Recent Advances on Conducting Polymers Based Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting
Abstract
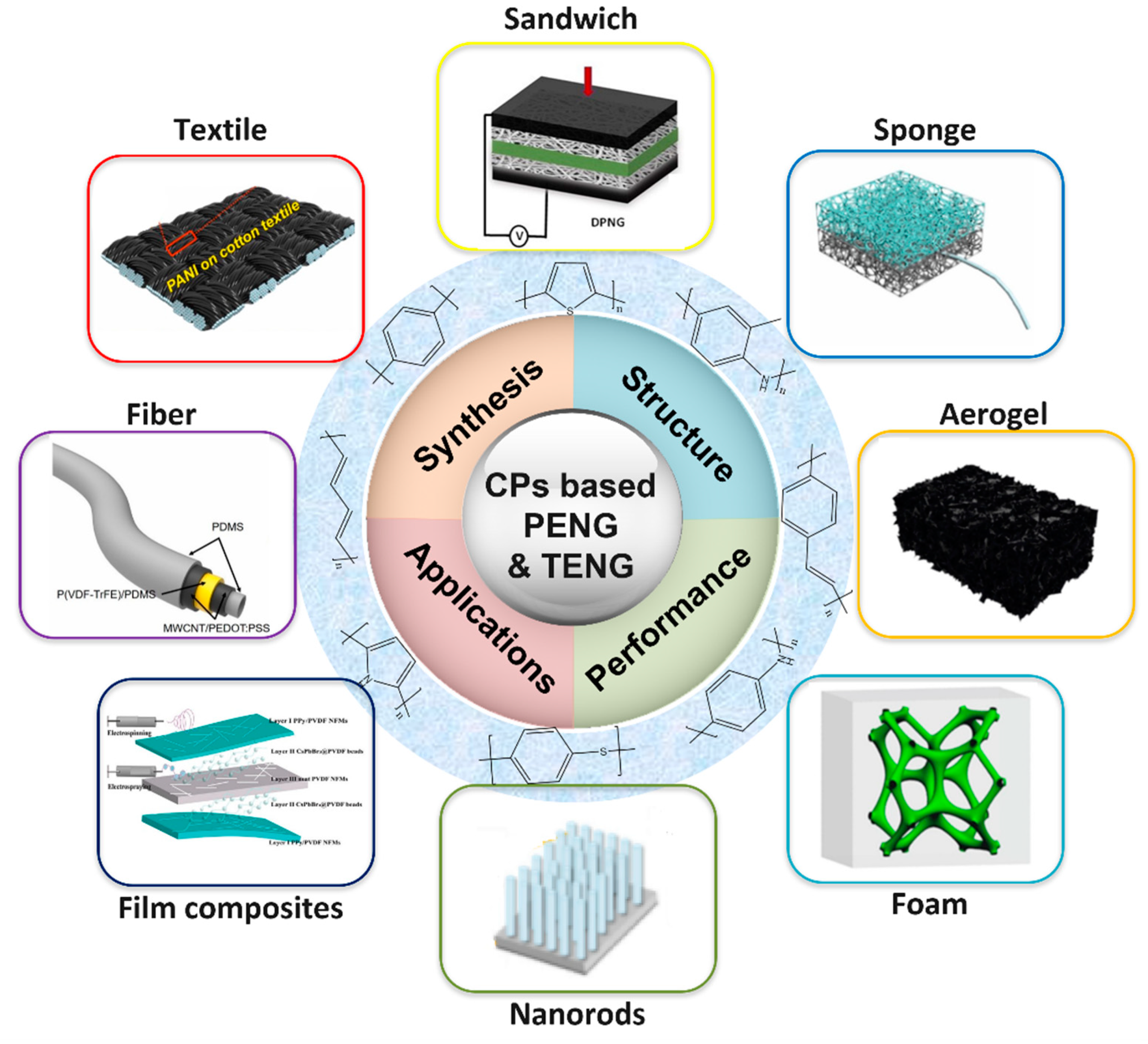
1. Introduction
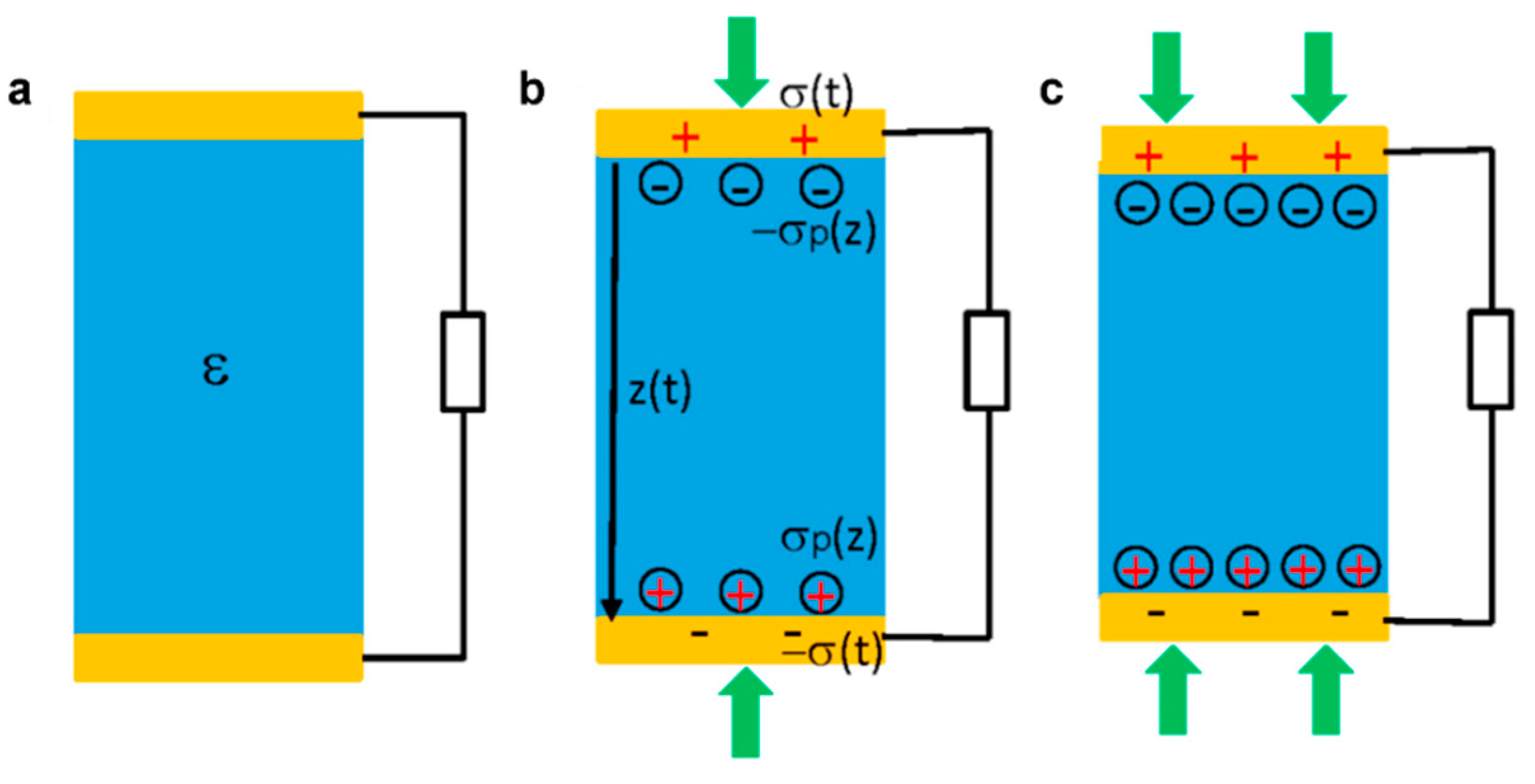
2. Conducting Polymer Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators
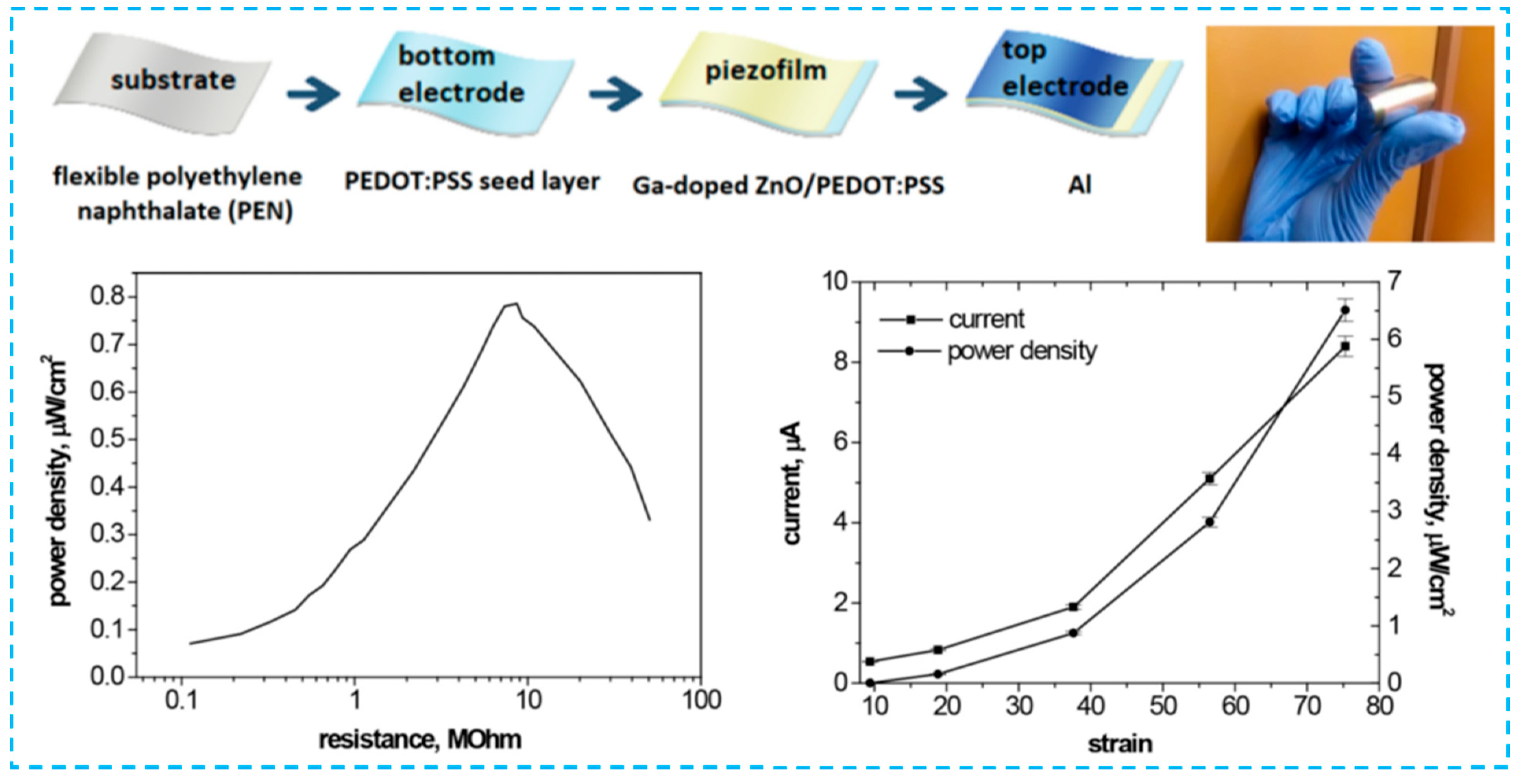
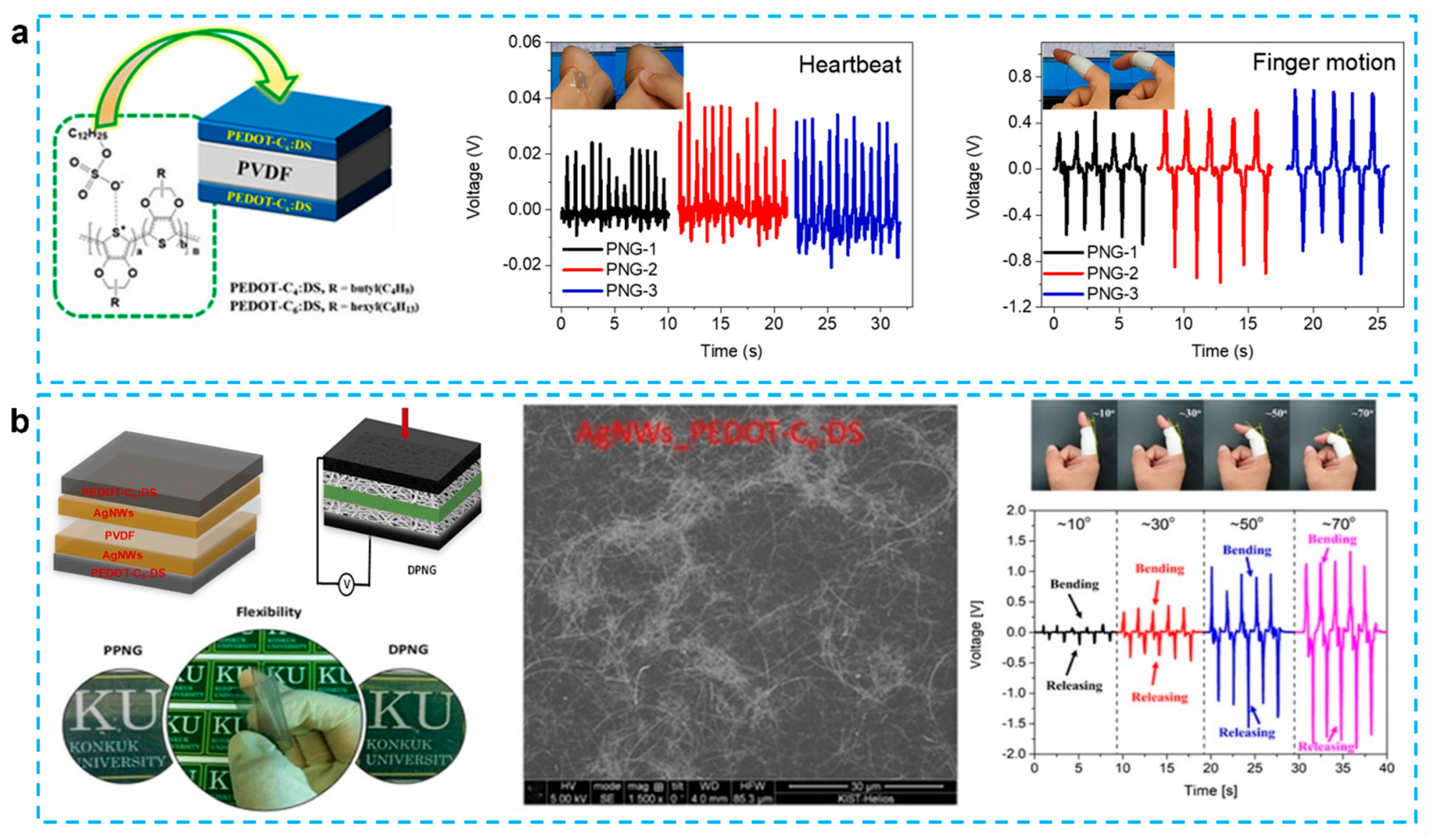
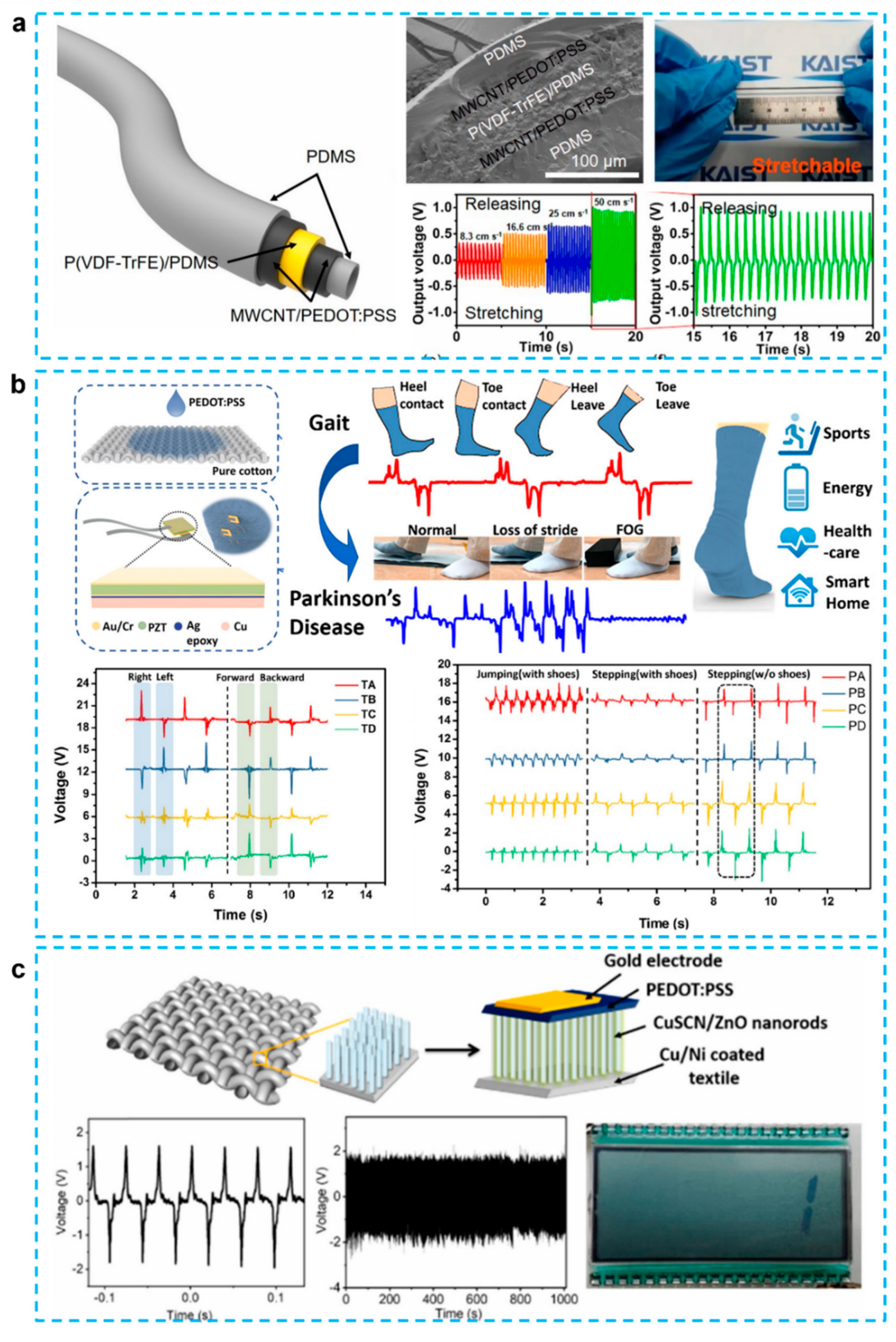
2.1. Sandwich Structured PENG
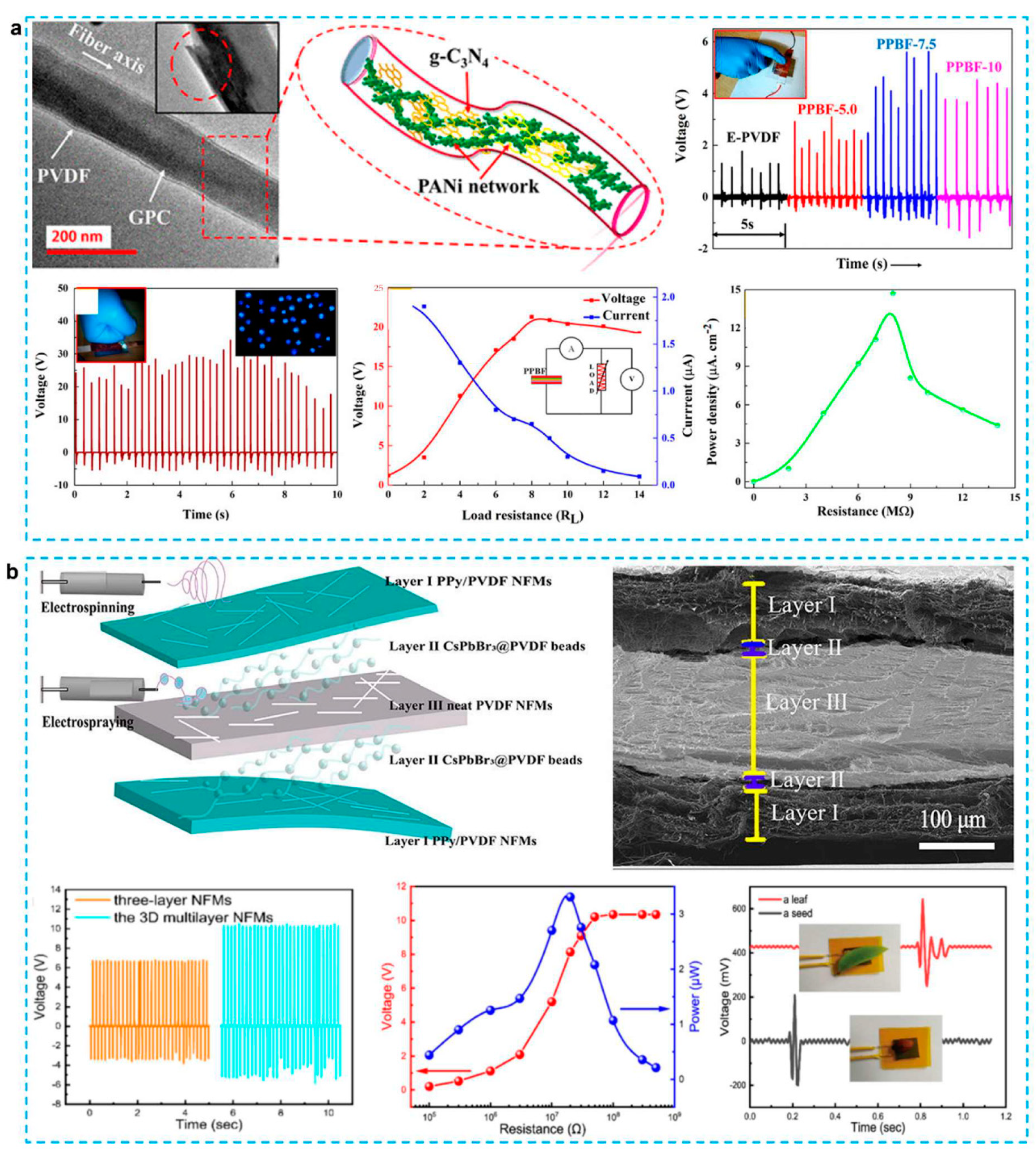
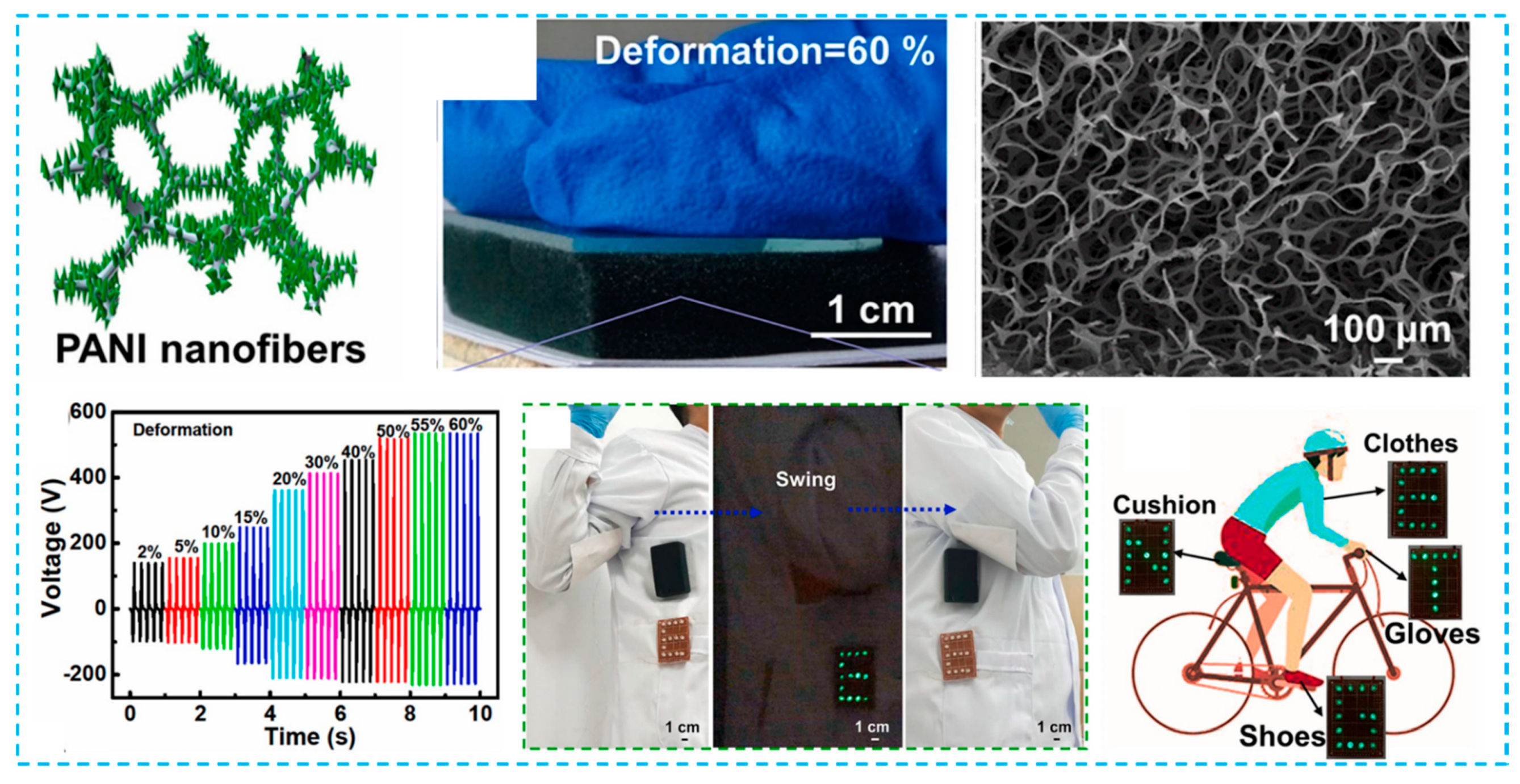
2.2. Textile Structured PENG
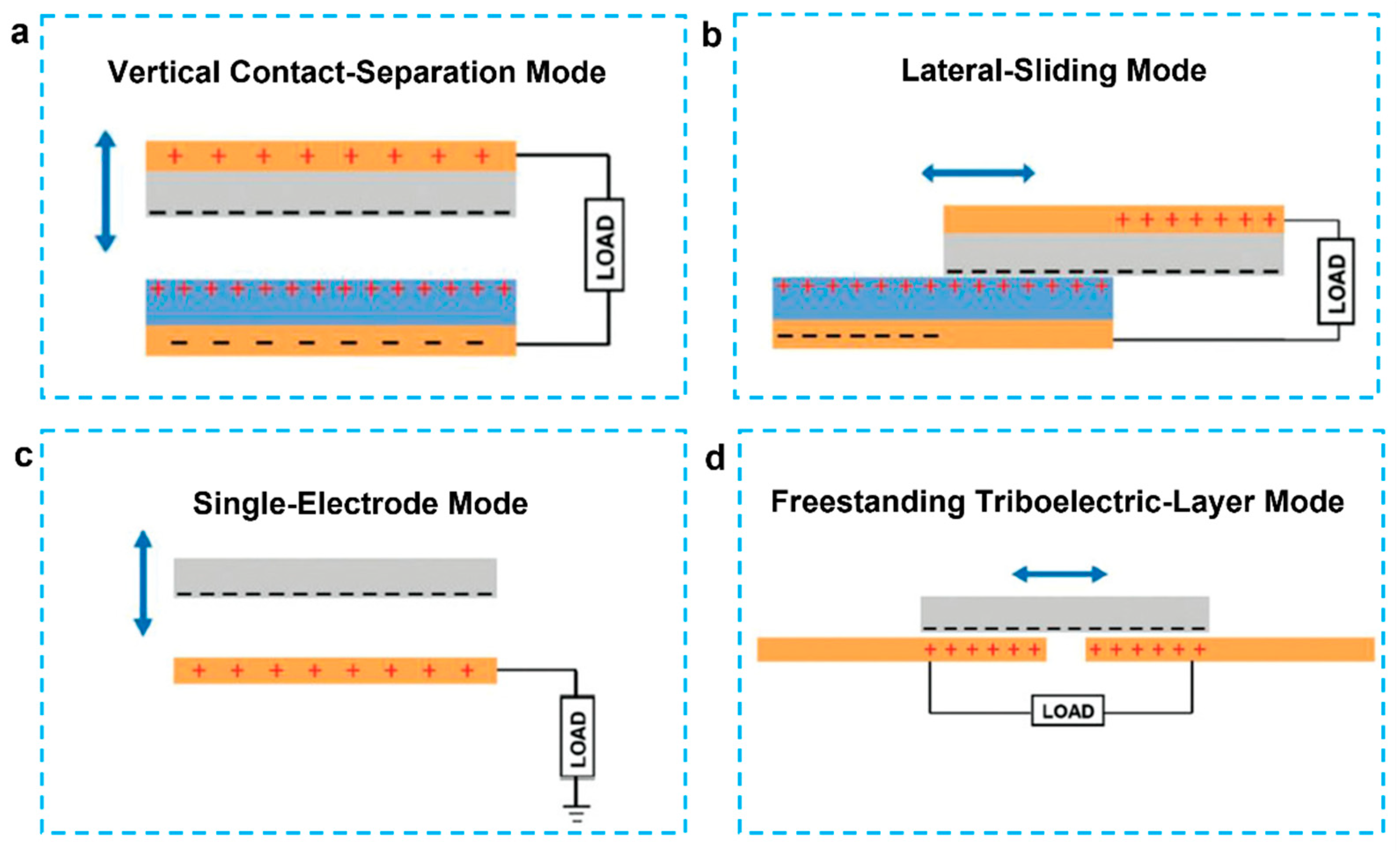
3. Conducting Polymer Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators
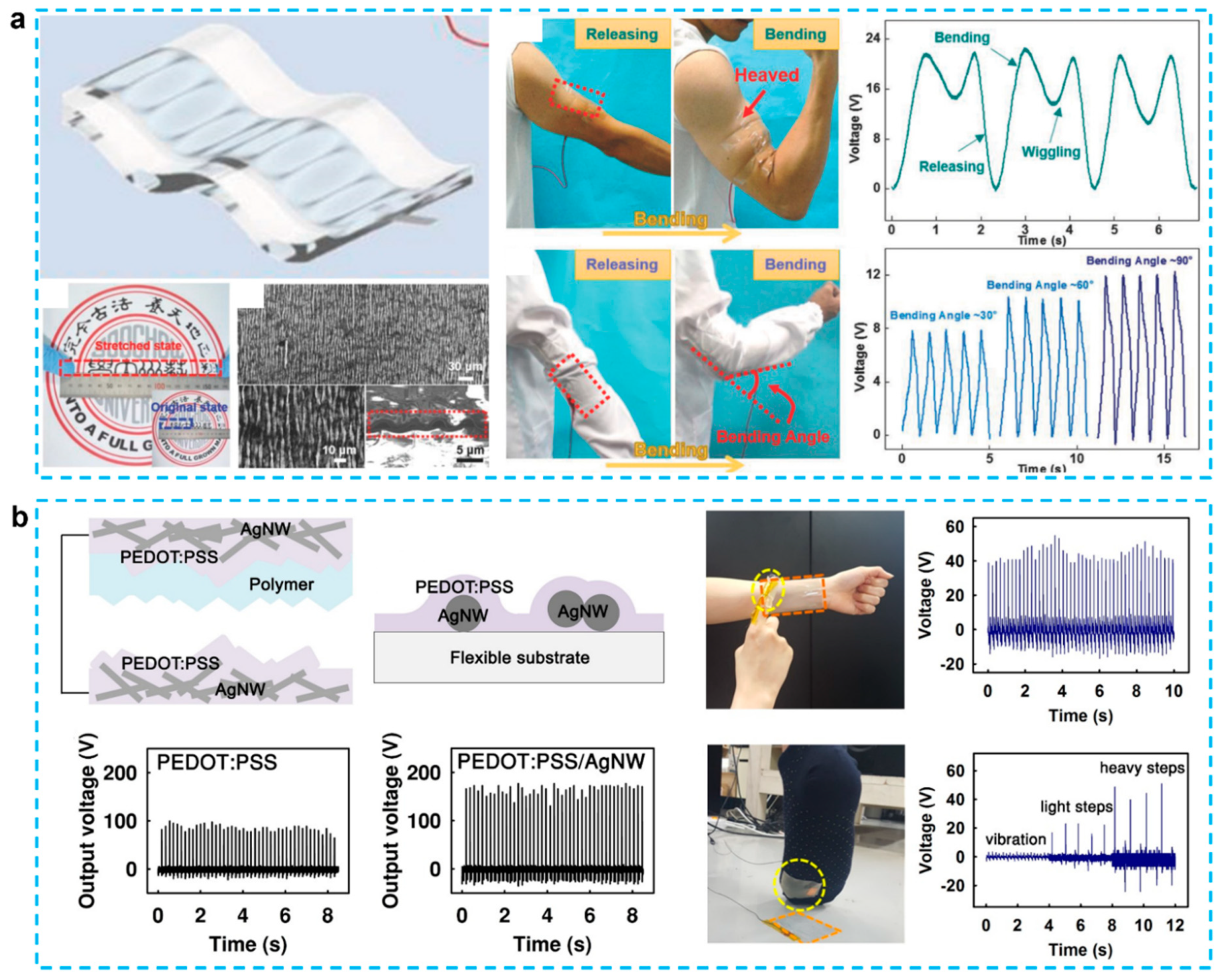
3.1. Nanostructured Films Based TENGs
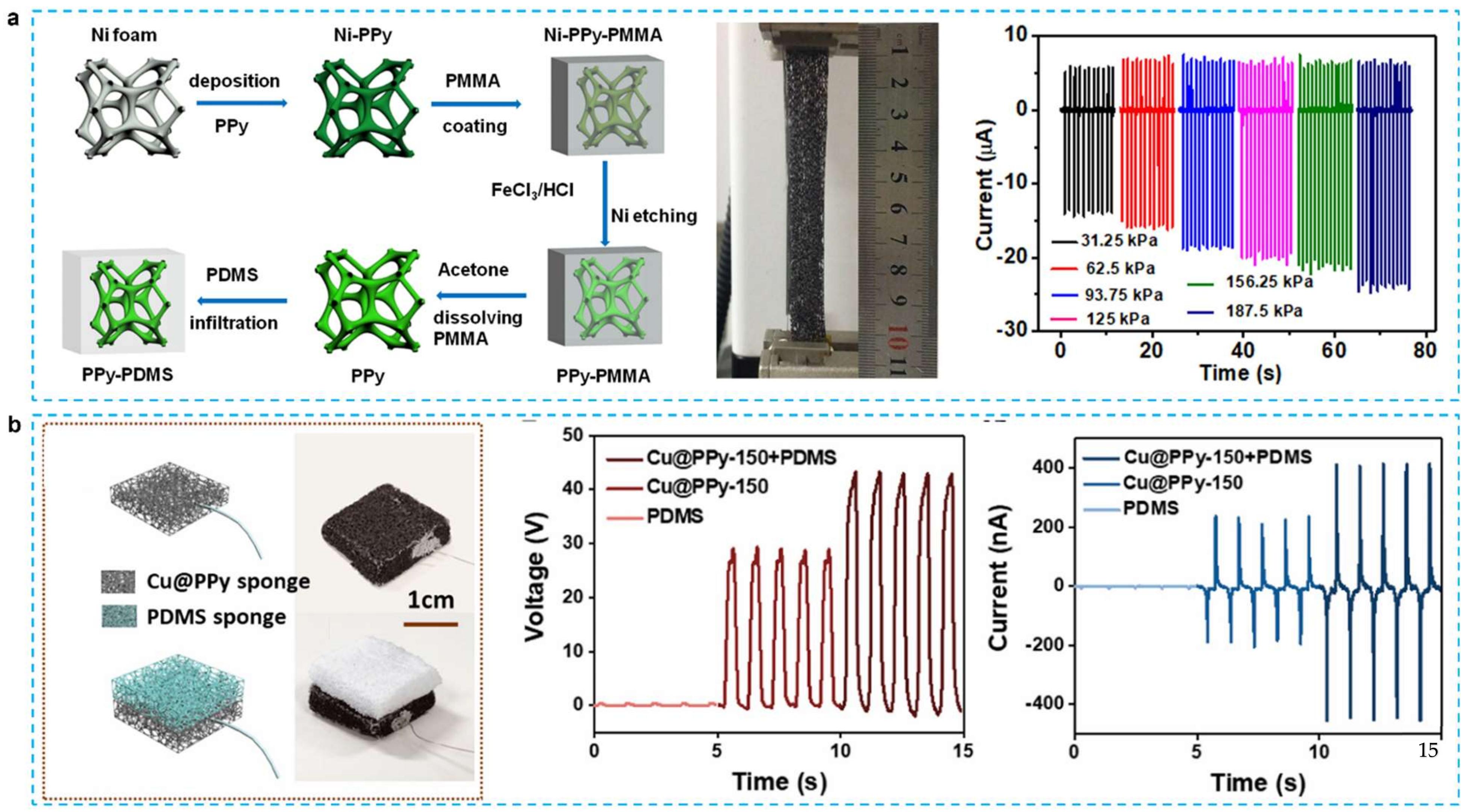
3.2. Sponges/Foam/Aerogel Structured TENG
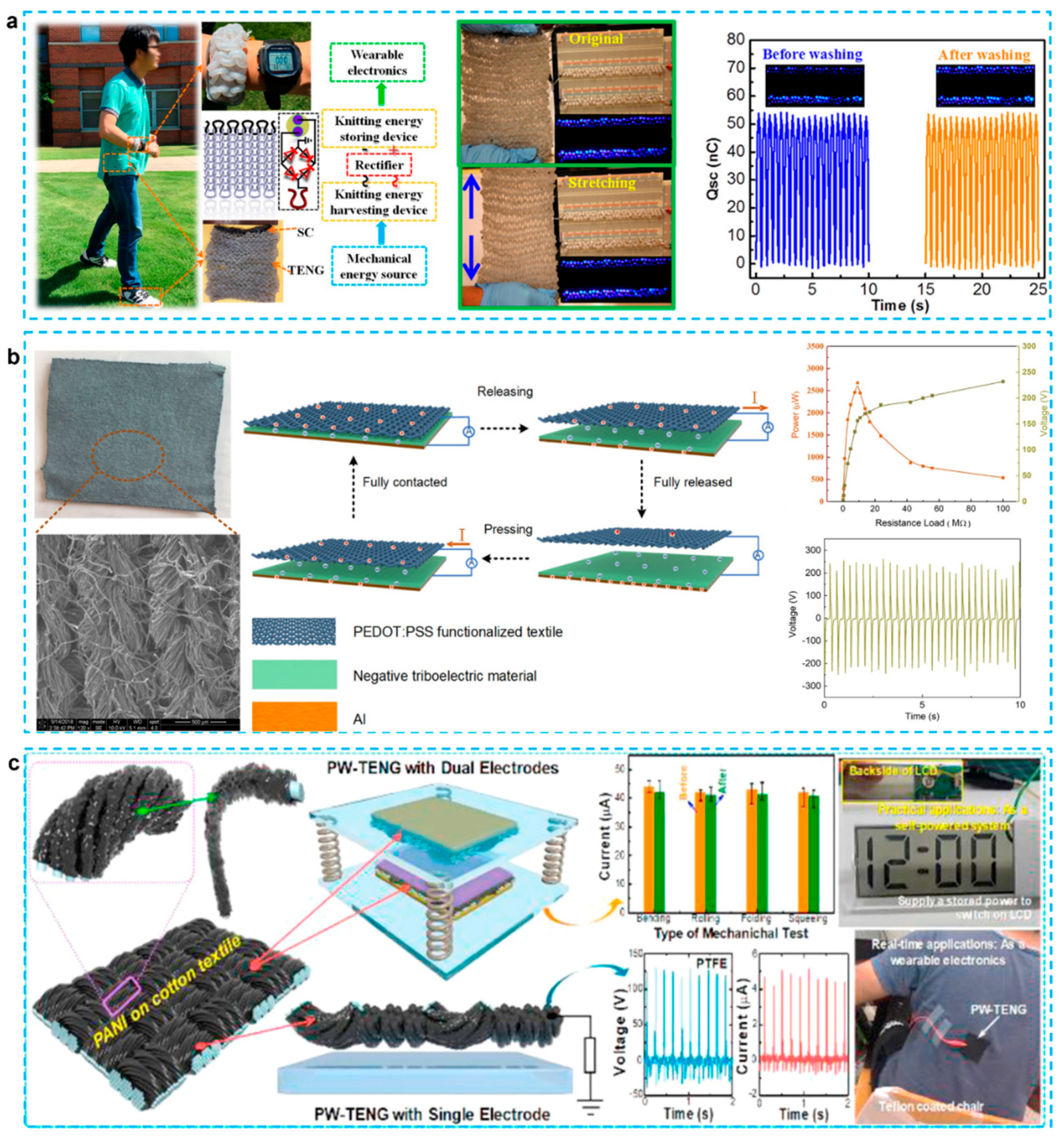
3.3. Textile Based TENGs
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, A.; Ahnood, A.; Cole, M.T.; Lee, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Popat, P.H.; Bonaccorso, F.; Hasan, T.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Dyadyusha, A.; et al. Flexible electronics: The next ubiquitous platform. Next Ubiquitous Platf. Proc. IEEE 2021, 100, 1486–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, Z.; Guo, C.F. Flexible Electronics: Stretchable Electrodes and Their Future. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1805924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Lim, S.; Ko, H. Wearable and flexible sensors for user-interactive health-monitoring devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 4043–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, Z. Nanogenerator-Based Self-Powered Sensors for Wearable and Implantable Electronics. Research 2020, 2020, 8710686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.-L. Wearable Electronics Based on 2D Materials for Human Physiological Information Detection. Small 2020, 16, 1901124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Du, W.; Nautiyal, A.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X. Recent progress on nanostructured conducting polymers and composites: Synthesis, application and future aspects. Sci. China Mater. 2018, 61, 303–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Poyraz, S.; Smith, J.; Kushvaha, V.; Tippur, H.; Zhang, X. An ultrafast microwave approach towards multi-component and multi-dimensional nanomaterials. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 9308–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyraz, S.; Zhang, L.; Schroder, A.; Zhang, X. Ultrafast Microwave Welding/Reinforcing Approach at the Interface of Thermoplastic Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22469–22477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Poyraz, S.; Cook, J.; Bozack, M.J.; Das, S.; Zhang, X.; Hu, L. Ultrafast Microwave Nano-manufacturing of Fullerene-Like Metal Chalcogenides. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Yin, R.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Dai, K.; Shan, C.; Guo, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Electrically conductive polymer composites for smart flexible strain sensors: A critical review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 12121–12141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Flexible conductive polymer composites for smart wearable strain sensors. SmartMat 2020, 1, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Biswas, M.C.; Guo, Z.; Jeon, J.-W.; Wujcik, E.K. Recent developments in bio-monitoring via advanced polymer nanocomposite-based wearable strain sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Ma, Z.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y. Properties of conductive polymer hydrogels and their application in sensors. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2019, 57, 1606–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, Q.; Cui, X.; Dong, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Fan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, Z. An overview of stretchable strain sensors from conductive polymer nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 11710–11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Poyraz, S.; Zhang, X. Conducting Polymer—Metal Nanocomposites Synthesis and Their Sensory Applications. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 2256–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, H.; Zheng, T.; Liu, K.; Ji, X.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Si, C. Cellulose based composite foams and aerogels for advanced energy storage devices. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, H. A review on conversion of crayfish-shell derivatives to functional materials and their environmental applications. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Jiang, S.; Rui, Z.; Zhang, K. Porous aerogel and sponge composites: Assisted by novel nanomaterials for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsheer, K.; Chandra, S.R. Conducting polymers: A comprehensive review on recent advances in synthesis, properties and applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 5659–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liao, M.; Lou, H.; Hu, Y.; Sun, X.; Peng, H. Conjugated Polymers for Flexible Energy Harvesting and Storage. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1704261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Nie, W.; Tsai, H.; Wang, N.; Huang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wen, R.; Ma, L.; Yan, F.; Xia, Y. PEDOT:PSS for Flexible and Stretchable Electronics: Modifications, Strategies, and Applications. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehler, C.; Aqrawe, Z.; Asplund, M. Applications of PEDOT in bioelectronic medicine. Bioelectron. Med. 2019, 2, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, E.N.; Makvandi, P.; Ashtari, B.; Rossi, F.; Motahari, A.; Perale, G. Progress in Conductive Polyaniline-Based Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications: A Review. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Roy, S. Polypyrrole and associated hybrid nanocomposites as chemiresistive gas sensors: A comprehensive review. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 121, 105332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadtare, S.; Ko, E.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, H.S.; Moon, D.K. A flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator using conducting polymer and silver nanowire hybrid electrodes for its application in real-time muscular monitoring system. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 299, 111575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, K.; Yang, M.; Zou, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, H.; Qu, X.; Tan, P.; Wang, C.; et al. Elastic Cu@PPy sponge for hybrid device with energy conversion and storage. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Miao, T.; Chi, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, C.; Du, Y.; An, M.; Ma, W.-G.; Zhang, X. Ultralight PEDOT:PSS/graphene oxide composite aerogel sponges for electric power harvesting from thermal fluctuations and moist environment. Nano Energy 2020, 77, 105096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Wang, N.; Ma, J.; Jie, Y.; Zou, J.; Cao, X. Stretchable 3D polymer for simultaneously mechanical energy harvesting and biomimetic force sensing. Nano Energy 2018, 47, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, M.-H.; Xia, Y.-S.; Wu, J.-M.; Sun, X.-K.; Wang, S.; Hu, G.-H.; Xiong, C.-X. Multilayer assembly of electrospun/electrosprayed PVDF-based nanofibers and beads with enhanced piezoelectricity and high sensitivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Lim, S.; Sim, J.Y.; Jeon, J.; No, K.; Park, S.; Hong, S. Intrinsically stretchable multi-functional fiber with energy harvesting and strain sensing capability. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Briscoe, J. P–N junction-based ZnO wearable textile nanogenerator for biomechanical energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudem, B.; Mule, A.R.; Patnam, H.R.; Yu, J.S. Wearable and durable triboelectric nanogenerators via polyaniline coated cotton textiles as a movement sensor and self-powered system. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Lei, T.; Qin, Y.; Yang, R. Flexible electronic skins based on piezoelectric nanogenerators and piezotronics. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On Maxwell’s displacement current for energy and sensors: The origin of nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, D.; Liu, W.; Zhou, S.; Ge, S.; Su, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhang, L. Effects of particle size of dielectric fillers on the output performance of piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators. J. Adv. Ceram. 2021, 10, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Dielectric composites with a high and temperature-independent dielectric constant. J. Adv. Ceram. 2012, 1, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Shan, X.; Wu, P.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Dielectric characteristics of CaCu3Ti4O12/P(VDF-TrFE) nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 107, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Z.-Y.; Brewer, J.C. Preparation process and dielectric properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–P(VDF–CTFE) nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 56, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Shan, X. Microstructure and dielectric response of BaSrTiO3/P(VDF-CTFE) nanocomposites. Mater. Lett. 2015, 159, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shan, X.; Bass, P.; Tong, Y.; Rolin, T.D.; Hill, C.W.; Brewer, J.C.; Tucker, D.S.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Process and Microstructure to Achieve Ultra-high Dielectric Constant in Ceramic-Polymer Composites. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabhane, G.H.; Giripunje, S.M.; Kondawar, S.B. Fabrication and dielectric performance of RGO-PANI reinforced PVDF/BaTiO3 composite for energy harvesting. Synth. Met. 2021, 279, 116845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Shi, Q.; He, T.; Yi, Z.; Ma, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, T.; Lee, C. Self-Powered and Self-Functional Cotton Sock Using Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Hybrid Mechanism for Healthcare and Sports Monitoring. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parangusan, H.; Bhadra, J.; Al-Thani, N. Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator based on [P(VDF-HFP)]/PANI-ZnS electrospun nanofibers for electrical energy harvesting. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 6358–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, M. Polymeric seed layer as a simple approach for nanostructuring of Ga-doped ZnO films for flexible piezoelectric energy harvesting. Microelectron. Eng. 2020, 233, 111434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Greenwood, P.C.; Meroni, S.; Troughton, J.; Novák, P.; Li, X.; Watson, T.; Briscoe, J. Self-adhesive electrode applied to ZnO nanorod-based piezoelectric nanogenerators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 105040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Han, S.; Liu, W.; Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Xu, Z. Flexible composites with Ce-doped BaTiO3/P(VDF-TrFE) nanofibers for piezoelectric device. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 200, 108386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q. Polymer-Based Dielectrics with High Energy Storage Density. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2015, 45, 433–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, Q. Novel Ferroelectric Polymers for High Energy Density and Low Loss Dielectrics. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2937–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Q. Ferroelectric Polymers and Their Energy-Related Applications. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2016, 217, 1228–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, P.; Thakur, V.K.; Gupta, R.K. Recent Progress on Ferroelectric Polymer-Based Nanocomposites for High Energy Density Capacitors: Synthesis, Dielectric Properties, and Future Aspects. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4260–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Development of Polymer-Based 0–3 Composites with High Dielectric Constant. J. Adv. Dielectr. 2011, 1, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Xia, W.; Zhu, X.; Sun, T.; Cao, C.; Zhang, L. Enhanced piezoelectric and acoustic performances of poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) films for hydroacoustic applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 5711–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, P.; Balasubramanian, S.; Anguchamy, Y.; Gong, S.; Wibowo, A.; Gao, H.; Ploehn, J.H.; Loye, H.-C.Z. Polymer Composite and Nanocomposite Dielectric Materials for Pulse Power Energy Storage. Materials 2009, 2, 1697–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Q.; Chu, B.; Zhang, Q. Recent development of high energy density polymers for dielectric capacitors. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2010, 17, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ding, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, B. Flexible PVDF based piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hou, L.; Zhang, L.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, G.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Piezoelectric-excited membrane for liquids viscosity and mass density measurement. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 261, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Zhang, L.; Gui, J.; Cui, H.; Guo, S. A Flexible Piezoelectric Nanogenerator Based on Aligned P(VDF-TrFE) Nanofibers. Micromachines 2019, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, E.J.; Jeon, S.J.; Han, Y.W.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kang, C.Y.; Sung, T.H.; Seong, K.W.; Moon, D.K. Synthesis and characterization of nanofiber-type hydrophobic organic materials as electrodes for improved performance of PVDF-based piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H. PANI/PVDF-TrFE porous aerogel bulk piezoelectric and triboelectric hybrid nanogenerator based on in-situ doping and liquid nitrogen quenching. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.E.; Ooi, P.C.; Haniff, M.A.S.M.; Goh, B.T.; Dee, C.F.; Chang, W.S.; Wee, M.F.M.R.; Mohamed, M.A. Performance of all-solution-processed, durable 2D MoS2 flakes−BaTiO3 nanoparticles in polyvinylidene fluoride matrix nanogenerator devices using N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone polar solvent. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 820, 153160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, K.; Mandal, D. All-Organic High-Performance Piezoelectric Nanogenerator with Multilayer Assembled Electrospun Nanofiber Mats for Self-Powered Multifunctional Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 18257–18269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.; Anandhan, S. PVDF Nanofibers with Embedded Polyaniline–Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheet Composites for Piezoelectric Energy Conversion. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 7328–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Fang, Z.; Wang, C.; Shu, L.; Han, J. Ultraviolet-protecting, flexible and stable photovoltaic-assisted piezoelectric hybrid unit nanogenerator for simultaneously harvesting ultraviolet light and mechanical energies. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 15222–15237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinya, I.; Sasmal, A.; Sen, S. Conducting polyaniline decorated in-situ poled Ferrite nanorod-PVDF based nanocomposite as piezoelectric energy harvester. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 815, 152312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lim, Y. Generating Power Enhancement of Flexible PVDF Generator by Incorporation of CNTs and Surface Treatment of PEDOT:PSS Electrodes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1700588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, E.J.; Hong, J.; Park, C.E.; Moon, D.K. Enhanced chemical and physical properties of PEDOT doped with anionic polyelectrolytes prepared from acrylic derivatives and application to nanogenerators. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4384–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.; Mahendran, A.; Anandhan, S. Durable, efficient, and flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator from electrospun PANi/HNT/PVDF blend nanocomposite. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, E.J.; Lee, E.J.; Choi, M.H.; Sung, T.H.; Moon, D.K. PVDF based flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators using conjugated polymer:PCBM blend systems. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 259, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.; Ma, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.L.; Sang, Y. BaTiO3 nanocrystal-mediated micro pseudo-electrochemical cells with ultrasound-driven piezotronic enhancement for polymerization. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.-F.; Yan, X.; Yu, M.; Jia, M.-Y.; Pan, W.; He, X.-X.; Han, W.-P.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Yu, L.-M.; Long, Y.-Z. Patterned, highly stretchable and conductive nanofibrous PANI/PVDF strain sensors based on electrospinning and in situ polymerization. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2944–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, F.; Shamshirsaz, M.; Latifi, M.; Asadi, S. Comparative evaluation of piezoelectric response of electrospun PVDF (polyvinilydine fluoride) nanofiber with various additives for energy scavenging application. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsur, R.; Rangari, V.K.; Jeelani, S.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z.Y. Fabrication of carbon nanotubes grown woven carbon fiber/epoxy composites and their electrical and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 214903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Bass, P.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Metal-polymer nanocomposites with high percolation threshold and high dielectric constant. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 232903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bass, P.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Revisiting the percolation phenomena in dielectric composites with conducting fillers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 042905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Nano-clip based composites with a low percolation threshold and high dielectric constant. Nano Energy 2016, 26, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Ye, W.; Chen, L.; Jiang, S.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Hou, H. Flexible hdC-G reinforced polyimide composites with high dielectric permittivity. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 101, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bass, P.; Wang, G.; Tong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Dielectric response and percolation behavior of Ni–P(VDF–TrFE) nanocomposites. J. Adv. Dielectr. 2017, 7, 1750015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Jin, L.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, Z.-Y. All-organic dielectric nanocomposites using conducting polypyrrole nanoclips as filler. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 167, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Ghosh, A.; Bose, N.; Mukherjee, S.; Chowdhury, A.R.; Datta, P. A comparative assessment of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/conducting polymer electrospun nanofiber membranes for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünsal, Ö.F.; Altin, Y.; Bedeloğlu, A. ÇELİK Poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber-based piezoelectric nanogenerators using reduced graphene oxide/polyaniline. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-Y.; Chou, S.-C.; Chang, J.-A. Development of flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator: Toward all wet chemical method. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 3015–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-E.; Lee, S.-M.; Kim, S.-S.; Kim, T.-W.; Koo, H.-W.; Kim, H.-K. Brush-paintable and highly stretchable Ag nanowire and PEDOT:PSS hybrid electrodes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhao, T.; Liu, H.; Jia, R.; Niu, D.; Chen, B.; Shi, Y.; Yin, L.; Lu, B. Laminated pyroelectric generator with spin coated transparent poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS) electrodes for a flexible self-powered. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 15134–15140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y.; Kim, E. Highly conductive PEDOT electrodes for harvesting dynamic energy through piezoelectric conversion. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5462–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Jin, Y.; Ou, H.; Huang, P.; Liu, C.; Luo, Y.; Xiao, Z. High-performance Ag nanowires/PEDOT:PSS composite electrodes for PVDF-HFP piezoelectric nanogenerators. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 21178–21187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.-H.; Wang, X.-X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.-Z.; Yu, M.; Fan, Z.-Y.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.-Z. A self-powered flexible hybrid piezoelectric–pyroelectric nanogenerator based on non-woven nanofiber membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3500–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.J.; Choi, C.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, Y.T.; Spinks, G.M.; Lima, M.D.; Baughman, R.H.; Kim, S.J. Flexible, stretchable and weavable piezoelectric fiber. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Qu, H.; Skorobogatiy, M. Piezoelectric Micro- and Nanostructured Fibers Fabricated from Thermoplastic Nanocomposites Using a Fiber Drawing Technique: Comparative Study and Potential Applications. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egusa, S.; Wang, Z.; Chocat, N.; Ruff, Z.; Stolyarov, A.M.; Shemuly, D.; Sorin, F.; Rakich, P.T.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Fink, Y. Multimaterial piezoelectric fibres. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, A.; Ding, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: A Foundation of the Energy for the New Era. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.L. Polymer Materials for High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Shu, S.; Tang, W. A Self-Powered Vector Angle/Displacement Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Micromachines 2021, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, K.; Yoo, D.; Kim, D.S.; Hwang, W.; Song, I.; Sim, J.-Y. A Spherical Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Enhanced Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Micromachines 2018, 9, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-W.; Huynh, N.D.; Kim, W.; Hwang, H.J.; Hong, H.; Choi, K.; Song, A.; Chung, K.-B.; Choi, D. Effects of Embedded TiO2−x Nanoparticles on Triboelectric Nanogenerator Performance. Micromachines 2018, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, X.; Mao, S.; Xiao, F. Polypyrrole Films Electrochemically Doped with Dodecylbenzenesulfonate for Copper Protection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, C445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Zi, Y.; Zhou, P.; Lin, J.; Guo, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. All-Plastic-Materials Based Self-Charging Power System Composed of Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Supercapacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Zi, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, C.; Guo, H.; Xi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Electrochemical Synthesis of Polypyrrole from the Pulsed Output of a Triboelectric Nanogenerator as a Sustainable Energy System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3542–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Feng, X.; Kuang, S.; Panwar, N.; Song, P.; Yang, C.; Yang, G.; Hemu, X.; Zhang, G.; Yoon, H.S.; et al. Self-powered, on-demand transdermal drug delivery system driven by triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Self-powered ammonia nanosensor based on the integration of the gas sensor and triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-Y.; Kim, S.-U.; Kang, S.; Lee, S.-D. Transparent and flexible high power triboelectric nanogenerator with metallic nanowire-embedded tribonegative conducting polymer. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Hassan, I.; Mosa, I.; Elsanadidy, E.; Phadke, G.S.; El-Kady, M.F.; Rusling, J.F.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Kaner, R.B. All printable snow-based triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, K.; Yan, C.; Zheng, G.; Huang, J.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Ultra-Stretchable, durable and conductive hydrogel with hybrid double network as high performance strain sensor and stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 105035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Li, T.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F. Conductive elastic sponge-based triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) for effective random mechanical energy harvesting and ammonia sensing. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Wang, Y.-C.; Deng, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Zou, H.; Gu, B.; Sun, B.; Wang, Z.L. A Highly Stretchable and Washable All-Yarn-Based Self-Charging Knitting Power Textile Composed of Fiber Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9490–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mule, A.R.; Dudem, B.; Patnam, H.; Graham, S.A.; Yu, J.S. Wearable Single-Electrode-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator via Conductive Polymer-Coated Textiles for Self-Power Electronics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16450–16458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, N.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Shi, J.; Xie, L.; Jiang, H.; Bao, D.; et al. A Wrinkled PEDOT:PSS Film Based Stretchable and Transparent Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wearable Energy Harvesters and Active Motion Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chen, X.; Li, G.; Sun, N.; Jiang, H.; Bao, D.; Xie, L.; Peng, M.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Z.; et al. A liquid PEDOT:PSS electrode-based stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for a portable self-charging power source. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7513–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pham, A.T.; Tohl, D.; Tang, Y. Simulation Guided Hand-Driven Portable Triboelectric Nanogenerator: Design, Optimisation, and Evaluation. Micromachines 2021, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Yin, X.; Yu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Wang, X. Chemically Functionalized Natural Cellulose Materials for Effective Triboelectric Nanogenerator Development. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, T.; Zeng, Q.; Lee, C. A Review and Perspective for the Development of Triboelectric Nanogenerator (TENG)-Based Self-Powered Neuroprosthetics. Micromachines 2020, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wei, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Smart Wearable Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Personal Healthcare Monitoring. Micromachines 2021, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, J.; Guo, X.; Chen, P.; Duan, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. A Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine-Filled Cellulose Aerogel for Solar-Enabled Water Remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 7617–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, L.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Huang, C.; Han, J.; Jiang, S. Anisotropic nanocellulose aerogels with ordered structures fabricated by directional freeze-drying for fast liquid transport. Cellulose 2019, 26, 6653–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Cheong, J.Y.; Nam, J.S.; Kim, I.-D.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. High-density Fibrous Polyimide Sponges with Superior Mechanical and Thermal Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19006–19014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mei, C.; Li, Y.; Duan, G.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Ma, C.; Jiang, S. Wood-Inspired Anisotropic Cellulose Nanofibril Composite Sponges for Multifunctional Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35513–35522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Cao, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Han, J.; Long, Y.; Han, G. Recent advances in cellulose-based flexible triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Kim, S.-W. Transparent flexible stretchable piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators for powering portable electronics. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, B.; Mao, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, L.; Sui, X. Flexible cellulose-based thermoelectric sponge towards wearable pressure sensor and energy harvesting. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Nie, J.; Li, H.; Xia, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, X.; Qi, R.; Wang, Z.L.; Lu, X. High-frequency supercapacitors based on carbonized melamine foam as energy storage devices for triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, P.K.; Nanjundan, A.K.; Dubal, D.P.; Baek, J. An Overview of Cellulose-Based Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2001164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, W.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. Cellulose II Aerogel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2001763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Pang, B.; Xu, W.; Duan, G.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, K. Recent Progress on Nanocellulose Aerogels: Preparation, Modification, Composite Fabrication, Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Shi, X. Chitin derived nitrogen-doped porous carbons with ultrahigh specific surface area and tailored hierarchical porosity for high performance supercapacitors. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Lin, J.; Bian, F. Utilization of discarded crop straw to produce cellulose nanofibrils and their assemblies. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Shah, A.R. Integrated lignocellulosic biorefinery: Gateway for production of second generation ethanol and value added products. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zou, H.; Geng, Z.; Wang, X.; Ding, W.; Hu, F.; Zi, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, S.L.; Yu, H.; et al. A Hierarchically Nanostructured Cellulose Fiber-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Healthcare Products. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1805540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Fang, L.; Guo, H.; Yang, K.; Cai, Z.; Meador, M.A.; Gong, S. Highly Porous Polymer Aerogel Film-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Deng, W.; Li, S.; Wu, Z.; Cai, J.; Luo, J. Sandwich-like Chitosan Porous Carbon Spheres/MXene Composite with High Specific Capacitance and Rate Performance for Supercapacitors. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zou, H.; Sun, B.; Jiang, P.; He, J.; Huang, X. Dielectric Modulated Cellulose Paper/PDMS-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Wireless Transmission and Electropolymerization Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1904536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paosangthong, W.; Torah, R.; Beeby, S. Recent progress on textile-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, F.; Chen, T.; Ouyang, J.; Lee, C. Beyond energy harvesting—multi-functional triboelectric nanosensors on a textile. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Contact Material | Electrode | Structure | Output Performance | Durability (Cycles) | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filler | Matrix | Voltage | Current | Load Resistance | Power Density | ||||
| PEDOT-C4:DS | PEDOT:PSS | AgNW, PEDOT:PSS | Sandwich | 1.54 V | 166.0 nA | 9 MΩ | 63.0 nW | 25,000 | [59] |
| PANI | PVDF-TrFE | Copper foil | Sandwich | 246 V | A | 100 Ω–100 MΩ | - | [60] | |
| PVDF | Cu film | PANI | - | - | 55.9 nA | - | - | - | [22] |
| PVDF, BaTiO3, MoS2 | PMF NMP | AgNWs/PEDOT: PSS | Sandwich | 750 mV | - | - | - | 5000 | [61] |
| PEDOT | PVDF NFs | PVDF NF | 3D Multilayer | 48 V | A | 30 MΩ | W | 21,000 | [62] |
| PANI/g-C3N4 | PVDF | copper | PVDF/ PANI/g-C3N4/ PPBF | ~30 V | A | 8 MΩ | 50,000 | [63] | |
| CsPbBr3 | PVDF NFM | PPy | 3D multilayer | 10.3 V | 20 MΩ | 3.31 W | - | [30] | |
| SCP/ZnO QDS | PVDF | PEDOT:PSS.Ag | 3D multilayer | 1.46 V | - | 0.97 | 3500 | [64] | |
| PANI/ZnS | P(VDF-HFP) | Carbon tape | coreshell | 3 V | - | - | 2.92 | - | [44] |
| PANI nanochain | PVDF | Ag | - | 4.2 V | - | - | [65] | ||
| CNT | PVDF | PEDOT:PSS | - | 1.2 V | 3.8 nA | ~9 Ω | - | - | [66] |
| Ga/ZnO | PEN | AI/PEDOT:PSS | - | 398 mV | A | 9 MΩ | - | [45] | |
| HBA CEA | PEDOT:PSS | PEDOT:P(SS-co-HBA)PEDOT:P(SS-co-CEA) | Sandwich | 4.12 V | 817.3 nA | - | 847.5 nW | 1000 | [67] |
| HNT PANI | PVDF | PVDF | Sandwich | 7.2 V | A | 0.5~15 MΩ | 2000 | [68] | |
| PCBM61 | PVDF | Ag/Ag with MoO3 | 3D multilayer | 43.1 V | 589 nA | - | - | - | [69] |
| - | PVDF | AgNWs/PEDOT-C6:DS | 3D multilayer | 7.02 V | 1.11 A | 1–11 MΩ | 1.18 W | 20,000 | [26] |
| TCA | PEDOT:PSS | TCA | nanorods | 0.72 V | - | ~13.9 KΩ | W | - | [46] |
| Contact Material | Electrode | Structure | Output Performance | Durability (Cycles) | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Voltage | Current | Load Resistance | Power Density | ||||
| PPy | PS | PTFE/Cu | Radial arrayed | 1.05 V | - | 1 MΩ–3.75 MΩ | - | - | [99] |
| PANI | PVDF | N-PANI | Arch-shaped | 1186 V | A | 100 MΩ | 15,000 | [100] | |
| PEDOT:PSS | ITO | AgNW | bilayer | 160 V | 2 MΩ | - | [101] | ||
| PANI@WCT | - | PANI@WCT | cotton textile | 460 V | 7.8 ± 2.1 kΩ | 5000 | [33] | ||
| The snow | PEDOT:PSS | AI | micropatterned Si layer | 8 V | 50 MΩ | 8000 | [102] | ||
| PAM | PEDOT:PSS | MGP hydrogel | hydrogel and sandwich | 383.8 V | 30 MΩ | 16,000 | [103] | ||
| PANI NW | elastic sponge | sponge | 3D reticular structure | 540 V | 20 MΩ | W | 30,000 | [104] | |
| PEDOT:PSS | CNF | CF | 3D nanonetwork | 150 V | 100 MΩ | 6000 | [105] | ||
| Human skin | MT-PDMS | PPy@CT | - | 200 V | 70 MΩ | 5000 | [106] | ||
| PTFE | hPPy | PPy | Sandwich-structure | 48 V | 100 MΩ–1 GΩ | 10,000 | [97] | ||
| PDMS | hogskin | PEDOT:PSS | - | 255.6 V | 100 MΩ | 200 | [107] | ||
| Human skin | Silicone rubber | PEDOT:PSS | Sandwich with liquid | 265 V | 100 KΩ–10 GΩ | W | 1000 | [108] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; You, L.; Meng, X.; Wang, B.; Lin, D. Recent Advances on Conducting Polymers Based Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111308
Zhang W, You L, Meng X, Wang B, Lin D. Recent Advances on Conducting Polymers Based Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting. Micromachines. 2021; 12(11):1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111308
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Weichi, Liwen You, Xiao Meng, Bozhi Wang, and Dabin Lin. 2021. "Recent Advances on Conducting Polymers Based Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting" Micromachines 12, no. 11: 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111308
APA StyleZhang, W., You, L., Meng, X., Wang, B., & Lin, D. (2021). Recent Advances on Conducting Polymers Based Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting. Micromachines, 12(11), 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111308







