Li-Doping Effect on Characteristics of ZnO Thin Films Resistive Random Access Memory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
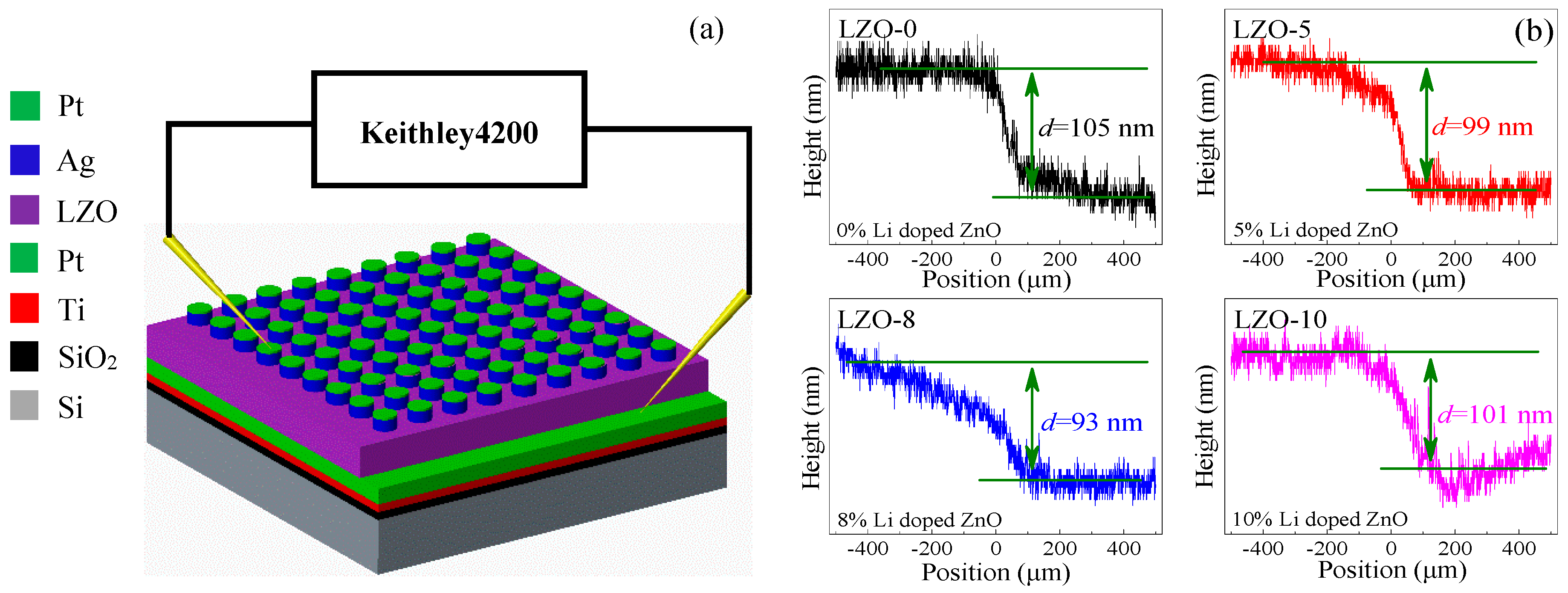
2.1. Fabrication of Device
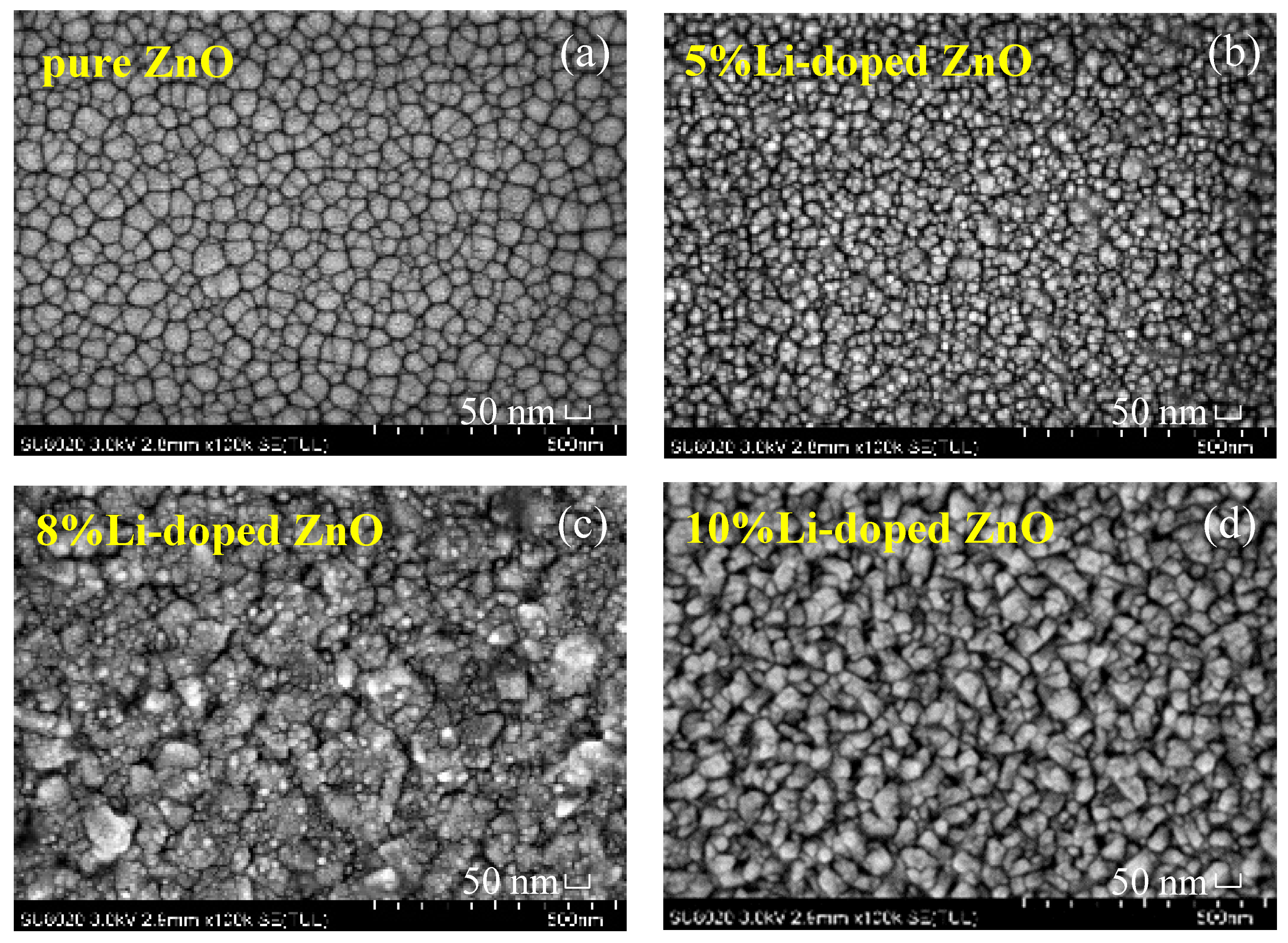
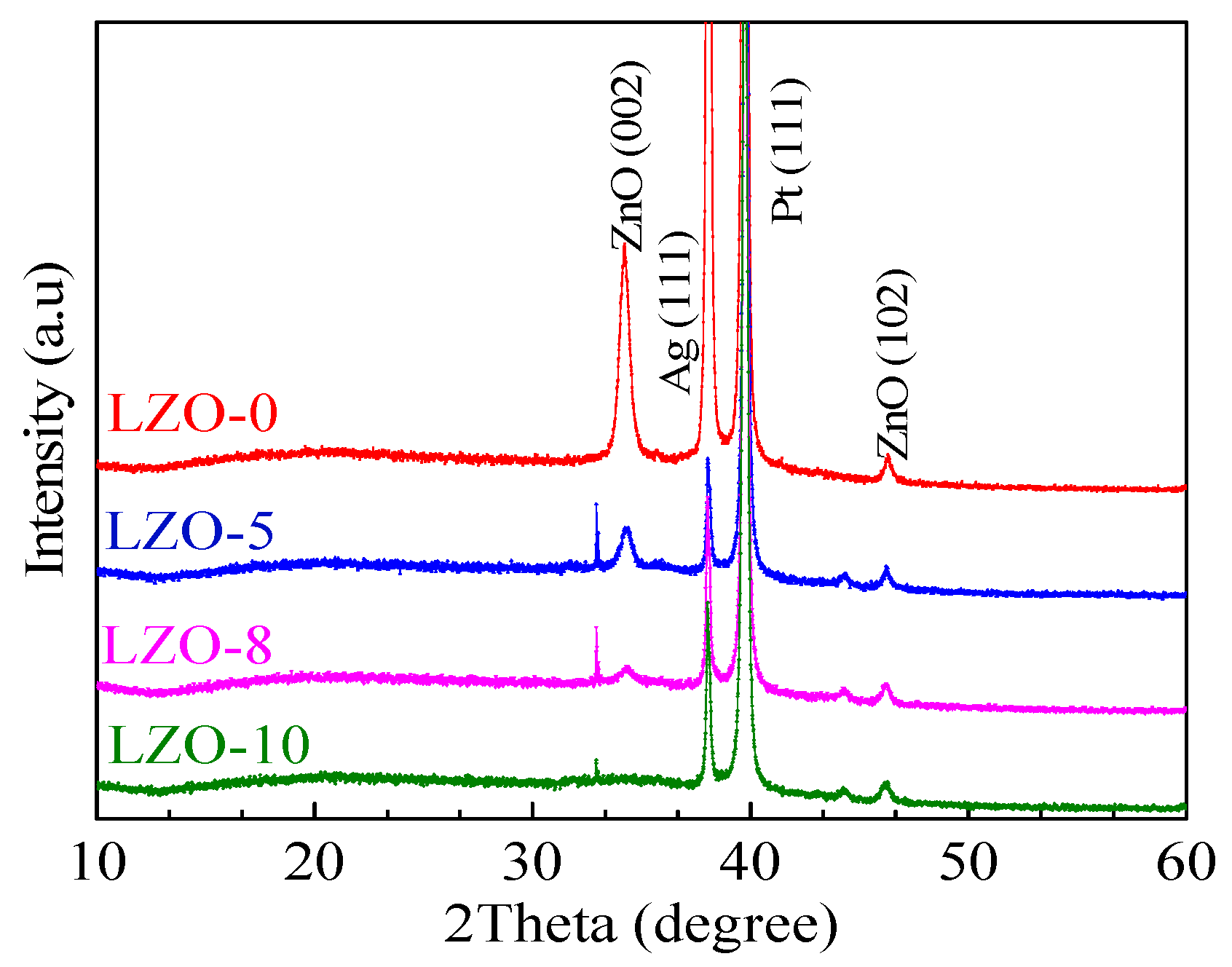
2.2. Material Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
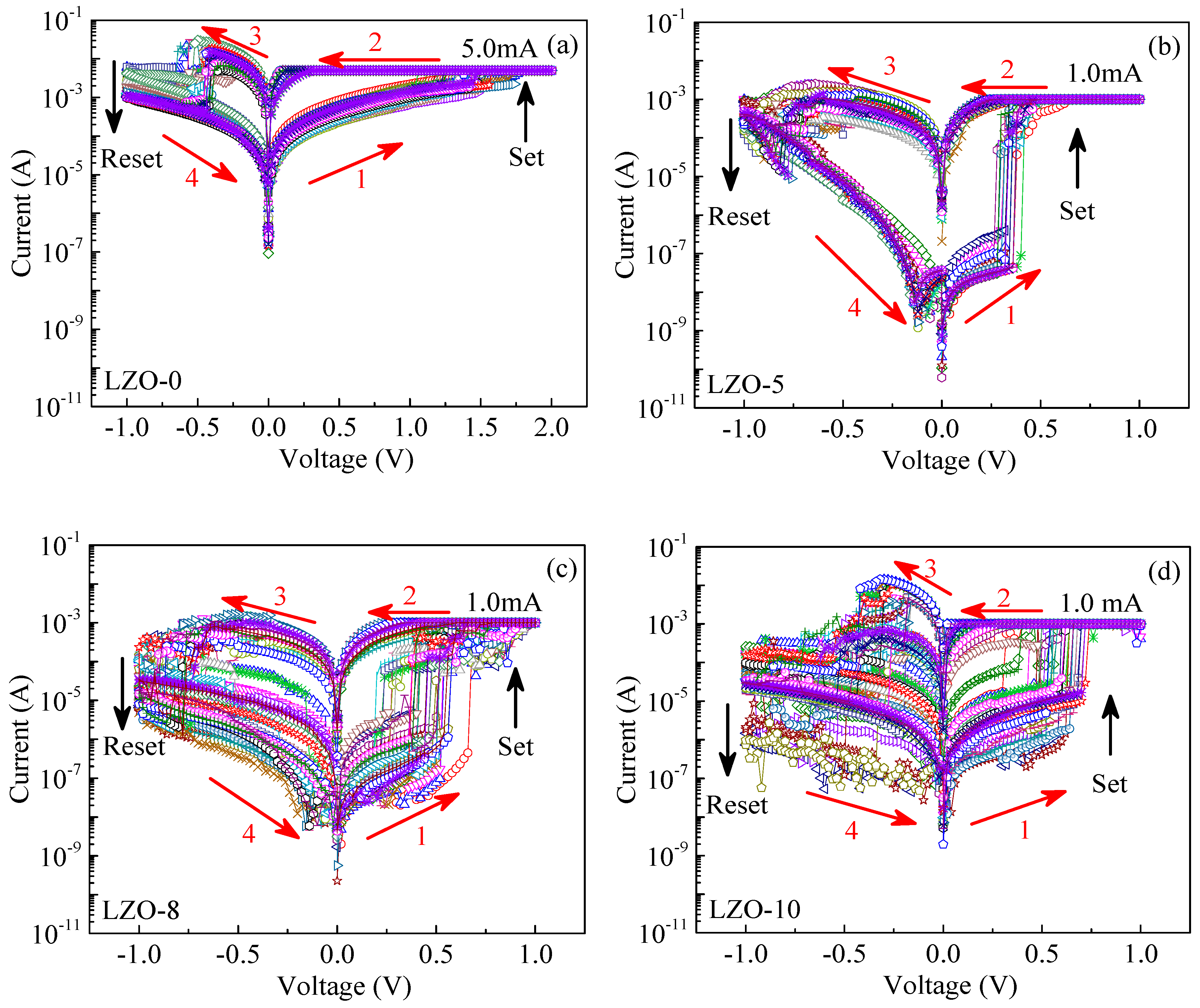
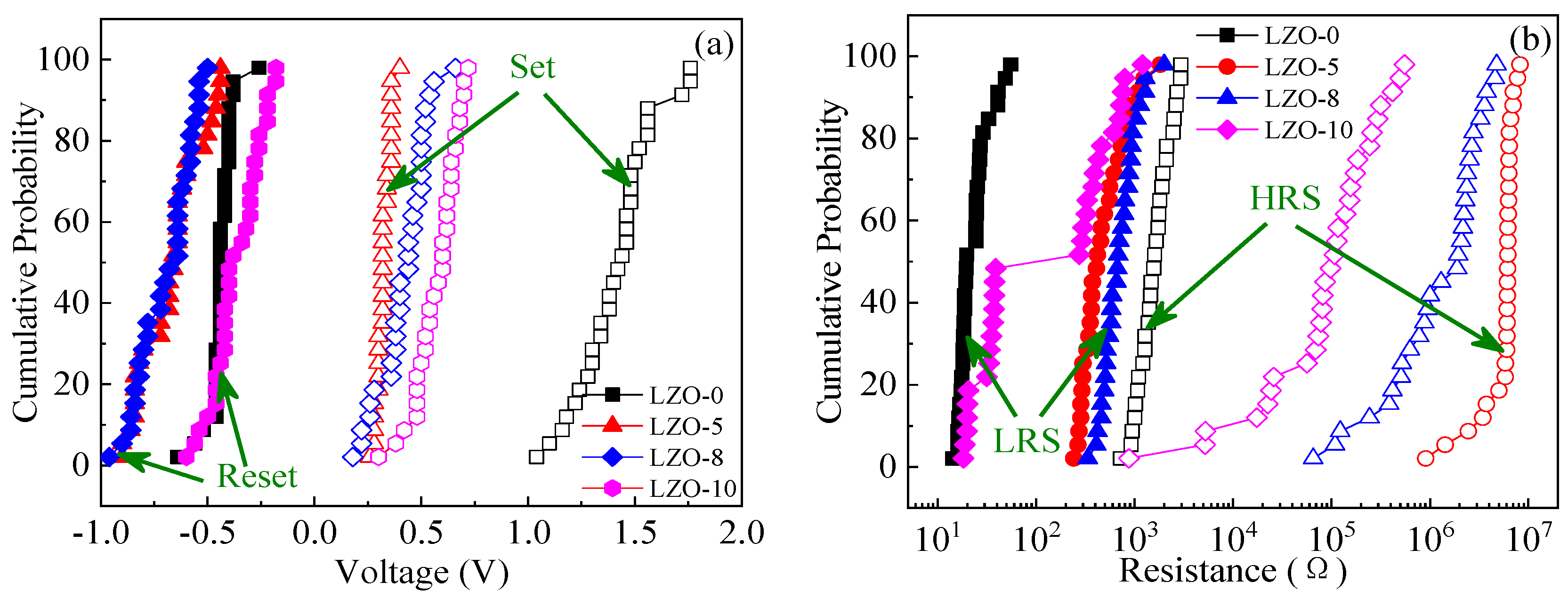
3.1. The I–V Characteristics of Devices under DC Voltage
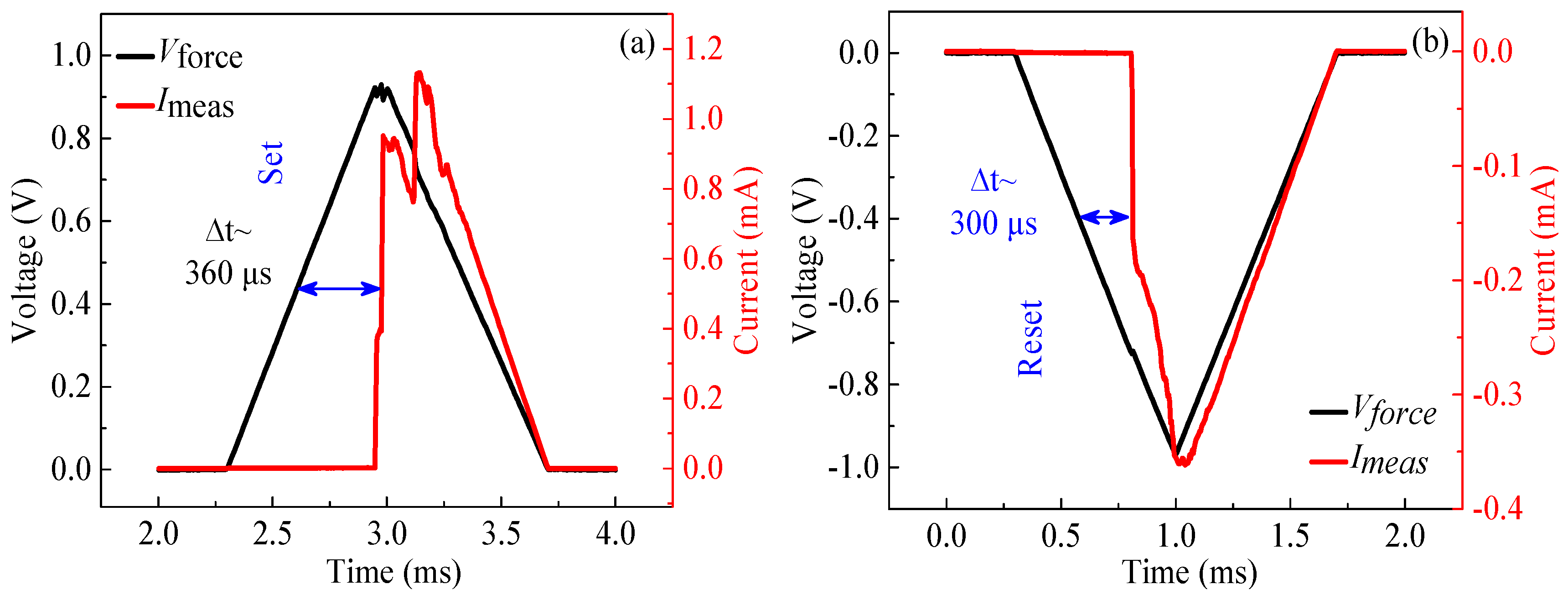
3.2. The RS Characteristics of LZO-5 Device under Pulse Voltage
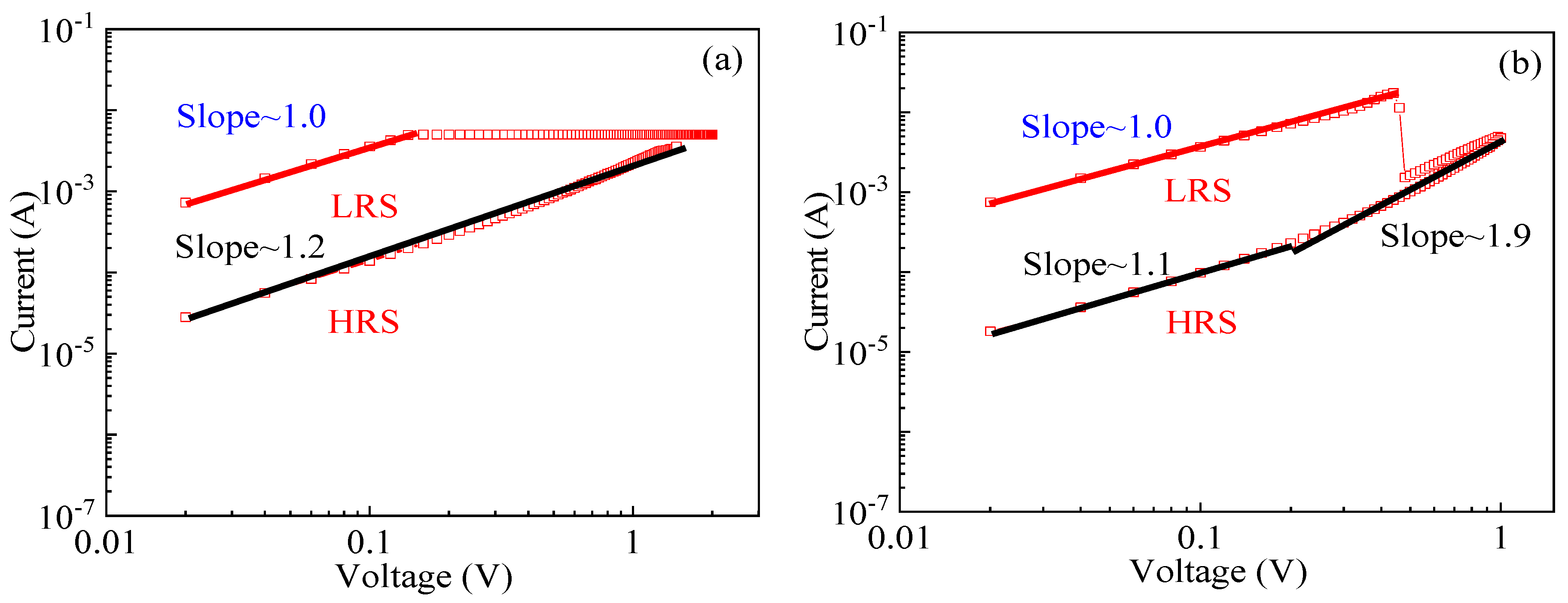
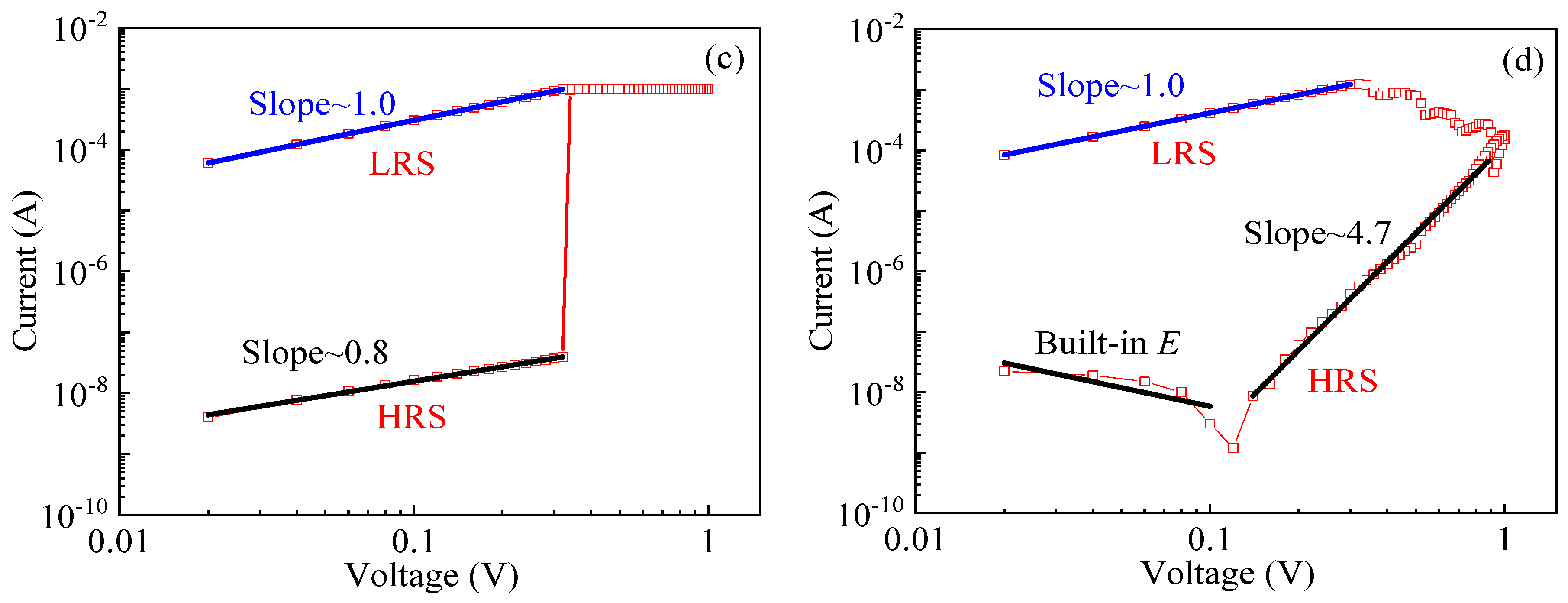
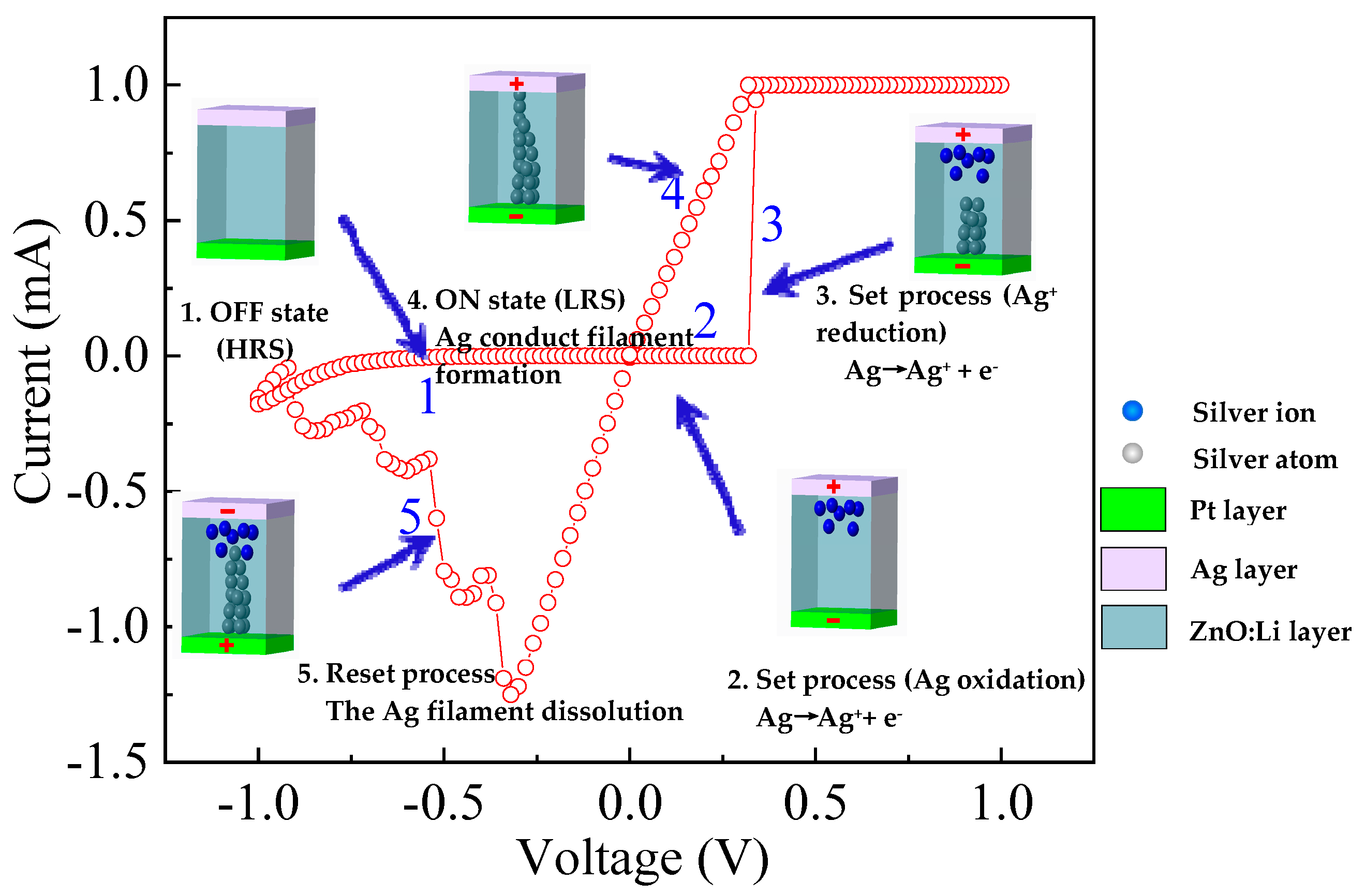
3.3. The Switching Mechanism of LZO-0 and -5 Devices
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, L.; Hu, W.; Xie, W.; Bao, D. Uniform resistive switching properties of fully transparent TiO2-based memory devices. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.-S.; Liu, P.-T.; Hsu, C.-H. Investigation on amorphous InGaZnO based resistive switching memory with low-power, high-speed, high reliability. Thin Solid Films 2013, 549, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackriya, V.M.; Kittur, H.M.; Chin, A. A novel read scheme for large size one-resistor resistive random access memory array. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; Wu, T.; Chen, F.; Wang, C.; Tzeng, P.J.; Tsai, M.J.; Lien, C. Low-power and nanosecond switching in robust hafnium oxide resistive memory with a thin Ti cap. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2010, 31, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, G. High-performance resistance-switchable multilayers of graphene oxide blended with 1,3,4-oxadiazole acceptor nanocomposite. Micromachines 2019, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Ma, G.; He, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Compact pure phase CsPbBr3 perovskite film with significantly improved stability for high-performance memory. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaja, K.; Andra, M.; Rana, V.; Waser, R.; Dittmann, R.; Baeumer, C. Reduction of the forming voltage through tailored oxygen non-stoichiometry in tantalum oxide ReRAM devices. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Fernandez, A.; Cagli, C.; Perniola, L.; Miranda, E.; Suñé, J. Characterization of HfO2-based devices with indication of second order memristor effects. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 195, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, H.; Gao, X. Effect of Interface layer engineering on resistive switching characteristics of ZrO2-based resistive switching devices. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2018, 65, 5390–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Aluguri, R.; Chand, U.; Tseng, T.Y. Metal oxide resistive switching memory: Materials, properties and switching mechanisms. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, S547–S556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ge, N.; Montgomery, E.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Dávila, N.; Graves, C.E.; et al. Analogue signal and image processing with large memristor crossbars. Nat. Electron. 2017, 1, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Kim, D.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lee, B.; Liu, C. Effect of Co doping on unipolar resistance switching in Pt/Co:ZnO/Pt structures. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D. Resistive switching memories based on metal oxides: Mechanisms, reliability and scaling. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Ting, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-T. Effects of substrate temperature on resistive switching behavior of planar ZnO resistive random access memories. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, U.-B.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.-S. Reliable current changes with selectivity ratio above 109 observed in lightly doped zinc oxide films. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Ai, C.; Wen, D. Resistive switching characteristics of Li-doped ZnO thin films based on magnetron sputtering. Materials 2019, 12, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Mao, Q.; Xi, J.; Ji, Z. Improvement of resistive switching in ZnO film by Ti doping. Thin Solid Films 2013, 537, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, F.M.; Prasad, O.K.; Panda, D.; Lin, C.-A.; Tsai, T.-L.; Wei, K.-H.; Tseng, T.-Y. Impacts of Co doping on ZnO transparent switching memory device characteristics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 183506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Hao, A.; Qin, N.; Bao, D. Unipolar resistive switching properties of Pr-doped ZnO thin films. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, S474–S480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Tseng, Z.-L.; Lo, K.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y.; Hong, C.-S.; Chu, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Wu, C.-J. Unipolar resistive switching behavior of Pt/LixZn1−xO/Pt resistive random access memory devices controlled by various defect types. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 203501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, S.U.; Hasanain, S.K.; Bertino, M.F.; Jaffari, G.H. Effects of substitutional Li on the ferromagnetic response of Li co-doped ZnO:Co nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2013, 25, 156005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Xie, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Cai, Z. Enhanced gas sensing performance of Li-doped ZnO nanoparticle film by the synergistic effect of oxygen interstitials and oxygen vacancies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 330, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, S.U.; Hasanain, S.K.; Mehmood, Z.; Anjum, D.H.; Shah, S.A.; Aftab, M.; Abbas, T.A. Study of room temperature Raman scattering and XPS, high temperature electrical and low temperature magnetic properties of Zn1−yLiyO (0.00 ≤ y ≤ 0.10) nanoparticles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Shang, D.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, X.; Chen, R.; Tang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Lv, H.; et al. Uniform, fast, and reliable LixSiOy-based resistive switching memory. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2019, 40, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Song, C.; Yin, J.; Qiao, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Yin, S.; Saleem, M.S.; Wu, H.; et al. Modulating metallic conductive filaments via bilayer oxides in resistive switching memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 193502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yang, R.; Guo, X. Coexistence of analog and digital resistive switching in BiFeO3-based memristive devices. Solid State Ion. 2016, 296, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xie, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, X.; Zeng, H. CuO/ZnO memristors via oxygen or metal migration controlled by electrodes. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 025018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yu, L.; Wu, Y.; Dong, C.; Deng, N.; Xu, X.; Miao, J.; Jiang, Y. Low-energy resistive random access memory devices with no need for a compliance current. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Shi, X.; Zeng, H. Amorphous ZnO based resistive random access memory. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17867–17872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qian, H.; Guan, L.; Wang, W.; Xing, B.; Yan, X.; Zhang, S.; Sha, J.; Wang, Y. Influence of metal electrode on the performance of ZnO based resistance switching memories. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 154301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, Z.-Y.; Wang, T.-Y.; Dai, Y.-W.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Q.-Q.; Zhang, D. CMOS compatible bio-realistic implementation with Ag/HfO2-based synaptic nanoelectronics for artificial neuromorphic system. Electronics 2018, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, G.; Yu, T.; Mao, S.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, Y. A flexible nonvolatile resistive switching memory device based on ZnO film fabricated on a foldable PET substrate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 520, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.R.; Chougale, M.Y.; Rane, T.D.; Khot, S.S.; Patil, A.A.; Bagal, O.S.; Jadhav, S.D.; Sheikh, A.D.; Kim, S.; Dongale, T.D. Solution-processable ZnO thin film memristive device for resistive random access memory application. Electronics 2018, 7, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Song, P.; Gai, H.; Li, Y.; Ai, C.; Wen, D. Li-Doping Effect on Characteristics of ZnO Thin Films Resistive Random Access Memory. Micromachines 2020, 11, 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100889
Zhao X, Song P, Gai H, Li Y, Ai C, Wen D. Li-Doping Effect on Characteristics of ZnO Thin Films Resistive Random Access Memory. Micromachines. 2020; 11(10):889. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100889
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaofeng, Ping Song, Huiling Gai, Yi Li, Chunpeng Ai, and Dianzhong Wen. 2020. "Li-Doping Effect on Characteristics of ZnO Thin Films Resistive Random Access Memory" Micromachines 11, no. 10: 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100889
APA StyleZhao, X., Song, P., Gai, H., Li, Y., Ai, C., & Wen, D. (2020). Li-Doping Effect on Characteristics of ZnO Thin Films Resistive Random Access Memory. Micromachines, 11(10), 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100889



