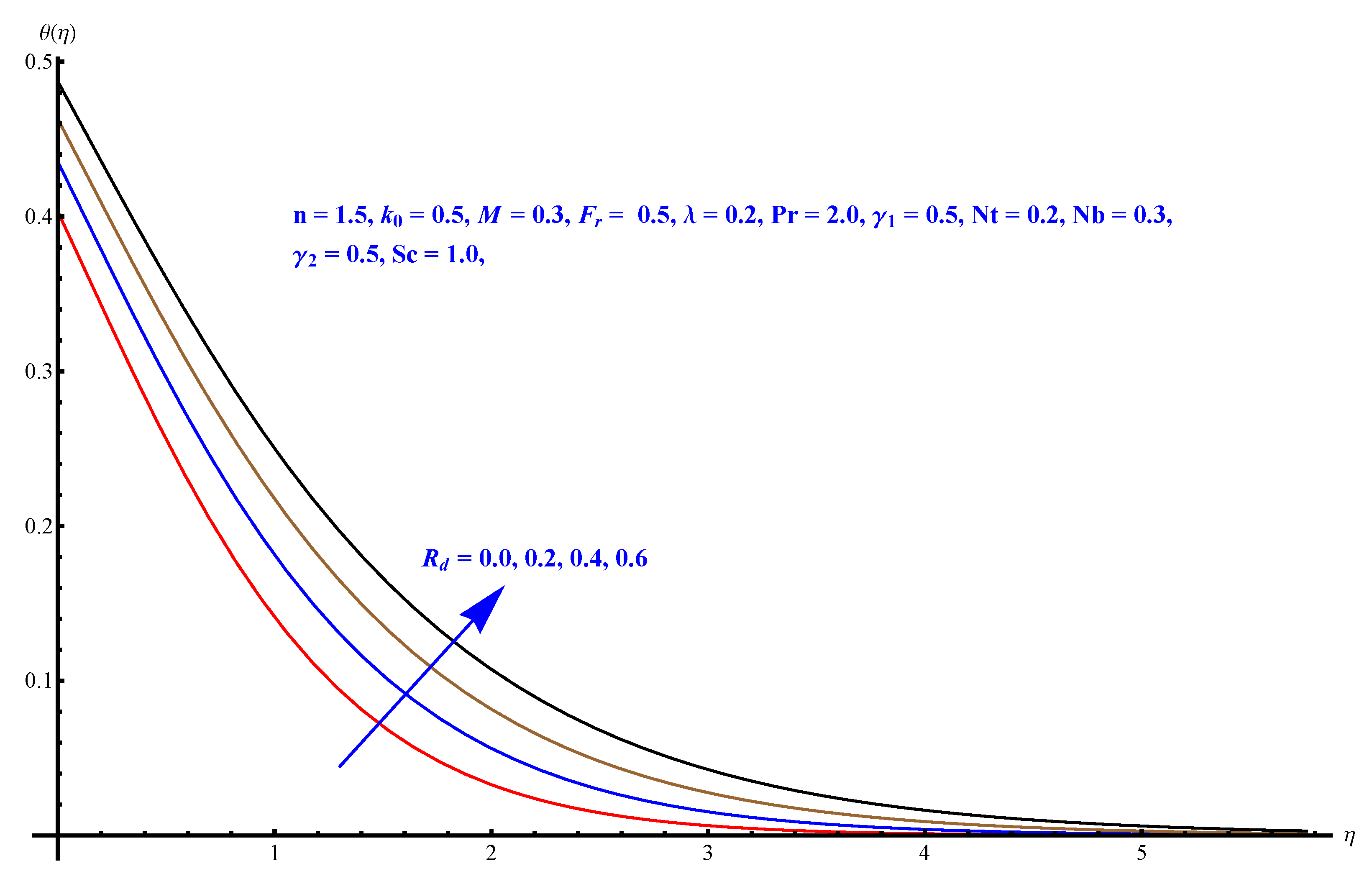
- The thermal layer receives significant modification in the incremental direction for augmented values of thermal radiation with a more convenient convection.
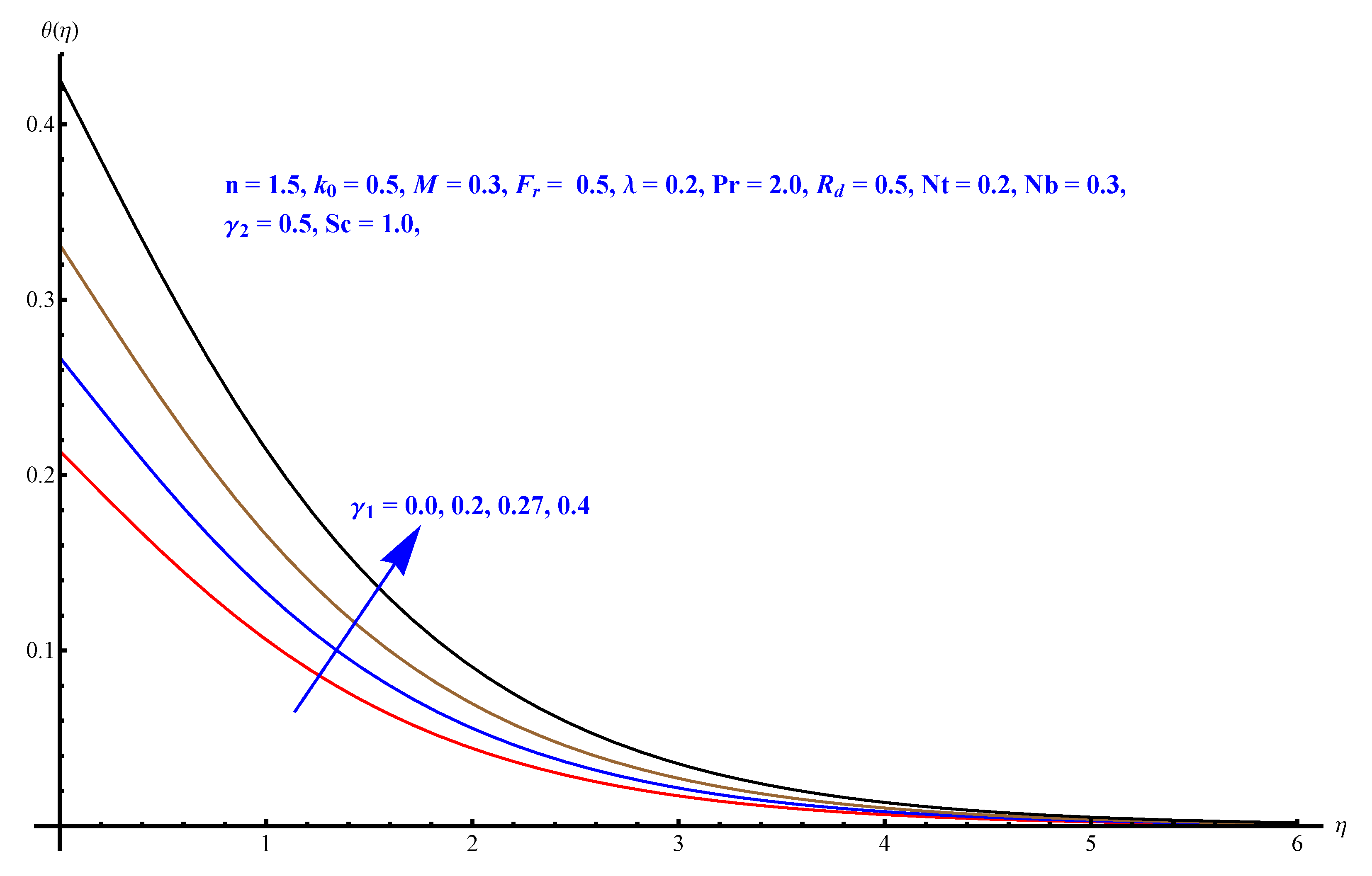
- Elevated values of thermal Biot number apparently result a in significant increase of the thermal layer.
- The two important factors of nanofluid flow and boundary layer phenomenon, the thermophoresis and the Brownian motion, apparently develop a rising trend in thermal profile.
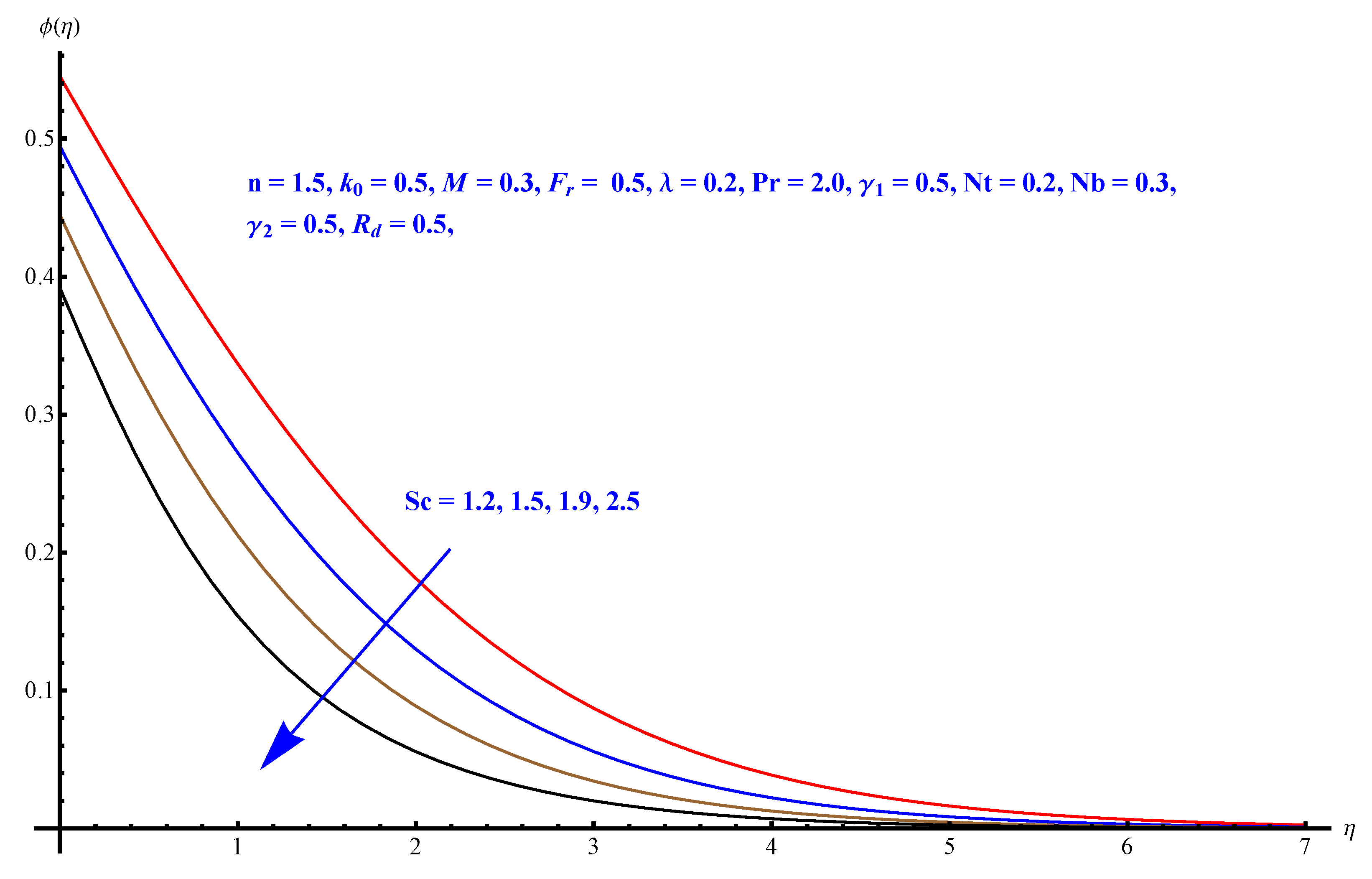
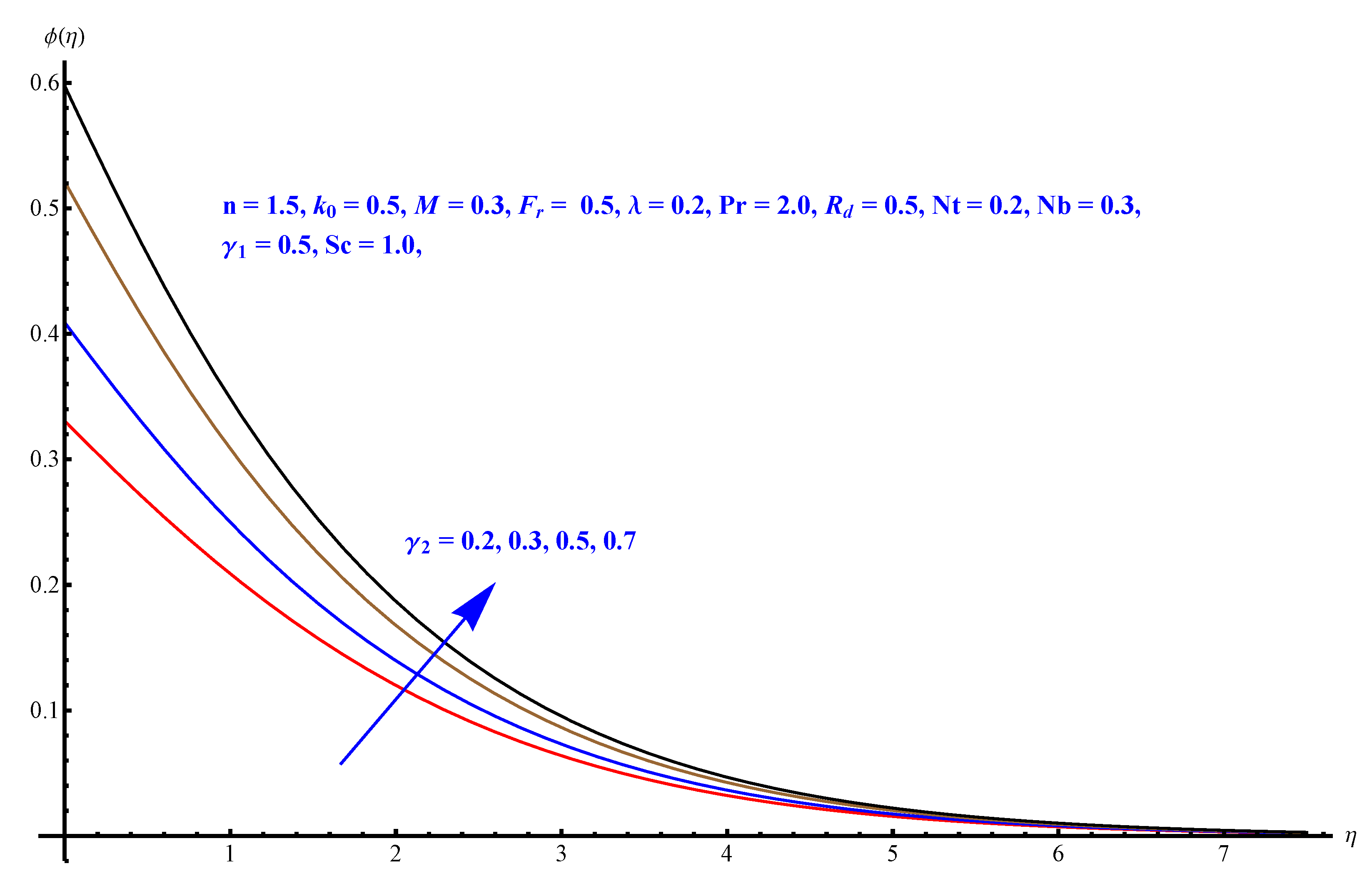
- The solute Biot number is an enhancing factor for the concentration profile.
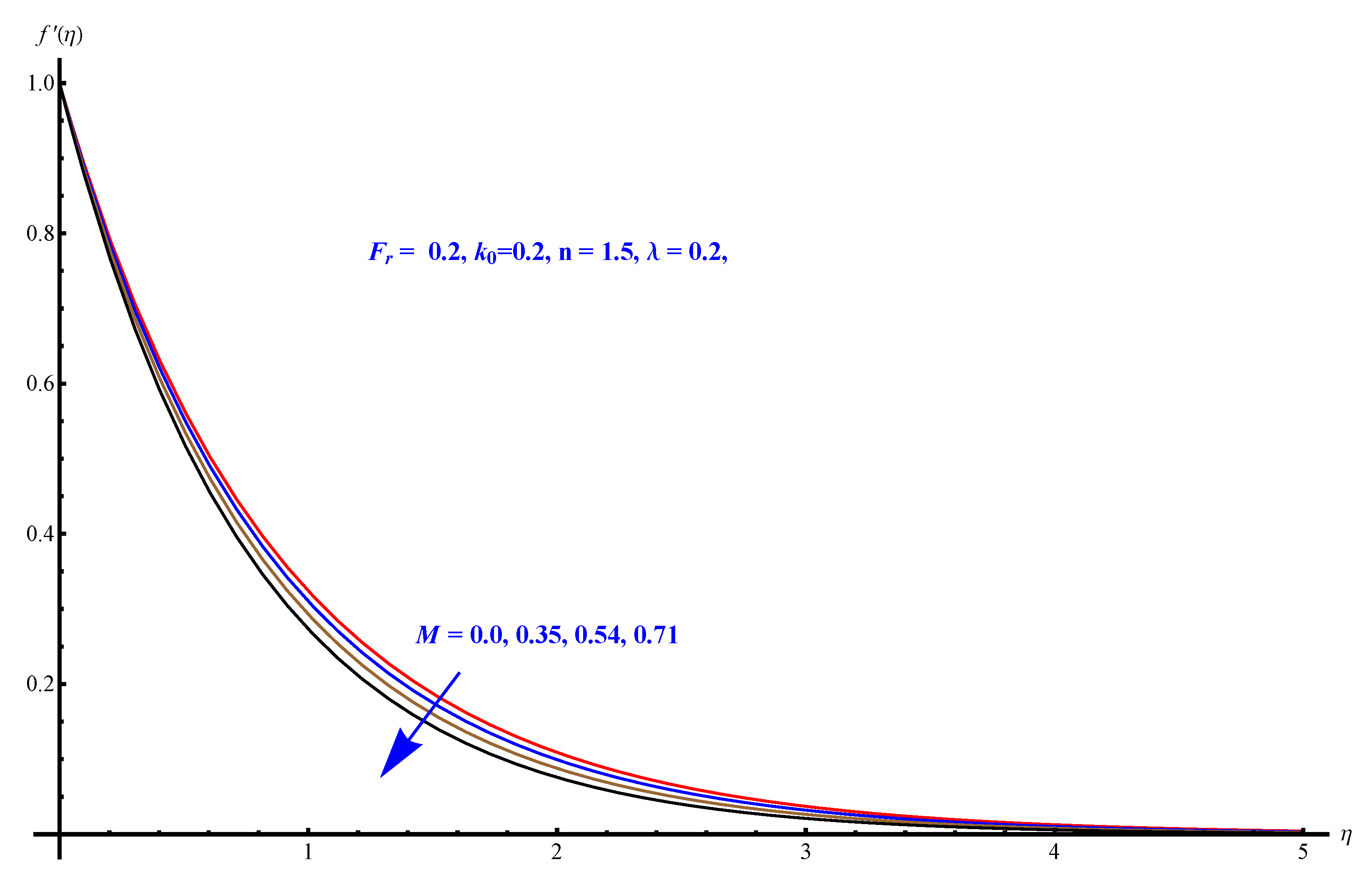
- Skin friction rises for larger porosity, while both the heat flux and mass flux receive a reduction for augmented values of Forchheimer number.
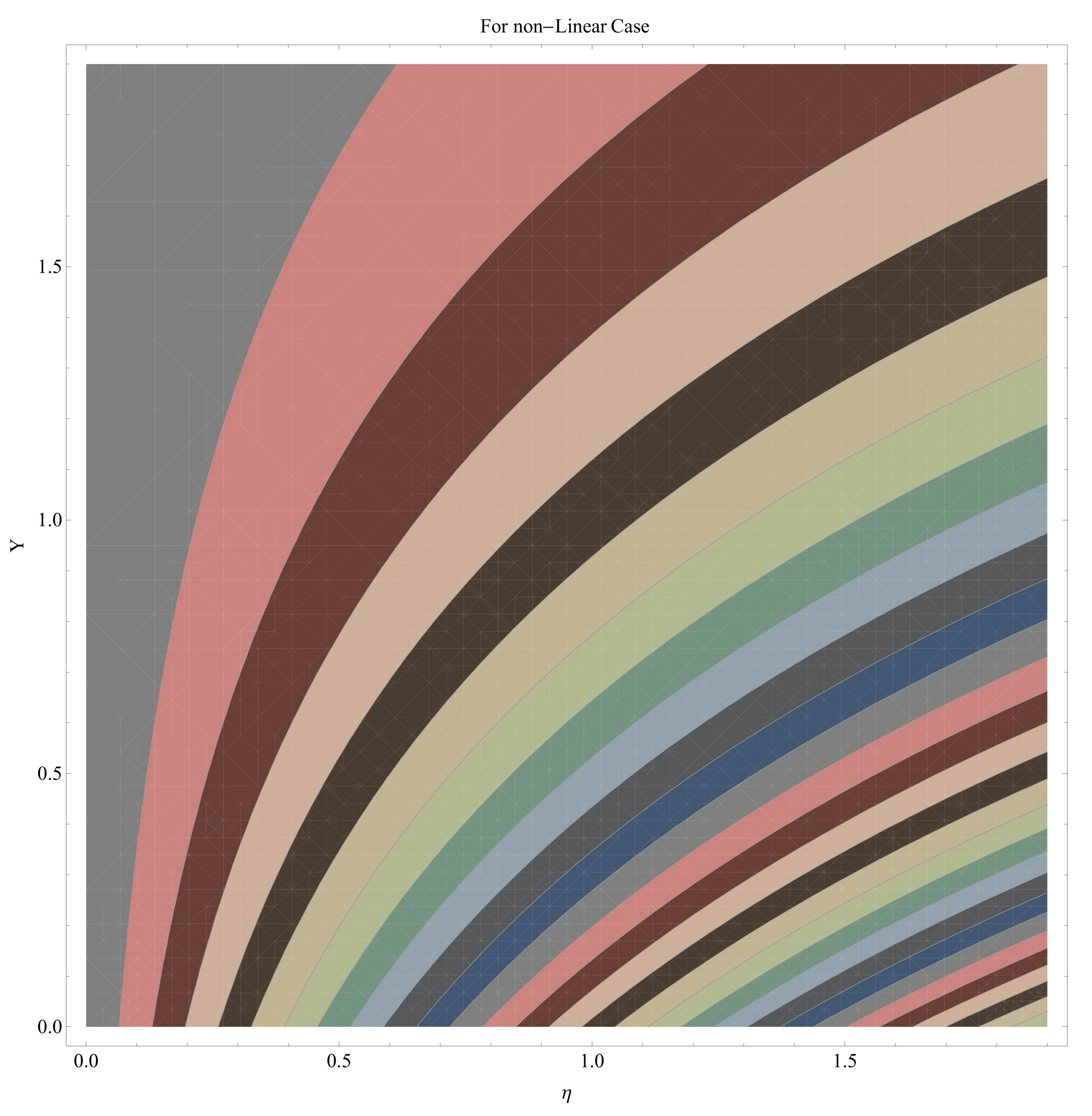
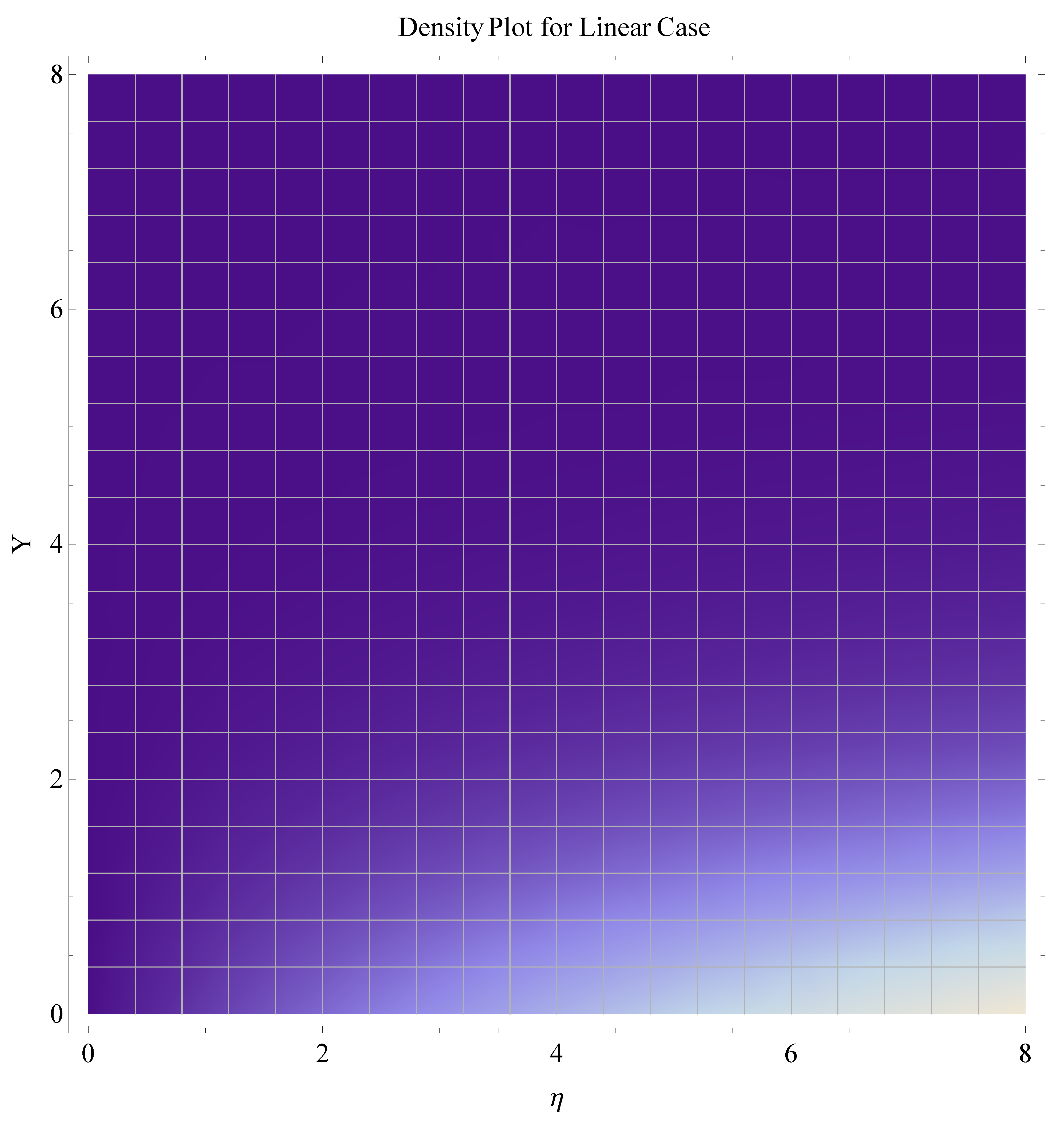
- A significant part of this study is the contour and density graphs.
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature:
| MHD | Magnetohydrodynamics |
| Runge Kutta 45 method | |
| PDE | Partial Differential Equation |
| ODE | Ordinary Differential Equation |
| velocity components in cartesian coordinates/m·s | |
| Horizontal velocity /m·s | |
| m | constant/s |
| Local temperature and concentration of nanoparticles | |
| Ambient temperature/K | |
| Drag coefficient | |
| K | Permeability/H · m |
| Magnetic field/A · m | |
| Electric conductivity/(Ohm · m) | |
| Density/kg·m | |
| viscoelastic coefficient | |
| Thermal diffusivisity/ms | |
| Radiation | |
| Local Nusselt number | |
| Skin-friction (wall drag force) | |
| Local Reynolds number | |
| Lewis number | |
| Brownian Diffusion/m s | |
| Thermophoretic diffusion/m s | |
| M | Magnetic number |
| viscoelastic parameter | |
| Prandtl number | |
| Thermophoresis parameter | |
| Brownian diffusion parameter | |
| Ratio of heat capacity of fluid and nanoparticles |
References
- Choi, S.U.S. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 66, pp. 99–105, FED 231/MD. [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Pop, I. Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Hayat, T.; Pop, I.; Asghar, S.; Obaidat, S. Stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid towards a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 5588–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.S.; Gul, T.; Islam, S.; Khan, A.; Shah, Z. Brownian motion and Thermophoresis effects on MHD mixed convective thin film second-grade nanofluid flow with hall effect and heat transfer past a stretching sheet. J. Nanofluids 2017, 6, 812–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Bessaih, R.; Mahanthesh, B.; Chamkha, A.J.; Raza, J. Magneto-Thermal-Convection Stability in an Inclined Cylindrical Annulus filled with a Molten Metal. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Shafiq, A. Numerical Exploration of the Features of Thermally Enhanced Chemically Reactive Radiative Powell-Eyring Nanofluid Flow via Darcy Medium over Non-linearly Stretching Surface Affected by a Transverse Magnetic Field and Convective Boundary Conditions. Appl. Nanosci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogonchi, A.S.; Selimefendigil, F.; Ganji, D.D. Magneto-hydrodynamic natural convection of CuO-water nanofluid in complex shaped enclosure considering various nanoparticle shapes. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 29, 1663–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Wakif, A. Numerical spectral examination of EMHD mixed convective flow of second-grade nanofluid towards a vertical Riga plate using an advanced version of the revised Buongiorno’s nanofluid model. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.S.; Gul, T.; Khan, M.A.; Bonyah, E.; Islam, S. Mixed convection in gravity-driven thin film non-Newtonian nanofluids flow with gyrotactic microorganisms. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 4033–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Shafiq, A.; Khalique, C.M.; Zhang, T. Magnetohydrodynamic Darcy Forchheimer nanofluid flow over nonlinear stretching sheet. Phys. Scr. 2019, 94, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaim, A.; Aissa, A.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Mahanthesh, B.; Lorenzini, G.; Sahnoun, M. Galerkin finite element analysis of magneto-hydrodynamic natural convection of Cu-water nanoliquid in a baffled U-shaped enclosure. Propuls. Power Res. 2020, 9, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Zhang, T. Darcy-Forchheimer nanofluidic flow manifested with Cattaneo-Christov theory of heat and mass flux over non-linearly stretching surface. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, K.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Abo-Dahab, S.M. Influence of MWCNT/Fe3O4 hybrid-nanoparticles on an exponentially porous shrinking sheet with variable magnetic field and chemical reaction. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Dahab, S.M.; Abdelhafez, M.A.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Bilal, S.M. MHD Casson Nanofluid Flow over Nonlinearly Heated Porous Medium in presence of Extending Surface effect with Suction/Injection. Indian J. Phys. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Shafiq, A.; Khan, I.; Baleanu, D.; Nisar, K.S.; Shahzadi, G. Entropy generation and consequences of MHD in Darcy-Forchheimer nanofluid flow bounded by non-linearly stretching surface. Symmetry 2020, 12, 652. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-8994/12/4/652 (accessed on 26 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Marzougui, S.; Bouabid, M.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Abu-Hamdeh, N.; Magherbi, M.; Ramesh, K. A computational analysis of heat transport irreversibility phenomenon in a magnetized porous channel. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Nasrin, R.; Alim, M.A.; Hossain, N.F.; Chamkha, A.J. Thermal conductivity variation on natural convection flow of water–alumina nanofluid in an annulus. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 5268–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrin, R.; Alim, M.A.; Chamkha, A.J. Combined convection flow in triangular wavy chamber filled with water–CuO nanofluid: Effect of viscosity models. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 39, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogonchi, A.S.; Ismael, M.A.; Chamkha, A.J.; Ganji, D.D. Numerical analysis of natural convection of Cu–water nanofluid filling triangular cavity with semicircular bottom wall. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 135, 3485–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.S.; Sreedevi, P.; Chamkha, A.J. MHD boundary layer flow, heat and mass transfer analysis over a rotating disk through porous medium saturated by Cu-water and Ag-water nanofluid with chemical reaction. Powder Technol. 2017, 307, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebarek-Oudina, F. Convective Heat Transfer of Titania Nanofluids of different base fluids in Cylindrical Annulus with discrete Heat Source. Heat-Transf. Asian Res. 2019, 48, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Raza, J.; Bakouri, M.; Tlili, I. Stability analysis of Darcy-Forchheimer flow of casson type nanofluid over an exponential sheet: Investigation of critical points. Symmetry 2019, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, K.; Mahanthesh, B.; Mebarek-Oudina, F. Heat transport and stagnation-point flow of magnetized nanoliquid with variable thermal conductivity with Brownian moment and thermophoresis aspects. Heat Transf. 2021, 50, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortell, R. Viscous flow and heat transfer over a nonlinearly stretching sheet. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 184, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajravelu, K. Viscous flow over a nonlinearly stretching sheet. Appl. Math. Comput. 2001, 124, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Bhargava, R. Flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet: A numerical study. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2012, 17, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.C.; Masuoka, T. Stokes first problem for second grade fluid in a porous half space. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2005, 40, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetecau, C.; Fetecau, C. Starting solutions for the motion of a second grade fluid due to longitudinal and torsional oscillations of a circular cylinder. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2006, 44, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A.J. MHD-free convection from a vertical plate embedded in a thermally stratified porous medium with Hall effects. Appl. Math. Model. 1997, 21, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Bilal, M. Time dependent MHD nano-second grade fluid flow induced by permeable vertical sheet with mixed convection and thermal radiation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Muhammad, T.; Shehzad, S.A.; Alsaedi, A. Similarity solution to three dimensional boundary layer flow of second grade nanofluid past a stretching surface with thermal radiation and heat source/sink. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 017107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Hussain, Z.; Farooq, M.; Alsaedi, A. Effects of homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions and melting heat in the viscoelastic fluid flow. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Ullah, I.; Muhammad, T.; Alsaedi, A. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) three-dimensional flow of second grade nanofluid by a convectively heated exponentially stretching surface. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| M | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | Pr | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasool, G.; Shafiq, A.; Alqarni, M.S.; Wakif, A.; Khan, I.; Bhutta, M.S. Numerical Scrutinization of Darcy-Forchheimer Relation in Convective Magnetohydrodynamic Nanofluid Flow Bounded by Nonlinear Stretching Surface in the Perspective of Heat and Mass Transfer. Micromachines 2021, 12, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040374
Rasool G, Shafiq A, Alqarni MS, Wakif A, Khan I, Bhutta MS. Numerical Scrutinization of Darcy-Forchheimer Relation in Convective Magnetohydrodynamic Nanofluid Flow Bounded by Nonlinear Stretching Surface in the Perspective of Heat and Mass Transfer. Micromachines. 2021; 12(4):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040374
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasool, Ghulam, Anum Shafiq, Marei S. Alqarni, Abderrahim Wakif, Ilyas Khan, and Muhammad Shoaib Bhutta. 2021. "Numerical Scrutinization of Darcy-Forchheimer Relation in Convective Magnetohydrodynamic Nanofluid Flow Bounded by Nonlinear Stretching Surface in the Perspective of Heat and Mass Transfer" Micromachines 12, no. 4: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040374
APA StyleRasool, G., Shafiq, A., Alqarni, M. S., Wakif, A., Khan, I., & Bhutta, M. S. (2021). Numerical Scrutinization of Darcy-Forchheimer Relation in Convective Magnetohydrodynamic Nanofluid Flow Bounded by Nonlinear Stretching Surface in the Perspective of Heat and Mass Transfer. Micromachines, 12(4), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040374










