Chemical and Morphological Constitutive Defensive Traits of Cyanobacteria Have Different Effects on the Grazing of a Small Tropical Cladoceran
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Grazing on Different Amounts of Food (Single Diets)
2.2. Grazing on on Mixed Diets
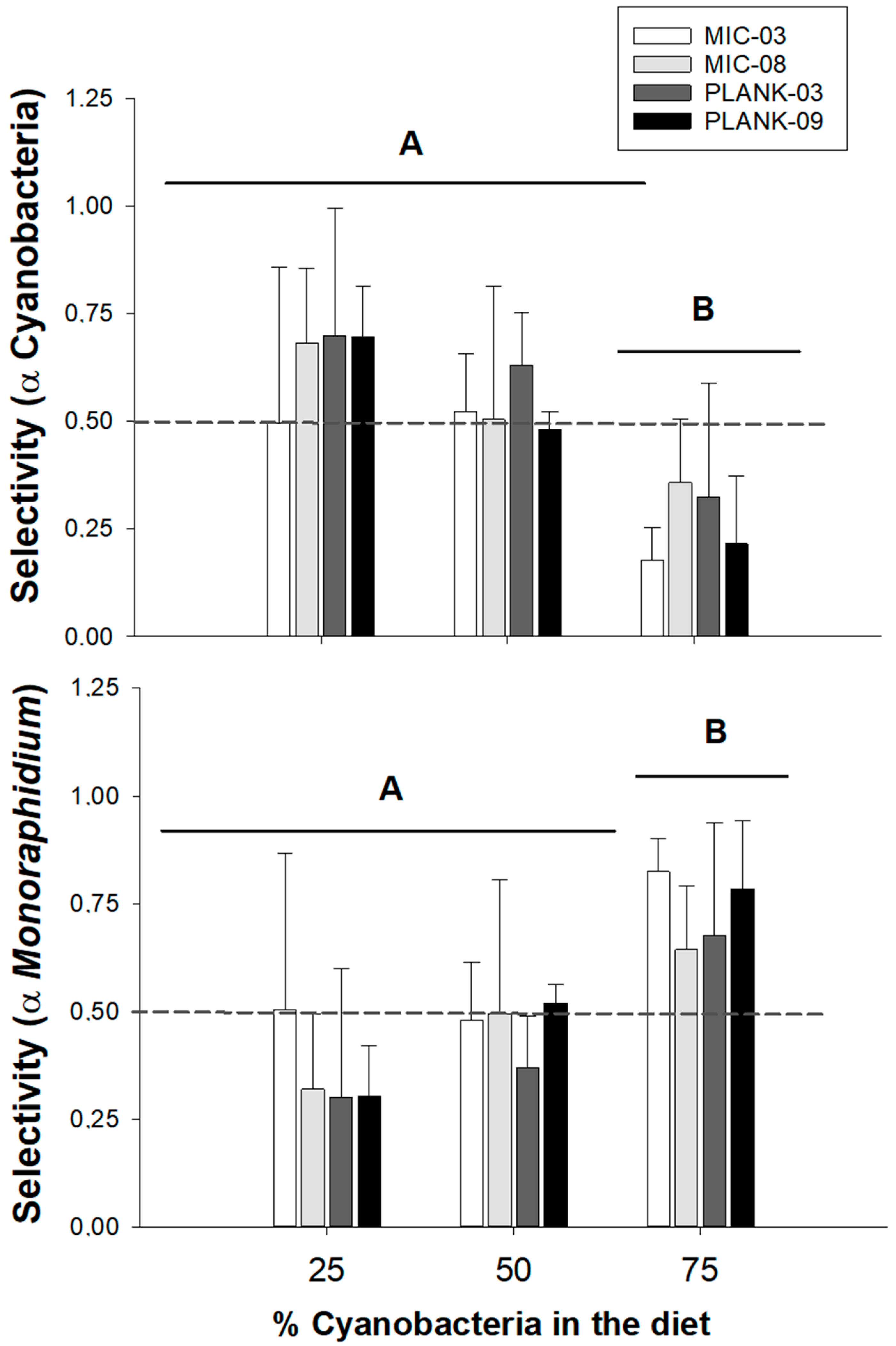
2.3. Selectivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Organisms
4.2. Toxin Analyses of the Cyanobacterial Strains
4.3. Experiments with Different Amounts of Food (Single Diets)
- two strains of Microcystis aeruginosa (MIC-03 and MIC-08) and;
- two strains of Planktothrix isothrix (PLANK-03 and PLANK-09).
4.4. Experiments with Mixed Diets
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smucker, N.J.; Beaulieu, J.J.; Nietch, C.T.; Young, J.L. Increasingly Severe Cyanobacterial Blooms and Deep Water Hypoxia Coincide with Warming Water Temperatures in Reservoirs. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 2507–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial Blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorus, I.; Fastner, J.; Welker, M. Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in a Changing Environment: Concepts, Controversies, Challenges. Water 2021, 13, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, T.G.V.; Gama, W.A.; Geraldes, V.; Yoon, J.; Crnkovic, C.M.; Pinto, E.; Jacinavicius, F.R. New Records on Toxic Cyanobacteria from Brazil: Exploring Their Occurrence and Geography. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svirčev, Z.; Lalić, D.; Bojadžija Savić, G.; Tokodi, N.; Drobac Backović, D.; Chen, L.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G.A. Global Geographical and Historical Overview of Cyanotoxin Distribution and Cyanobacterial Poisonings. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 2429–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganelli, M.; Testai, E.; Tazart, Z.; Scardala, S.; Codd, G.A. Co-Occurrence of Taste and Odor Compounds and Cyanotoxins in Cyanobacterial Blooms: Emerging Risks to Human Health? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorus, I.; Welker, M. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.D.; Reinl, K.L.; Azarderakhsh, M.; Berger, S.A.; Berman, M.C.; Bizic, M.; Bhattacharya, R.; Burnet, S.H.; Cianci-Gaskill, J.A.; de Senerpont Domis, L.N.; et al. What Makes a Cyanobacterial Bloom Disappear? A Review of the Abiotic and Biotic Cyanobacterial Bloom Loss Factors. Harmful Algae 2024, 133, 102599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel, L.M.; Silva, L.H.S.; Faassen, E.J.; Lürling, M.; Ger, K.A. Copepod Prey Selection and Grazing Efficiency Mediated by Chemical and Morphological Defensive Traits of Cyanobacteria. Toxins 2020, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Hansson, L.-A.; Lurling, M. Understanding Cyanobacteria-Zooplankton Interactions in a More Eutrophic World. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1783–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadouani, A.; Pinel-Alloul, B.; Prepas, E.E. Effects of Experimentally Induced Cyanobacterial Blooms on Crustacean Zooplankton Communities. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xie, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, C. Increasing Dominance of Small Zooplankton with Toxic Cyanobacteria. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiørboe, T. How Zooplankton Feed: Mechanisms, Traits and Trade-Offs. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2011, 86, 311–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Ger, K.A.; Silva, L.H.S.; Soares, M.C.S.; Faassen, E.J.; Lürling, M. Toxicity Overrides Morphology on Cylindrospermopsis Raciborskii Grazing Resistance to the Calanoid Copepod Eudiaptomus Gracilis. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ger, K.A.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Frost, P.C.; Hansson, L.-A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E.; Lürling, M. The Interaction between Cyanobacteria and Zooplankton in a More Eutrophic World. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.S. The Ecology of Phytoplankton (Ecology, Biodiversity and Conservation); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 1139454897. [Google Scholar]
- Kruk, C.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Peeters, E.T.H.M.; Bonilla, S.; Costa, L.S.; Lürling, M.; Reynolds, C.S.; Scheffer, M. A Morphological Classification Capturing Functional Variation in Phytoplankton. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pančić, M.; Kiørboe, T. Phytoplankton Defence Mechanisms: Traits and Trade-Offs. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 1269–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M. Grazing Resistance in Phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; Yu, Y.; Shi, L. Seasonal Shifts in the Morphological Traits of Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria in Lake Chaohu, China. Diversity 2022, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meester, L.; Declerck, S.A.J.; Ger, K.A. Beyond Daphnia: A Plea for a More Inclusive and Unifying Approach to Freshwater Zooplankton Ecology. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 4693–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchman, E.; Klausmeier, C.A. Trait-Based Community Ecology of Phytoplankton. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 615–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, C.; Segura, A.M. The Habitat Template of Phytoplankton Morphology-Based Functional Groups. Hydrobiologia 2012, 698, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Li, M.; Reynolds, C.S. Colony Formation in the Cyanobacterium Microcystis. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 1399–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Leitao, E.; Panosso, R. Potential Mechanisms for the Tropical Copepod Notodiaptomus to Tolerate Microcystis Toxicity. J. Plankton Res. 2016, 38, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, E.; Ger, K.A.; Panosso, R. Selective Grazing by a Tropical Copepod (Notodiaptomus iheringi) Facilitates Microcystis Dominance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorokhova, E.; El-Shehawy, R.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Garbaras, A. How Copepods Can Eat Toxins Without Getting Sick: Gut Bacteria Help Zooplankton to Feed in Cyanobacteria Blooms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 589816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E. Local Adaptation of Daphnia Pulicaria to Toxic Cyanobacteria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chislock, M.F.; Sarnelle, O.; Jernigan, L.M.; Wilson, A.E. Do High Concentrations of Microcystin Prevent Daphnia Control of Phytoplankton? Water Res. 2013, 47, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenberger, A.; Kuster, C.J.; Von Elert, E. Molecular Mechanisms of Tolerance to Cyanobacterial Protease Inhibitors Revealed by Clonal Differences in Daphnia Magna. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 4898–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S. Experimental Studies on Zooplankton-Toxic Cyanobacteria Interactions: A Review. Toxics 2023, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; de Abreu, S.; Silva, D.; de Oliveira, T.A.; de Magalhães, V.F.; Pflugmacher, S.; da Silva, E.M. Single and Combined Effects of Microcystin- and Saxitoxin-Producing Cyanobacteria on the Fitness and Antioxidant Defenses of Cladocerans. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aquino Santos, A.S.; Vilar, M.C.P.; Amorim, C.A.; Molica, R.J.R.; do Nascimento Moura, A. Exposure to Toxic Microcystis via Intact Cell Ingestion and Cell Crude Extract Differently Affects Small-Bodied Cladocerans. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 23194–23205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colina, M.; Calliari, D.; Carballo, C.; Kruk, C. A Trait-Based Approach to Summarize Zooplankton–Phytoplankton Interactions in Freshwaters. Hydrobiologia 2016, 767, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fintelman-Oliveira, E.; Kruk, C.; Lacerot, G.; Klippel, G.; Branco, C.W.C. Zooplankton Functional Groups in Tropical Reservoirs: Discriminating Traits and Environmental Drivers. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Sommer, F. Cladocerans versus Copepods: The Cause of Contrasting Top–down Controls on Freshwater and Marine Phytoplankton. Oecologia 2006, 147, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, R.S. Grazing on Filamentous Algae by Herbivorous Zooplankton. Freshw. Biol. 1988, 20, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M. Feeding of Tropical Cladocerans (Moina Micrura, Diaphanosoma Excisum) and Rotifer (Brachionus Calyciflorus) on Natural Phytoplankton: Effect of Phytoplankton Size–Structure. J. Plankton. Res. 2008, 30, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.M.; Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Effects of Saxitoxin- and Non-Saxitoxin-Producing Strains of the Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis Raciborskii on the Fitness of Temperate and Tropical Cladocerans. Harmful Algae 2013, 28, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kâ, S.; Mendoza-Vera, J.M.; Bouvy, M.; Champalbert, G.; N’Gom-Kâ, R.; Pagano, M. Can Tropical Freshwater Zooplankton Graze Efficiently on Cyanobacteria? Hydrobiologia 2011, 679, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Morales, A.; Sarma, S.S.S.; Nandini, S. Feeding and Filtration Rates of Zooplankton (Rotifers and Cladocerans) Fed Toxic Cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa). J. Environ. Biol. 2014, 35, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kruk, C.; Devercelli, M.; Huszar, V.L. Reynolds Functional Groups: A Trait-Based Pathway from Patterns to Predictions. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Soares, M.C.S.; Paiva, R.; Silva, L.H.S. Morphology-Based Functional Groups as Effective Indicators of Phytoplankton Dynamics in a Tropical Cyanobacteria-Dominated Transitional River–Reservoir System. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 64, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.; Aubriot, L.; Soares, M.C.S.; González-Piana, M.; Fabre, A.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Lürling, M.; Antoniades, D.; Padisák, J.; Kruk, C. What Drives the Distribution of the Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Planktothrix Agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis Raciborskii? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprocaryota. 2. Oscillatoriales. In Subwasserflora von Mittleuropa; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; p. 759. [Google Scholar]
- Jüttner, F.; Watson, S.B.; von Elert, E.; Köster, O. β-Cyclocitral, a Grazer Defence Signal Unique to the Cyanobacterium Microcystis. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik-Skowrońska, B.; Bownik, A. Cyanobacterial Anabaenopeptin-B, Microcystins and Their Mixture Cause Toxic Effects on the Behavior of the Freshwater Crustacean Daphnia Magna (Cladocera). Toxicon 2021, 198, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Magalhães, L.; Noyma, N.P.; Furtado, L.L.; Mucci, M.; van Oosterhout, F.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Marinho, M.M.; Lürling, M. Efficacy of Coagulants and Ballast Compounds in Removal of Cyanobacteria (Microcystis) from Water of the Tropical Lagoon Jacarepaguá (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.M.d.A.; Sampaio, P.L.; Ferrão-Filho, A.d.S.; Magalhães, V.d.F.; Marinho, M.M.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; dos Santos, V.B.; Domingos, P.; de Oliveira e Azevedo, S.M.F. Toxic Cyanobacterial Blooms in an Eutrophicated Coastal Lagoon in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Effects on Human Health. Oecologia Aust. 2009, 13, 322–345. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.d.S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Accumulation of Microcystins by a Tropical Zooplankton Community. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 59, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchman, E.; Ohman, M.D.; Kiorboe, T. Trait-Based Approaches to Zooplankton Communities. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigler, F.H. The Relation between Concentration of Food and Feeding Rate of Daphnia Magna Straus. Can. J. Zool. 1961, 39, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teegarden, G.; Campbell, R.; Durbin, E. Zooplankton Feeding Behavior and Particle Selection in Natural Plankton Assemblages Containing Toxic Alexandrium spp. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 218, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, I.V. Dinâmica Da Comunidade Fitoplanctônica de Uma Lagoa Costeira Tropical Eutrofizada e Suas Respostas à Aplicação Da Técnica Flock & Lock Para a Mitigação de Florações de Cianobactérias. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Reis, G.C.; de Carvalho, G.H.A.; Vilar, M.C.P.; de Oliveira e Azevedo, S.M.F.; Ferrão-Filho, A.d.S. Saxitoxin-Producing Raphidiopsis Raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) Constrains Daphnia Fitness and Feeding Rate despite High Nutritious Food Availability. Toxics 2023, 11, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panosso, R.; Lürling, M. Daphnia Magna Feeding on Cylindrospermopsis Raciborskii: The Role of Food Composition, Filament Length and Body Size. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.C.S.; Lürling, M.; Panosso, R.; Huszar, V. Effects of the Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis Raciborskii on Feeding and Life-History Characteristics of the Grazer Daphnia Magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, M.C.P.; da Silva Ferrão-Filho, A.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Single and Mixed Diets of the Toxic Cyanobacteria Microcystis Aeruginosa and Raphidiopsis Raciborskii Differently Affect Daphnia Feeding Behavior. Food Webs 2022, 32, e00245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.A.; Echeverri, L.F.; Ferrão-Filho, A.S. Effects of Phytoplankton Extracts Containing the Toxin Microcystin-LR on the Survival and Reproduction of Cladocerans. Toxicon 2015, 95, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrlack, T.; Christoffersen, K.; Dittmann, E.; Nogueira, I.; Vasconcelos, V.; Börner, T. Ingestion of Microcystins by Daphnia: Intestinal Uptake and Toxic Effects. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.d.S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B. Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and Effects on Aquatic Animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2729–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.C.S.; Lurling, M.; Huszar, V.L.M. Responses of the Rotifer Brachionus Calyciflorus to Two Tropical Toxic Cyanobacteria (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Microcystis aeruginosa) in Pure and Mixed Diets with Green Algae. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Panosso, R.; Lürling, M. Consequences of Acclimation to Microcystis on the Selective Feeding Behavior of the Calanoid Copepod Eudiaptomus Gracilis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, V.F.; Moraes Soares, R.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Microcystin Contamination in Fish from the Jacarepaguá Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil): Ecological Implication and Human Health Risk. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M. Daphnia Growth on Microcystin-Producing and Microcystin-Free Microcystis Aeruginosa in Different Mixtures with the Green Alga Scenedesmus Obliquus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 2214–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M. Effects of Microcystin-Free and Microcystin-Containing Strains of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis Aeruginosa on Growth of the Grazer Daphnia Magna. Environ. Toxicol. 2003, 18, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrlack, T.; Henning, M.; Kohl, J.G. Mechanisms of the Inhibitory Effect of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis Aeruginosa on Daphnia Galeata’s Ingestion Rate. J. Plankton Res. 1999, 21, 1489–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Variability in the Provision and Function of Mucilage in Phytoplankton: Facultative Responses to the Environment. Hydrobiologia 2007, 578, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Kong, F.; Shi, X.; Cao, H. Morphological Response of Microcystis Aeruginosa to Grazing by Different Sorts of Zooplankton. Hydrobiologia 2006, 563, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Kong, F. Formation of Large Colonies: A Defense Mechanism of Microcystis Aeruginosa under Continuous Grazing Pressure by Flagellate Ochromonas sp. J. Limnol. 2012, 71, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, R.S.; Paerl, H.W. Toxic and Inhibitory Effects of the Blue-Green Alga Microcystis Aeruginosa on Herbivorous Zooplankton. J. Plankton Res. 1987, 9, 837–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.C.; Hart, R.C.; Combrink, S. Zooplankton Feeding on Size Fractionated Microcystis Colonies and Chlorella in a Hypertrophic Lake (Hartbeespoort Dam, South Africa): Implications to Resource Utilization and Zooplankton Succession. J. Plankton Res. 1987, 9, 1231–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarska, A.; Pietrzak, B.; Pijanowska, J. Effect of Poor Manageability and Low Nutritional Value of Cyanobacteria on Daphnia Magna Life History Performance. J. Plankton Res. 2014, 36, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.E.; Sarnelle, O.; Tillmanns, A.R. Effects of Cyanobacterial Toxicity and Morphology on the Population Growth of Freshwater Zooplankton: Meta-Analyses of Laboratory Experiments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Stibor, H. Copepoda—Cladocera—Tunicata: The Role of Three Major Mesozooplankton Groups in Pelagic Food Webs. Ecol. Res. 2002, 17, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.J.; Finlay, K.; Beisner, B.E. Functional Diversity of Crustacean Zooplankton Communities: Towards a Trait-Based Classification. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 796–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W. The Role of Grazers in Phytoplankton Succession. In Phytoplankton Ecology. Succession in Plankton Communities; Sommer, U., Ed.; Brock/Springer Series in Contemporary Bioscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 107–170. ISBN 978-3-642-74892-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bednarska, A.; Dawidowicz, P. Change in Filter-Screen Morphology and Depth Selection: Uncoupled Responses of Daphnia to the Presence of Filamentous Cyanobacteria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 2358–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.d.A.; Lürling, M.; Marinho, M.M. Assessment of the Effects of Light Availability on Growth and Competition Between Strains of Planktothrix Agardhii and Microcystis Aeruginosa. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Beekman, W. Grazer-Induced Defenses in Scenedesmus (Chlorococcales; Chlorophyceae): Coenobium and Spine Formation. Phycologia 1999, 38, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, O.; Duncan, A. The Relationship between Cell Carbon and Cell Volume in Freshwater Algal Species Used in Zooplanktonic Studies. J. Plankton Res. 1985, 7, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastner, J.; Flieger, I.; Neumann, U. Optimised Extraction of Microcystins from Field Samples—A Comparison of Different Solvents and Procedures. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3177–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K.; Namikoshi, M.; Evans, W.R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Sun, F.; Rouhiainen, L.; Luukkainen, R.; Rinehart, K.L. Isolation and Characterization of a Variety of Microcystins from Seven Strains of the Cyanobacterial Genus Anabaena. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lürling, M.; Verschoor, A.M. FO-Spectra of Chlorophyll Fluorescence for the Determination of Zooplankton Grazing. Hydrobiologia 2003, 491, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, J. Measuring Preference in Selective Predation. Ecology 1978, 59, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Faassen, E.J.; Pennino, M.G.; Lürling, M. Effect of the Toxin (Microcystin) Content of Microcystis on Copepod Grazing. Harmful Algae 2016, 52, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delignette-Muller, M.L.; Dutang, C. Fitdistrplus: An R Package for Fitting Distributions. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 64, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 14 November 2024).



| Coefficients | Estimate | SE | t Value | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.60 | 0.09 | −6.66 | <0.001 |
| Log 10 (Concentration) | −0.19 | 0.17 | −0.11 | 0.91 |
| Monoraphidium vs. MIC-03 | −0.62 | 0.13 | −4.86 | <0.001 |
| Monoraphidium vs. MIC-08 | −1.02 | 0.13 | −8.04 | <0.001 |
| Monoraphidium vs. PLANK-03 | −1.03 | 0.13 | −8.09 | <0.001 |
| Monoraphidium vs. PLANK-09 | −1.09 | 0.13 | −8.52 | <0.001 |
| Concentration: Monoraphidium vs. MIC-03 | −0.02 | 0.24 | −0.07 | 0.94 |
| Concentration: Monoraphidium vs. MIC-08 | −0.78 | 0.24 | −3.19 | <0.001 |
| Concentration: Monoraphidium vs. PLANK-03 | −0.52 | 0.24 | −2.12 | <0.01 |
| Concentration: Monoraphidium vs. PLANK-09 | −0.65 | 0.24 | −2.67 | <0.001 |
| Estimate | SE | t Value | p |
| MIC-03: MIC-08 | 0.002 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.85 |
| MIC-03: PLANK-03 | −0.03 | 0.13 | −2.68 | <0.05 |
| MIC-03: PLANK-09 | −0.03 | 0.13 | −2.50 | <0.05 |
| MIC-08: PLANK-03 | 0.37 | 0.13 | 2.87 | <0.01 |
| MIC-08: PLANK-09 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 2.87 | <0.05 |
| PLANK-03: PLANK-09 | −0.002 | 0.13 | −0.18 | 0.85 |
| Estimate | SE | t Value | p |
| MIC-03: MIC-08 | −0.21 | 0.11 | −1.85 | 0.07 |
| MIC-03: PLANK-03 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.89 |
| MIC-03: PLANK-09 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 2.25 | <0.05 |
| MIC-08: PLANK-03 | 0.23 | 0.11 | 1.99 | 0.05 |
| MIC-08: PLANK-09 | 0.47 | 0.11 | 4.09 | <0.001 |
| PLANK-03: PLANK-09 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 2.10 | <0.05 |
| Estimate | SE | t Value | p |
| MIC-03: MIC-08 | −0.08 | 0.08 | −0.91 | 0.37 |
| MIC-03: PLANK-03 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 2.18 | <0.05 |
| MIC-03: PLANK-09 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 3.23 | <0.01 |
| MIC-08: PLANK-03 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 3.09 | <0.01 |
| MIC-08: PLANK-09 | 0.35 | 0.08 | 4.14 | <0.001 |
| PLANK-03: PLANK-09 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 1.05 | 0.30 |
| Estimate | SE | t Value | p |
| 50:25 | −0.11 | 0.07 | −1.54 | 0.13 |
| 75:25 | −0.37 | 0.07 | −5.34 | <0.001 |
| 75:50 | −0.27 | 0.07 | −3.79 | <0.001 |
| Estimate | SE | t Value | p |
| 50:25 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 1.54 | 0.13 |
| 75:25 | 0.37 | 0.07 | 5.33 | <0.001 |
| 75:50 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 3.79 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rangel, L.M.; Mesquita, M.C.B.; Barros, S.R.d.; Neres-Lima, V.; Celano, M.R.; Vilar, M.C.P.; Azevedo, S.M.F.d.O.e.; Marinho, M.M. Chemical and Morphological Constitutive Defensive Traits of Cyanobacteria Have Different Effects on the Grazing of a Small Tropical Cladoceran. Toxins 2025, 17, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070343
Rangel LM, Mesquita MCB, Barros SRd, Neres-Lima V, Celano MR, Vilar MCP, Azevedo SMFdOe, Marinho MM. Chemical and Morphological Constitutive Defensive Traits of Cyanobacteria Have Different Effects on the Grazing of a Small Tropical Cladoceran. Toxins. 2025; 17(7):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070343
Chicago/Turabian StyleRangel, Luciana Machado, Marcella Coelho Berjante Mesquita, Shara Rosa de Barros, Vinicius Neres-Lima, Michael Ribas Celano, Mauro Cesar Palmeira Vilar, Sandra Maria Feliciano de Oliveira e Azevedo, and Marcelo Manzi Marinho. 2025. "Chemical and Morphological Constitutive Defensive Traits of Cyanobacteria Have Different Effects on the Grazing of a Small Tropical Cladoceran" Toxins 17, no. 7: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070343
APA StyleRangel, L. M., Mesquita, M. C. B., Barros, S. R. d., Neres-Lima, V., Celano, M. R., Vilar, M. C. P., Azevedo, S. M. F. d. O. e., & Marinho, M. M. (2025). Chemical and Morphological Constitutive Defensive Traits of Cyanobacteria Have Different Effects on the Grazing of a Small Tropical Cladoceran. Toxins, 17(7), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070343







