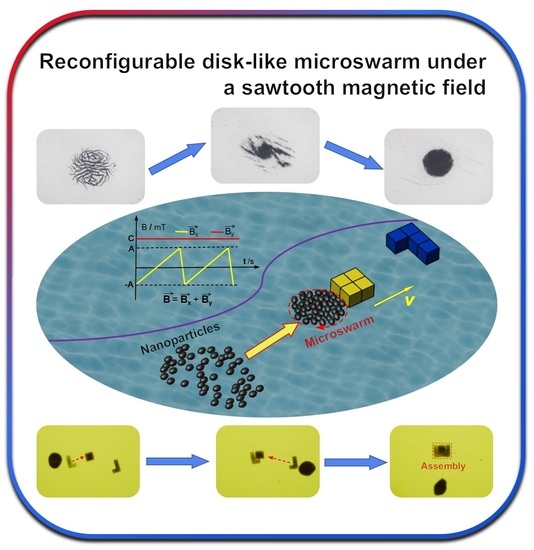
Reconfigurable Disk-like Microswarm under a Sawtooth Magnetic Field
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Materials
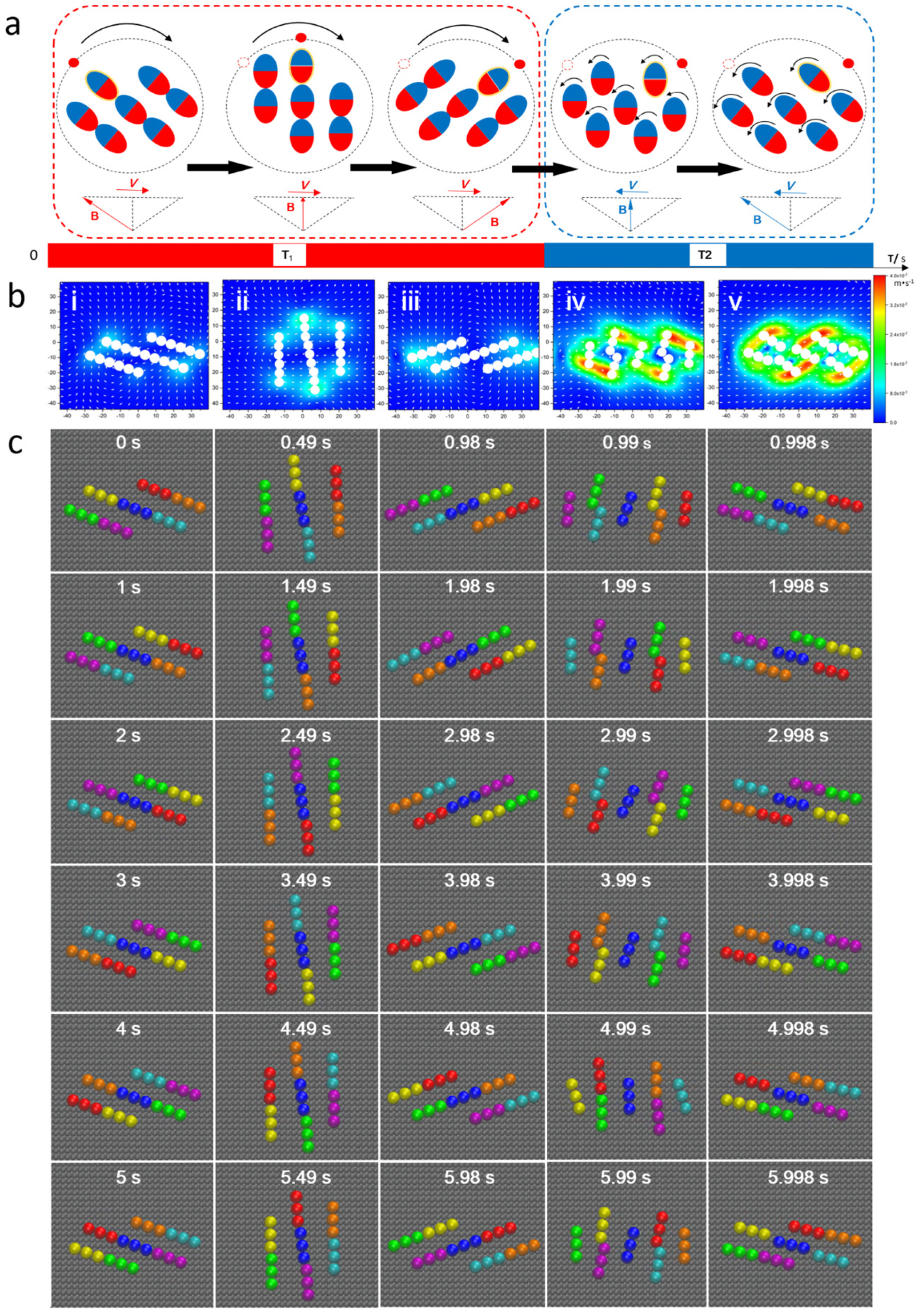
2.3. Computer Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
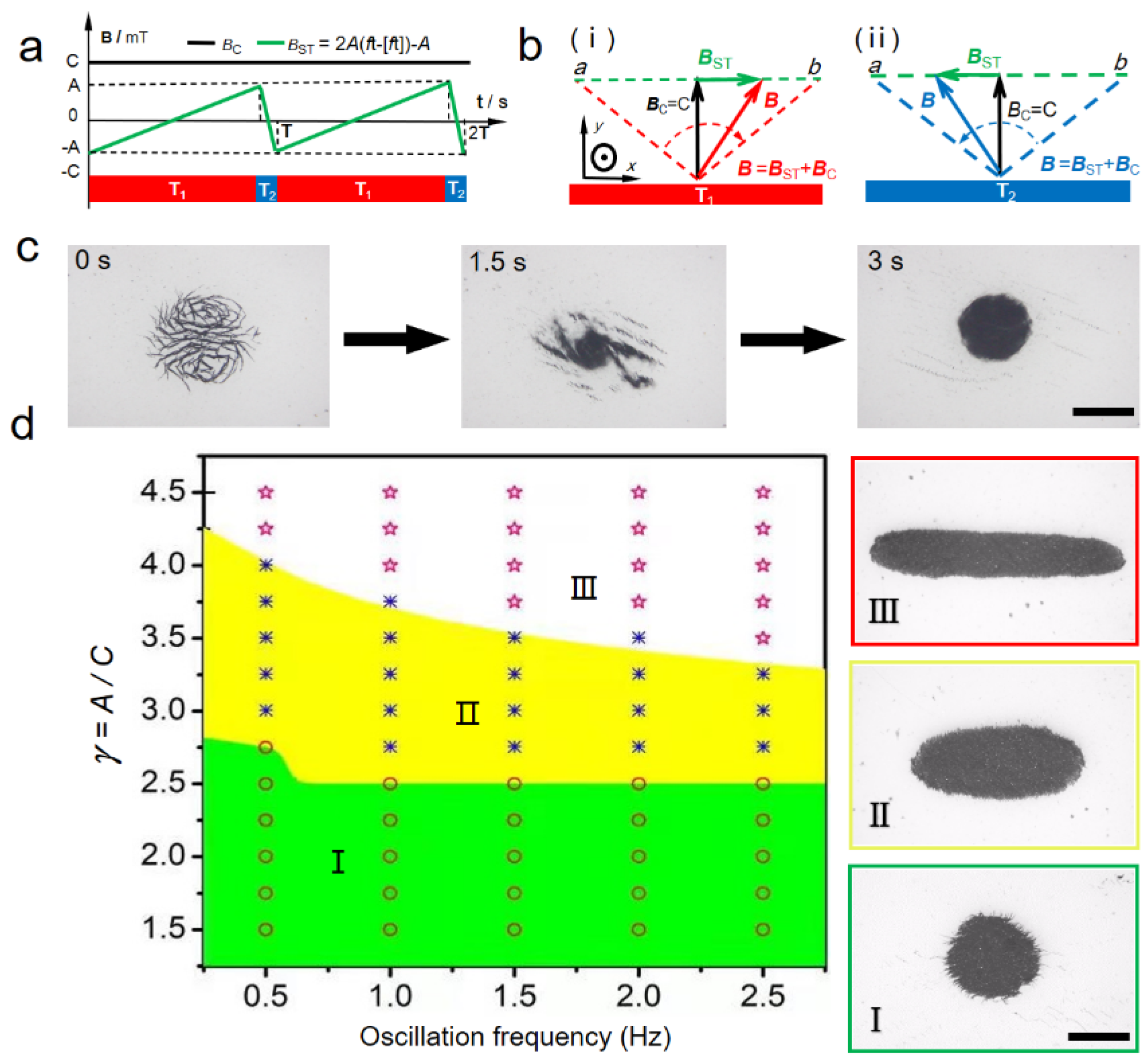
3.1. Formation of a Disk-like Microswarm
3.2. Controllable Transformation of Swarm Pattern
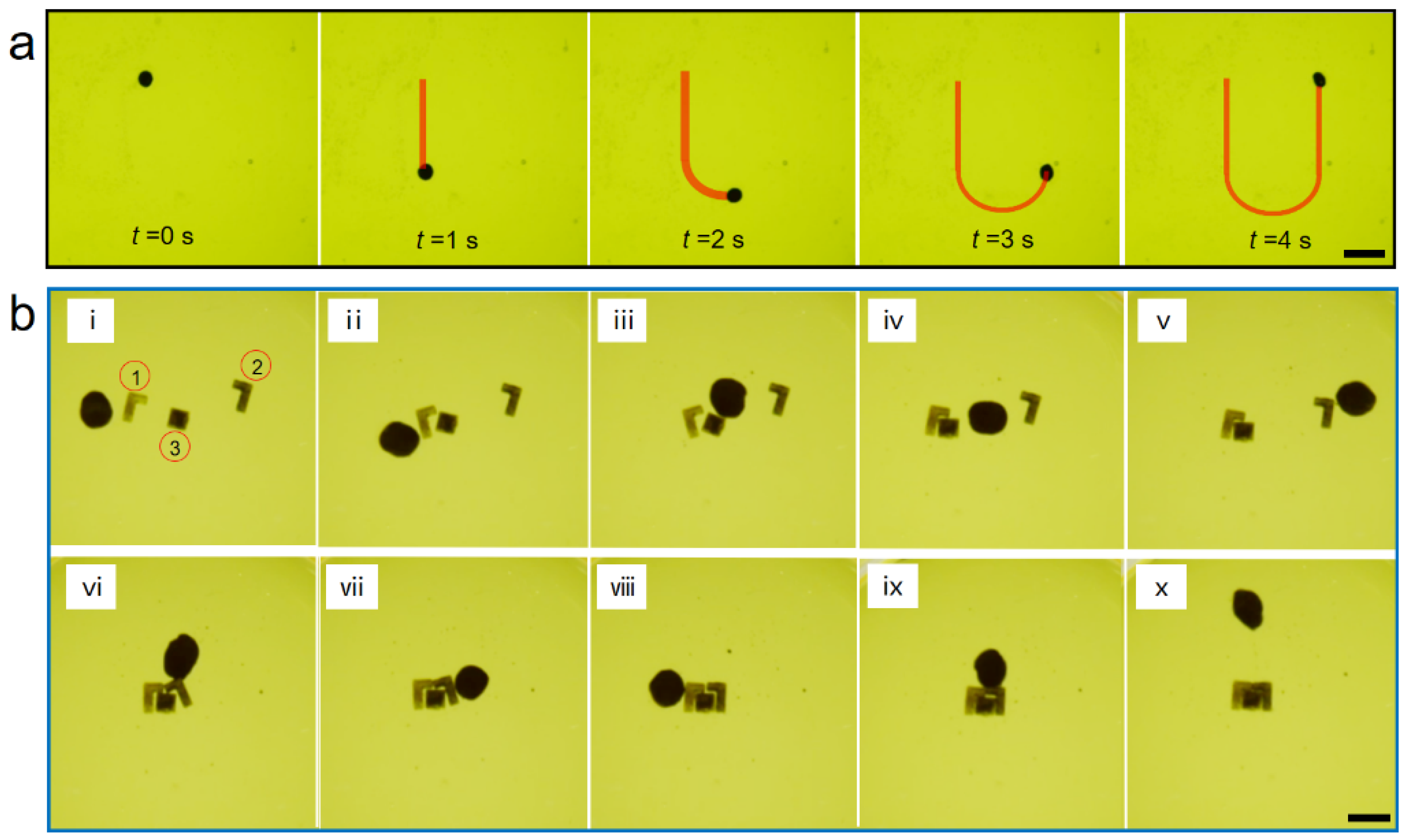
3.3. Practical Applications of Micromanipulation and Microassembly
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Felfoul, O.; Mohammadi, M.; Taherkhani, S.; Lanauze, D.; Xu, Y.; Loghin, D.; Essa, S.; Jancik, S.; Houle, D.; Lafleur, M.; et al. Magne-to-aerotactic bacteria deliver drug-containing nanoliposomes to tumour hypoxic regions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelblum, A.; Pinkoviezky, I.; Fonio, E.; Ghosh, A.; Gov, N.; Feinerman, O. Ant groups optimally amplify the effect of transiently informed individuals. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, C.; Theraulaz, G.; Deneubourg, J.-L. Self-assemblages in insect societies. Insectes Sociaux 2002, 49, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, D.; Balasubramanian, S.; Wang, J. Chemically Triggered Swarming of Gold Microparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servant, A.; Qiu, F.; Mazza, M.; Kostarelos, K.; Nelson, B.J. Controlled In Vivo Swimming of a Swarm of Bacteria-Like Microrobotic Flagella. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melde, K.; Mark, A.; Qiu, T.; Fischer, P. Holograms for acoustics. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 537, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovev, A.A.; Mei, Y.; Schmidt, O.G. Catalytic Microstrider at the Air-Liquid Interface. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4340–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Medina-Sánchez, M.; Maitz, M.F.; Werner, C.; Schmidt, O.G. Sperm Micromotors for Cargo Delivery through Flowing Blood. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2982–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joh, H.; Fan, D.E. Materials and Schemes of Multimodal Reconfigurable Micro/Nanomachines and Robots: Review and Perspective. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Xing, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Du, X. Advanced micro/nanomotors for enhanced bioadhesion and tissue penetration. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 23, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhou, Q.; Vincent, M.; Deng, Y.; Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, T.; Tang, T.; Bian, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Multifunctional biohybrid magnetite microrobots for imaging-guided therapy. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaaq1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.; Yin, T.; Li, S.; Xu, T.; Ma, A.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Y.; Lai, Z.; Lv, Y.; Pan, H.; et al. Targeted Cancer Therapy: Sequential Magneto-Actuated and Optics-Triggered Biomicrorobots for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, P2008262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xu, T.; Lu, Z.; Vong, C.I.; Zhang, L. On-Demand Disassembly of Paramagnetic Nanoparticle Chains for Microrobotic Cargo Delivery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, B.; Du, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Ultra-extensible ribbon-like magnetic microswarm. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Bloom, M.; Bae, S.C.; Luijten, E.; Granick, S. Linking synchronization to self-assembly using magnetic Janus colloids. Nature 2012, 491, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snezhko, A.; Aranson, I.S. Magnetic manipulation of self-assembled colloidal asters. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Sun, M.; Fan, X.; Lin, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Dong, L.; He, Q. Reconfigurable magnetic microrobot swarm: Multimode transformation, locomotion, and manipulation. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaav8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Pei, A.; Dong, R.; Wang, J. Catalytic Iridium-Based Janus Micromotors Powered by Ultralow Levels of Chemical Fuels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 2276–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.X.; Wang, N.; Lim, Y.D.; Miao, J. Chemical reaction dependency, magnetic field and surfactant effects on the propulsion of disk-like micromotor and its application for E. coli transportation. Nano Select. 2020, 1, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Miao, J.; Grüber, G. Disk-like nanojets with steerable trajectory using platinum nozzle nanoengines. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3399–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Duan, W.; Sen, A.; Mallouk, T.E. Catalytically powered dynamic assembly of rod-shaped nanomotors and passive tracer particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17744–17749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bricard, A.; Caussin, J.-B.; Das, D.; Savoie, C.; Chikkadi, V.; Shitara, K.; Chepizhko, O.; Peruani, F.; Saintillan, D.; Bartolo, D. Emergent vortices in populations of colloidal rollers. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Han, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.Y.J.Z.C.; Luijten, E.; Granick, S. Reconfiguring active particles by electrostatic imbalance. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Wang, S.; Wu, D.T.; Wu, N. Electric-field–induced assembly and propulsion of chiral colloidal clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6307–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, F.; Jin, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L. Light-Driven Hovering of a Magnetic Microswarm in Fluid. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 6990–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacci, J.; Sacanna, S.; Steinberg, A.P.; Pine, D.J.; Chaikin, P.M. Living Crystals of Light-Activated Colloidal Surfers. Science 2013, 339, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Ren, B. Photocatalytic Micro/Nanomotors: From Construction to Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1940–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibele, M.; Mallouk, T.E.; Sen, A. Schooling Behavior of Light-Powered Autonomous Micromotors in Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3308–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, R.; Chang, X.; Ren, B.; Tong, Z. Spiropyran-Decorated SiO2–Pt Janus Micromotor: Preparation and Light-Induced Dynamic Self-Assembly and Disassembly. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24585–24591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Diaz, M.; Córdova-Figueroa, U.M.; Sen, A. Light-Driven Titanium-Dioxide-Based Reversible Microfireworks and Micromotor/Micropump Systems. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Soto, F.; Gao, W.; Dong, R.; Garcia-Gradilla, V.; Magaña, E.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Reversible Swarming and Separation of Self-Propelled Chemically Powered Nanomotors under Acoustic Fields. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2163–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Cheng, G.; Liu, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. Dynamic Assembly of Microspheres under an Ultrasound Field. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 2440–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Chang, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, T.; Li, L. Multi-response biocompatible Janus micromotor for ultrasonic imaging contrast enhancement. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 23, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, T.; Xu, L.-P.; Zhang, X. Controllable Swarming and Assembly of Micro/Nanomachines. Micromachines 2017, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Bae, S.C.; Granick, S. Colloidal Superstructures Programmed into Magnetic Janus Particles. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, M.; Delmotte, B.; Youssef, M.; Sacanna, S.; Donev, A.; Chaikin, P. Unstable fronts and motile structures formed by microrollers. Nat. Phys. 2016, 13, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Pedrero, F.; Ortiz-Ambriz, A.; Pagonabarraga, I.; Tierno, P. Colloidal microworms propelling via a cooperative hydrodynamic convey or belt. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 138301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokot, G.; Piet, D.; Whitesides, G.M.; Aranson, I.S.; Snezhko, A. Emergence of reconfigurable wires and spinners via dynamic self-assembly. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Si, T.; Wu, Z.; Gao, C.; Lin, X.; He, Q. Light-Activated Active Colloid Ribbons. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 13702–13705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massana-Cid, H.; Pedrero, F.M.; Argemí, E.N.; Pagonabarraga, I.; Tierno, P. Propulsion and hydrodynamic particle transport of magnetically twisted colloidal ribbons. New J. Phys. 2017, 19, 103031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Bae, S.C.; Granick, S. Rotating crystals of magnetic Janus colloids. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokot, G.; Snezhko, A. Manipulation of emergent vortices in swarms of magnetic rollers. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L. Closed-Loop Control of a Helmholtz Coil System for Accurate Actuation of Magnetic Microrobot Swarms. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L. Pattern generation and motion control of a vortex-like paramagnetic nanoparticle swarm. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2018, 37, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Li, T.; Yu, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L. Propulsion Gait Analysis and Fluidic Trapping of Swinging Flexible Nanomotors. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5118–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Ma, N.; Yu, H.; Sun, H.; Chang, X.; Wu, Z.; Deng, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; et al. Self-Propelled Janus Microdimer Swimmers under a Rotating Magnetic Field. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Yu, J.; Yan, X.; Choi, H.; Zhang, L. Magnetic Actuation Based Motion Control for Microrobots: An Overview. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1346–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Chang, X.; Song, W.; Hu, Y.; Shao, G.; Sandraz, E.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; et al. Magnetically propelled fish-like nanoswimmers. Small 2016, 12, 6098–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, A.; Shao, G. Janus Microdimer Surface Walkers Propelled by Oscillating Magnetic Fields. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, P1706066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Doolen, G.D. Lattice Boltzmann Method for Fluid Flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1998, 30, 329–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackay, F.; Ollila, S.; Denniston, C. Hydrodynamic forces implemented into LAMMPS through a lattice-Boltzmann fluid. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2013, 184, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, B.; Liu, J.; Su, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, W. Reconfigurable Disk-like Microswarm under a Sawtooth Magnetic Field. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121529
Zhang T, Deng Y, Zhou B, Liu J, Su Y, Li M, Zhang W. Reconfigurable Disk-like Microswarm under a Sawtooth Magnetic Field. Micromachines. 2021; 12(12):1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121529
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao, Yuguo Deng, Bo Zhou, Jiayu Liu, Yufeng Su, Mu Li, and Weiwei Zhang. 2021. "Reconfigurable Disk-like Microswarm under a Sawtooth Magnetic Field" Micromachines 12, no. 12: 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121529
APA StyleZhang, T., Deng, Y., Zhou, B., Liu, J., Su, Y., Li, M., & Zhang, W. (2021). Reconfigurable Disk-like Microswarm under a Sawtooth Magnetic Field. Micromachines, 12(12), 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121529