Multipurpose HTS Coagulation Analysis: Assay Development and Assessment of Coagulopathic Snake Venoms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
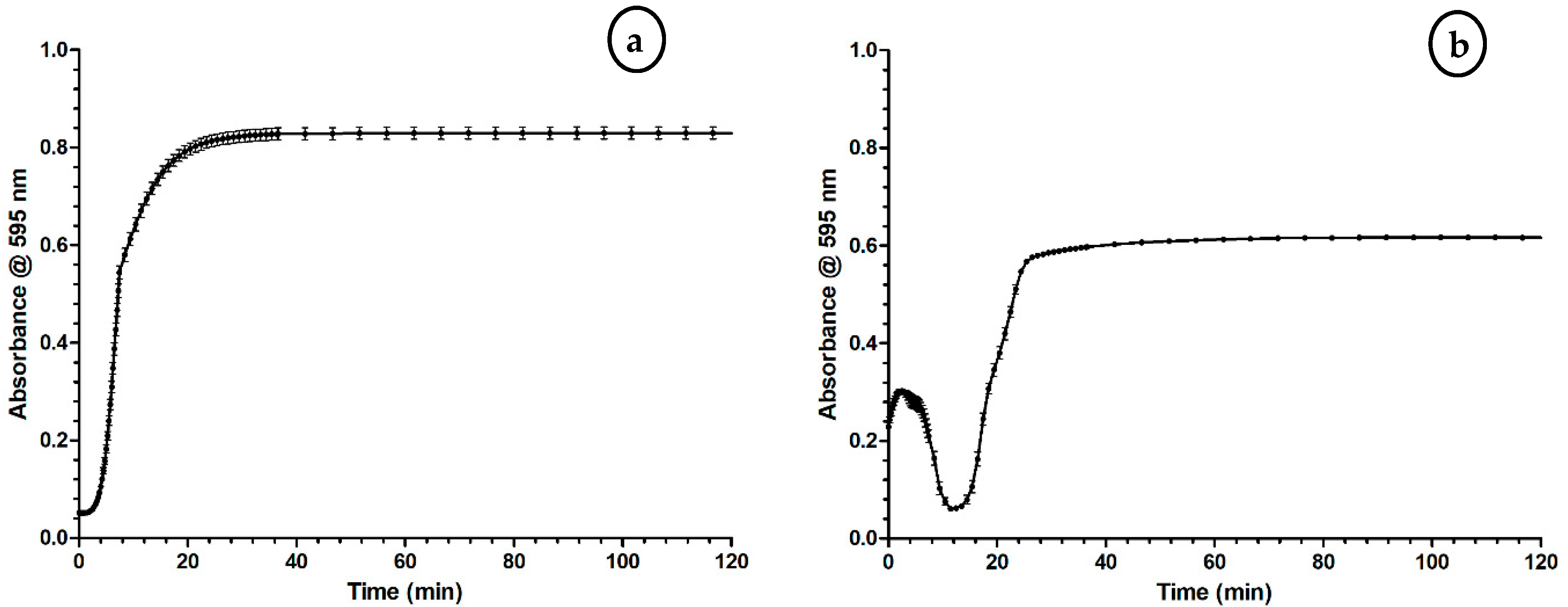
2.1. Optimization of the Coagulation Assay
2.2. Evaluation of the Coagulation Assay with Anti- and Procoagulants
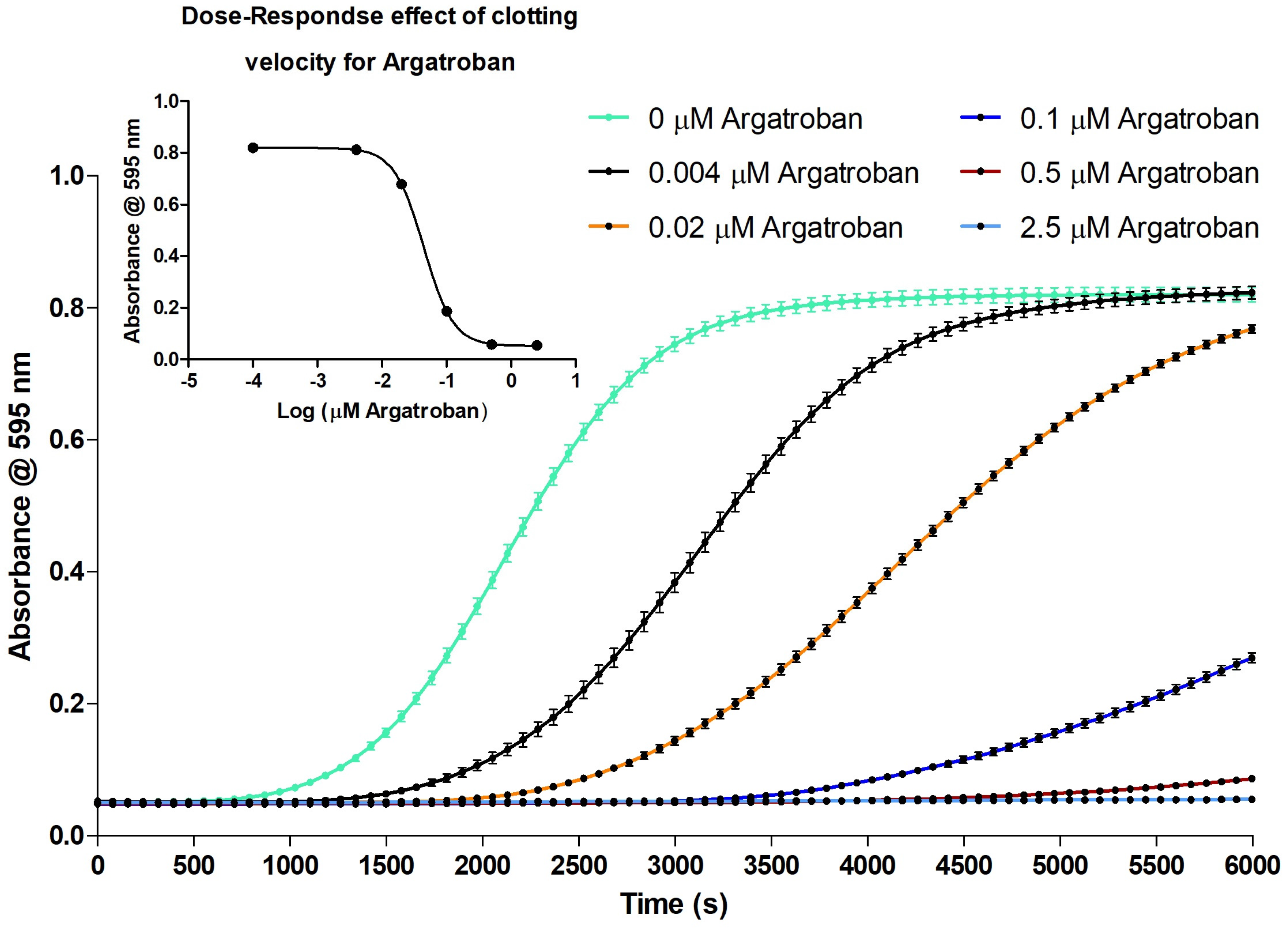
2.2.1. Evaluation of the Coagulation Assay Using Anticoagulant Compounds
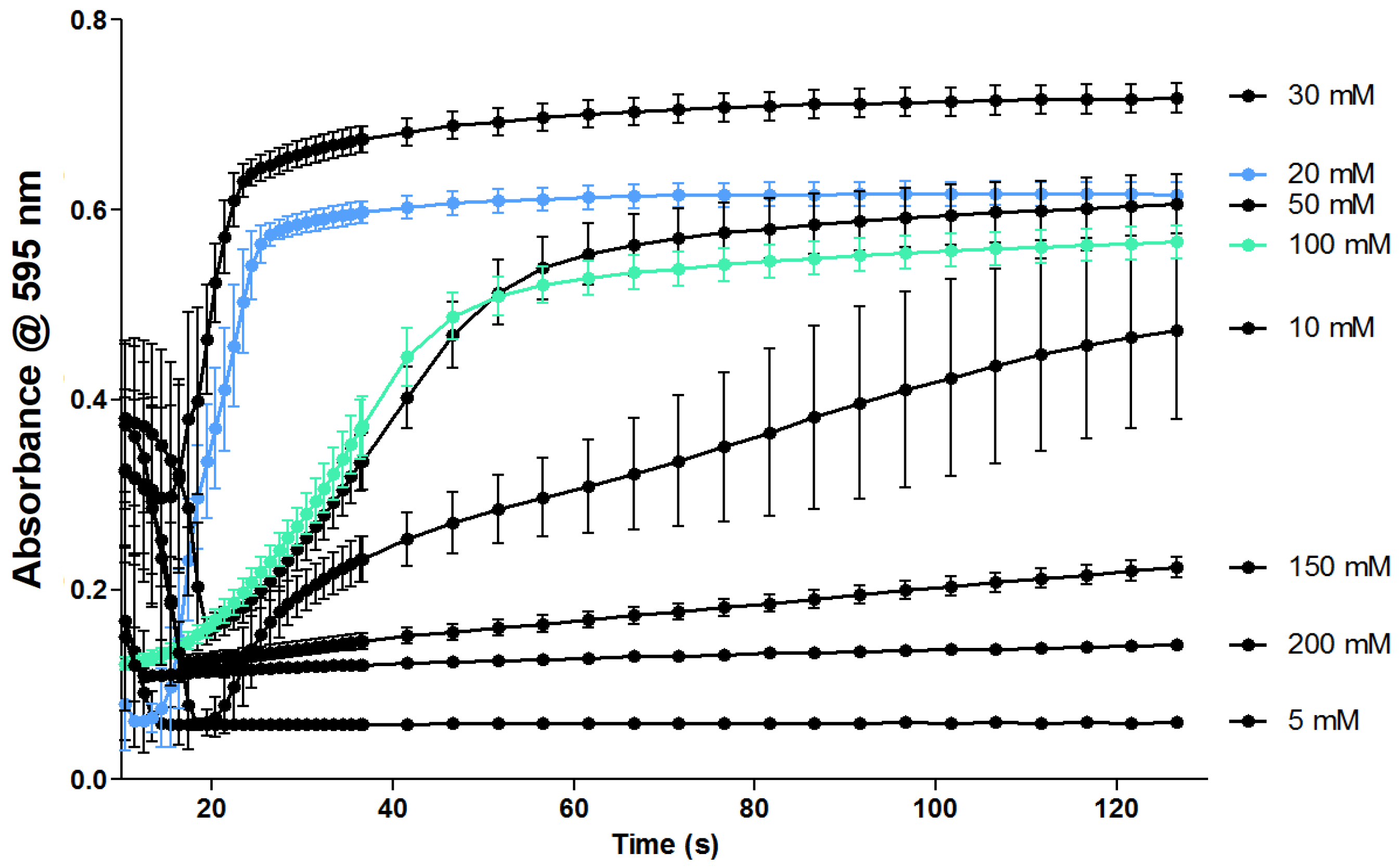
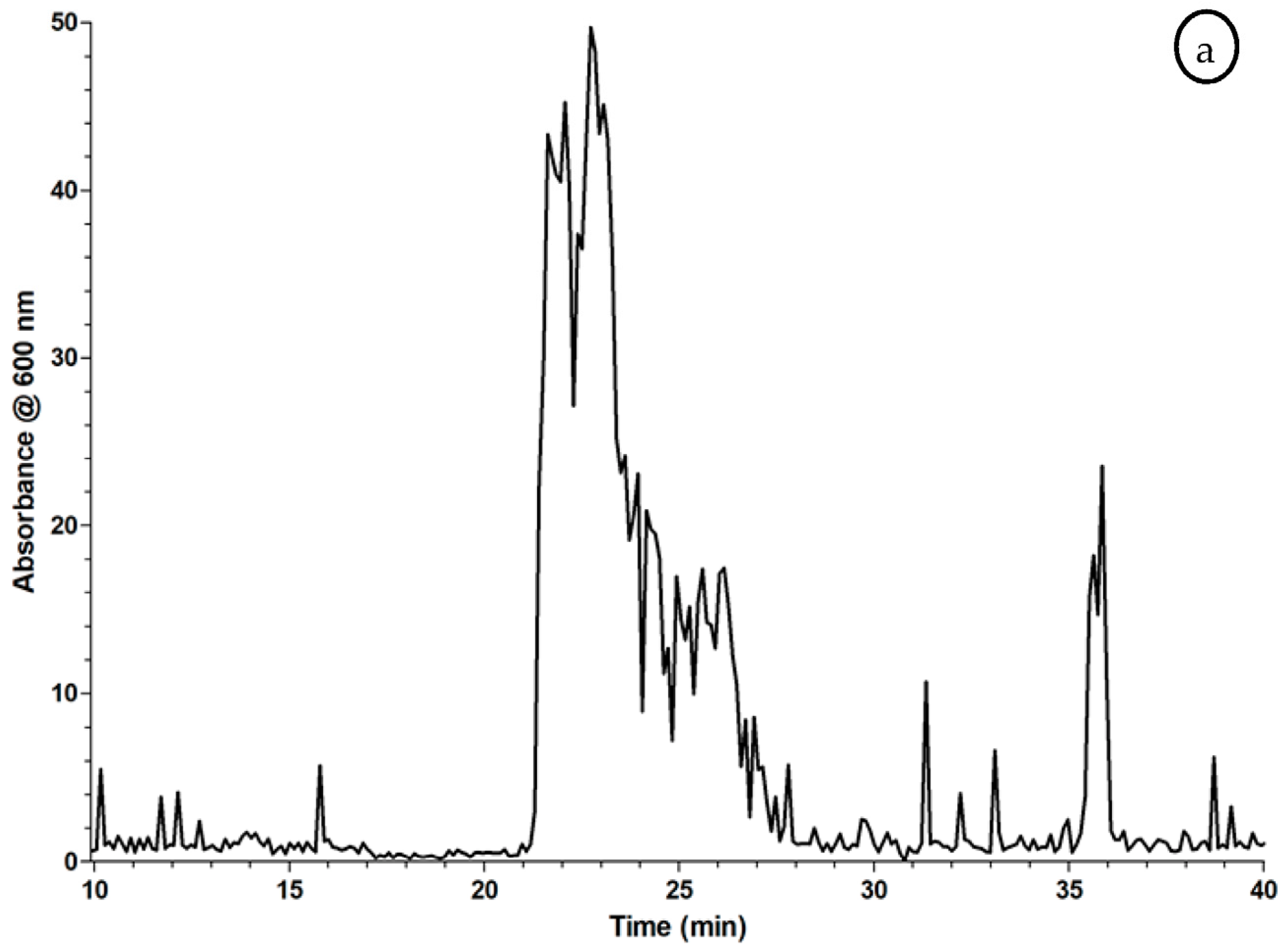
2.2.2. Evaluation of the Coagulation Assay Using Russell’s Viper Venom
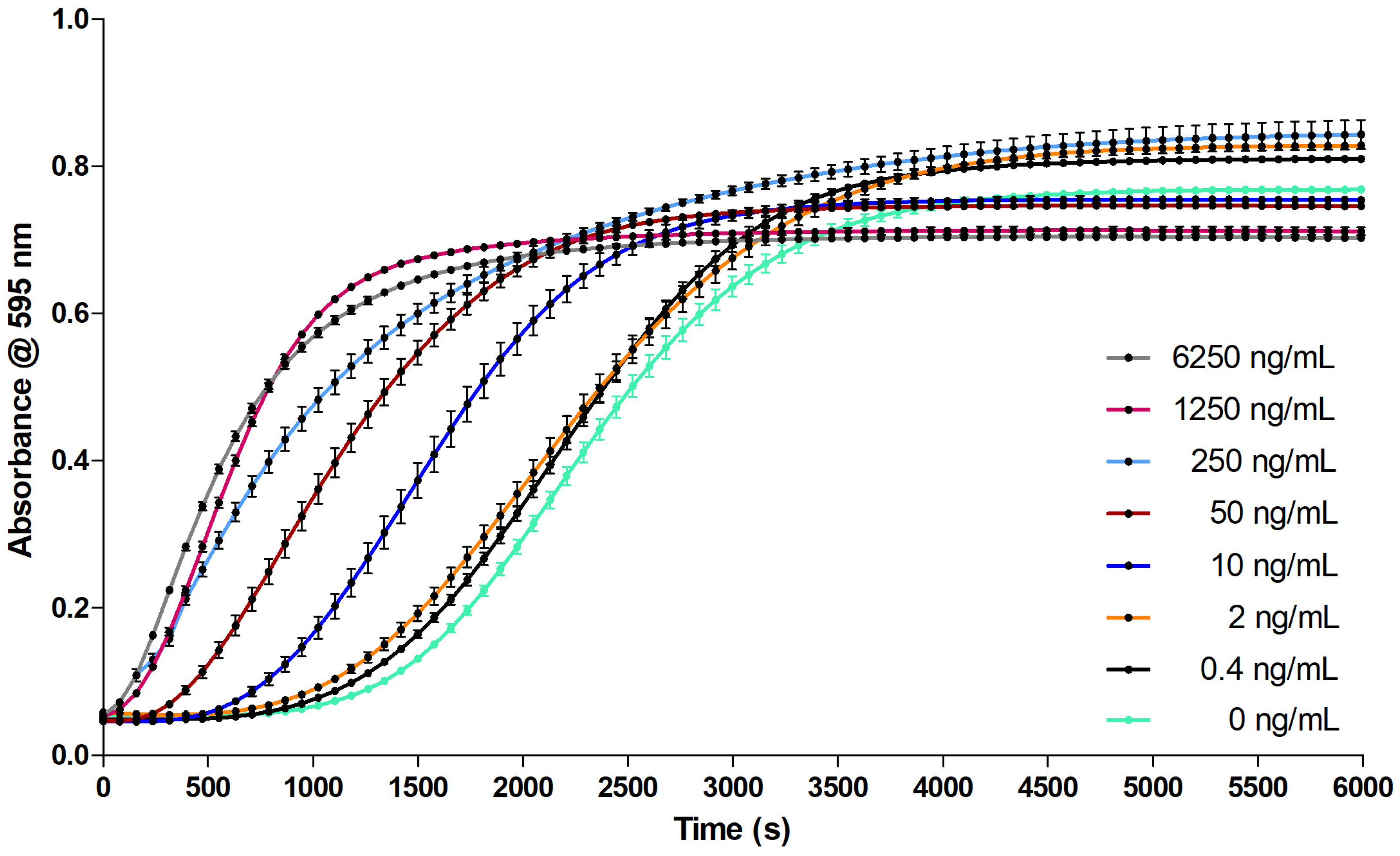
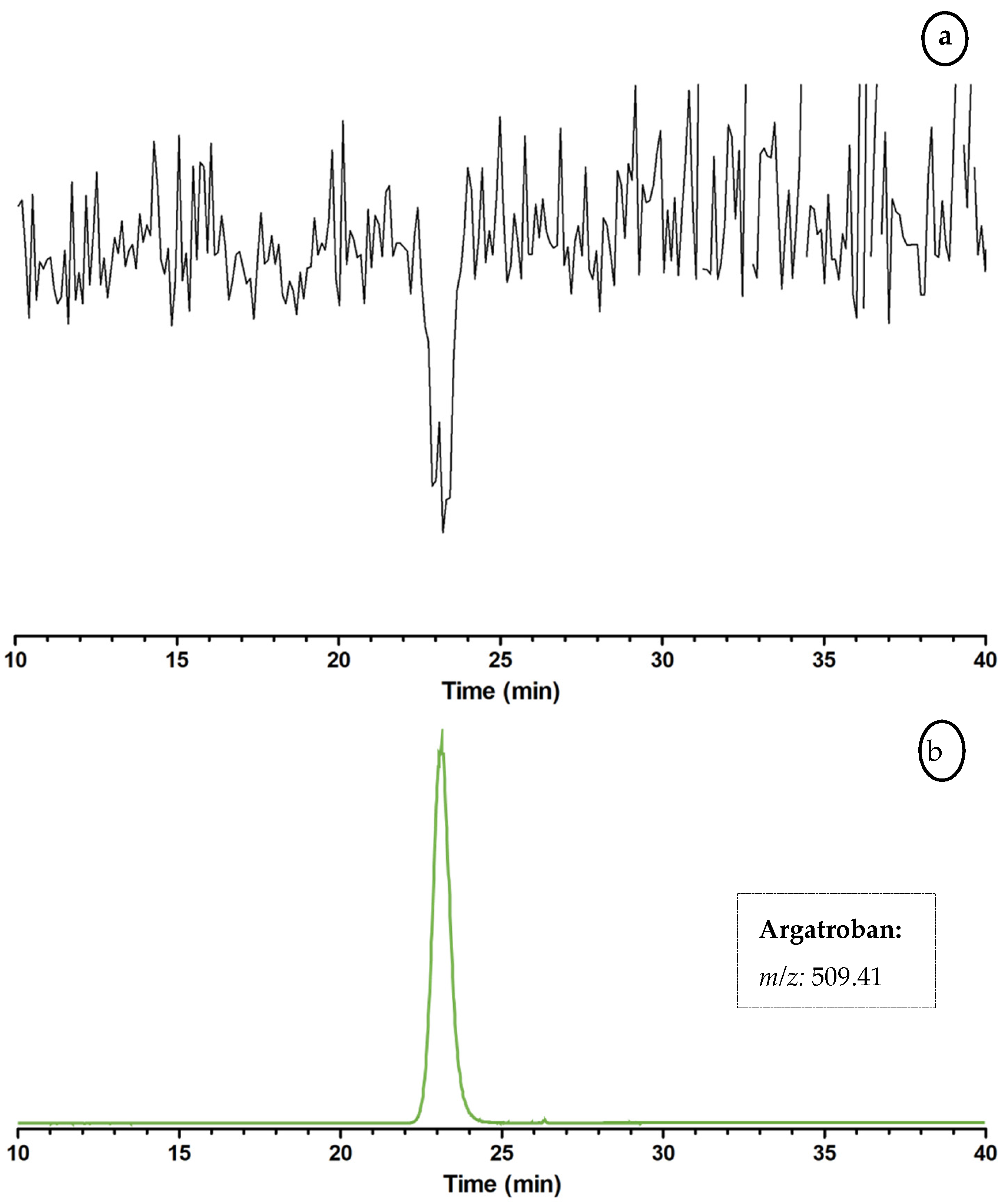
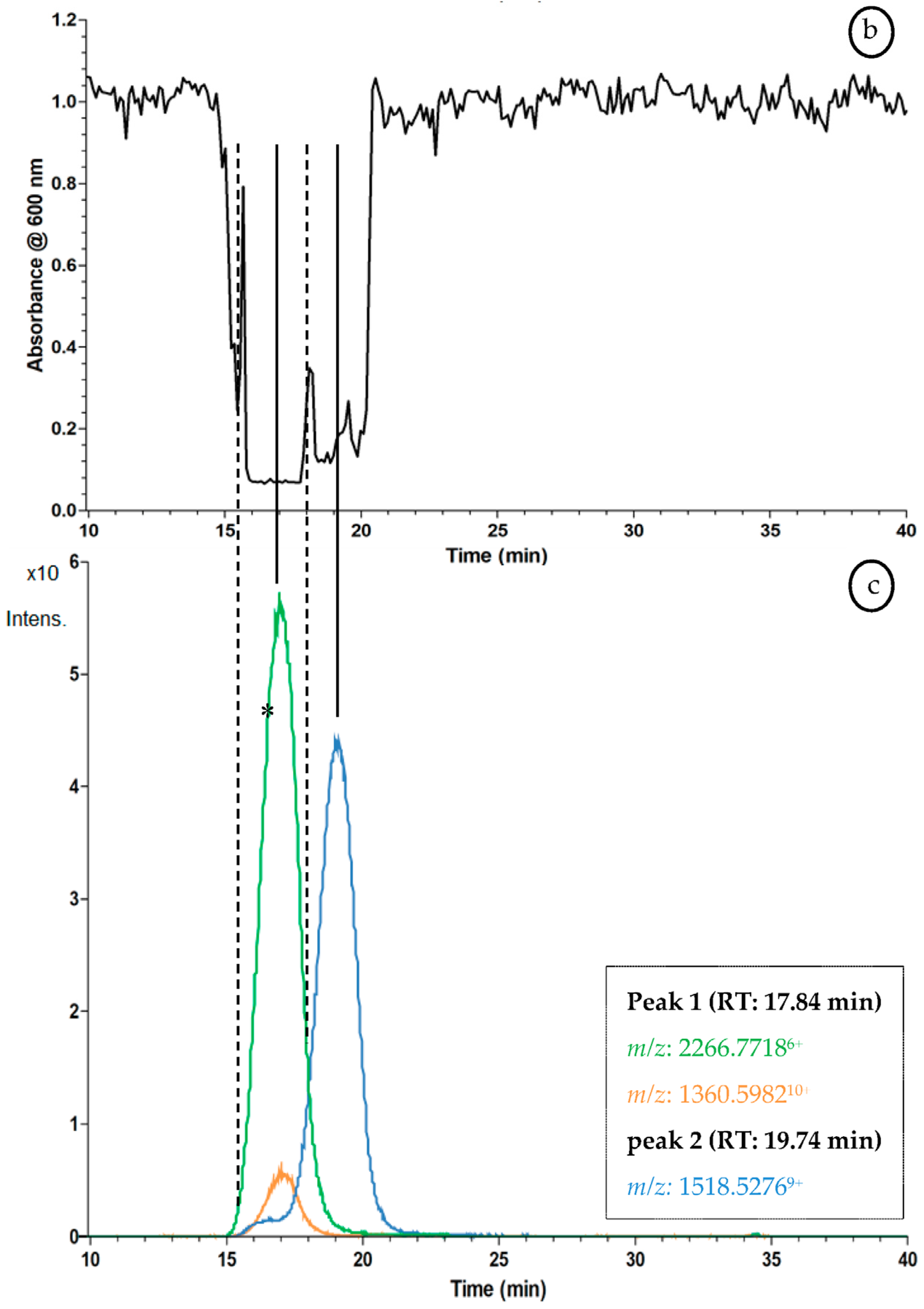
2.3. Proof of Concept for the Assessment of Individual Clotting Modulators by Using the Bioassay in Combination with a Nanofractionation LC–MS/MS Workflow
3. Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Coagulation Assay
3.2. Evaluation of the Coagulation Assay with Anti- and Procoagulants
3.2.1. Evaluation of the Coagulation Assay Using Anticoagulant Compounds
3.2.2. Evaluation of the Coagulation Assay Using Russell’s Viper Venom
3.3. Proof of Concept for the Assessment of Individual Clotting Modulators by Using the Bioassay in Combination with a Nanofractionation LC–MS/MS Workflow
3.4. Summary & Research Applications
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical and Biological Reagents
4.2. Coagulation Activity Assay
4.3. Instrumental Setup
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butenas, S.; Mann, K.G. Blood coagulation. Biochemistry 2002, 67, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolittle, R.F. Step-by-Step Evolution of Vertebrate Blood Coagulation. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2009, 74, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, E.; Wilson, L.; Wickramasinghe, K.; Bhatnagar, P.; Leal, J.; Luengo-Fernandez, R.; Burns, R.; Rayner, M.; Townsend, N. European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2017 edition. Eur. Heart Netw. Brussels 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eurostat. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Cardiovascular_diseases_statistics (accessed on 25 November 2017).
- Benjamin, E.; Blaha, M.; Chiuve, S.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.; Deo, R.; Ferranti de, S.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillesple, C.; et al. Amarican Heart Association Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics 2017 At-a-Glance. Circulation 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.; Yeom, J.; Han, E.H.; Lim, Y.H. Inhibitory effect of bee venom on blood coagulation via anti-serine protease activity. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marghescu, D. Blood Laboratory: Hemostasis: PT and PTT tests The McGill Physiology Virtual Lab Blood Laboratory. Available online: https://www.medicine.mcgill.ca/physio/vlab/bloodlab/PT_PTT.htm (accessed on 21 May 2017).
- Stago Diagnostica Stago, Inc. Product Catalog 2016; Diagnostica Stago, Inc.: Parsippany, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kuruvilla, M.; Gurk-turner, C.; Gurk-Turner, C. A review of warfarin dosing and monitoring. Bumc Proc. 2001, 14, 305–306. [Google Scholar]
- Ansell, J.; Hirsh, J.; Hylek, E.; Jacobson, A.; Crowther, M.; Palareti, G. Pharmacology and management of the vitamin K antagonists: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest 2008, 133, 160S–198S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonaco, T.; Ghimenti, S.; Piga, I.; Biagini, D.; Onor, M.; Fuoco, R.; Paolicchi, A.; Ruocco, L.; Pellegrini, G.; Trivella, M.G.; Di Francesco, F. Monitoring of warfarin therapy: Preliminary results from a longitudinal pilot study. Microchem. J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, D.W.; Ondetti, M.A. History of the design of captopril and related inhibitors of angiotensin converting enzyme. Hypertension 1991, 17, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, E.D.; Cooper, R.A.; Lewis, E.J. Review of the Overall Experience of Captopril in Hypertension. Arch. Intern. Med. 1984, 144, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slagboom, J.; Kool, J.; Harrison, R.A.; Casewell, N.R. Haemotoxic snake venoms: Their functional activity, impact on snakebite victims and pharmaceutical promise. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladic, M.; Zietek, B.M.; Iyer, J.K.; Hermarij, P.; Niessen, W.M.; Somsen, G.W.; Kini, R.M.; Kool, J. At-line nanofractionation with parallel mass spectrometry and bioactivity assessment for the rapid screening of thrombin and factor Xa inhibitors in snake venoms. Toxicon 2016, 110, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padula, A.M.; Winkel, K.D. Antivenom production in the alpaca (Vicugna pacos): Monovalent and polyvalent antivenom neutralisation of lethal and procoagulant toxins in Australian elapid venoms. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 149, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, K.G.; Whelihan, M.F.; Butenas, S.; Orfeo, T. Citrate anticoagulation and the dynamics of thrombin generation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stief, T.W. The Recalcified Coagulation Activity. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2008, 14, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramström, S. Clotting time analysis of citrated blood samples is strongly affected by the tube used for blood sampling. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2005, 16, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walenga, J.M. An overview of the direct thrombin inhibitor argatroban. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2002, 32, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, P.C.; Kaur, N.; Thong, C.L. Direct thrombin inhibitors: Pharmacology and clinical relevance. Anaesthesia 2005, 60, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochet, L.; Servais, A.C.; Farcas, E.; Bettonville, V.; Bouckaert, C.; Fillet, M. Determination of inhibitory potency of argatroban toward thrombin by electrophoretically mediated microanalysis. Talanta 2013, 116, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantgan, R.R.; Jerome, W.G.; Hursting, M.J. No effect of clot age or thrombolysis on argatroban’s inhibition of thrombin. Blood 1998, 92, 2064–2074. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, H. Studies on the different modes of action of the anticoagulant protease inhibitors DX-9065a and argatroban: I. Effects on thrombin generation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 50439–50444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobu, M.; Iqbal, O.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Neville, B.; Messmore, H.L.; Fareed, J. Anti-Xa and anti-IIa drugs alter international normalized ratio measurements: Potential problems in the monitoring of oral anticoagulants. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2004, 10, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex cocktails: The evolutionary novelty of venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.M. Anticoagulant proteins from snake venoms: Structure, function and mechanism. Biochem. J. 2006, 397, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J. Snake venoms and coagulopathy. Toxicon 2005, 45, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.M.; Koh, C.Y. Metalloproteases Affecting Blood Coagulation, Fibrinolysis and Platelet Aggregation from Snake Venoms: Definition and Nomenclature of Interaction Sites. Toxins 2016, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.M. The intriguing world of prothrombin activators from snake venom. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, R.; Mukherjee, A.K.; Biotechnology, M. A Brief Appraisal on Russell’s Viper Venom (Daboia russelii russelii) Proteinases. Snake Venoms 2015, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Das, D.; Iyer, J.K.; Kini, R.M.; Doley, R. Unveiling the complexities of Daboia russelii venom, a medically important snake of India, by tandem mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2015, 107, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.; Kuruppu, S.; Othman, I.; Goode, R.J. A.; Hodgson, W.C.; Isbister, G.K. Neurotoxicity in Sri Lankan Russell?s Viper (Daboia russelii) Envenoming is Primarily due to U1-viperitoxin-Dr1a, a Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxin. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 31, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.K.; Kalita, B.; Mackessy, S.P. A proteomic analysis of Pakistan Daboia russelii russelii venom and assessment of potency of Indian polyvalent and monovalent antivenom. J. Proteom. 2016, 144, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.E.; Dennis, E.A. Phospholipase A2 structure/function, mechanism, and signaling. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Still, K.B.M.; Nandlal, R.S.S.; Slagboom, J.; Somsen, G.W.; Casewell, N.R.; Kool, J. Multipurpose HTS Coagulation Analysis: Assay Development and Assessment of Coagulopathic Snake Venoms. Toxins 2017, 9, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120382
Still KBM, Nandlal RSS, Slagboom J, Somsen GW, Casewell NR, Kool J. Multipurpose HTS Coagulation Analysis: Assay Development and Assessment of Coagulopathic Snake Venoms. Toxins. 2017; 9(12):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120382
Chicago/Turabian StyleStill, Kristina B. M., Randjana S. S. Nandlal, Julien Slagboom, Govert W. Somsen, Nicholas R. Casewell, and Jeroen Kool. 2017. "Multipurpose HTS Coagulation Analysis: Assay Development and Assessment of Coagulopathic Snake Venoms" Toxins 9, no. 12: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120382
APA StyleStill, K. B. M., Nandlal, R. S. S., Slagboom, J., Somsen, G. W., Casewell, N. R., & Kool, J. (2017). Multipurpose HTS Coagulation Analysis: Assay Development and Assessment of Coagulopathic Snake Venoms. Toxins, 9(12), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120382






