Neurotoxicity of Sri Lankan Krait (Bungarus ceylonicus) and Common Krait (Bungarus caeruleus) Venoms and Their Neutralisation by Commercial Antivenoms In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
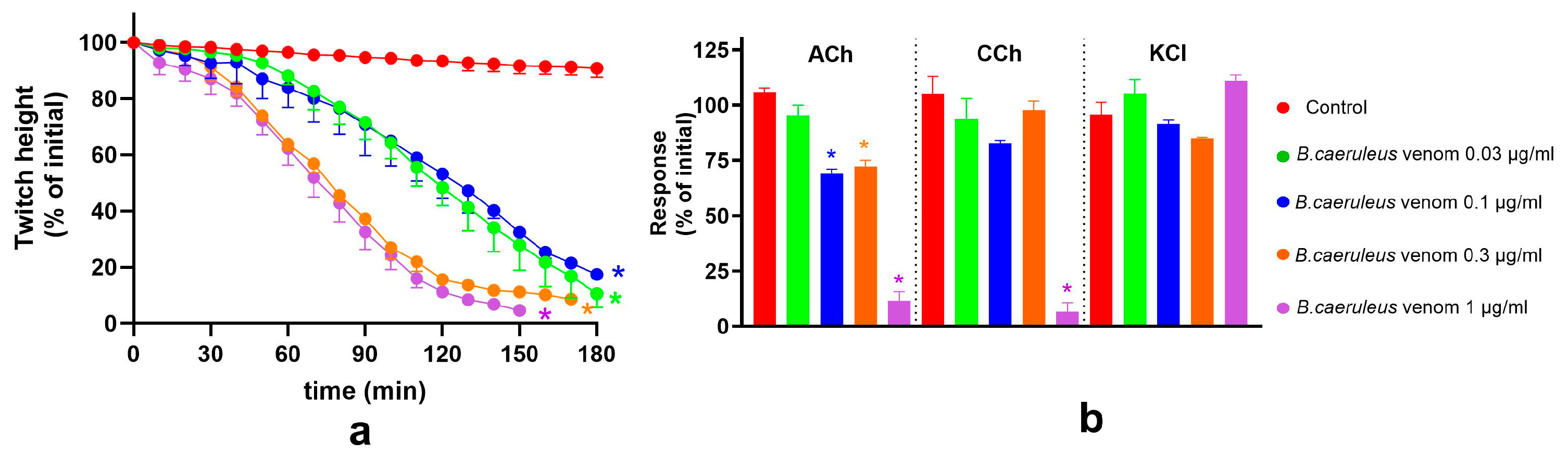
2.1. Concentration-Dependent Neurotoxicity of B. ceylonicus and B. caeruleus Venoms
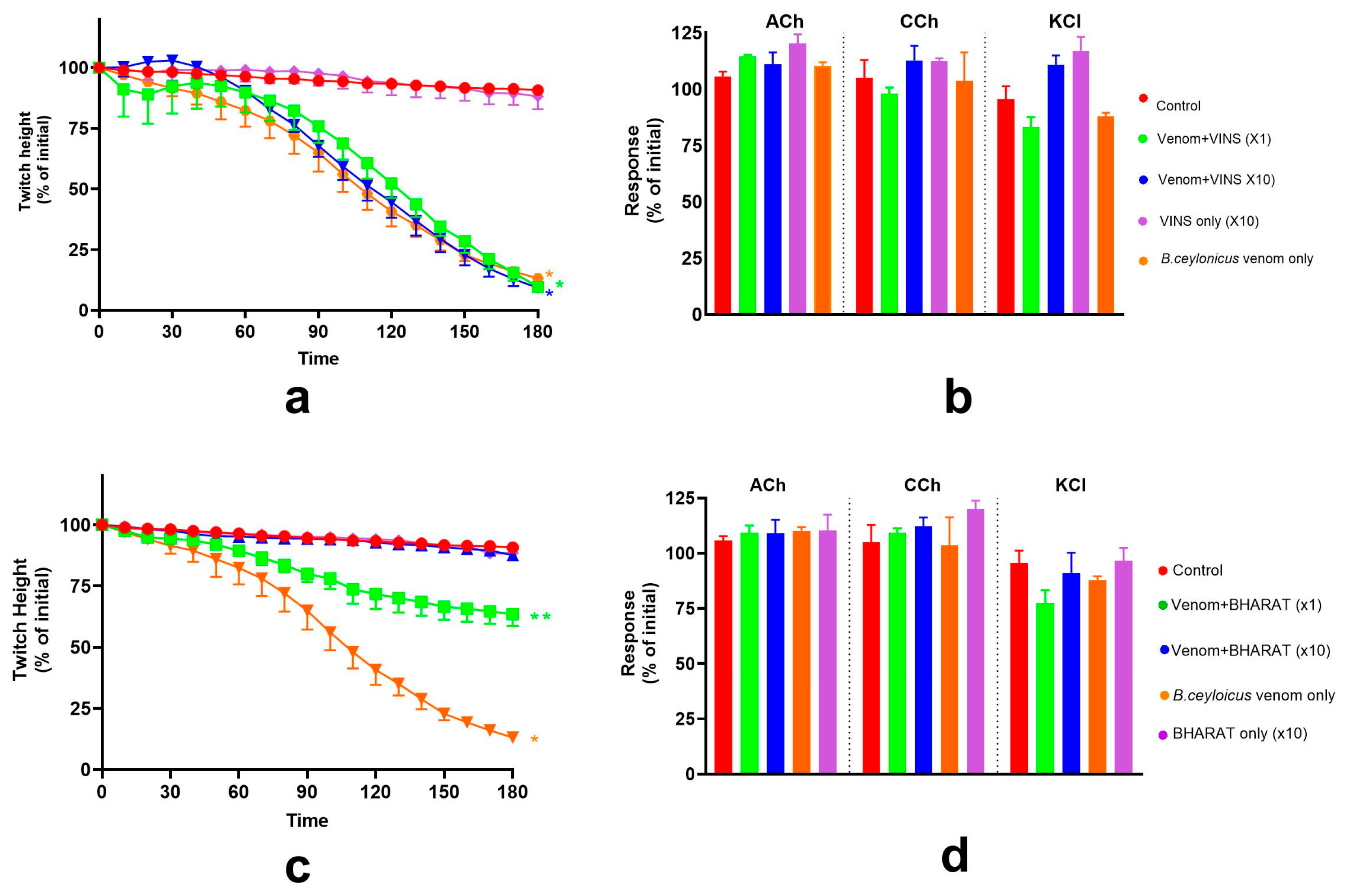
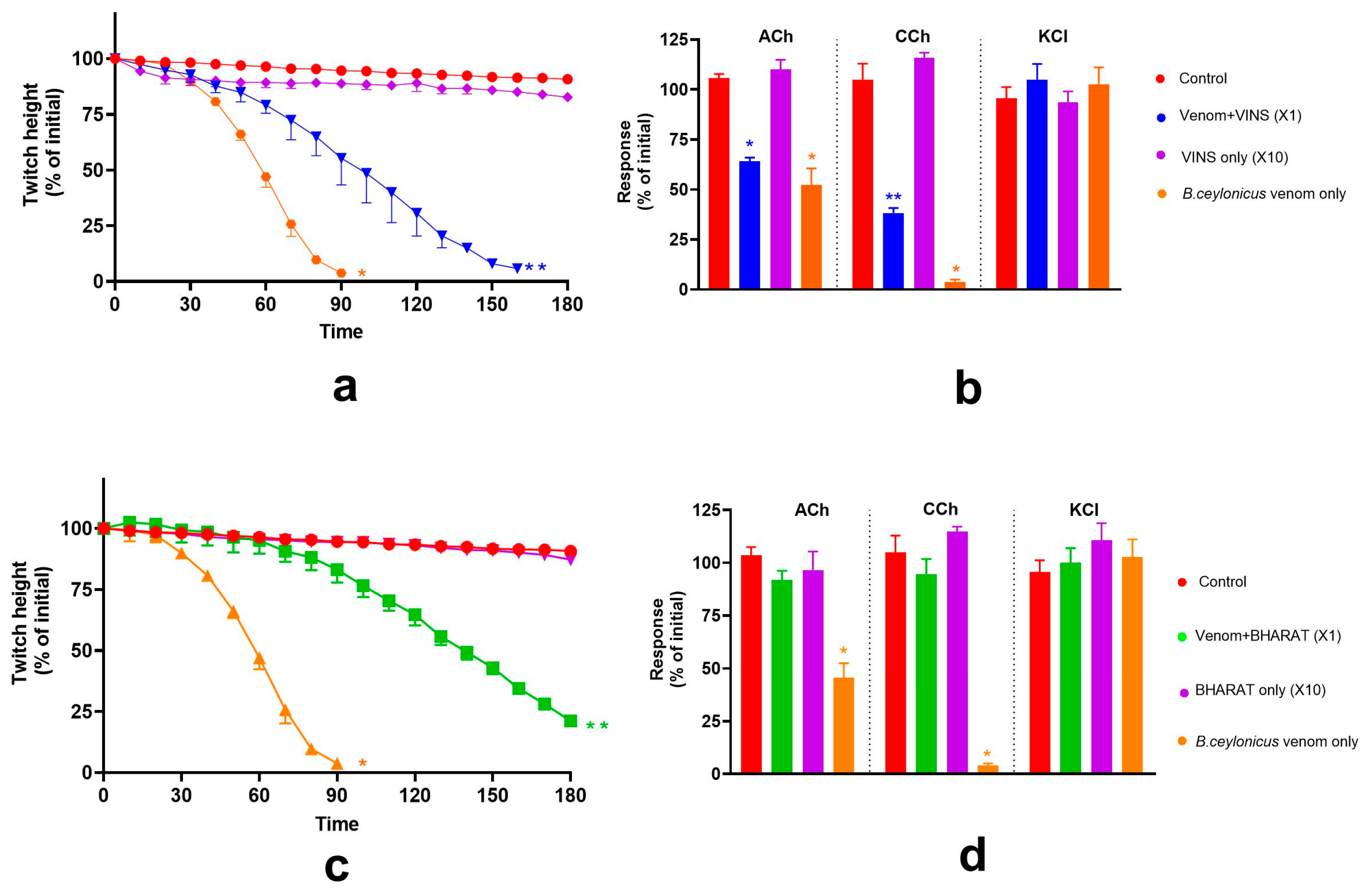
2.2. Effect of Indian Polyvalent Antivenoms on the Pre-Synaptic and Post-Synaptic Activity of B. ceylonicus Venom
2.2.1. Pre-Synaptic Activity of B. ceylonicus Venom
2.2.2. Post-Synaptic Activity of B. ceylonicus Venom
2.3. Effect of Thai Banded Krait Antivenom and Australian Polyvalent Antivenom on the Pre-Synaptic and Post-Synaptic Activity of B. ceylonicus Venom
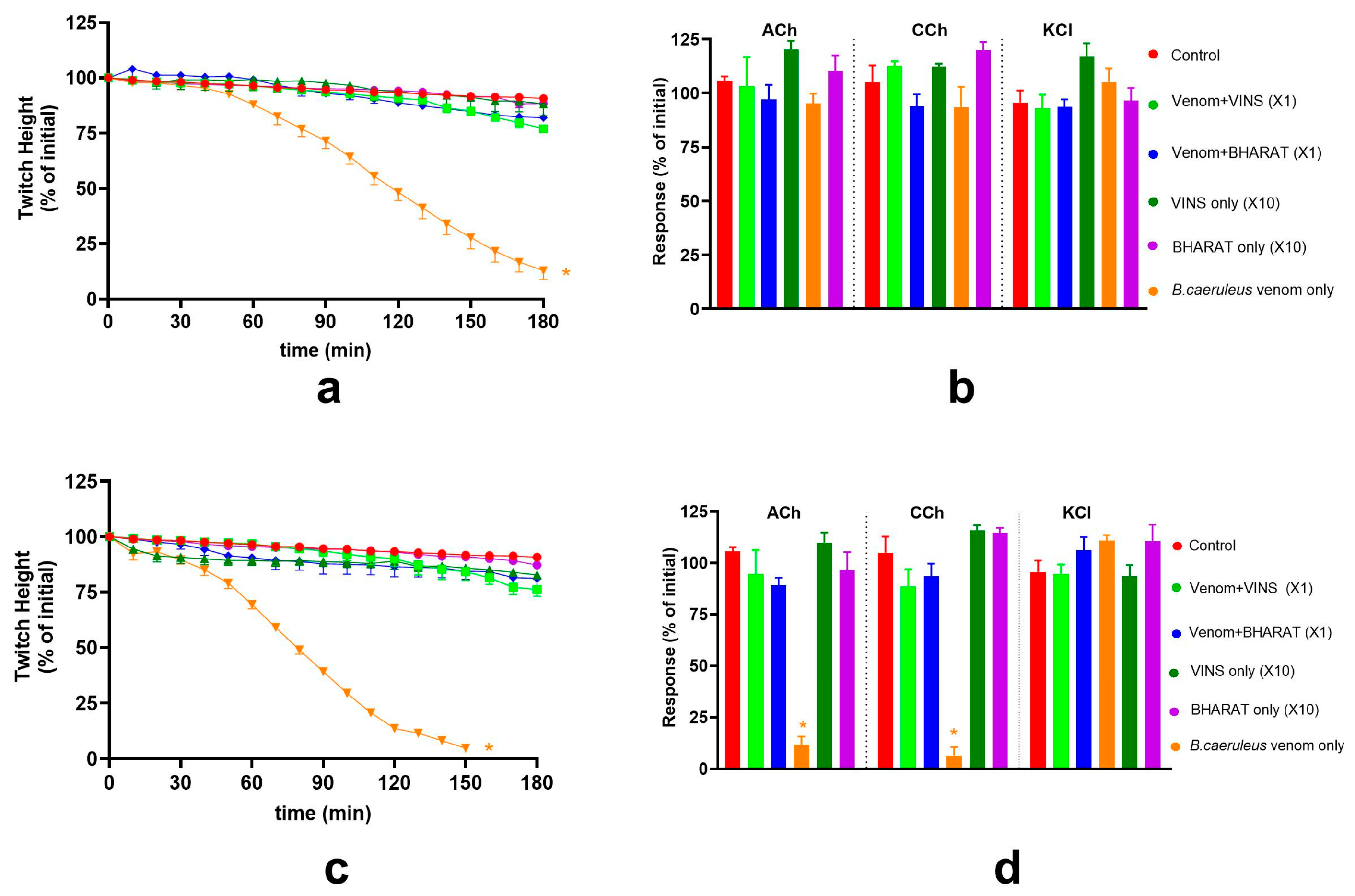
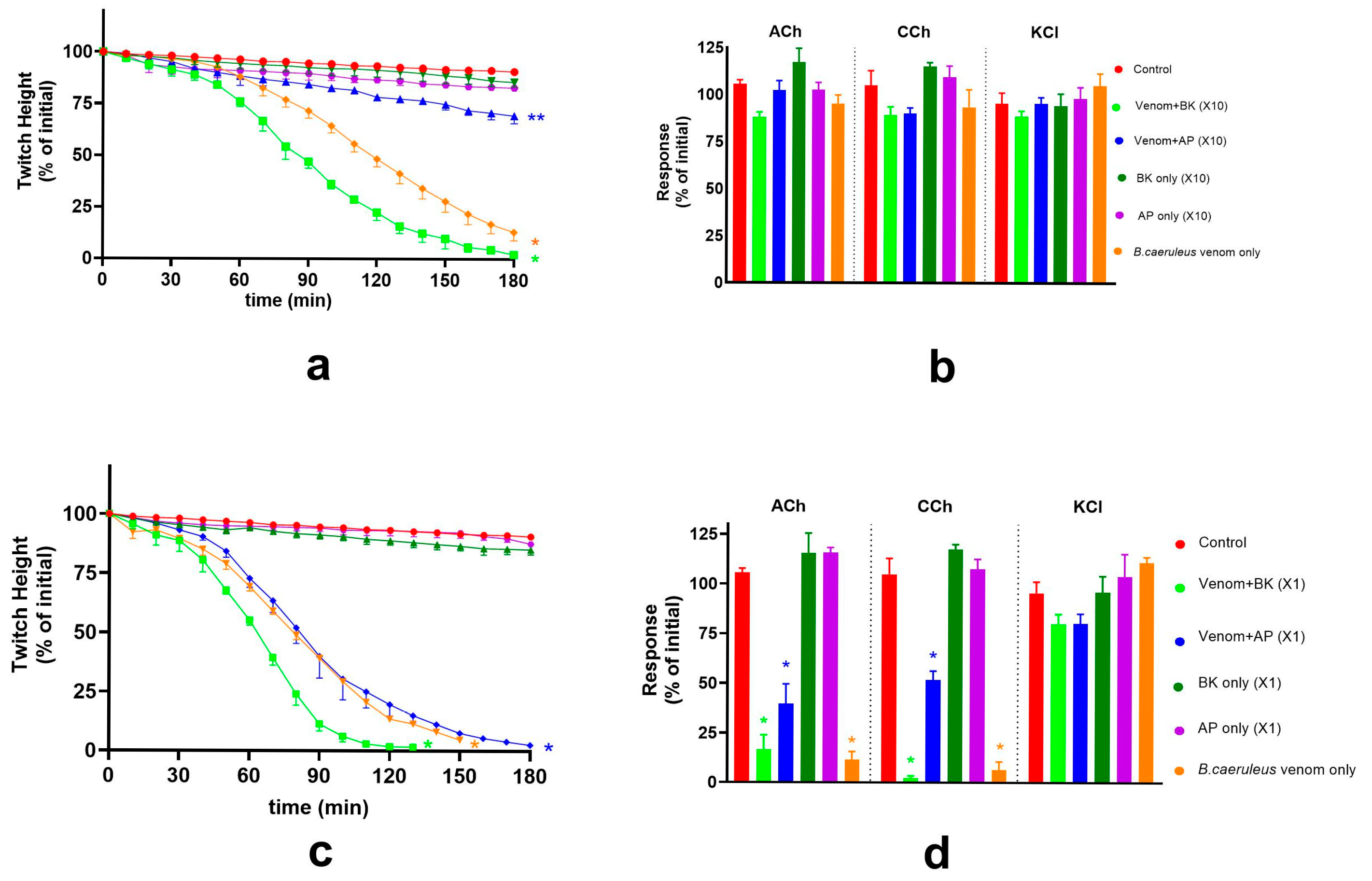
2.4. Effect of Indian Polyvalent Antivenoms on the Pre-Synaptic and Post-Synaptic Activity of B. caeruleus Venom
2.5. Effect of Thai Banded Krait and Australian Polyvalent Antivenoms on the Pre-Synaptic and Post-Synaptic Activity of B. caeruleus Venom
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Venoms and Antivenoms
5.2. Chick Biventer Cervicis Nerve-Muscle Preparation
5.3. Experimental Design
5.4. Interpretations and Definitions
5.4.1. Neurotoxicity
5.4.2. Pre-Synaptic vs. Post-Synaptic Neurotoxicity
5.4.3. Data Analysis and Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
| NMJ | Neuromuscular junction |
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| CCh | Carbachol |
| KCl | Potassium Chloride |
| NaCl | Sodium Chloride |
| MgSO4 | Magnesium Sulphate |
| KH2PO4 | Potassium dihydrogen phosphate |
| CaCl2 | Calcium Chloride |
| NaHCO3 | Sodium hydrogen carbonate |
| O2 | Oxygen |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
References
- Alirol, E.; Sharma, S.K.; Bawaskar, H.S.; Kuch, U.; Chappuis, F. Snake Bite in South Asia: A Review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blessmann, J.; Kreuels, B. Urgent Administration of Antivenom Following Proven Krait Bites in Southeast Asia Irrespective of Neurotoxic Symptoms. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.; Hodgson, W.C.; Isbister, G.K. Antivenom for Neuromuscular Paralysis Resulting from Snake Envenoming. Toxins 2017, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasarnpun, S.; Walsh, J.; Awad, S.S.; Harris, J.B. Envenoming Bites by Kraits: The Biological Basis of Treatment-Resistant Neuromuscular Paralysis. Brain 2005, 128, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasarnpun, S.; Walsh, J.; Harris, J.B. Beta-Bungarotoxin-Induced Depletion of Synaptic Vesicles at the Mammalian Neuromuscular Junction. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigoni, M.; Paoli, M.; Milanesi, E.; Caccin, P.; Rasola, A.; Bernardi, P.; Montecucco, C. Snake Phospholipase A2 Neurotoxins Enter Neurons, Bind Specifically to Mitochondria, and Open Their Transition Pores. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34013–34020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, C.M.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. Alpha Neurotoxins. Toxicon 2013, 66, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Armstrong, B.C.; Rash, L.D.; Hodgson, W.C.; Isbister, G.K. Defining the Role of Post-Synaptic α-Neurotoxins in Paralysis Due to Snake Envenoming in Humans. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4465–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; De Alwis, T.; Wijesekara, S.; Somaweera, R. Minimising Misidentification of Common Medically Important Snakes of Sri Lanka in the Hospital Setting. Anuradhapura Med. J. 2023, 17, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, A.M.F.; Tan, C.H.; Ariaranee, G.C.; Quraishi, N.; Tan, N.H. Venomics of Bungarus Caeruleus (Indian Krait): Comparable Venom Profiles, Variable Immunoreactivities among Specimens from Sri Lanka, India and Pakistan. J. Proteom. 2017, 164, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snakebite Expert Committee of Sri Lanka Medical Association. SLMA Guidelines for the Management of Snakebite in Hospital—2021; Snakebite Expert Committee of Sri Lanka Medical Association: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Namal Rathnayaka, R.M.M.K.; Nishanthi Ranathunga, P.E.A.; Kularatne, S.A.M. Paediatric Cases of Ceylon Krait (Bungarus ceylonicus) Bites and Some Similar Looking Non-Venomous Snakebites in Sri Lanka: Misidentification and Antivenom Administration. Toxicon 2021, 198, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kularatne, S.A.M.; Colombage, A.; de Silva, A.; Weerasinghe, V.; Rathnayaka, R.M.M.K.N. Acute Neuromuscular Paralysis, Rhabdomyolysis and Long Lasting Neurological Deficits in Ceylon Krait (Bungarus Ceylonicus) Bites: Two Authentic Cases from a Serpentarium in Sri Lanka. Toxicon X 2019, 4, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, A.; Mendis, S.; Warrell, D.A. Neurotoxic Envenoming by the Sri Lankan Krait (Bungarus ceylonicus) Complicated by Traditional Treatment and a Reaction to Antivenom. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 87, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Maduwage, K.; Sedgwick, M.; Pilapitiya, S.; Weerawansa, P.; Dahanayaka, N.J.; Buckley, N.A.; Johnston, C.; Siribaddana, S.; Isbister, G.K. Neuromuscular Effects of Common Krait (Bungarus caeruleus) Envenoming in Sri Lanka. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnayaka, R.M.M.K.N.; Kularatne, S.A.M.; Kumarasinghe, K.D.M.; Jeganadan, K.; Ranathunga, P.E.A.N. Two Rare Case Reports of Confirmed Ceylon Krait (Bungarus ceylonicus) Envenoming in Sri Lanka. Toxicon 2017, 127, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalugama, C.; Gawarammana, I.B. Confirmed Ceylon Krait (Bungarus ceylonicus) Envenoming in Sri Lanka Resulting in Neuromuscular Paralysis: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduwage, K.; Silva, A.; O’Leary, M.A.; Hodgson, W.C.W.C.; Isbister, G.K. Efficacy of Indian Polyvalent Snake Antivenoms against Sri Lankan Snake Venoms: Lethality Studies or Clinically Focussed in Vitro Studies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Hodgson, W.C.; Isbister, G.K. Cross-Neutralisation of In Vitro Neurotoxicity of Asian and Australian Snake Neurotoxins and Venoms by Different Antivenoms. Toxins 2016, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Isbister, G.K. Current Research into Snake Antivenoms, Their Mechanisms of Action and Applications. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhushani, U.; Isbister, G.K.; Tasoulis, T.; Hodgson, W.C.; Silva, A. In-Vitro Neutralization of the Neurotoxicity of Coastal Taipan Venom by Australian Polyvalent Antivenom: The Window of Opportunity. Toxins 2020, 12, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Lingam, T.M.C.; Tan, K.Y. Varespladib (LY315920) Rescued Mice from Fatal Neurotoxicity Caused by Venoms of Five Major Asiatic Kraits (Bungarus Spp.) in an Experimental Envenoming and Rescue Model. Acta Trop. 2022, 227, 106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Venom Concentration | Extent of Twitch Inhibition | B. ceylonicus (n = 3–6) Mean +/− SD min | B. caeruleus (n = 3–6) Mean +/− SD min | Comparison (Unpaired t-test, p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.03 μg/mL | t50 | 115.3 (5.0) | 123.0 (8.7) | 0.2576 |
| t90 | N/A | N/A | ||
| 0.1 μg/mL | t50 | 94.0 (8.9) | 119.0 (10.0) | 0.0326 |
| t90 | 149.3 (1.2) | N/A | ||
| 0.3 μg/mL | t50 | 76.3 (6.7) | 74.7 (0.6) | 0.6881 |
| t90 | 118.0 (1.7) | 150.7 (1.2) | <0.0001 | |
| 0.1 μg/mL | t50 | 58.7 (4.7) | 71.0 (8.0) | 0.0830 |
| t90 | 79.7 (4.0) | 129.3 (2.1) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galappaththige, J.; Isbister, G.K.; Maduwage, K.; Hodgson, W.C.; Silva, A. Neurotoxicity of Sri Lankan Krait (Bungarus ceylonicus) and Common Krait (Bungarus caeruleus) Venoms and Their Neutralisation by Commercial Antivenoms In Vitro. Toxins 2025, 17, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090439
Galappaththige J, Isbister GK, Maduwage K, Hodgson WC, Silva A. Neurotoxicity of Sri Lankan Krait (Bungarus ceylonicus) and Common Krait (Bungarus caeruleus) Venoms and Their Neutralisation by Commercial Antivenoms In Vitro. Toxins. 2025; 17(9):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090439
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalappaththige, Jithmi, Geoffrey K. Isbister, Kalana Maduwage, Wayne C. Hodgson, and Anjana Silva. 2025. "Neurotoxicity of Sri Lankan Krait (Bungarus ceylonicus) and Common Krait (Bungarus caeruleus) Venoms and Their Neutralisation by Commercial Antivenoms In Vitro" Toxins 17, no. 9: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090439
APA StyleGalappaththige, J., Isbister, G. K., Maduwage, K., Hodgson, W. C., & Silva, A. (2025). Neurotoxicity of Sri Lankan Krait (Bungarus ceylonicus) and Common Krait (Bungarus caeruleus) Venoms and Their Neutralisation by Commercial Antivenoms In Vitro. Toxins, 17(9), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090439






