Temporal Observation of Adipocyte Microfiber Using Anchoring Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Preparation
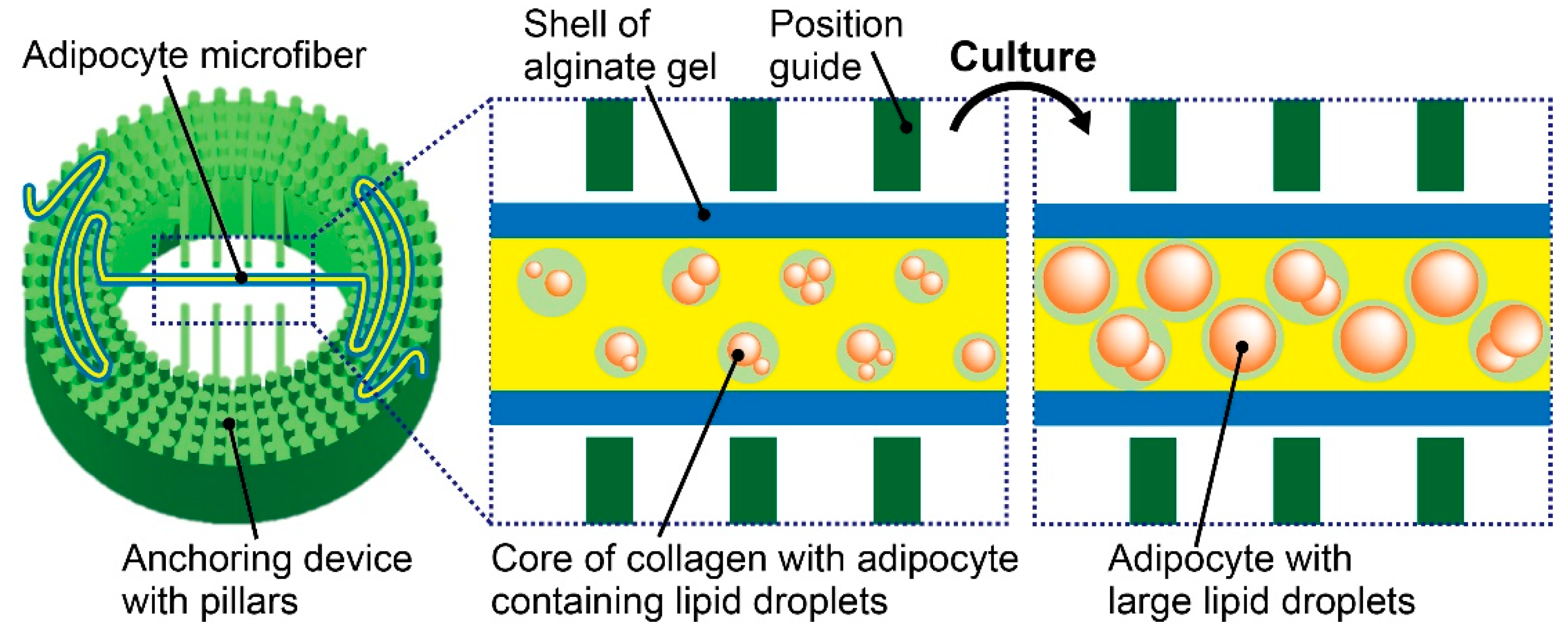
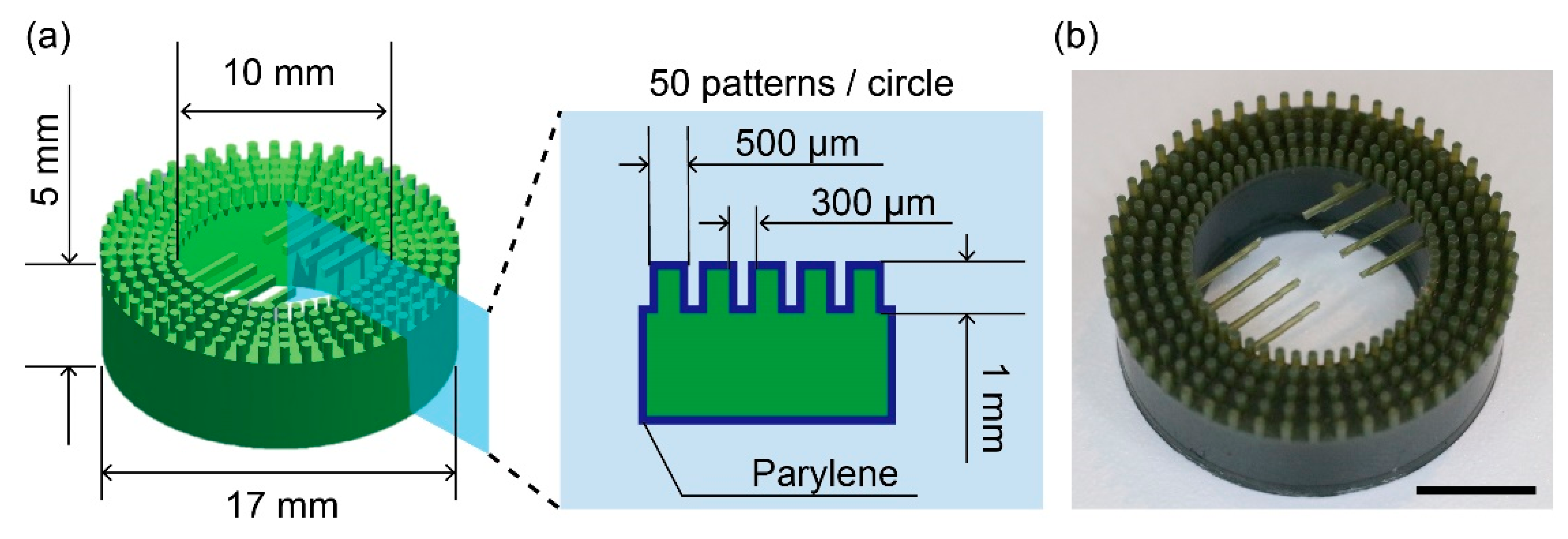
2.2. Fabrication of the Anchoring Device
2.3. Formation of Adipocyte Microfibers
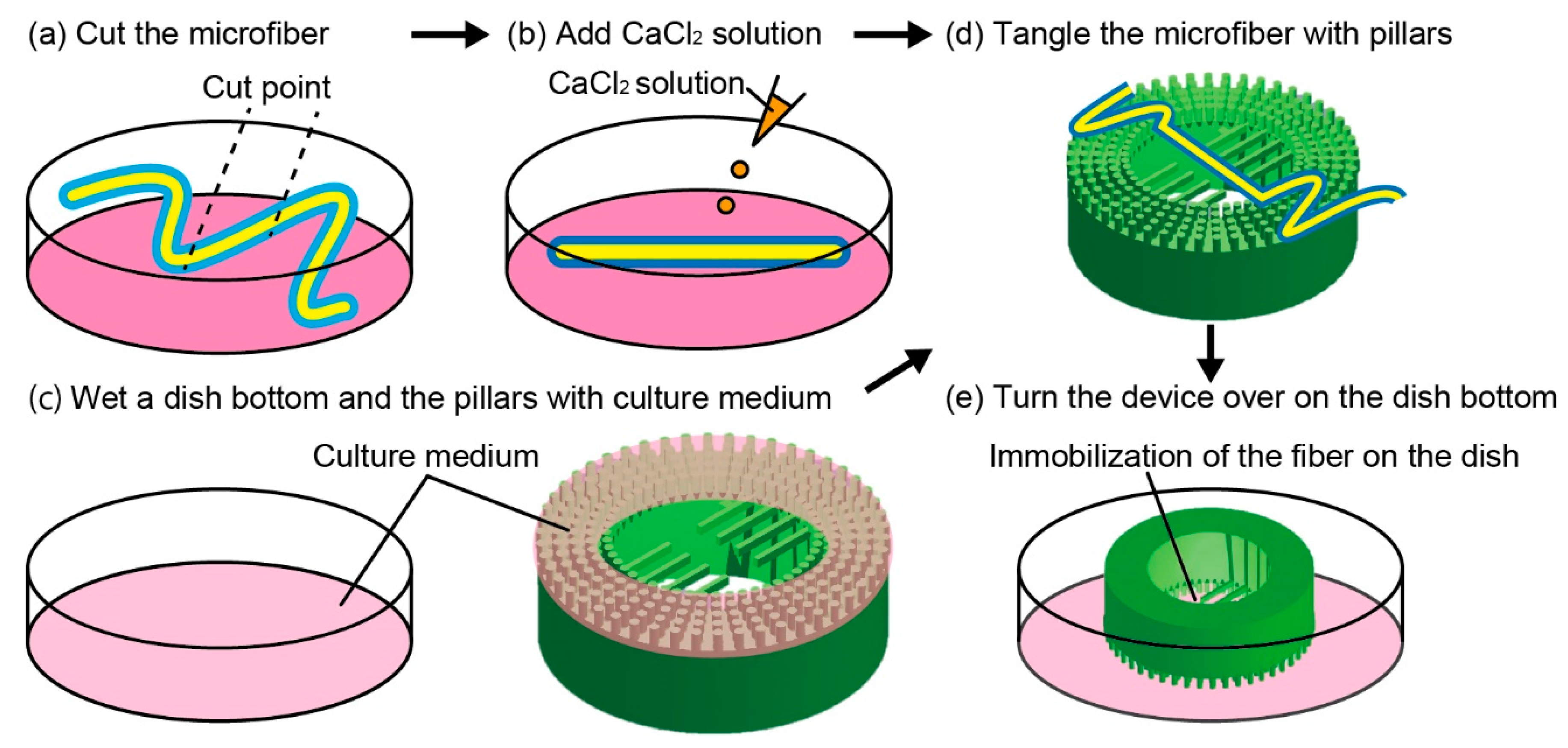
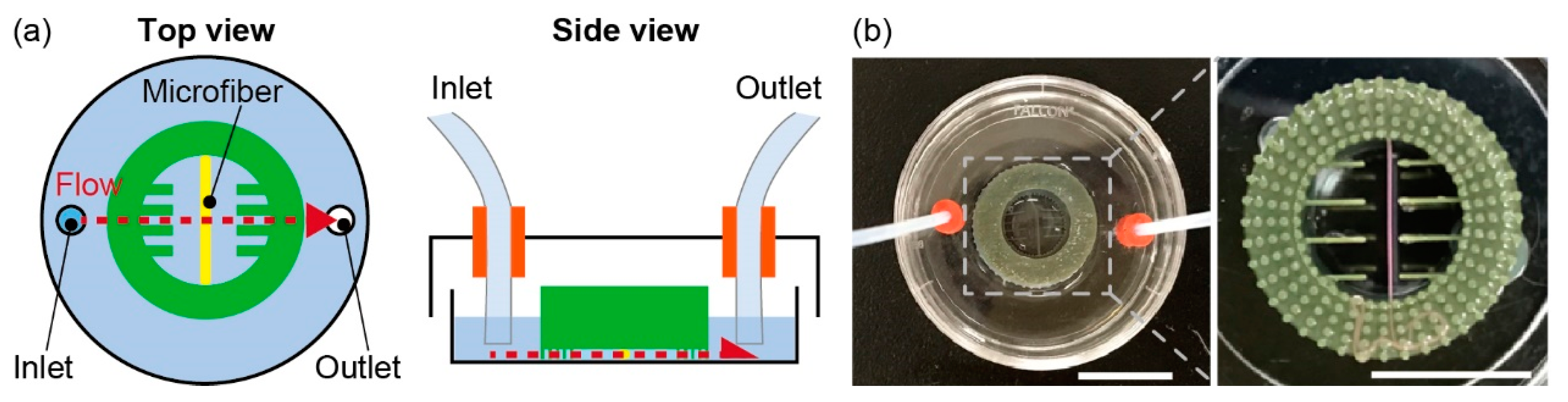
2.4. Microfiber Immobilization
2.5. Morphology Evaluation of the Microfiber
2.6. Evaluation of Lipolysis in Adipocyte Microfiber
3. Results and Discussion
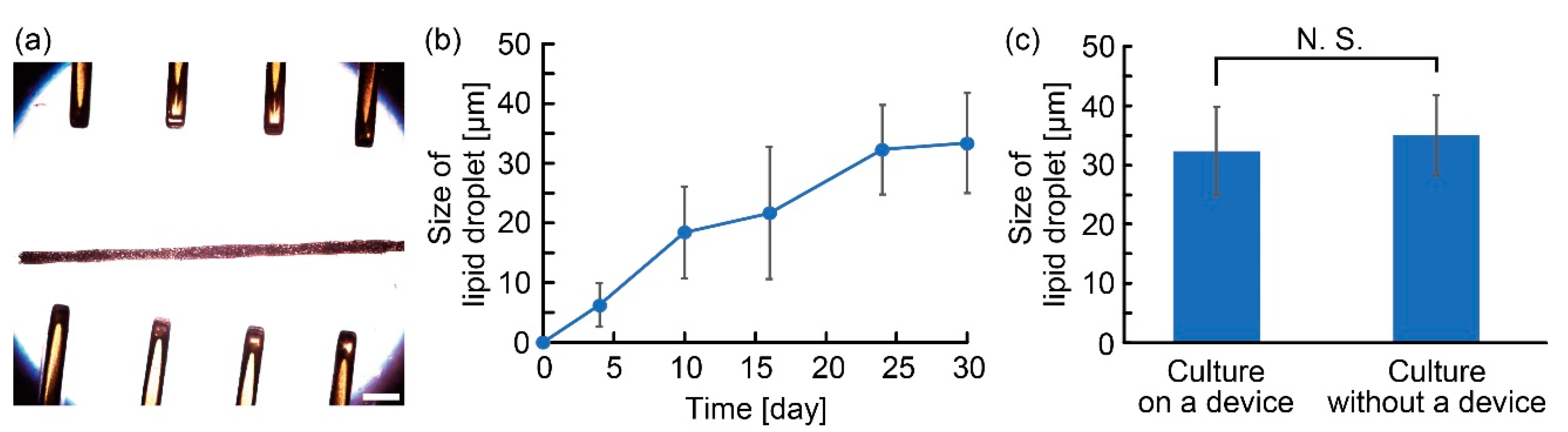
3.1. Characterization of the Anchoring Device
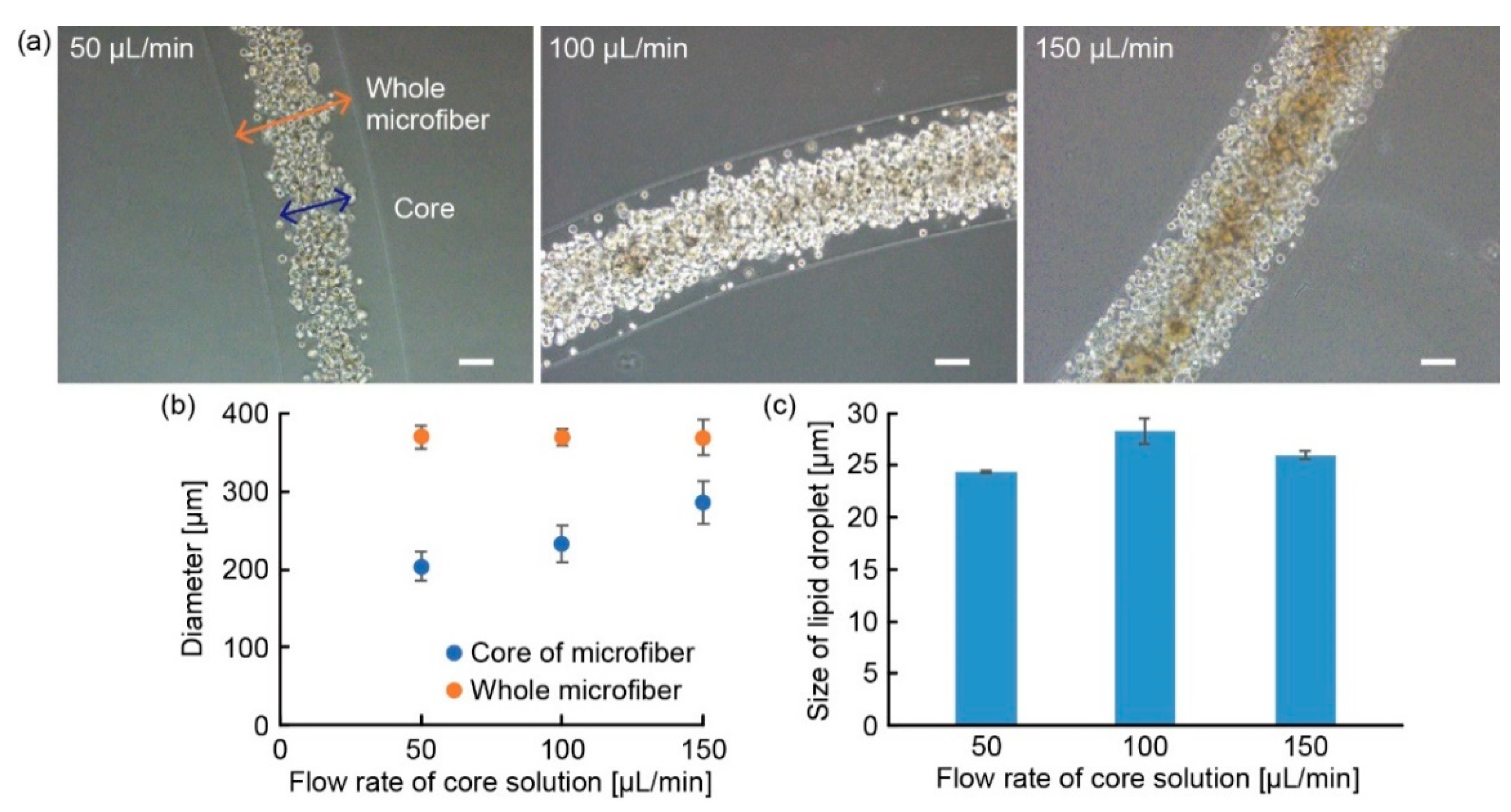
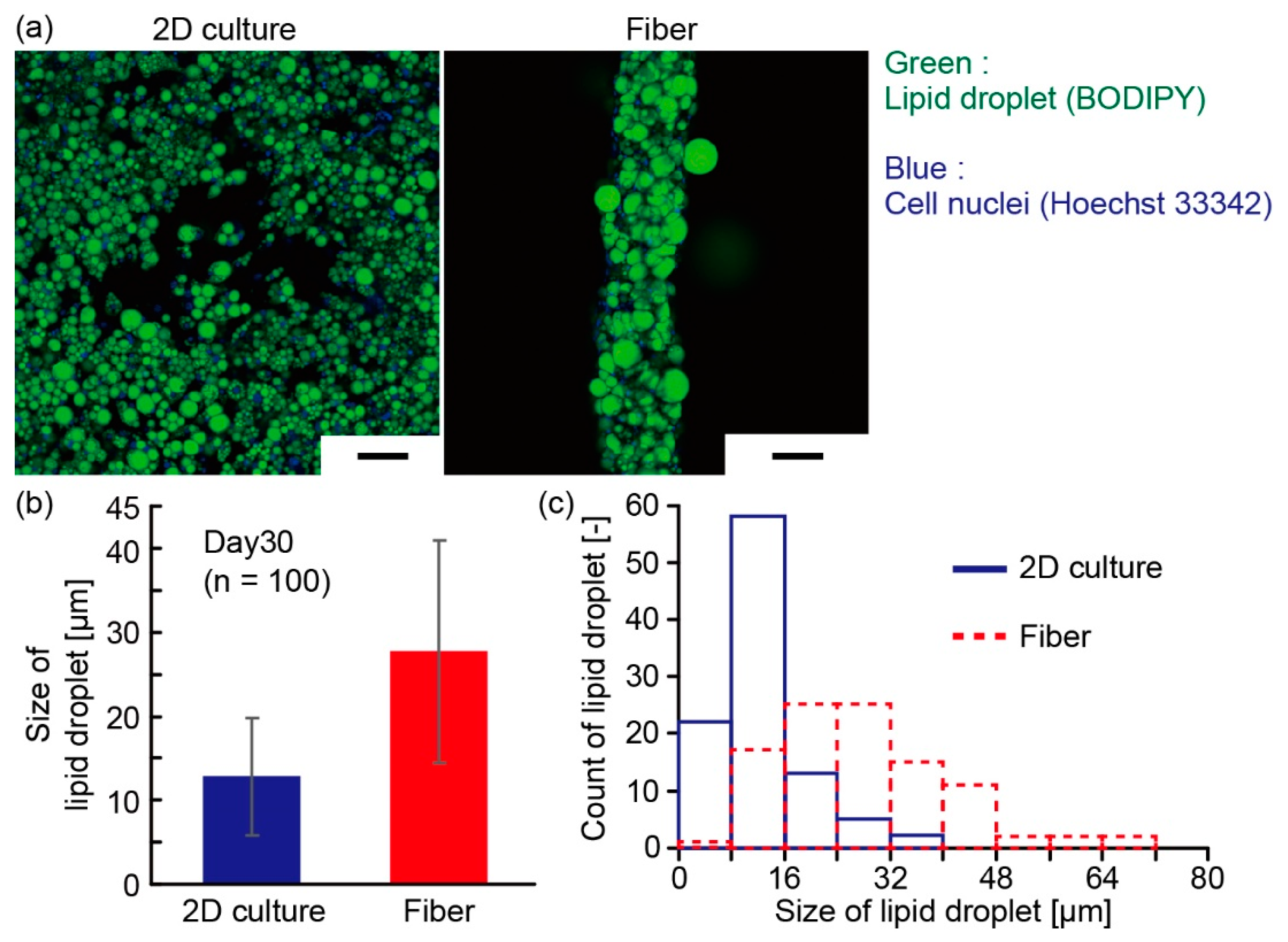
3.2. Characterization of Adipocyte Microfiber
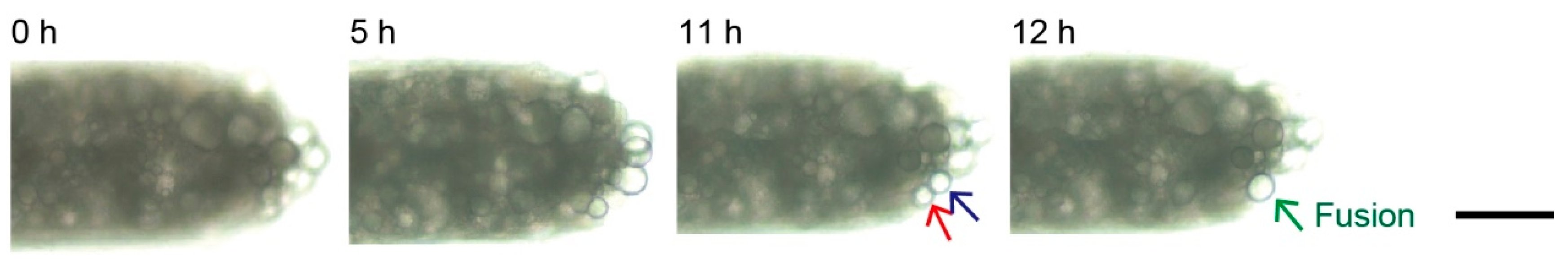
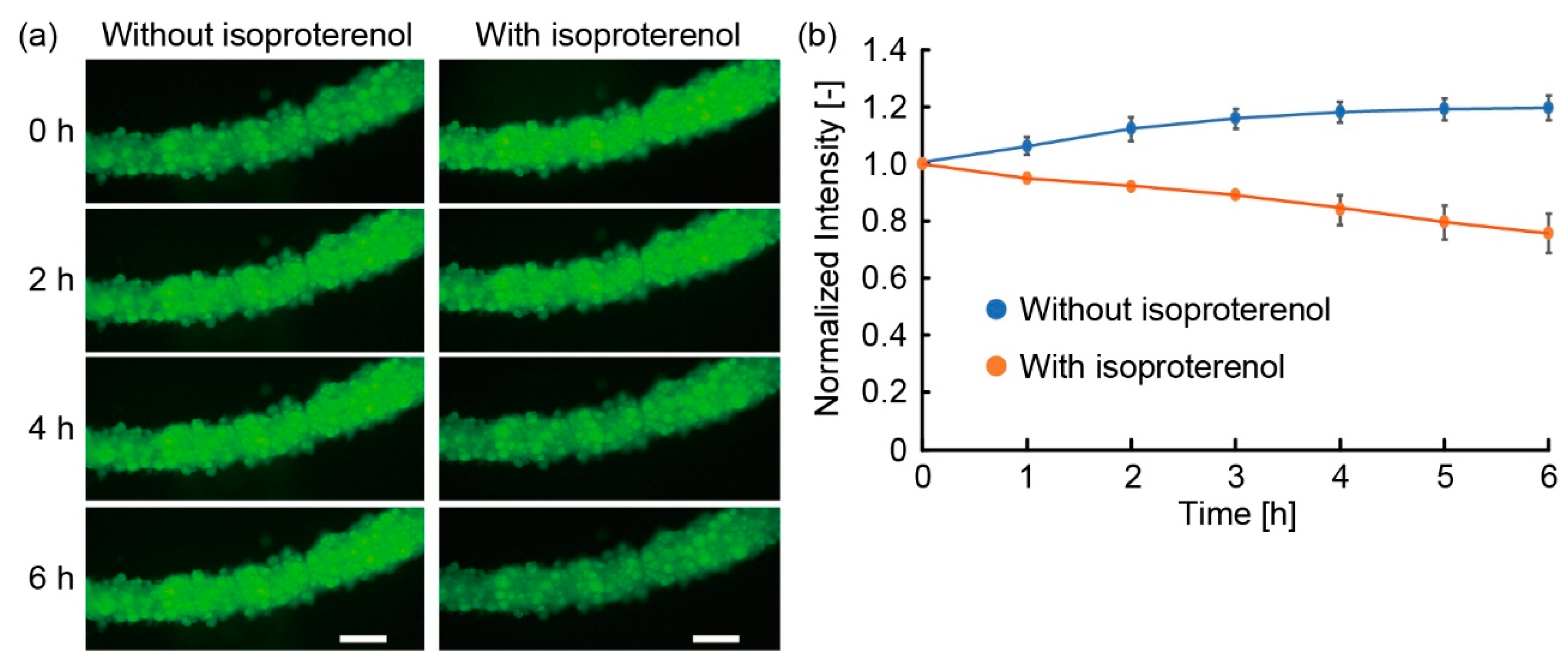
3.3. Lipolysis of Adipocyte Microfiber
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morimoto, Y.; Hsiao, A.Y.; Takeuchi, S. Point-, line-, and plane-shaped cellular constructs for 3D tissue assembly. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2015, 95, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoe, H.; Okitsu, T.; Itou, A.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Gojo, R.; Kiriya, D.; Sato, K.; Miura, S.; Iwanaga, S.; Kuribayashi-Shigetomi, K.; et al. Metre-long cell-laden microfibres exhibit tissue morphologies and functions. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, P.; Aied, A.; Alexander, M.; Shakesheff, K.; Bennett, A.; Yang, J. Bioprinting Using Mechanically Robust Core–shell Cell-Laden Hydrogel Strands. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Zhong, Z.; Hu, N.; Zhou, Y.X.; Maggio, L.; Miri, A.K.; Fragasso, A.; Jin, X.Y.; Khademhosseini, A.; Zhang, Y.S. Coaxial extrusion bioprinting of 3D microfibrous constructs with cell-favorable gelatin methacryloyl microenvironments. Biofabrication 2018, 10, 024102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, Y.; Kiyosawa, M.; Takeuchi, S. Three-dimensional printed microfluidic modules for design changeable coaxial microfluidic devices. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 274, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoe, H.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Itou, A.; Takeuchi, S. Differentiation Induction of Mouse Neural Stem Cells in Hydrogel Tubular Microenvironments with Controlled Tube Dimensions. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G. Vitrification of stem cell-laden core-shell microfibers with unusually low concentrations of cryoprotective agents. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Nagata, S.; Okitsu, T.; Takeuchi, S. Cell fiber-based three-dimensional culture system for highly efficient expansion of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.A.; Kim, M.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.W. Utilizing Core-Shell Fibrous Collagen-Alginate Hydrogel Cell Delivery System for Bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Liu, L.B.; Ouyang, J.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, X.Z.; Lan, Q.; Xu, T. Coaxial 3D bioprinting of self-assembled multicellular heterogeneous tumor fibers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, A.Y.; Okitsu, T.; Onoe, H.; Kiyosawa, M.; Teramae, H.; Iwanaga, S.; Kazama, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Takeuchi, S. Smooth Muscle-Like Tissue Constructs with Circumferentially Oriented Cells Formed by the Cell Fiber Technology. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, A.Y.; Okitsu, T.; Teramae, H.; Takeuchi, S. 3D Tissue Formation of Unilocular Adipocytes in Hydrogel Microfibers. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, B.D.; Warren, C.R.; Parker, K.K.; Cowan, C.A. Microenvironmental control of adipocyte fate and function. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Kumar, S.; Barnett, A.H.; Eggo, M.C. Ceiling culture of mature human adipocytes: use in studies of adipocyte functions. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 164, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paar, M.; Jüngst, C.; Steiner, N.A.; Magnes, C.; Sinner, F.; Kolb, D.; Lass, A.; Zimmermann, R.; Zumbusch, A.; Kohlwein, S.D.; et al. Remodeling of Lipid Droplets during Lipolysis and Growth in Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11164–11173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.N.; Yang, J.-Y.; England, E.; Yin, A.; Baile, C.A.; Rayalam, S. Isoproterenol Increases Uncoupling, Glycolysis, and Markers of Beiging in Mature 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, C.; Van den Daelen, C.; Tinant, G.; Bourez, S.; Thomé, J.-P.; Donnay, I.; Larondelle, Y.; Debier, C. Efficient in vitro adipocyte model of long-term lipolysis: a tool to study the behavior of lipophilic compounds. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2014, 50, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Mori, S.; Sakai, F.; Takeuchi, S. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived fiber-shaped cardiac tissue on a chip. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Onoe, H.; Takeuchi, S. Biohybrid robot powered by an antagonistic pair of skeletal muscle tissues. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Sugaya, S.; Naganuma, Y.; Seki, M. Microfluidic synthesis of chemically and physically anisotropic hydrogel microfibers for guided cell growth and networking. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 3122–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Jeong, G.S.; Choi, Y.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Khademhosseini, A.; Lee, S.-H. Digitally tunable physicochemical coding of material composition and topography in continuous microfibres. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Shin, S.J.; Kim, C.-B.; Kim, J.K.; Cho, Y.W.; Chung, B.G.; Lee, S.-H. Microfluidic synthesis of pure chitosan microfibers for bio-artificial liver chip. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Park, Y.; Sun, K.; Lee, S.-H. Microfluidic chip-based fabrication of PLGA microfiber scaffolds for tissue engineering. Langmuir 2008, 24, 6845–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Shin, S.J.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.-H. Synthesis of Cell-Laden Alginate Hollow Fibers Using Microfluidic Chips and Microvascularized Tissue-Engineering Applications. Small 2009, 5, 1264–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Arneri, A.; Bersini, S.; Shin, S.R.; Zhu, K.; Goli-Malekabadi, Z.; Aleman, J.; Colosi, C.; Busignani, F.; Dell’Erba, V.; et al. Bioprinting 3D microfibrous scaffolds for engineering endothelialized myocardium and heart-on-a-chip. Biomaterials 2016, 110, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilherme, A.; Virbasius, J.V.; Puri, V.; Czech, M.P. Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2008, 9, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Adipocyte stress: the endoplasmic reticulum and metabolic disease. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yokomizo, A.; Morimoto, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Takeuchi, S. Temporal Observation of Adipocyte Microfiber Using Anchoring Device. Micromachines 2019, 10, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060358
Yokomizo A, Morimoto Y, Nishimura K, Takeuchi S. Temporal Observation of Adipocyte Microfiber Using Anchoring Device. Micromachines. 2019; 10(6):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060358
Chicago/Turabian StyleYokomizo, Akiyo, Yuya Morimoto, Keigo Nishimura, and Shoji Takeuchi. 2019. "Temporal Observation of Adipocyte Microfiber Using Anchoring Device" Micromachines 10, no. 6: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060358
APA StyleYokomizo, A., Morimoto, Y., Nishimura, K., & Takeuchi, S. (2019). Temporal Observation of Adipocyte Microfiber Using Anchoring Device. Micromachines, 10(6), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060358




