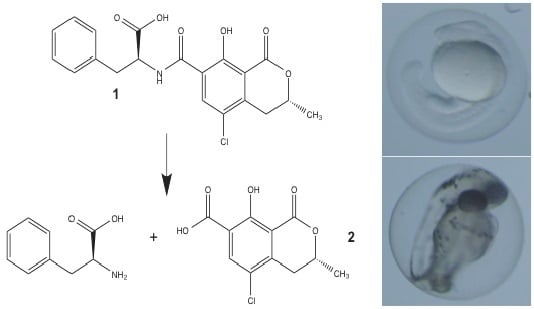
Teratogenicity of Ochratoxin A and the Degradation Product, Ochratoxin α, in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryo Model of Vertebrate Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Assay
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
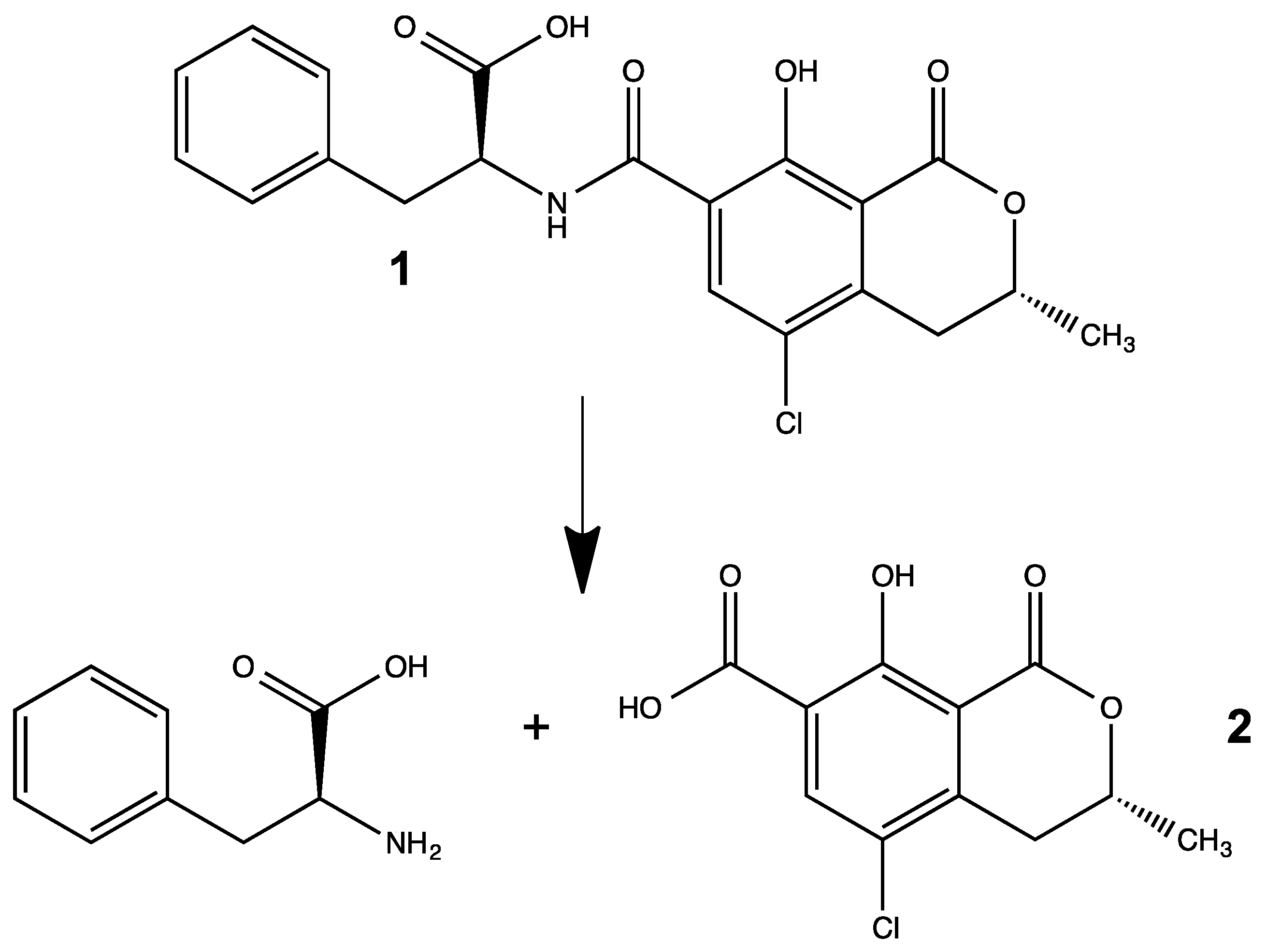
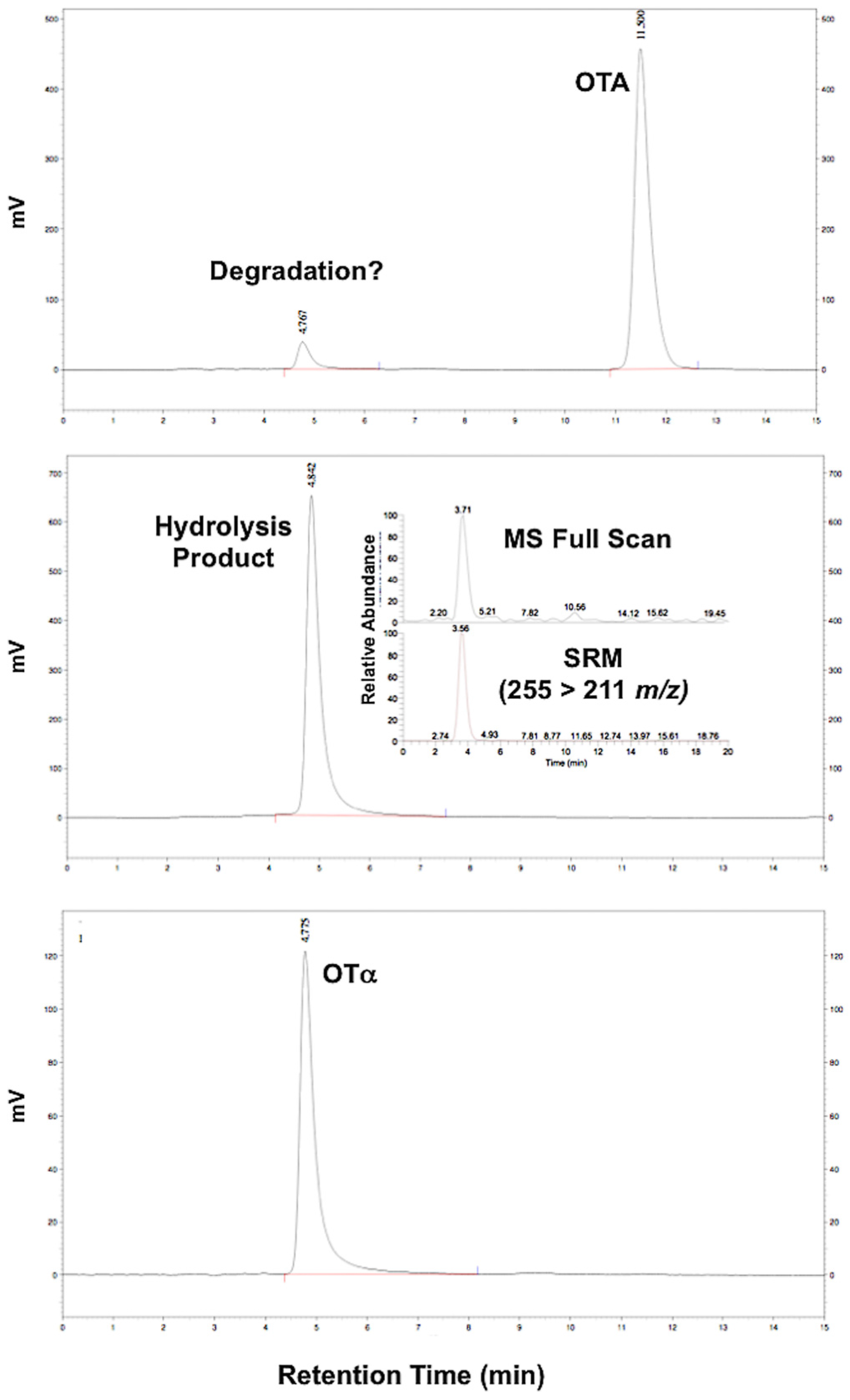
3.1. Synthesis of OTα by Hydrolysis of OTA
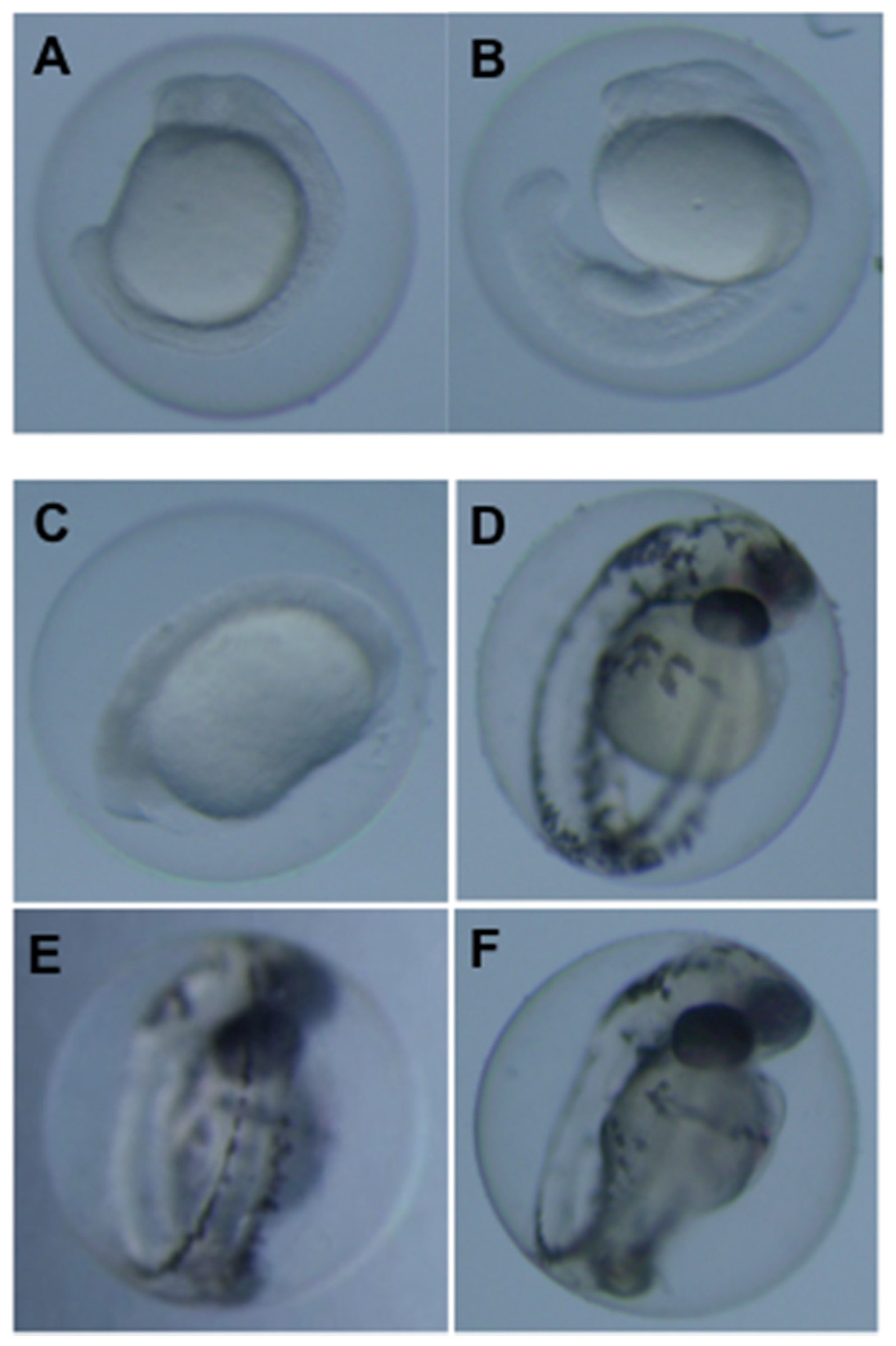
3.2. Teratogenicity of OTA and OTα

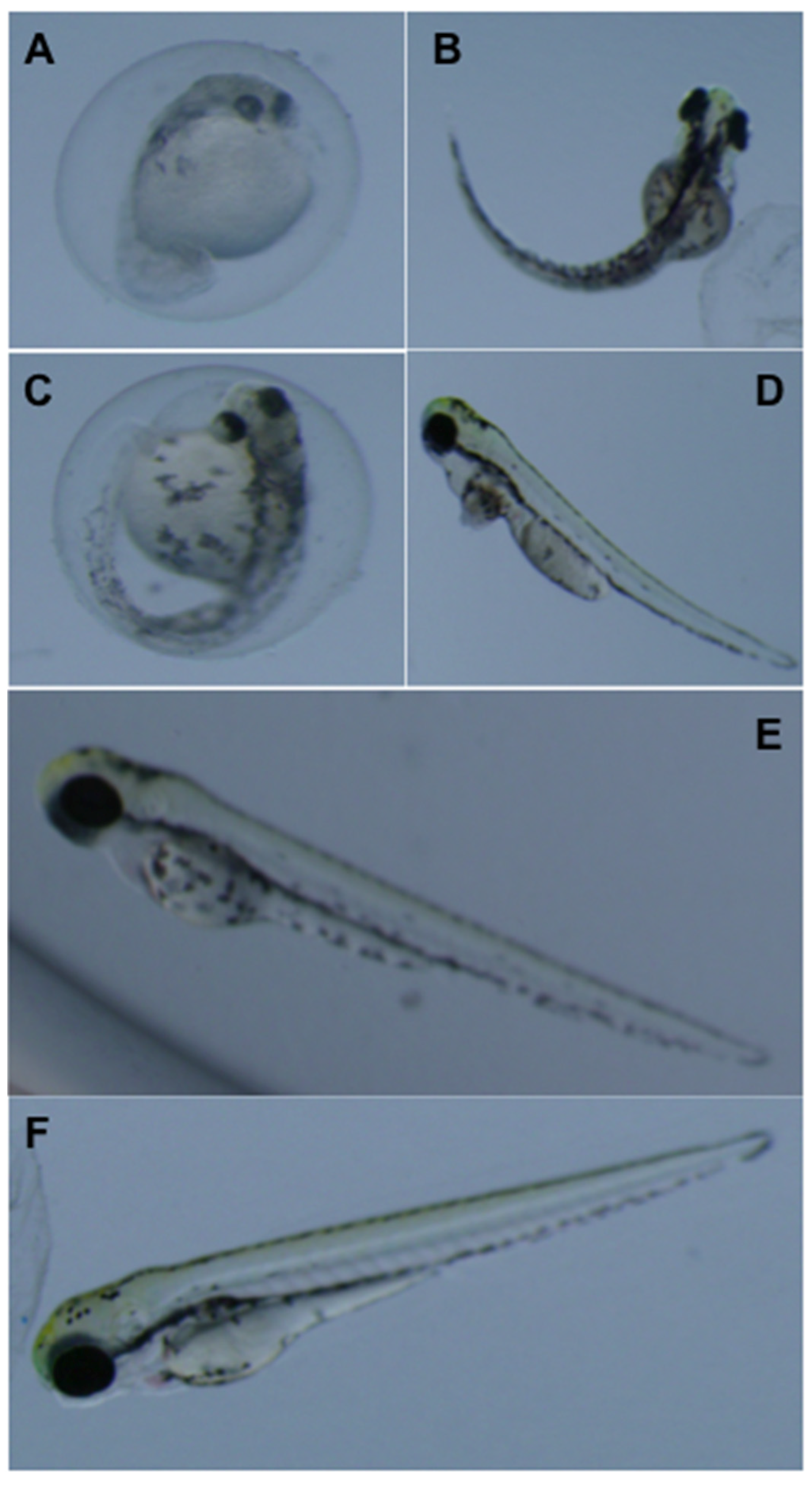
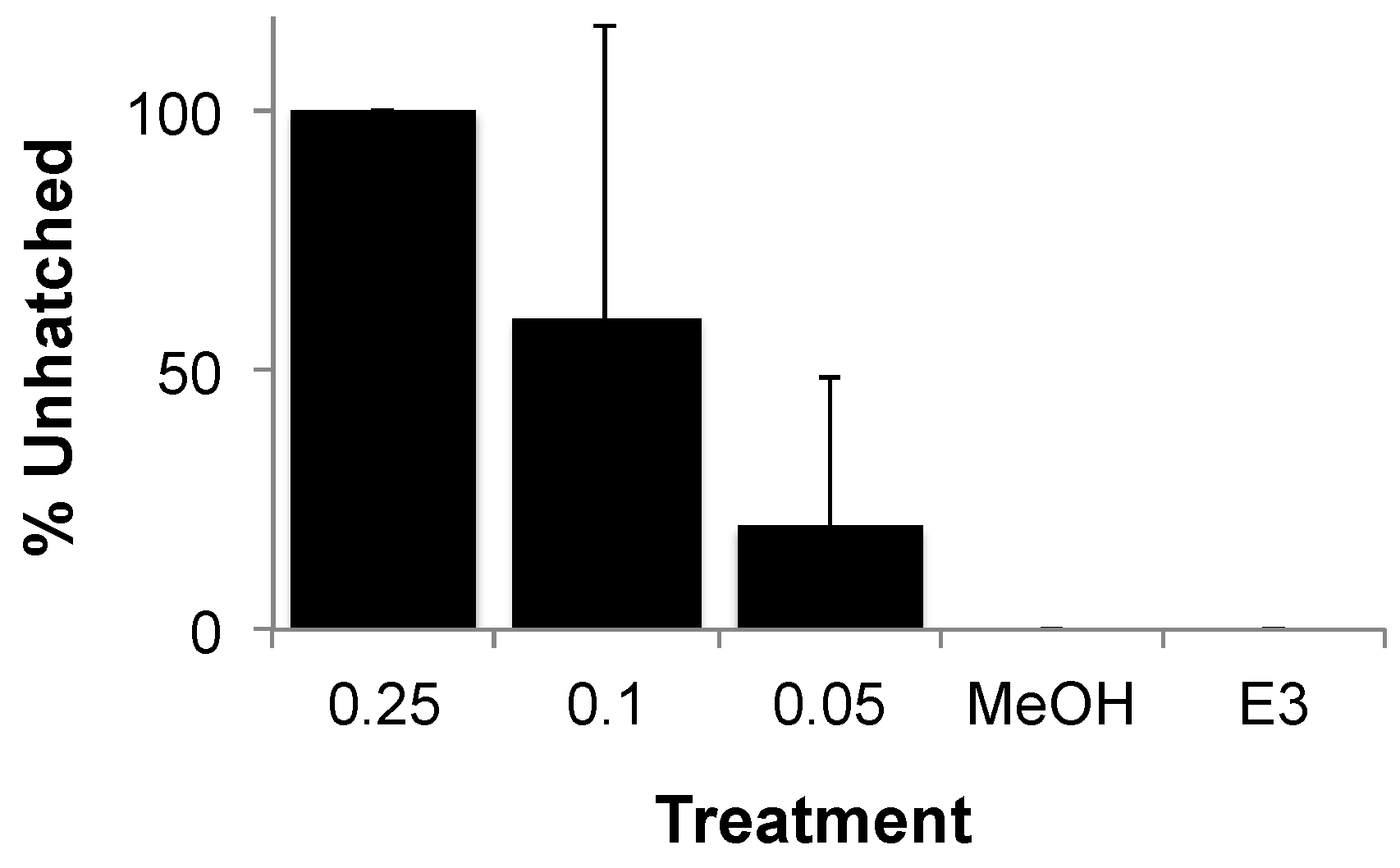

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bui-Klimke, T.R.; Wu, F. Ochratoxin A and human health risk: A review of the evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, E.; Prietz, A.; Dietrich, D.R. Investigation of the teratogenic potential of ochratoxin A and B using the FETAX system. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 74, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringot, D.; Chango, A.; Schneider, Y.J.; Larondelle, Y. Toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics of ochratoxin A, an update. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 159, 18–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrenti, V.; Di Giacoma, C.; Acquaviva, R.; Barbagallo, I.; Bognanno, M.; Galvano, F. Toxicity of ochratoxin A and its modulation by antioxidants: A review. Toxins 2013, 5, 1742–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, P. Epidemiology of mycotoxic porcine nephropathy. Nord. Vet. Med. 1976, 28, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Limonciel, A.; Jennings, P. A review of the evidence that ochratoxin A is a Nrf2 inhibitor: Implications for nephrotoxicity and renal carcinogenicity. Toxins 2014, 6, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, F.; Xue, H.; Huang, Y.; Pan, C.; Huang, K. Selenium alleviates porcine neprotoxicity A by improving selenoenzyme expression in vitro. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R. Review on ochratoxin A: An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manderville, R.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Bioactivation and DNA adduction as a rationale for ochratoxin A carcinogenesis. World Mycotoxin J. 2008, 1, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. An update on direct genotoxicity as molecular mechanism of ochratoxin A carcinogenicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjeba-Medjdoub, K.; Tozlovanu, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Frenette, C.; Paugh, R.J.; Manderville, R.A. Structure-activity relationship imply different mechanisms of action for ochratoxin A-mediated cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Petkova-Bocharova, T.; Chernozemsky, I.N.; Castegnaro, M. Balkan endemic nephropathy and the associated urinary tract tumours: Review on etiological causes, potential role of mycotoxins. Food Add. Contam. 2002, 19, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batuman, V. Fifty years of Balkan endemic nephropathy: Daunting questions, elusive answers. Kidney Intl. 2006, 69, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Ochratoxin A and aristolochic acid in the nephropathies and associated urothelial tract tumours development. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 2009, 60, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzzi, L.; Sinigaglia, M.; Corbo, M.R.; Campaniello, D.; Speranza, B.; Bevilacqua, A. Decontamination of ochratoxin A by yeasts: Possible approaches and factors leading to toxin removal in wine. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6555–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobashar, M.; Hummel, J.; Blank, R.; Südekum, K.H. Ochratoxin A in ruminants—A review on its degradation by by gut microbes and effects on animals. Toxins 2010, 2, 809–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitholtz-Emmanuelsson, A.; Palminger-Hallén, I.; Wohlin, P.O.; Oskarsson, A.; Hult, K.; Olsen, M. Transfer of ochratoxin A from lactating rats to their offspring: A short term study. Nat. Toxins 1993, 1, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, K.; Blaszkewicz, M.; Campos, V.; Vega, M.; Degen, G.H. Exposure of infants to ochratoxin A with breast milk. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrunhosa, L.; Paterson, R.R.M.; Venancio, A. Biodegradation of ochratoxin A for food and feed decontamination. Toxins 2010, 2, 1078–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrunhosa, L.; Ines, A.; Rodrigues, A.I.; Guimarães, A.; Pereira, V.L.; Parpot, P.; Mendes-Faia, A.; Venãncio, A. Biodegradation of ochratoxin A by Pediococcus parvulus isolated from Duoro wines. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 188, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenczi, S.; Cserhati, M.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Kukolya, J.; Szöke, Z.; Köszegi, B.; Albert, M.; Barna, T.; Mézes, M.; et al. A new ochratoxin A biodegradation strategy using Cupriavidus basilensis Or16 strain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruinink, A.; Rasonyi, T.; Sidler, C. Differences in neurotoxic effects of ochratoxin A, ochracin and ochratoxin-alpha in vitro. Nat. Toxins 1998, 6, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.P.; Gantar, M.; Gibbs, P.D.; Schmale, M.C. The zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo as a model system for identification and characterization of developmental toxins from marine and freshwater microalgae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 145, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Marquardt, R.R.; Frohlich, A.A.; Ling, Y.Z. Synthesis and structural elucidation of analogs of ochratoxin A. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Téren, J.; Varga, J.; Hamari, Z.; Rinyu, E.; Kevei, F. Immunochemical detection of ochratoxin A in black Aspergillus strains. Mycopathologia 1996, 134, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaut, A.; De Saeger, S.; Schneider, Y.J.; Larondelle, Y.; Pussemier, L.; Blank, R.; Van Peteghem, C. Liquid chromatographic methods for biotransformation studies of ochratoxin A. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abruhnosa, L.; Serra, R.; Venancio, A. Biodegradation of ochratoxin A by fungi isolated from grapes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7493–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.; Granato, M.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Keeping and Raising Zebrafish. In Zebrafish; Nüsslein-Volhard, C., Dahm, R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002; Chapter 1; pp. 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N. Teratology in Zebrafish Embryos: A Tool for Risk Assessment. Master’s Thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wiger, R.; Stormer, F.C. Effects of ochratoxins A and B on prechondrogenic mesenchymal cells from chick embryo limb buds. Toxicol. Lett. 1990, 54, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.H.; Szczech, G.M.; Purmalis, B.P. Teratogenic and toxic effects of ochratoxin A in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1976, 37, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.G.; Froelein, H.; Fellner-Feldegg, H. Inhibition of ochratoxin A teratogenesis by zearalenone and diethylstilbestrol. Fundament. Chem. Toxicol. 1983, 21, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, R.D.; Naughton, M.J.; Hayes, A.W. Prenatal effects of ochratoxin A in hamsters. Teratology 2005, 13, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union Commission Regulation No. 105/2010 (amending Regulation No. 1881/2006). 5 February 2010.
- Karlovsky, P. Biological detoxification of fungal toxins and its use in plant breeding, feed and food production. Nat. Toxin 1999, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, A.; Cramer, B.; Harrer, H.; Humpf, H.U. Structure elucidation and in vitro cytotoxicity of ochratoxin α amide, a new degradation product of ochratoxin A. Mycotoxin Res. 2015, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Madhyastha, S.; Marquardt, R.R.; Li, S.; Vodela, J.K.; Frohlich, A.A.; Kemppainen, B.W. Toxicity of ochratoxin A, its opened lactone form and several of its analogs: Structure-activitiy relationships. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1996, 137, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haq, M.; Gonzalez, N.; Mintz, K.; Jaja-Chimedza, A.; De Jesus, C.L.; Lydon, C.; Welch, A.Z.; Berry, J.P. Teratogenicity of Ochratoxin A and the Degradation Product, Ochratoxin α, in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryo Model of Vertebrate Development. Toxins 2016, 8, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8020040
Haq M, Gonzalez N, Mintz K, Jaja-Chimedza A, De Jesus CL, Lydon C, Welch AZ, Berry JP. Teratogenicity of Ochratoxin A and the Degradation Product, Ochratoxin α, in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryo Model of Vertebrate Development. Toxins. 2016; 8(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaq, Mehreen, Nelson Gonzalez, Keenan Mintz, Asha Jaja-Chimedza, Christopher Lawrence De Jesus, Christina Lydon, Aaron Z. Welch, and John P. Berry. 2016. "Teratogenicity of Ochratoxin A and the Degradation Product, Ochratoxin α, in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryo Model of Vertebrate Development" Toxins 8, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8020040
APA StyleHaq, M., Gonzalez, N., Mintz, K., Jaja-Chimedza, A., De Jesus, C. L., Lydon, C., Welch, A. Z., & Berry, J. P. (2016). Teratogenicity of Ochratoxin A and the Degradation Product, Ochratoxin α, in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryo Model of Vertebrate Development. Toxins, 8(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8020040