A New Kv1.3 Channel Blocker from the Venom of the Ant Tetramorium bicarinatum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
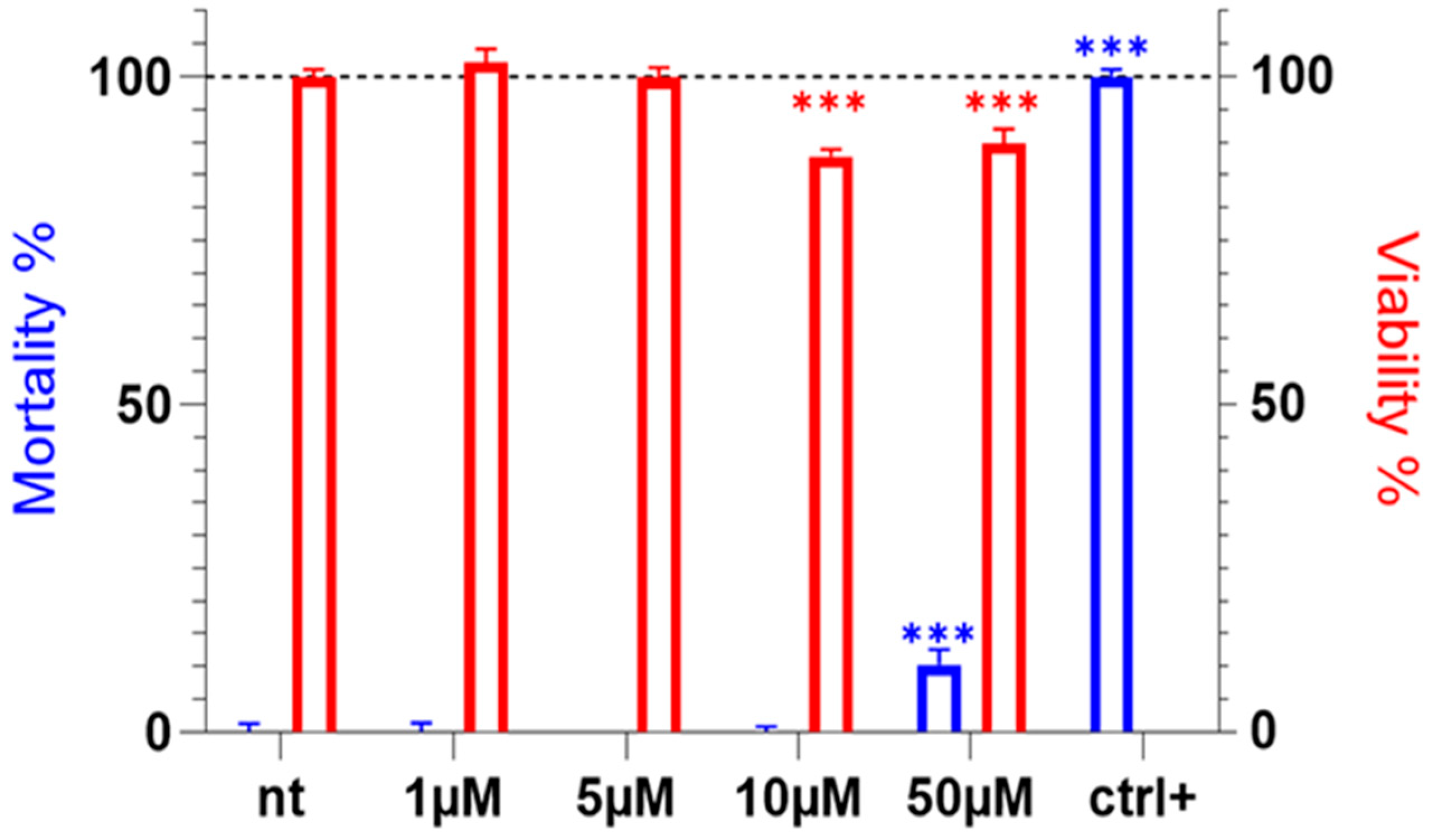
2.1. Tb11a Exhibits No Cytotoxic Activity in HEK293T
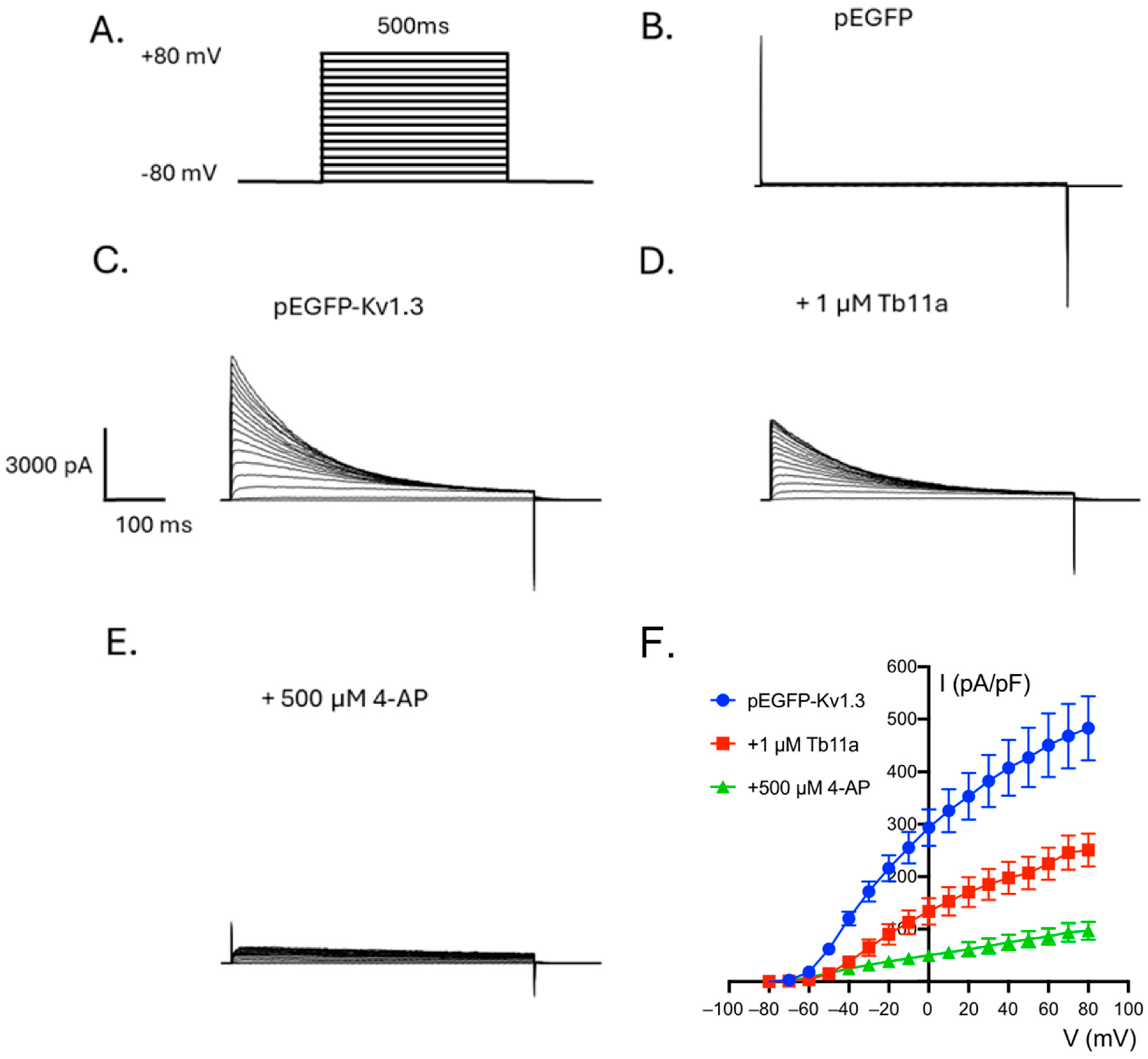
2.2. Tb11a Is a Kv1.3 Channel Blocker
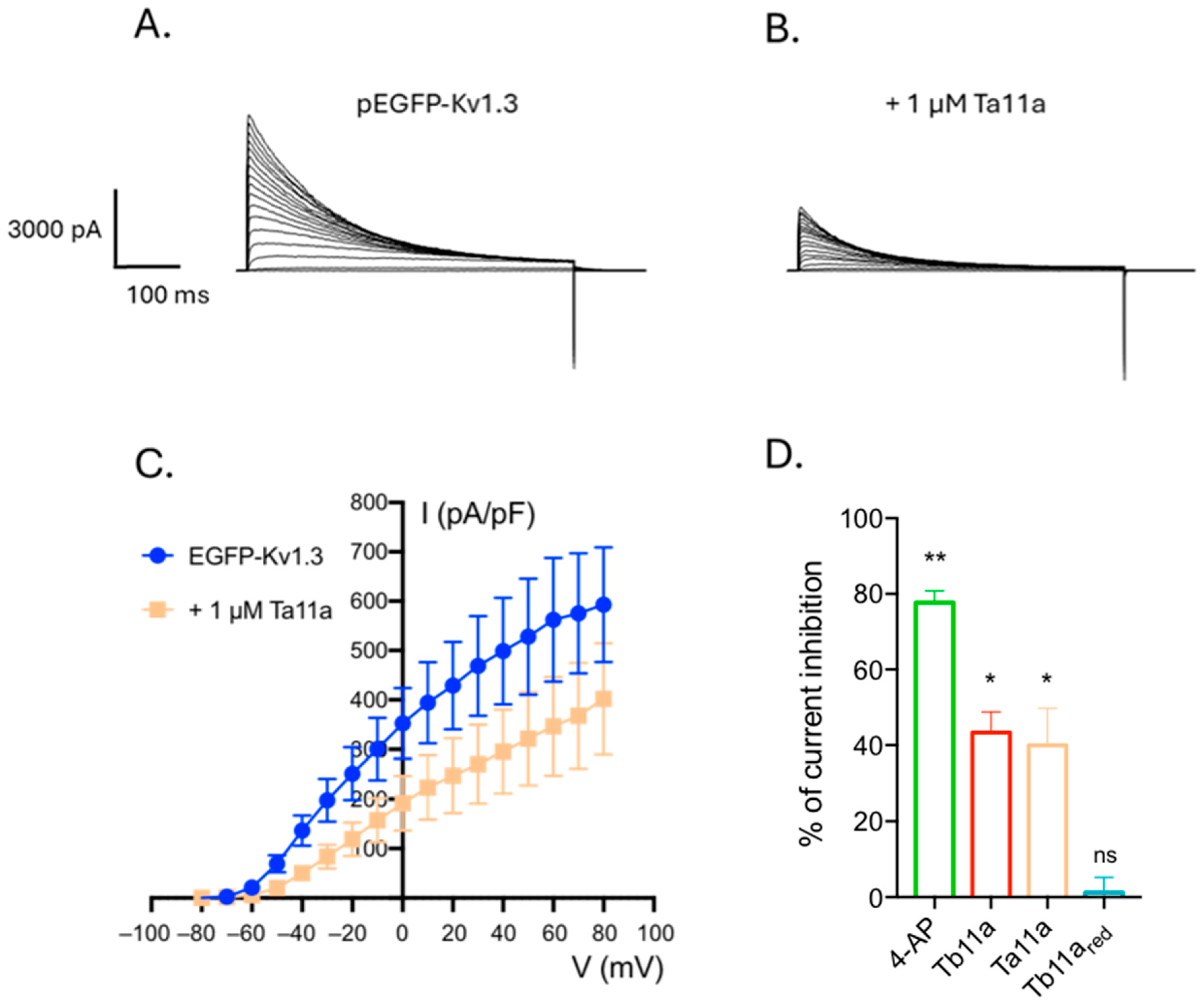
2.3. Ta11a, an Analog of Tb11a also Affects Kv1.3
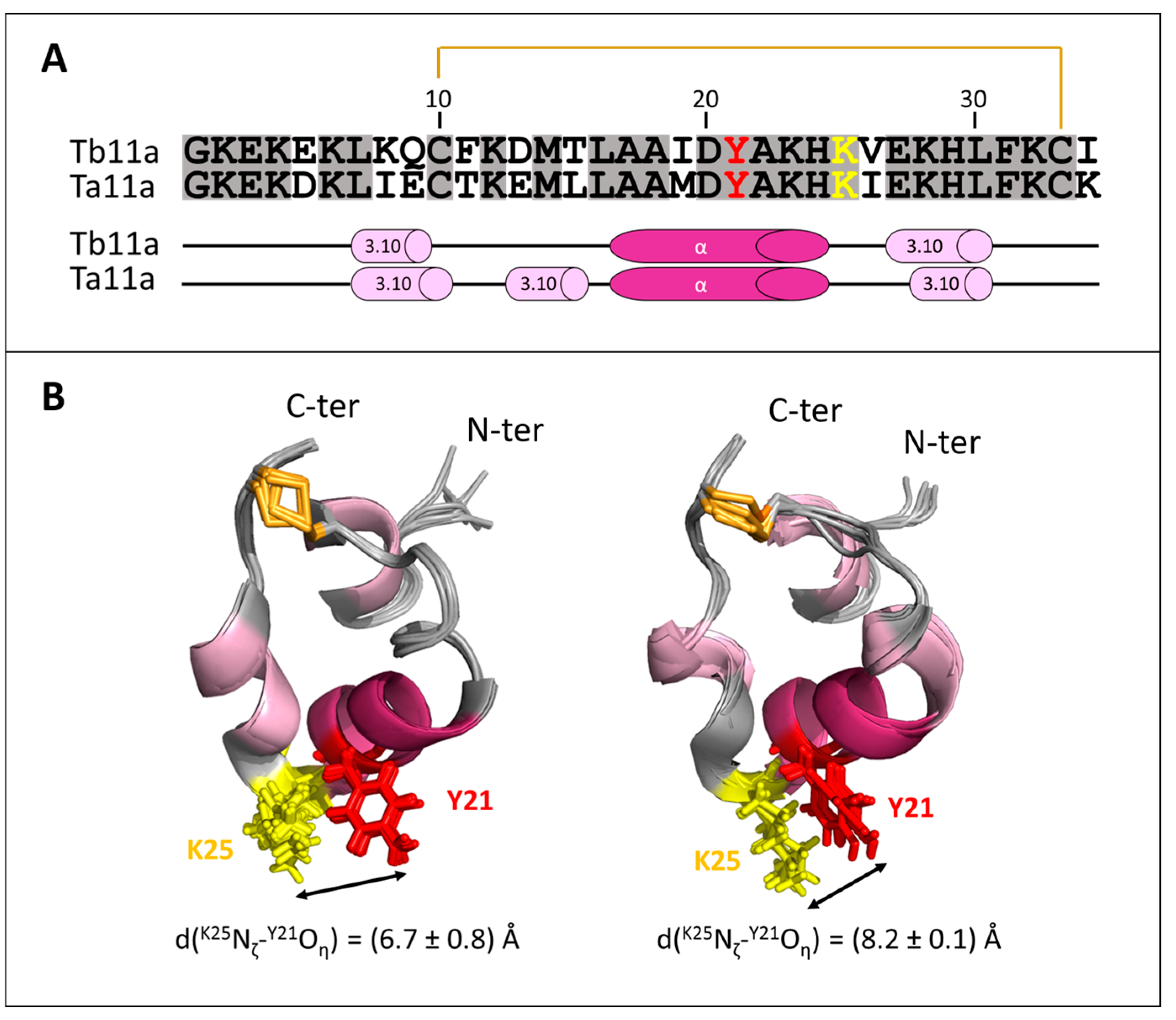
2.4. Structure Analysis of Ta11a
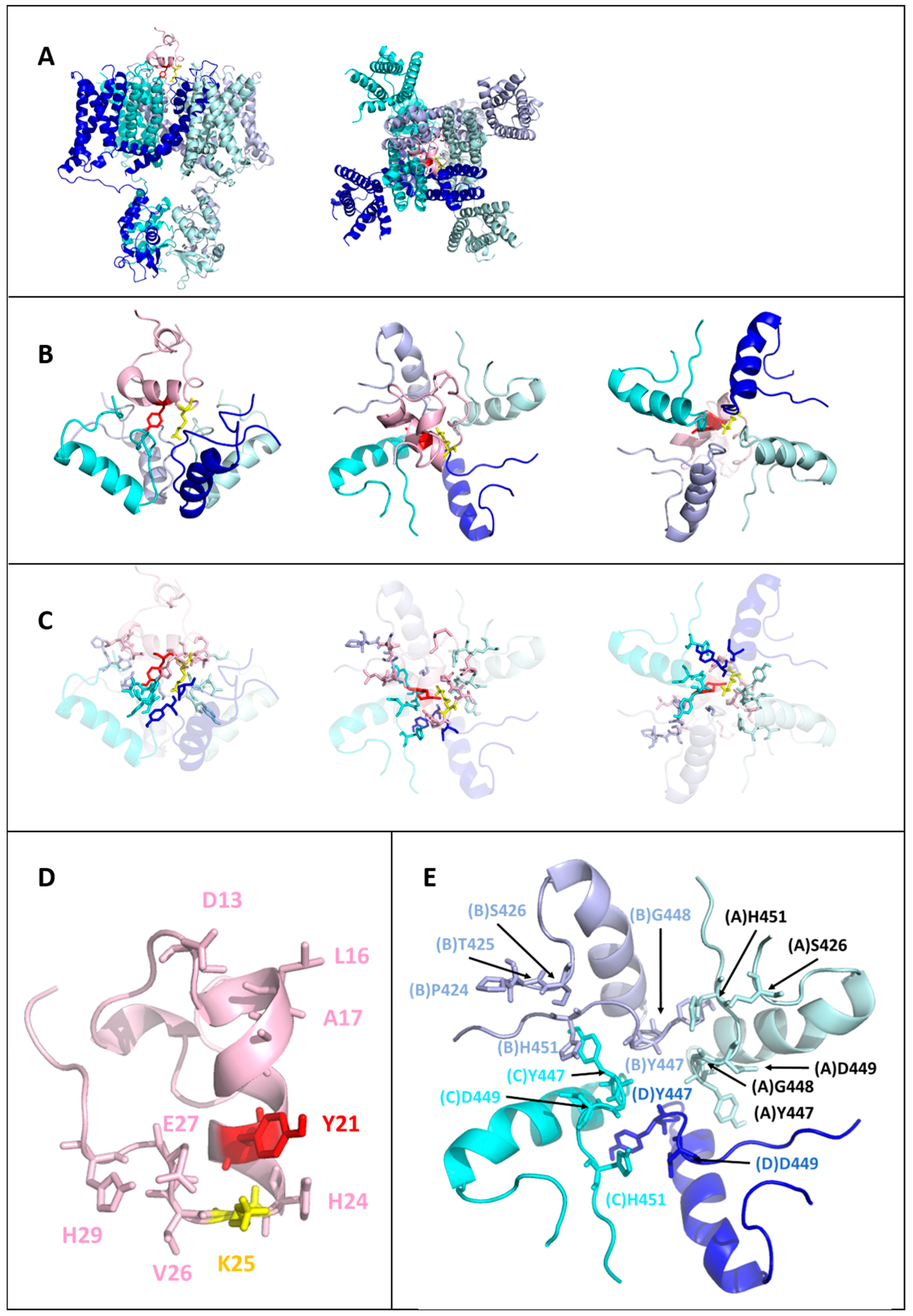
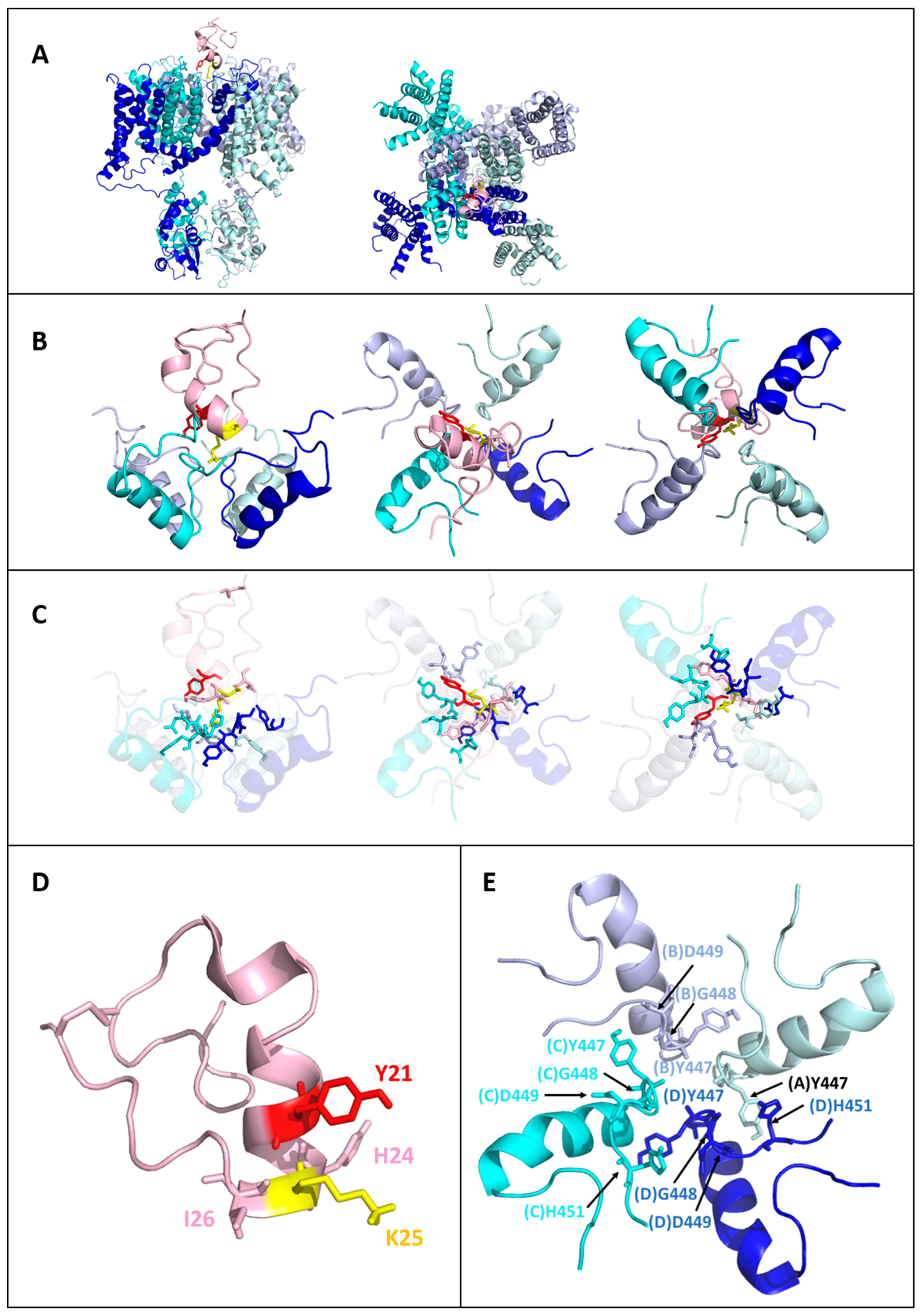
2.5. Models of the Tb11a-Kv1.3 and Ta11a-Kv1.3 Complexes
2.6. Toxin-Kv1.3 Interfaces
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Cell Culture
5.2. Transient Transfection of Potassium Channels
5.3. Cytotoxicity Assays
5.4. Patch Clamp Experiments
5.5. Chemicals and Peptide Synthesis
5.6. Statistics
5.7. Homology Modeling of Ta11a
5.8. Docking of Tb11a and Ta11a to Kv1.3
- The presence of multiple potential hydrogen bonds between the NζH3+ side-chain ammonium group of K25 and the backbone carbonyl oxygen (O) of Y447 across the four subunits of Kv1.3 (distance (Nζ-O) < 4 Å).
- Structural compactness and the number of secondary structure elements in the peptides, as the disulfide bridge is known to confer reduced flexibility and enhanced fold stability in a tridimensional structure.
- The best HADDOCK scores among the structures selected according to criteria (1) and (2).
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pennington, M.W.; Czerwinski, A.; Norton, R.S. Peptide therapeutics from venom: Current status and potential. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2738–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, H.; Christophersen, P.; Colussi, P.; Chandy, K.G.; Yarov-Yarovoy, V. Antibodies and venom peptides: New modalities for ion channels. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, R.S.; Chandy, K.G. Venom-derived peptide inhibitors of voltage-gated potassium channels. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansom, M.S.; Shrivastava, I.H.; Bright, J.N.; Tate, J.; Capener, C.E.; Biggin, P.C. Potassium channels: Structures, models, simulations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Biomembr. 2002, 1565, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.T.; Tyagi, A.; Chandy, K.G.; Bhushan, S. Mechanisms Underlying C-type Inactivation in Kv Channels: Lessons From Structures of Human Kv1.3 and Fly Shaker-IR Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 924289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Yokogawa, M.; Osawa, M. Peptide Toxins Targeting KV Channels. In Pharmacology of Potassium Channels; Gamper, N., Wang, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 481–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, S.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.-M. Contribution of the functional dyad of animal toxins acting on voltage-gated Kv1-type channels. J. Pept. Sci. 2005, 11, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, I.; Chang, S.C.; Li, Y.; Chhabra, S.; Palmer, A.G.; Norton, R.S.; Chill, J.H. Conformational Flexibility in the Binding Surface of the Potassium Channel Blocker ShK. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouirou, B.; Mouhat, S.; Andreotti, N.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.-M. Toxin determinants required for interaction with voltage-gated K+ channels. Toxicon 2004, 43, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouhat, S.; Mosbah, A.; Visan, V.; Wulff, H.; Delepierre, M.; Darbon, H.; Grissmer, S.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.-M. The functional dyad of scorpion toxin Pi1 is not itself a prerequisite for toxin binding to the voltage-gated Kv1.2 potassium channels. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchard, A.; Aili, S.R.; Fox, E.G.P.; Escoubas, P.; Orivel, J.; Nicholson, G.M.; Dejean, A. The Biochemical Toxin Arsenal from Ant Venoms. Toxins 2016, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, S.R.; Touchard, A.; Escoubas, P.; Padula, M.P.; Orivel, J.; Dejean, A.; Nicholson, G.M. Diversity of peptide toxins from stinging ant venoms. Toxicon 2014, 92, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchard, A.; Téné, N.; Song, P.C.T.; Lefranc, B.; Leprince, J.; Treilhou, M.; Bonnafé, E. Deciphering the Molecular Diversity of an Ant Venom Peptidome through a Venomics Approach. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3503–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascoët, S.; Touchard, A.; Téné, N.; Lefranc, B.; Leprince, J.; Paquet, F.; Jouvensal, L.; Barassé, V.; Treilhou, M.; Billet, A.; et al. The mechanism underlying toxicity of a venom peptide against insects reveals how ants are master at disrupting membranes. iScience 2023, 26, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.D.; Deuis, J.R.; Touchard, A.; Keramidas, A.; Mueller, A.; Schroeder, C.I.; Barassé, V.; Walker, A.A.; Brinkwirth, N.; Jami, S.; et al. Ant venoms contain vertebrate-selective pain-causing sodium channel toxins. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisamy, K.; Singh, K.; Kumar, M.; Lefranc, B.; Bonnafé, E.; Treilhou, M.; Leprince, J.; Chow, B.K. P17 induces chemotaxis and differentiation of monocytes via MRGPRX2-mediated mast cell-line activation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 149, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barassé, V.; Jouvensal, L.; Boy, G.; Billet, A.; Ascoët, S.; Lefranc, B.; Leprince, J.; Dejean, A.; Lacotte, V.; Rahioui, I.; et al. Discovery of an Insect Neuroactive Helix Ring Peptide from Ant Venom. Toxins 2023, 15, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigneur, S.; Tibery, D.; Tytgat, J. The Helix Ring Peptide U11 from the Venom of the Ant, Tetramorium bicarinatum, Acts as a Putative Pore-Forming Toxin. Membranes 2024, 14, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.A.; Dekan, Z.; Robinson, S.D.; Guo, S.; Vetter, I.; Kotze, A.C.; Alewood, P.F.; King, G.F.; Herzig, V. It Takes Two: Dimerization Is Essential for the Broad-Spectrum Predatory and Defensive Activities of the Venom Peptide Mp1a from the Jack Jumper Ant Myrmecia pilosula. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-X.; King, M.; Donovan, G.; Alewood, D.; Alewood, P.; Sawyer, W.; Baldo, B. Cytotoxicity of pilosulin 1, a peptide from the venom of the jumper ant Myrmecia pilosula. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Gen. Subj. 1998, 1425, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrola, G.B.; Hernández-López, R.A.; Rodríguez de la Vega, R.C.; Varga, Z.; Batista, C.V.; Salas-Castillo, S.P.; Panyi, G.; del Río-Portilla, F.; Possani, L.D. Structure, Function, and Chemical Synthesis of Vaejovis mexicanus Peptide 24: A Novel Potent Blocker of Kv1.3 Potassium Channels of Human T Lymphocytes. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 4049–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.G.; Peigneur, S.; Esaki, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Tytgat, J.; Kim, J.I.; Sato, K. Solution structure and functional analysis of HelaTx1: The first toxin member of the κ-KTx5 subfamily. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilquin, B.; Braud, S.; Eriksson, M.A.; Roux, B.; Bailey, T.D.; Priest, B.T.; Garcia, M.L.; Ménez, A.; Gasparini, S. A Variable Residue in the Pore of Kv1 Channels Is Critical for the High Affinity of Blockers from Sea Anemones and Scorpions. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27093–27102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Garcia, M.L. Interaction of agitoxin2, charybdotoxin, and iberiotoxin with potassium channels: Selectivity between voltage-gated and Maxi-K channels. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2003, 52, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauer, H.; Pennington, M.; Cahalan, M.; Chandy, K.G. Structural conservation of the pores of calcium-activated and voltage-gated potassium channels determined by a sea anemone toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21885–21892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barassé, V.; Téné, N.; Klopp, C.; Paquet, F.; Tysklind, N.; Troispoux, V.; Lalägue, H.; Orivel, J.; Lefranc, B.; Leprince, J.; et al. Venomics survey of six myrmicine ants provides insights into the molecular and structural diversity of their peptide toxins. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 151, 103876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchard, A.; Barassé, V.; Malgouyre, J.-M.; Treilhou, M.; Klopp, C.; Bonnafé, E. The genome of the ant Tetramorium bicarinatum reveals a tandem organization of venom peptides genes allowing the prediction of their regulatory and evolutionary profiles. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchard, A.; Aili, S.R.; Téné, N.; Barassé, V.; Klopp, C.; Dejean, A.; Kini, R.M.; Mrinalini; Coquet, L.; Jouenne, T.; et al. Venom Peptide Repertoire of the European Myrmicine Ant Manica rubida: Identification of Insecticidal Toxins. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1800–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.W.; Wulff, H.; Singh, S.; Nugent, D.; Crossley, G.; Khaytin, I.; Calabresi, P.A.; Chen, C.-Y.; Gutman, G.A.; et al. Targeting effector memory T cells with a selective peptide inhibitor of Kv1.3 channels for therapy of autoimmune diseases. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teisseyre, A.; Palko-Labuz, A.; Sroda-Pomianek, K.; Michalak, K. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel Kv1.3 as a Target in Therapy of Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Cepko, C.L. Electroporation and RNA interference in the rodent retina in vivo and in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; DiMaio, F.; Wang, R.Y.-R.; Kim, D.; Miles, C.; Brunette, T.; Thompson, J.; Baker, D. High resolution comparative modeling with RosettaCM. Structure 2013, 21, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honorato, R.V.; Trellet, M.E.; Jiménez-García, B.; Schaarschmidt, J.J.; Giulini, M.; Reys, V.; Koukos, P.I.; Rodrigues, J.P.G.L.M.; Karaca, E.; van Zundert, G.C.P.; et al. The HADDOCK2.4 web server for integrative modeling of biomolecular complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 3219–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, P.; Fernández-Mariño, A.I.; Khanra, N.; He, C.; Paquette, A.J.; Wang, B.; Huang, R.; Smider, V.V.; Rice, W.J.; Swartz, K.J.; et al. Structures of the T cell potassium channel Kv1.3 with immunoglobulin modulators. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, K.; Prypoten, V.; Chandy, K.G.; Chalmers, D.K.; Norton, R.S. Interaction of the Inhibitory Peptides ShK and HmK with the Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel KV1.3: Role of Conformational Dynamics. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 3043–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A. PDBsum 1: A standalone program for generating PDBsum analyses. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, e4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]

| Criteria | Tb11a-Kv1.3 | Ta11a-Kv1.3 |
|---|---|---|
| None (all refined structures in water) | 200 | 200 |
| K25 in selectivity filter | 80 | 111 |
| 2 H-bond with Y447 | 63 | 19 |
| 3 H-bonds with Y447 | 7 | 10 |
| 4 H-bonds with Y447 | 10 | 57 |
| K25 in selectivity filter and conserved structural compactness of the toxin | 42 | 45 |
| 2 H-bond with Y447 | 34 | 0 |
| 3 H-bonds with Y447 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 H-bonds with Y447 | 5 | 45 |
| Haddock score | −61.48 ± 6.28 | −36.36 ± 5.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boy, G.; Jouvensal, L.; Téné, N.; Carayon, J.-L.; Bonnafé, E.; Paquet, F.; Treilhou, M.; Loth, K.; Billet, A. A New Kv1.3 Channel Blocker from the Venom of the Ant Tetramorium bicarinatum. Toxins 2025, 17, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080379
Boy G, Jouvensal L, Téné N, Carayon J-L, Bonnafé E, Paquet F, Treilhou M, Loth K, Billet A. A New Kv1.3 Channel Blocker from the Venom of the Ant Tetramorium bicarinatum. Toxins. 2025; 17(8):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080379
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoy, Guillaume, Laurence Jouvensal, Nathan Téné, Jean-Luc Carayon, Elsa Bonnafé, Françoise Paquet, Michel Treilhou, Karine Loth, and Arnaud Billet. 2025. "A New Kv1.3 Channel Blocker from the Venom of the Ant Tetramorium bicarinatum" Toxins 17, no. 8: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080379
APA StyleBoy, G., Jouvensal, L., Téné, N., Carayon, J.-L., Bonnafé, E., Paquet, F., Treilhou, M., Loth, K., & Billet, A. (2025). A New Kv1.3 Channel Blocker from the Venom of the Ant Tetramorium bicarinatum. Toxins, 17(8), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080379







