A High-Precision Magnetic-Assisted Heading Angle Calculation Method Based on a 1D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in a Complicated Magnetic Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Principle of the System
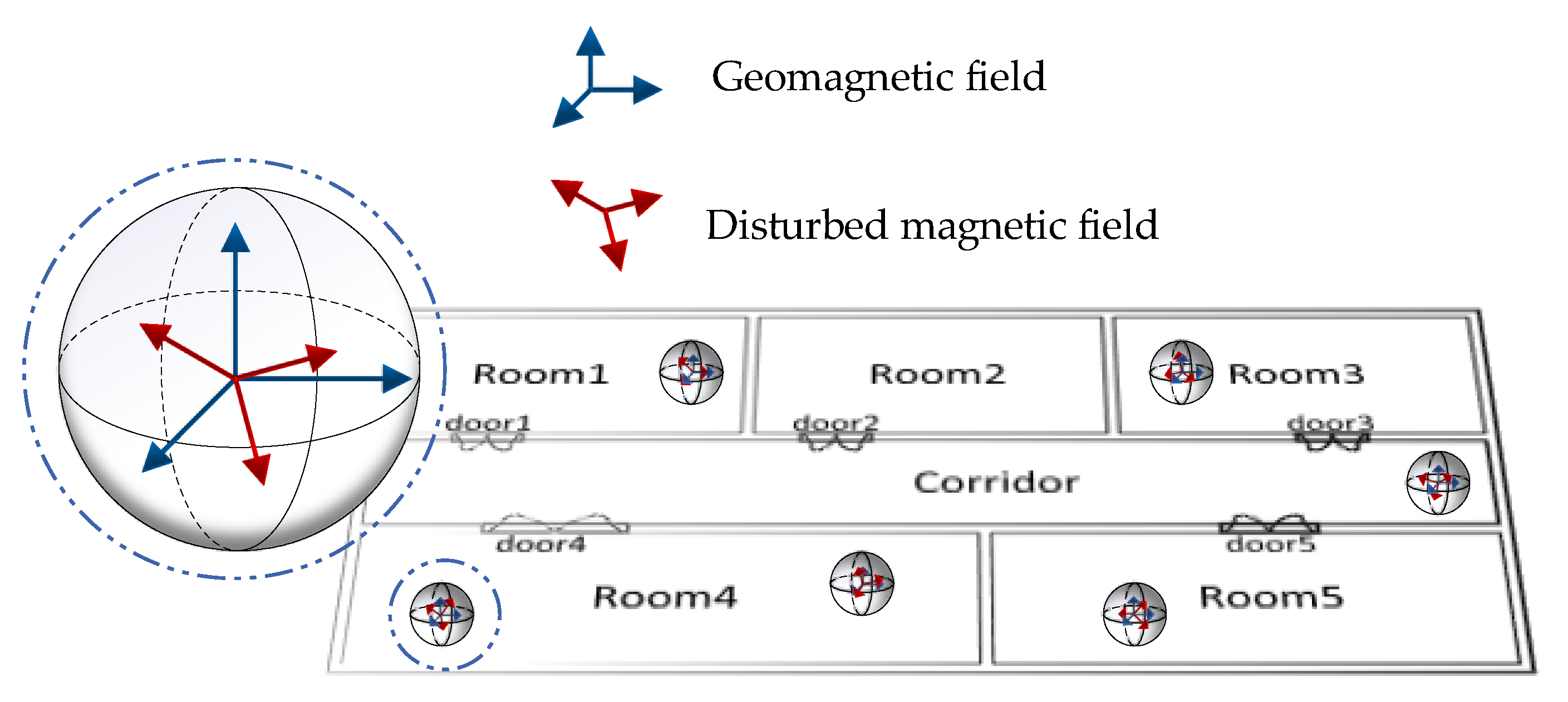
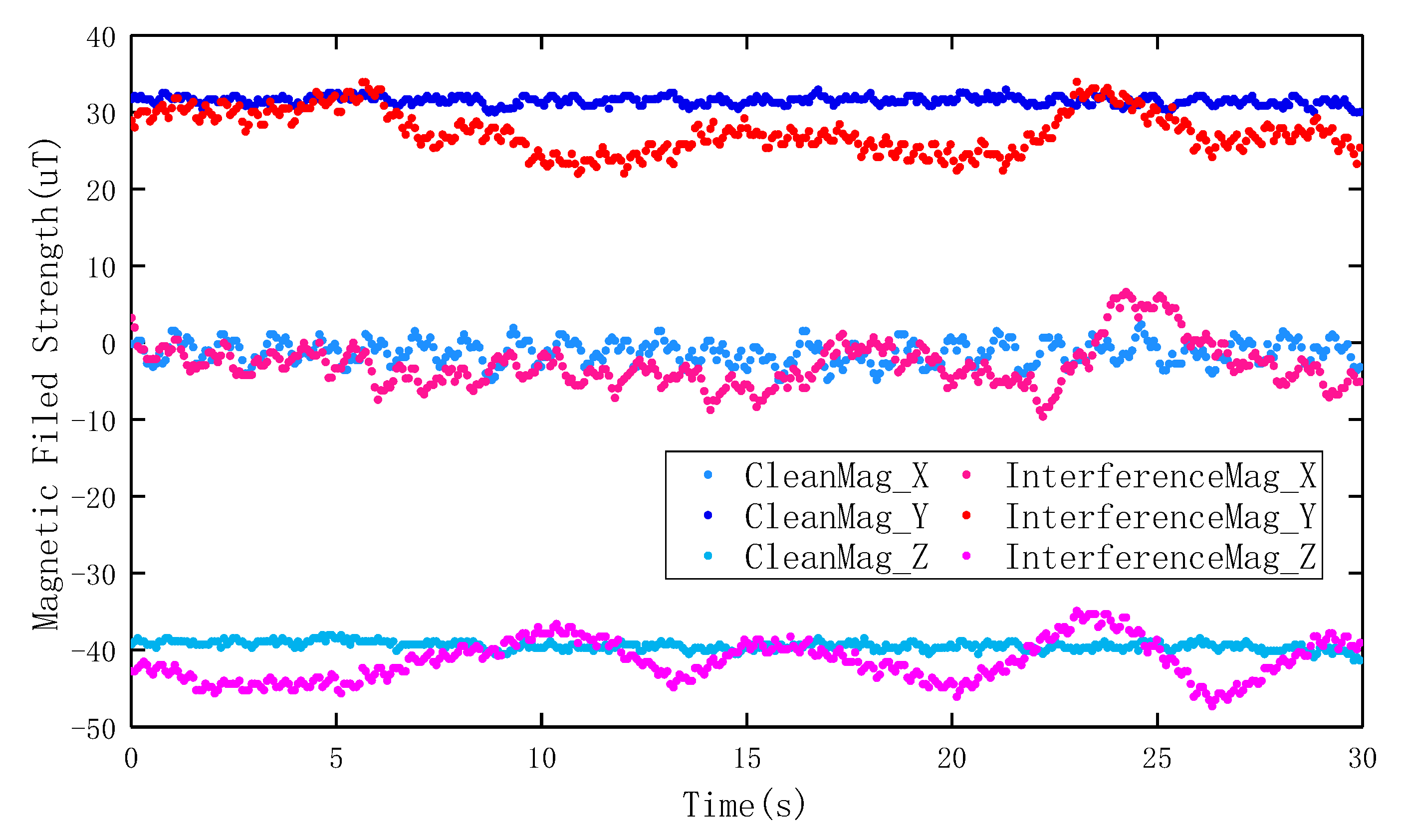
2.1. Geomagnetic Signal Analysis
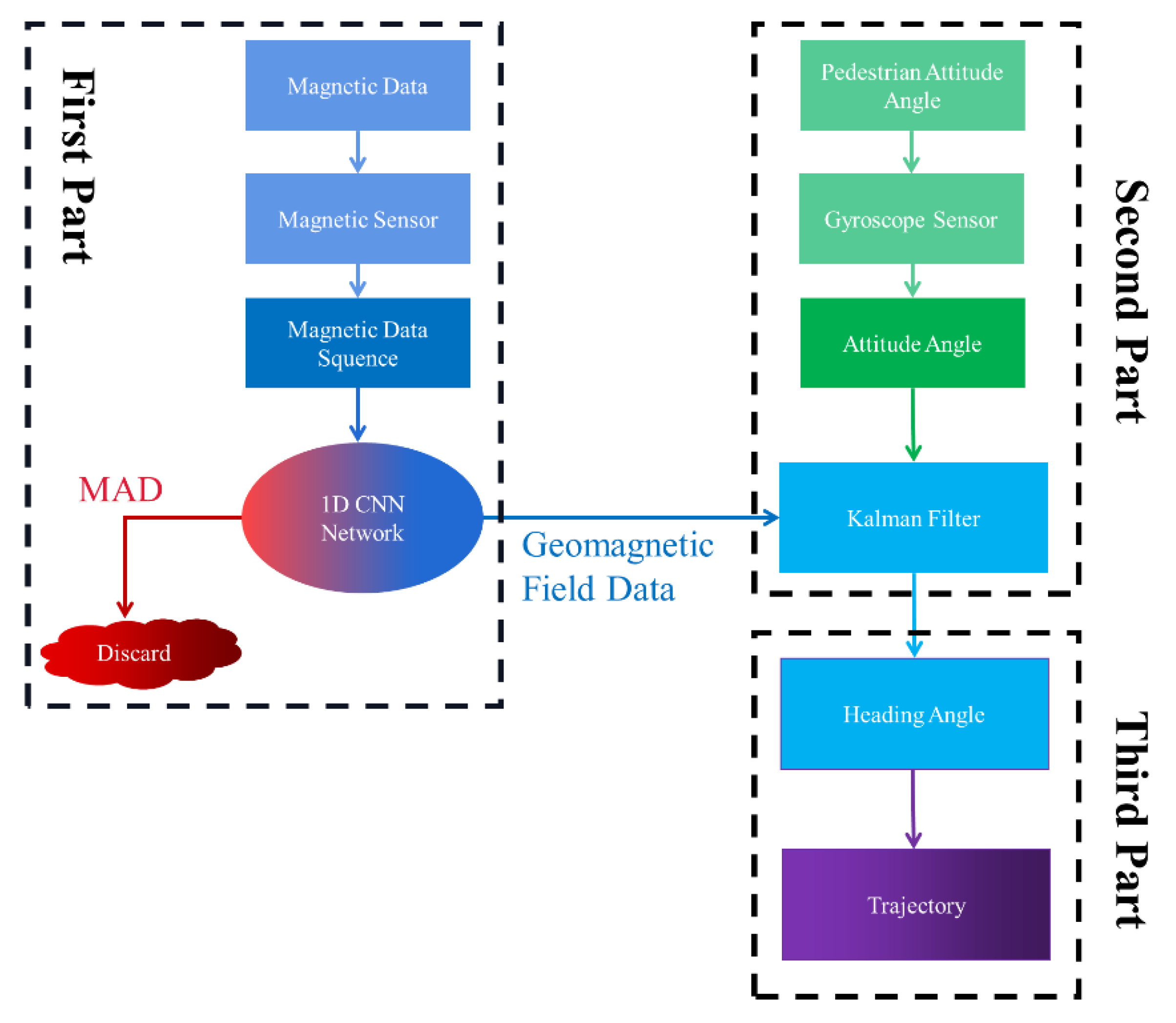
2.2. Algorithm Structure and Process
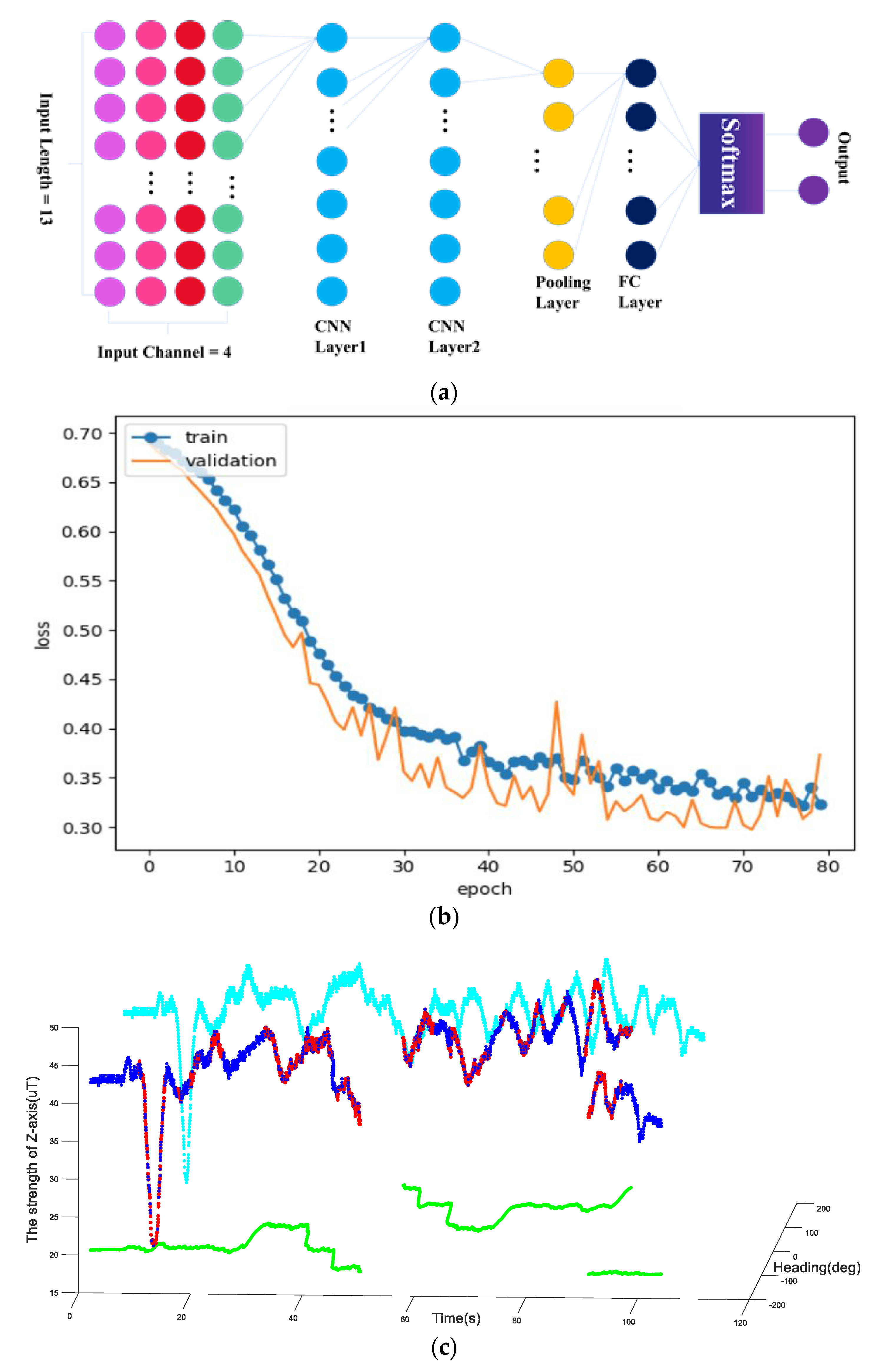
2.3. Magnetic Anomaly Detection Based on Unsupervised Learning
2.4. Geomagnetic Signal-Assisted Heading Angle Calculation
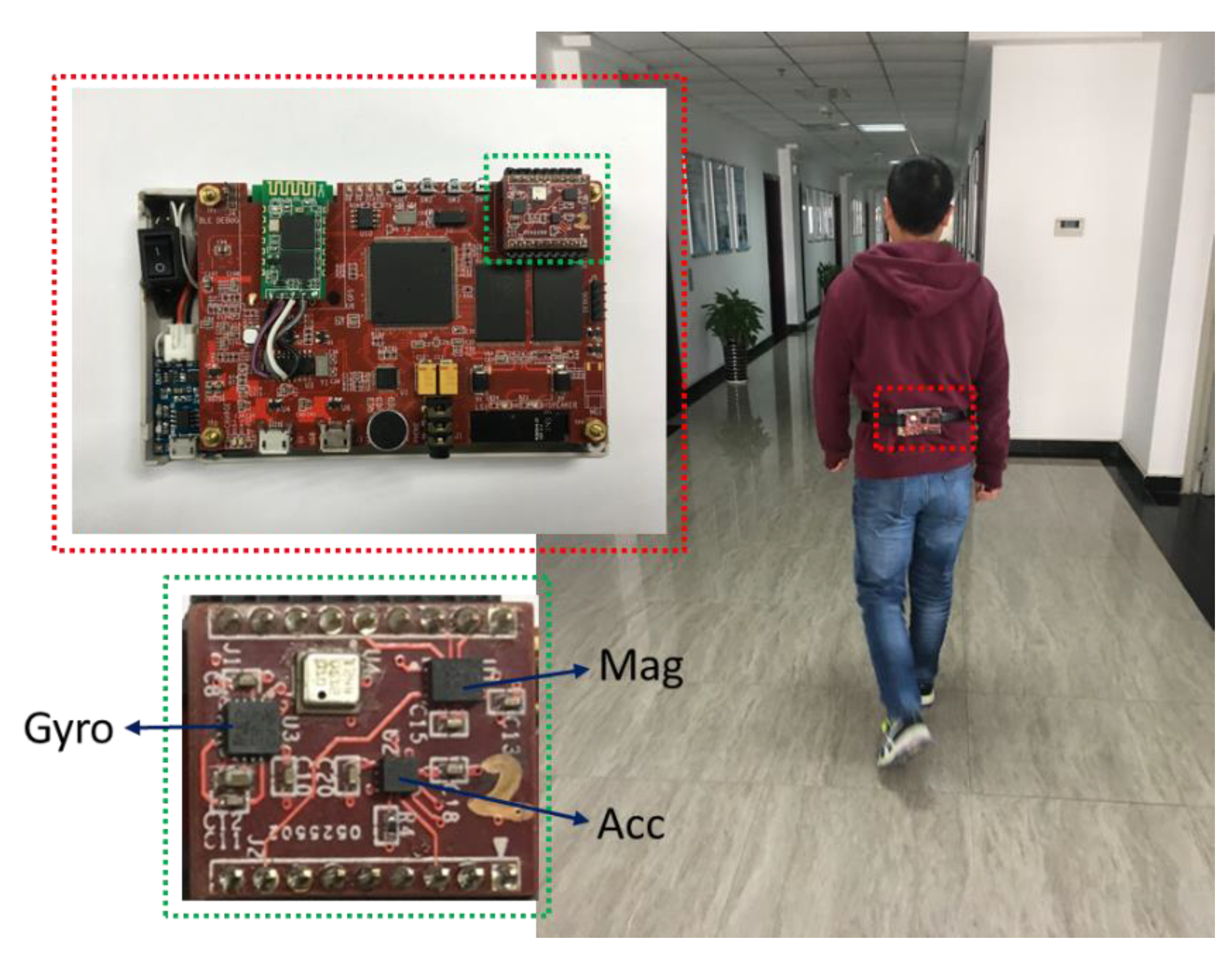
3. Experiments and Results
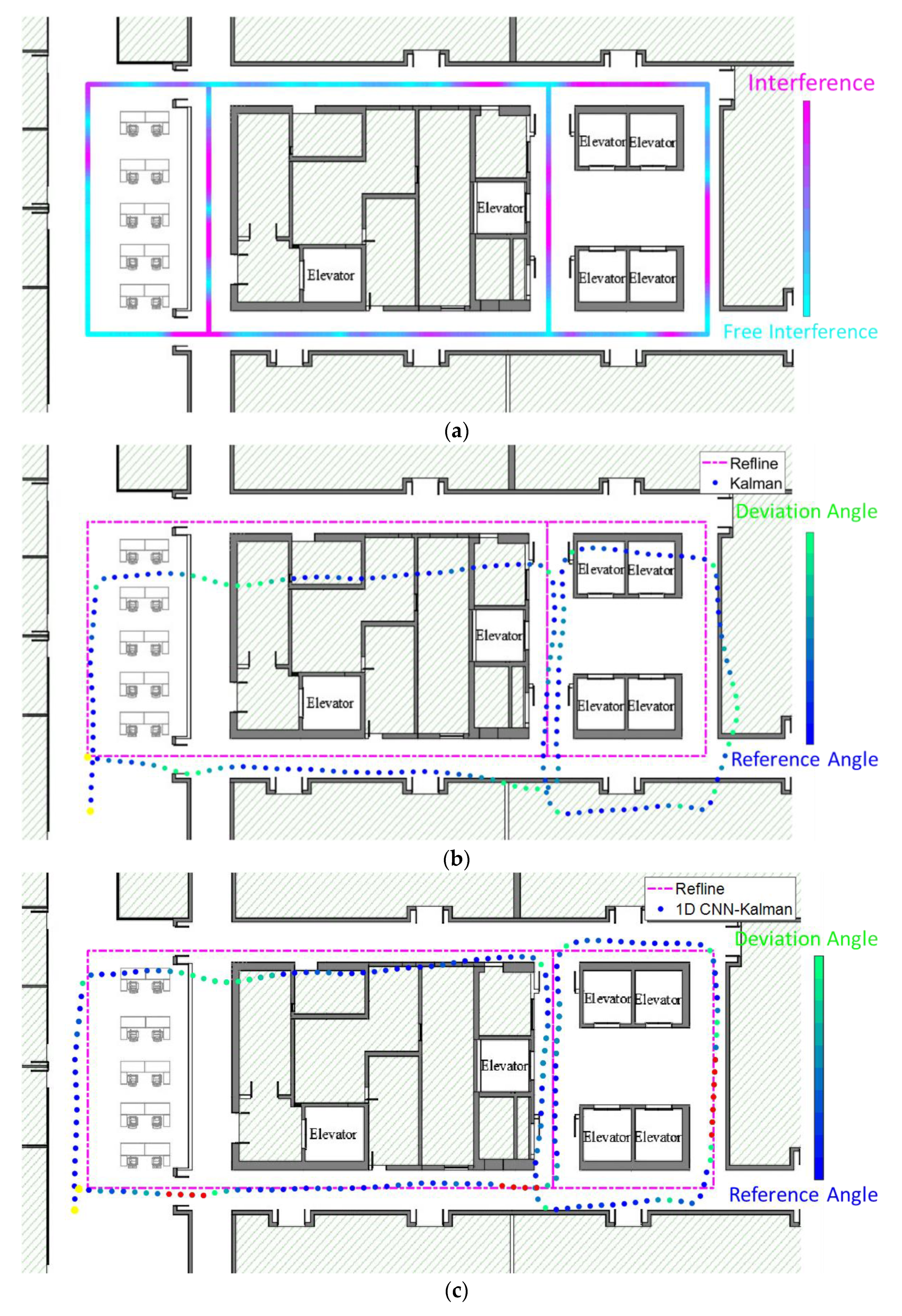
3.1. Magnetic Anomaly Detection and Trajectory Experiments
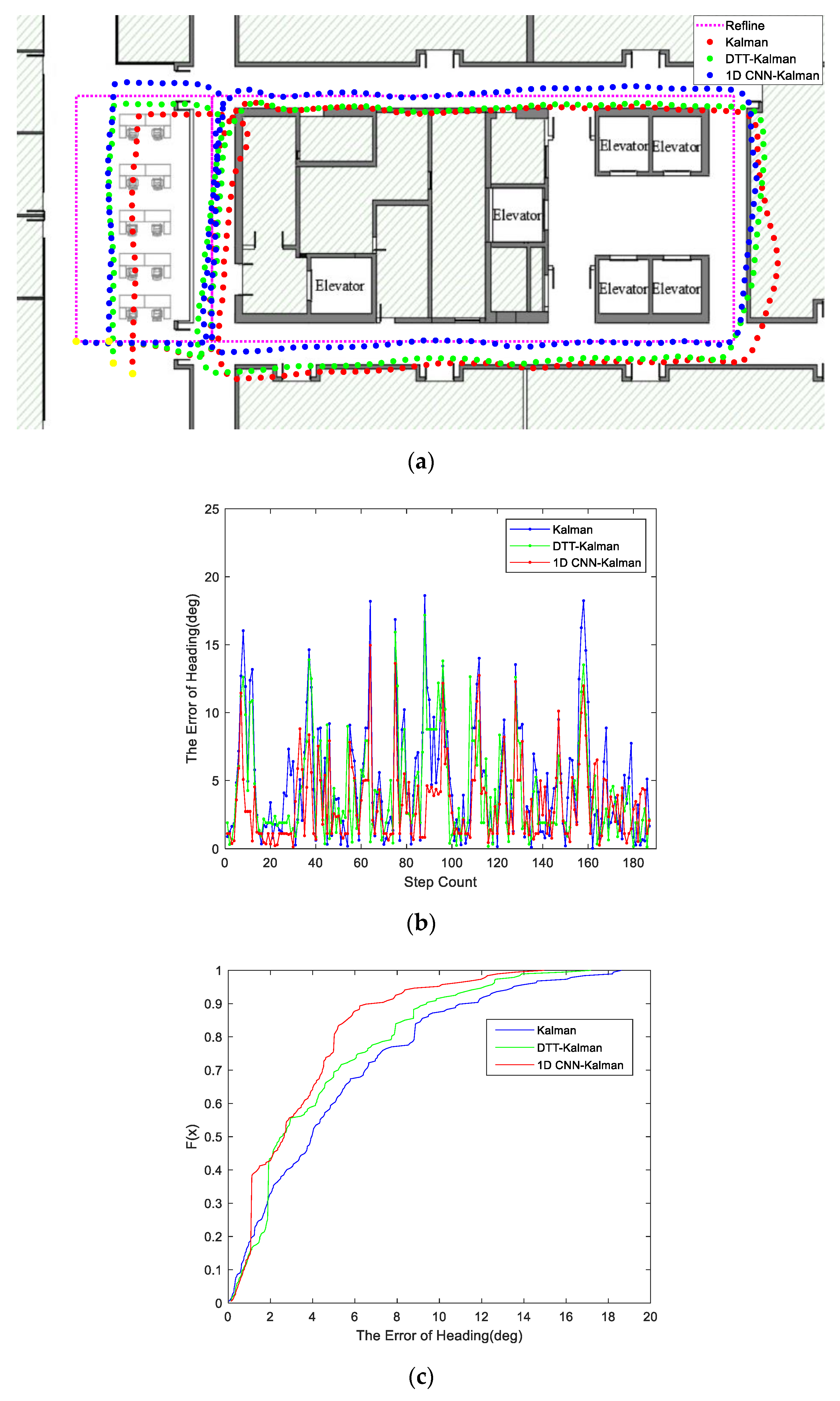
3.2. New Comparative Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantón Paterna, V.; Calveras Augé, A.; Paradells Aspas, J.; Pérez Bullones, M.A. A Bluetooth Low Energy Indoor Positioning System with Channel Diversity, Weighted Trilateration and Kalman Filtering. Sensors 2017, 17, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.; Kirkko-Jaakkola, M.; Rantanen, J.; Ruotsalainen, L. Proof of Concept Tests on Cooperative Tactical Pedestrian Indoor Navigation. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Cambridge, UK, 10–13 July 2018; pp. 1369–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Shao, H. WiFi-based indoor positioning. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, M. Low-Cost BD/MEMS Tightly-Coupled Pedestrian Navigation Algorithm. Micromachines 2016, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Meng, M.Q.-H. WiFi signal strength-based robot indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), Hailar, China, 28–30 July 2014; pp. 250–256. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Meng, M.Q.-H. Improving RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments: A motion removal approach. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 89, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. SmartMTra: Robust Indoor Trajectory Tracing Using Smartphones. IEEE Sens. J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.X. Dual MIMU Pedestrian Navigation by Inequality Constraint Kalman Filtering. Sensors 2017, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, N.; Arif, S.; Qadeer, N.; Khan, Z.H. Development of a Low Cost Wireless IMU Using MEMS Sensors for Pedestrian Navigation; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Suprem, A.; Deep, V.; Elarabi, T. Orientation and Displacement Detection for Smart phone Device Based IMUs. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prateek, G.V.; Girisha, R.; Hari, K.V.S.; Handel, P. Data Fusion of Dual Foot-Mounted INS to Reduce the Systematic Heading Drift. In Fourth International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Modelling and Simulation; AlDabass, D., Uthayopas, P., Sanguanpong, S., Niramitranon, J., Eds.; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.Y. Heading Estimation with Real-time Compensation Based on Kalman Filter Algorithm for an Indoor Positioning System. ISPRS Int. GeoInf. 2016, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.A.; Wang, G.F.; Hu, Y.; Wu, D. Heading Estimation for Indoor Pedestrian Navigation Using a Smartphone in the Pocket. Sensors 2015, 15, 21518–21536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ou, G.; Peng, A.; Zheng, L.; Shi, J. An INS/Floor-Plan Indoor Localization System Using the Firefly Particle Filter. ISPRS Int. GeoInf. 2018, 7, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; El-Sheimy, N. Tightly-Coupled Integration of WiFi and MEMS Sensors on Handheld Devices for Indoor Pedestrian Navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combettes, C.; Renaudin, V. Delay Kalman Filter to Estimate the Attitude of a Mobile Object with Indoor Magnetic Field Gradients. Micromachines 2016, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjhai, C.; Keefe, K.O. Comparing Heading Estimates from Multiple Wearable Inertial and Magnetic Sensors Mounted on Lower Limbs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Nantes, France, 24–27 September 2018; pp. 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.Y. A Bluetooth/PDR Integration Algorithm for an Indoor Positioning System. Sensors 2015, 15, 24862–24885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Rahim, K. Heading Drift Mitigation for Low-Cost Inertial Pedestrian Navigation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 29 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, M.; Cho, K.; Baeg, S.-H.; Park, S. Drift Reduction in Pedestrian Navigation System by Exploiting Motion Constraints and Magnetic Field. Sensors 2016, 16, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svendsen, D.H.; Martino, L.; Camps-Valls, G. Active emulation of computer codes with Gaussian processes–Application to remote sensing. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 100, 107103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps-Valls, G.; Verrelst, J.; Munoz-Mari, J.; Laparra, V.; Mateo-Jiménez, F.; Gómez-Dans, J. A survey on Gaussian processes for earth-observation data analysis: A comprehensive investigation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiranyaz, S.; Avci, O.; Abdeljaber, O.; Ince, T.; Gabbouj, M.; Inman, D.J. 1D Convolutional Neural Networks and Applications: A Survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.03554. [Google Scholar]
- Längkvist, M.; Karlsson, L.; Loutfi, A. A review of unsupervised feature learning and deep learning for time-series modeling. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 42, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.C.; Vincent, P. Unsupervised Feature Learning and Deep Learning: A Review and New Perspectives. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1206.5538. [Google Scholar]
- Cheah, H.; Nisar, H.; Yap, V.; Lee, C.-Y. Convolutional neural networks for classification of music-listening EEG: Comparing 1D convolutional kernels with 2D kernels and cerebral laterality of musical influence. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.H. Earth Magnetism: A Guided Tour through Magnetic Fields; Elsevier Science: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Martino, L.; Read, J.; Elvira, V.; Louzada, F. Cooperative parallel particle filters for online model selection and applications to urban mobility. Digital Signal. Process. 2017, 60, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, F.; Davy, M.; Duflos, E.; Vanheeghe, P. Particle filtering for multisensor data fusion with switching observation models: Application to land vehicle positioning. IEEE Trans. Signal. Process. 2007, 55, 2703–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, H. Using the ADXL202 in Pedometer and Personal Navigation Applications. In Application Notes American Devices; One Technology Way: Norwood, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
| Method | Kalman | 1D CNN–Kalman |
|---|---|---|
| Error | 2.68 m | 1.06 m |
| Method | Kalman | DTT–Kalman | CNN–Kalman |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error | 2.85 m | 1.75 m | 1.21 m |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, G.; Wan, H.; Li, X. A High-Precision Magnetic-Assisted Heading Angle Calculation Method Based on a 1D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in a Complicated Magnetic Environment. Micromachines 2020, 11, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070642
Hu G, Wan H, Li X. A High-Precision Magnetic-Assisted Heading Angle Calculation Method Based on a 1D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in a Complicated Magnetic Environment. Micromachines. 2020; 11(7):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070642
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Guanghui, Hong Wan, and Xinxin Li. 2020. "A High-Precision Magnetic-Assisted Heading Angle Calculation Method Based on a 1D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in a Complicated Magnetic Environment" Micromachines 11, no. 7: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070642
APA StyleHu, G., Wan, H., & Li, X. (2020). A High-Precision Magnetic-Assisted Heading Angle Calculation Method Based on a 1D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in a Complicated Magnetic Environment. Micromachines, 11(7), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070642





