Shape Programming Using Triangular and Rectangular Soft Robot Primitives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
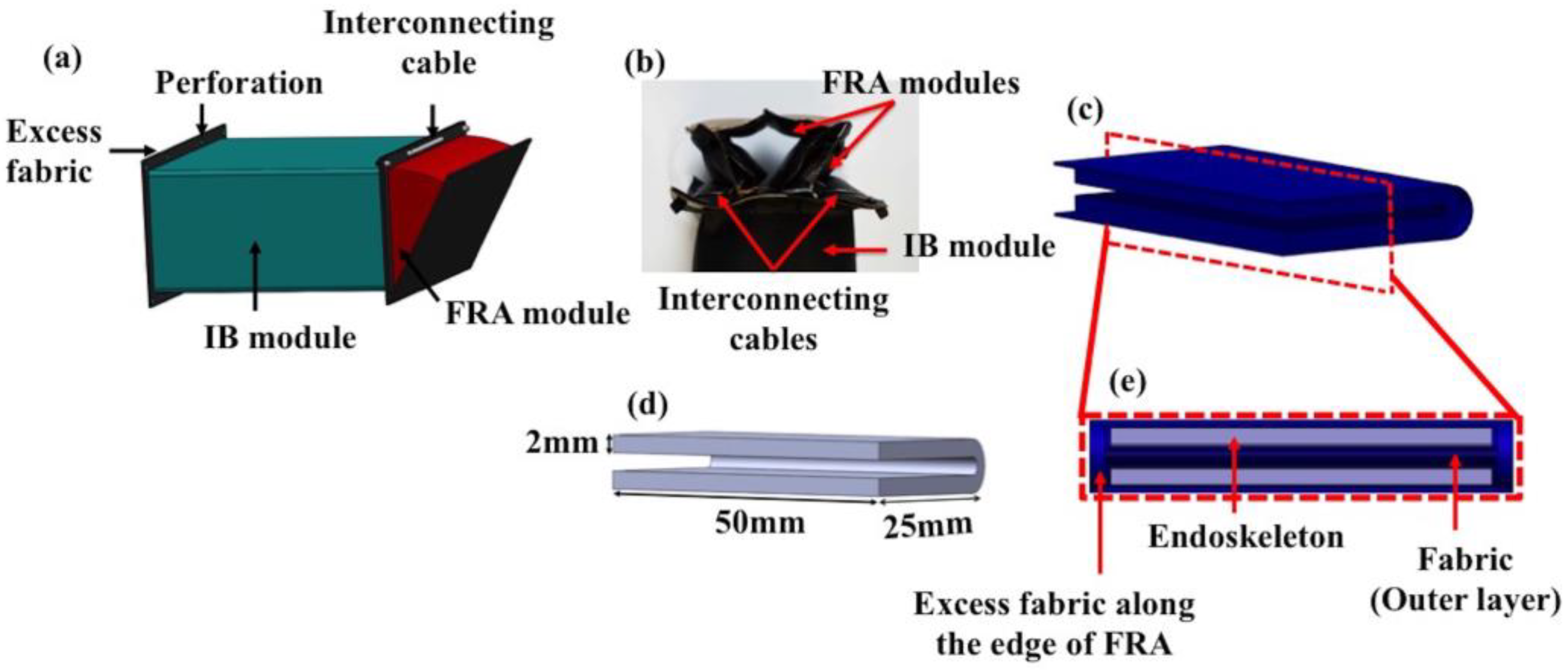
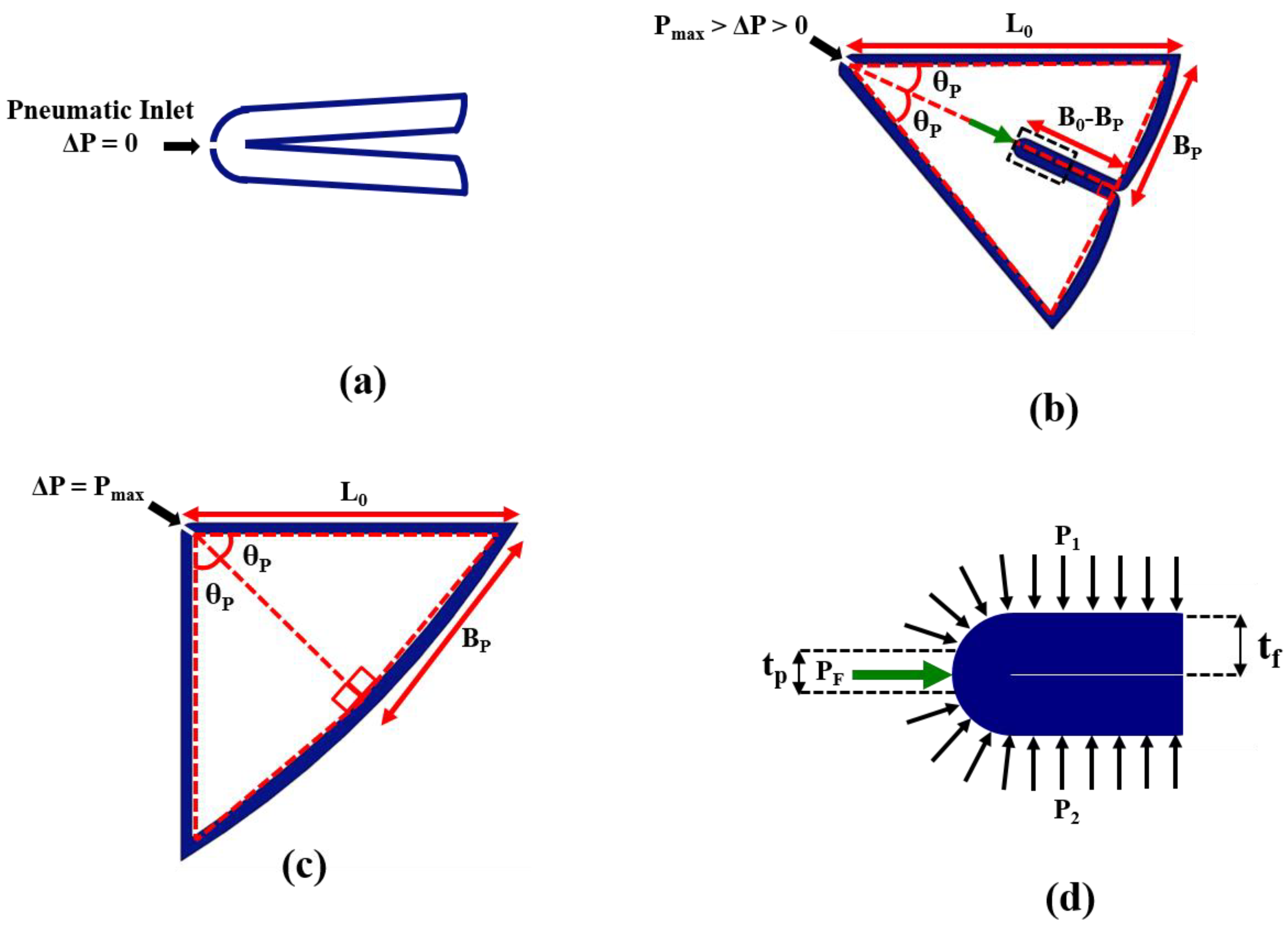
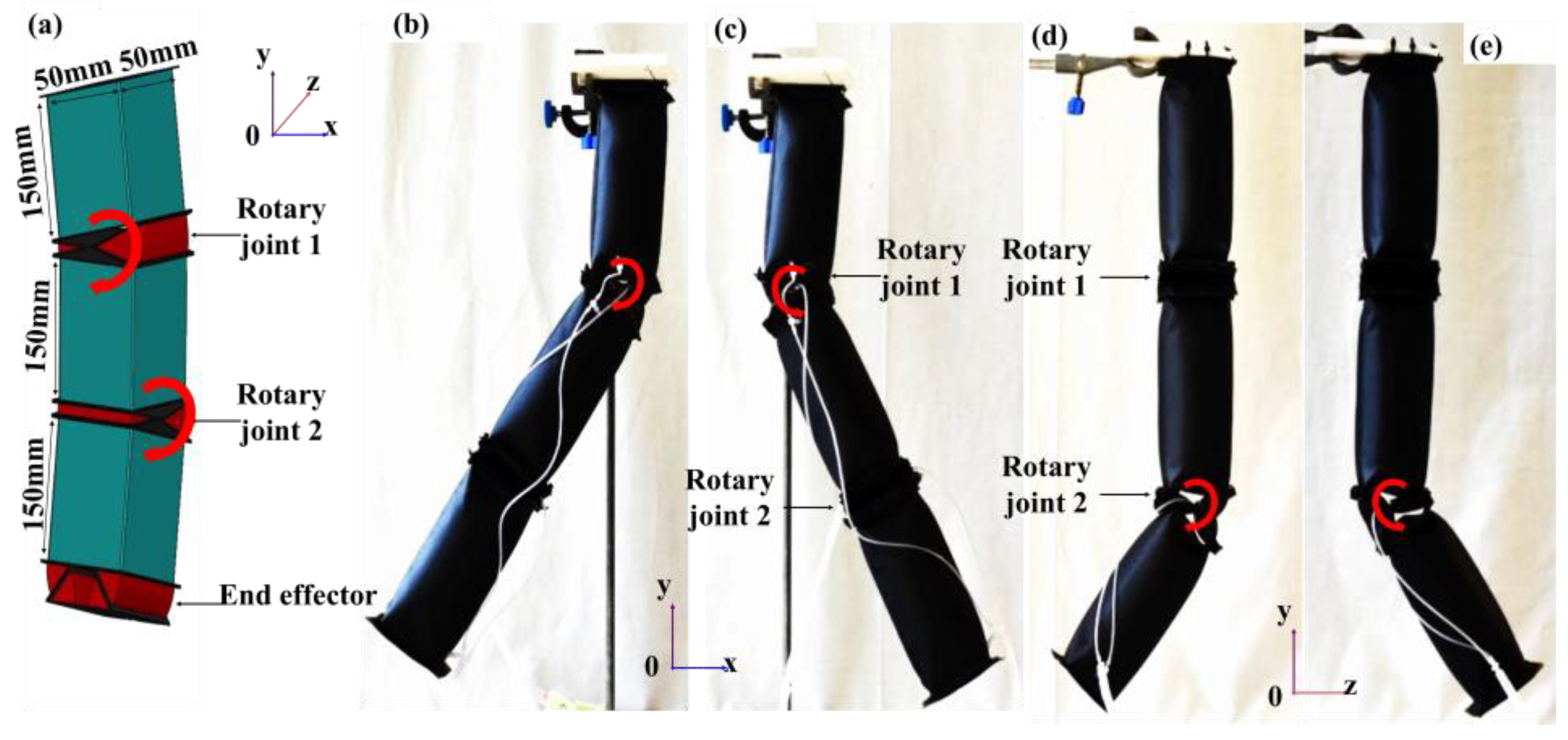
3. Materials and Methods
4. Experiments
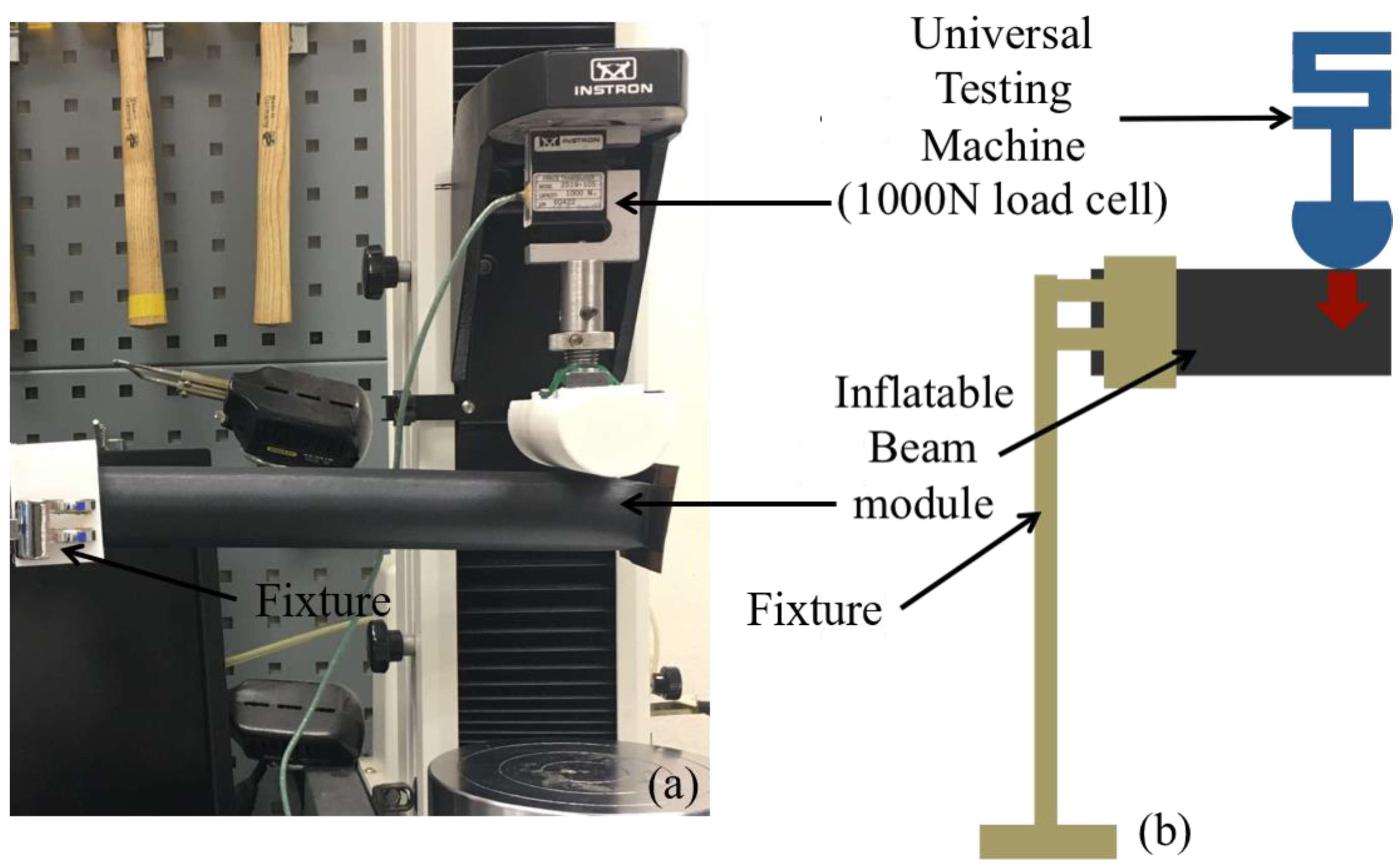
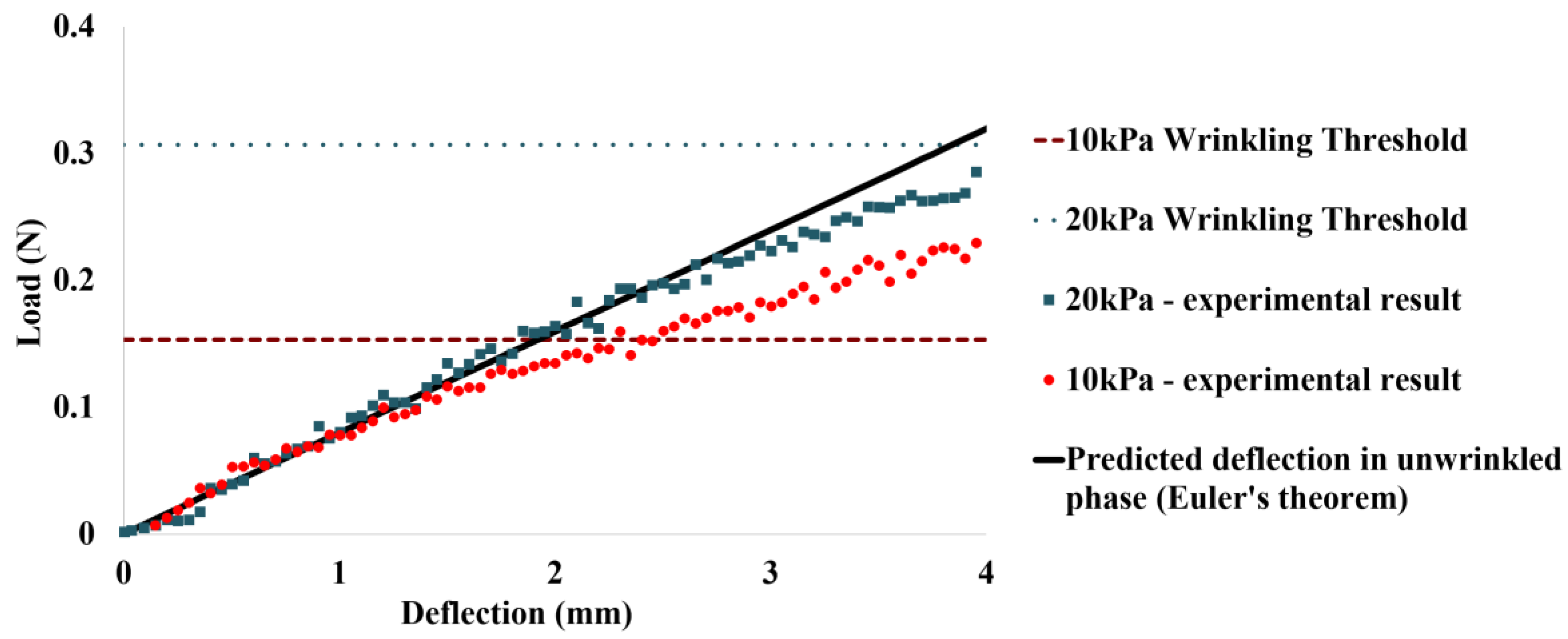
4.1. Deflection Behavior of IB Module
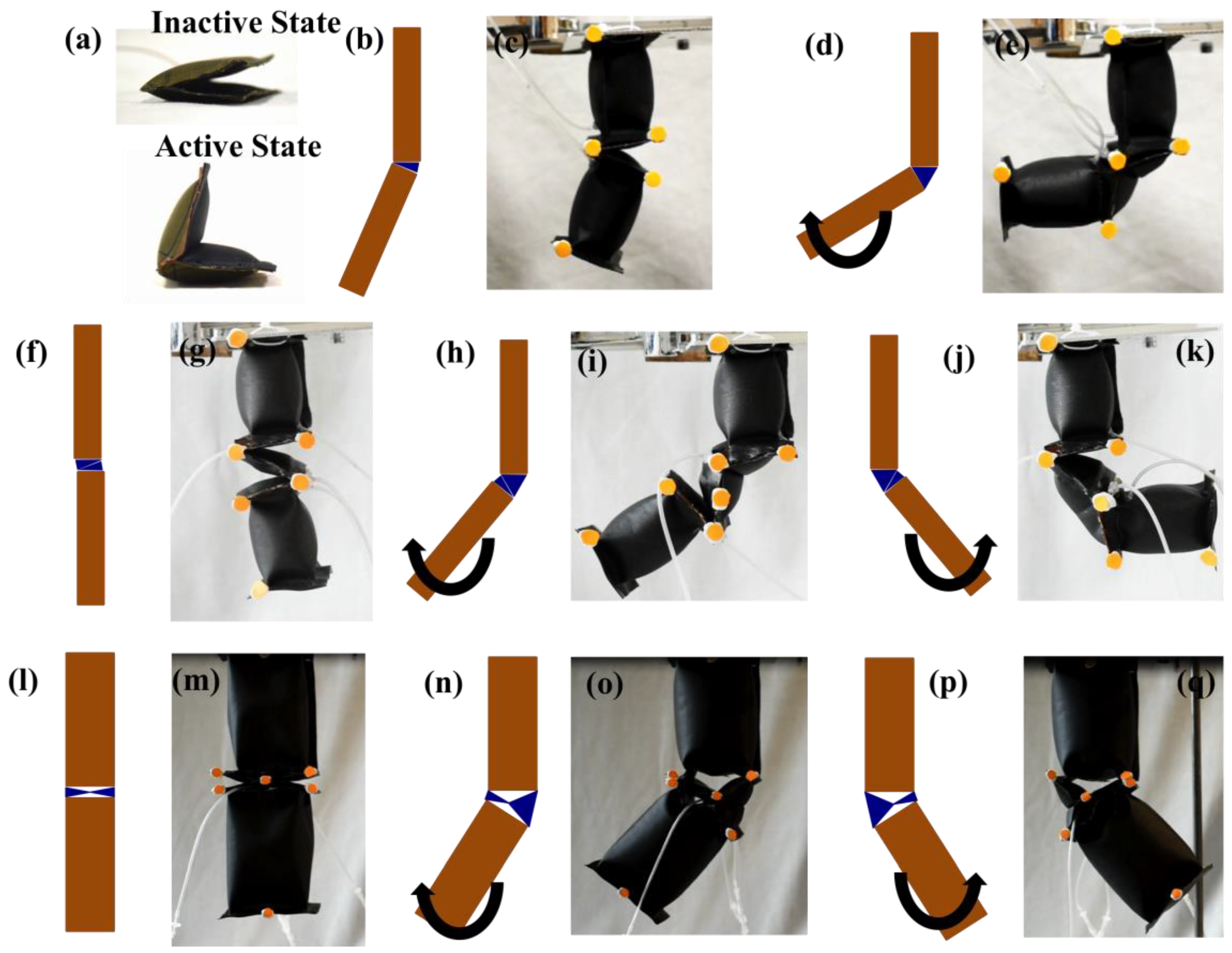
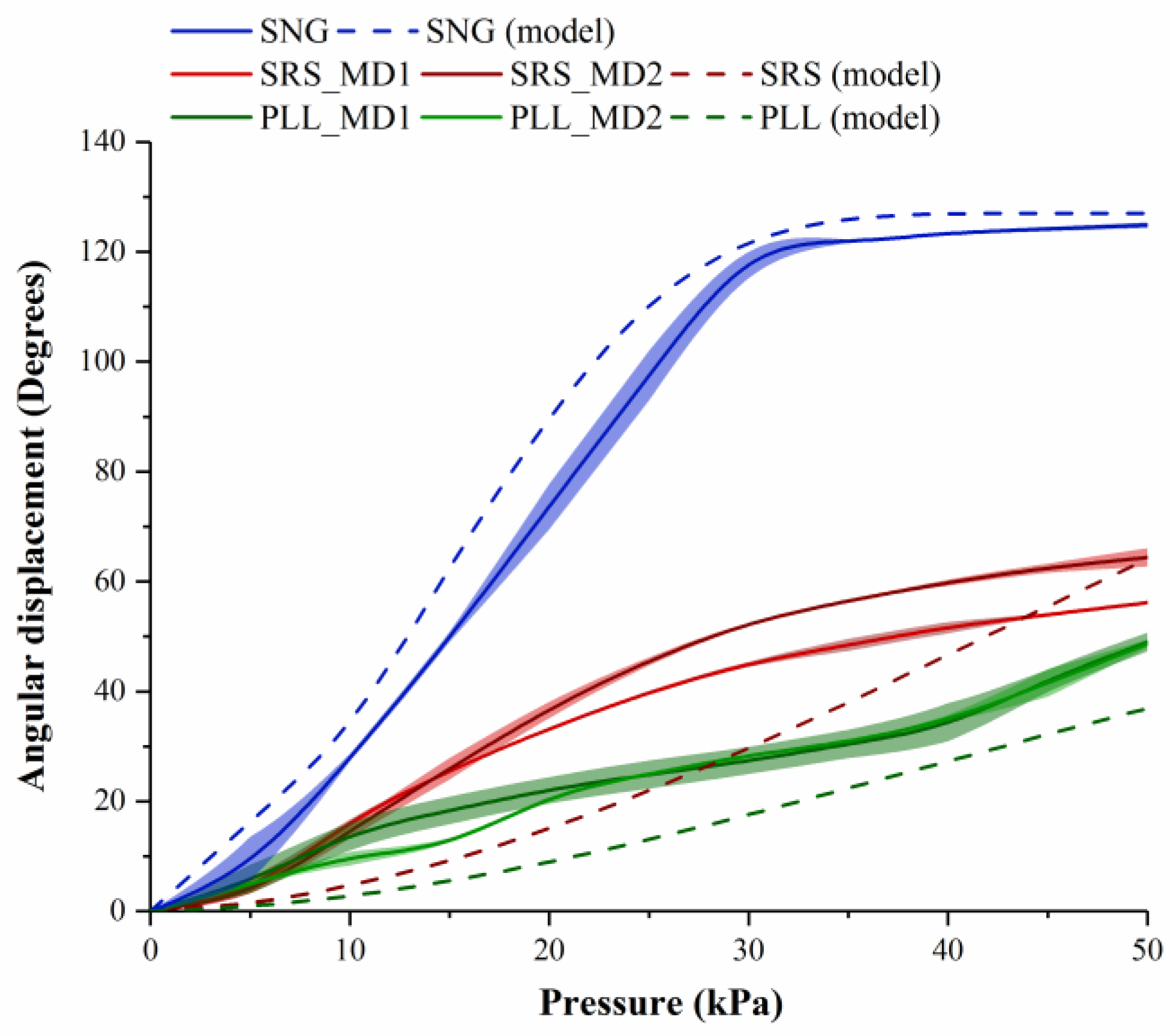
4.2. Angular Displacement Profile of Assembled Modules
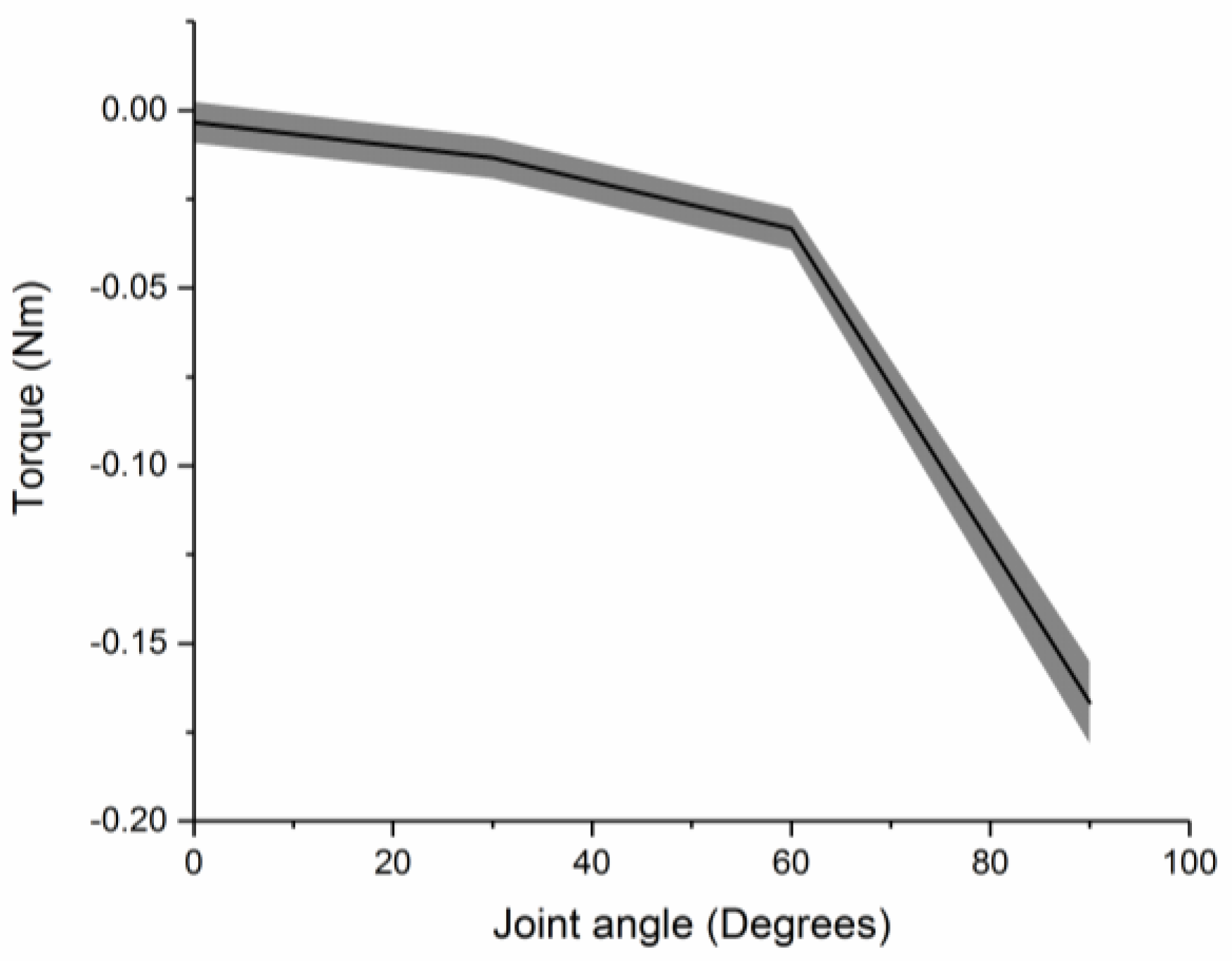
4.3. Stiffness of Assembled Modules
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Deflection Behavior of IB Module
5.2. Angular Displacement Profile of Assembled Modules
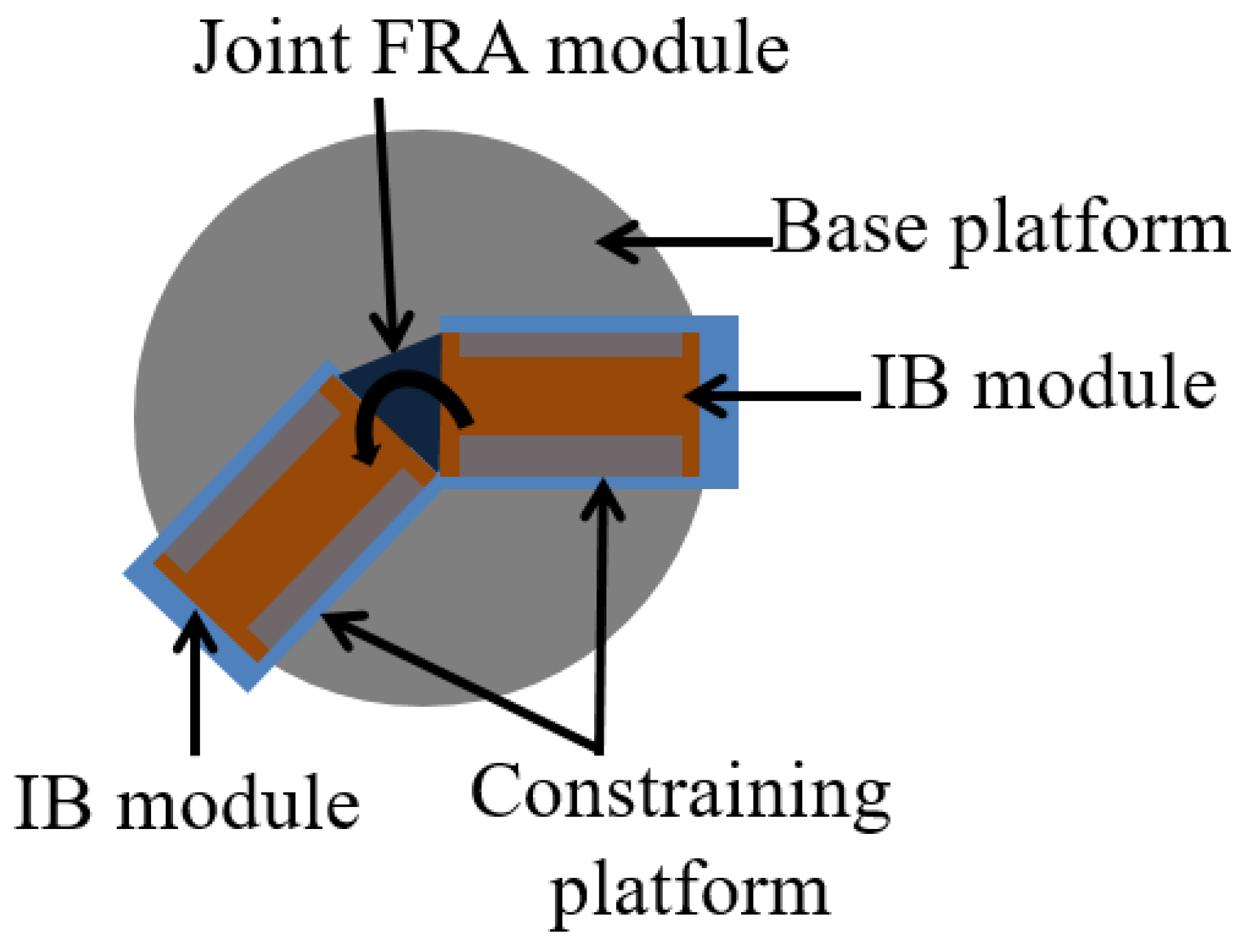
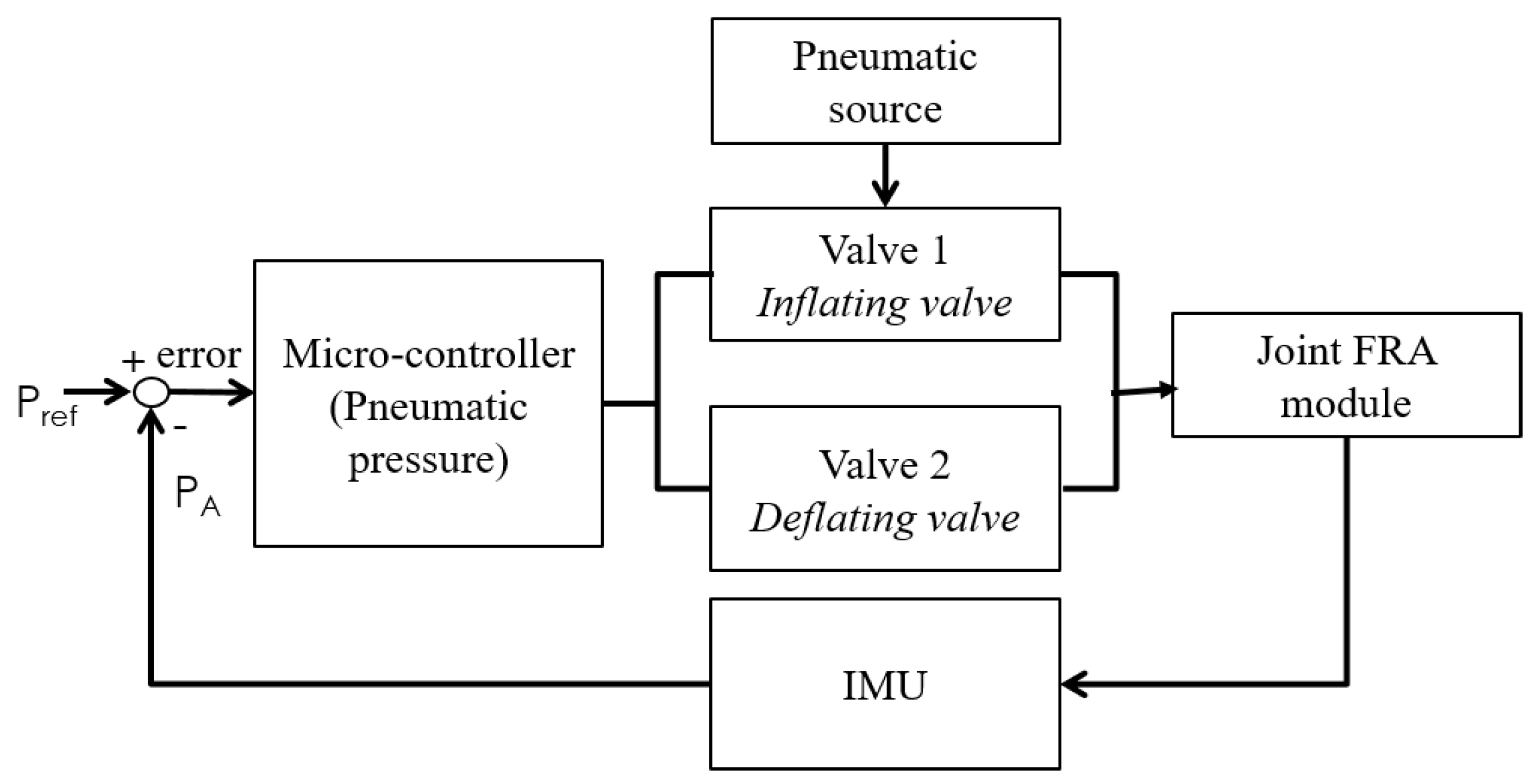
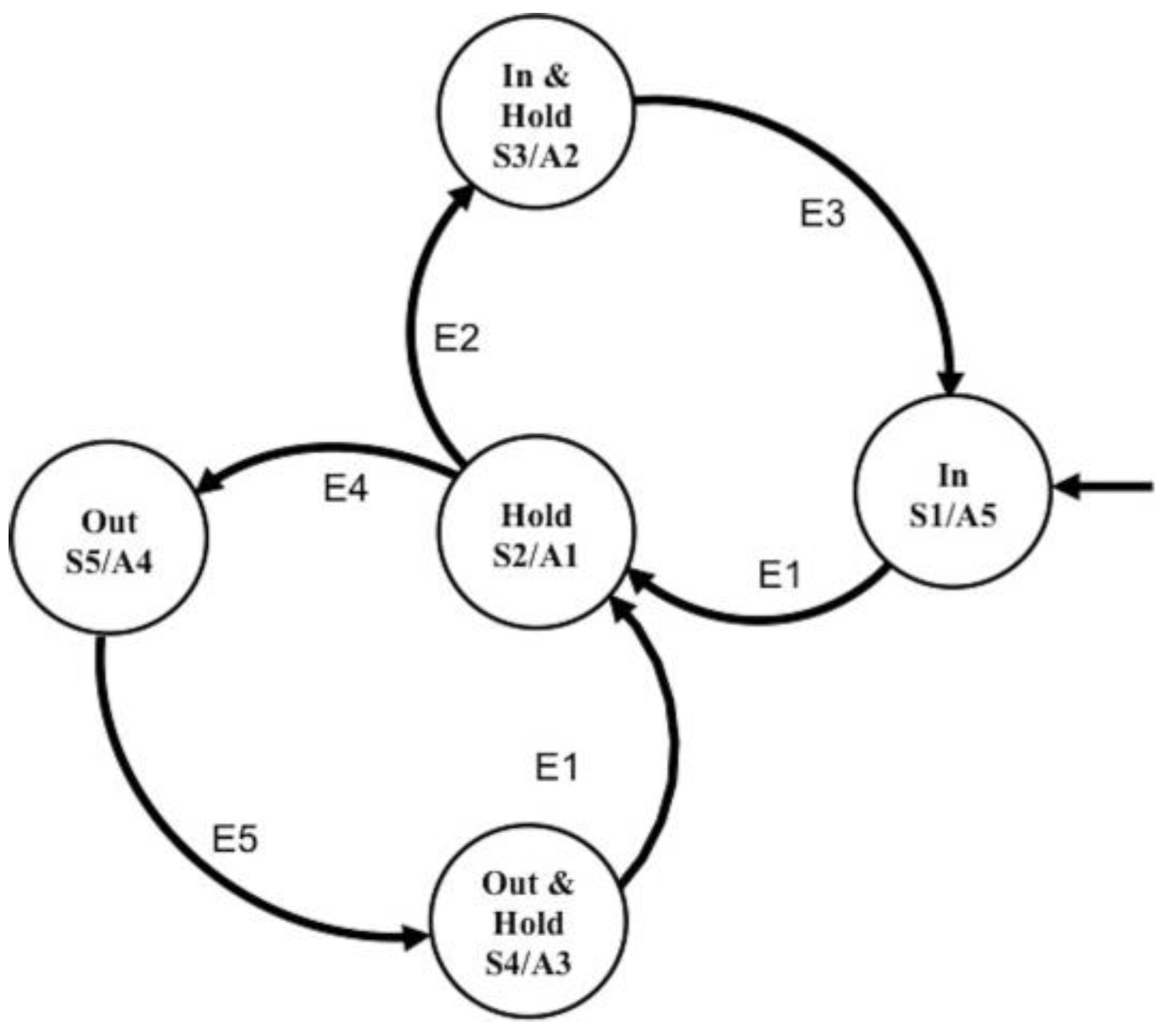
6. Design of Control System
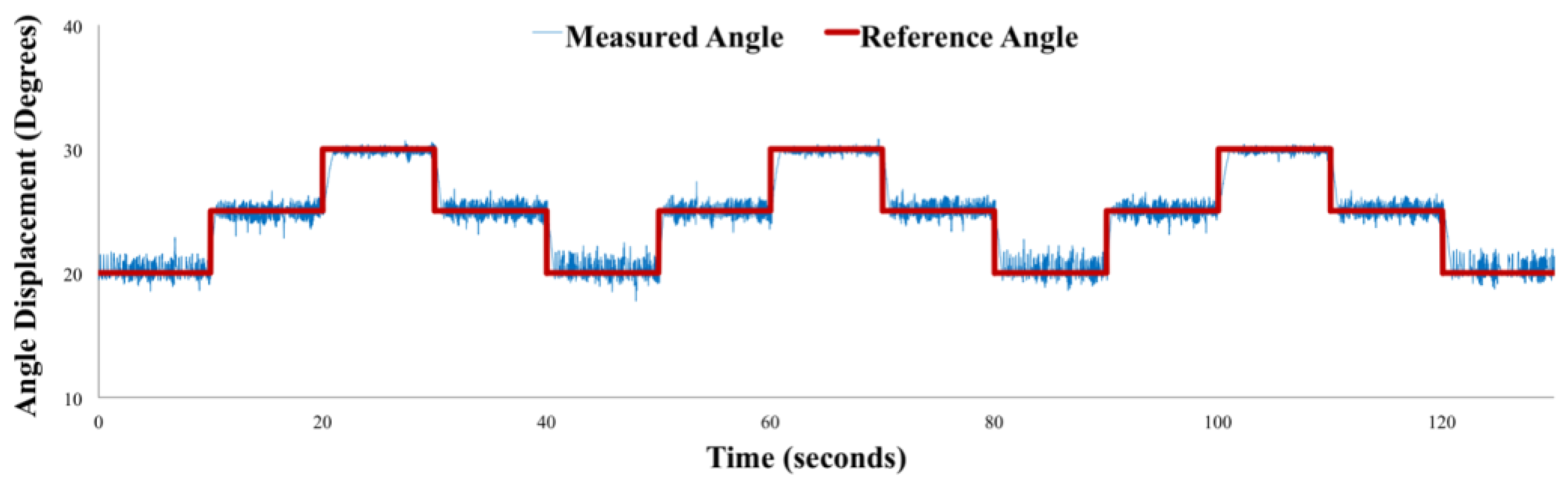
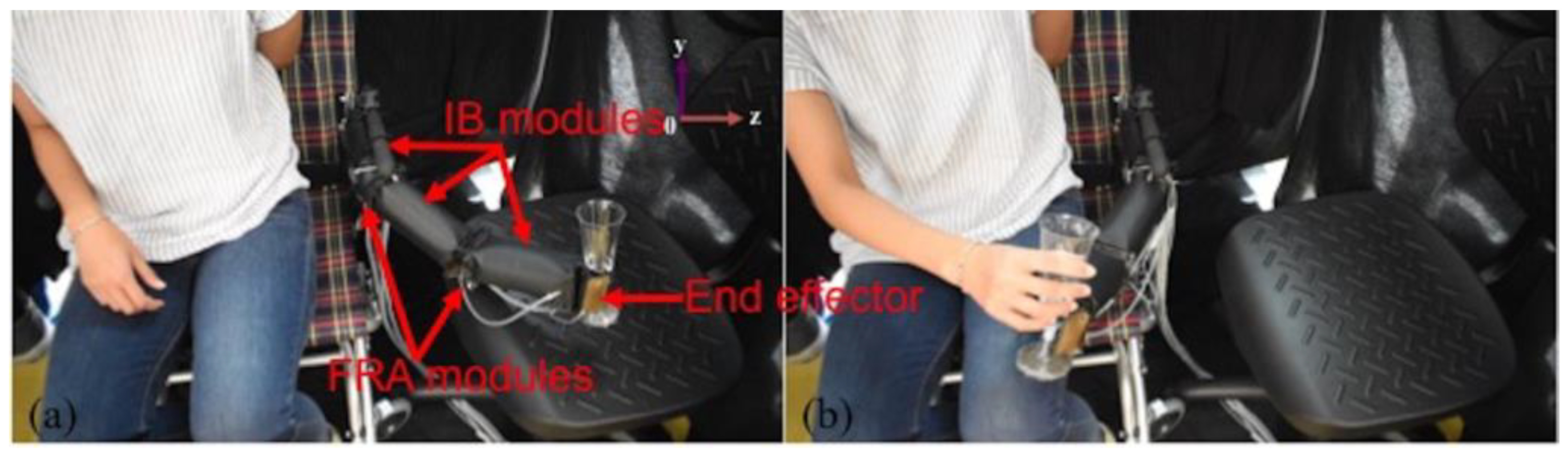
7. Implementation
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Euclid; Heath, T.L.; Densmore, D. Euclid’s Elements: All Thirteen Books Complete in One Volume; Green Lion Press: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose, J. Design of Building Trusses; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- McCartin, B.J. Mysteries of the Equilateral Triangle; Hikari Ltd.: Rousse, Bulgaria, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 9–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ilievski, F.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Shepherd, R.F.; Chen, X.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft robotics for chemists. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laschi, C.; Cianchetti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Margheri, L.; Follador, M.; Dario, P. Soft robot arm inspired by the octopus. Adv. Robot. 2012, 26, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onal, C.; Rus, D. Autonomous undulatory serpentine locomotion utilizing body dynamics of a fluidic soft robot. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Leisk, G.; Trimmer, B. Soft robots in space: A perspective for soft robotics. Acta Futura 2013, 6, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, R.; Ilievski, F.; Choi, W.; Morin, S.; Stokes, A.; Mazzeo, A.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Whitesides, G. Multigait soft robot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 51, 20400–20403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, K.; Polygerinos, P.; Walsh, C.; Wood, R. Mechanically programmable bend radius for fiber-reinforced soft actuators. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Advanced Robotics, ICAR 2013, Montevideo, Uruguay, 25–29 November 2013; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, H.K.; Lim, J.H.; Nasrallah, F.; Goh, C.H.; Yeow, C.H. Characterisation and evaluation of soft elastomeric actuators for hand assistive and rehabilitation applications. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2016, 40, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, J.H.; Lee, W.W.; Khin, P.M.; Thakor, N.; Kukreja, S.; Ren, H.L.; Yeow, C.H. Hybrid tele-manipulation system using a sensorized 3-D-printed soft robotic gripper and a soft fabric-based haptic glove. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Ng, H.Y.; Yeow, C.H. High-force soft printable pneumatics for soft robotic applications. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, W.; Choi, W.; Cho, K. Soft robotic blocks: Introducing SoBL, a fast-build modularized design block. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016, 23, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onal, C.D.; Rus, D. A modular approach to soft robots. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, 24–27 June 2012; pp. 1038–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, S.; Shevchenko, Y.; Lessing, J.; Kwok, S.; Shepherd, R.; Stokes, A.; Whitesides, G.M. Using “Click-e-Bricks” to make 3D elastomeric structures. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5991–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, Y.; Uesu, M.; Tsuboi, H.; Kawamura, S. Proposal of an extremely lightweight soft actuator using plastic films with a pleated structure. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice, Auckland, New Zealand, 28–30 November 2012; pp. 474–479. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, H.K.; Ang, B.W.K.; Lim, J.H.; Goh, J.C.H.; Yeow, C.H. A fabric-regulated soft robotic glove with user intent detection using emg and rfid for hand assistive application. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3537–3542. [Google Scholar]
- Voisembert, S.; Mechbal, N.; Riwan, A.; Aoussat, A. Design of a novel long-range inflatable robotic arm: Manufacturing and numerical evaluation of the joints and actuation. J. Mech. Robot. 2013, 5, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, C.M.; Wilson, J.P.; Killpack, M.D. Control of a pneumatically actuated, fully inflatable, fabric-based, humanoid robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE-RAS 15th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Seoul, Korea, 3–5 November 2015; pp. 1133–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Sanan, S.; Lynn, P.S.; Griffith, S.T. Pneumatic Torsional Actuators for Inflatable Robots. J. Mech. Robot. 2014, 6, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, J.A.; Peterson, S.W.; Strauss, A.M. Load–deflection behaviour of space-based inflatable fabric beams. J. Aerosp. Eng. 1994, 2, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Seth, R.K.; Quine, B.M. Experimental investigation of inflatable cylindrical cantilevered beams. JP J. Solids Struct. 2008, 2, 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- Paez, L.; Agarwal, G.; Paik, J. Design and analysis of a soft pneumatic actuator with origami shell reinforcement. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, R.; Del Rosario, M.; Chen, P.; Yeow, C.H. A hybrid plastic-fabric soft bending actuator with reconfigurable bending profiles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Jalving, J.; Huang, R.; Knepper, R.; Ruina, A.; Shepherd, R. A helping hand: Soft orthosis with integrated optical strain sensors and EMG control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016, 23, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oneill, C.T.; Phipps, N.S.; Cappello, L.; Paganoni, S.; Walsh, C.J. A soft wearable robot for the shoulder: Design, characterization, and preliminary testing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017. [Google Scholar]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khin, P.M.; Low, J.H.; Ang, M.H.; Yeow, C.-H. Shape Programming Using Triangular and Rectangular Soft Robot Primitives. Micromachines 2019, 10, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10040236
Khin PM, Low JH, Ang MH, Yeow C-H. Shape Programming Using Triangular and Rectangular Soft Robot Primitives. Micromachines. 2019; 10(4):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10040236
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhin, Phone May, Jin Huat Low, Marcelo H. Ang, and Chen-Hua Yeow. 2019. "Shape Programming Using Triangular and Rectangular Soft Robot Primitives" Micromachines 10, no. 4: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10040236
APA StyleKhin, P. M., Low, J. H., Ang, M. H., & Yeow, C.-H. (2019). Shape Programming Using Triangular and Rectangular Soft Robot Primitives. Micromachines, 10(4), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10040236





