A Proteomics and Transcriptomics Investigation of the Venom from the Barychelid Spider Trittame loki (Brush-Foot Trapdoor)
Abstract
1. Introduction
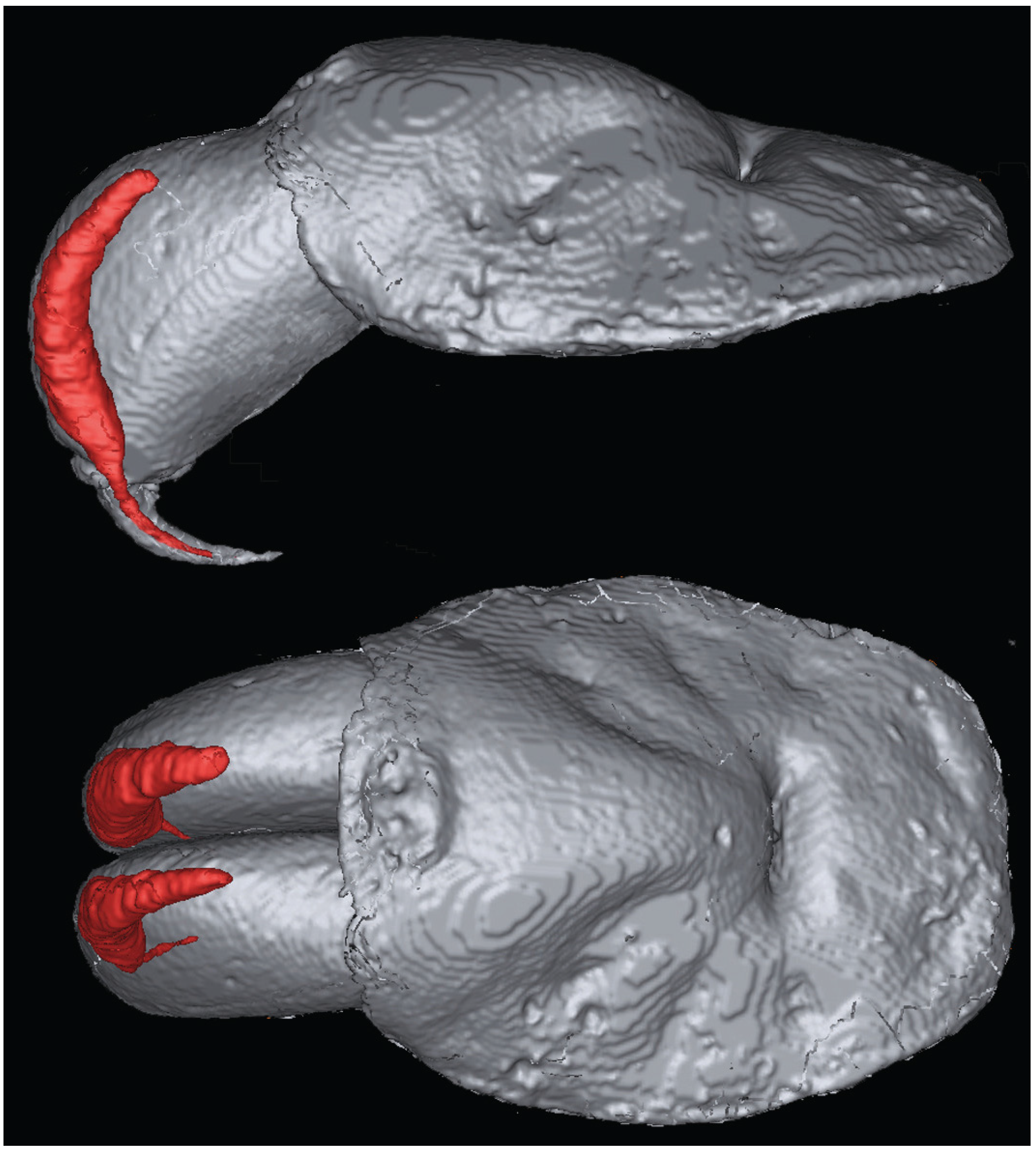
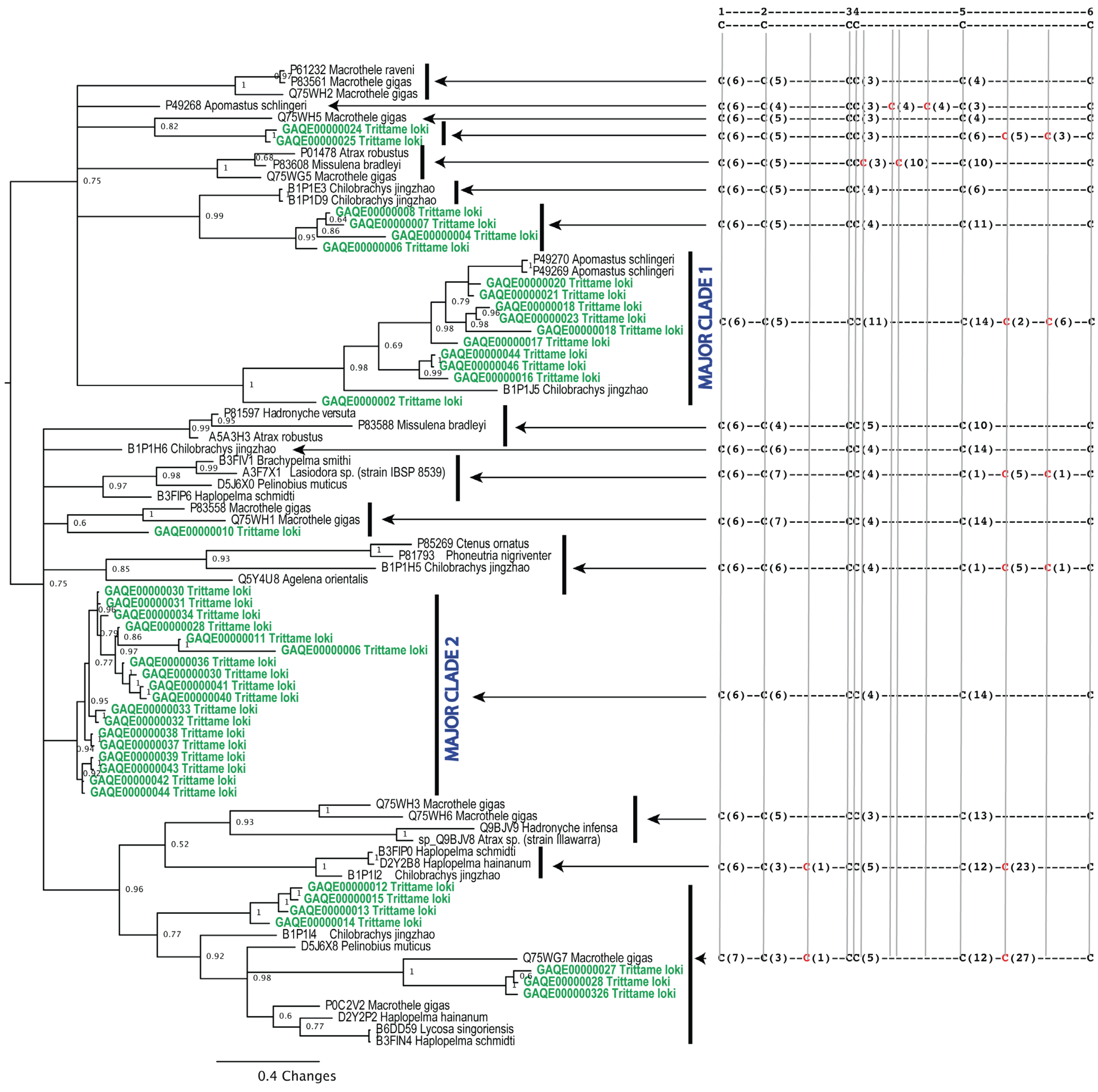
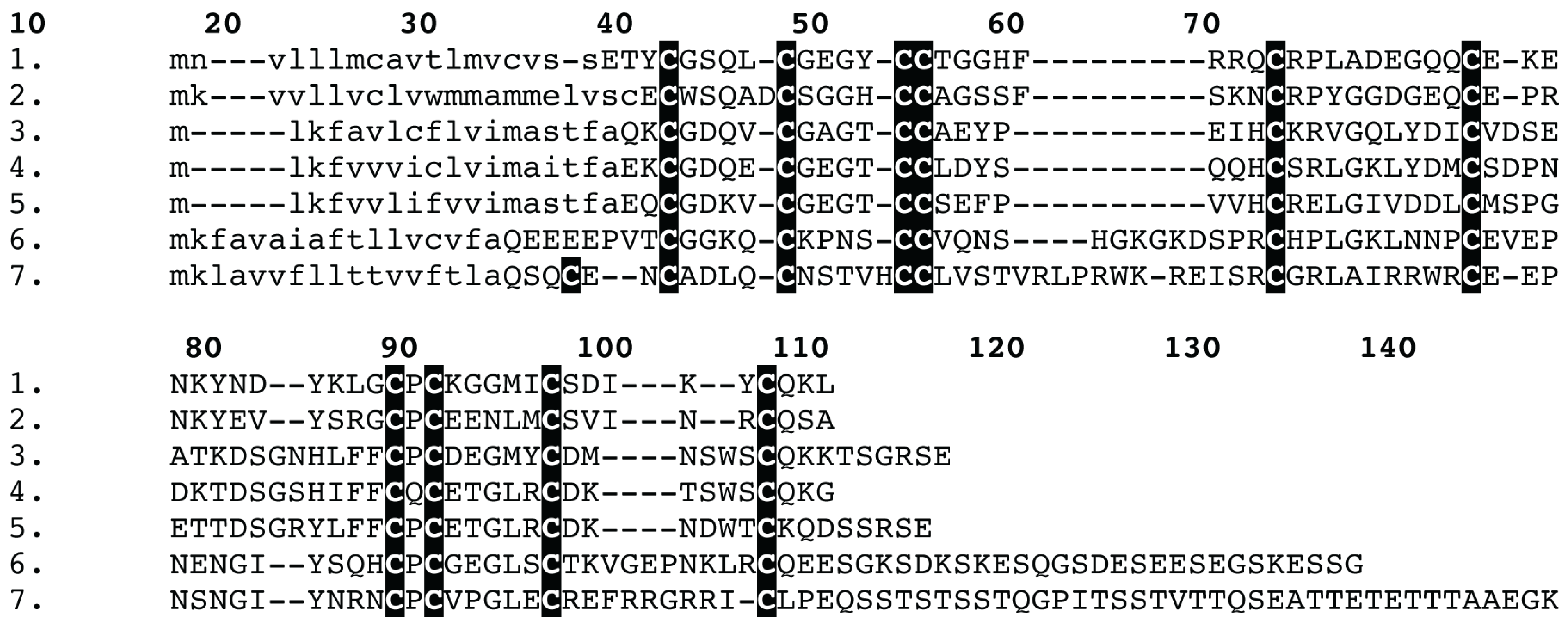
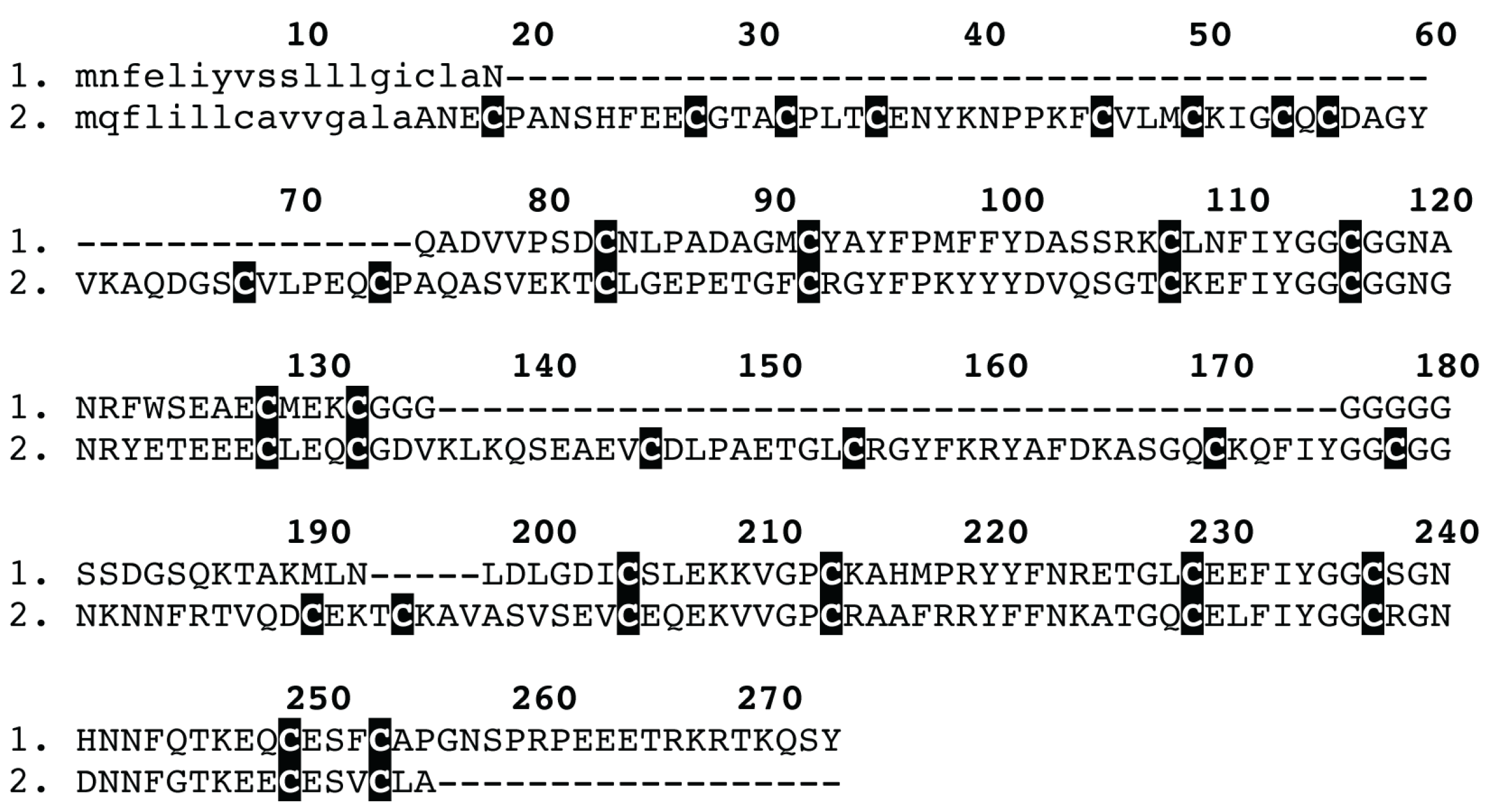
2. Results and Discussion


| SLAC a | FEL b | REL c | MEME d | FUBAR e | Integrative f | BSR g | PAML h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLAC + FEL + REL + MEME | M8 | M2a | ||||||||
| Clade I | ω > 1 i | 0 | 2 | 22 | 2 sites | 13 | 22 | 3 | 17 | 12 |
| ω < 1 j | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | (9 + 8) | (6 + 6) | |||
| ω = | 1.41 | - | 1.62 | - | - | 1.81 | 1.81 | |||
| Clade II | ω > 1 i | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 sites | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| ω < 1 j | 3 | 11 | 0 | 14 | 15 | (1 + 4) | (1 + 2) | |||
| ω = | 0.42 | - | 0.47 | - | - | 0.67 | 0.67 | |||
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Specimens
3.2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
3.3. Transcriptome Construction
3.4. Bioinformatics
3.4.1. Phylogenetics
3.4.2. Test for Recombination
3.4.3. Selection Analyses
3.5. Proteomics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bond, J.E.; Hendrixson, B.E.; Hamilton, C.A.; Hedin, M.A. A reconsideration of the classification of the spider infraorder Mygalomorphae (Arachnida: Araneae) based on three nuclear genes and morphology. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.F. The wonderful world of spiders: Preface to the special Toxicon issue on spider venoms. Toxicon 2004, 43, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, N.I. The poverty of the phylocode: A reply to de Queiroz and Donoghue. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego-García, E.; Peigneur, S.; Waelkens, E.; Debaveye, S.; Tytgat, J. Venom components from Citharischius crawshayi spider (Family Theraphosidae): Exploring transcriptome, venomics, and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2799–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, V.; King, G. The neurotoxic mode of action of venoms from the spider family Theraphosidae. In Spider Ecophysiol; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Xu, D.; Tao, H.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liang, S. Molecular diversification of peptide toxins from the tarantula Haplopelma hainanum (Ornithoctonus hainana) venom based on transcriptomic, peptidomic, and genomic analyses. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 2550–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Jin, Q.; Tang, X.; Hu, W.; Cao, R.; Yang, S.; Xiong, J.; Xie, C.; Xie, J.; Liang, S. Proteomic and peptidomic characterization of the venom from the Chinese bird spider, Ornithoctonus huwena Wang. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 2792–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, V.; Wood, D.L.; Newell, F.; Chaumeil, P.-A.; Kaas, Q.; Binford, G.J.; Nicholson, G.M.; Gorse, D.; King, G.F. ArachnoServer 2.0, an updated online resource for spider toxin sequences and structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D653–D657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.F.; Hardy, M.C. Spider-venom peptides: Structure, pharmacology, and potential for control of insect pests. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn-Nentwig, L.; Stöcklin, R.; Nentwig, W. Venom composition and strategies in spiders: Is everything possible? Adv. Insect Physiol. Spider Physiol. Behav. 2011, 40, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klint, J.K.; Senff, S.; Rupasinghe, D.B.; Er, S.Y.; Herzig, V.; Nicholson, G.M.; King, G.F. Spider-venom peptides that target voltage-gated sodium channels: Pharmacological tools and potential therapeutic leads. Toxicon 2012, 60, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selden, P.A.; Penney, D. Fossil spiders. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2010, 85, 171–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, N.J.; Senff, S.; Jensen, J.E.; Er, S.Y.; Herzig, V.; Rash, L.D.; King, G.F. Spider-venom peptides as therapeutics. Toxins 2010, 2, 2851–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windley, M.J.; Herzig, V.; Dziemborowicz, S.A.; Hardy, M.C.; King, G.F.; Nicholson, G.M. Spider-venom peptides as bioinsecticides. Toxins 2012, 4, 191–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, T.H.; Wang, X.H.; Smith, R.; Connor, M.; Christie, M.J.; Nicholson, G.M.; King, G.F. Isolation of a funnel-web spider polypeptide with homology to mamba intestinal toxin 1 and the embryonic head inducer Dickkopf-1. Toxicon 2000, 38, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Wilson, D.T.R.; Kuruppu, S.; Korsinczky, M.L.J.; Hedrick, J.; Pang, L.; Szeto, T.; Hodgson, W.C.; Alewood, P.F.; Nicholson, G.M. Discovery of an MIT-like atracotoxin family: Spider venom peptides that share sequence homology but not pharmacological properties with AVIT family proteins. Peptides 2005, 26, 2412–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotz, S.; Arnold, R.; Sebastian-Leon, P.; Martin-Rodriguez, S.; Tischler, P.; Jehl, M.A.; Dopazo, J.; Rattei, T.; Conesa, A. B2G-FAR, a species-centered GO annotation repository. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S. Blast2GO: A comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int. J. Plant Genomics 2008, 2008, 619832:1–619832:12. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. The effect of recombination on the accuracy of phylogeny estimation. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 396–402. [Google Scholar]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Frost, S.D.W.; Muse, S.V. HyPhy: Hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Posada, D.; Gravenor, M.B.; Woelk, C.H.; Frost, S.D.W. Automated phylogenetic detection of recombination using a genetic algorithm. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, N.; Yang, Z. A codon-based model of nucleotide substitution for protein-coding DNA sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1994, 11, 725–736. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z. Likelihood ratio tests for detecting positive selection and application to primate lysozyme evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.; Yang, Z. Likelihood models for detecting positively selected amino acid sites and applications to the HIV-1 envelope gene. Genetics 1998, 148, 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wong, W.S.W.; Nielsen, R. Bayes empirical bayes inference of amino acid sites under positive selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Frost, S.D.W. Not so different after all: A comparison of methods for detecting amino acid sites under selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1208–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Pond, S.L.K. Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, S.; Johnson, J.; Smith, M.J.; Crandall, K.A.; McClellan, D.A. TreeSAAP: Selection on amino acid properties using phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 671–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delport, W.; Poon, A.F.; Frost, S.D.; Pond, S.L.K. Datamonkey 2010: A suite of phylogenetic analysis tools for evolutionary biology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2455–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Murrell, B.; Fourment, M.; Frost, S.D.W.; Delport, W.; Scheffler, K. A random effects branch-site model for detecting episodic diversifying selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Harrison, R.A.; Renjifo, C.; Wuster, W. Domain loss facilitates accelerated evolution and neofunctionalization of duplicate snake venom metalloproteinase toxin genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2637–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, V.J. Inventing an arsenal: Adaptive evolution and neofunctionalization of snake venom phospholipase A2 genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunagar, K.; Johnson, W.E.; O’Brien, S.J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Evolution of CRISPs associated with toxicoferan-reptilian venom and mammalian reproduction. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1807–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, D.H.W.; Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Ali, S.A.; Alagon, A.C.; Ruder, T.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Pineda Gonzalez, S.; King, G.F.; Jones, A.; et al. Dracula’s children: Molecular evolution of vampire bat venom. J. Proteomics 2013, 89, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Files
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Undheim, E.A.B.; Sunagar, K.; Herzig, V.; Kely, L.; Low, D.H.W.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Jones, A.; Kurniawan, N.; King, G.F.; Ali, S.A.; et al. A Proteomics and Transcriptomics Investigation of the Venom from the Barychelid Spider Trittame loki (Brush-Foot Trapdoor). Toxins 2013, 5, 2488-2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5122488
Undheim EAB, Sunagar K, Herzig V, Kely L, Low DHW, Jackson TNW, Jones A, Kurniawan N, King GF, Ali SA, et al. A Proteomics and Transcriptomics Investigation of the Venom from the Barychelid Spider Trittame loki (Brush-Foot Trapdoor). Toxins. 2013; 5(12):2488-2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5122488
Chicago/Turabian StyleUndheim, Eivind A. B., Kartik Sunagar, Volker Herzig, Laurence Kely, Dolyce H. W. Low, Timothy N. W. Jackson, Alun Jones, Nyoman Kurniawan, Glenn F. King, Syed A. Ali, and et al. 2013. "A Proteomics and Transcriptomics Investigation of the Venom from the Barychelid Spider Trittame loki (Brush-Foot Trapdoor)" Toxins 5, no. 12: 2488-2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5122488
APA StyleUndheim, E. A. B., Sunagar, K., Herzig, V., Kely, L., Low, D. H. W., Jackson, T. N. W., Jones, A., Kurniawan, N., King, G. F., Ali, S. A., Antunes, A., Ruder, T., & Fry, B. G. (2013). A Proteomics and Transcriptomics Investigation of the Venom from the Barychelid Spider Trittame loki (Brush-Foot Trapdoor). Toxins, 5(12), 2488-2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5122488










