Disposable Pencil Graphite Electrode for Diosmin Voltammetric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Materials
- Instrumentation
- Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Working Conditions
3.1.1. Selection of the Working Electrode
3.1.2. Selection of the Supporting Electrolyte
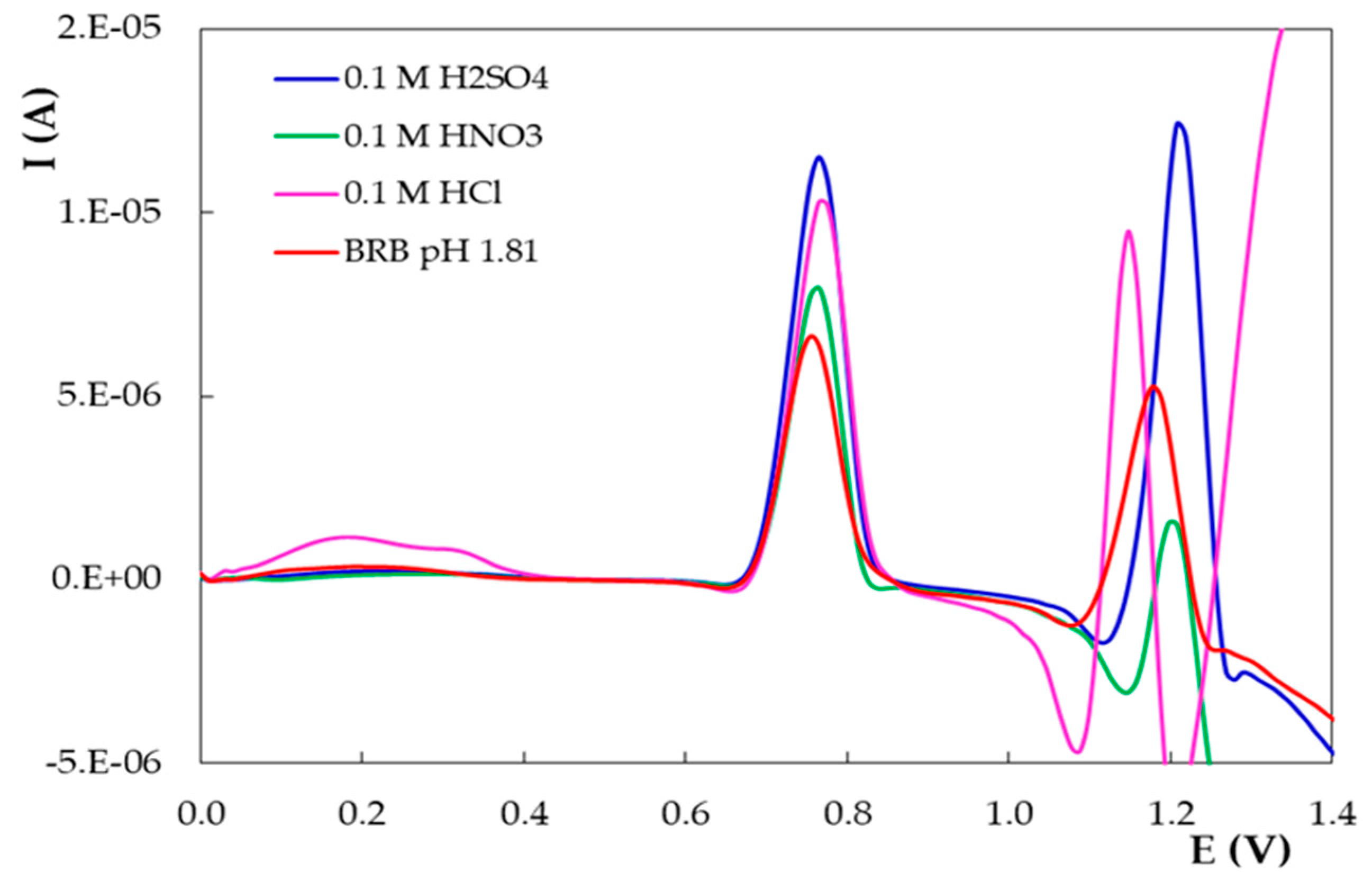
- The influence of the pH of the supporting electrolyte
- The influence of the nature of the supporting electrolyte
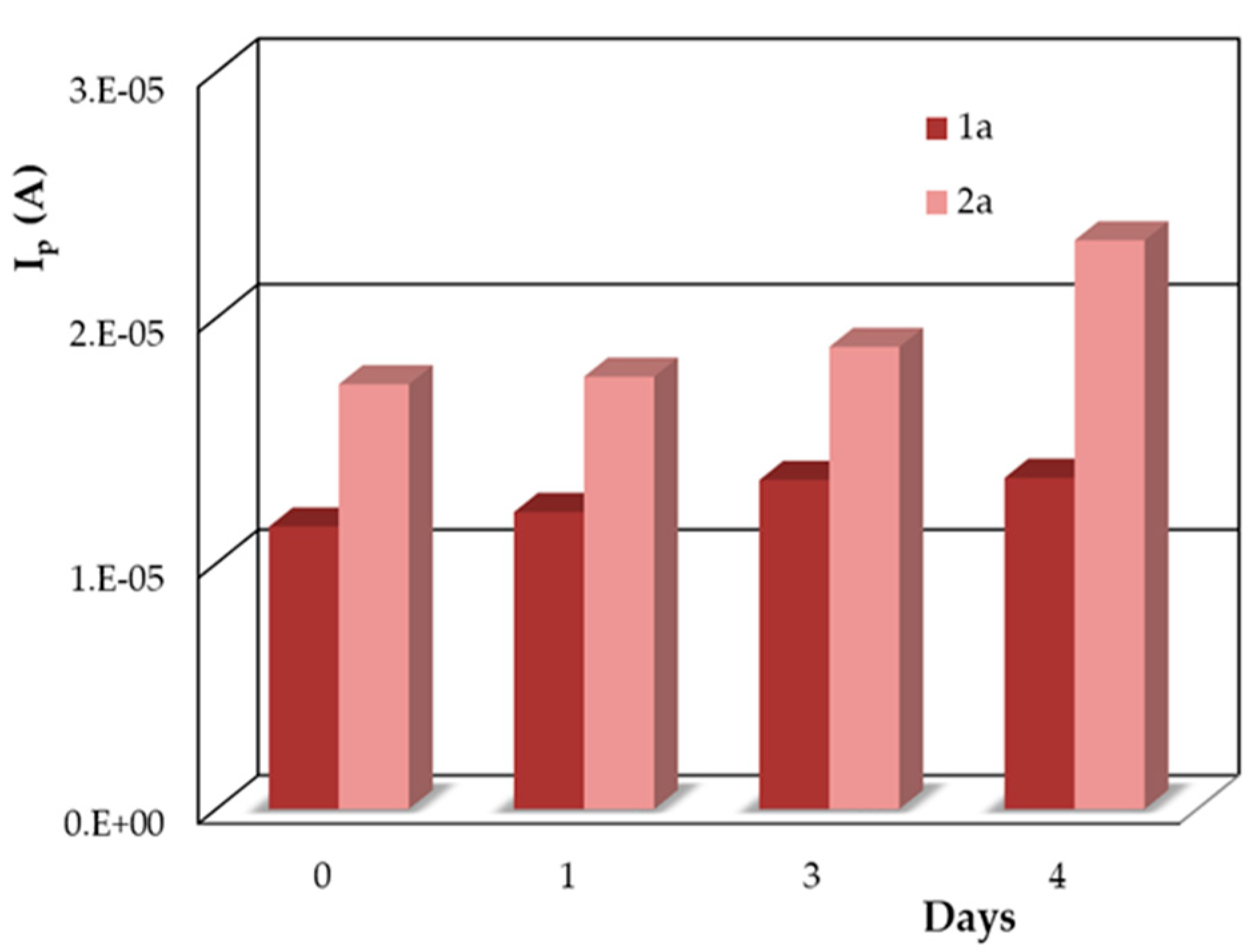
3.1.3. The Stability of the DIO Solution
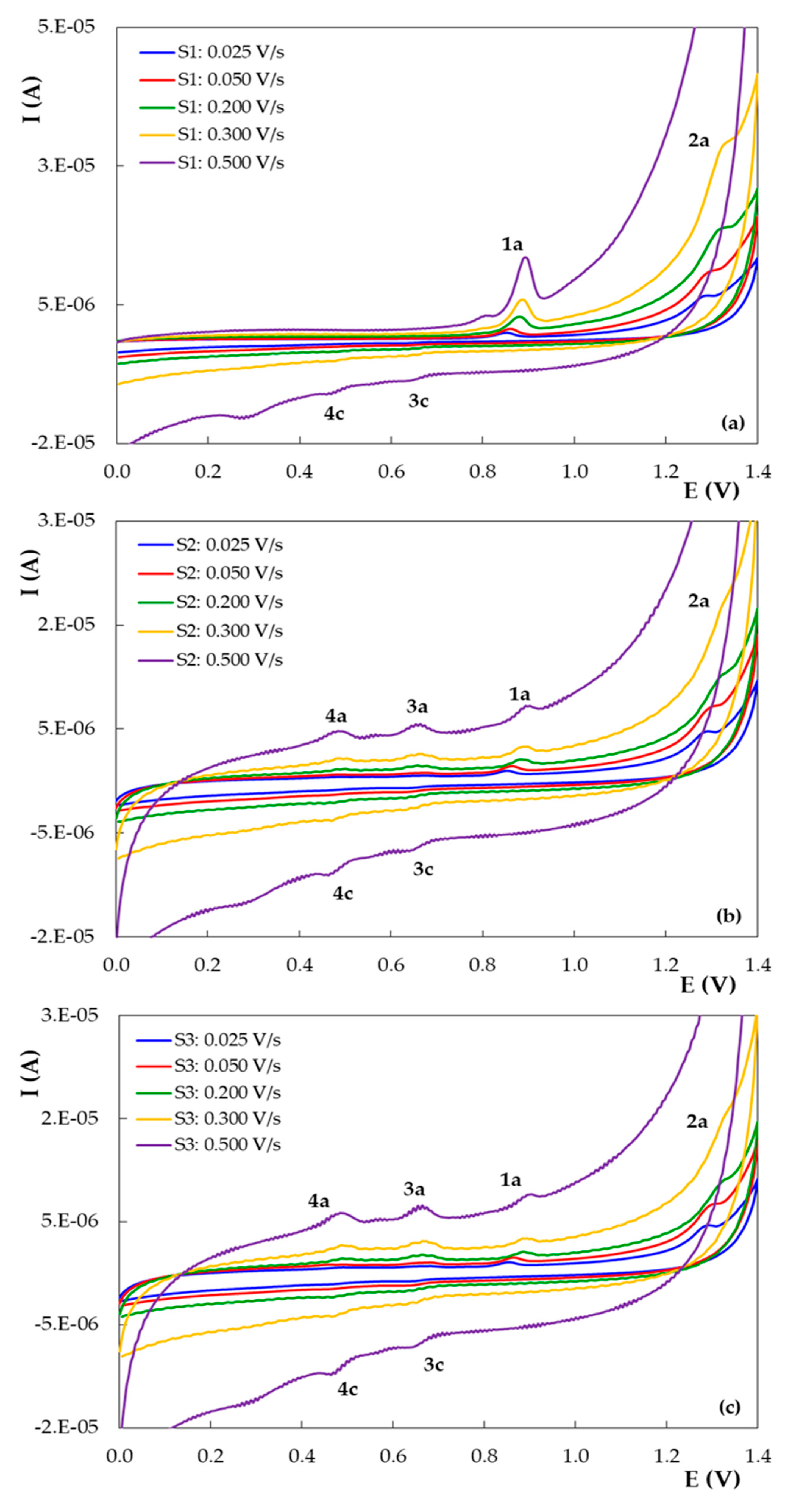
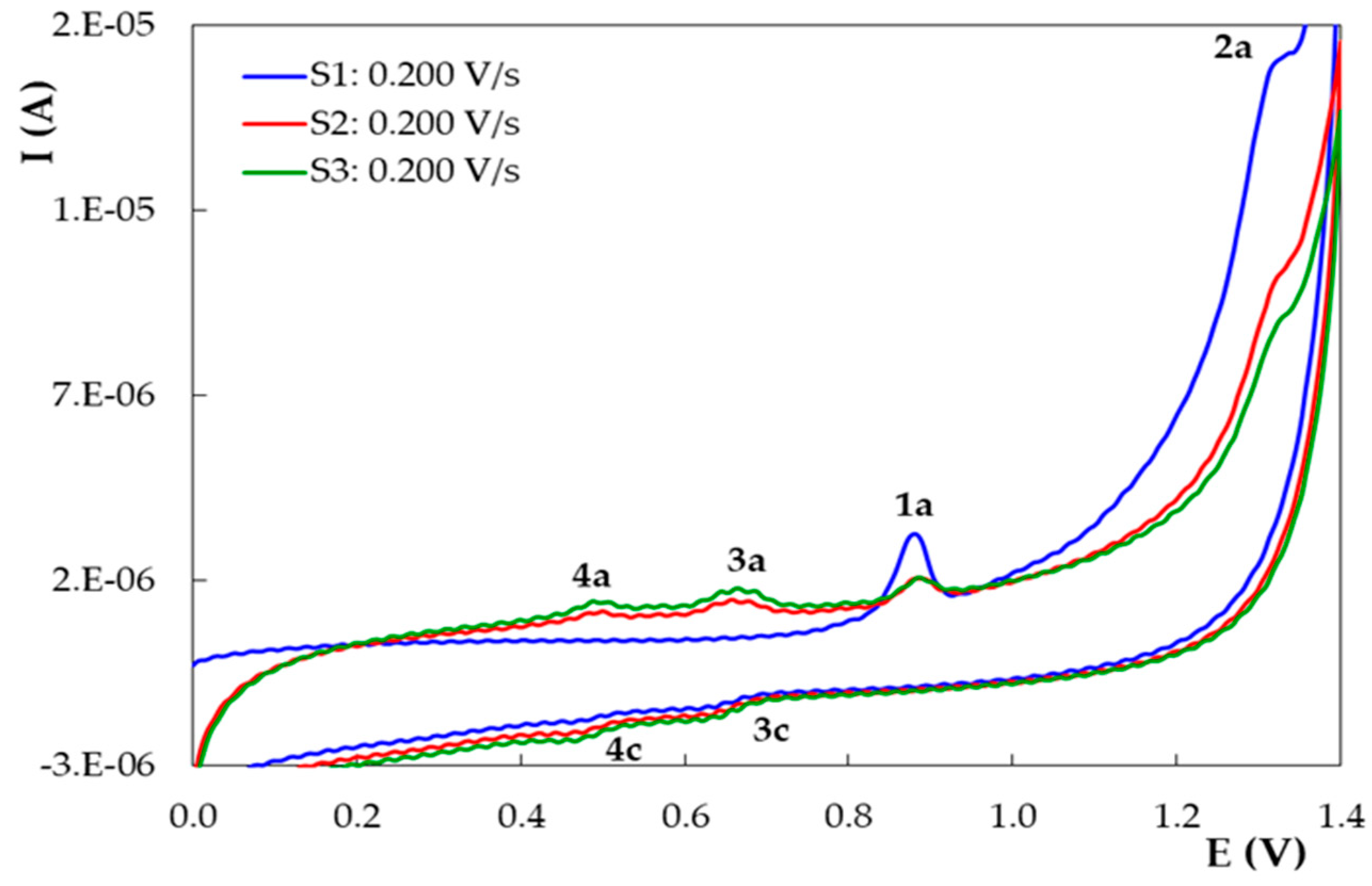
3.2. Voltammetric Behavior of DIO on the Pencil Graphite Electrode (PGE_H)
3.3. The Development and Validation of a Voltammetric Method for DIO Quantification with the Pencil Graphite Electrode
3.3.1. Linearity and Limits of Detection and Quantification
3.3.2. Repeatability
3.3.3. Selectivity Studies
3.3.4. Recovery Studies and Analytical Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Woźniak, M.; Feldo, M.; Kocki, J.; Szewczyk, K. Diosmin—Isolation Techniques, Determination in Plant Material and Pharmaceutical Formulations, and Clinical Use. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Jaldappagari, S. Binding of an anticancer Rutaceae plant flavonoid glycoside with calf thymus DNA: Biophysical and electrochemical studies. J. Lumin. 2013, 142, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Shi, W.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, L. Metabolism and pharmacological activities of the natural health-benefiting compound diosmin. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8472–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawmiller, D.; Habib, A.; Li, S.; Darlington, D.; Hou, H.; Tian, J.; Shytle, R.D.; Smith, A.; Giunta, B.; Mori, T. Diosmin reduces cerebral Aβ levels, tau hyperphosphorylation, neuroinflammation, and cognitive impairment in the 3 × Tg-AD mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 299, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, S.; Mirshekar, M.A. Diosmin is neuroprotective in a rat model of scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirshekar, M.A.; Fanaei, H.; Keikhaei, F.; Javan, F.S. Diosmin improved cognitive deficit and amplifiedbrain electrical activity in the rat model of traumatic brain injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Douglas Shytle, R.; Bai, Y.; Tian, J.; Hou, H.; Mori, T.; Zeng, J.; Obregon, D.; Town, T.; Tan, J. Flavonoid-mediated presenilin-1 phosphorylation reduces Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid production. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saghaei, E.; Boroujeni, S.N.; Safavi, P.; Boroujeni, Z.B.; Bijad, E. Diosmetin Mitigates Cognitive and Memory Impairment Provoked by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress in Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 5725361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldo, M.; Woźniak, M.; Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Sowa, I.; Kot-Waśik, A.; Aszyk, J.; Bogucki, J.; Zubilewicz, T.; Bogucka-Kocka, A. Influence of Diosmin Treatment on the Level of Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients with Chronic Venous Insufficiency. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2561705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Qing, L.-S.; Yong, L.; Xu, X.-S.; Hu, B.; Tang, M.-Q.; Xie, J. Determination of Flavonoid Glycosides by UPLC-MS to Authenticate Commercial Lemonade. Molecules 2019, 24, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, I.; Hadjmohammadi, M.R.; Peyrovi, M.; Iranshahi, M.; Barfi, B.; Babaei, A.B.; Dust, A.M. HPLC determination of hesperidin, diosmin and eriocitrin in Iranian lime juice using polyamide as an adsorbent for solid phase extraction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 56, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foudah, A.I.; Alam, P.; Anwer, K.; Yusufoglu, H.S.; Abdel-Kader, M.S.; Shakeel, F. A Green RP-HPTLC-Densitometry Method for the Determination of Diosmin in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Processes 2020, 8, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, Z.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. A Sensitive Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Diosmin Using Sodium Nitroprusside as a Chromogenic Reagent. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2011, 39, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunaciu, A.A.; Udristioiu, G.E.; Ruta, L.L.; Fleschin, S.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Determination of diosmin in pharmaceutical formulations using Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry. Saudi Pharm. J. 2009, 17, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, Z.; Bunaciu, A.A.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. A Spectrophotometric Method for Diosmin Determination. Open Chem. Biomed. Methods J. 2010, 3, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, D.; Tawakkol, S.M. Fluorimetric determination of diosmin and hesperidin in combined dosage forms and in plasma through complex formation with terbium. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2013, 51, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanustiak, P.; Mikelova, R.; Potesil, D.; Hodek, P.; Stiborova, M.; Kizek, R. Electrochemical behaviour of flavonoids on a surface of a carbon paste electrode. Biomed. Pap. 2005, 149 (Suppl. 1), 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, V.; Mikelova, R.; Hubalek, J.; Hanustiak, P.; Beklova, M.; Hodek, P.; Horna, A.; Trnkova, L.; Stiborova, M.; Zeman, L.; et al. Utilizing of Square Wave Voltammetry to Detect Flavonoids in the Presence of Human Urine. Sensors 2007, 7, 2402–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shahawi, M.S.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Mogy, T. Determination of trace levels of diosmin in a pharmaceutical preparation by adsorptive stripping voltammetry at a glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Sci. 2006, 22, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teradal, N.L.; Satpati, A.K.; Seetharamappa, J. Unzipped carbon nanotubes: Analytical and binding applications of semisynthetic phlebotropic flavonoid, diosmin. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 55550–55560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Sheng, K.; Zou, L.; Ye, B. Electrochemical behavior of Diosmin and its sensitive determination on ZrO2-NPs-coated poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)-functionalized graphene modified electrode. Microchem. J. 2018, 143, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diculescu, V.C.; Satana, H.E.; Gil, E.D.S.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Methoxylation and Glycosylation Effect on the Redox Mechanism of Citroflavones. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buleandra, M.; Popa, D.E.; David, I.G.; Bacalum, E.; David, V.; Ciucu, A.A. Electrochemical behavior study of some selected phenylurea herbicides at activated pencil graphite electrode. Electrooxidation of linuron and monolinuron. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annu; Sharma, S.; Jain, R.; Raja, A.N. Review—Pencil Graphite Electrode: An Emerging Sensing Material. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 167, 037501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buleandră, M.; Popa, D.E.; David, I.G.; Ciucu, A.A. A simple and efficient cyclic square wave voltammetric method for simultaneous determination of epinephrine and norepinephrine using an activated pencil graphite electrode. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calam, T.T. A modified pencil graphite electrode with 2-thiobarbituric acid for the efficient and cheap voltammetric sensing of 4-aminophenol in water samples and child syrup sample. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 98, 103809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, I.G.; Popa, D.-E.; Buleandra, M. Pencil Graphite Electrodes: A Versatile Tool in Electroanalysis. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2017, 2017, 1905968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathani, A.; Vishnu, N.; Sharma, C.S. Review—Pencil Graphite Electrodes as Platform for Enzyme and Enzyme-Like Protein Immobilization for Electrochemical Detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, I.G.; Bizgan, A.-M.C.; Popa, D.E.; Buleandra, M.; Moldovan, Z.; Badea, I.A.; Tekiner, T.A.; Basaga, H.; Ciucu, A.A. Rapid determination of total polyphenolic content in tea samples based on caffeic acid voltammetric behaviour on a disposable graphite electrode. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, I.G.; Buleandră, M.; Popa, D.E.; Bîzgan, A.-M.C.; Moldovan, Z.; Badea, I.-A.; Iorgulescu, E.E.; Tekiner, T.A.; Basaga, H. Voltammetric determination of polyphenolic content as rosmarinic acid equivalent in tea samples using pencil graphite electrodes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, I.G.; Popa, D.E.; Buleandra, M.; Moldovan, Z.; Iorgulescu, E.E.; Badea, I.A. Cheap pencil graphite electrodes for rapid voltammetric determination of chlorogenic acid in dietary supplements. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6537–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardım, Y.; Keskin, E.; Şentürk, Z. Voltammetric determination of mixtures of caffeine and chlorogenic acid in beverage samples using a boron-doped diamond electrode. Talanta 2013, 116, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Du, G.-H. Diosmin. In Natural Small Molecule Drugs from Plants; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Chandradhara, D.; De Tommasi, N. Comparative Bioavailability of Two Diosmin Formulations after Oral Administration to Healthy Volunteers. Molecules 2018, 23, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, M.C.; Buchanan, J.W. Observational Models of Graphite Pencil Materials. Comput. Graph. Forum 2000, 19, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, I.G.; Litescu, S.C.; Popa, D.E.; Buleandra, M.; Iordache, L.; Albu, C.; Alecu, A.; Penu, R.L. Voltammetric analysis of naringenin at a disposable pencil graphite electrode—Application to polyphenol content determination in citrus juice. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5763–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiorcea-Paquim, A.; Enache, T.A.; Gil, E.D.S.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Natural phenolic antioxidants electrochemistry: Towards a new food science methodology. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1680–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 5th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Edinburgh, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Guidelines for Standard Method Performance Requirements; Appendix F; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Blasco, A.J.; Rogerio, M.; González, M.; Escarpa, A. “Electrochemical Index” as a screening method to determine “total polyphenolics” in foods: A proposal. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 539, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
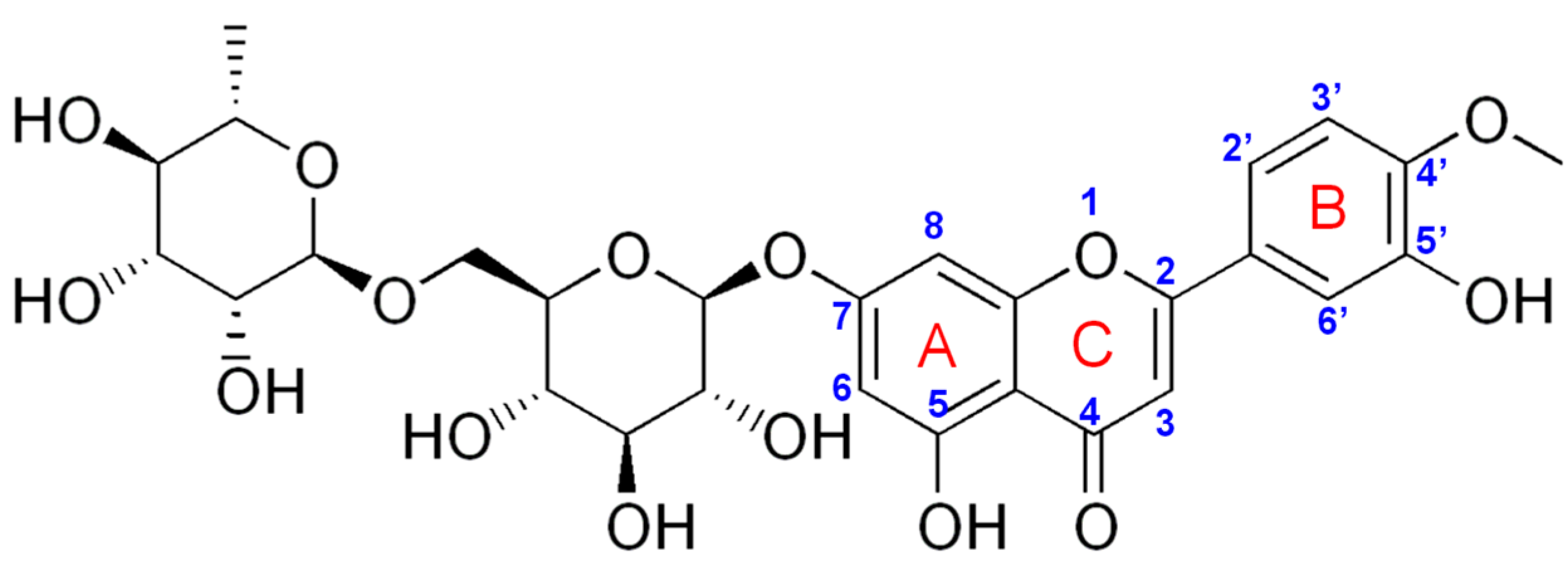
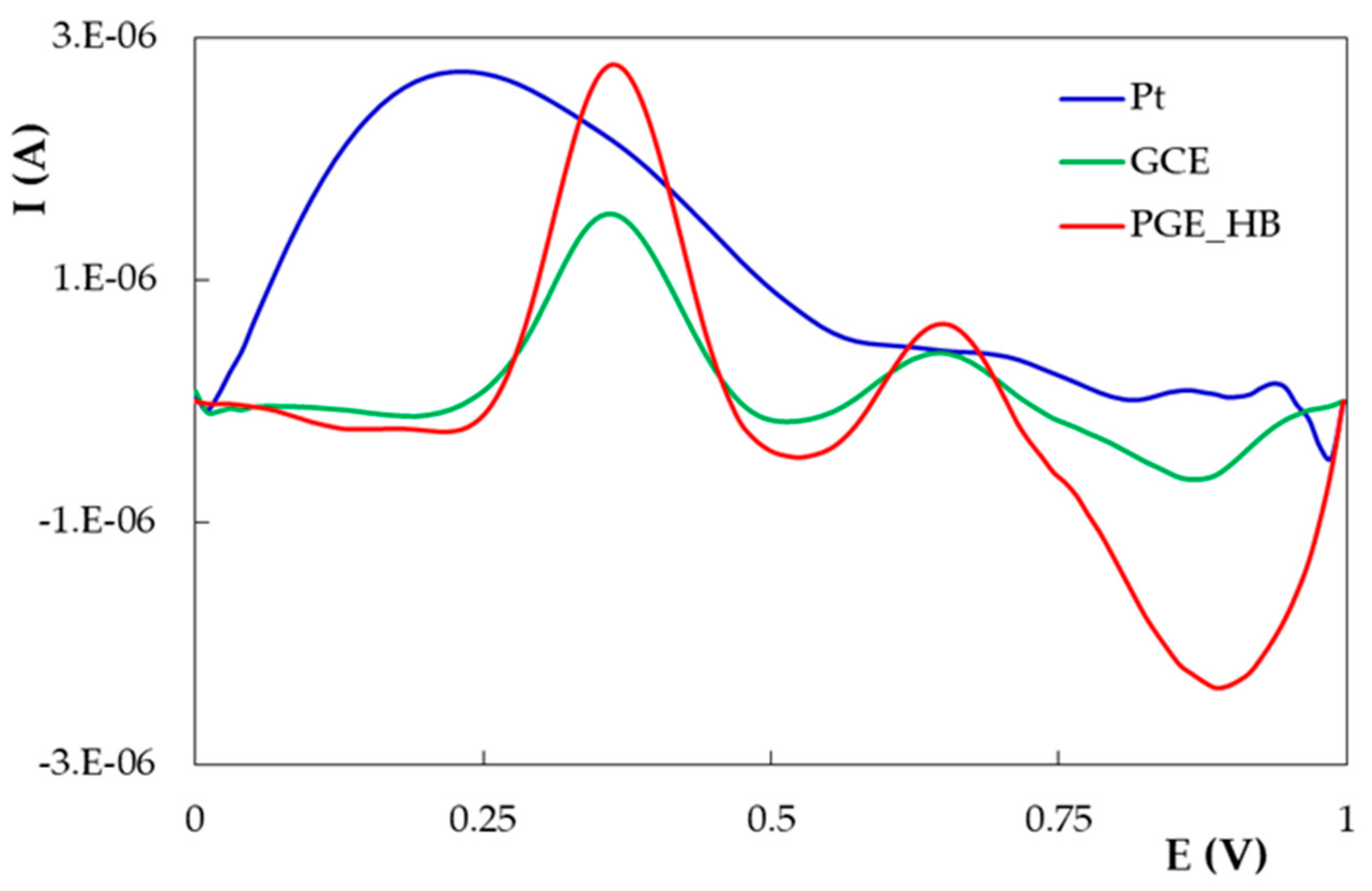
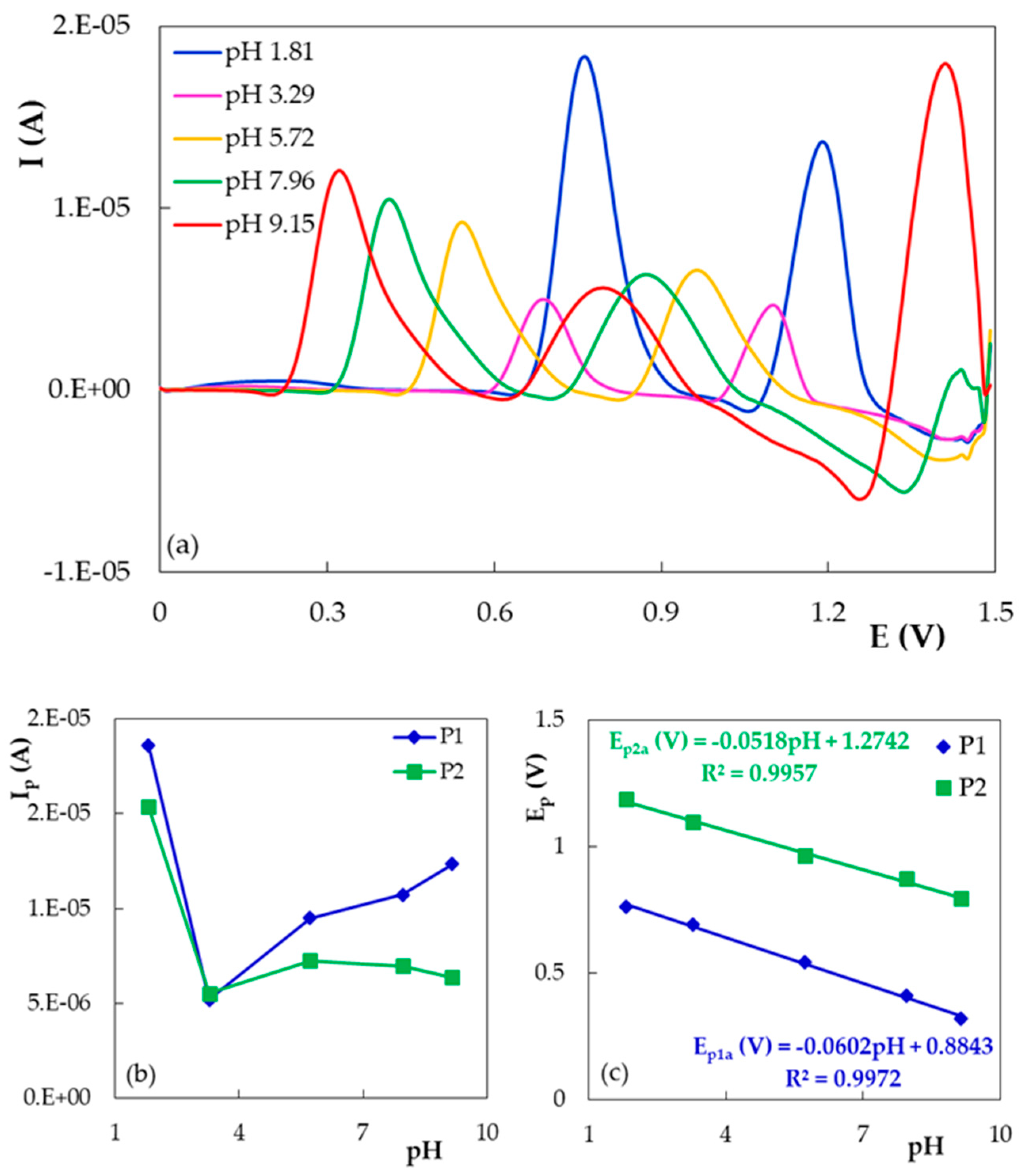
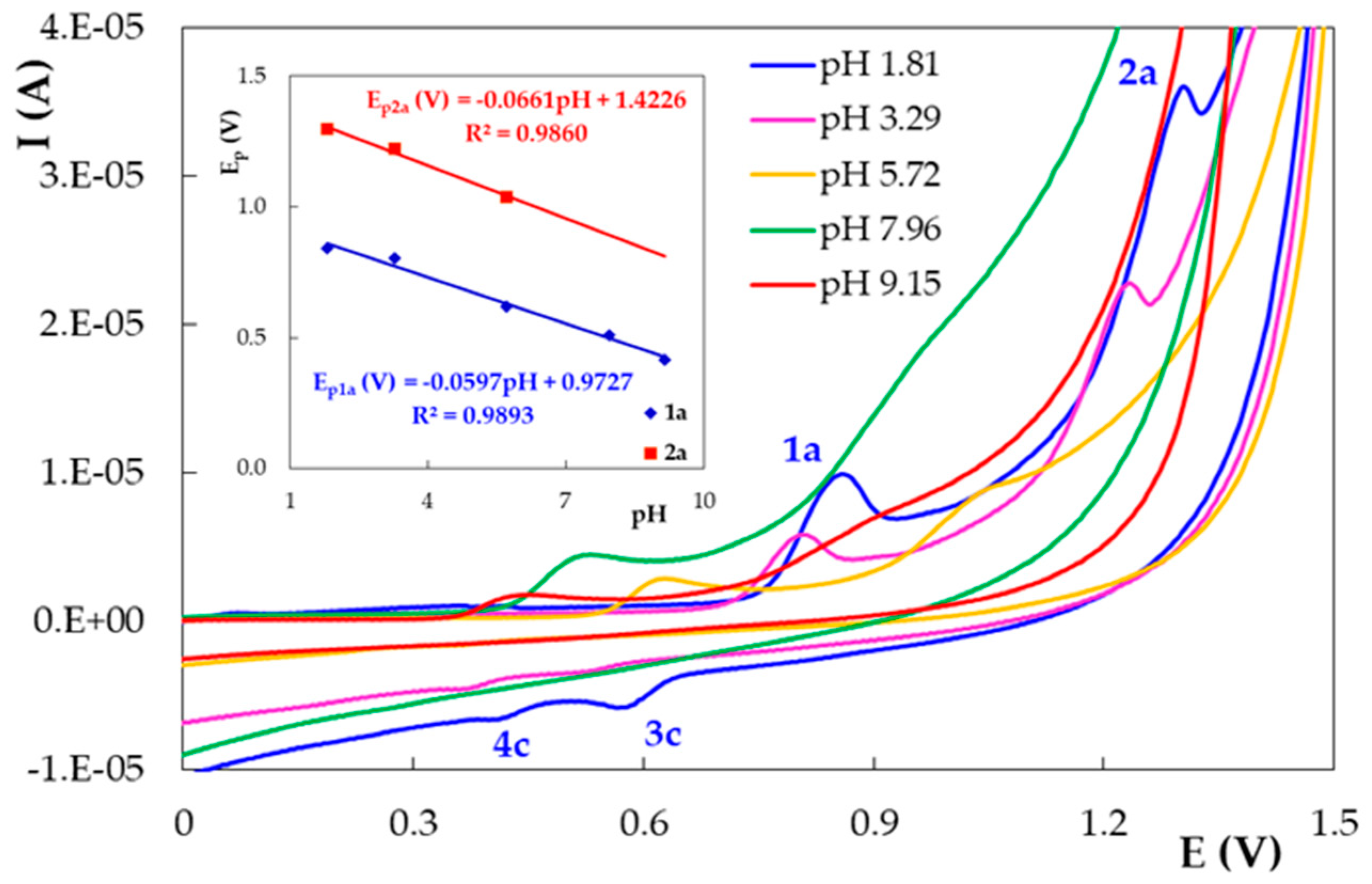

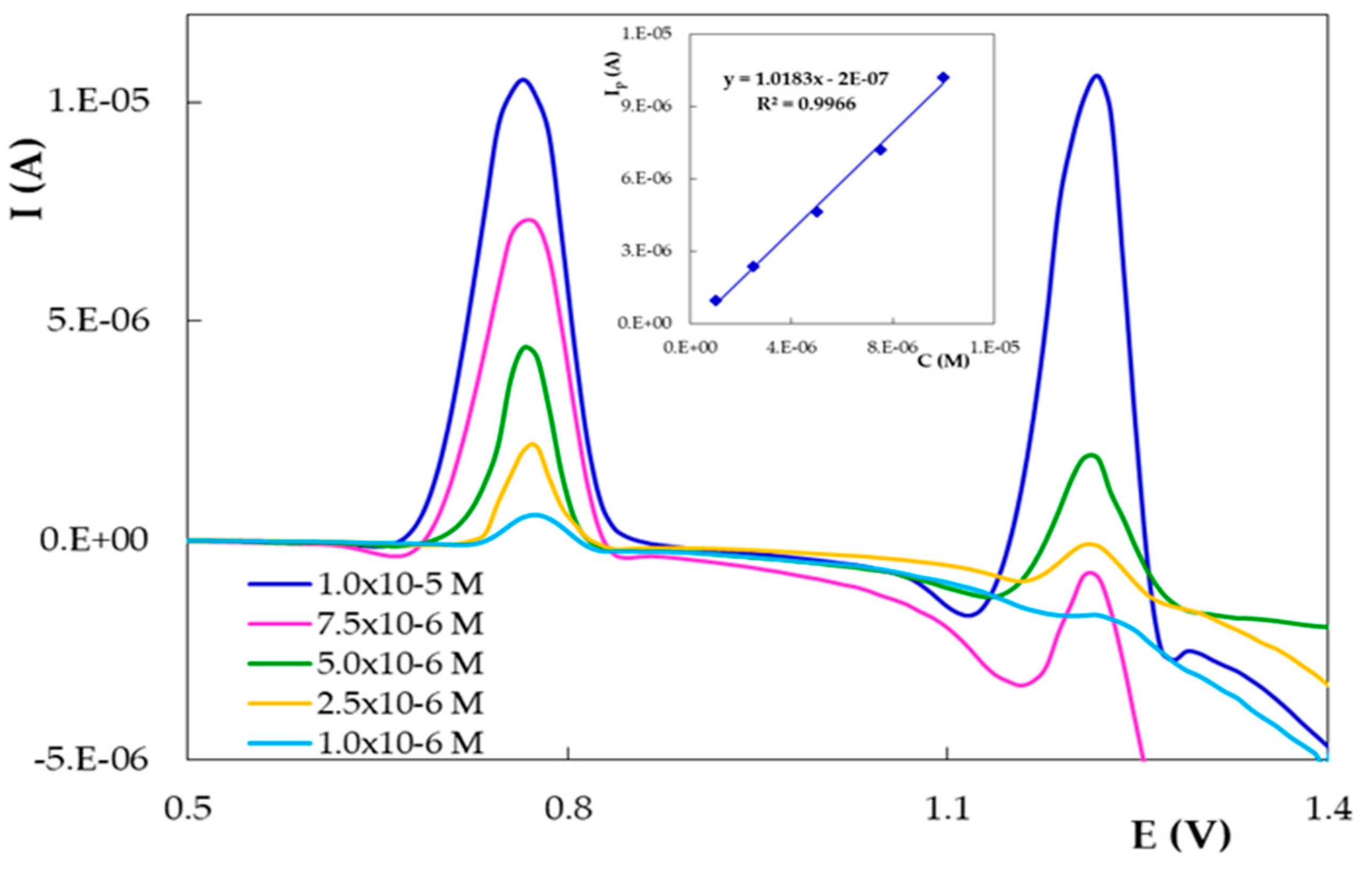
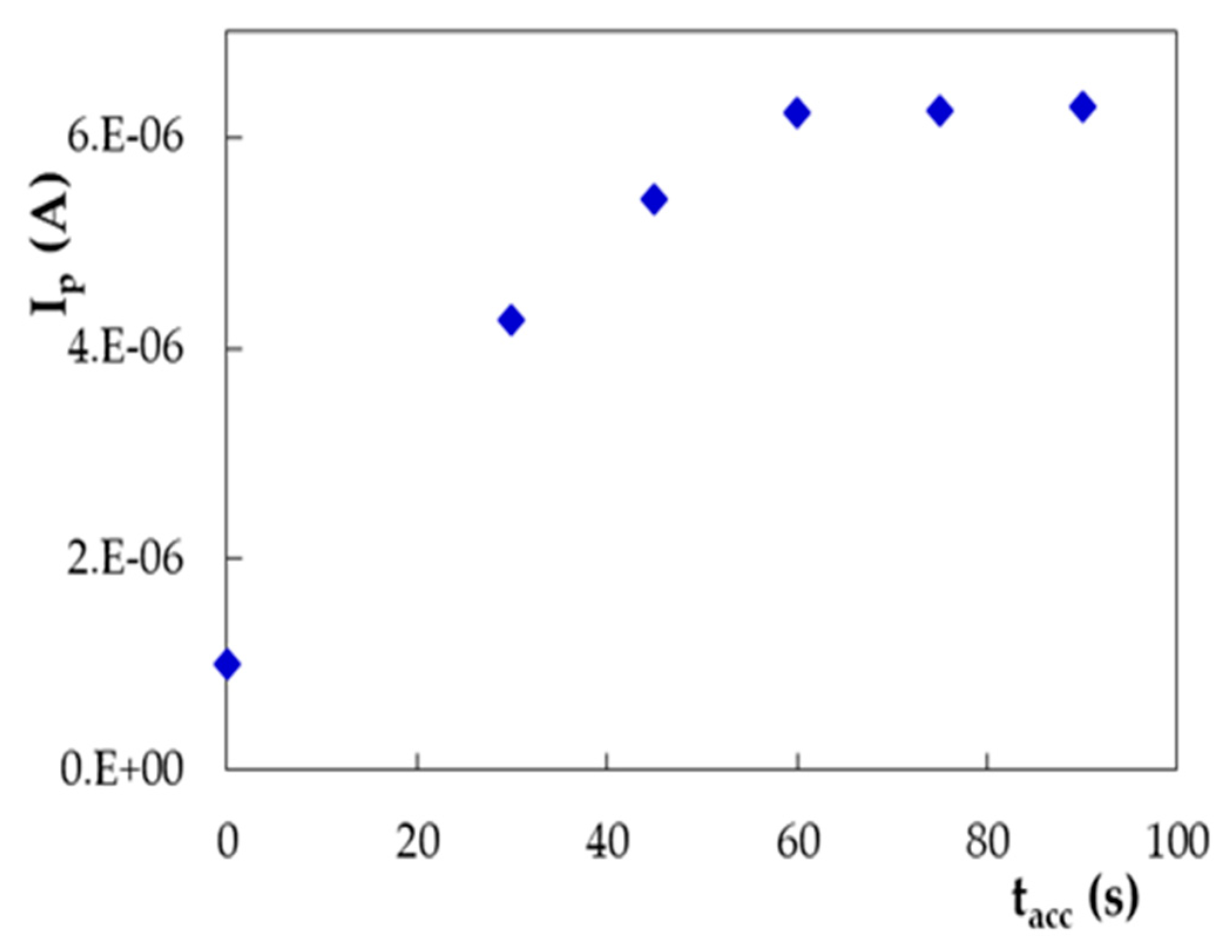
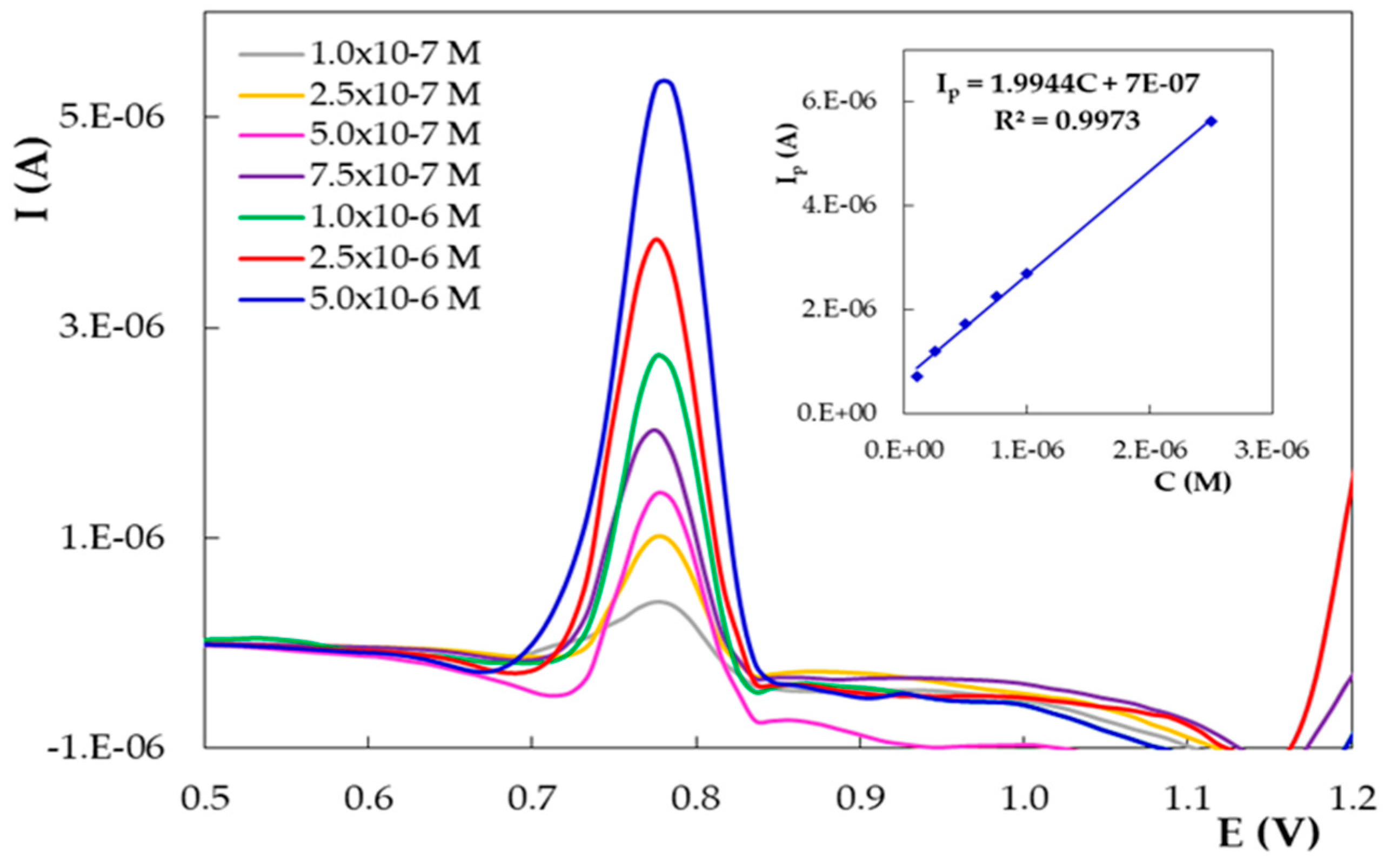

| PGE Type | Ep1 (V) | S1 (A × L/mol × cm2) | Ep2 (V) | S2 (A × L/mol × cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 mol/L NaOH | ||||
| 2H | 0.353 | 0.077 | 0.645 | 0.030 |
| H | 0.353 | 0.110 | 0.645 | 0.065 |
| HB | 0.363 | 0.113 | 0.655 | 0.028 |
| B | 0.383 | 0.065 | 0.655 | 0.024 |
| 2B | 0.383 | 0.049 | 0.655 | 0.026 |
| BRB pH 1.81 | ||||
| 2H | 0.755 | 0.331 | 1.178 | 0.279 |
| H | 0.775 | 0.343 | 1.178 | 0.337 |
| HB | 0.755 | 0.182 | 1.178 | 0.095 |
| B | 0.785 | 0.130 | 1.178 | 0.096 |
| 2B | 0.765 | 0.120 | 1.178 | 0.153 |
| Peak/Scan 1 | Ip = f(v) | Ip = f(v1/2) | logIp = f(logv) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | Intercept | R2 | Slope | Intercept | R2 | ||
| 1a/1 | 1 × 10−5 | 3 × 10−7 | 0.9889 | Non linear | 0.7669 | −5.0028 | 0.9861 |
| 2a/1 | 3 × 10−6 | 2 × 10−7 | 0.9974 | Non linear | 0.6662 | −5.5863 | 0.9999 |
| 3c/1 | 9 × 10−7 | 2 × 10−8 | 0.9818 | Non linear | 0.7747 | −6.1465 | 0.9826 |
| 3a/2 | 2 × 10−6 | 4 × 10−8 | 0.9933 | Non linear | 0.8556 | −5.7936 | 0.9850 |
| 4a/2 | 9 × 10−7 | 9 × 10−8 | 0.9841 | Non linear | 0.8151 | −6.0323 | 0.9861 |
| 4c/2 | 1 × 10−6 | 9 × 10−8 | 0.9804 | Non linear | 0.9825 | −5.9052 | 0.9847 |
| Electrode | Technique | Linear Range (mol/L) | LoD (mol/L) | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPE | SWV | - | 2.66 × 10−6 | - | [17] |
| CPE | SWV | 1.25 × 10−5 to 2.00 × 10−4 | 2.66 × 10−6 | human urine | [18] |
| GCE | AdSDPV | 5.00 × 10−8 to 9.00 × 10−6 | 3.50 × 10−8 | pharmaceuticals, serum | [19] |
| ErGONRs/GCE | SWV DPV | 2.50 × 10−8 to 3.48× 10−6 5.10 × 10−8 to 3.92 × 10−6 | 1.10 × 10−8 1.50 × 10−8 | pharmaceuticals | [20] |
| ZrO2-PDDA-Gr/GCE | DPV | 5.00 × 10−9 to 2.00 × 10−6 | 2.00 × 10−9 | fresh lemon leaves, tablets | [21] |
| PGE | DPV AdSDPV | 1.00 × 10−6 to 1.00 × 10−5 1.00 × 10−7 to 2.50 × 10−6 | 2.76 × 10−7 7.42 × 10−8 | dietary supplements | This work |
| Technique | DPV | AdSDPV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (mol/L) | 1.00 × 10−6 | 5.00 × 10−6 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 5.00 × 10−7 | 2.50 × 10−6 |
| RSD%intraday | 5.72 | 3.21 | 1.96 | 4.84 | 3.91 | 2.21 |
| RSD %interday | 6.05 | 3.89 | 2.45 | 6.01 | 4.67 | 3.15 |
| Claimed DIO content (mg) | 600 |
| Found DIO content by DPV ± SD (mg) | 599.22 ± 29.31 |
| RSD, % | 4.89 |
| Average %R ± SD | 99.87 ± 4.88 |
| RSD, % | 4.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
David, I.G.; Oancea, A.-G.; Buleandră, M.; Popa, D.E.; Iorgulescu, E.E.; Ciobanu, A.M. Disposable Pencil Graphite Electrode for Diosmin Voltammetric Analysis. Micromachines 2021, 12, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040351
David IG, Oancea A-G, Buleandră M, Popa DE, Iorgulescu EE, Ciobanu AM. Disposable Pencil Graphite Electrode for Diosmin Voltammetric Analysis. Micromachines. 2021; 12(4):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040351
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavid, Iulia Gabriela, Alexandra-Gabriela Oancea, Mihaela Buleandră, Dana Elena Popa, Emilia Elena Iorgulescu, and Adela Magdalena Ciobanu. 2021. "Disposable Pencil Graphite Electrode for Diosmin Voltammetric Analysis" Micromachines 12, no. 4: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040351
APA StyleDavid, I. G., Oancea, A.-G., Buleandră, M., Popa, D. E., Iorgulescu, E. E., & Ciobanu, A. M. (2021). Disposable Pencil Graphite Electrode for Diosmin Voltammetric Analysis. Micromachines, 12(4), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040351










