Integrated Cytotoxicity and Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Cell-Type-Specific Responses to Co-Exposure of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Toxicity of T-2 and Ht-2 Toxins on Four Porcine Cell Lines
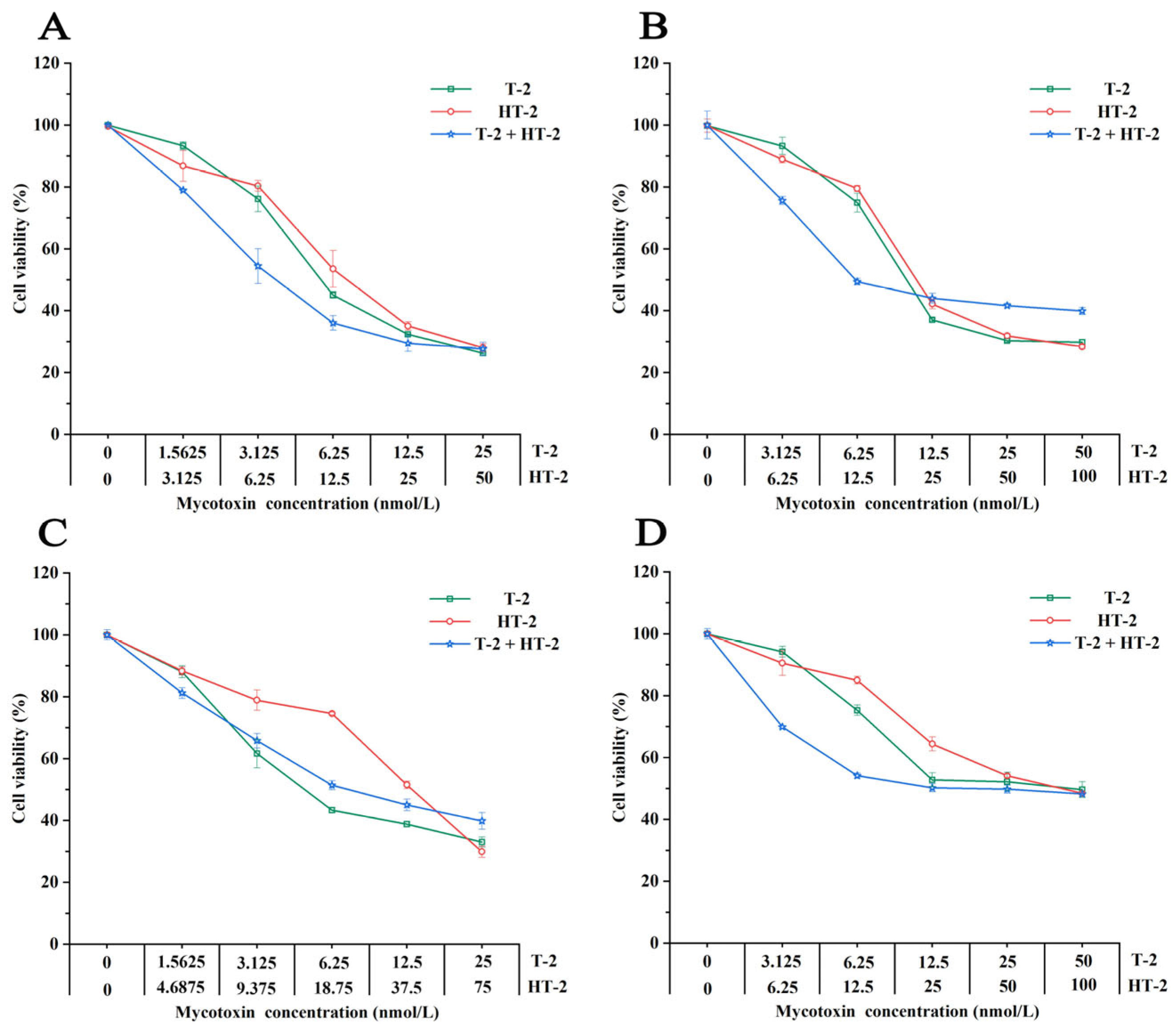
2.2. Combined Toxicity of T-2 + HT-2 in Four Porcine Cell Lines
2.3. Interactive Analysis of T-2 and HT-2 in Four Porcine Cell Lines
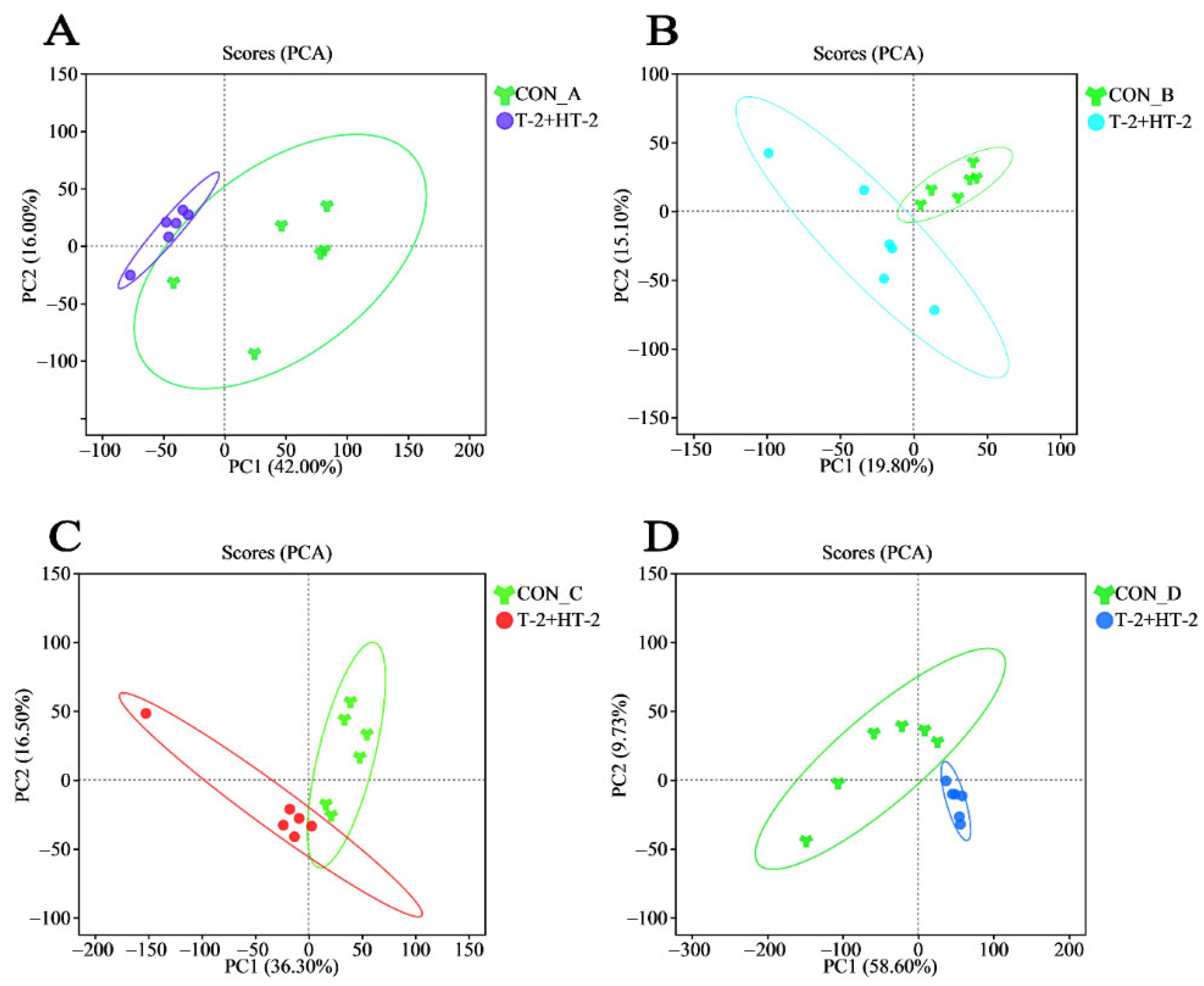
2.4. Evaluation of Experimental Data Quality
2.5. Characteristics of Overall Metabolite Changes
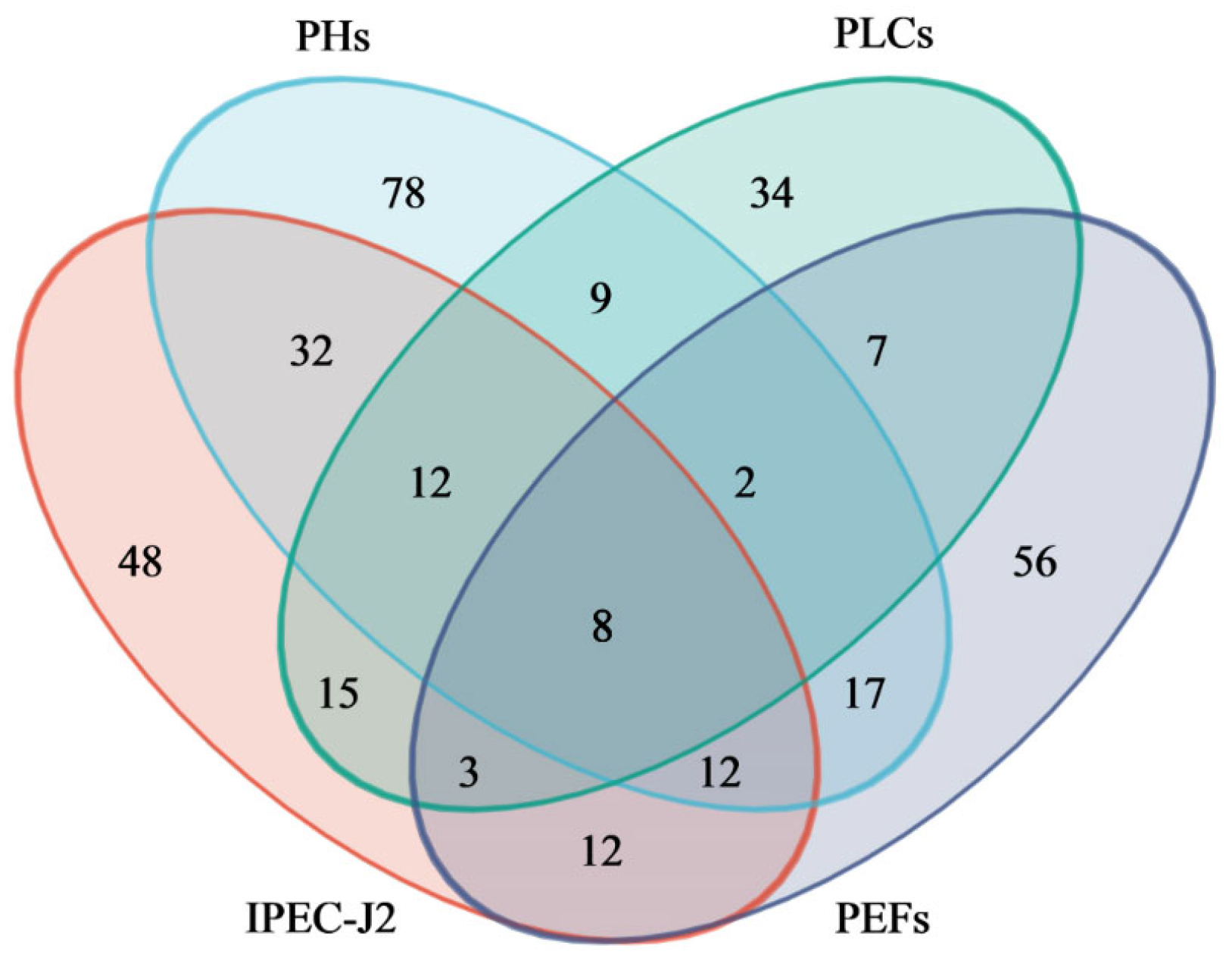
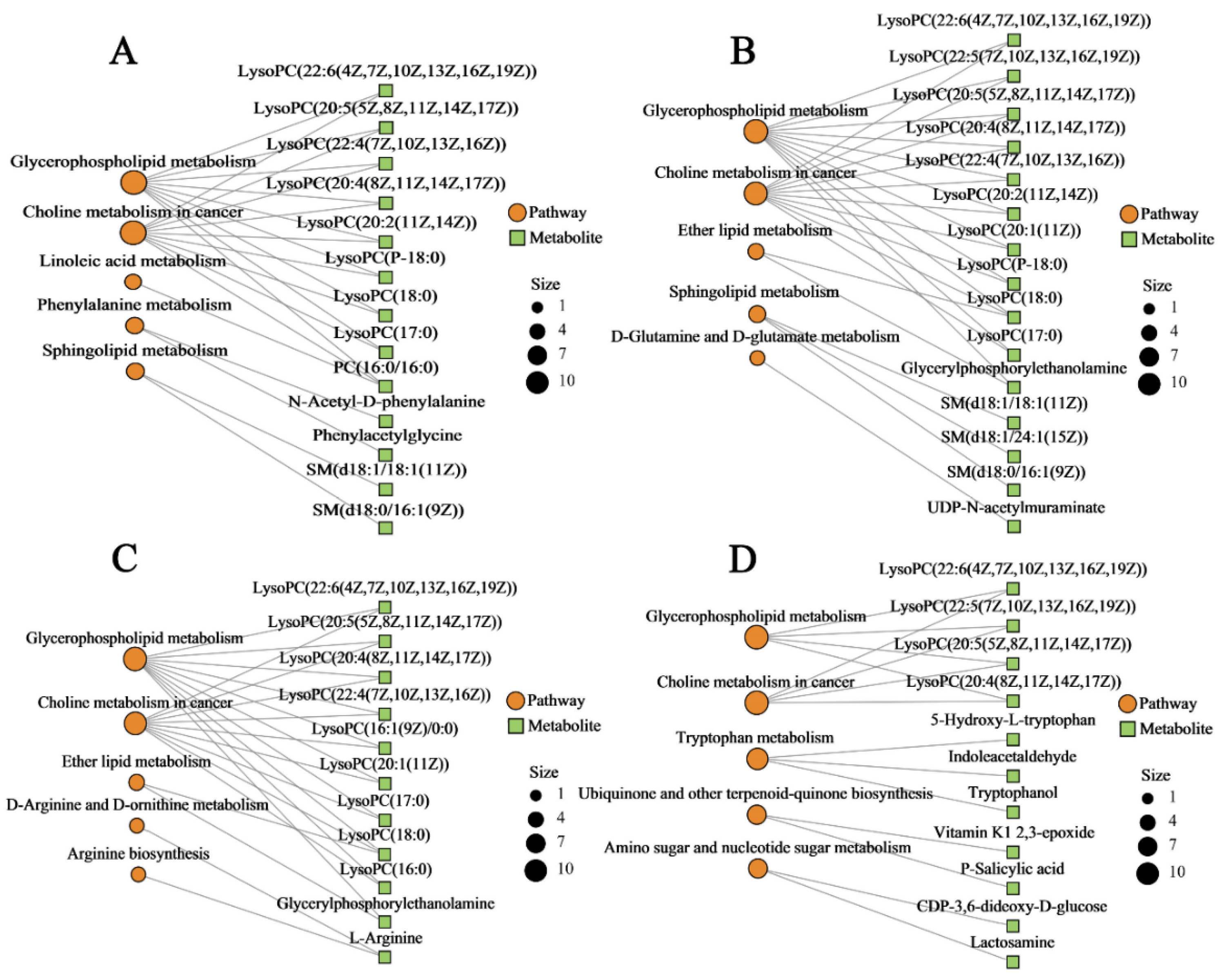
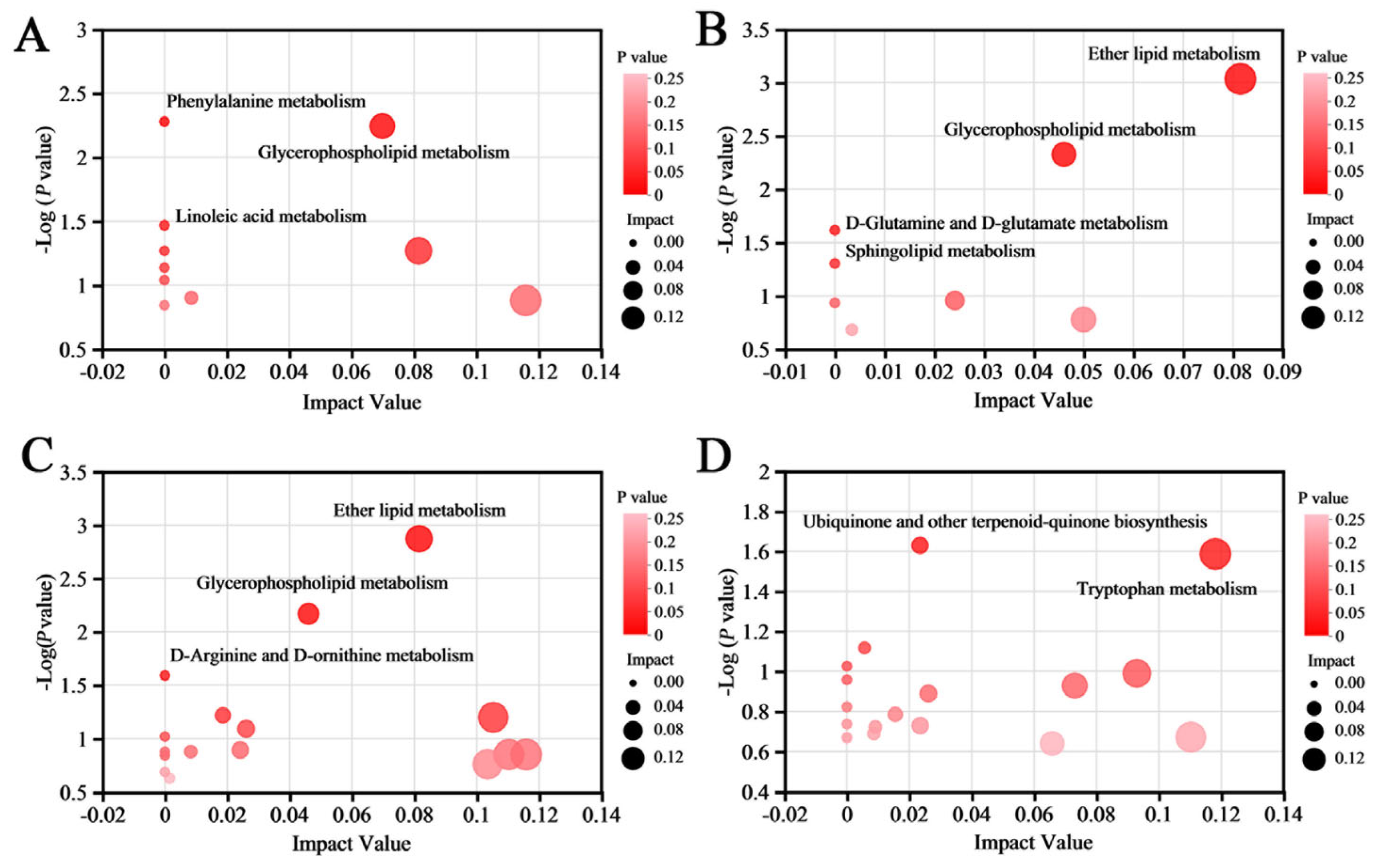
2.6. Identification and Analysis of Overlapping Metabolites
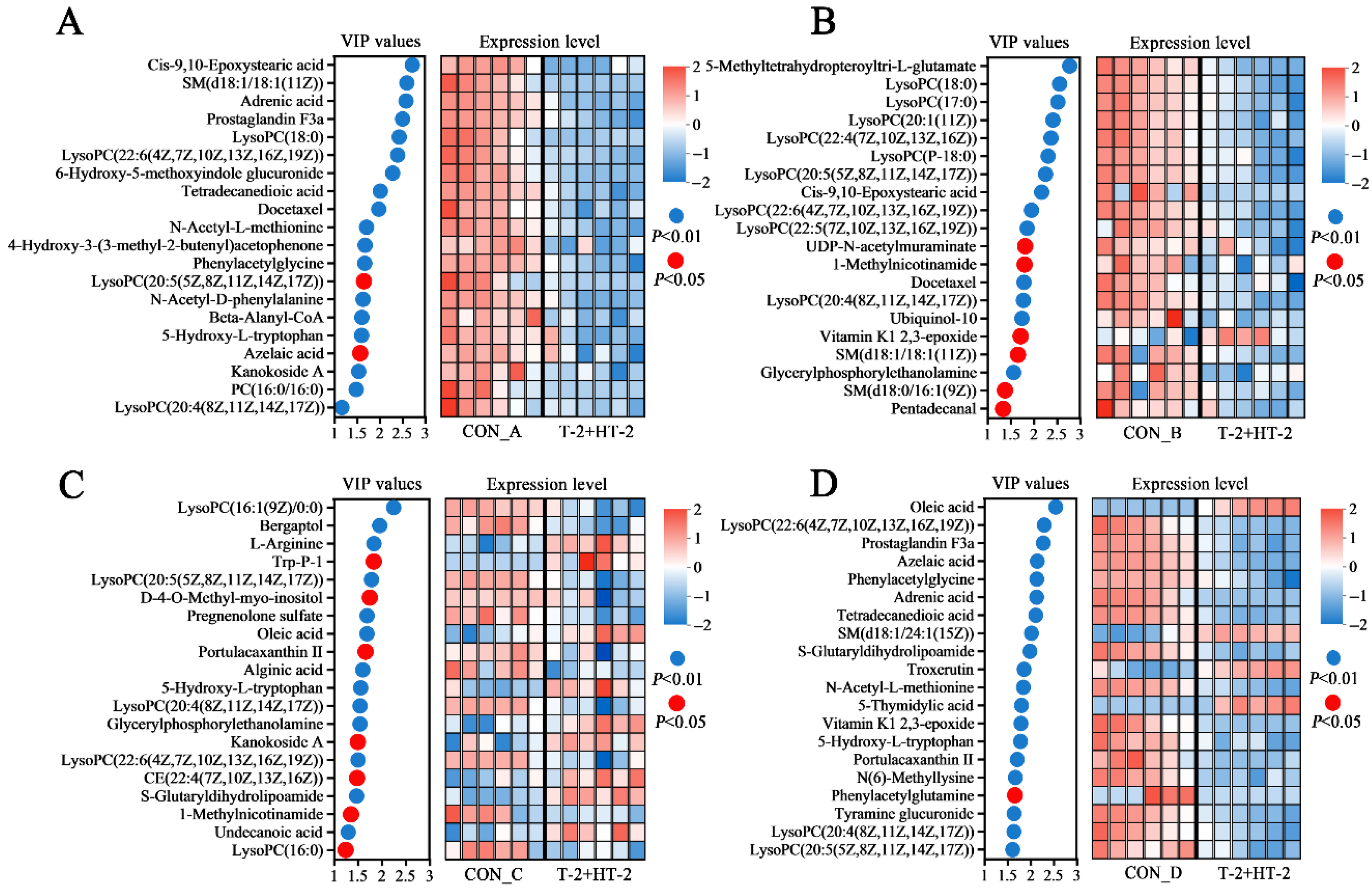
2.7. Analysis of Differential Metabolites
2.8. Metabolic Pathway and Network Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents
5.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
5.3. Cell Viability Assay
5.4. Combined Index Analysis of Mycotoxin Mixtures
5.5. Extraction of Cell Metabolites
5.6. LC-Q-TOF/MS Conditions
5.7. Statistical Analysis and Data Visualization
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piotrowska, M.; Slizewska, K.; Nowak, A.; Zielonka, L.; Zakowska, Z.; Gajecka, M.; Gajecki, M. The Effect of Experimental Fusarium Mycotoxicosis on Microbiota Diversity in Porcine Ascending Colon Contents. Toxins 2014, 6, 2064–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schollenberger, M.; Mueller, H.M.; Ruefle, M.; Terry-Jara, H.; Suchy, S.; Plank, S.; Drochner, W. Natural occurrence of Fusarium toxins in soy food marketed in Germany. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 113, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.S.; Wang, Z.H.; Beier, R.C.; Shen, J.Z.; De Smet, D.; De Saeger, S.; Zhang, S.X. T-2 Toxin, a Trichothecene Mycotoxin: Review of Toxicity, Metabolism, and Analytical Methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3441–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, R. Betulinic acid attenuates T-2 toxin-induced cytotoxicity in porcine kidney cells by blocking oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2021, 249, 109124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzio, V.M.T.; Pascale, M.; Visconti, A. Current analytical methods for trichothecene mycotoxins in cereals. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Wan, K. Contamination Level of T-2 and HT-2 Toxin in Cereal Crops from Aba Area in Sichuan Province, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvaez, A.; Rodriguez-Carrasco, Y.; Ritieni, A.; Manes, J. Novel quadrupole-time of flight-based methodology for determination of multiple mycotoxins in human hair. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1191, 123117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovac, M.; Bulaic, M.; Nevistic, A.; Rot, T.; Babic, J.; Panjicko, M.; Kovac, T.; Sarkanj, B. Regulated Mycotoxin Occurrence and Co-Occurrence in Croatian Cereals. Toxins 2022, 14, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, N.; Marley, E.; Leeman, D.; Poplawski, C.; Donnelly, C. Analysis of Aflatoxins, Fumonisins, Deoxynivalenol, Ochratoxin A, Zearalenone, HT-2, and T-2 Toxins in Animal Feed by LC-MS/MS Using Cleanup with a Multi-Antibody Immunoaffinity Column. J. AOAC Int. 2022, 105, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, P.; Cui, Y.; Xiao, B.; Liu, M.; Song, M.; Huang, W.; Li, Y. Review of the Reproductive Toxicity of T-2 Toxin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Negi, B.; Kaushik, N.; Adhikari, A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. T-2 mycotoxin: Toxicological effects and decontamination strategies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33933–33952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Engemann, A.; Cramer, B.; Welsch, T.; Yuan, Z.; Humpf, H.-U. Intestinal metabolism of T-2 toxin in the pig cecum model. Mycotoxin Res. 2012, 28, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufuor-Mensah, E.; Reed, W.M.; Sleight, S.; Pestka, J.; Fadly, A.M.; Dunn, J.R. Effects of T-2 Toxin on Turkey Herpesvirus-Induced Vaccinal Immunity Against Marek’s Disease. Avian Dis. 2016, 60, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroncher, M.; Carrasco, Y.; Ruiz, M. Interactions between T-2 toxin and its metabolites in HepG2 cells and in silico approach. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 148, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z. T-2 Toxin-Induced Oxidative Stress Leads to Imbalance of Mitochondrial Fission and Fusion to Activate Cellular Apoptosis in the Human Liver 7702 Cell Line. Toxins 2020, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, A.; Sun, L.; Guo, W.; Sun, S.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Z. Individual and combined cytotoxic effects of T-2 toxin and its four metabolites on porcine Leydig cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 139, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, D.K.; Pandhi, S.; Kamle, M.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, B.; Panda, B.K.; Srivastava, S.; Kumar, M.; Selvakumar, R.; Pandey, A.K. Trichothecenes in food and feed: Occurrence, impact on human health and their detection and management strategies. Toxicon 2020, 208, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, K.; Long, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y. An update on immunotoxicity and mechanisms of action of six environmental mycotoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 163, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.W. Mycotoxins, mycotoxicoses, mycotoxicology and Mycopathologia. Mycopathologia 1987, 100, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcella, D.; Gergelova, P.; Innocenti, M.L.; Steinkellner, H.; European Food Safety Authority. Human and animal dietary exposure to T-2 and HT-2 toxin. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04972. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, K.; Tan, L.; Yi, S.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, A.; Yang, L. Low-Concentration T-2 Toxin Attenuates Pseudorabies Virus Replication in Porcine Kidney 15 Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Du, Y.; Yao, F.; Zhao, M.; Cai, C.; Zhu, R.; Shao, S. Metabolomics study reveals DON-induced intestinal toxicity in adult zebrafish through disruption of amino acid metabolism and sphingolipid signaling pathway. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 282, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; He, X.; Liu, j. Integrated metabolomic and microbiome analysis identifies Cupriavidus metallidurans as a potential therapeutic target for β-thalassemia. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 5169–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Metabolomics analysis underlay mechanisms in the renal impairment of mice caused by combination of aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A. Toxicology 2021, 458, 152835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, A.; Liao, S.; Tan, B.; Liao, P. Integrated lncRNA transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics to identify early cellular response variation in deoxynivalenol-treated IPEC-J2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 177, 113863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Matias, F.B.; Yi, J.-E.; Wu, J. T-2 toxin-induced cytotoxicity and damage on TM3 Leydig cells. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2016, 181, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolf-Clauw, M.; Sassahara, M.; Lucioli, J.; Rubira-Gerez, J.; Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Lyazhri, F.; Borin, C.; Oswald, I.P. The emerging mycotoxin, enniatin B1, down-modulates the gastrointestinal toxicity of T-2 toxin in vitro on intestinal epithelial cells and ex vivo on intestinal explants. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenigs, M.; Mulac, D.; Schwerdt, G.; Gekle, M.; Humpf, H.-U. Metabolism and cytotoxic effects of T-2 toxin and its metabolites on human cells in primary culture. Toxicology 2009, 258, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.-J.; Macakova, P.; Juan-Garcia, A.; Font, G. Cytotoxic effects of mycotoxin combinations in mammalian kidney cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tu, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Liu, T.; Tan, L.; Li, Y.; Lei, H.; Zhan, Y. Distribution and persistence of residual T-2 and HT-2 toxins from moldy feed in broiler chickens. Toxicon 2020, 178, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, N.C.; Caperna, T.J.; Blomberg, L.; Graninger, P.G.; Stodieck, L.S. The effects of space flight and microgravity on the growth and differentiation of PICM-19 pig liver stem cells. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2010, 46, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Blanco, C.; Elmo, L.; Waldner, T.; Ruiz, M.-J. Cytotoxic effects induced by patulin, deoxynivalenol and toxin T2 individually and in combination in hepatic cells, HepG2. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madalena, M.; Sobral, C.; Faria, M.A.; Cunha, S.C.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O. Toxicological interactions between mycotoxins from ubiquitous fungi: Impact on hepatic and intestinal human epithelial cells. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, W.; Ling, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Potential Role of Individual and Combined Effects of T-2 Toxin, HT-2 Toxin and Neosolaniol on the Apoptosis of Porcine Leydig Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Wang, J.; Han, M.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, J.; Zhai, X.; Yang, J. Potential Toxicity and Mechanisms of T-2 and HT-2 Individually or in Combination on the Intestinal Barrier Function of Porcine Small Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2023, 15, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Tu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, J. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by mixed mycotoxins, T-2 and HT-2 toxin on primary hepatocytes of broilers in vitro. Toxicon 2017, 129, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yan, C.; Du, H.; Li, Z. Ochratoxin A and fumonisin B1 exhibit synergistic cytotoxic effects by inducing apoptosis on rat liver cells. Toxicon 2020, 181, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.-C.; Hymery, N.; Troadec, S.; Pawtowski, A.; Coton, E.; Madec, S. Hepatotoxicity of fusariotoxins, alone and in combination, towards the HepaRG human hepatocyte cell line. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alovskaia, A.A.; Gabdulkhakova, A.G.; Safronova, V.G. Role of phospholipase A2 and epoxygenase in inhibi-tion of respiration burst in neutrophils by low intensity radiation of extremely high frequency. Biofizika 2001, 46, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Zhang, W.; Gu, X.; Chen, X.; Hong, L.; Laird, J.M.; Salomon, R.G. Lysophosphatidylcholine is Generated by Spontaneous Deacylation of Oxidized Phospholipids. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.-H.; Chan, M.-L.; Marathe, G.K.; Parveen, F.; Chen, C.-H.; Ke, L.-Y. An Updated Review of Lysophosphatidylcholine Metabolism in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, G.; Aitken, D.; Likhodii, S.; Liu, M.; Martin, G.; Furey, A.; Randell, E.; Rahman, P.; Jones, G.; et al. Lysophosphatidylcholines to phosphatidylcholines ratio predicts advanced knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B.; Schiller, E.; Wagner, U.; Häntzschel, H.; Arnold, K. The phosphatidylcholine/lysophosphatidylcholine ratio in human plasma is an indicator of the severity of rheumatoid arthritis: Investigations by 31 P NMR and MALDI-TOF MS. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Li, G.; Zheng, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Su, Y.; Chu, Q.; Yuan, X.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J.; et al. Tryptophan metabo-lism in health and disease. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1304–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Chang, X. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals perturbed glycerophospholipid metabolism in mouse neural stem cells exposed to cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunachalam, C.; Doohan, F.M. Trichothecene toxicity in eukaryotes: Cellular and molecular mechanisms in plants and animals. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 217, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Peng, J.; Hao, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, P.; Li, S.; Shi, H. Integrated multiomics approach and pathological analyses provide new insights into hepatic injury and metabolic alterations in Saanen goats after dietary exposure to aflatoxin B1. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 1431–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.M.; Lodhi, I.J. Structural and functional roles of ether lipids. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platten, M.; Nollen, E.A.A.; Rohrig, U.F.; Fallarino, F.; Opitz, C.A. Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Shapiro, T.A.; Fu, J.; Chou, J.H.; Ulrich, G.S. Computerized quantification of drugs synergism in animal studies or in clinical trials using only ten data points. Synergy 2019, 9, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Song, P.; Yu, J. New insights into mechanism of ellagic acid alleviating arsenic-induced oxidative stress through MAPK/keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway response, molecular docking and metabolomics analysis in HepG2 cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. 2024, 285, 117029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, I.; Thapaliya, M.; Boroujerdi, A.; Chowdhury, K. NMR-based metabolomics study of the biochemical relationship between sugarcane callus tissues and their respective nutrient culture media. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5997–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cell Lines | T-2 (nmol/L) | HT-2 (nmol/L) | Ratio of HT-2 to T-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPEC-J2 | 9.96 ± 0.51 c | 20.55 ± 0.13 b | 2.06 |
| PLCs | 15.83 ± 1.16 b | 34.69 ± 2.38 b | 2.19 |
| PEFs | 17.75 ± 1.59 b | 57.80 ± 1.41 a | 3.26 |
| PHs | 43.72 ± 2.21 a | 98.92 ± 6.06 a | 2.26 |
| Cells Lines | Toxins | Ratio | 25% Cytotoxicity | 50% Cytotoxicity | 75% Cytotoxicity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI Values | DRI | CI Values | DRI | CI Values | DRI | ||||||
| IPEC-J2 | T-2 | 1:2 | 0.88 | + | 2.75 | 1.00 | ± | 1.98 | 1.16 | – | 1.43 |
| HT-2 | 1.94 | 2.05 | 2.16 | ||||||||
| PLCs | T-2 | 1:2 | 0.43 | + + + | 5.30 | 1.65 | – – – | 1.23 | 6.38 | – – – – | 0.28 |
| HT-2 | 4.10 | 1.20 | 0.35 | ||||||||
| PEFs | T-2 | 1:3 | 0.77 | + + | 2.27 | 1.09 | ± | 1.76 | 1.57 | – – – | 1.37 |
| HT-2 | 3.05 | 1.91 | 1.20 | ||||||||
| PHs | T-2 | 1:2 | 0.10 | + + + + | 18.61 | 1.04 | ± | 1.82 | 10.69 | – – – – – | 0.18 |
| HT-2 | 21.02 | 2.04 | 0.20 | ||||||||
| HMDB ID | Metabolite | Chemical Formula | m/z |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMDB0010404 | LysoPC(22:6) | C30H50NO7P | 612.33 |
| HMDB0010397 | LysoPC(20:5) | C28H48NO7P | 586.32 |
| HMDB0010396 | LysoPC(20:4) | C28H50NO7P | 588.33 |
| HMDB0010393 | LysoPC(20:3) | C28H52NO7P | 590.35 |
| HMDB0010386 | LysoPC(18:2) | C26H50NO7P | 564.33 |
| HMDB0011491 | LysoPE(0:0/22:1) | C27H54NO7P | 580.37 |
| HMDB0035264 | Avenestergenin A1 | C38H55NO7 | 618.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, W.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhai, X.; Yang, J. Integrated Cytotoxicity and Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Cell-Type-Specific Responses to Co-Exposure of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins. Toxins 2025, 17, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080381
He W, Zhu Z, Xu J, Huang C, Wang J, Wang Q, Zhai X, Yang J. Integrated Cytotoxicity and Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Cell-Type-Specific Responses to Co-Exposure of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins. Toxins. 2025; 17(8):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080381
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Weihua, Zuoyin Zhu, Jingru Xu, Chengbao Huang, Jianhua Wang, Qinggong Wang, Xiaohu Zhai, and Junhua Yang. 2025. "Integrated Cytotoxicity and Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Cell-Type-Specific Responses to Co-Exposure of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins" Toxins 17, no. 8: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080381
APA StyleHe, W., Zhu, Z., Xu, J., Huang, C., Wang, J., Wang, Q., Zhai, X., & Yang, J. (2025). Integrated Cytotoxicity and Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Cell-Type-Specific Responses to Co-Exposure of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins. Toxins, 17(8), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080381








