Research on the Shearer Positioning Method Based on the MEMS Inertial Sensors/Odometer Integrated Navigation System and RTS Smoother
Abstract
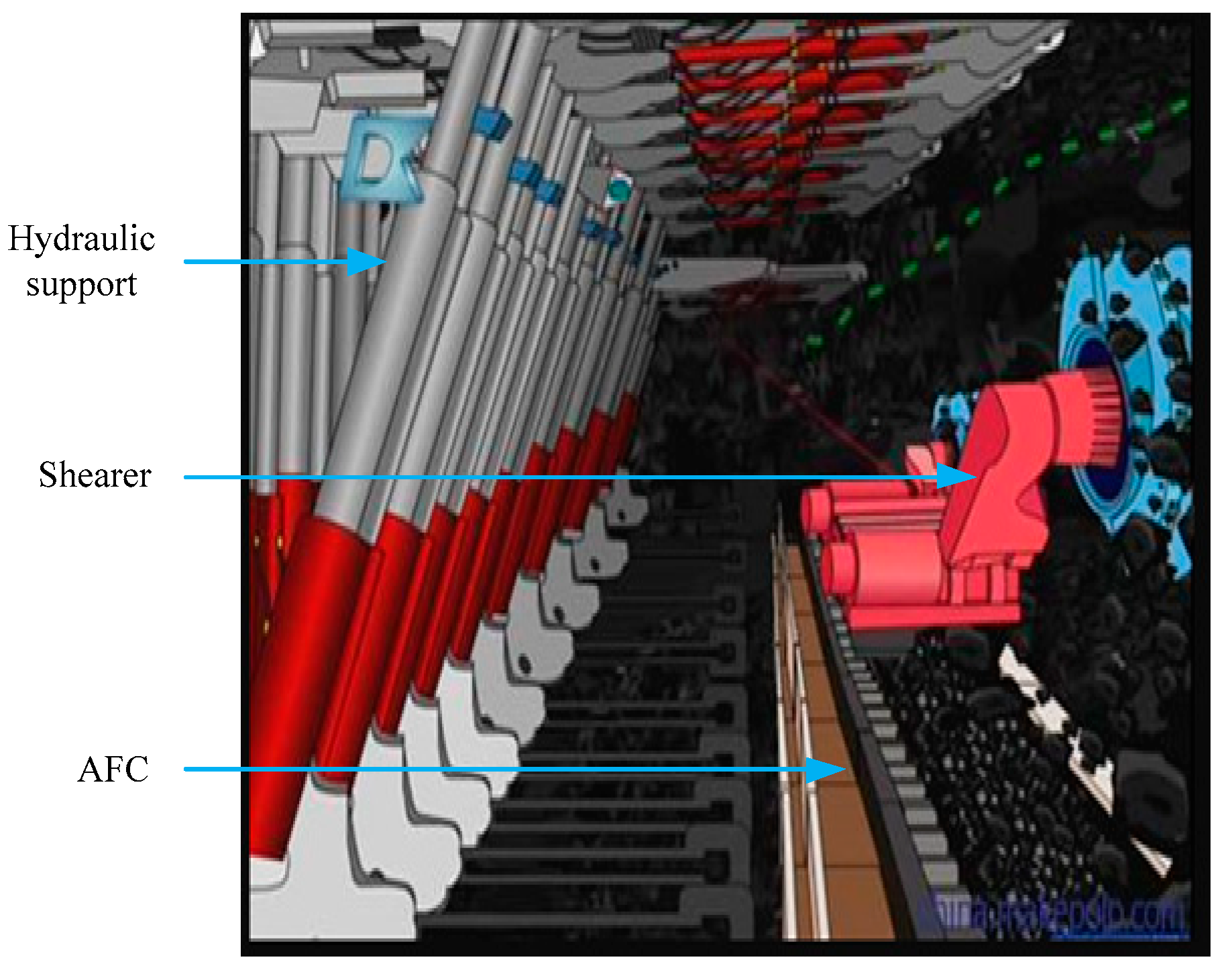
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Models of Velocity and Position
2.1. Measured Velocity Model
2.2. Measured Position Model
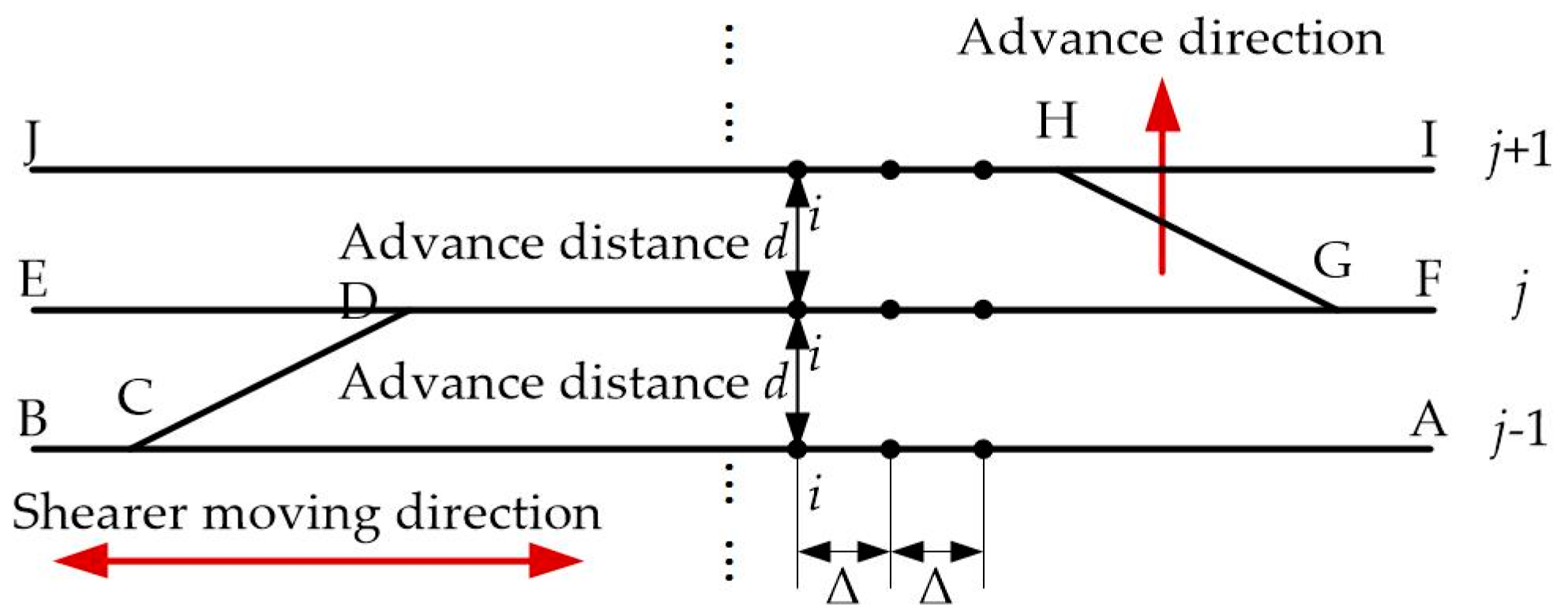
- To avoid additional surveying and mapping, the initial positions of the remaining optimal points can be obtained using the position estimates of the integrated system in the first cutting cycle. This initial value assignment method is mentioned in [1].
3. Integrated Navigation and RTS Smoother Models
3.1. Error State Equation of Integrated Navigation System
3.2. Measurement Equations of Velocity and Position
3.3. Observability Analysis of Integrated System
3.3.1. Observability Analysis Based on the Velocity Measurement
- The velocity errors, , are observable, and the estimation accuracy is related to the estimation degree of other error states.
- The position errors, , are unobservable, but the estimation accuracy will still be improved with the effective estimation of the velocity errors.
- The acceleration and deceleration process of the shearer is the premise of exciting the error states , , and , which contribute to the positioning errors. The error is unobservable.
- The error is observable. The separation of and , and the distinction of and , improving the estimation accuracy of , depend on the turning motion of the shearer. The azimuth error, , is directly related to the lateral positioning error, thus, restricting the estimation accuracy of error .
3.3.2. Observability Analysis Based on the Position Measurement
3.4. RTS Smoothing
- Backward Smoothing Initialization
- 2.
- Backward Smoothing Update
4. Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Ge, S. Dynamic precise positioning method of shearer based on closing path optimal estimation model. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q. A joint positioning and attitude solving method for shearer and scraper conveyor under complex conditions. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 3793412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Li, W.; Luo, C.; Zhang, J.; Si, Z. Research on error compensation property of strapdown inertial navigation system using dynamic model of shearer. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2045–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, F. Information-reusing alignment technology for rotating inertial navigation system. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S. Kalman Filtering and Integrated Navigation Principle, 3rd ed.; Northwestern Polytechnical University Press: Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhu, H.; Ze, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, C. IMU-aided ultra-wideband based localization for coal mine robots. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Shenyang, China, 2 August 2019; pp. 256–268. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Wang, S.; Ge, S.; Liu, W. Improving positioning accuracy of UWB in complicated underground NLOS scenario using calibration, VBUKF, and WCA. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, M.; Reid, D.; Ralston, J. Control of automated mining machinery using aided inertial navigation. In Machine Vision and Mechatronics in Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, M.; Thompson, J.; Reid, P.; Reid, D. High accuracy inertial navigation for underground mining machinery. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Seoul, Korea, 20–24 August 2012; pp. 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Zhao, C. A comparison of ZUPT estimation methods for inertial survey systems. J. Chin. Inertial Technol. 1995, 3, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Inertial navigation algorithm aided by motion constraints of vehicle. J. Chin. Inertial Technol. 2012, 20, 640–643. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Li, W.; Luo, T.; Luo, C.; Liang, H.; Zhang, H.; Gu, Y. Research on the strategy of motion constraint-aided ZUPT for the SINS positioning system of a shearer. Micromachines 2017, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, S.; Su, Z.; Li, A.; Wang, S.; Hao, S.; Liu, W.; Meng, L. Study on the positioning and orientation of a shearer based on geographic information system. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 40, 2503–2508. [Google Scholar]
- Ralston, J.; Reid, D.; Hargrave, C.; Hainsworth, D. Sensing for advancing mining automation capability: A review of underground automation technology development. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, A. Shape detection of scraper conveyor based on shearer trajectory. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 40, 2514–2521. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Ge, S. Dynamic zero-velocity update technology to shearer inertial navigation positioning. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 578–583. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Zhou, Q.; Cui, X.; Qin, Y. Research on SINS/DR integrated navigation system algorithm. Electron. Des. Eng. 2013, 21, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, Q.; Fu, M.; Zhang, J. INS in-motion alignment for land-vehicle aided by odometer. J. Chin. Inertial Technol. 2012, 20, 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Miao, L.; Shao, H. Adaptive two-stage kalman filter for SINS/odometer integrated navigation systems. J. Navig. 2016, 70, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, M.; Wang, Z. Precise shearer positioning technology using shearer motion constraint and magnetometer aided SINS. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1679014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q. Key Technologies for Vehicular Positioning and Orientation System. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, S.; Li, A.; Wang, S.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, S. Effects of shearer inertial navigation installation noncoincidence on shearer positioning error. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 40, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Zhang, R.; Fang, J. Fixed-interval smoother and its applications in integrated navigation system. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2012, 20, 687–693. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Ye, W.; Liu, Y. Variational bayesian cubature RTS smoothing for transfer alignment of DPOS. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 3270–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Chang, H. An ANN embedded RTS smoother for an INS/GPS integrated positioning and orientation system. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2011, 11, 2633–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Fang, J. Application of SVD-based RTS optimal smoothing algorithm to POS for airborne SAR motion compensation. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2009, 30, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, W.; Sun, F.; Liu, S. Fixed-interval smoothing post-processing algorithms based on tightly coupled carrier phase DGNSS/INS method. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2015, 35, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Wu, J. Fixed-interval smoothing post-processing algorithms for low-cost MEMS-based integrated navigation system. J. Chin. Inertial Technol. 2017, 25, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J. Application of optimal smoothing algorithm to the post-mission analysis of GPS/SINS integrated system. J. Proj. Rocket. Missiles Guid. 2004, 24, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, K.; Duong, T.; Liao, J.; Lai, Y.; Chang, C.; Cai, J.; Huang, S. On-line smoothing for an integrated navigation system with low-cost MEMS inertial sensors. Sensors 2012, 12, 17372–17389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Kong, X. Zero velocity update with stepwise smoothing for inertial pedestrian navigation. In Proceedings of the International Global Navigation Satellite Systems Society, Outrigger Gold Coast, Australia, 16–18 July 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Xue, L.; Fan, H.; Yang, X. SINS/Odometer/Doppler radar high-precision integrated navigation method for land vehicle. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 15090–15100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Ge, S. Effects of initial alignment error and installation noncoincidence on the shearer positioning accuracy and calibration method. J. China Coal Soc. 2017, 42, 789–795. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Guan, B. High-accuracy SINS/LDV integration for long-distance land navigation. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron 2018, 23, 2952–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MTi Documentation Overview. Available online: https://mtidocs.xsens.com/output-specifications$gyroscopes (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- FindCM. Available online: https://www.qxwz.com/products/findcm?spm=102.markettrials.menu1sub0.0.0.07oal9q56tp6 (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Fu, Q. Research on the shearer positioning method based on SINS and LiDAR with velocity and absolute position constraints. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Initial errors | [0.3;0.3;1] | |
| Initial velocity errors (m/s) | [0.01;0.01;0.01] | |
| Initial position errors (m) | [0.05;0.05;0.05] | |
| Gyroscope | ) | 720 |
| ) | 0.6 | |
| Accelerometer | ) | 3 |
| ) | 0.08 |
| Gyroscope | Accelerometer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Par 1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Par 2 | 200 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Par 3 | 300 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Par 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Par 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Par 6 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Par 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Par 8 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Par 9 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Par 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Par 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Par 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Cutting Cycle | SEP (m) | |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional method without compensation | A1 | 1.75 |
| A2 | 1.99 | |
| A3 | 2.28 | |
| A4 | 2.31 | |
| Traditional method with compensation | A1 | 0.21 |
| A2 | 0.29 | |
| A3 | 0.33 | |
| A4 | 0.17 | |
| Proposed method | A1 | 0.50 |
| A2 | 0.32 | |
| A3 | 0.13 | |
| A4 | 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Guan, B.; Wei, D.; Fu, Q. Research on the Shearer Positioning Method Based on the MEMS Inertial Sensors/Odometer Integrated Navigation System and RTS Smoother. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121527
Zheng J, Li S, Liu S, Guan B, Wei D, Fu Q. Research on the Shearer Positioning Method Based on the MEMS Inertial Sensors/Odometer Integrated Navigation System and RTS Smoother. Micromachines. 2021; 12(12):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121527
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Jiangtao, Sihai Li, Shiming Liu, Bofan Guan, Dong Wei, and Qiangwen Fu. 2021. "Research on the Shearer Positioning Method Based on the MEMS Inertial Sensors/Odometer Integrated Navigation System and RTS Smoother" Micromachines 12, no. 12: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121527
APA StyleZheng, J., Li, S., Liu, S., Guan, B., Wei, D., & Fu, Q. (2021). Research on the Shearer Positioning Method Based on the MEMS Inertial Sensors/Odometer Integrated Navigation System and RTS Smoother. Micromachines, 12(12), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121527







