Plasmonic Optical Biosensors for Detecting C-Reactive Protein: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Detection
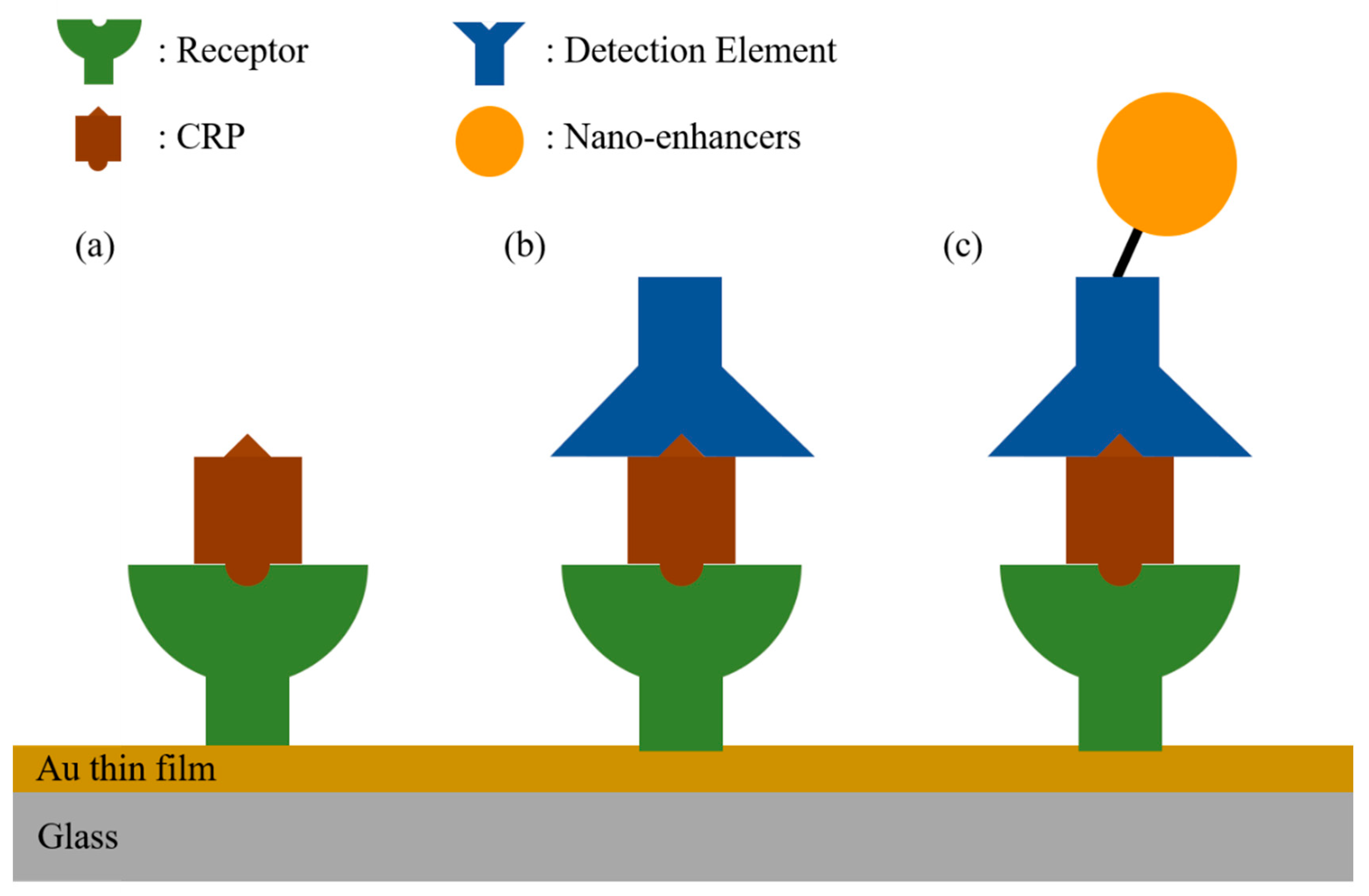
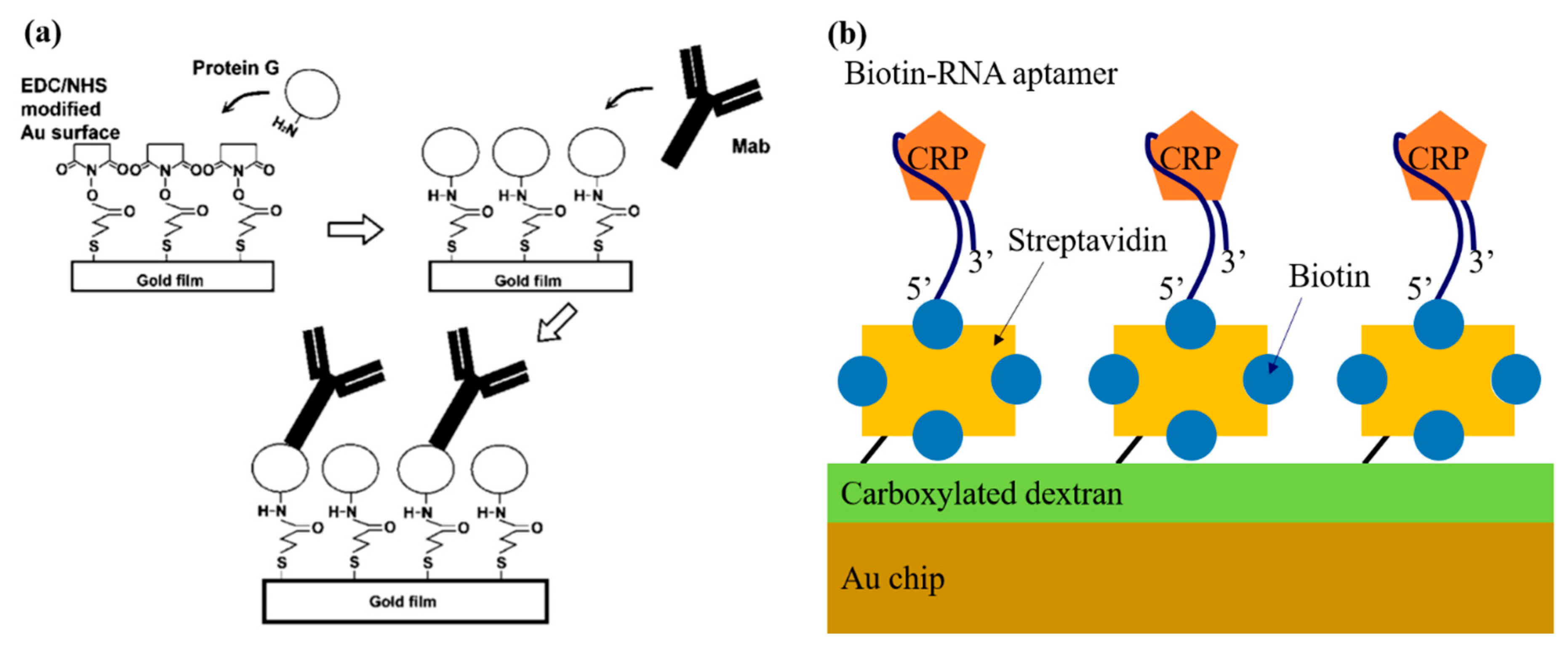
2.1. Direct Immunoassay
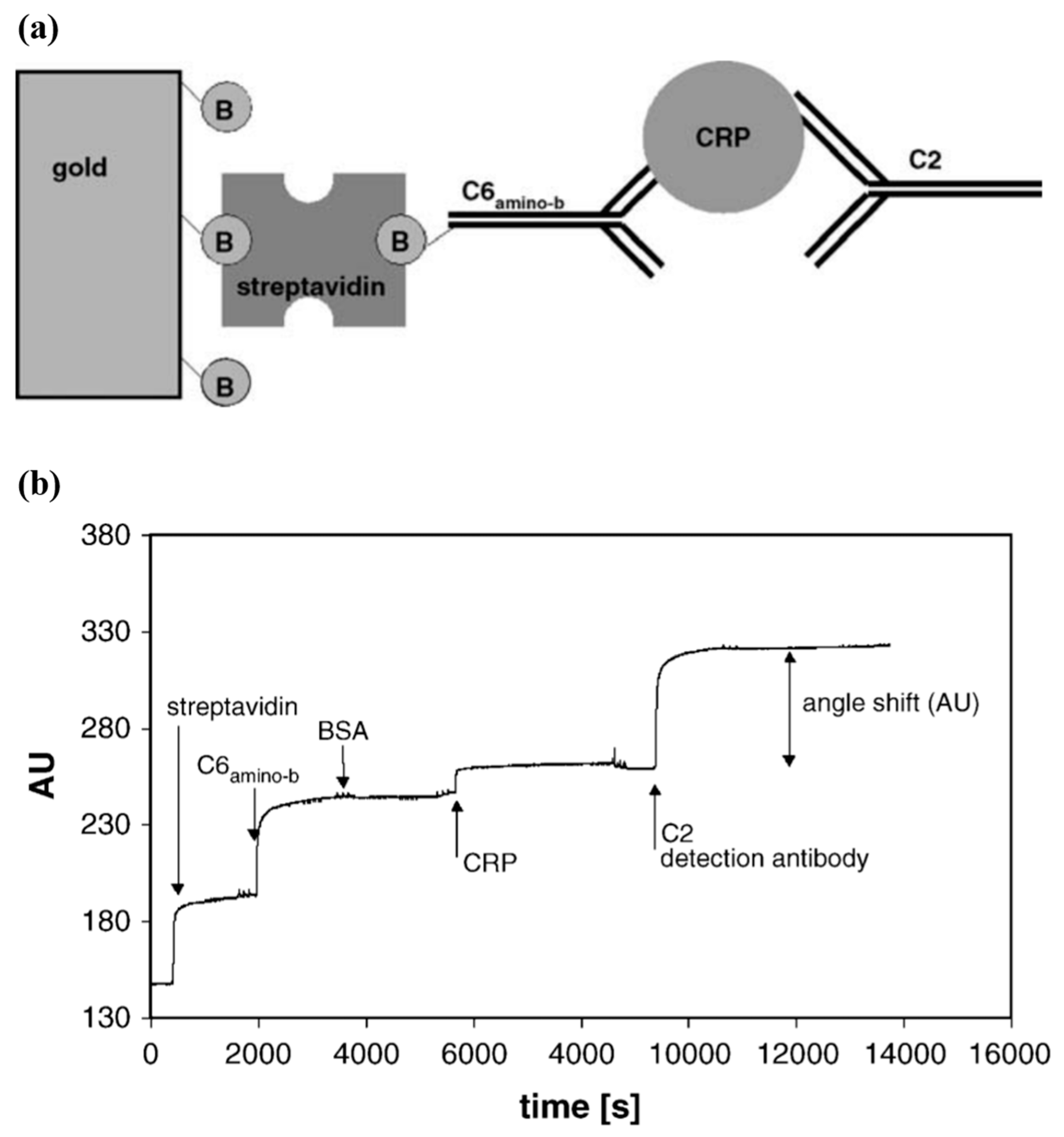
2.2. Sandwich Immunoassay
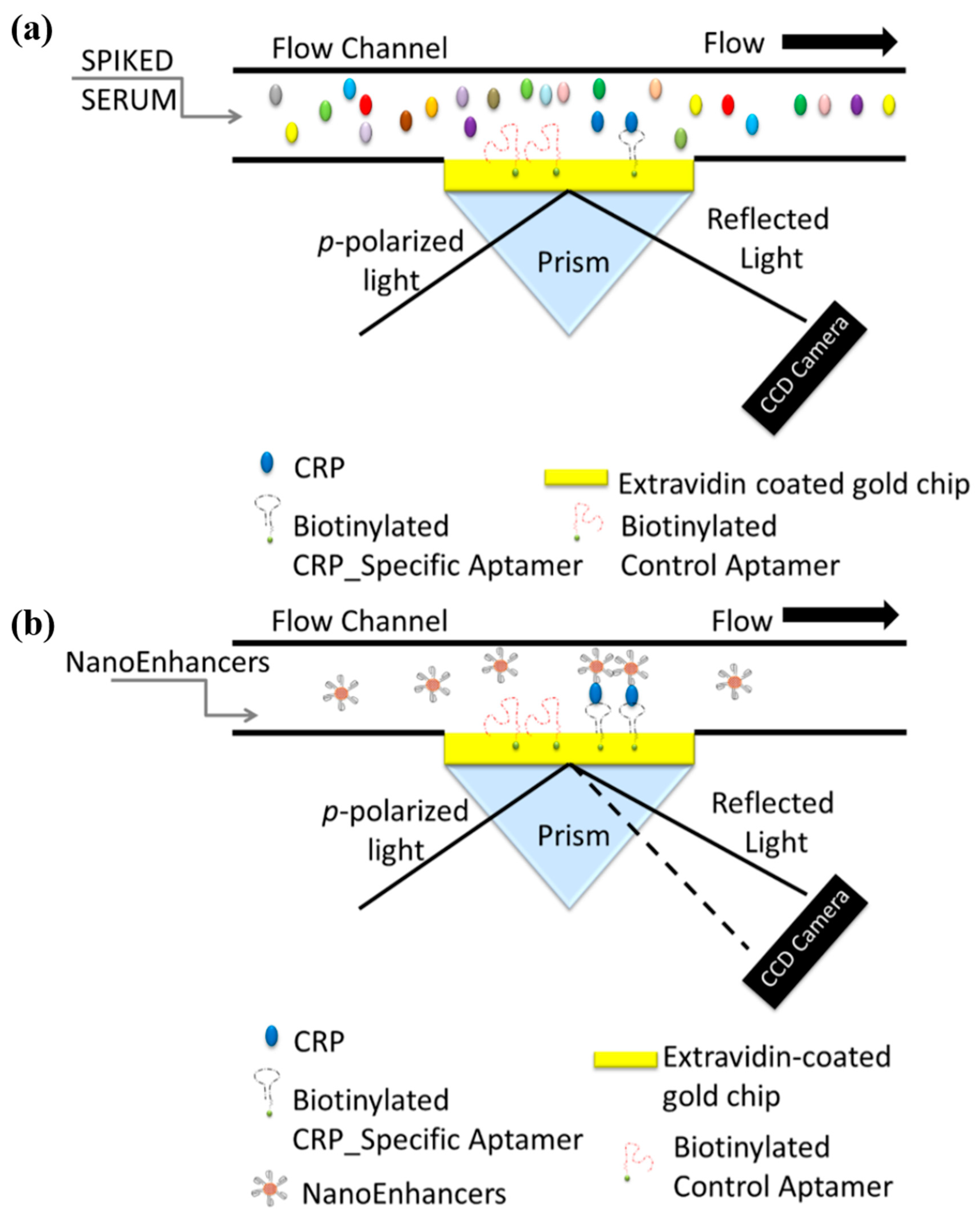
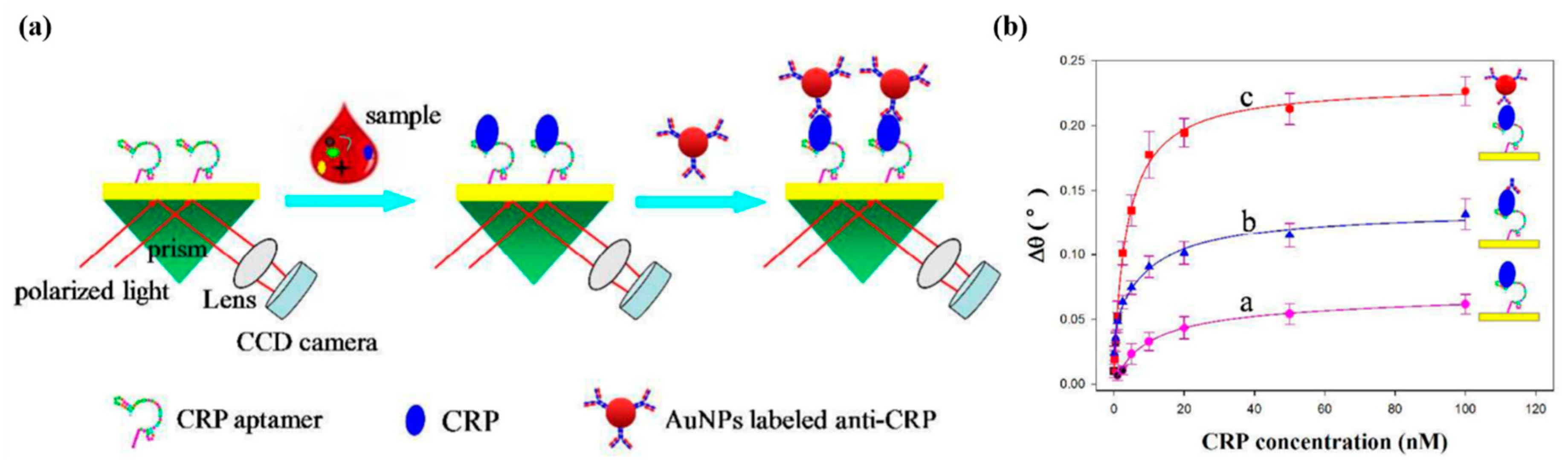
2.3. Nano-Enhancers for Sensitivity Enhancement
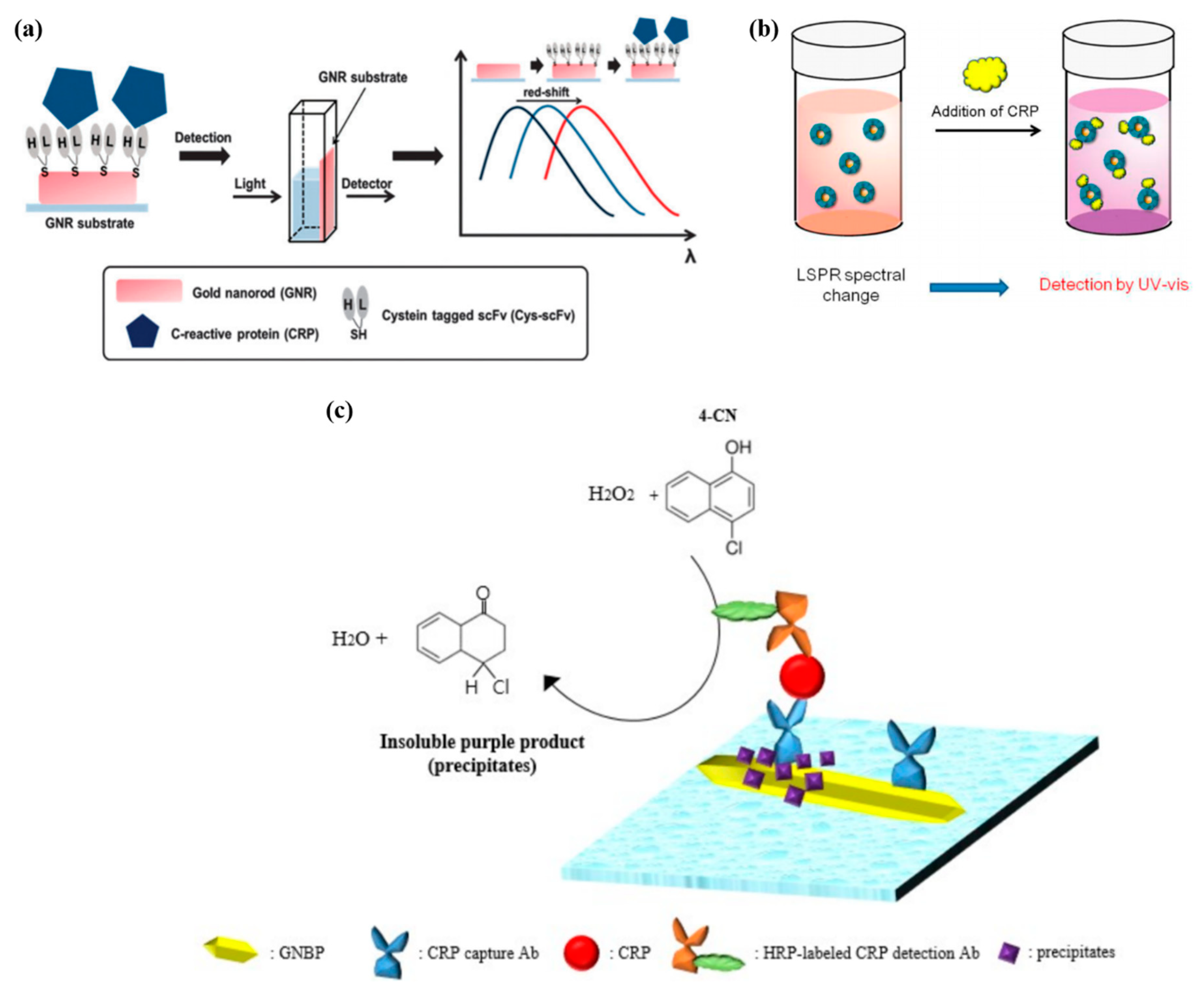
3. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance for Detecting CRP
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tillett, W.S.; Francis, T. Serological Reactions in Pneumonia with a Non-Protein Somatic Fraction of Pneumococcus. J. Exp. Med. 1930, 52, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sproston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvo, P.; Dini, V.; Kirchhain, A.; Janowska, A.; Oranges, T.; Chiricozzi, A.; Lomonaco, T.; Di Francesco, F.; Romanelli, M. Sensors and Biosensors for C-Reactive Protein, Temperature and pH, and Their Applications for Monitoring Wound Healing: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, W.A.; Rossi, P.J.; Cooper, S.; Master, V.A.; Jani, A.B. C-Reactive Protein (CRP): Initial Exploratory Study of an Inflammatory Biomarker for Prostate Cancer Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, S710–S711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, E.C.; Fidan, C.; Guzel, S.; Paketci, C. C-reactive protein (CRP)/mean platelet volume (MPV) ratio as a new biomarker for community-acquired pneumonia in children. Cukurova Med. J. 2017, 42, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, O.D.; Ohlsson, A.; Kenyon, C. Accuracy of leukocyte indices and C-reactive protein for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 1995, 14, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, T.; Pandey, A.; Deepa, D.; Asthana, A.K. C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and its Association with Periodontal Disease: A Brief Review. J. Clin. Diagn Res. 2014, 8, ZE21–ZE24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepys, M.B.; Hirschfield, G.M. C-reactive protein: A critical update. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.; Fahey, J.L.; Detels, R.; Butch, A.W. Analytical performance of a highly sensitive C-reactive protein-based immunoassay and the effects of laboratory variables on levels of protein in blood. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ridker, P.M. Clinical Application of C-Reactive Protein for Cardiovascular Disease Detection and Prevention. Circulation 2003, 107, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergenroeder, G.; Redell, J.B.; Moore, A.N.; Dubinsky, W.P.; Funk, R.T.; Crommett, J.; Clifton, G.L.; Levine, R.; Valadka, A.; Dash, P.K. Identification of serum biomarkers in brain-injured adults: Potential for predicting elevated intracranial pressure. J. Neurotrauma 2008, 25, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genest, J. C-reactive protein: Risk factor, biomarker and/or therapeutic target? Can. J. Cardiol. 2010, 26, 41A–44A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Kihara, K. C-reactive protein as a biomarker for urological cancers. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2011, 8, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, B.; Gleeson, M.; Cripps, A.W. C-reactive protein: A critical review. Pathology 1991, 23, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepys, M.B. C-reactive protein fifty years on. Lancet 1981, 1, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Clos, T.W. Function of C-reactive protein. Ann. Med. 2000, 32, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, J.P.; Shah, T.; Hingorani, A.D.; Danesh, J.; Pepys, M.B. C-reactive protein and coronary heart disease: A critical review. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 264, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigushin, D.M.; Pepys, M.B.; Hawkins, P.N. Metabolic and scintigraphic studies of radioiodinated human C-reactive protein in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.H.F.; Hartmann, M.; Keusgen, M. SPR-based immunosensor for the CRP detection—A new method to detect a well known protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1987–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clyne, B.; Olshaker, J.S. The C-reactive protein. J. Emerg. Med. 1999, 17, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkanova, V.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Allan, C.L. CRP, IL-6 and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 150, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostner, A.H.; Kersten, C.; Lowenmark, T.; Ydsten, K.A.; Peltonen, R.; Isoniemi, H.; Haglund, C.; Gunnarsson, U.; Isaksson, B. The prognostic role of systemic inflammation in patients undergoing resection of colorectal liver metastases: C-reactive protein (CRP) is a strong negative prognostic biomarker. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 114, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhong, X.; Cheng, G.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Hong, Y.; Wan, Q.; He, R.; Wang, Z. Hs-CRP and all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality risk: A meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2017, 259, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, W.; Gong, D.; Man, C.; Fan, Y. Hs-CRP in stroke: A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 453, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speidl, W.S.; Graf, S.; Hornykewycz, S.; Nikfardjam, M.; Niessner, A.; Zorn, G.; Wojta, J.; Huber, K. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein in the prediction of coronary events in patients with premature coronary artery disease. Am. Heart J. 2002, 144, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M. C-reactive protein-A simple test to help predict risk of heart attack and stroke. Circulation 2003, 108, E81–E85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, T.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Alexander, R.W.; Anderson, J.L.; Cannon, R.O., III; Criqui, M.; Fadl, Y.Y.; Fortmann, S.P.; Hong, Y.; Myers, G.L.; et al. Markers of inflammation and cardiovascular disease: Application to clinical and public health practice: A statement for healthcare professionals from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2003, 107, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnell, L.; Mold, C.; Du Clos, T.W. C-reactive protein: Ligands, receptors and role in inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 117, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.P.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chiou, A.; Tseng, K.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Chang, G.L.; Chen, S.J. Immunodetection of pentamer and modified C-reactive protein using surface plasmon resonance biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, S.; Kaufmann, J.; Roos, W.; Pohl, S. Development of a new microparticle-enhanced turbidimetric assay for C-reactive protein with superior features in analytical sensitivity and dynamic range. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1998, 12, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamwi, A.; Vukovich, T.; Wagner, O.; Rumpold, H.; Spies, R.; Stich, M.; Langecker, C. Evaluation of Turbidimetric High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Assays for Cardiovascular Risk Estimation. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 2044–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, S.H.; Qi, S.S.; Shen, X.Q.; Zeng, G.F.; Zhou, H.N. The effect of atorvastatin on serum myeloperoxidase and CRP levels in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 368, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, L.C.L.; Lima, J.C.; Gerstenblith, G.; Magalhães, L.P.; Moreira, A.; Barbosa, O., Jr.; Dumet, J.; Passos, L.C.S.; D’Oliveira Júnior, A.; Esteves, J.P. Correlation between turbidimetric and nephelometric methods of measuring C-reactive protein in patients with unstable angina or non-ST elevation acute myocardial infarction. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2003, 81, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thuillier, F.; Demarquilly, C.; Szymanowicz, A.; Gaillard, C.; Boniface, M.; Braidy, C.; Daunizeau, A.; Gascht, D.; Gruson, A.; Lagabrielle, J.F.; et al. Nephelometry or turbidimetry for the determination of albumin, ApoA, CRP, haptoglobin, IgM and transthyretin: Which choice? Ann. Biol. Clin. 2008, 66, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, L.H.; Gertz, M.A.; Skinner, M.; Cohen, A.S. Nephelometric measurement of human serum prealbumin and correlation with acute-phase proteins CRP and SAA: Results in familial amyloid polyneuropathy. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1984, 104, 538–545. [Google Scholar]
- Montagne, P.; Laroche, P.; Cuilliere, M.L.; Varcin, P.; Pau, B.; Duheille, J. Microparticle-enhanced nephelometric immunoassay for human C-reactive protein. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1992, 6, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.L.; Tsao, K.C.; Chang, C.P.; Li, C.N.; Sun, C.F.; Wu, J.T. Development of ELISA on microplate for serum C-reactive protein and establishment of age-dependent normal reference range. Clin. Chim. Acta 2002, 322, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjelgaard-Hansen, M.; Kristensen, A.T.; Jensen, A.L. Evaluation of a Commercially Available Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for the Determination of C-Reactive Protein in Canine Serum. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 2003, 50, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Moon, J.D.; Park, S.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Nahm, K.B.; Choi, E.Y. Evaluation of fluorescence hs-CRP immunoassay for point-of-care testing. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 356, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolov, D.E.; Ro Cker, C.; Hombach, V.; Nienhaus, G.U.; Torzewski, J. Ultrasensitive Confocal Fluorescence Microscopy of C-Reactive Protein Interacting With FcγRIIa. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 2372–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Keegan, G.L.; Stranik, O.; Brennan-Fournet, M.E.; McDonagh, C. Highly sensitive C-reactive protein (CRP) assay using metal-enhanced fluorescence (MEF). J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casa, E.; Kurosawa, C.; Kurosawa, S.; Aizawa, H.; Park, J.W.; Suzuki, H. Immunosensor using surface plasmon resonance for C-reactive protein detection. Electrochemistry 2006, 74, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.H.; Jung, J.W.; Suh, I.B.; Yuk, J.S.; Kim, W.J.; Choi, E.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Ha, K.S. Analysis of C-reactive protein on amide-linked N-hydroxysuccinimide-Dextran arrays with a spectral surface plasmon resonance biosensor for serodiagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5703–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, A.; Centi, S.; Tombelli, S.; Minunni, M.; Mascini, M. Development of an optical RNA-based aptasensor for C-reactive protein. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Ko, H.; Lee, G.Y.; Chang, S.Y.; Chang, Y.W.; Kang, M.J.; Pyun, J.C. Development of a sensitive SPR biosensor for C-reactive protein (CRP) using plasma-treated parylene-N film. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2015, 207, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, S.A.; Sandros, M.G. Zeptomole Detection of C-Reactive Protein in Serum by a Nanoparticle Amplified Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging Aptasensor. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Jiang, R.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.H.; Wang, K.M.; Li, W.S.; Chen, N.D.; Li, Q. Detection of C-reactive protein using nanoparticle- enhanced surface plasmon resonance using an aptamer-antibody sandwich assay. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3568–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aray, A.; Chiavaioli, F.; Arjmand, M.; Trono, C.; Tombelli, S.; Giannetti, A.; Cennamo, N.; Soltanolkotabi, M.; Zeni, L.; Baldini, F. SPR-based plastic optical fibre biosensor for the detection of C-reactive protein in serum. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.Y.; Shin, Y.B.; Li, T.; Park, J.H.; Kim, D.M.; Choi, D.H.; Kim, M.G. The use of an engineered single chain variable fragment in a localized surface plasmon resonance method for analysis of the C-reactive protein. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9497–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Nanosensing of C-Reactive Protein with Poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine)-Grafted Gold Nanoparticles Prepared by Surface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5587–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Byun, J.-Y.; Ahn, Y.-D.; Kim, M.-G. A localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) immunosensor for CRP detection using 4-chloro-1-naphtol (4-CN) precipitation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Nano-Bio Sensing, Imaging, and Spectroscopy, Jeju, Korea, 22–24 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.D.; White, I.M.; Shopova, S.I.; Zhu, H.Y.; Suter, J.D.; Sun, Y.Z. Sensitive optical biosensors for unlabeled targets: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 620, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damborský, P.; Švitel, J.; Katrlík, J. Optical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spackova, B.; Wrobel, P.; Bockova, M.; Homola, J. Optical Biosensors Based on Plasmonic Nanostructures: A Review. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 2380–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.T.; Yoon, W.J.; Lee, J.H.; Ju, H. DNA sequence-induced modulation of bimetallic surface plasmons in optical fibers for sub-ppq (parts-per-quadrillion) detection of mercury ions in water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 23894–23902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.T.; Trinh, K.T.L.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, W.J.; Ju, H. Reproducible Enhancement of Fluorescence by Bimetal Mediated Surface Plasmon Coupled Emission for Highly Sensitive Quantitative Diagnosis of Double-Stranded DNA. Small 2018, 14, e1801385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.H.T.; Phan, B.T.; Yoon, W.J.; Khym, S.; Ju, H. Dielectric Metal-Based Multilayers for Surface Plasmon Resonance with Enhanced Quality Factor of the Plasmonic Waves. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 3654–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nu, T.T.V.; Tran, N.H.T.; Nam, E.; Nguyen, T.T.; Yoon, W.J.; Cho, S.; Kim, J.; Chang, K.A.; Ju, H. Blood-based immunoassay of tau proteins for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using surface plasmon resonance fiber sensors. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7855–7862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Son, C.; Choi, S.; Yoon, W.J.; Ju, H. A Plasmonic Fiber Based Glucometer and Its Temperature Dependence. Micromachines 2018, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qureshi, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. Biosensors for cardiac biomarkers detection: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homola, J.; Yee, S.S.; Gauglitz, G. Surface plasmon resonance sensors: Review. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 1999, 54, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J.; Koudela, I.; Yee, S.S. Surface plasmon resonance sensors based on diffraction gratings and prism couplers: Sensitivity comparison. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 1999, 54, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, R. SPR for molecular interaction analysis: A review of emerging application areas. J. Mol. Recognit. 2004, 17, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ming, H. Review of surface plasmon resonance and localized surface plasmon resonance sensor. Photonic Sens. 2012, 2, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghrera, A.S.; Pandey, M.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Quantum dot monolayer for surface plasmon resonance signal enhancement and DNA hybridization detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Cronin, S.B. A Review of Surface Plasmon Resonance-Enhanced Photocatalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepys, M.B.; Baltz, M.L. Acute Phase Proteins with Special Reference to C-Reactive Protein and Related Proteins (Pentaxins) and Serum Amyloid A Protein. In Advances in Immunology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1983; Volume 34, pp. 141–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugimiya, A.; Takeuchi, T. Surface plasmon resonance sensor using molecularly imprinted polymer for detection of sialic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.M.; Chen, S.F.; Taylor, A.D.; Homola, J.; Hock, B.; Jiang, S.Y. Detection of low-molecular-weight domoic acid using surface plasmon resonance sensor. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2005, 107, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, B.; Calle, A.; Lechuga, L.M.; Armelles, G. Highly sensitive detection of biomolecules with the magneto-optic surface-plasmon-resonance sensor. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J. Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 462–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabowo, B.A.; Purwidyantri, A.; Liu, K.-C. Surface Plasmon Resonance Optical Sensor: A Review on Light Source Technology. Biosensors 2018, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolduc, O.R.; Live, L.S.; Masson, J.-F. High-resolution surface plasmon resonance sensors based on a dove prism. Talanta 2009, 77, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.S.; Park, K.N.; Kang, C.D.; Kim, J.P.; Sim, S.J.; Lee, K.S. Optical fiber SPR biosensor with sandwich assay for the detection of prostate specific antigen. Opt. Commun. 2009, 282, 2827–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Massarotti, D.; Conte, L.; Zeni, L. Low Cost Sensors Based on SPR in a Plastic Optical Fiber for Biosensor Implementation. Sensors 2011, 11, 11752–11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Trinh, K.T.L.; Yoon, W.J.; Lee, N.Y.; Ju, H. Integration of a microfluidic polymerase chain reaction device and surface plasmon resonance fiber sensor into an inline all-in-one platform for pathogenic bacteria detection. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2017, 242, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Lee, E.C.; Ju, H. Bimetal coated optical fiber sensors based on surface plasmon resonance induced change in birefringence and intensity. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 5590–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Deng, Z.-Q.; Wang, Q. Fiber optic SPR sensor for liquid concentration measurement. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofas, S.; Malmqvist, M.; Ronnberg, I.; Stenberg, E.; Liedberg, B.; Lundstrom, I. Bioanalysis with Surface-Plasmon Resonance. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 1991, 5, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedberg, B.; Nylander, C.; Lundstrom, I. Biosensing with surface-plasmon resonance-how it all started. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, R1–R9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piliarik, M.; Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors: Approaching their limits? Opt. Express 2009, 17, 16505–16517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazyan, T.V. Landau damping of surface plasmons in metal nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillon, C.; Langot, P.; Del Fatti, N.; Vallee, F. Ultrafast Surface Plasmon Resonance Landau Damping and Electron Kinetics in Metal Nanoparticles; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5352. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Lee, R.; Li, T.; Yun, C.; Ham, Y.; An, S.S.A.; Ju, H. Label-Free Quantitative Immunoassay of Fibrinogen in Alzheimer Disease Patient Plasma Using Fiber Optical Surface Plasmon Resonance. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 2354–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Bea, S.O.; Kim, D.M.; Yoon, W.J.; Park, J.W.; An, S.S.A.; Ju, H. A regenerative label-free fiber optic sensor using surface plasmon resonance for clinical diagnosis of fibrinogen. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Cushing, S.K.; Wu, N. Plasmon-enhanced optical sensors: A review. Analyst 2015, 140, 386–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaushal, S.; Nanda, S.S.; Yi, D.K.; Ju, H. Effects of Aspect Ratio Heterogeneity of an Assembly of Gold Nanorod on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 5972–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryayeva, E.; Krull, U.J. Localized surface plasmon resonance: Nanostructures, bioassays and biosensing-A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haes, A.J.; Van Duyne, R.P. A unified view of propagating and localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 379, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rica, R.; Fratila, R.M.; Szarpak, A.; Huskens, J.; Velders, A.H. Multivalent Nanoparticle Networks as Ultrasensitive Enzyme Sensors. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2011, 50, 5703–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rica, R.; Velders, A.H. Supramolecular Au Nanoparticle Assemblies as Optical Probes for Enzyme-Linked Immunoassays. Small 2011, 7, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, A.; Kitayama, Y.; Takano, E.; Ooya, T.; Takeuchi, T. Supraparticles comprised of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles and modified gold nanoparticles as a nanosensor platform. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 25306–25311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Kawata, S.; Minami, S. Multilayer system for a high-precision surface plasmon resonance sensor. Opt. Lett. 1990, 15, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamon, Z.; Tollin, G. Optical Anisotropy in Lipid Bilayer Membranes: Coupled Plasmon-Waveguide Resonance Measurements of Molecular Orientation, Polarizability, and Shape. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chyou, J.-J.; Chu, C.-S.; Shih, C.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Huang, K.-T.; Chen, S.-J.; Shu, S.-F. High-Efficiency Electro-Optic Polymer Light Modulator Based On Waveguide-Coupled Surface Plasmon Resonance; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; Volume 5221. [Google Scholar]
- Wark, A.W.; Lee, H.J.; Corn, R.M. Long-Range Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging for Bioaffinity Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3904–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavík, R.; Homola, J. Ultrahigh resolution long range surface plasmon-based sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostálek, J.; Kasry, A.; Knoll, W. Long Range Surface Plasmons for Observation of Biomolecular Binding Events at Metallic Surfaces. Plasmonics 2007, 2, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, A.; Auslender, M.; Abdulhalim, I. Sensitivity enhancement of guided-wave surface-plasmon resonance sensors. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 2539–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Assay Type | Receptor | Detection Element | LOD | Detection Range | Detection Time[s] | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] | direct assay | antibody | CRP | 1 μg/mL | 1~10 μg/mL | 1200 | |
| [29] | direct assay | antibody | CRP | - | 1~26 μg/mL | 2400 | |
| [44] | direct assay | aptamer | CRP | 5 ng/mL | 5~100 ng/mL | 1400 | reusable |
| [45] | direct assay | parylene N film | CRP | - | 1 ng/mL~1 μg/mL | 5000 | |
| [48] | direct assay | antibody | CRP | 9 ng/mL | 9 ng/mL~70 μg/mL | 1200 | Fiber used |
| [19] | sandwich assay | antibody | antibody | 1 μg/mL | 2~5 μg/mL | 8000 | |
| [46] | nano-enhancer-sandwich assay | aptamer | QD-antobody | 5 fg/mL | 5 fg/mL~5 pg/mL | 11,000 | |
| [47] | nano-enhancer-sandwich assay | aptamer | AuNP-antibody | 1.15 ng/mL | 1.15 ng/mL~11.5 μg/mL | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seok, J.S.; Ju, H. Plasmonic Optical Biosensors for Detecting C-Reactive Protein: A Review. Micromachines 2020, 11, 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100895
Seok JS, Ju H. Plasmonic Optical Biosensors for Detecting C-Reactive Protein: A Review. Micromachines. 2020; 11(10):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100895
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeok, Joo Seon, and Heongkyu Ju. 2020. "Plasmonic Optical Biosensors for Detecting C-Reactive Protein: A Review" Micromachines 11, no. 10: 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100895
APA StyleSeok, J. S., & Ju, H. (2020). Plasmonic Optical Biosensors for Detecting C-Reactive Protein: A Review. Micromachines, 11(10), 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100895





