Trajectory Definition with High Relative Accuracy (HRA) by Parametric Representation of Curves in Nano-Positioning Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Curve Fitting in Computer Aided Geometric Design (CAGD)
3. Materials and Methods
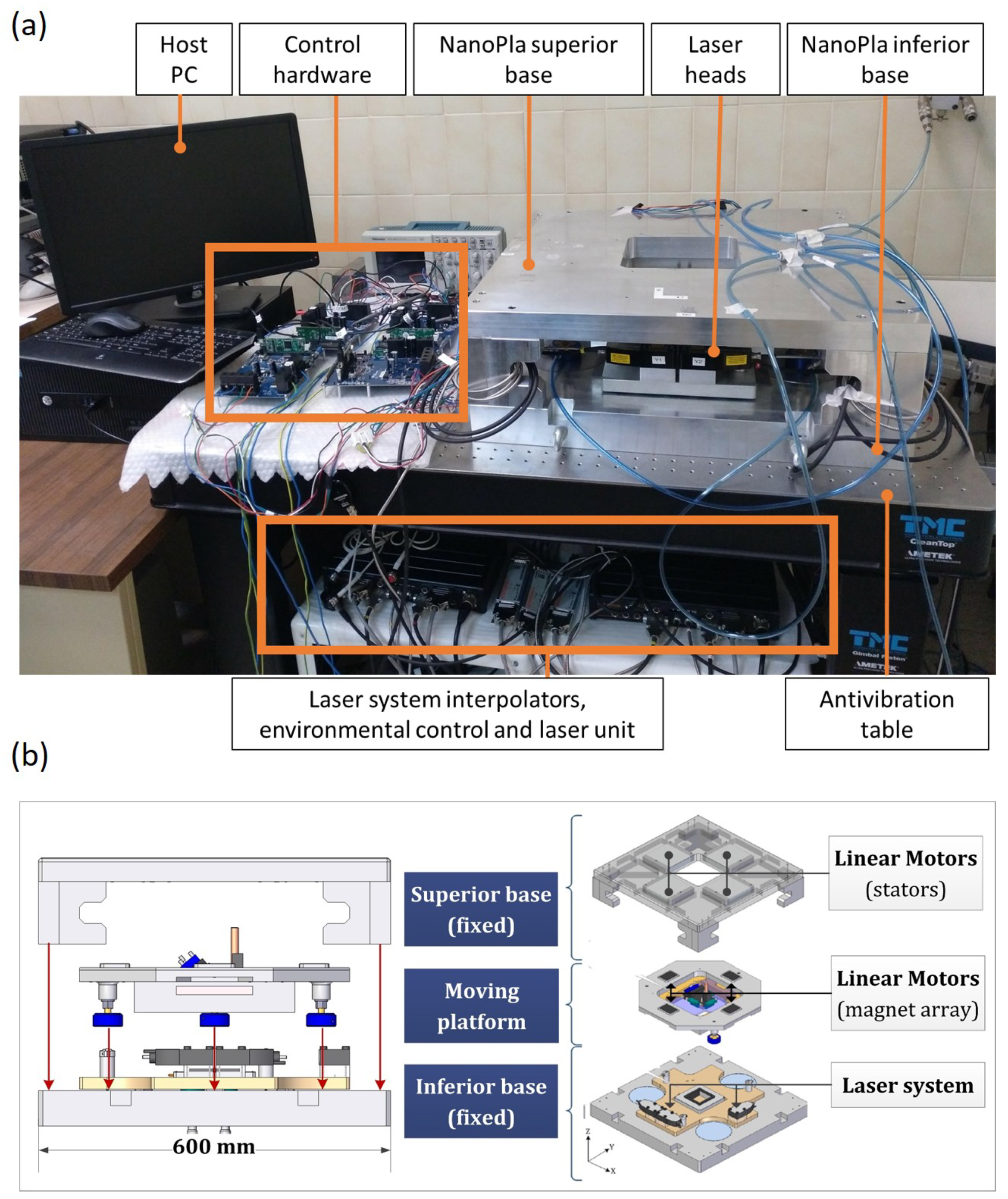
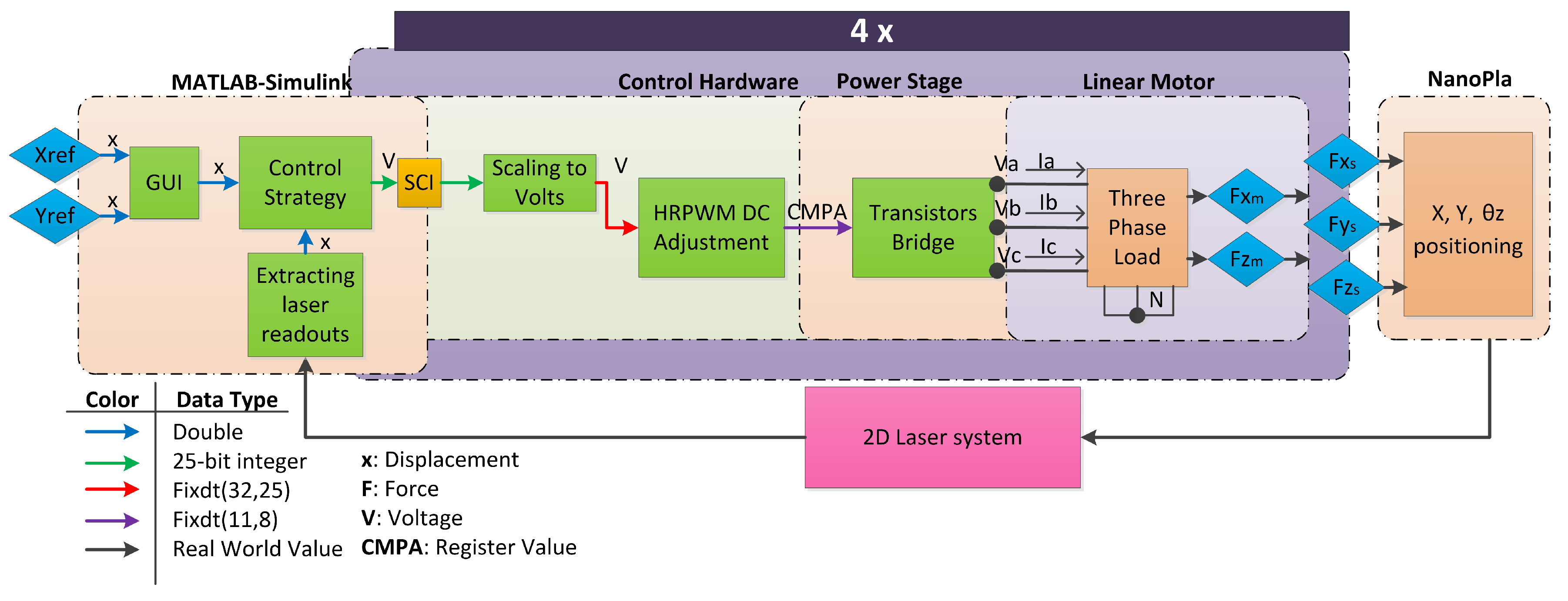
3.1. Nanopositioning Platform (NanoPla)
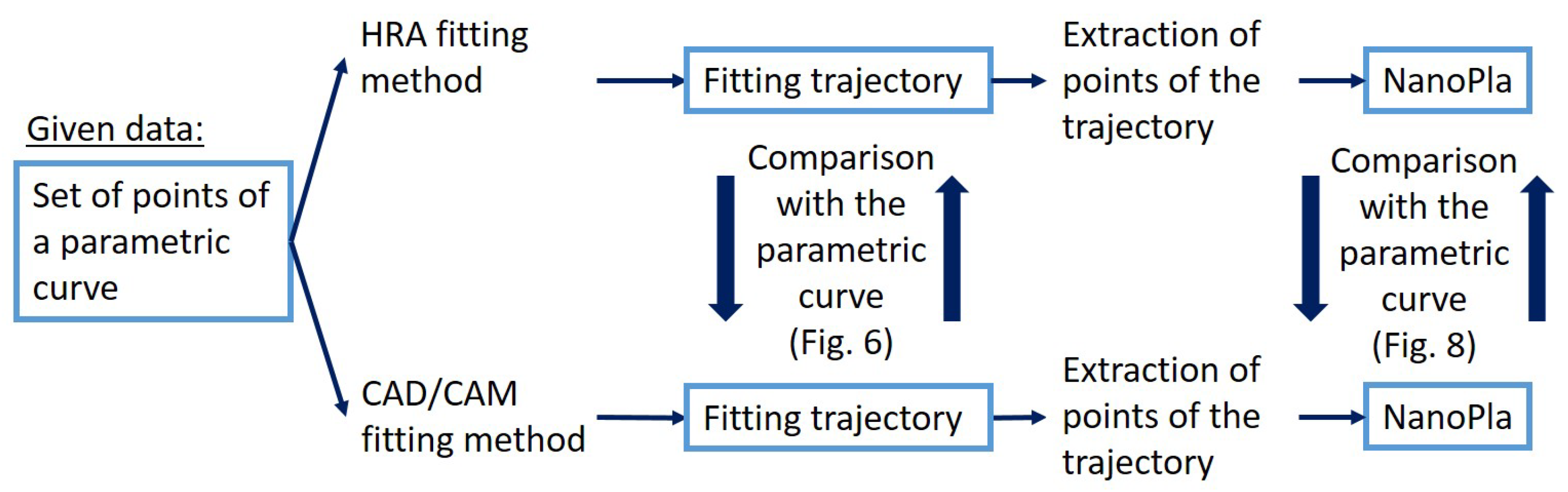
3.2. Analysis Procedure
4. Accurate Curve Fitting with Shape-Preserving Representations: HRA Method
4.1. High Relative Accuracy and Bidiagonal Factorizations
4.2. The Class of Fg-Bernstein Bases
4.3. Curve Fitting with Fg-Bernstein Bases
5. Positioning uncertainty of the NanoPla
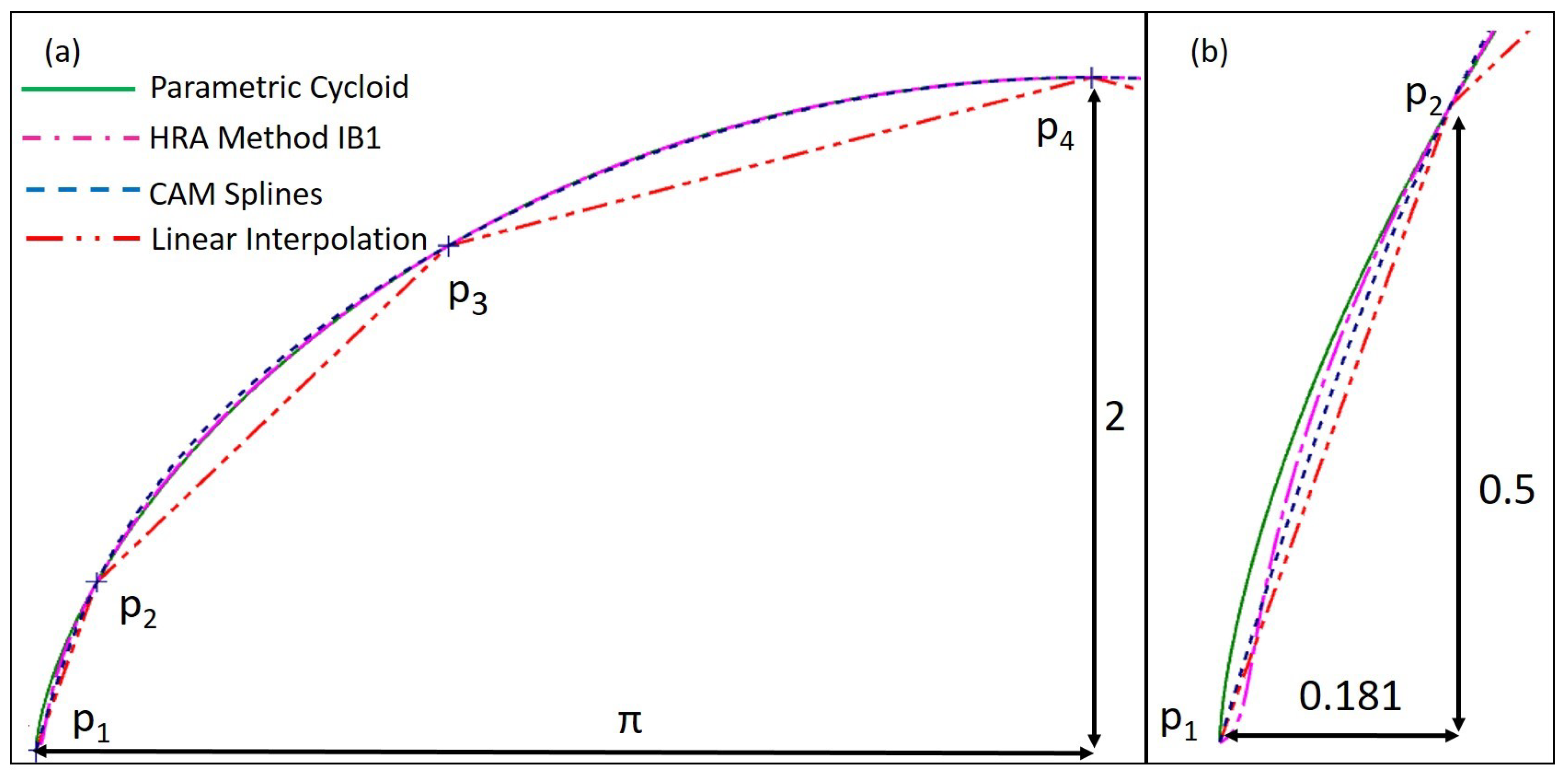
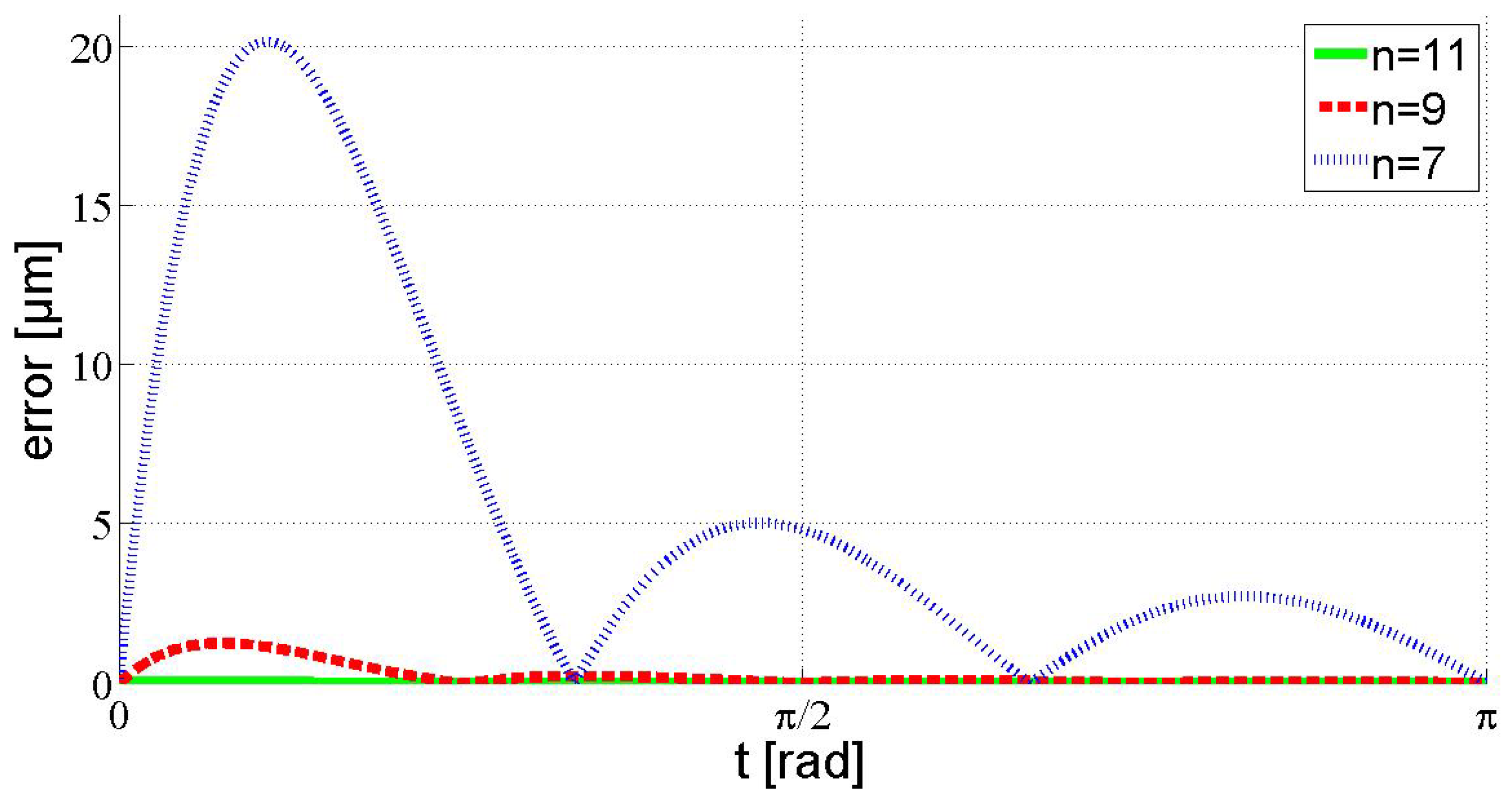
6. Analysis of the Curve Fitting Errors
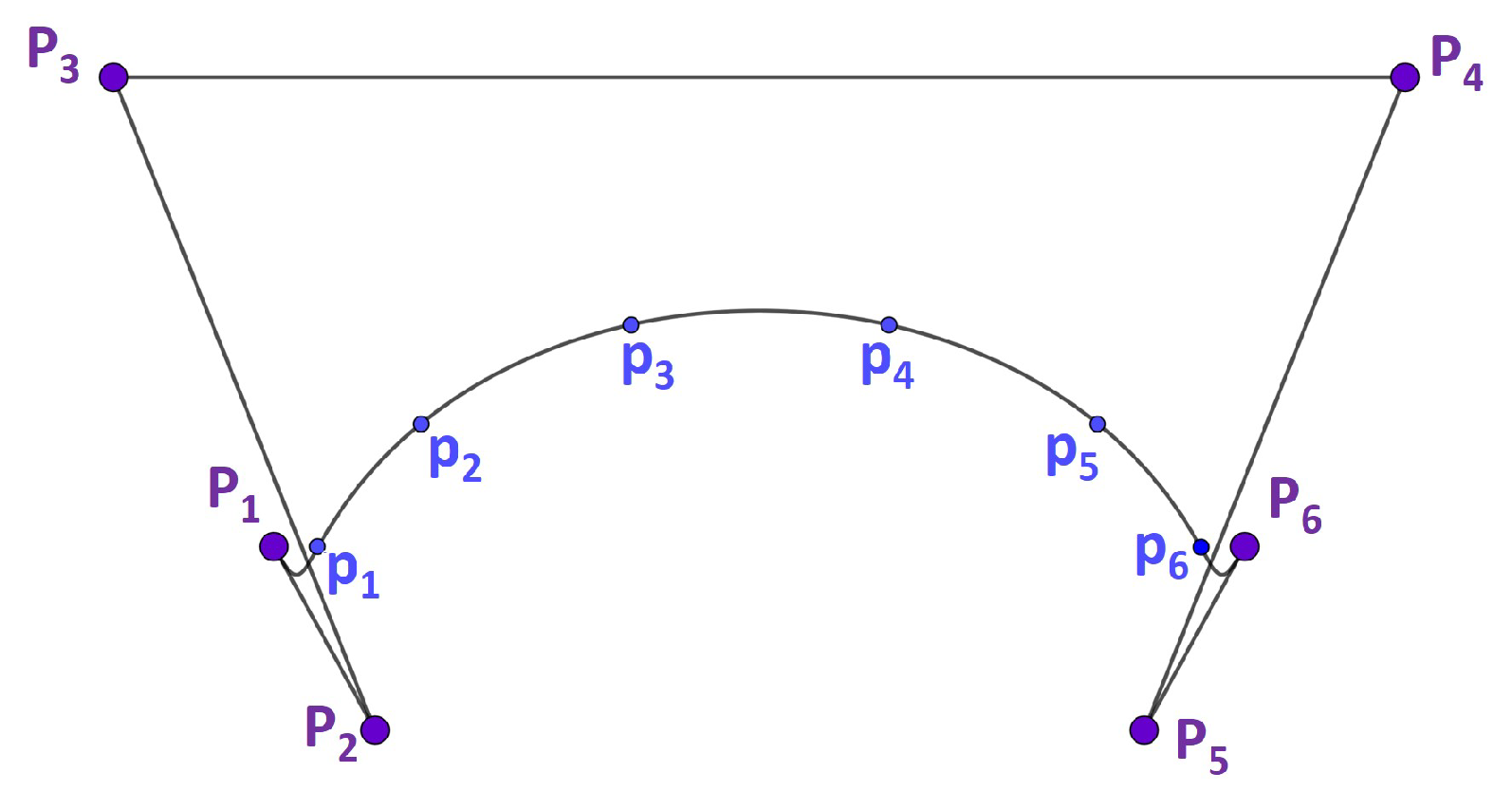
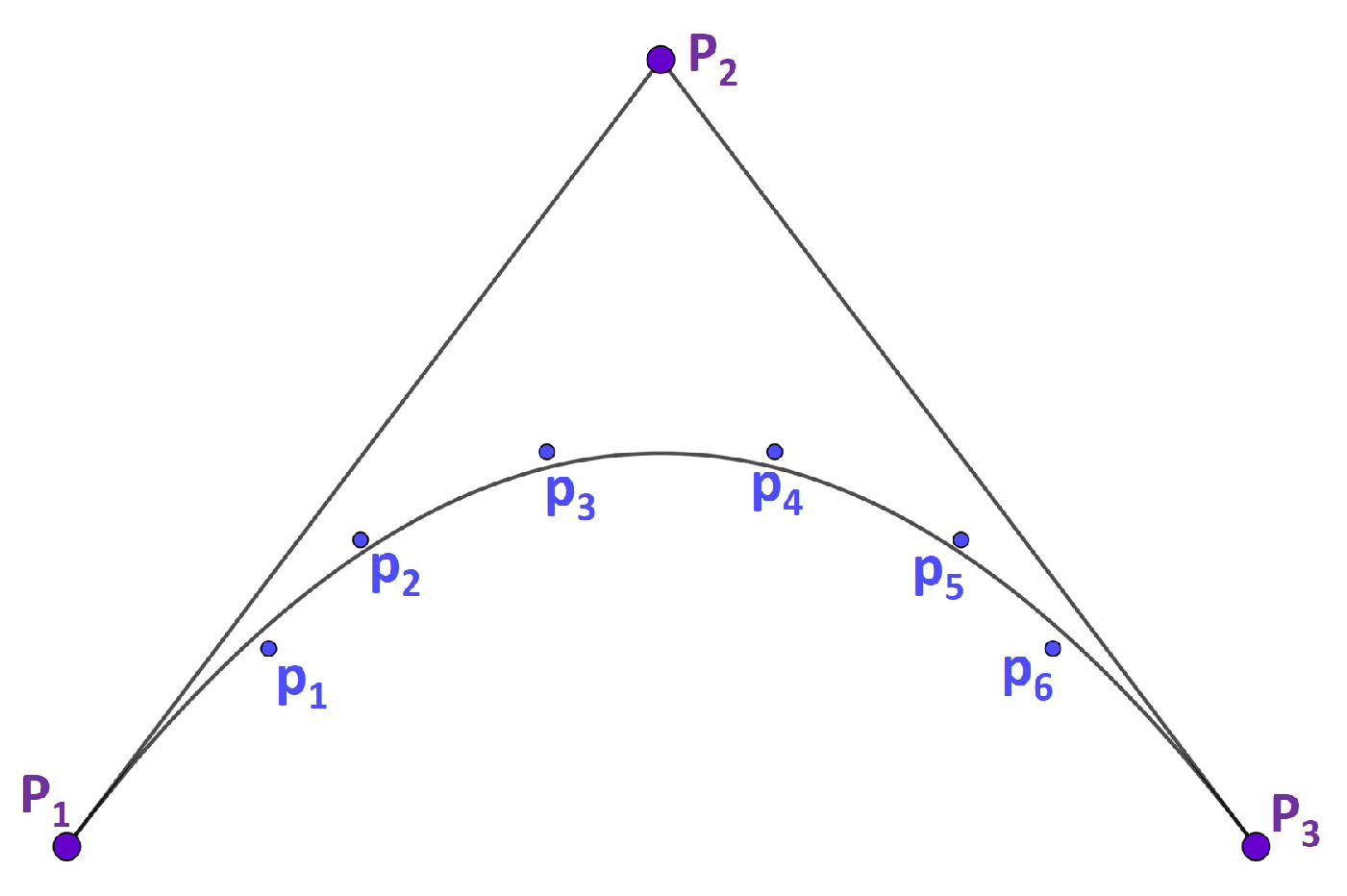
6.1. Curve Fitting By Interpolation
6.2. Curve Fitting by Least Squares Approximation
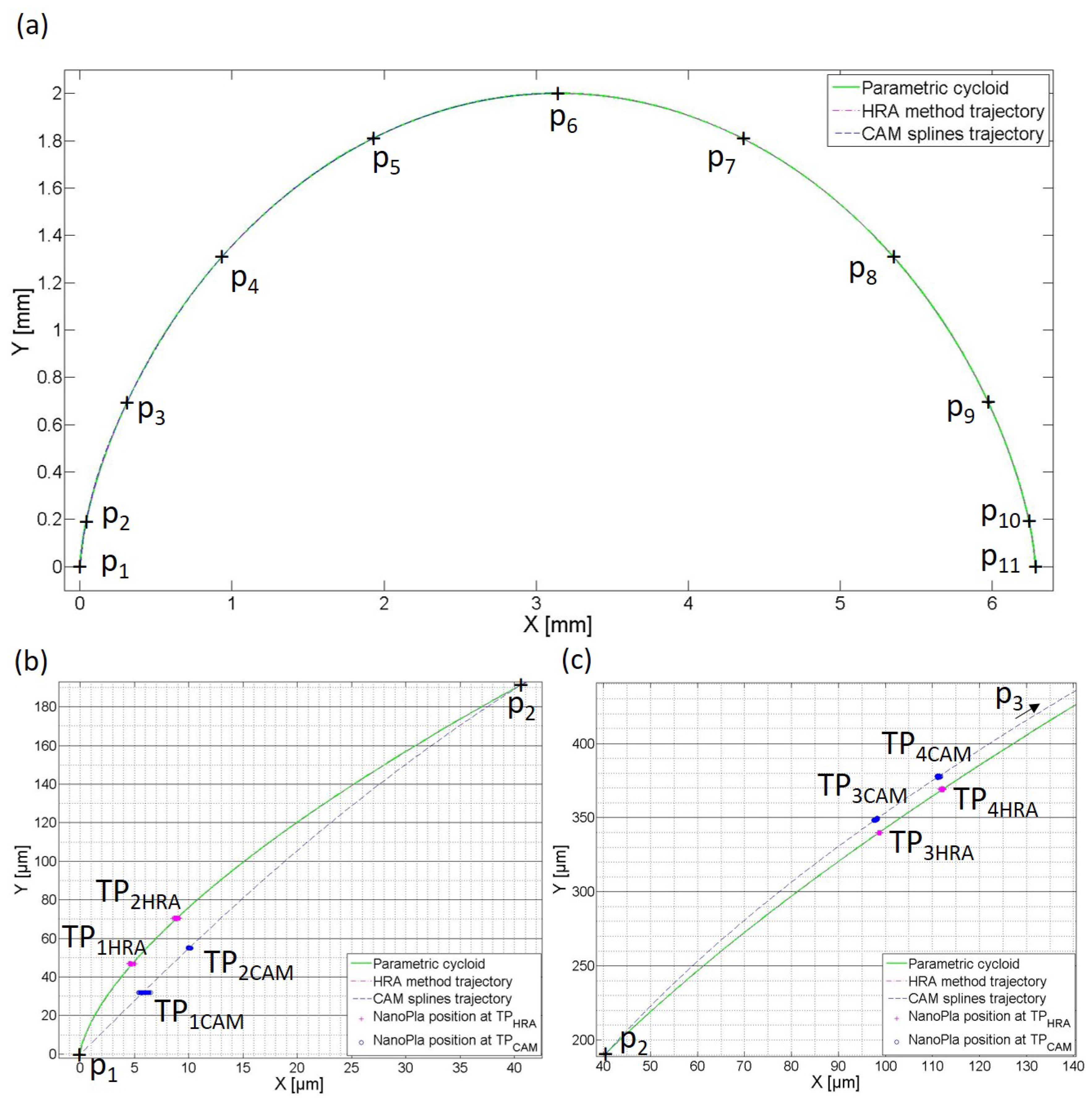
7. Experimental Results
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ouyang, P.R.; Tjiptoprodjo, R.C.; Zhang, W.J.; Yang, G.S. Micro-motion devices technology: The state of arts review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 38, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manske, E.; Jäger, G.; Hausotte, T.; Füßl, R. Recent developments and challenges of nanopositioning and technology. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 74001–74010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba, M.; Valenzuela, M.; Yagüe-Fabra, J.A.; Albajez, J.A.; Aguilar, J.J. Large range nanopositioning stage design: A three-layer and two-stage platform. Measurement 2016, 89, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Cullinan, M. Design of a flexure based XY precision nanopositioner with a two inch travel range for micro-scale selective laser sintering. In Proceedings of the ASPE 2016 Annual Meeting, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 October 2016; pp. 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Vavruska, P. Machine tool control systems and interpolations of spline type. J. Eng. Mech. 2012, 19, 219–229. [Google Scholar]
- Božek, P.; Lozkin, A.; Gorbushin, A. Geometrical Method for Increasing Precision of Machine Building Parts. Procedia Eng. 2016, 149, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.; Bo, C.; Wu, J.; Wei, G.; Hou, F. Modeling of Free-Form Complex Curves Using SG-Bézier Curves with Constraints of Geometric Continuities. Symmetry 2018, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitter, H.N.; Pandey, A.B.; Patel, D.D.; Mistry, J.M. A Review on Approaches for Handling Bezier Curves in CAD for Manufacturing. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Zhou, H. Curve Fitting with Bézier Cubics. Graph Models 1996, 58, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Shen, L.; Yuan, C.; Mi, Z. Certified space curve fitting and trajectory planning for CNC machining with cubic B-splines. Comput. Aided Des. 2019, 106, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencera, B.; Dumanlia, A.; Yamadab, Y. Spline interpolation with optimal frequency spectrum for vibration avoidance. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 67, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msaddek, B.; Bouaziz, Z.; Baili, M.; Dessein, G. Influence of interpolation type in high-speed machining (HSM). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mainar, E.; Peña, J.M. Accurate computations with collocation matrices of a general class of bases. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 2018, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Perez, L.C.; Torralba, M.; Albajez, J.A.; Yagüe-Fabra, J.A. One-dimensional control system for a linear motor of a two-dimensional nanopositioning stage using a commercial control hardware. Micromachines 2018, 9, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, F.; Gofuku, S.; Maekawa, T.; Mukundan, H.; Patrikalakis, N.M. Approximation of involute curves for CAD-system processing. Eng. Comput. 2007, 23, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koev, P. Accurate computations with totally nonnegative matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2007, 29, 731–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T. Totally positive matrices. Linear Algebra Appl. 1987, 90, 165–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasca, M.; Peña, J.M. Total positivity and Neville elimination. Linear Algebra Appl. 1992, 165, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasca, M.; Peña, J.M. On factorizations of totally positive matrices. In Total Positivity and Its Applications; Gasca, M., Micchelli, C.A., Eds.; Kluver Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gasca, M.; Peña, J.M. A matricial description of Neville elimination with applications to total positivity. Linear Algebra Appl. 1994, 202, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koev, P. Available online: http://www.math.sjsu.edu/koev/software/TNTool.html (accessed on 16 November 2018).
- Marco, A.; Martínez, J.J. Polynomial least squares fitting in the Bernstein basis. Linear Algebra Appl. 2010, 433, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Björck, A. Numerical Methods for Least Squares Problems; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gasca, M.; Peña, J.M. Total Positivity, QR Factorization, and Neville Elimination. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 1993, 14, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, M.; Goch, G.; Forbes, A.; Sprauel, J.M.; Clément, A.; Haertig, F.; Gao, W. Modelling and traceability for computationally-intensive precision engineering and metrology. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 67, 815–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba, M.; Díaz-Pérez, L.C.; Valenzuela, M.; Albajez, J.A.; Yagüe-Fabra, J.A. Geometrical Characterisation of a 2D Laser System and Calibration of a Cross-Grid Encoder by Means of a Self-Calibration Methodology. Sensors 2017, 17, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/TR 230-9. Test Code for Machine Tools. Estimation of Measurement Uncertainty for Machine Tools Test According to Series ISO 230, Basic Equations; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Pérez, L.C.; Albajez, J.A.; Torralba, M.; Yagüe-Fabra, J.A. Vector control strategy for a Halbach linear motor implemented in a commercial control hardware. Electronics 2018, 7, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msaddek, B.; Bouaziz, Z.; Baili, M.; Dessein, G.; Mohsen, A. Simulation of machining errors of Bspline and Cspline. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 9, 3323–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n | HRA | |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | ||
| 20 | ||
| 25 | ||
| 50 |
| Source | Justification | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution at the HRPWM | Resolution of V [14] | nm |
| Laser system resolution | Resolution of nm | ( nm) |
| Calibrated Laser system | Geometrical errors + measuring system calibration [26] | 99 nm |
| RMS positioning error | Laser system noise + phase currents noise + vibrations | 110 nm |
| Positioning uncertainty () | 501 nm |
| Intervals | Linear | CAM | HRA IB1 | HRA IB2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | m | 18.0 m | 20.17 m | 17.84 m | |
| 7 | 93.5 m | 17.1 m | 5.31 m | 5.60 m | |
| 9 | 11.8 m | 8.0 m | 1.25 m | 3.95 m | |
| 9 | 41.9 m | 8.5 m | 0.22 m | 0.93 m | |
| 11 | 6.1 m | 4.0 m | 0.05 m | 0.94 m | |
| 11 | 22.0 m | 4.5 m | <0.01 m | 0.18 m | |
| 21 | 0.7 m | 0.5 m | ≪1 nm | <0.01 m | |
| 21 | 2.8 m | 0.6 m | ≪1 nm | <1 nm |
| CAD | HRA LSB1 | HRA LSB2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce | Ce | Ce | ||||
| 51 | 21 | m | 10 | m | 12 | m |
| 101 | 38 | m | 11 | m | 13 | m |
| 251 | 44 | m | 11 | m | 14 | m |
| 501 | 34 | m | 11 | m | 14 | m |
| 1001 | 38 | m | 11 | m | 14 | m |
| Trajectory Points | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| m | m | m | |
| m | m | m | |
| m | m | m | |
| m | m | m | |
| m | m | m | |
| m | m | m | |
| m | m | m | |
| m | m | m |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz Pérez, L.; Rubio Serrano, B.; Albajez García, J.A.; Yagüe Fabra, J.A.; Mainar Maza, E.; Torralba Gracia, M. Trajectory Definition with High Relative Accuracy (HRA) by Parametric Representation of Curves in Nano-Positioning Systems. Micromachines 2019, 10, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10090597
Díaz Pérez L, Rubio Serrano B, Albajez García JA, Yagüe Fabra JA, Mainar Maza E, Torralba Gracia M. Trajectory Definition with High Relative Accuracy (HRA) by Parametric Representation of Curves in Nano-Positioning Systems. Micromachines. 2019; 10(9):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10090597
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz Pérez, Lucía, Beatriz Rubio Serrano, José A. Albajez García, José A. Yagüe Fabra, Esmeralda Mainar Maza, and Marta Torralba Gracia. 2019. "Trajectory Definition with High Relative Accuracy (HRA) by Parametric Representation of Curves in Nano-Positioning Systems" Micromachines 10, no. 9: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10090597
APA StyleDíaz Pérez, L., Rubio Serrano, B., Albajez García, J. A., Yagüe Fabra, J. A., Mainar Maza, E., & Torralba Gracia, M. (2019). Trajectory Definition with High Relative Accuracy (HRA) by Parametric Representation of Curves in Nano-Positioning Systems. Micromachines, 10(9), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10090597





