Recent Advances in Continuous-Flow Particle Manipulations Using Magnetic Fluids
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Magnetic Particles
1.2. Magnetic Fluids
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Magnetic Force and Translation
2.2. Magnetic Torque and Rotation
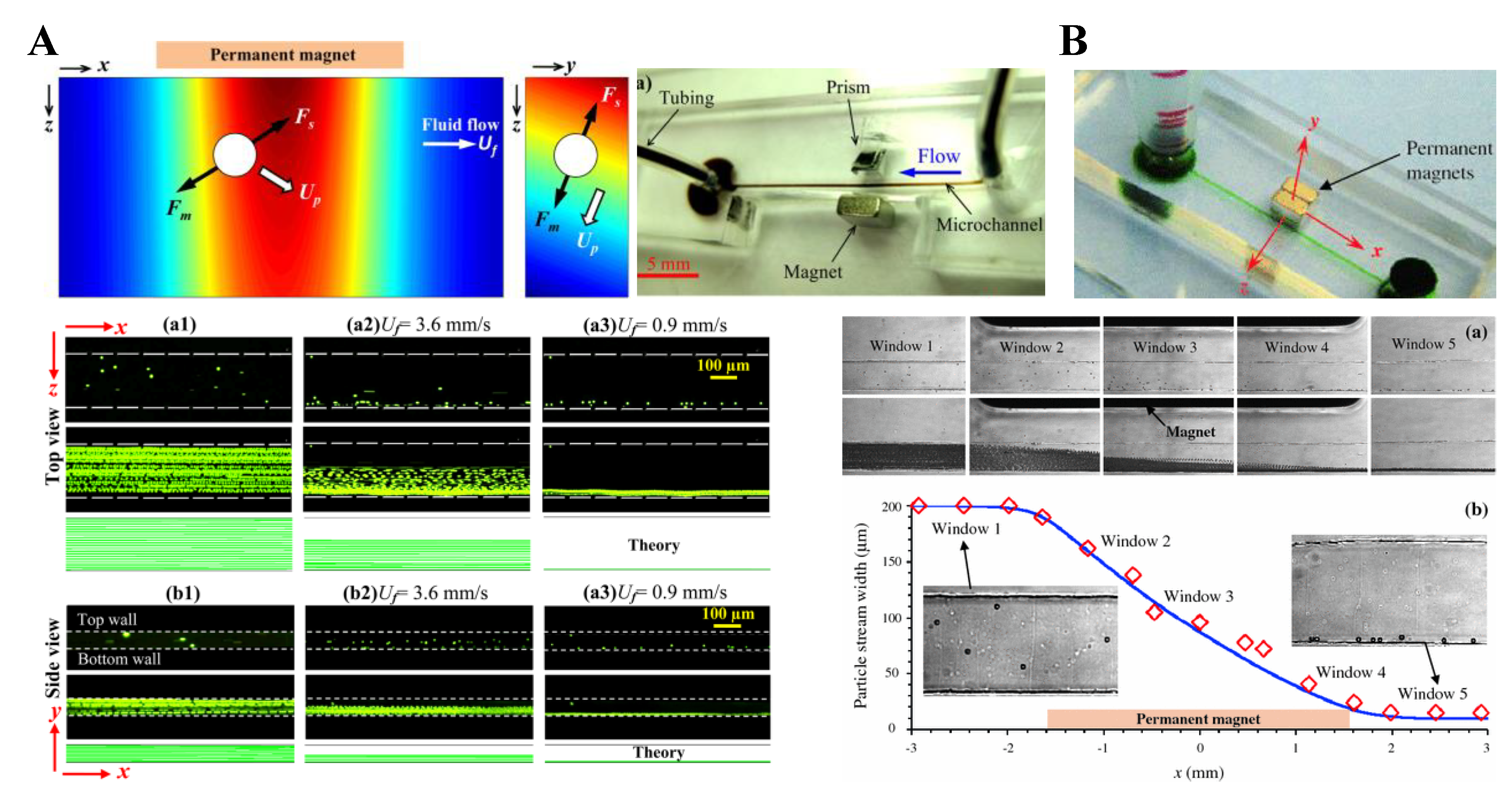
3. Particle Deflection
3.1. Non-Uniform Magnetic Field
3.2. Uniform Magnetic Field
3.3. Summary
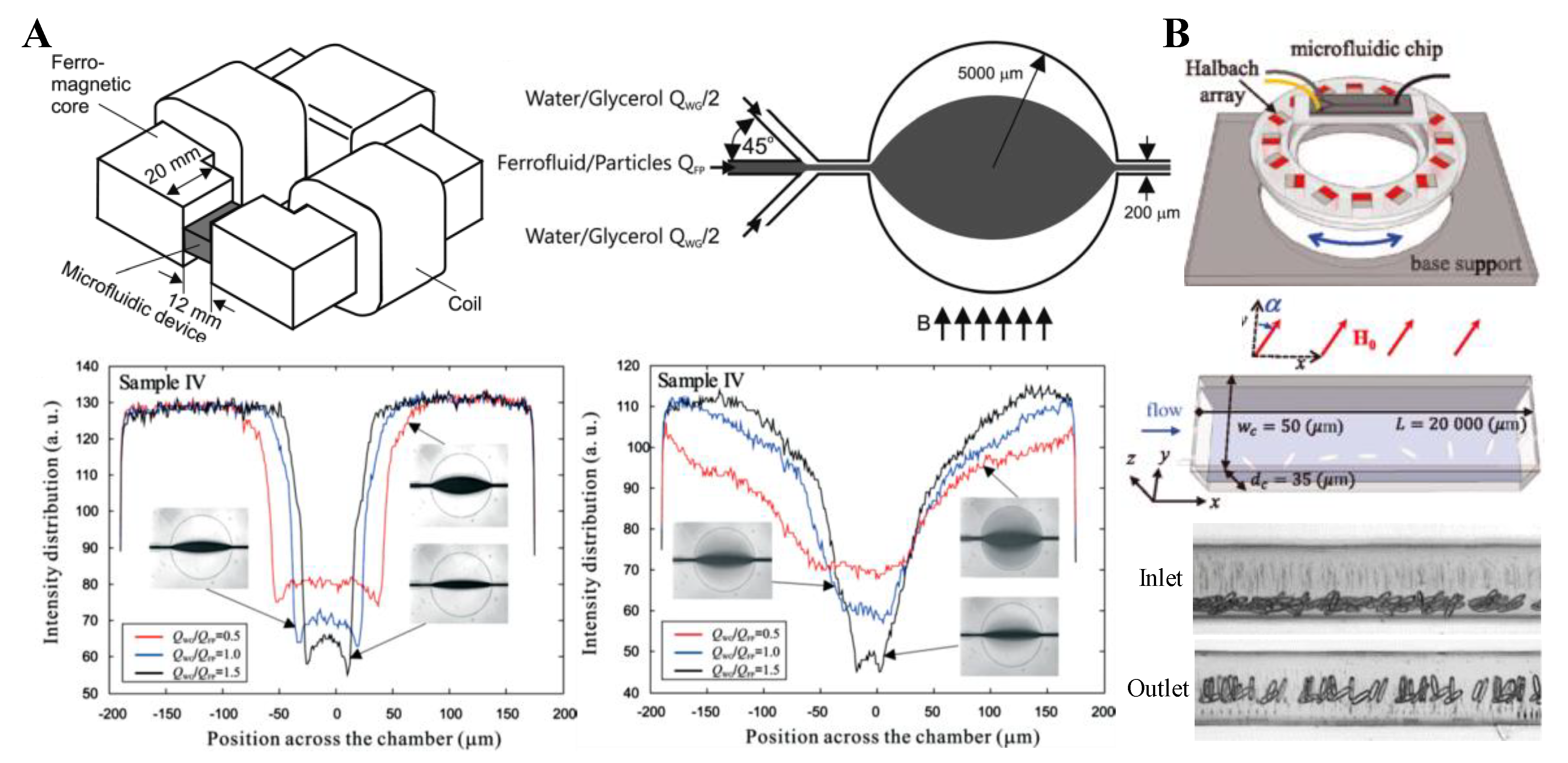
4. Particle Focusing
4.1. Repulsing Magnet Pair
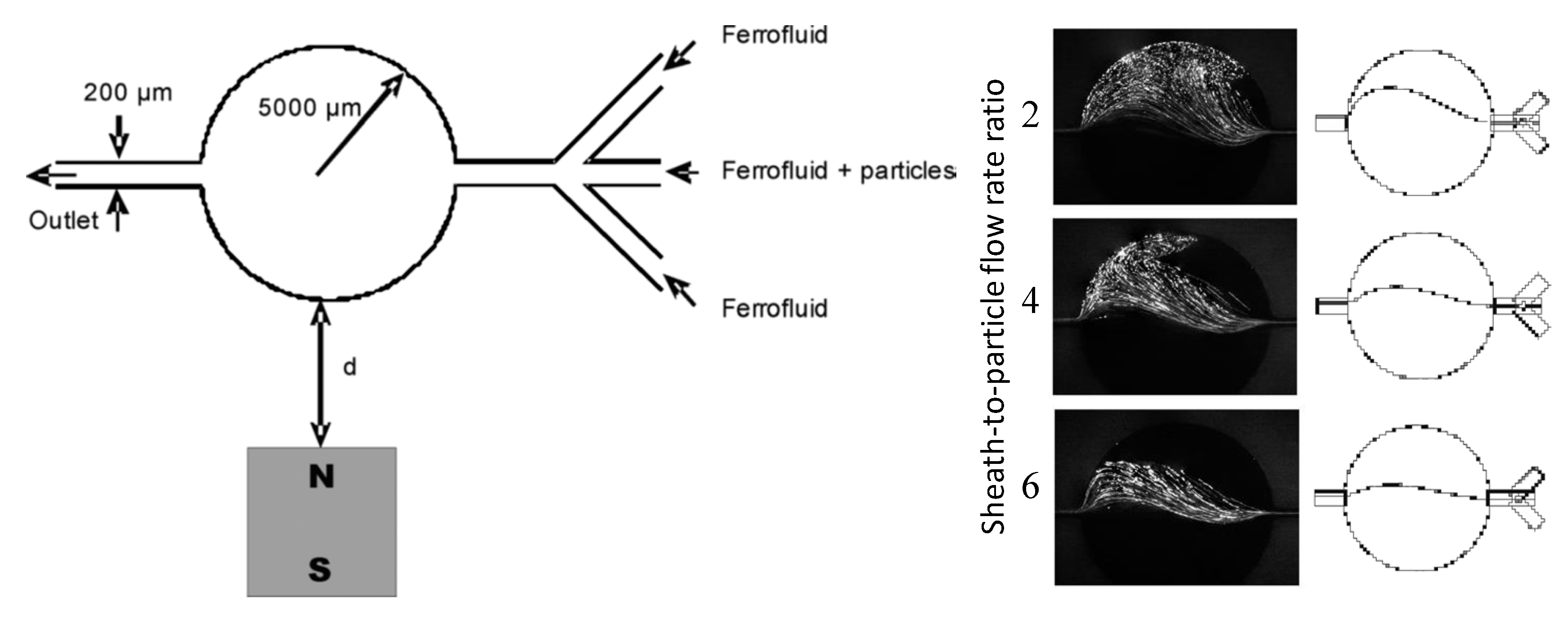
4.2. Single Magnet with a Sheath Flow
4.3. Single Magnet Only
4.4. Summary
| Sheath | Particles | Fluid | Magnet | Particle Flow Rate | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Type | |||||
| - | 10 µm PS | 0.79 M MnCl2 | repulsing pair | permanent | 43 µL/h | [90] |
| - | 10/20 µm PS HaCaT cells | 0.79 M MnCl2/GdCl3 | repulsing pair | permanent | 30 µL/h | [44] |
| - | 10 µm PS | 50 mM Gadavist | repulsing pair | permanent | ~500 µL/h | [91] |
| - | 4.8/5.8/7.3 µm PS | 1.2% ferrofluid | repulsing pair | permanent | 60–480 µL/h | [92] |
| - | 5 µm PS yeast cells | 0.3% ferrofluid | repulsing pair | permanent | 50 µL/h | [93] |
| water sheath | 5/10 µm PS | 0.012% ferrofluid | single | permanent | ~50 µL/h | [94] |
| water sheath | 2/7 µm PS | 0.36/0.6% ferrofluid | single | permanent + micromagnet | 90 µL/h | [95] |
| - | 5–13 µm PS | 0.024–0.12% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 0.6–4.8 mL/h | [96] |
| - | 5/10/20 µm PS | 0.6–1.2% ferrofluid | stacked | permanent | 0.1–2 mL/h | [97] |
5. Particle Enrichment
5.1. Magnet Pair
5.2. Single Magnet
5.3. Summary
| Particles | Fluid | Magnet | Particle Flow Rate | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Type | ||||
| 5/10/21 µm PS | 0.005% ferrofluid | repulsing pair | permanent | 0.24–1.2 mL/h | [104] |
| 10 µm PS | 0.79 M MnCl2 | attracting pair | permanent | 43 µL/h | [90] |
| 10 µm PS 8 µm mag | 0.79 M MnCl2 | attracting pair | permanent | 10 µL/h | [105] |
| 5 µm PS | 0.24% ferrofluid | attracting pair | permanent | 100–200 µL/h | [108] |
| 5 µm PS yeasts | 0.06% ferrofluid | attracting pair | permanent | 240 µL/h | [106] |
| 3.1/4.8 µm PS | 0.005–1% ferrofluid | attracting array | permanent | 0.6–6 mL/h | [107] |
| 9.9 µm PS 2.85 µm mag | 0.06% ferrofluid | single | permanent | ~50 µL/h | [109] |
6. Particle Separation
6.1. One-Sheath-Flow Focusing
6.2. Two-Sheath-Flow Focusing
6.3. Sheath Free
6.4. Hybrid
6.5. Summary
| Pre-Focused | Particles | Fluid | Magnet | Particle Flow Rate | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Type | |||||
| 1 sheath | 5/10 µm PS | 0.79 M MnCl2 | single | permanent | 20–60 µL/h | [90] |
| 1 sheath | 5/10 µm PS | 0.24–0.48 M MnCl2 | single | superconducting | 70 µL/h | [125] |
| 1 sheath | 1/3/6 µm PS | 1 M MnCl2 | single | superconducting | 58 µL/h | [126] |
| 1 sheath | 8/10 µm PS RBC/U937 | 0–80 mM Gd-DTPA | single | permanent + micromagnet | 19.2 µL/h | [127] |
| 1 sheath | 1/1.9/3.1/9.9 µm PS | 1.2% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 180 µL/h | [131] |
| 1 sheath | 1/7.3 µm PS yeast/E.coli | 1.2% ferrofluid | stacked | permanent | 90 µL/h | [132] |
| 1 sheath | 5.8/15. µm PS HeLa RBC | 0.3% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 480 µL/h | [128] |
| 1 sheath | cancer cells WBC | 0.26% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 1.2–6 mL/h | [133] |
| 1 sheath | cell containing droplets | 0.08% ferrofluid | single | permanent | - | [129] |
| 1 sheath | 6 µm spheres/peanuts | 0.36% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 6 µL/h | [135] |
| 1 sheath | drug treated yeasts | 0.12% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 9 µL/h | [130] |
| 2 sheathes | 15 µm PS/PMMA/BS | 125 mM Gd-DTPA | single | permanent + micromagnet | - | [137] |
| 2 sheathes | 6/10 µm PS+biomarkers | 10/25 mM Gd-DTPA | single | permanent + micromagnet | 1.2 µL/h | [47] |
| 2 sheathes | 2.2/4.8/9.9 µm PS | 5.8% ferrofluid | electrodes in quadrature | electromagnet | 24 µL/h | [138] |
| 2 sheathes | 2/7 µm PS | 0.36/0.6% ferrofluid | single | permanent + micromagnet | 50–120 µL/h | [95] |
| 2 sheathes | 3.2/4.8 µm PS | 0.25–1% ferrofluid | array | permanent | 60 µL/h | [139] |
| - | 2.2/9.9 µm PS RBC sickle cells bacteria | customized ferrofluid | electrodes in quadrature | electromagnet | - | [140] |
| - | 5/15 µm PS | 0.012% ferrofluid | single | permanent | ~20 µL/h | [141] |
| - | 5/15 µm PS | 0.6% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 450 µL/h | [142] |
| - | 3/10 µm PS yeast cells | 0.06% ferrofluid | two offset | permanent | 10–20 µL/h | [143] |
| - | 10 µm PS 2.85 µm mag | 0.12% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 240 µL/h | [144] |
| - | 4.2/7.3 µm PS 2.6/7.9 µm mag | 1.2% ferrofluid | single | permanent | ~200 µL/h | [145] |
| - | 10 µm PS blood | 50 mM Gadavist | repulsing pair | permanent | ~100 µL/h | [91] |
| - | 75–100 µm Merrifield resins | 250 mM GdCl3 | repulsing pair | permanent | 6–15 mL/h | [146] |
| elastic | 5/20 µm PS | 0.12% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 5–200 µL/h | [148] |
| elastic | 5/13 µm PS | 0.12% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 900 µL/h | [149] |
| inertial | 10/20 µm PS | 0.36–0.84% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 0.5–1.5 mL/h | [150] |
| Hydrophoretic | 13 µm PS 6 µm mag | 0.06% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 0.3–4.8 mL/h | [151] |
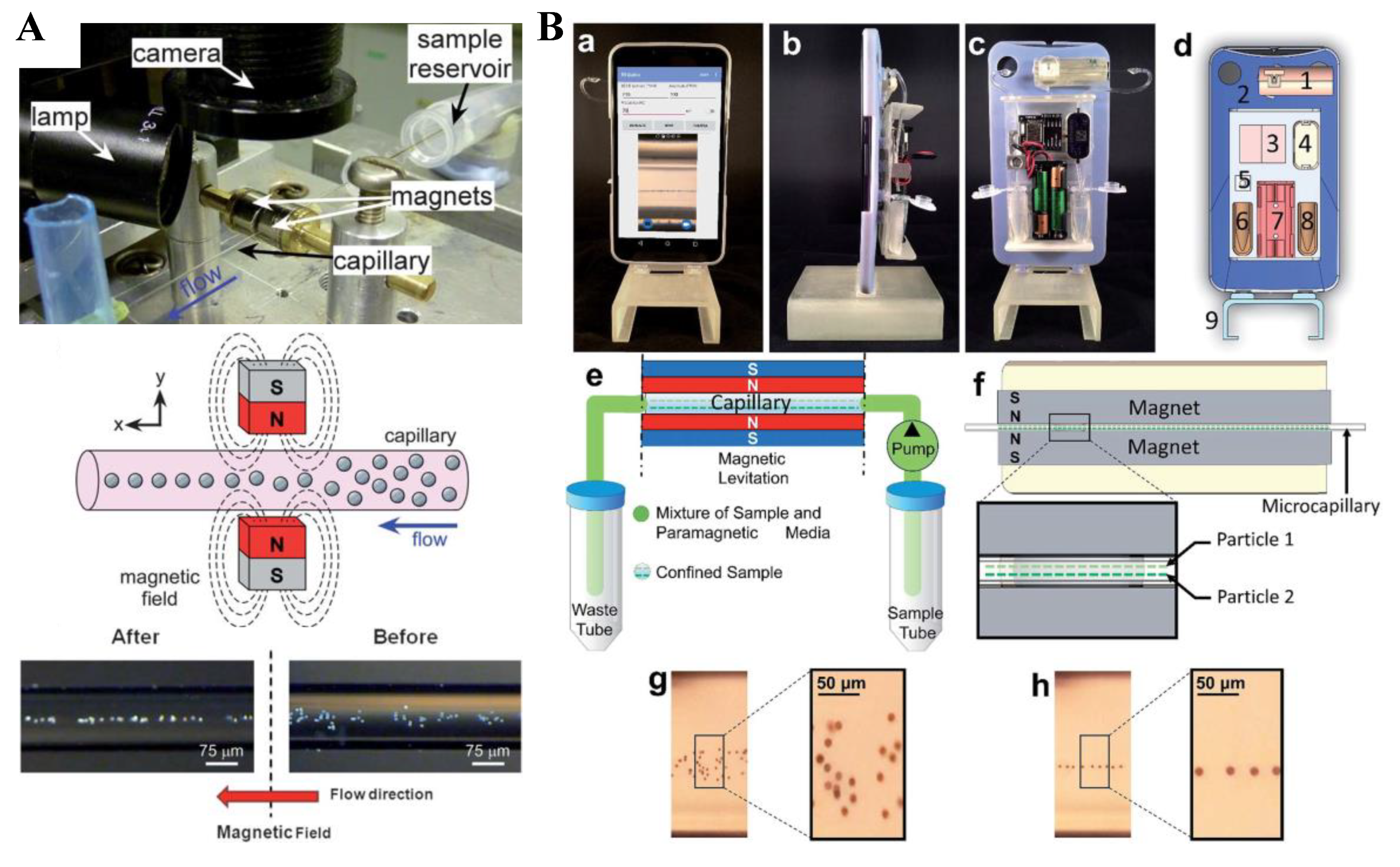
7. Particle Medium Exchange
7.1. Biocompatibility of Magnetic Fluids
7.2. Single Magnet
7.3. Summary
| Exchange Medium | Particles | Fluid | Magnet | Particle Flow Rate | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Type | |||||
| buffer sheath | 4.3 µm PS | 0.79 M MnCl2 | single | permanent | 0.52 µL/h | [164] |
| buffer sheath | 5.8/15.7 µm PS cancer cells WBC | 0.26% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 1.2 mL/h | [165] |
| water sheath | 10/20 µm PS | 0.9% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 1 mL/h | [166] |
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yousuff, C.M.; Ho, E.T.W.; Hussain, K.I.; Hamid, N.H.B. Microfluidic platform for cell isolation and manipulation based on cell properties. Micromachines 2017, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Hejazian, M.; Ooi, C.H.; Kashaninejad, N. Recent advances and future perspectives on microfluidic liquid handling. Micromachines 2017, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Rivas, A.; Gonzalez-Quijano, G.K.; Proa-Coronado, S.; Severac, C.; Dague, E. Methods of micropatterning and manipulation of cells for biomedical applications. Micromachines 2017, 8, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.Z.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Lin, J.H. A review on micromixers. Micromachines 2017, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Chang, H.L.; Neuzil, P. DEP-on-a-chip: Dielectrophoresis applied to microfluidic platforms. Micromachines 2019, 10, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; He, Y.Q.; Jiao, F. Advances of particles/cells magnetic manipulation in microfluidic chips. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Bachman, H.; Huang, T.J. Acoustofluidic methods in cell analysis. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2019, 117, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, A.A.; Khoshmanesh, K.; Ward, S.A.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Optofluidics incorporating actively controlled micro and nano-particles. Biomicrofluid. 2012, 6, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamme, N. Magnetism and microfluidics. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T. Micro-magnetofluidics: Interactions between magnetism and fluid flow on the microscale. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaimat, F.; Dagher, S.; Mathew, B.; Hilal-Alnqbi, A.; Khashan, S. Microfluidics based magnetophoresis: A review. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 1596–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Magnetic separation techniques in sample preparation for biological analysis: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 101, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Huang, Y.; Hoshino, K.; Zhang, X. Multiscale immunomagnetic enrichment of circulating tumor cells: From tubes to microchips. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejazian, M.; Li, W.; Nguyen, N.T. Lab on a chip for continuous flow magnetic cell separation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlido, L.; Azevedo, A.M.; Roque, A.C.A.; Aires-Barros, M.R. Magnetic separations in biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1374–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Han, X.; Li, L. Configurations and control of magnetic fields for manipulating magnetic particles in microfluidic applications: Magnet systems and manipulation mechanisms. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2762–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaz, A.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Nguyen, N.T. Recent advances and current challenges in magnetophoresis based micro magnetofluidics. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zborowski, M.; Ostera, G.R.; Moore, L.R.; Milliron, S.; Chalmers, J.J.; Schechter, A.N. Red blood cell magnetophoresis. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 2638–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Purdon, A.M.; Chu, V.; Westervelt, R.M. Controlled assembly of magnetic nanoparticles from magnetotactic bacteria using microelectromagnets arrays. Nano. Lett. 2004, 4, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watarai, H.; Suwa, M.; Iiguni, Y. Magnetophoresis and electromagnetophoresis of microparticles in liquids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwa, M.; Watarai, H. Magnetoanalysis of micro/nanoparticles: A review. Anal. Chimica Acta 2011, 690, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Hou, H.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Micro-magnetofluidics in microfluidic systems: A review. Sens. Act. B 2016, 224, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cheng, R.; Miller, J.R.; Mao, L. Label-free microfluidic manipulation of particles and cells in magnetic liquids. Adv. Fun. Mat. 2016, 26, 3916–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.H.; Zhang, W.M.; Zou, H.X.; Li, W.B.; Yan, H.; Peng, Z.K.; Meng, G. Label-free manipulation via the magneto-archimedes effect: Fundamentals, methodology and applications. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1359–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.B. Electromechanics of Particles; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, Q.; Gijs, M.A.M. Microfluidic applications of functionalized magnetic particles for environmental analysis: Focus on waterborne pathogen detection. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 13, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouffe, B.D.; Murthy, S.K.; Lewis, L.H. Fundamentals and application of magnetic particles in cell isolation and enrichment: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 016601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voltairas, P.A.; Fotiadis, D.I.; Michalis, L.K. Hydrodynamics of magnetic drug targeting. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijs, M.A.M. Magnetic bead handling on-chip: New opportunities for analytical applications. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2004, 1, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamme, N. On-chip bioanalysis with magnetic particles. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2012, 16, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamme, N.; Wilhelm, C. Continuous sorting of magnetic cells via on-chip free-flow magnetophoresis. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.D.; Thévoz, P.; Shea, H.; Bruus, H.; Soh, H.T. Integrated acoustic and magnetic separation in microfluidic channels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 254103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberta, D.; Pamme, N.; Conjeauda, H.; Gazeaua, F.; Ilesb, A.; Wilhelm, C. Cell sorting by endocytotic capacity in a microfluidic magnetophoresis device. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.H.; Frazier, A.B. Paramagnetic capture mode magnetophoretic microseparator for high efficiency blood cell separations. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.D.; Kim, U.; Soh, H.T. Multi-target magnetic activated cell sorter (MT-MACS). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18165–18170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.S.; Carpino, F.; Zborowski, M. Magnetic nanoparticle drug carriers and their study by quadrupole magnetic field-flow fractionation. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1290–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacharme, F.; Vandevyver, C.; Gijs, M.A.M. Full on-chip nanoliter immunoassay by geometrical magnetic trapping of nanoparticle chains. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Stakenborg, T.; Peeters, S.; Lagae, L. Cell manipulation with magnetic particles toward microfluidic cytometry. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 102011–102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijs, M.A.M.; Lacharme, F.; Lehmann, U. Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1518–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, H.C.; Gijs, M.A.M. Ultrasensitive protein detection: A case for microfluidic magnetic bead-based assays. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4711–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikken, R.S.M.; Nolte, R.J.M.; Maan, J.C.; van Hest, J.C.M.; Wilson, D.A.; Christianen, P.C.M. Manipulation of micro- and nanostructure motion with magnetic fields. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirica, K.A.; Phillips, S.T.; Shevkoplyas, S.S.; Whitesides, G.M. Measuring densities of solids and liquids using magnetic levitation: Fundamentals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10049–10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Villarreal, A.I.; Tarn, M.D.; Madden, L.A.; Lutz, J.B.; Greenman, J.; Samitier, J.; Pamme, N. Flow focusing of particles and cells based on their intrinsic properties using a simple diamagnetic repulsion setup. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarn, M.D.; Hirota, N.; Hes, A.; Pamme, N. On-chip diamagnetic repulsion in continuous flow. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2009, 10, 014611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkleman, A.; Gudiksen, K.L.; Ryan, D.; Whitesides, G.M. A magnetic trap for living cells suspended in a paramagnetic buffer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 2411–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, Y.K.; Park, J.K. Versatile immunoassays based on isomagnetophoresis. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2045–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosensweig, R.E. Magnetic fluids. Annu. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 1987, 19, 437–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosensweig, R.E. Ferrohydrodynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch, A.; Kamholz, A.E.; Holman, G.; Yager, P.; Bohringer, K.F. A ferrofluidic magnetic micropump. J. MEMS 2001, 10, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellen, B.B.; Friedman, G.; Feinerman, A. Printing superparamagnetic colloidal particle arrays on patterned magnetic film. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 7331–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellen, B.B.; Friedman, G. Programmable assembly of colloidal particles using magnetic microwell templates. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2553–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellen, B.B.; Hovorka, O.; Friedman, G. Arranging matter by magnetic nanoparticle assemblers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8860–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halverson, D.; Kalghatgi, S.; Yellen, B.; Friedman, G. Manipulation of nonmagnetic nanobeads in dilute ferrofluid. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08P504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, R.M.; Yellen, B.B. Concentration gradients in mixed magnetic and nonmagnetic colloidal suspensions. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 07A312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, R.M.; Son, H.S.; Samanta, B.; Rotello, V.M.; Yellen, B.B. Magnetic assembly of colloidal superstructures with multipole symmetry. Nature 2009, 457, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.H.; Yellen, B.B. Magnetically tunable self-assembly of colloidal rings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 083105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, R.M.; Yellen, B.B. Nanoscale magnetic materials and applications. In Magnetic Manipulation of Colloidal Particles; Liu, J.P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 563–590. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, G.; Yellen, B.B. Magnetic separation, manipulation, and assembly of solid phase in fluids. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 10, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, H.A. Dielectrophoresis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H. On the recent developments of insulator-based dielectrophoresis: A review. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, E.P. Permanent Magnet and Electromechanical Devices: Materials, Analysis, and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, C.Y.; Liang, K.P.; Chen, H.; Fu, L.M. Numerical analysis of a rapid magnetic microfluidic mixer. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 3268–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Nguyen, N.T. Magnetofluidic spreading in microchannels. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 13, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Nguyen, N.T. Rapid magnetofluidic mixing in a uniform magnetic field. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4772–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Varma, V.B.; Wang, Z.P.; Ramanujan, R.V. Tuning magnetofluidic spreading in microchannels. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 124001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Varma, V.B.; Xia, H.M.; Wang, Z.P.; Ramanujan, R.V. Spreading of a ferrofluid core in three-stream micromixer channels. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 052004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, I.K.; Ganguly, R. Particle transport in therapeutic magnetic fields. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 407–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happel, J.; Brenner, H. Low Reynolds Number Hydrodynamics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Turker, E.; Arslan-Yildiz, A. Recent advances in magnetic levitation: A biological approach from diagnostics to tissue engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Nemiroski, A.; Mirica, K.A.; Mace, C.R.; Hennek, J.W.; Kumar, A.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Magnetic levitation in chemistry, materials science, and biochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 2019. in Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, C. An invariant general solution for the magnetic fields within and surrounding a small spherical particle in an imposed arbitrary magnetic field and the resulting magnetic force and couple. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2009, 197, 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Díaz, I.; Rinaldi, C. Brownian dynamics simulations of ellipsoidal magnetizable particle suspensions. J. Phys. D 2014, 47, 235003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Sobecki, C.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. Magnetic control of lateral migration of ellipsoidal microparticles in microscale flows. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 8, 024019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okagawa, A.; Cox, R.G.; Mason, S.G. Particle behavior in shear and electric fields. VI. The microrheology of rigid spheroids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, A.D.; Armstrong, R.C. The rotation of a suspended axisymmetric ellipsoid in a magnetic field. Rheol. Acta 1987, 26, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Pamme, N.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; Manz, A. On-chip free-flow magnetophoresis: Separation and detection of mixtures of magnetic particles in continuous flow. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 307, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamme, N.; Manz, A. On-chip free-flow magnetophoresis: Continuous flow separation of magnetic particles and agglomerates. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 7250–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Zhu, J.; Xuan, X. Three-dimensional diamagnetic particle deflection in ferrofluid microchannel flows. Biomicrofluid 2011, 5, 034110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Liang, L.; Xuan, X. On-chip manipulation of nonmagnetic particles in paramagnetic solutions using embedded permanent magnets. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 12, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Lichlyter, D.J.; Haidekker, M.A.; Mao, L. Analytical model of microfluidic transport of non-magnetic particles in ferrofluids under the influence of a permanent magnet. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2011, 10, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Zhu, T.; Mao, L. Three-dimensional and analytical modeling of microfluidic particle transport in magnetic fluids. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 16, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazian, M.; Nguyen, N.T. Negative magnetophoresis in diluted ferrofluid flow. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.P.; Hejiazan, M.; Huang, X.; Nguyen, N.T. Magnetophoresis of diamagnetic microparticles in a weak magnetic field. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4609–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.D.; Kim, H.C. Recent advances in miniaturized microfluidic flow cytometry for clinical use. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 4511–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Song, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, D. A novel microfluidic resistive pulse sensor with multiple voltage input channels and a side sensing gate for particle and cell detection. Anal. chimica Acta 2019, 1052, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X.; Zhu, J.; Church, C. Particle focusing in microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2010, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, J.M.; Toner, M. Inertial focusing in microfluidics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 16, 371–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Yuan, D.; Alici, G.; Nguyen, N.T.; Warkiani, M.E.; Li, W. Fundamentals and applications of inertial microfluidics: A review. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 10–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyman, S.A.; Kwan, E.Y.; Margarson, O.; Iles, A.; Pamme, N. Diamagnetic repulsion—A versatile tool for label-free particle handling in microfluidic devices. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 9055–9062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, R.; Knowlton, S.; Yenilmez, B.; Hart, A.; Joshi, A.; Tasoglu, S. Smart-phone attachable, flow-assisted magnetic focusing device. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 93922–93931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Cheng, R.; Mao, L. Focusing microparticles in a microchannel with ferrofluids. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2011, 11, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Chen, C.; Vedantam, P.; Brown, V.; Tzeng, T.; Xuan, X. Three-dimensional magnetic focusing of particles and cells in ferrofluid flow through a straight microchannel. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xuan, X. Diamagnetic particle focusing in ferromicrofluidics using a single magnet. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 13, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, C. Multiphase ferrofluid flows for micro-particle focusing and separation. Biomicrofluid 2016, 10, 034101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Yuan, D.; Alici1, G.; Du, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, W. Development of a novel magnetophoresis-assisted hydrophoresis microdevice for rapid particle ordering. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, D.; Malekanfard, A.; Cao, Q.; Lin, J.; Wang, M.H.; Han, X.; Xuan, X. Tunable, sheathless focusing of diamagnetic particles in ferrofluid microflows with a single set of overhead permanent magnets. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8600–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johann, R.M. Cell trapping in microfluidic chips. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, E.D.; Huang, C.; Hawkins, B.G.; Gleghorn, J.P.; Kirby, B.J. Rare cell capture in microfluidic devices. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 1508–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, D.; Mo, X.; Iliescu, C.; Tan, L.L.; Tong, W.H.; Yu, H. Exploitation of physical and chemical constraints for three-dimensional microtissue construction in microfluidics. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 022203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Evander, M.; Hammarstrom, B.; Laurell, T. Review of cell and particle trapping in microfluidic systems. Anal. Chimica Acta 2009, 649, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Bian, S.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, G.; Liu, P.; Ye, X.; Wang, W. Microfluidics cell sample preparation for analysis: Advances in efficient cell enrichment and precise single cell capture. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 011501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, A.; Thompson, M. Recent advances in AC electrokinetic sample enrichment techniquesfor biosensor development. Sens. and Actuat. B 2018, 255, 3601–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, E.; Prentiss, M. Three-dimensional self-assembly of structures using the pressure due to a ferrofluid in a magnetic field gradient. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 064901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, M.D.; Peyman, S.A.; Pamme, N. Simultaneous trapping of magnetic and diamagnetic particle plugs for separations and bioassays. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 7209–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazian, M.; Nguyen, N.T. Magnetofluidic concentration and separation of non-magnetic particles using two magnet arrays. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 044103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Chen, C.; Vedantam, P.; Tzeng, T.; Xuan, X. Magnetic concentration of particles and cells in ferrofluid flow through a straight microchannel using attracting magnets. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2013, 15, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbanks, J.J.; Kiessling, G.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, C.; Xuan, X. Exploiting magnetic asymmetry to concentrate diamagnetic particles in ferrofluid microflows. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 044907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Thanjavur Kumar, D.; Lu, X.; Kale, A.; DuBose, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Xuan, X. Simultaneous diamagnetic and magnetic particle trapping in ferrofluid microflows via a single permanent magnet. Biomicrofluidics 2015, 9, 044102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenshof, A.; Laurell, T. Continuous separation of cells and particles in microfluidic systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, A.; Yazdi, S.; Ardekani, A.M. Hydrodynamic mechanisms of cell and particle trapping in microfluidics. Biomicrofluid 2013, 7, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeesh, P.; Sen, A.K. Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: A review. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields IV, C.W.; Reyes, C.D.; Lopez, G.P. Microfluidic cell sorting: A review of the advances in the separation of cells from debulking to rare cell isolation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1230–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X. Recent advances in direct current electrokinetic manipulation of particles for microfluidic applications. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2484–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ozcelik, A.; Rufo, J.; Wang, Z.; Fang, R.; Huang, T.J. Acoustofluidic separation of cells and particles. Microsys. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Yoon, S.Y.; Sung, H.J.; Kim, S.S. Cross-type optical particle separation in a microchannel. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2628–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, G.; Xuan, X. Particle manipulations in non-Newtonian microfluidics: A review. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2017, 500, 182–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Hu, G. High-throughput particle manipulation based on hydrodynamic effects in microchannels. Micromachines 2017, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, S.; Tang, S.Y.; Alici, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, W. Recent progress of particle migration in viscoelastic fluids. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antfolk, M.; Laurell, T. Continuous flow microfluidic separation and processing of rare cells and bioparticles found in blood—A review. Anal. Chimica Acta 2017, 965, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibbitts, J.; Sellens, K.A.; Jia, S.; Klasner, S.A.; Culbertson, C.T. Cellular analysis using microfluidics. Anal Chem. 2018, 90, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Jiang, D.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Shi, J.; Yang, J.; Xiang, N. Recent advances in microfluidic cell sorting techniques based on both physical and biochemical principles. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 930–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.; Manz, A. High-speed free-flow electrophoresis on chip. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5759–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, M.D.; Peyman, S.A.; Robert, D.; Iles, A.; Wilhelm, C.; Pamme, N. The importance of particle type selection and temperature control for on-chip free-flow magnetophoresis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 4115–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtíšek, M.; Tarn, M.D.; Hirota, N.; Pamme, N. Microfluidic devices in superconducting magnets: On-chip free-flow diamagnetophoresis of polymer particles and bubbles. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 13, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, M.; Watarai, H. Two-dimensional flow magnetophoresis of microparticle. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2645–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Hwang, H.; Hahn, Y.K.; Park, J.K. Label-free cell separation using a tunable magnetophoretic repulsion force. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3075–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, T.; Cheng, R.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Qiu, H.; Wang, L.; Nagy, T.; Querec, T.D.; Unger, E.R.; et al. Label-free and continuous-flow ferrohydrodynamic separation of HeLa cells and blood cells in biocompatible ferrofluids. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3990–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navi, M.; Abbasi, N.; Jeyhani, M.; Gnyawalibcd, W.; Tsai, S.S.H. Microfluidic diamagnetic water-in-water droplets: A biocompatible cell encapsulation and manipulation platform. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3361–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, D.; Zielinski, J.; Kozubowski, L.; Lin, J.; Wang, M.H.; Xuan, X. Yeast cell fractionation by morphology in dilute ferrofluids. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 064102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Marrero, F.; Mao, L. Continuous separation of non-magnetic particles inside ferrofluids. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2010, 9, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Cheng, R.; Lee, S.A.; Rajaraman, E.; Eiteman, M.A.; Querec, T.D.; Unger, E.R.; Mao, L. Continuous-flow ferrohydrodynamic sorting of particles and cells in microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 13, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cheng, R.; Jenkins, B.D.; Zhu, T.; Okonkwo, N.E.; Jones, C.E.; Davis, M.B.; Kavuri, S.K.; Hao, Z.; Schroeder, C.; et al. Label-free ferrohydrodynamic cell separation of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3097–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Feng, Y.; Cao, Q.; Li, L. Three‑dimensional analysis and enhancement of continuous magnetic separation of particles in microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2015, 18, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xuan, X. Diamagnetic particle separation by shape in ferrofluids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Bai, F.; Wang, C. Magnetic separation of microparticles by shape. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Choi, S.; Lee, W.; Park, J.K. Isomagnetophoresis to discriminate subtle difference in magnetic susceptibility. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 396–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, A.R.; Koser, H. Ferrofluid mediated nanocytometry. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munaz, A.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Nguyen, N.T. Magnetophoretic separation of diamagnetic particles through parallel ferrofluid streams. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 275, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, A.R.; Fischer, B.; Mao, L.; Koser, H. Label-free cellular manipulation and sorting via biocompatible ferrofluids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21478–21483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xuan, X. Continuous sheath-free magnetic separation of particles in a U-shaped microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 044106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Song, L.; Yu, L.; Xuan, X. Continuous-flow sheathless diamagnetic particle separation in ferrofluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 412, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Deng, Y.; Vedantam, P.; Tzeng, T.R.; Xuan, X. Magnetic separation of particles and cells in ferrofluid flow through a straight microchannel using two offset magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 346, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhang, C.; Xuan, X. Enhanced separation of magnetic and diamagnetic particles in a dilute ferrofluid. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 234101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Cheng, R.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Mao, L. Combining positive and negative magnetophoreses to separate particles of different magnetic properties. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkleman, A.; Perez-Castillejos, R.; Gudiksen, K.L.; Phillips, S.T.; Prentiss, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Density-based diamagnetic separation: Devices for detecting binding events and for collecting unlabeled diamagnetic particles in paramagnetic solutions. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6542–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, D.; Li, W. Hybrid microfluidics combined with active and passive approaches for continuous cell separation. Electrophoresis 2017, 37, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Lee, D.J.; Youn, J.R.; Song, Y.S. Two step label free particle separation in a microfluidic system using elasto-inertial focusing and magnetophoresis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 32090–32097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, Q.; Tan, S.; Nguyen, N.T.; Li, W. A novel viscoelastic-based ferrofluid for continuous sheathless microfluidic separation of nonmagnetic microparticles. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3947–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Song, L.; Yu, L.; Xuan, X. Inertially focused diamagnetic particle separation in ferrofluids. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2017, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, J.; Li, W. High-throughput, sheathless, magnetophoretic separation of magnetic and nonmagnetic particles with a groove-based channel. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 214101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, M.D.; Lopez-Martinez, M.J.; Pamme, N. On-chip processing of particles and cells via multilaminar flow streams. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornay, R.; Braschler, T.; Demierre, N.; Steitz, B.; Finka, A.; Hofmann, H.; Hubbell, J.A.; Renaud, P. Continuous-flow cell dipping and medium exchange in a microdevice using dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; D’Silva, J.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Microfluidic chemical processing with on-chip washing by deterministic lateral displacement arrays with separator walls. Biomicrofluidics 2015, 9, 054105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudani, J.S.; Go, D.E.; Gossett, D.R.; Tan, A.P.; Di Carlo, D. Mediating millisecond reaction time around particles and cells. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Tan, S.H.; Sluyter, R.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, S.; Nguyen, N.T.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W. On-chip microparticle and cell washing using coflow of viscoelastic fluid and newtonian fluid. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9574–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravan, P.; Ellison, J.J.; McMurry, T.J.; Lauffer, R.B. Gadolinium(III) Chelates as MRI contrast agents: Structure, dynamics, and applications. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2293–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmus, N.G.; Tekin, H.C.; Guven, S.; Sridhar, K.; Yildiz, A.A.; Calibasi, G.; Ghiran, I.; Davis, R.W.; Steinmetz, L.M.; Demirci, U. Magnetic levitation of single cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3661–E3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffmann, P.; Ith, A.; OBrien, D.; Gaude, V.; Boue, F.; Combe, S.; Bruckert, F.; Schaack, B.; Dempsey, N.M.; Haguet, V.; et al. Diamagnetically trapped arrays of living cells above micromagnets. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3153–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Lu, Z.R. Gadolinium-based contrast agents for magnetic resonance cancer imaging. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.D.; Erb, R.M.; Yellen, B.B.; Samanta, B.; Bajaj, A.; Rotello, V.M.; Alsberg, E. Formation of ordered cellular structures in suspension via label-free negative magnetophoresis. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1812–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Jenkins, B.D.; Cheng, R.; Harris, B.N.; Zhang, W.; Xie, J.; Murrow, J.R.; Hodgson, J.; Egan, M.; et al. Tumor antigen-independent and cell size variation-inclusive enrichment of viable circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1860–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaterabadi, Z.; Nabiyouni, G.; Soleymani, M. High impact of in situ dextran coating on biocompatibility, stability and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, M.D.; Elders, L.T.; Peyman, S.A.; Pamme, N. Diamagnetic repulsion of particles for multilaminar flow assays. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 103776–103781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cheng, R.; Lim, S.H.; Miller, J.R.; Zhang, W.; Tang, W.; Xie, J.; Mao, L. Biocompatible and label-free separation of cancercells from cell culture lines from white blood cellsin ferrofluids. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, D.; Lin, J.; Wang, M.; Xuan, X. Simultaneous washing and separation of nonmagnetic particles in an inertial ferrofluid/water co-flow. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6915–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z.; Ramanujan, R.V. Magnetic trapping of bacteria at low magnetic fields. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
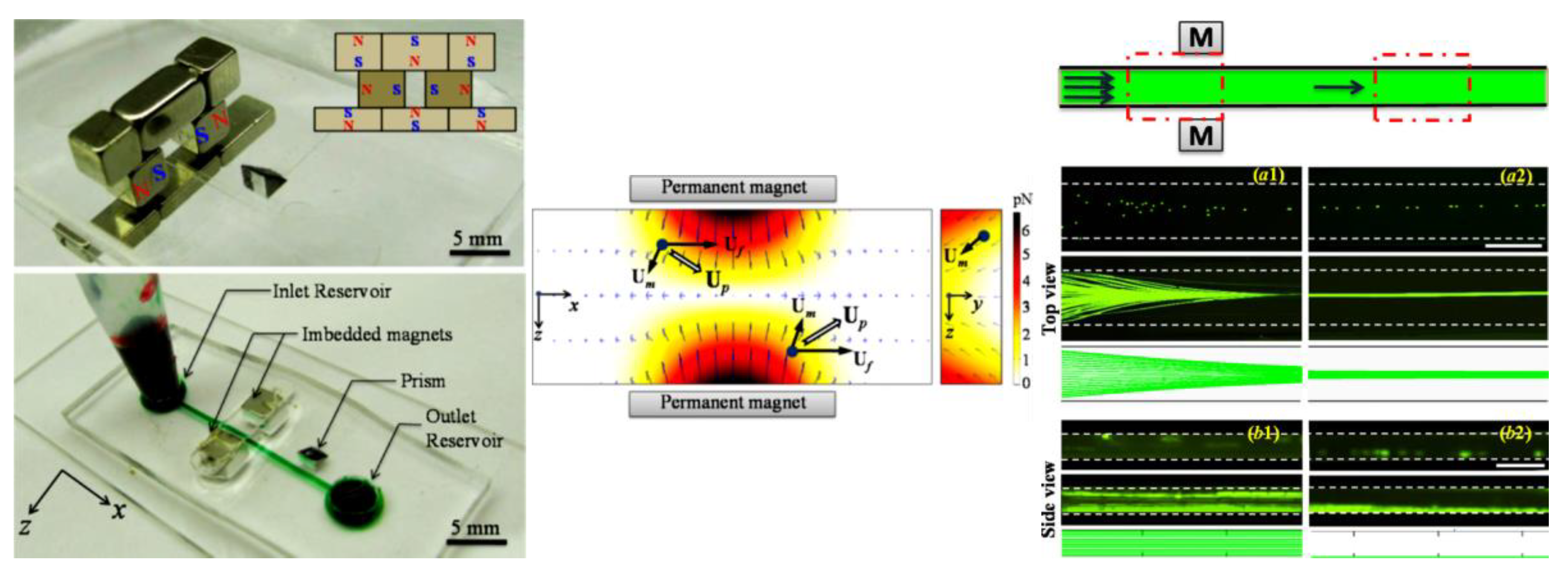
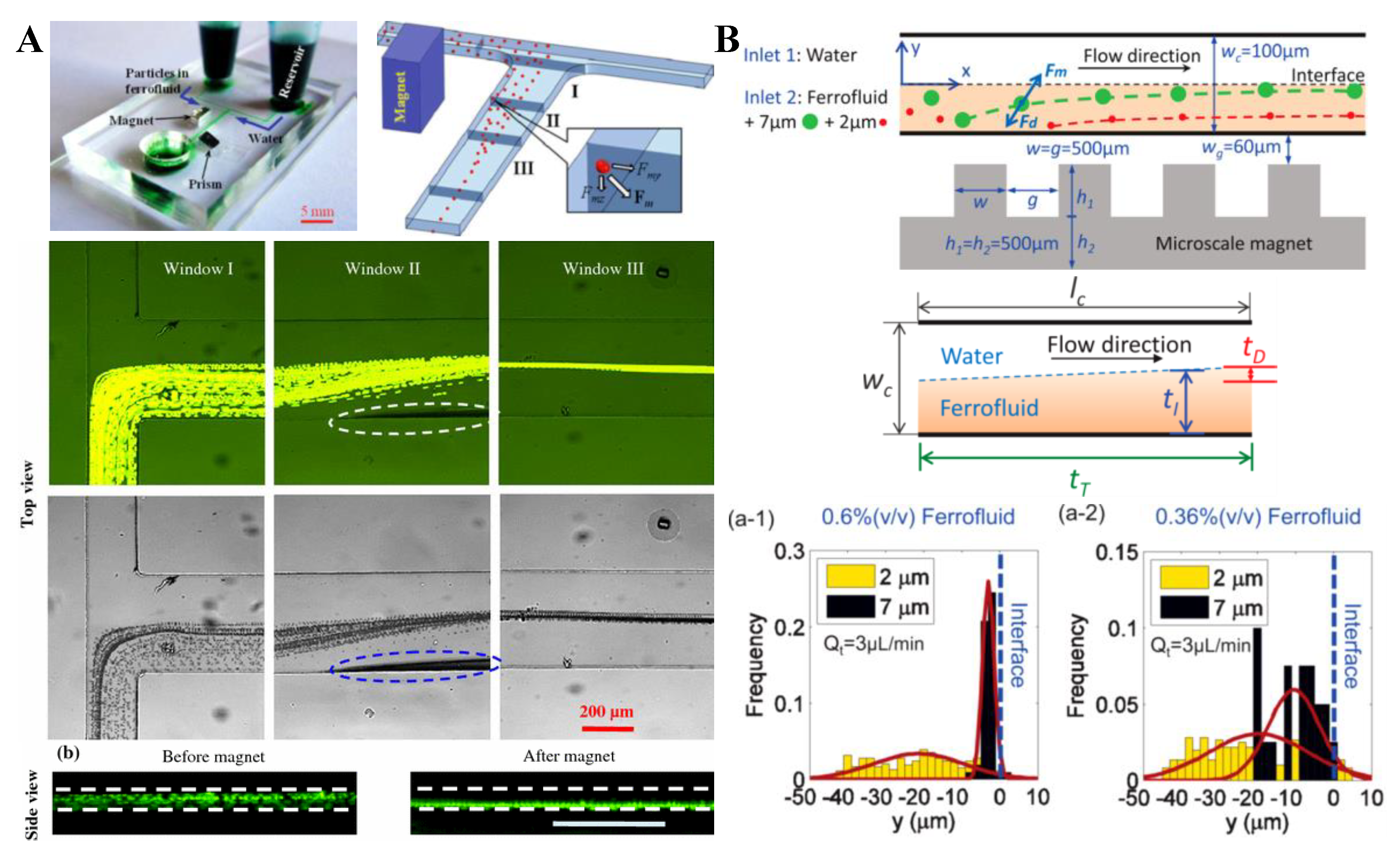
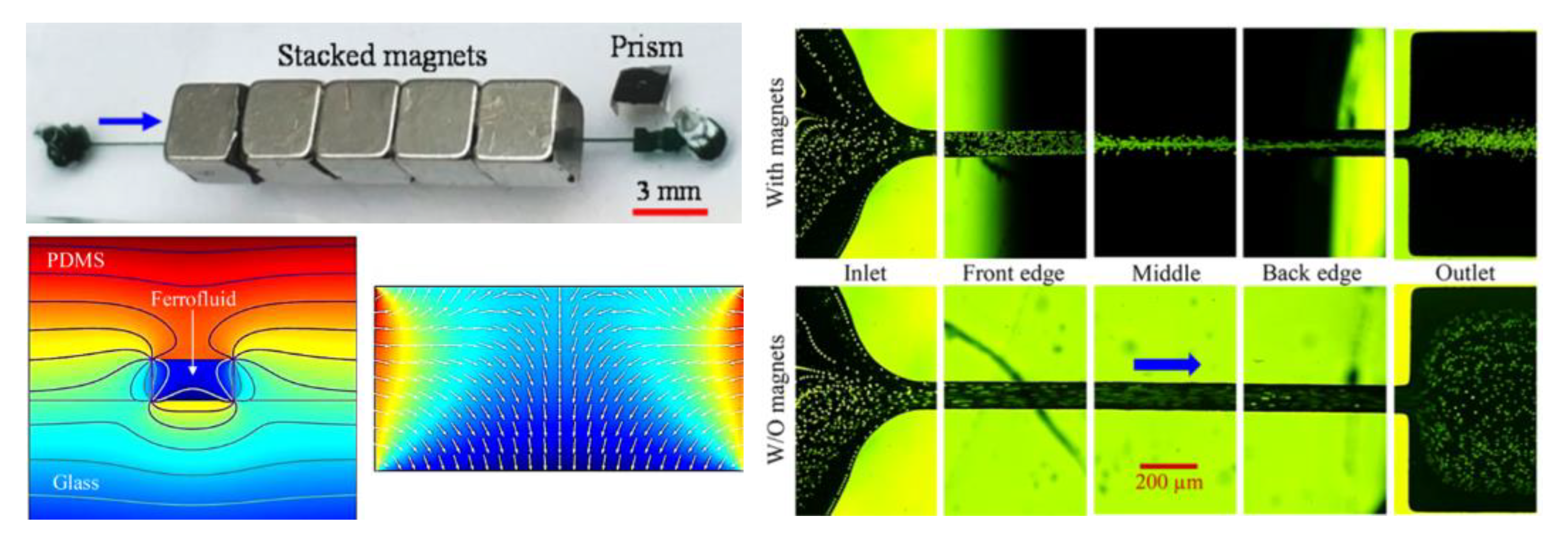
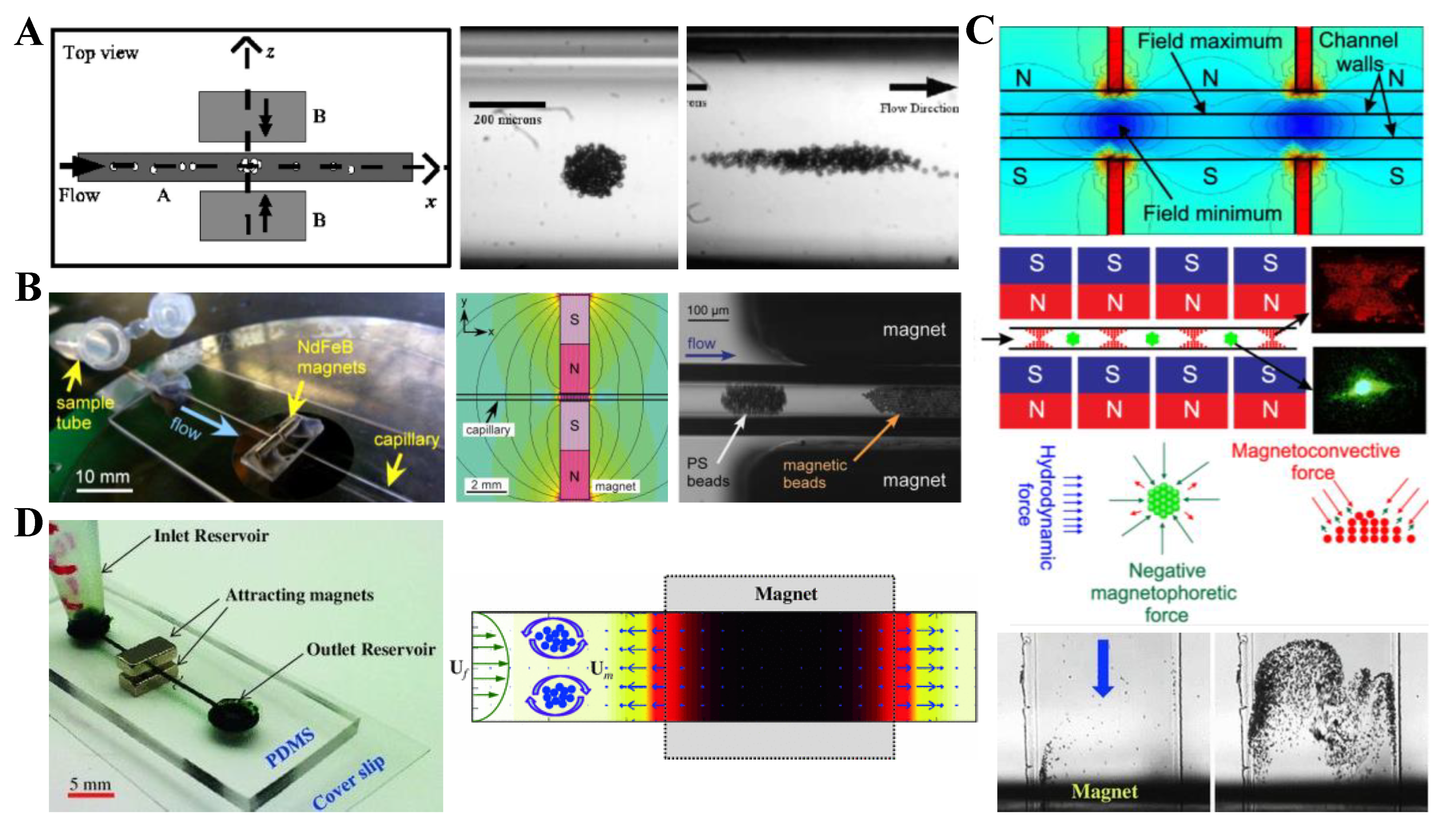
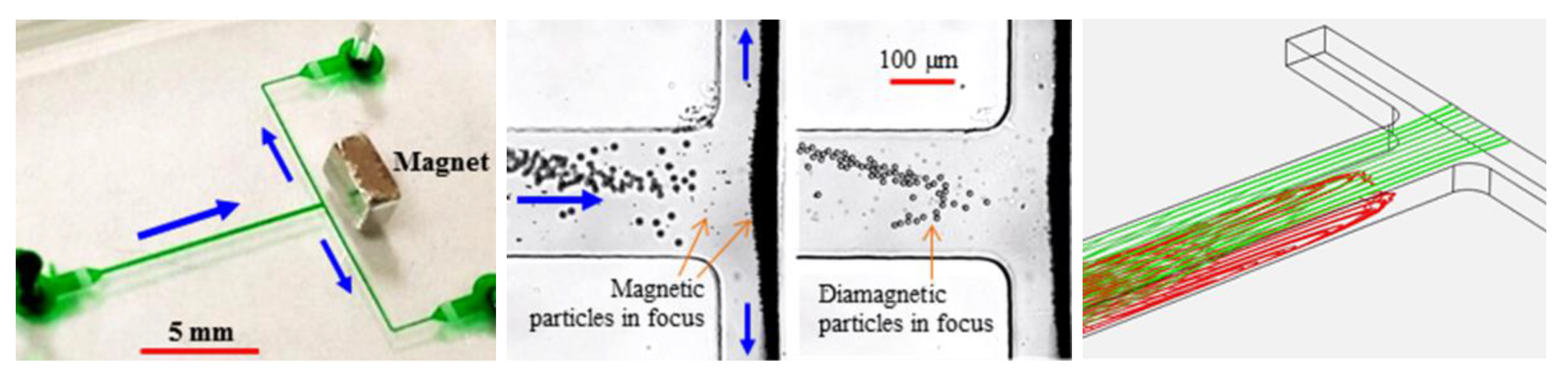
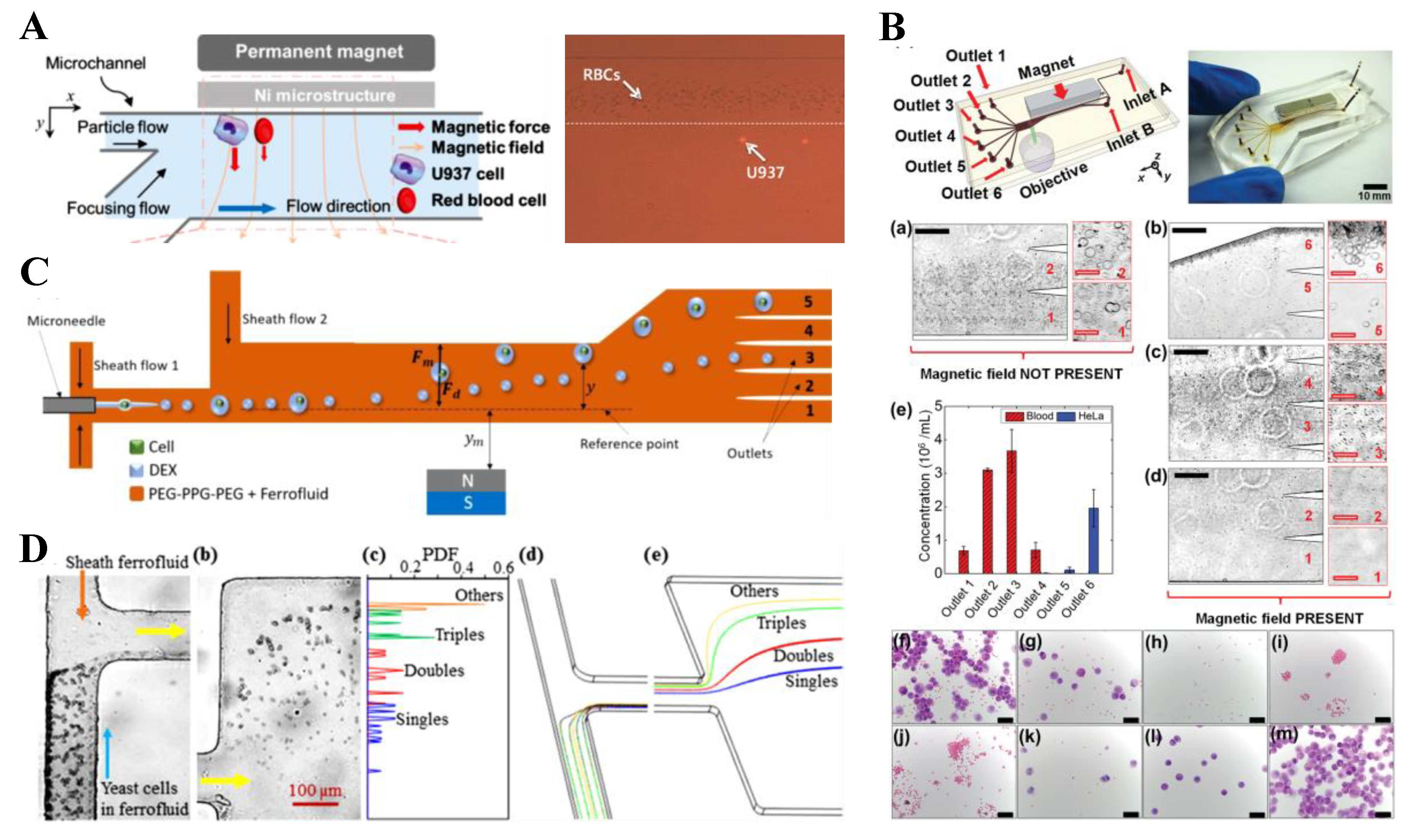
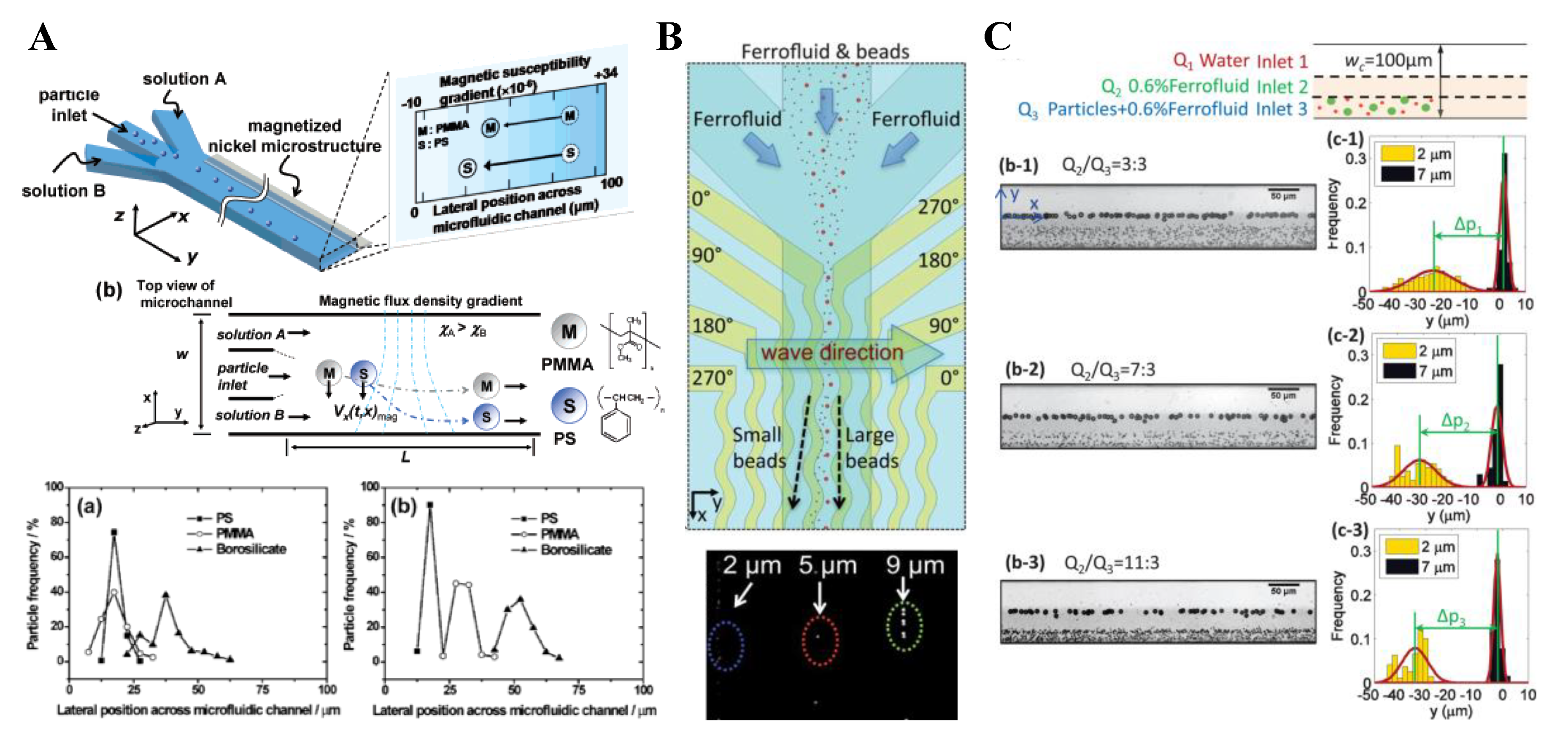
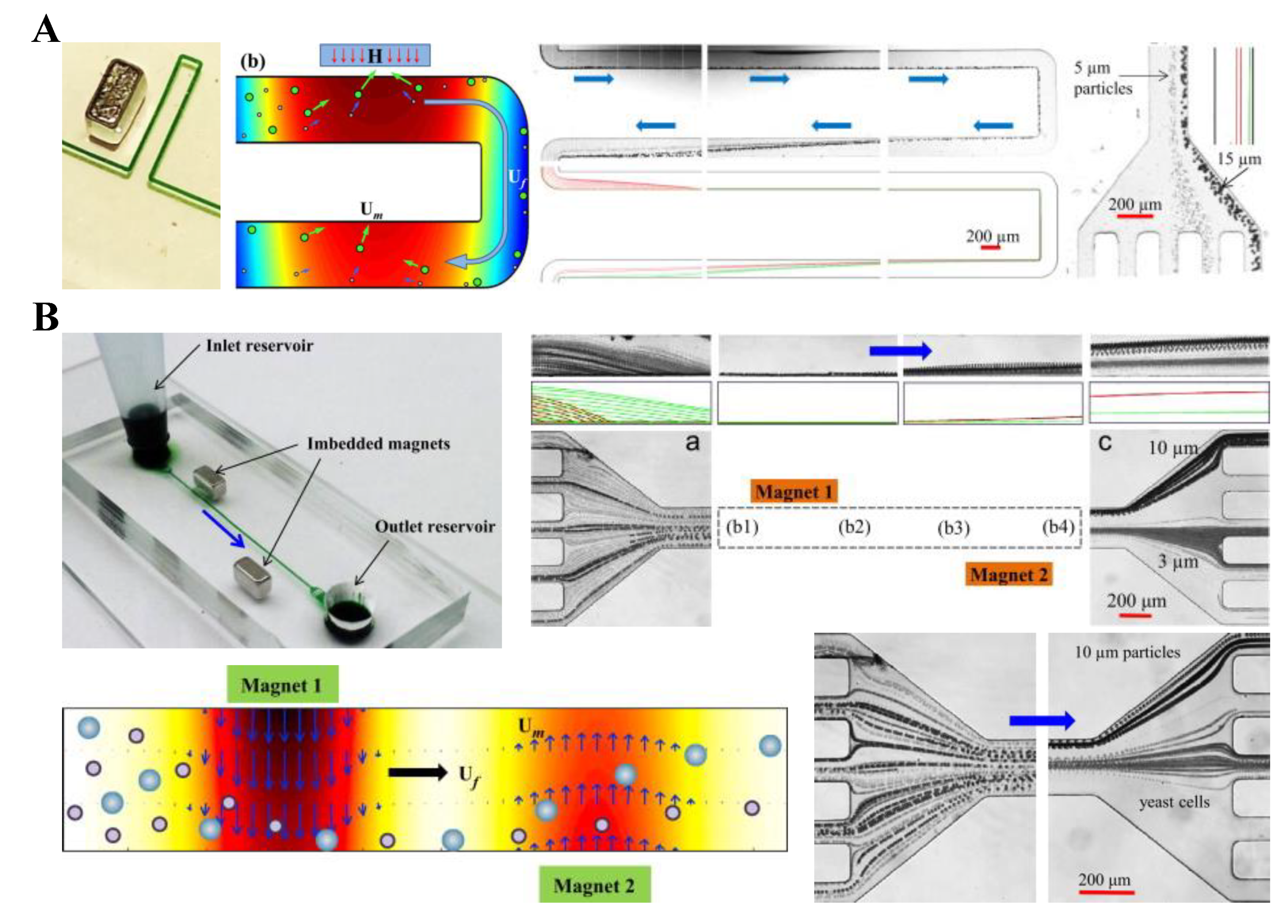
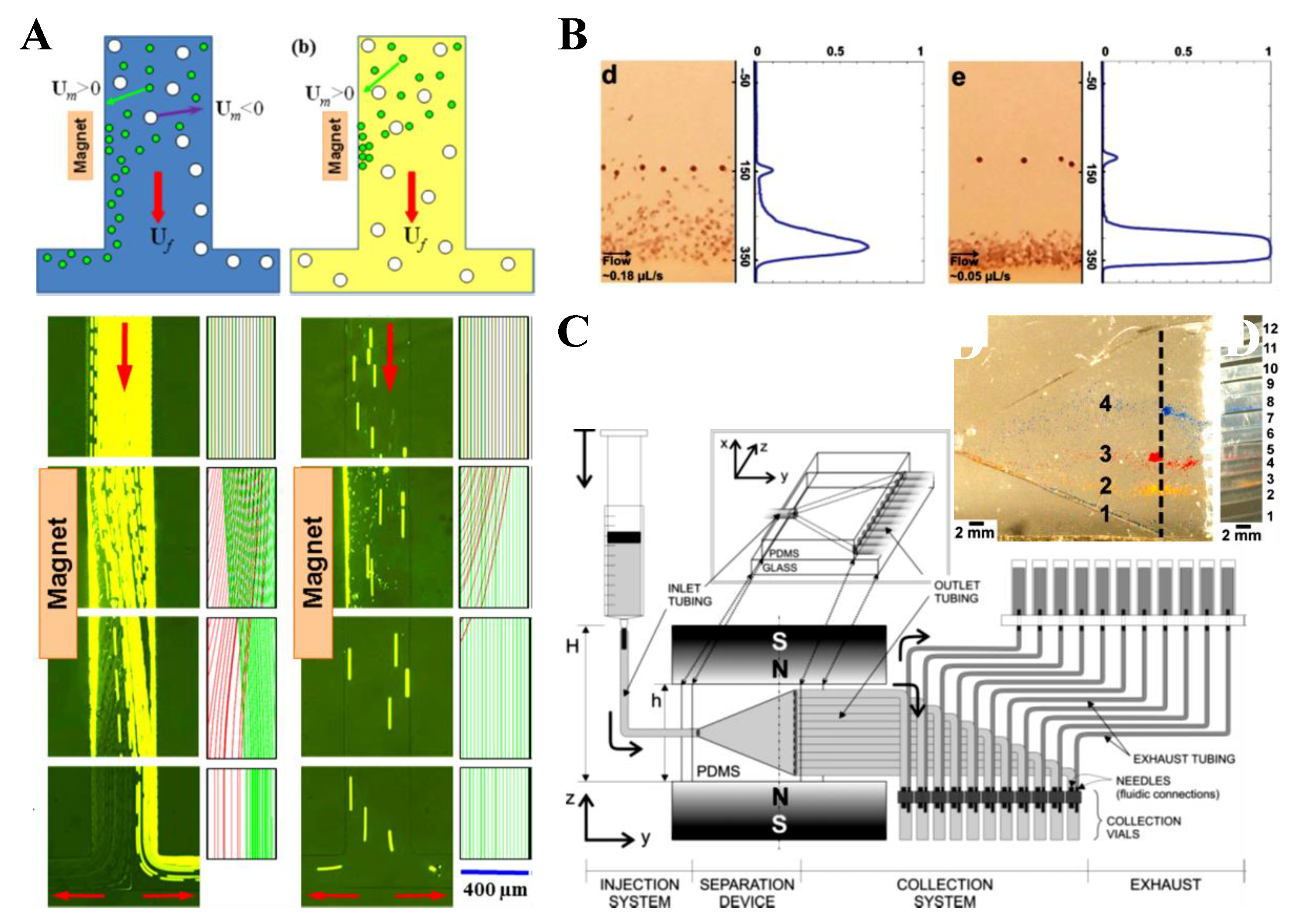
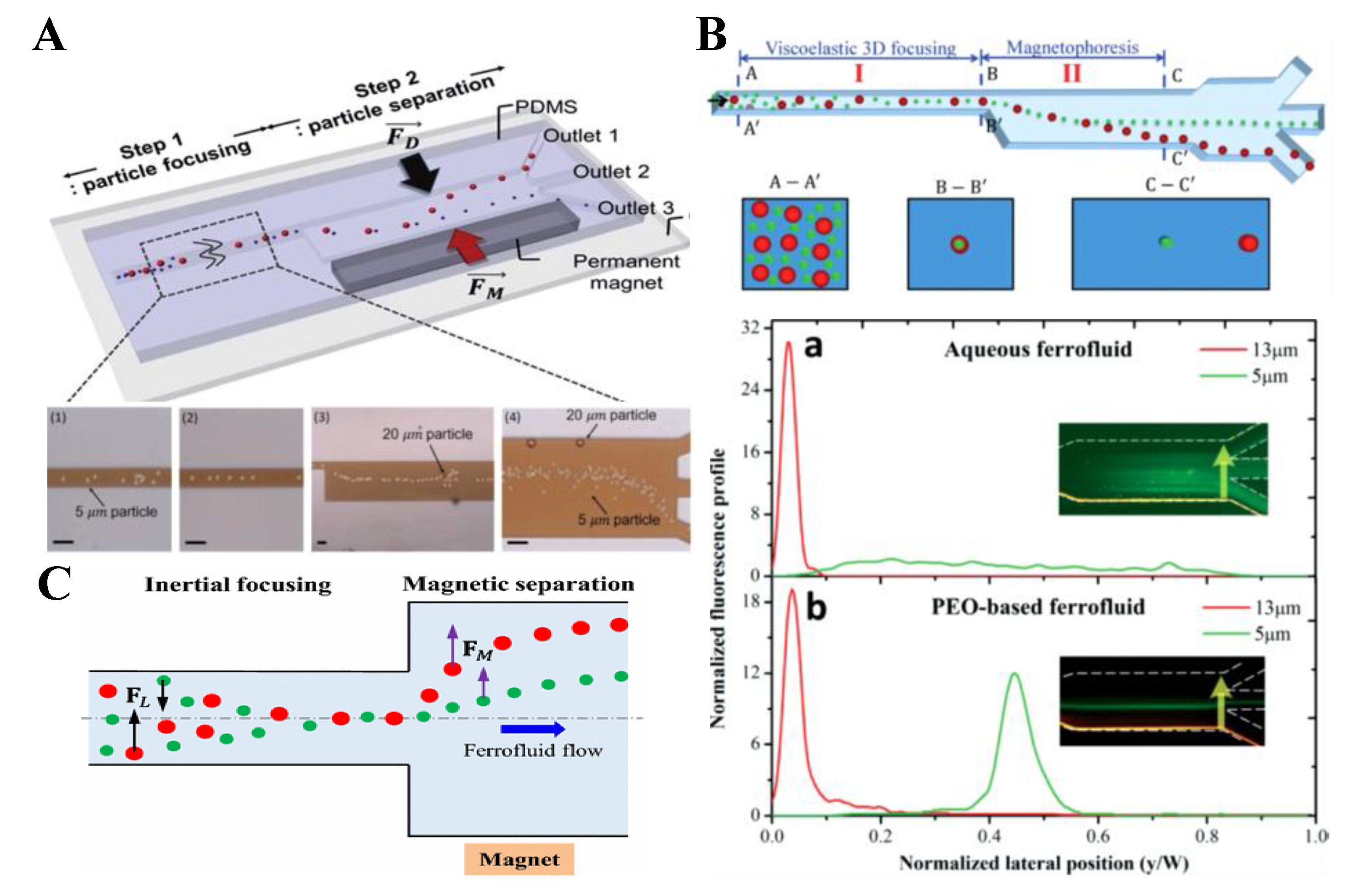
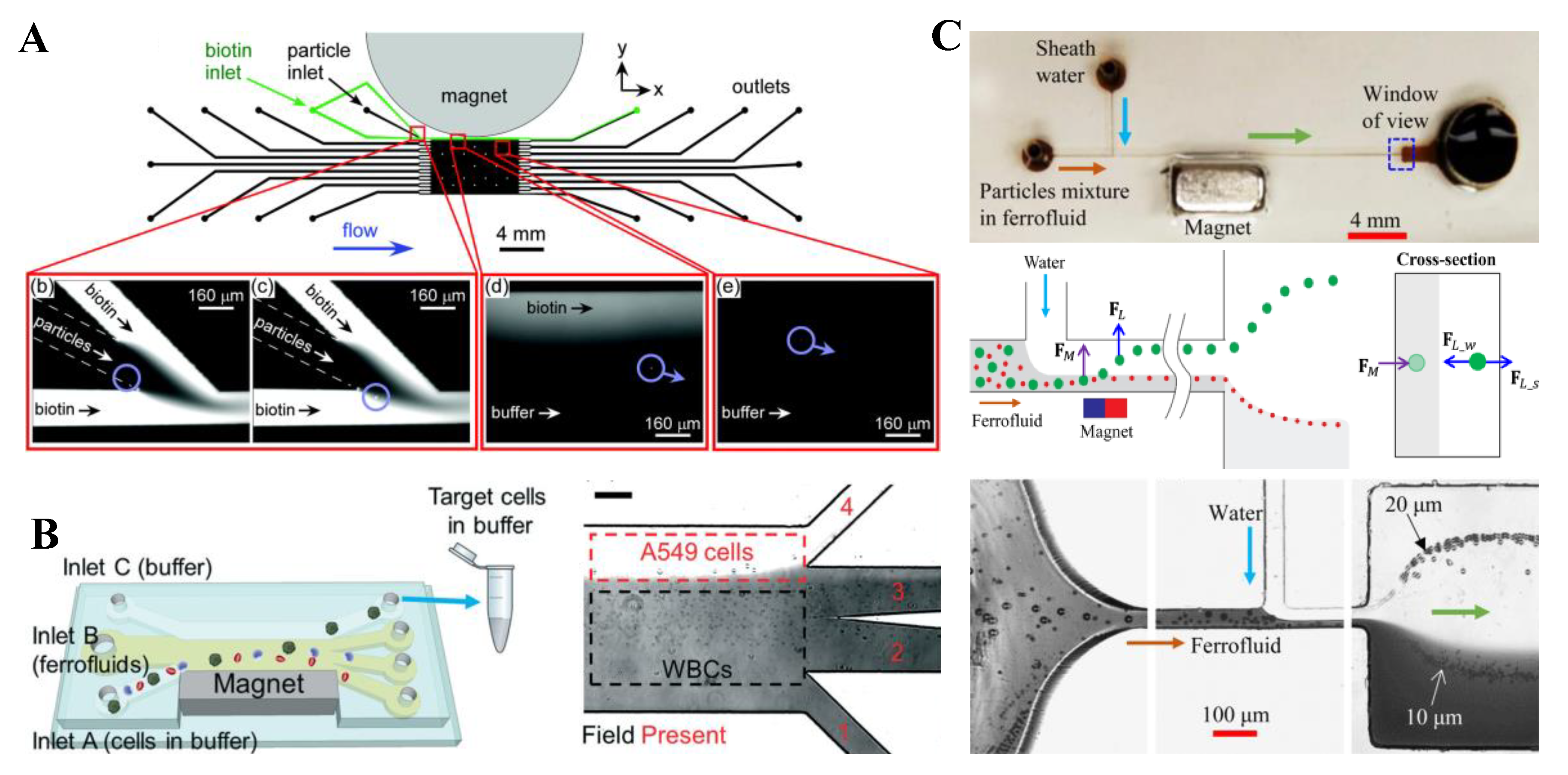
| Pre-Focused | Particles | Fluid | Magnet | Particle Flow Rate | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Type | |||||
| - | 5/10 µm PS | 6/10% MnCl2 | single | superconducting | 400 µL/h | [45] |
| - | 2.2/5/10 µm PS | 0.3–1.2% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 45–960 µL/h | [79] |
| - | 5/10/15 µm PS | 0.04–1 M MnCl2 | stacked | permanent | 3.6–14.4 µL/h | [80] |
| ferrofluid sheath | 4.8/7.3 µm PS | 1.2% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 300 µL/h | [81] |
| ferrofluid sheath | 3.1/4.8 µm PS | 0.1% ferrofluid | single | permanent | 60 µL/h | [83] |
| water sheath | 1 µm PS | 1.0% ferrofluid | uniform field | electromagnet | 500 µL/h | [84] |
| ferrofluid sheath | 7 µm PS ellipsoid | 0.6% ferrofluid | Halbach array uniform field | permanent | 12 µL/h | [74] |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xuan, X. Recent Advances in Continuous-Flow Particle Manipulations Using Magnetic Fluids. Micromachines 2019, 10, 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10110744
Xuan X. Recent Advances in Continuous-Flow Particle Manipulations Using Magnetic Fluids. Micromachines. 2019; 10(11):744. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10110744
Chicago/Turabian StyleXuan, Xiangchun. 2019. "Recent Advances in Continuous-Flow Particle Manipulations Using Magnetic Fluids" Micromachines 10, no. 11: 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10110744
APA StyleXuan, X. (2019). Recent Advances in Continuous-Flow Particle Manipulations Using Magnetic Fluids. Micromachines, 10(11), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10110744





