Isolation and Pharmacological Characterization of α-Elapitoxin-Ot1a, a Short-Chain Postsynaptic Neurotoxin from the Venom of the Western Desert Taipan, Oxyuranus temporalis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
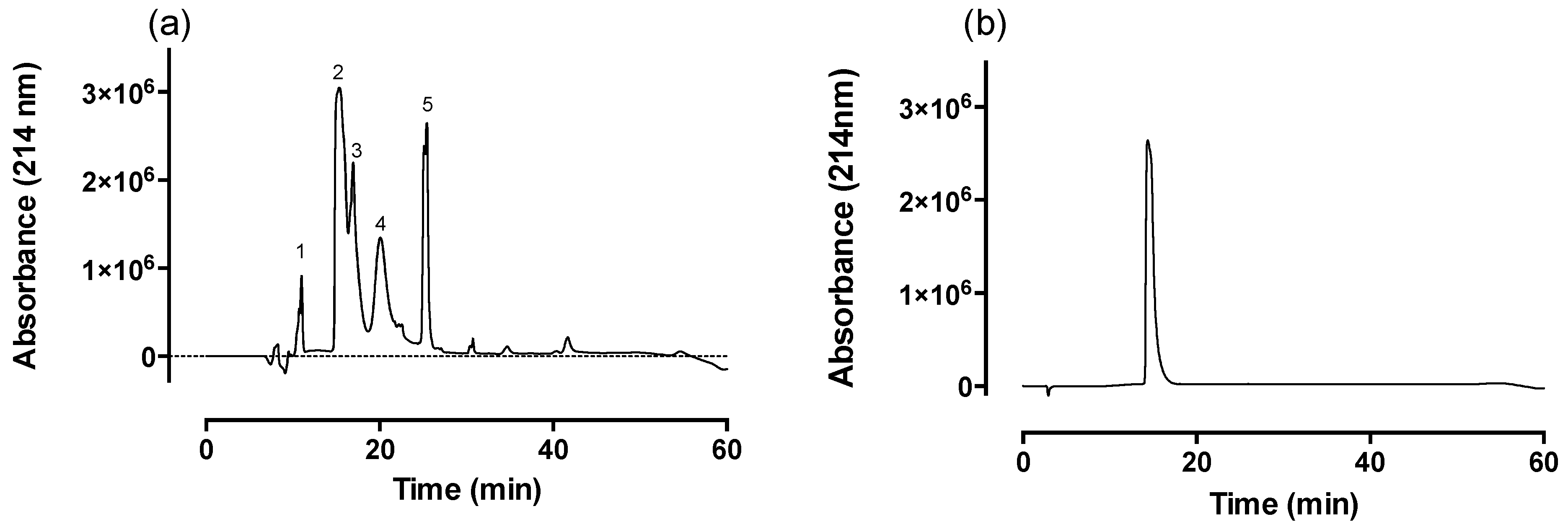
2.1. Fractionation of Venom via Reverse-Phase HPLC
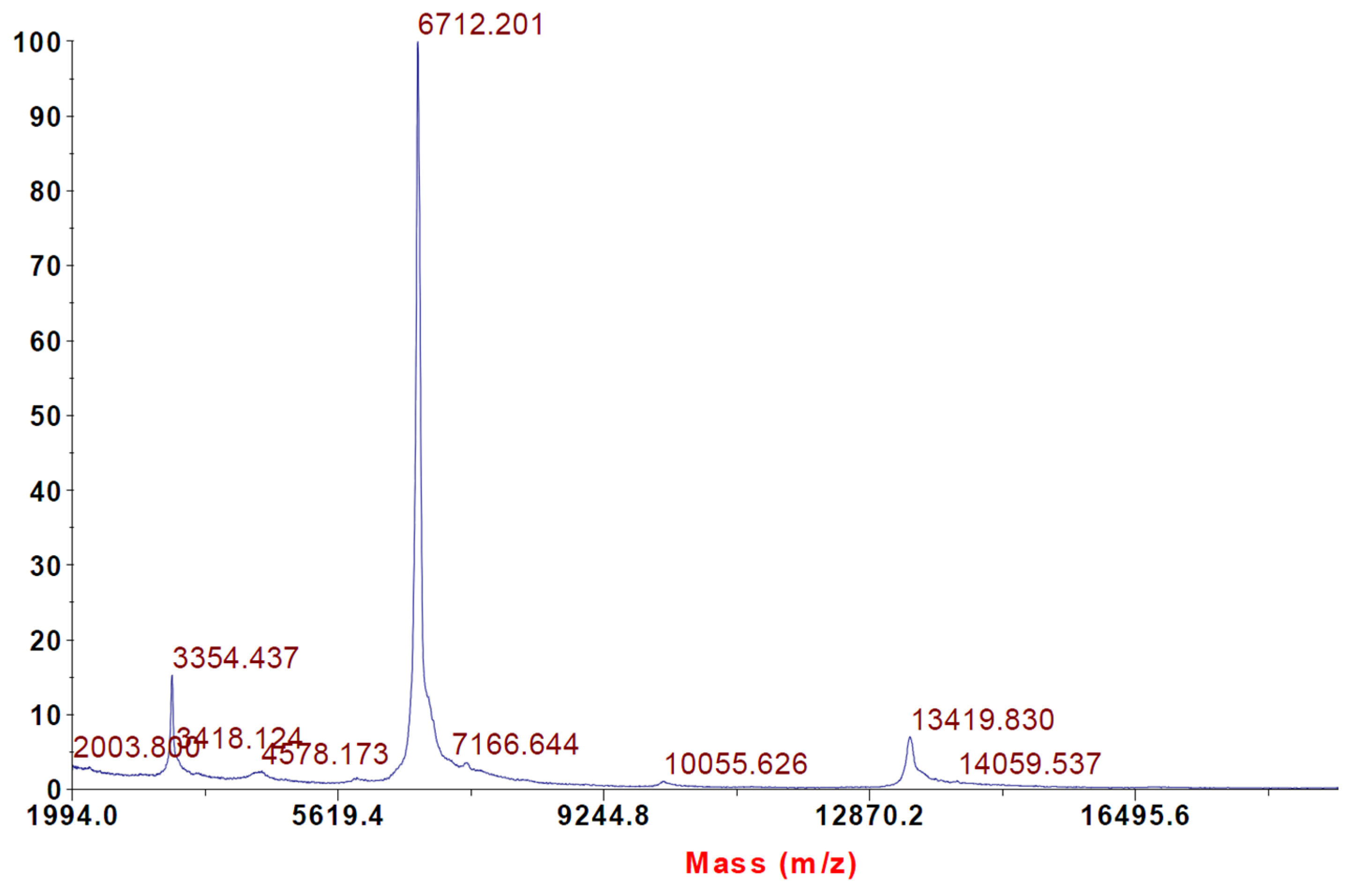
2.2. Intact Protein Analysis with MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
2.3. Identification and de Novo Sequencing by LCMS/MS
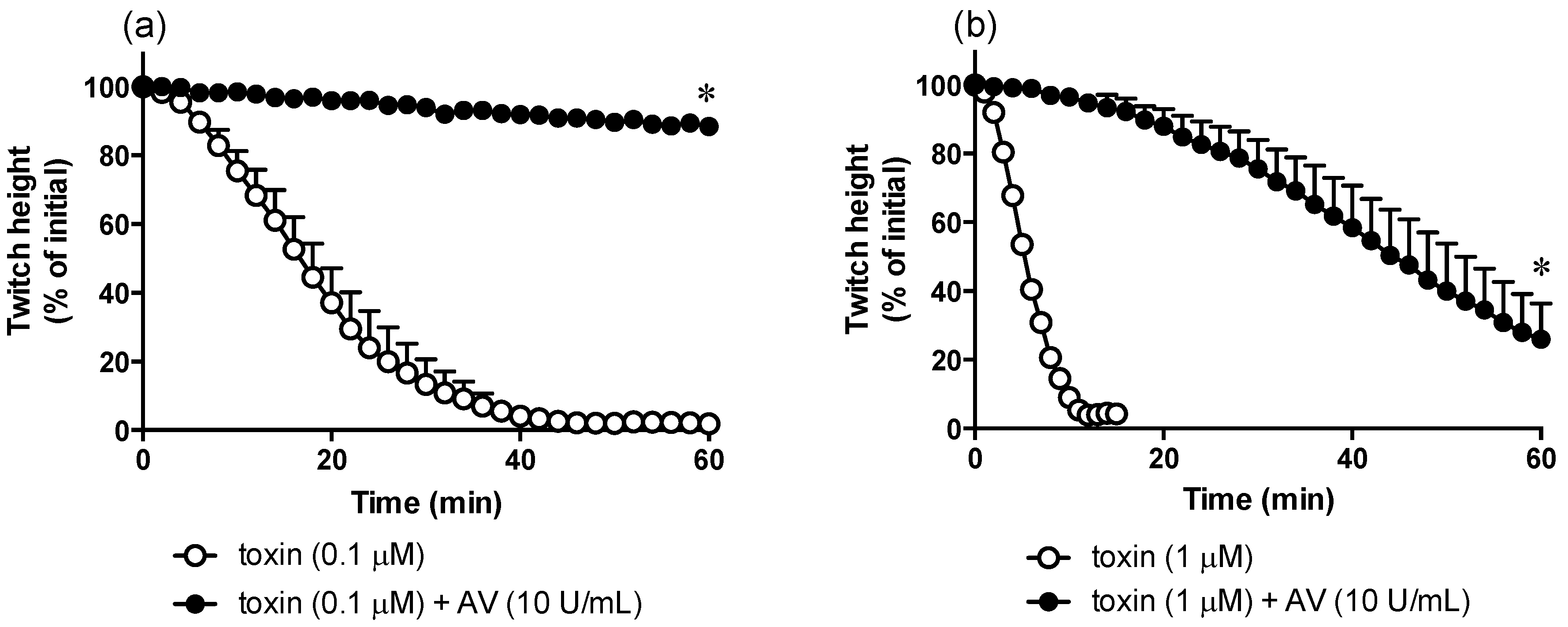
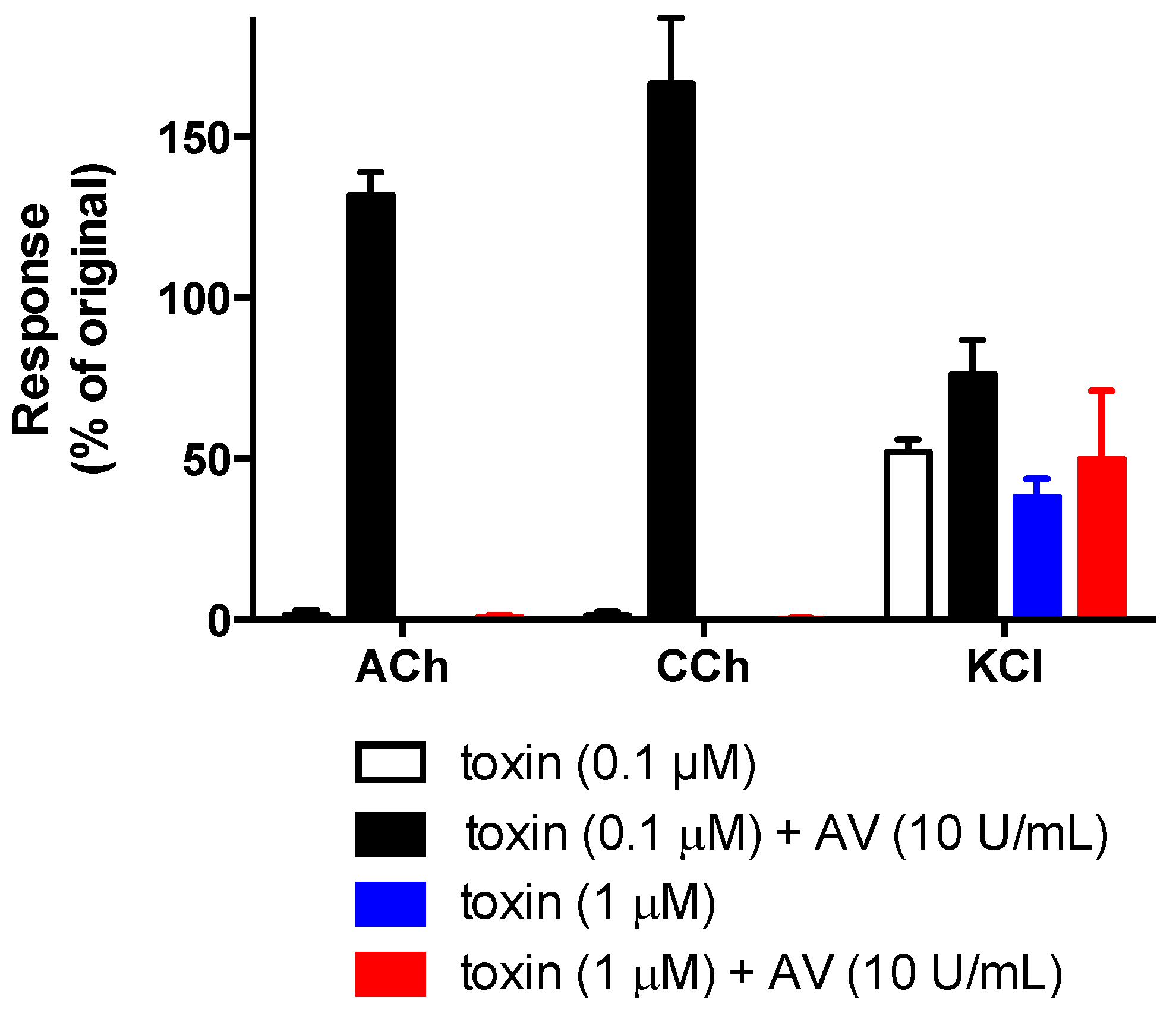
2.4. In Vitro Neurotoxicity
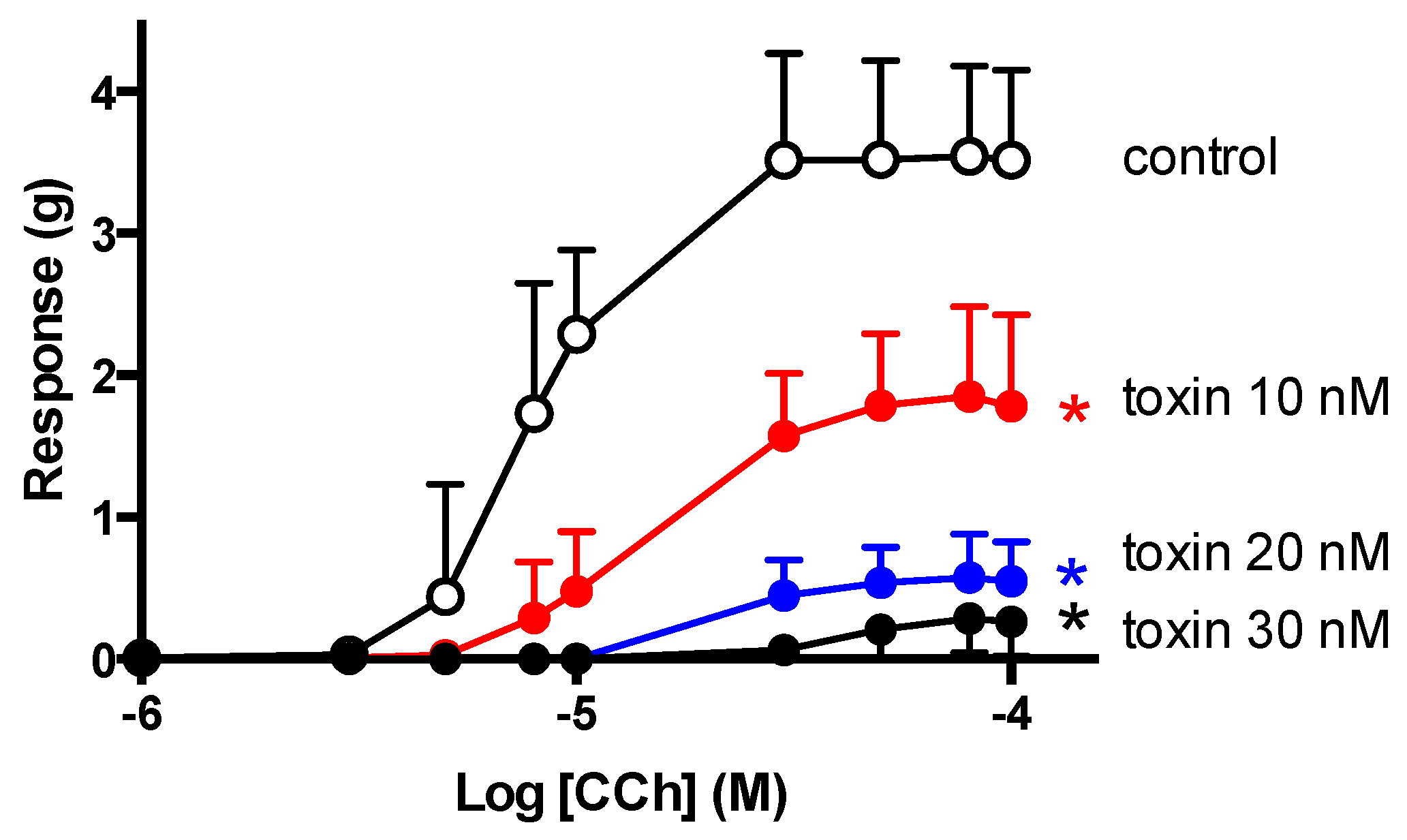
2.5. CCh Cumulative Concentration-Response Curves
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venom Supply
4.2. Purification α-Elapitoxin-Ot1a
4.3. Mass Spectrometry and Amino Acid Sequencing
4.3.1. Intact Protein Analysis Using Matrix Associated Laser Desorption Time of Flight (MALDI-TOF) Mass Spectrometry
4.3.2. In-Solution Digestion of Sample in Preparation for Electrospray-Ionization Coupled with Mass-Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry (ESI-LCMS/MS)
4.3.3. Nanoflow Liquid Chromatography ESI-LCMS/MS
4.3.4. Protein Identification by Automated de Novo Sequencing
4.4. Neurotoxicity Studies
4.5. CCh Cumulative Concentration-Response Curves
4.6. Data Analysis
4.7. Chemicals and Drugs
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACh | acetylcholine |
| CCh | carbachol |
| HPLC | high performance liquid chromatography |
| ESI-LCMS/MS | electrospray-ionization coupled with mass-spectrometry/mass spectrometry |
References
- Doughty, P.; Maryan, B.; Donnellan, S.C.; Hutchinson, M.N. A new species of taipan (Elapidae: Oxyuranus) from central Australia. Zootaxa 2007, 1422, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, G.M. A possible second record of the central ranges Taipan, Oxyuranus temporalis (Elapidae). Herpetofauna 2007, 37, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, K.E.C.; Morley, T.; Hutchinson, M.; Donnellan, S. Redescription of the western desert taipan, Oxyuranus temporalis (Serpentes: Elapidae), with notes on its distribution, diet and genetic variation. Aust. J. Zool. 2012, 59, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, C.M.; Madaras, F.; Turnbull, R.K.; Morley, T.; Dunstan, N.; Allen, L.; Kuchel, T.; Mirtschin, P.; Hodgson, W.C. Comparative studies of the venom of a new taipan species, Oxyuranus temporalis, with other members of its genus. Toxins 2014, 6, 1979–1995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Wickramaratana, J.C.; Lemme, S.; Beuve, A.; Garbers, D.; Hodgson, W.C.; Alewood, P. Novel natriuretic peptides from the venom of the inland taipan (Oxyuranus microlepidotus): Isolation, chemical and biological characterisation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; Ferandez, J.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Segura, A.; Leon, G.; Angulo, Y.; Paiva, O.; Matainaho, T.; Jensen, S.D.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of the venom of the taipan snake, Oxyuranus scutellatus, from Papua New Guinea and Australia: Role of neurotoxic and procoagulant effects in venom toxicity. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2128–2140. [Google Scholar]
- Speijer, H.; Govers-Riemslag, J.W.P.; Zwaal, R.F.A.; Rosing, J. Prothrombin activation by an activator from the venom of Oxyuranus scutellatus (Taipan snake). J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 13258–13267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, F.J.; Owen, W.G.; Esmon, C.T. Characterization of the prothrombin activator from the venom of Oxyuranus scutellatus scutellatus (Taipan venom). Biochemistry 1980, 19, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welton, R.E.; Burnell, J.N. Full length nucleotide sequence of a Factor V-like subunit of oscutarin from Oxyuranus scutellatus scutellatus (coastal Taipan). Toxicon 2005, 46, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Possani, L.D.; Martin, B.M.; Yatani, A.; Mochca-Morales, J.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Gurrola, G.B.; Brown, A.M. Isolation and physiological characterization of taicatoxin, a complex toxin with specific effects on calcium channels. Toxicon 1992, 30, 1343–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, S.T.H.; Richards, R.; Johnson, L.A.; Flight, S.; Anderson, S.; Liao, A.; de Jersey, J.; Masci, P.P.; Lavin, M.F. Identification and characterisation of Kunitz-type plasma kallikrein inhibitors unique to Oxyuranus sp. snake venoms. Biochimie 2012, 94, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fohlman, J. Comparison of two highly toxic Australian snake venoms: The taipan (Oxyuranus s. scutellatus) and the fierce snake (Parademansia microlepidotus). Toxicon 1979, 17, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fohlman, J.; Eaker, D.; Karlsson, E.; Thesleff, S. Taipoxin, an extremely potent presynaptic neurotoxin from the venom of the Australian snake taipan (Oxyuranus s. scutellatus). Isolation, characterization, quaternary structure and pharmacological properties. Eur. J. Biochem. 1976, 68, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuruppu, S.; Reeve, S.; Banerjee, Y.; Kini, R.M.; Smith, A.I.; Hodgson, W.C. Isolation and pharmacological characterization of cannitoxin, a presynaptic neurotoxin from the venom of the Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus canni). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, C.M.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. Solving the “Brown snake paradox”: In vitro characterisation of Australasian snake presynaptic neurotoxin activity. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 210, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, C.; Kuruppu, S.; Reeve, S.; Smith, A.I.; Hodgson, W.C. Oxylepitoxin-1, a reversible neurotoxin from the venom of the inland taipan (Oxyuranus microlepidotus). Peptides 2006, 27, 2655–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornhauser, R.; Hart, A.J.; Reeve, S.; Smith, A.I.; Fry, B.G.; Hodgson, W.C. Variations in the pharmacological profile of post-synaptic neurotoxins isolated from the venoms of the Papuan (Oxyuranus scutellatus canni) and coastal (Oxyuranus scutellatus scutellatus) taipans. Neuro Toxicol. 2010, 31, 239–243. [Google Scholar]
- Zamudio, F.; Wolf, K.M.; Martin, B.M.; Possani, L.D.; Chiappinelli, V.A. Two novel α-neurotoxins isolated from the taipan snake, Oxyuranus scutellatus, exhibit reduced affinity for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in brain and skeletal muscle. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 7910–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, C.M.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. Alpha neurotoxins. Toxicon 2013, 66, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.; Isbister, G.K.; O’Donnell, P.; Williamson, N.A.; Hodgson, W.C. Species differences in the neuromuscular activity of post-synaptic neurotoxins from two Australian black snakes (Pseudechis porphyriacus and Pseudechis colletti). Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 219, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruppu, S.; Reeve, S.; Smith, A.I.; Hodgson, W.C. Isolation and pharmacological characterisation of papuantoxin-1, a postsynaptic neurotoxin from the venom of the Papuan black snake (Pseudechis papuanus). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.C.; Kuruppu, S.; Smith, A.I.; Reeve, S.; Hodgson, W.C. Isolation and pharmacological characterisation of hostoxin-1, a postsynaptic neurotoxin from the venom of the Stephen’s banded snake (Hoplocephalus stephensi). Neuropharmacology 2006, 51, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramaratna, J.C.; Fry, B.G.; Loiacono, R.E.; Aguilar, M.I.; Alewood, P.F.; Hodgson, W.C. Isolation and characterization at cholinergic nicotinic receptors of a neurotoxin from the venom of the Acanthophis sp. Seram death adder. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, M.R.; Sato, A.; Richardson, J.S.; Rosen, L.S.; Low, B.W. Molecular conformation of erabutoxin B; atomic coordinates at 2.5 A resolution. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979, 88, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, W.C.; Wickramaratna, J.C. In vitro neuromuscular activity of snake venoms. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.; Scott-Davey, T.; Harris, J. Venom of Collett’s snake (Pseudechis colletti) blocks the binding of α-bungarotoxin to acetylcholine receptors at chick but not human neuromuscular junctions: A histochemical study. Toxicon 2008, 52, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Kano, M.; Tamiya, N.; Shimada, Y. Acetylcholine receptors of human skeletal muscle: A species difference detected by snake neurotoxins. Brain Res. 1985, 346, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.; Jacobson, L.; Curran, L. α-Bungarotoxin binding to human muscle acetylcholine receptor: Measurement of affinity, delineation of AChR subunit residues crucial to binding, and protection of AChR function by synthetic peptides. Neurochem. Int. 1998, 32, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Species | α-Neurotoxin | MW | Partial/Full N-Terminal Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| O. temporalis | α-elapitoxin-Ot1a a | 6712 | MTCYNQQSSQ AKTTTTCSGG VSSCYRKTWS DTRGTIIERG CGCPSVKKGI ERICCGTDKC NN |
| O. scutellatus | α-scutoxin 1 b | 6781 | MTCYNQQSSE AKTTTTCSGG VSSCYKKTWY DGRGTRIERG |
| O. scutellatus | α-oxytoxin 1 b | 6770 | MTCYNQQSSE AKTTTTCSGG VSSCYKETWY DGRGTT |
| O. microlepidotus | oxylepitoxin-1 c | 6789 | MTCYNQQSSE AKTTTTCSGG VSSCYKETWY |
| O. scutellatus | Taipan toxin 1 d | 6726 | MTCYNQQSSE AKTTTTCSGG VSSCYKKTWS DGRGTIIERG CGCPSVKKGI ERICCRTDKC NN |
| O. scutellatus | Taipan toxin 2 d | 6781 | MTCYNQQSSE AKTTTTCSGG VSSCYKKTWS DIRGTIIERG CGCPSVKKGI ERICCRTDKC NN |
| P. colletti | α-elapitoxin-Pc1a e | 6759.6 | MTCCNQQSSQ PKTTTTCAGG ETSCYKKTWS DHRGSRTERG CGCPHVKPGI KLTCCKTDEC NN |
| P. porphyriacus | α-elapitoxin-Ppr1 e | 6746.5 | MTCCNQQSSQ PKTTTTCAGG ESSCYKKTWS DHRGSRTERG CGCPHVKPGI KLTCCETDEC NN |
| P. papuanus | Papuantoxin-1 f | 6738 | MTCCNQQSSQ PKTTTT |
| H. stephensi | Hostoxin-1 g | 6660 | MTPCNQQSSQ PKTTK |
| Species | Common Name | Postsynaptic Neurotoxin | t90 (min) at 1 µM |
|---|---|---|---|
| O. temporalis | Western Desert Taipan | α-elapitoxin-Ot1a | 9.83 ± 0.36 a |
| O. scutellatus | Coastal Taipan | α-scutoxin 1 | ~12 b |
| O. scutellatus | Papuan Taipan | α-oxytoxin 1 | ~25 b |
| O. microlepidotus | Inland Taipan | oxylepitoxin-1 | ~55 c |
| H. stephensi | Stephen’s Banded snake | hostoxin-1 | ~10 d |
| A. sp. Seram | Seram death adder | Acantoxin IVa | 9.7 ± 1.1 e |
| Snake Species | Common Name | Toxin | pA2 Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bungarus multicinctus | Various kraits | α-bungarotoxin | 8.71 ± 0.06 a |
| Hoplocephalus stephensi | Stephen’s Banded snake | hostoxin-1 | 8.45 ± 0.32 b |
| Oxyuranus scutellatus | Coastal Taipan | α-scutoxin 1 | 8.38 ± 0.59 c |
| Acanthophis sp. Seram | Seram death adder | acantoxin Iva | 8.36 ± 0.17 a |
| Oxyuranus temporalis | Western Desert Taipan | α-elapitoxin-Ot1a | 8.02 ± 0.05 * |
| Oxyuranus scutellatus | Papuan Taipan | α-oxytoxin 1 | 7.62 ± 0.04 c |
| Oxyuranus microlepidotus | Inland Taipan | oxylepitoxin-1 | 7.16 ± 0.28 d |
| Pseudechis colletti | Collett’s snake | α -elapitoxin-Pc1 | 7.04 ± 0.07 e |
| Pseudechis prophyriacus | Red bellied black snake | α-elapitoxin-Ppr1 | 6.97 ± 0.03 e |
| Pseudechis papuanus | Papuan black snake | papuantoxin-1 | 6.90 ± 0.30 f |
| Not applicable | - | d-tubocurarine | 6.29 ± 0.06 a |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barber, C.M.; Ahmad Rusmili, M.R.; Hodgson, W.C. Isolation and Pharmacological Characterization of α-Elapitoxin-Ot1a, a Short-Chain Postsynaptic Neurotoxin from the Venom of the Western Desert Taipan, Oxyuranus temporalis. Toxins 2016, 8, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030058
Barber CM, Ahmad Rusmili MR, Hodgson WC. Isolation and Pharmacological Characterization of α-Elapitoxin-Ot1a, a Short-Chain Postsynaptic Neurotoxin from the Venom of the Western Desert Taipan, Oxyuranus temporalis. Toxins. 2016; 8(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarber, Carmel M., Muhamad Rusdi Ahmad Rusmili, and Wayne C. Hodgson. 2016. "Isolation and Pharmacological Characterization of α-Elapitoxin-Ot1a, a Short-Chain Postsynaptic Neurotoxin from the Venom of the Western Desert Taipan, Oxyuranus temporalis" Toxins 8, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030058
APA StyleBarber, C. M., Ahmad Rusmili, M. R., & Hodgson, W. C. (2016). Isolation and Pharmacological Characterization of α-Elapitoxin-Ot1a, a Short-Chain Postsynaptic Neurotoxin from the Venom of the Western Desert Taipan, Oxyuranus temporalis. Toxins, 8(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030058






