Improved Rectification and Osmotic Power in Polyelectrolyte-Filled Mesopores
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
3. Results and Discussion
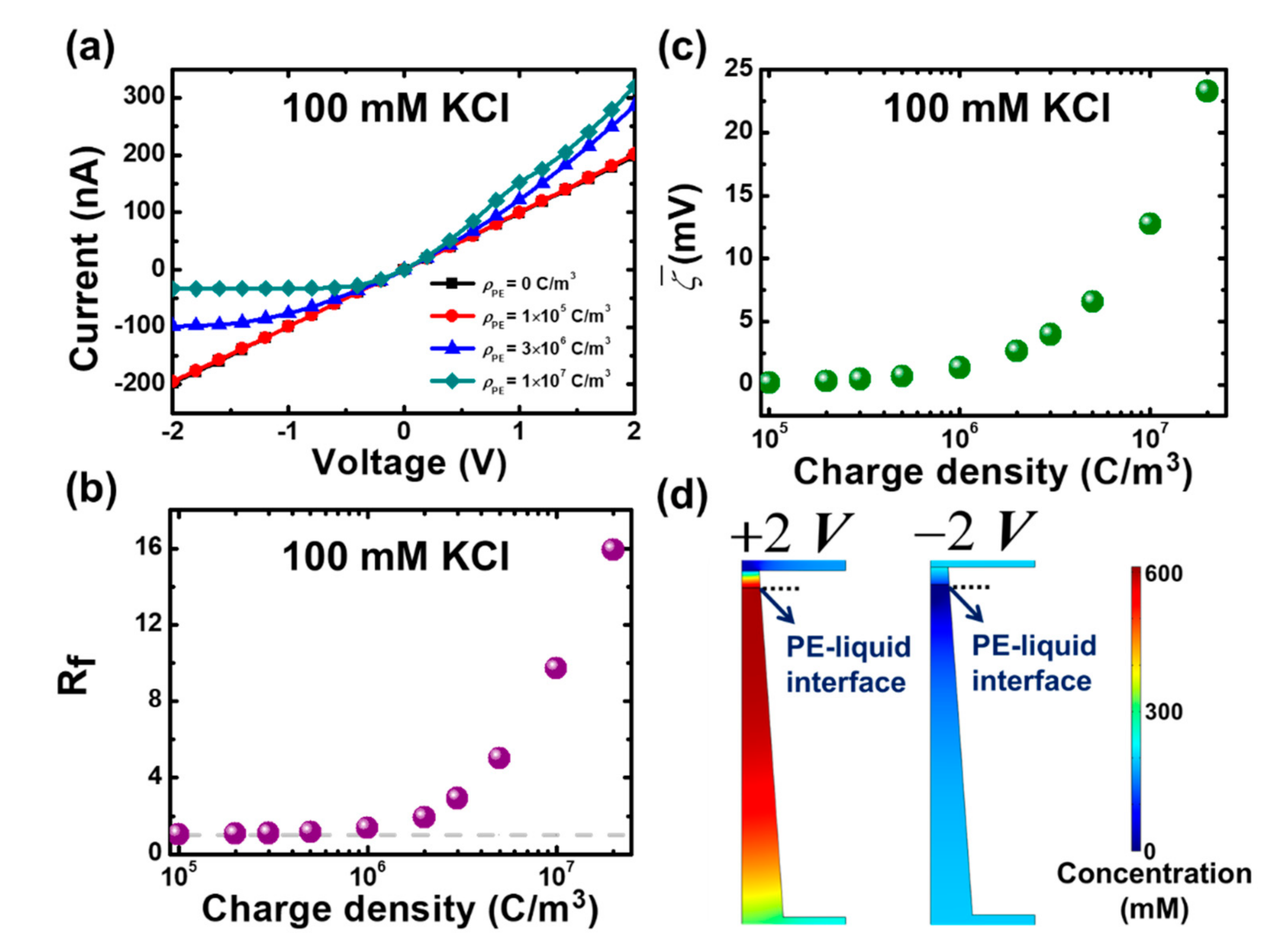
3.1. Modeling of Mesoscale Ionic Diode
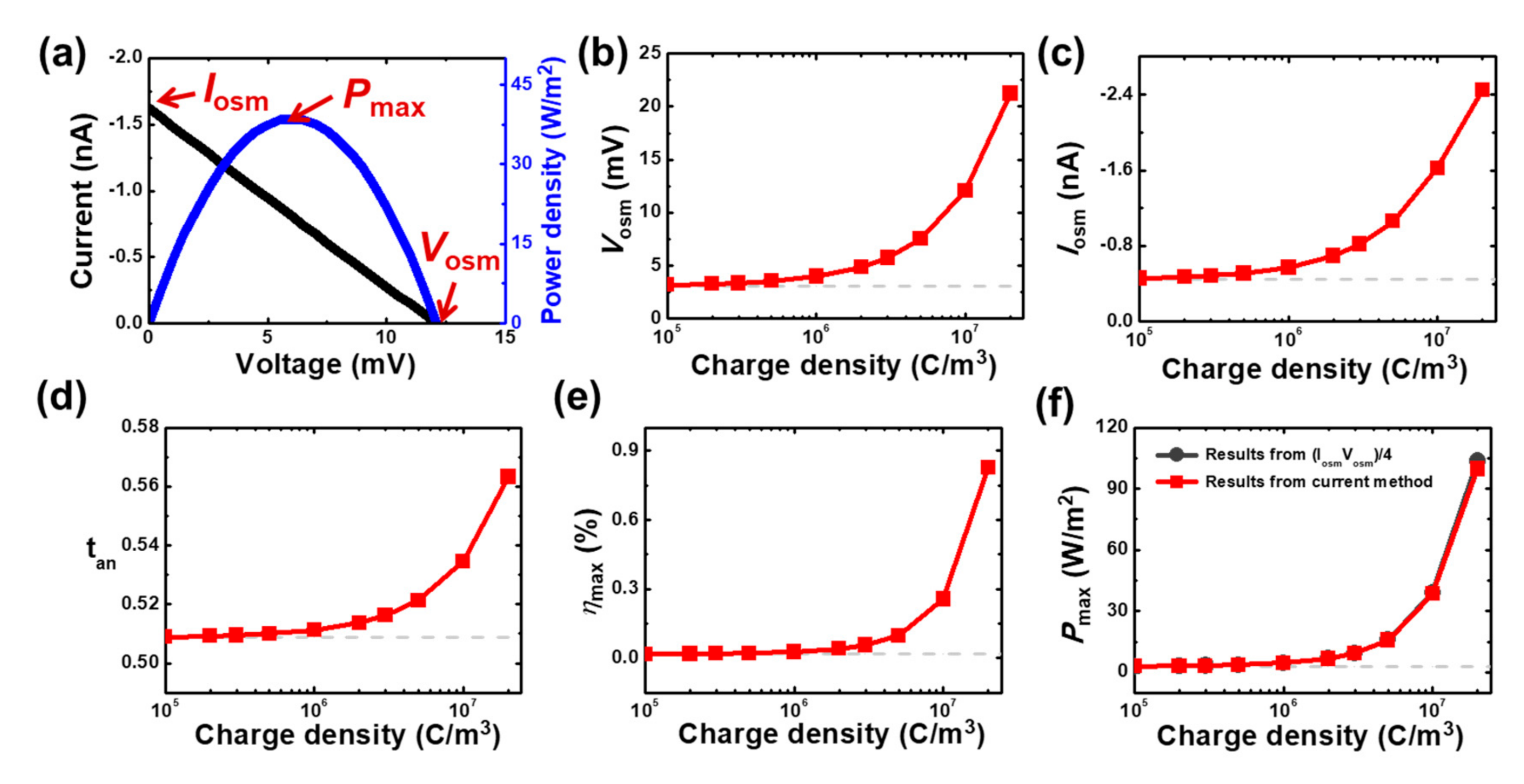
3.2. Modeling of Mesoscale Osmotic Power Conversion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schoch, R.B.; Han, J.Y.; Renaud, P. Transport phenomena in nanofluidics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 839–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Nanofluidics: A new arena for materials science. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1702419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, L.H.; Xue, S.; Joo, S.W.; Qian, S.; Hsu, J.P. Field effect control of surface charge property and electroosmotic flow in nanofluidics. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 4209–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, C.; Xuan, X.C. Electrokinetic energy conversion in slip nanochannels. J. Power Sources 2008, 179, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.K.; Qian, S. Field effect regulation of DNA translocation through a nanopore. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8217–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, L.H.; Zhang, M.K.; Joo, S.W.; Qian, S.Z. Slowing Down DNA translocation through a nanopore by lowering fluid temperature. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 3458–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.H.; Hughes, C.; Zeng, Z.; Qian, S. Tuning ion transport and selectivity by a salt gradient in a charged nanopore. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2681–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Hinkle, P.; Plett, T.S.; Yang, C.; Chacko, J.V.; Digman, M.A.; Yeh, L.H.; Hsu, J.P.; Siwy, Z.S. Highly charged particles cause a larger current blockage in micropores compared to neutral particles. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8413–8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Yeh, L.H.; Qian, S. Buffer anions can enormously enhance the electrokinetic energy conversion in nanofluidics with highly overlapped double layers. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.W.; Yang, D.R.; Wang, C.; Xia, X.H. Nanochannel-ion channel hybrid Device for ultrasensitive monitoring of Biomolecular recognition events. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.H.; Huang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Deng, M.J.; Chou, T.H.; Yang, H.C.O.; Ahamad, T.; Alshehri, S.M.; Wu, K.C.W. A nanofluidic osmotic power generator demonstrated in polymer gel electrolytes with substantially Enhanced performance. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2019, 7, 26791–26796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Gao, L.C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L.J.; Wen, L.P.; Jiang, L. Engineered nanochannel membranes with diode-like behavior for energy conversion over a wide pH range. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 23815–23821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, I.S.; Choi, K. Multi-asymmetric ion-diode membranes with superior selectivity and zero concentration polarization effect. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10761–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Wen, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhou, M.; Jin, X.Y.; Ding, L.P.; Dong, H.L.; Lu, D.N.; Jiang, L.; Guo, W. Highly efficient ionic photocurrent generation through WS2-based 2D nanofluidic channels. Small 2019, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.J.; Balanzat, E.; Janot, J.M.; Balme, S. Nanopore functionalized by highly charged hydrogels for osmotic energy harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12578–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.F.; Gao, P.C.; Ma, Q.; Wang, D.G.; Xia, F. Biomolecule-functionalized solid-state ion nanochannels/nanopores: Features and techniques. Small 2019, 15, 1804878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.X.; Yao, L.N.; Su, B. Bionic thermoelectric response with nanochannels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8608–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwy, Z.S. Ion-current rectification in nanopores and nanotubes with broken symmetry. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.J.; Guo, L.J. Nanofluidic diodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.H.; Siwy, Z.S.; Wanunu, M. Abnormal ionic-current rectification caused by reversed electroosmotic flow under viscosity gradients across thin nanopores. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.N.; Du, G.H.; Mao, G.B.; Guo, J.L.; Zhao, J.; Wu, R.Q.; Liu, W.J. Electrical field regulation of ion transport in polyethylene terephthalate nanochannels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38055–38060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.C.; Hou, J.; Ou, R.W.; Zhu, Y.L.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.T. Effect of anion species on ion current rectification properties of positively charged nanochannels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 28915–28922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Zhang, M.K.; Joo, S.W.; Cheney, M.A.; Qian, S. Effects of electroosmotic flow on ionic current rectification in conical nanopores. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 114, 3883–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.K.; Qian, S. Ionic current rectification in a conical nanofluidic field effect transistor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2011, 157, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Ai, Y.; Qian, S. pH-regulated ionic current rectification in conical nanopores functionalized with polyelectrolyte brushes. Phys. Chem. 2014, 16, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Yeh, L.H.; Hsu, J.P.; Tseng, S. Regulating current rectification and nanoparticle transport through a salt gradient in bipolar nanopores. Small 2015, 11, 4594–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.P.; Wu, H.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Tseng, S. Ion current rectification behavior of bioinspired nanopores having a pH-tunable zwitterionic surface. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3952–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Han, X.W.; Qian, S.Z.; Yang, Y.J.; Hu, N. Tuning ion transport through a nanopore by self-oscillating chemical reactions. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4600–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, W.K.; Huang, W.C.; Hsu, J.P. Ion current rectification behavior of a nanochannel having nonuniform cross-section. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Y.; Sun, Y.J.; Yan, H.; Ren, Y.K.; Song, C.L.; Wu, Q.S. A simulation analysis of nanofluidic ion current rectification using a metal-dielectric janus nanopore driven by induced-charge electrokinetic phenomena. Micromachines 2020, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E.; Farrell, T.; Psaltis, S. Mathematical modeling of ion transport through nanopores. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 23728–23738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.C.; He, Q.F.; Song, L.B.; Han, L.H.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.D.; Chen, W.; Zhan, D.P. Ion current rectification behavior of conical nanopores filled with spatially distributed Fixed charges. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 26299–26308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macha, M.; Marion, S.; Nandigana, V.V.R.; Radenovic, A. 2D materials as an emerging platform for nanopore-based power generation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 588–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.X.; Yao, L.N.; Yan, F.; Liu, S.S.; Yang, R.J.; Su, B. Thermo-osmotic energy conversion and storage by nanochannels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 25258–25261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laucirica, G.; Albesa, A.G.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Trautmann, C.; Marmisolle, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Shape matters: Enhanced osmotic energy harvesting in bullet-shaped nanochannels. Nano Energy 2020, 71, 104612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, L.; Zhu, C.C.; Qian, Y.C.; Wen, L.P.; Jiang, L. Improved osmotic energy conversion in heterogeneous membrane boosted by three-dimensional hydrogel interface. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Dong, T.D.; Lu, C.X.; Xin, W.W.; Yang, L.S.; Liu, P.; Qian, Y.C.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Kong, X.Y.; Wen, L.P.; et al. Tailoring a poly(ether sulfone) bipolar membrane: Osmotic-energy generator with high power density. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2020, 59, 17423–17428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Xiao, H.; Kong, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Niu, B.; Qian, Y.; Teng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wen, L. Biomimetic nacre-like silk-crosslinked membranes for osmotic energy harvesting. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9701–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.B.; Hao, J.R.; Bao, B.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Pang, J.H.; Jiang, Z.H.; Jiang, L. Unique ion rectification in hypersaline environment: A high-performance and sustainable power generator system. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.P.; Su, T.C.; Peng, P.H.; Hsu, S.C.; Zheng, M.J.; Yeh, L.H. Unraveling the anomalous surface-charge-dependent osmotic power using a single funnel-shaped nanochannel. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13374–13381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Combs, C.; Su, Y.S.; Yeh, L.H.; Siwy, Z.S. Rectification of concentration polarization in mesopores leads to high conductance ionic diodes and high performance osmotic power. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3691–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Yeh, L.H.; Siwy, Z.S. Voltage-induced modulation of ionic concentrations and ion current rectification in mesopores with highly charged pore walls. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.H.; Yang, H.C.O.; Tsai, P.C.; Yeh, L.H. Thermal dependence of the mesoscale ionic diode: Modeling and experimental verification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 17139–17146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, L.H.; Chen, F.; Chiou, Y.T.; Su, Y.S. Anomalous pH-dependent nanofluidic salinity gradient power. Small 2017, 13, 1702691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.P.; Lin, S.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Tseng, S. Power generation by a pH-regulated conical nanopore through reverse electrodialysis. J. Power Sources 2017, 366, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, X.L.; Jiang, Y.N.; Ding, L.P.; Jiang, L.; Guo, W. Understanding the giant gap between single-pore- and membrane-based nanofluidic osmotic power generators. Small 2019, 15, 1804279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Luo, Z.Q.; Kuang, Z.F.; Liu, Z.C.; Liu, W. Effects of heat transfer and the membrane thermal conductivity on the thermally nanofluidic salinity gradient energy conversion. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.H.; Zhang, M.; Qian, S.; Hsu, J.P.; Tseng, S. Ion concentration polarization in polyelectrolyte-modified nanopores. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 8672–8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.H.; Zhang, M.; Hu, N.; Joo, S.W.; Qian, S.; Hsu, J.P. Electrokinetic ion and fluid transport in nanopores functionalized by polyelectrolyte brushes. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5169–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Yeh, L.H.; Zhang, M.; Qian, S. Ion transport and selectivity in biomimetic nanopores with pH-tunable zwitterionic polyelectrolyte brushes. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17020–17029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Hsu, J.P. Regulating the ionic current rectification behavior of branched nanochannels by filling polyelectrolytes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 557, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.C.; Hsu, J.P.; Tseng, S. Electrodiffusioosmosis in a solid-state nanopore connecting two large reservoirs: Optimum pore size. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 19498–19504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wong, P.H.; Wang, P.H.; Siwy, Z.S.; Yeh, L.H. Electrodiffusioosmosis-induced negative differential resistance in pH-regulated mesopores containing purely monovalent solutions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 3198–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.H.; Zhang, M.; Qian, S.; Hsu, J.P. Regulating DNA translocation through functionalized soft nanopores. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2685–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, L.H.; Zhang, M.K.; Joo, S.W.; Qian, S.; Hsu, J.P. Controlling pH-regulated bionanoparticles translocation through nanopores with polyelectrolyte brushes. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9615–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Hsu, J.P.; Yeh, L.H. Rectification of ionic current in nanopores functionalized with bipolar polyelectrolyte brushes. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 258, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.P.; Wu, H.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Tseng, S. Importance of polyelectrolyte modification for rectifying the ionic current in conically shaped nanochannels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 5351–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.H.; Zhang, M.; Qian, S. Ion transport in a pH-regulated nanopore. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7527–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chen, F.; Yeh, L.H.; Hsu, J.P. Salt gradient driven ion transport in solid-state nanopores: The crucial role of reservoir geometry and size. Phys. Chem. 2016, 18, 30160–30165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Yeh, L.H.; Ma, Y.; Qian, S.Z. Tunable streaming current in a pH-regulated nanochannel by a field effect transistor. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 6090–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, J.F.L.; Gaboriaud, F. Progress in electrohydrodynamics of soft microbial particle interphases. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.W.; Hsu, J.P.; Lin, C.Y.; Tseng, S. Dual pH gradient and voltage modulation of ion transport and current rectification in biomimetic nanopores functionalized with a pH-Tunable POLYELECTROLYTE. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 12437–12443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Hsu, J.P. Ultrashort nanopores of large radius can generate anomalously high salinity gradient power. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 353, 136613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Kuang, Z.F.; Liu, Z.C.; Liu, W. Reverse electrodialysis in bilayer nanochannels: Salinity gradient-driven power generation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 7295–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, D.-C.; Yeh, L.-H. Improved Rectification and Osmotic Power in Polyelectrolyte-Filled Mesopores. Micromachines 2020, 11, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100949
Zheng D-C, Yeh L-H. Improved Rectification and Osmotic Power in Polyelectrolyte-Filled Mesopores. Micromachines. 2020; 11(10):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100949
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Ding-Cheng, and Li-Hsien Yeh. 2020. "Improved Rectification and Osmotic Power in Polyelectrolyte-Filled Mesopores" Micromachines 11, no. 10: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100949
APA StyleZheng, D.-C., & Yeh, L.-H. (2020). Improved Rectification and Osmotic Power in Polyelectrolyte-Filled Mesopores. Micromachines, 11(10), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100949





