Toxicodynamic Assessment of Aqueous Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) Seed Extract on Mortality and Carboxylesterase Activity in Key Organs of Bombyx mori L. Larvae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of ANSE on Fifth Instar Silkworm Larvae
2.1.1. Larvae Mortality
2.1.2. Survival Rate of Larvae
2.1.3. Toxicity Value
2.2. Effects of ANSE on CarE Activity in Fifth Instar Silkworm Larvae
2.2.1. CarE Activity in Midgut
2.2.2. CarE Activity in Fat Body
2.2.3. CarE Activity Malpighian Tubules
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of ANSE on Mortality and Toxicity in Silkworm Larvae
3.2. Effects of ANSE on CarE Activity in Essential Organs of Silkworm Larvae
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Silkworm Rearing
5.2. ANSE Preparation
5.3. Toxicity Assessment
5.4. CarE Activity Evaluation
5.4.1. Extraction of CarE
- (1)
- Silkworm Tissue Preparation
- (2)
- Enzyme Extraction
5.4.2. Assay of CarE Activity Elucidation
5.4.3. Protein Content Determination
5.5. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANSE | Aqueous neem seed extract |
| h | Hour |
References
- Souto, A.L.; Sylvestre, M.; Tölke, E.D.; Tavares, J.F.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G. Plant-Derived Pesticides as an Alternative to Pest Management and Sustainable Agricultural Production: Prospects, Applications and Challenges. Molecules 2021, 26, 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngegba, P.M.; Cui, G.; Khalid, M.Z.; Zhong, G. Use of Botanical Pesticides in Agriculture as an Alternative to Synthetic Pesticides. Agriculture 2022, 12, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Hu, H.; Zhu, L.; Liu, K.; Bai, J.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, C. Pyrethrins in Tanacetum Cinerariifolium: Biosynthesis, Regulation, and Agricultural Application. Ornam. Plant Res. 2024, 4, e015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavela, R.; Benelli, G. Essential Oils as Ecofriendly Biopesticides? Challenges and Constraints. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.V.R.; Oliveira, J.L.d.; Páscoli, M.; Lima, R.d.; Fraceto, L.F. Neem Oil and Crop Protection: From Now to the Future. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Sehgal, A.; Cahill, D.M.; Barrow, C.J.; Sehgal, R.; Kanwar, J.R. Progress on Azadirachta indica Based Biopesticides in Replacing Synthetic Toxic Pesticides. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadir, A.; Ghosh, T.; Ilango, K.; Deshmukh, V.N.; Mahato, P.; Krishna, K.V.V.S.; Bali, S.; Dhubkaria, Y.; Kumar, A. In-depth Review on Taxonomy, Phytochemistry, Traditional Uses and Pharmacological Significance of Azadirachta indica plant. Eur. J. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 11, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Mordue, A.J.; Nisbet, A.J. Azadirachtin from the Neem Tree Azadirachta indica: Its Action against Insects. An. Da Soc. Entomológica Do Bras. 2000, 29, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil-Nathan, S. Physiological and Biochemical Effect of Neem and Other Meliaceae Plants Secondary Metabolites against Lepidopteran Insects. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusei, S.; Azupio, S. Neem: A Novel Biocide for Pest and Disease Control of Plants. J. Chem. 2022, 1, 6778554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, G.; Soni, R.K. Azadirachta indica in Focus: Investigating Neem’s Diverse Applications. J. Chem. Health Risks 2023, 13, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Kordy, A.M. Residual Effect of Certain Pesticides on the Mulberry Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). Middle East J. Appl. Sci. 2014, 4, 711–717. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.S.; Naika, R.; Banuprakash, K.; Murali, K.; Mohan, K.; Sadatulla, F. Studies on Efficacy of Green Insecticides on Mulberry Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. through Rearing Performance. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2019, 7, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Sharath, M.; Narayanaswamy, K.C.; Gowda, M. Efficacy of Pesticides Against Yellow Mite in Mulberry and its Residual Toxicity on Silkworm. Mysore J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 56, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, S.; Jekinakatti, B.; Bharathi, B.; Charitha, K.; Shruthi, G.; Harika, K.R.; Kumar, K.; Rahman, T. Impact of Novel Insecticides in Mulberry Ecosystem and Its Residual Effect on Silkworm Growth & Productivity. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2024, 46, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumutha, P.; Padmalatha, C.; Doss, S.S.M.; Singh, A.J.A.R. Toxicity Evaluation of Neem Oil and Metacid on the Development on Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Uttar Pradesh J. Zool. 2009, 29, 220–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhong, G.; Yi, X. Azadirachtin Induced Apoptosis in the Prothoracic Gland in Bombyx mori and a Pronounced ca2+ Release Effect in Sf9 Cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Bandey, S.A.; Himantharaj, M.T. Eucalyptus and Neem Based Crude Extraction Effect in Acceleration of Natural Mounting Process in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2020, 9, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Gaurav, K.; Hassan, S.M. Effect of Azadirachta ndica (Neem) Extract on the Growth and Development of the Larvae of Bombyx mori. Samdarshi 2023, 16, 1156–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Qiao, H.; Peng, W.; Moussian, B.; Wang, Y. Xenobiotic Responses in Insects. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 109, e21869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelock, C.E.; Shan, G.; Ottea, J.A. Overview of Carboxylesterases and Their Role in the Metabolism of Insecticides. Nippon. Nōyaku Gakkaishi 2005, 30, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruse, C.; Moural, T.W.; Zhu, F. Dynamic Roles of Insect Carboxyl/Cholinesterases in Chemical Adaptation. Insects 2023, 14, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lǚ, K.; Li, Y.; Xiao, T.; Sun, Z. The Metabolic Resistance of Nilaparvata lugens to Chlorpyrifos Is Mainly Driven by the Carboxylesterase CarE17. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Chen, K.; Yao, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. A Study on the Activity of Carboxylesterase and the Differential Expression of Its Gene in the Midguts of Bombyx Mori Resistant to BmDNV-Z. Agric. Sci. China 2007, 6, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.-Y.; Lu, C.; Li, W.; Xiang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Annotation and Expression of Carboxylesterases in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, P.; Bedini, S.; Conti, B. Multiple Functions of Malpighian Tubules in Insects: A Review. Insects 2022, 13, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveenkumar, C.; Pradeep, S.; Pungavi, R. Insect Physiology and Biochemistry: Mechanisms and Signalling Pathways. In Entomology Redefined, Insect-Based Solutions For Agriculture, 1st ed.; Nadaf, A.R.M., Venukumar, S., Kumar, S.V., Kamleshbhai, T.P., Sangavi, R., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2024; pp. 160–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubota, T.; Shiotsuki, T. Genomic Analysis of Carboxyl/Cholinesterase Genes in the Silkworm Bombyx mori. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Xin, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Gui, Z. Transcriptional Response of Detoxifying Enzyme Genes in Bombyx mori under Chlorfenapyr Exposure. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 177, 104899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, H.; Tonoike, A.; Narushima, K.; Horie, R.; Sekimizu, K. Silkworm as a Model Animal to Evaluate Drug Candidate Toxicity and Metabolism. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 149, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanapan, A.; Sujayanont, P. Impact of Neem Seed Extract on Mortality, Esterase and Glutathione-S-Transferase Activities in Thai Polyvoltine Hybrid Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Insects 2024, 15, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viduya, M.M.; Ulat, M.E.; Supsup, G.E.; Abuan, J.P.; Sanchez, E.P.; Supsup, R.D. Multivoltine and Bivoltine Silkworm F1 Hybrids Adaptable to Type One (1) Climatic Conditions in the Philippines. Int. J. Ind. Entomol. Biomater. 2023, 47, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Wu, W.; Liu, H. Effects of Fraxinellone on the Midgut Enzyme Activities of the 5th Instar Larvae of Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata Walker. Toxins 2014, 6, 2708–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiotsuki, T.; Suzuki, R.; Tsuchiya, W.; Yamazaki, T.; Shimomura, M.; Tsubota, T.; Nakakura, T.; Henmi, S. Characteristics of the Takeout Protein Ce-0330 in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2023, 58, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.W.; Kobets, T. Hayes’ Principles and Methods of Toxicology, 7th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; 2140p, ISBN 9781003390008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozman, K.K.; Doull, J. Dose and Time as Variables of Toxicity. Toxicology 2000, 144, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekinakatti, B.; Doreswamy, C.; Karur, A.S.; Kallimani, C.S.; Kumar, N.R.; Navi, S. Effect of Feeding Pesticides Sprayed Mulberry Leaves on Rearing Parameters of Silkworm. Plant Arch. 2024, 24, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, Y.W.; Hu, X.; Wu, S.; Cai, L.M.; Zhao, X. Individual and Joint Acute Toxicities of Selected Insecticides against Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 109, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zheng, Q.; Qin, D.; Luo, P.; Ye, C.; Shen, S.; Cheng, D.; Huang, S.; Liu, L.; Xu, H.; et al. Azadirachtin Inhibits the Development and Metabolism of the Silk Glands of Spodoptera frugiperda and Affects Spinning Behavior. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 5293–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaş, M. Bio-control effect of neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss, 1830) leaf and seed powders against adult bean weevil (Acanthoscelides obtectus Say- 1831) mortality. Int. J. Biol. Res. 2023, l.8, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, N.; Roychoudhury, N.; Chandra, G. Probit Analysis for Toxicological Experiments against Forest Insect Pests. In Statistics in Forestry: Methods and Applications; Chandra, G., Nautiyal, R., Chandra, H., Roychoudhury, N., Mohammad, N., Eds.; Tropical Forest Research Institute (Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education): Jabalpur, India, 2015; pp. 125–129. Available online: https://shorturl.asia/F8OSR (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Uçar, A. LC50 Determination and Probit Analysis. In Aquatic Toxicology in Freshwater; Atamanalp, M., Alak, G., Uςar, A., Parlak, V., Eds.; Springer Water: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 95–105. ISBN 978-3-031-56669-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil-Nathan, S.; Kalaivani, K.; Kim, S.H.; Murugan, K. The Toxicity and Behavioural Effects of Neem Limonoids on Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenée), the Rice Leaffolder. Chemosphere 2005, 62, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Hao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, R.; Chen, R.; Zheng, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H. Biochemical Toxicity and Transcriptome Aberration Induced by Dinotefuran in Bombyx mori. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, S.; Xiu, Y.; Yan, H.; Wang, K.; Ba, X.; Wang, H. Sublethal Effects of Neonicotinoid Insecticides on the Development, Body Weight and Economic Characteristics of Silkworm. Toxics 2023, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roel, A.R.; Dourado, D.M.; Matias, R.; Porto, K.R.A.; Bednaski, A.V.; Costa, R.B.D. The Effect of Sub-Lethal Doses of Azadirachta indica (Meliaceae) Oil on the Midgut of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Rev. Bras. De Entomol. 2010, 54, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulashie, S.K.; Adjei, F.; Abraham, J.; Addo, E. Potential of Neem Extracts as Natural Insecticide against Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelock, C.E.; Nakagawa, Y. Carboxylesterases—From Function to the Field: An Overview of Carboxylesterase Biochemistry, Structure–Activity Relationship, and Use in Environmental Field Monitoring. Nippon Nōyaku Gakkaishi 2010, 35, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, J.M.; Sun, S.-s.; Wang, B.B.; Jin, Y.; Shen, W.D.; Li, B. Changes in the Activity and the Expression of Detoxification Enzymes in Silkworms (Bombyx mori) after Phoxim Feeding. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 105, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, R.; Sendi, J.J. Effect of Neem Pesticide (Achook) on Midgut Enzymatic Activities and Selected Biochemical Compounds in the Hemolymph of Lesser Mulberry Pyralid, Glyphodes pyloalis Walker (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Plant Prot. Res. 2013, 53, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.N.; Sharma, R. Azadirachtin Induced Changes in Feeding, Dietary Utilization and Midgut Carboxylesterase Activity of the Final Instar Larvae of Spodoptera Litura (Fabricius) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 1996, 31, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, G.D.; Zanuncio, J.C.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Pratissoli, D.; Polanczyk, R.A.; Azevedo, D.O.; Serrão, J.E. Cytotoxicity in the midgut and fat body of Anticarsia gemmatalis (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) larvae exerted by neem seeds extract. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2014, 11, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, R.; Chen, W.; Isman, M.B. Synergism of Malathion and Inhibition of Midgut Esterase Activities by an Extract from Melia toosendan (Meliaceae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1995, 53, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, H. Disruption of Carboxylesterase DaEST3 Reduces Tolerance to Host Allelochemicals in Dendroctonus armandi. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2023, 17, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Teng, F.-y.; Wei, H.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qi, Y.-x. AANAT1 Regulates Insect Midgut Detoxification through the ROS/CncC Pathway. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect Fat Body: Energy, Metabolism, and Regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronek, P.; Wojcik, L.; Strachecka, A. Fat Body—Multifunctional Insect Tissue. Insects 2021, 12, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, T.; Li, F.; Fang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Lu, Z.; Qu, J.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; et al. Effects of Chlorantraniliprole Exposure on Detoxification Enzyme Activities and Detoxification-Related Gene Expression in the Fat Body of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-E.; Ma, H.-J.; Feng, D.-D.; Lai, X.-F.; Chen, Z.-M.; Xu, M.-Y.; Yu, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Induction of Detoxification Enzymes by Quercetin in the Silkworm. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.S. Shifts in Glycogen Metabolism in Hemolymph and Fat Body of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) in Response to Organophosphorus Insecticides Toxicity. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2002, 74, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.Z.; Hu, L.; Ye, M.; Wang, R.L.; Zhu, K.Y.; Zeng, R.S.; Cai, W. Effects of soybean trypsinase inhibitor and defense signaling compounds on detoxification enzymes in Spodoptera litura (F.) larvae. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Birner-Gruenberger, R.; Bickmeyer, I.; Lange, J.; Hehlert, P.; Hermetter, A.; Kollroser, M.; Rechberger, G.N.; Kühnlein, R.P. Functional Fat Body Proteomics and Gene Targeting Reveal in Vivo Functions of Drosophila melanogaster α-Esterase-7. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Xiong, C.; Cao, X.; Shan, T.; Jin, Q.; Jiang, H. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification, and Expression Profiling of Serine Esterases and Other Esterase-Related Proteins in the Tobacco Hornworm, Manduca sexta. Insect Sci. 2022, 30, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, D.; Wang, G.; He, Q.; Song, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, P. Adaptive Changes in Detoxification Metabolism and Transmembrane Transport of Bombyx mori Malpighian Tubules to Artificial Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, A.; Brandmayr, P. Structural and Functional Alterations in Malpighian Tubules as Biomarkers of Environmental Pollution: Synopsis and Prospective. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cintra, P.; Nocelli, R.C.F.; Roat, T.C.; Silva-Zacarín, E.C.M.; Malaspina, O. Comparative Physiology of Malpighian Tubules: Form and Function. Insect Physiol. 2016, 6, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, J.A.T. Insights into the Malpighian Tubule from Functional Genomics. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, S.; O’Donnell, M.J. Interactions between Detoxification Mechanisms and Excretion in Malpighian Tubules of Drosophila Melanogaster. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zou, Y.; Liu, S.; Yi, Q.; Hu, C.; Wang, C.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, P. Proteomic-Based Insight into Malpighian Tubules of Silkworm Bombyx mori. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassam, S.M.; Iqbal, Z.; Jabbar, A.; Sindhu, Z.-u.-D.; Chattha, A.I. Efficacy of Crude Neem Seed Kernel Extracts against Natural Infestation of Sarcoptes scabiei Var. Ovis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 115, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finney, D.J. A Statistical Treatment of the Sigmoid Response Curve. Probit Analysis; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1971; pp. 1–318. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Laboratory and Field Testing of Mosquito Larvicides. 2005. Available online: https://shorturl.asia/J972V (accessed on 31 May 2025).
- Kaneko, Y.; Yasanga, T.; Suzuki, M.; Sakurai, S. Larval Fat Body Cells Die during the Early Pupal Stage in the Frame of Metamorphosis Remodelation in Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Ye, A.; Cao, J.; He, R.; Pan, M.; Jin, F.; Ma, H.; Zhou, W. Multi-Tissue Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Potential Mechanisms of Cocoon Yield in Silkworms (Bombyx mori) Fed Formula Feed versus Mulberry Leaves. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 977047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yooboon, T.; Pengsook, A.; Ratwatthananon, A.; Pluempanupat, W.; Bullangpoti, V. A Plant-Based Extract Mixture for Controlling Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2019, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Suprima, M.S.; Ravindran, J. Anti-feedant activity of Pachygone laurifolia (DC.) L. Lian & Wei Wang bark extracts in tobacco cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) is mediated through biochemical responses and pathological damage. J. Agric. Rural Dev. Trop. Subtrop. (JARTS) 2024, 125, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunarathne, P.; Pocquet, N.; Labbé, P.; Milesi, P. BioRssay: An R Package for Analyses of Bioassays and Probit Graphs. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
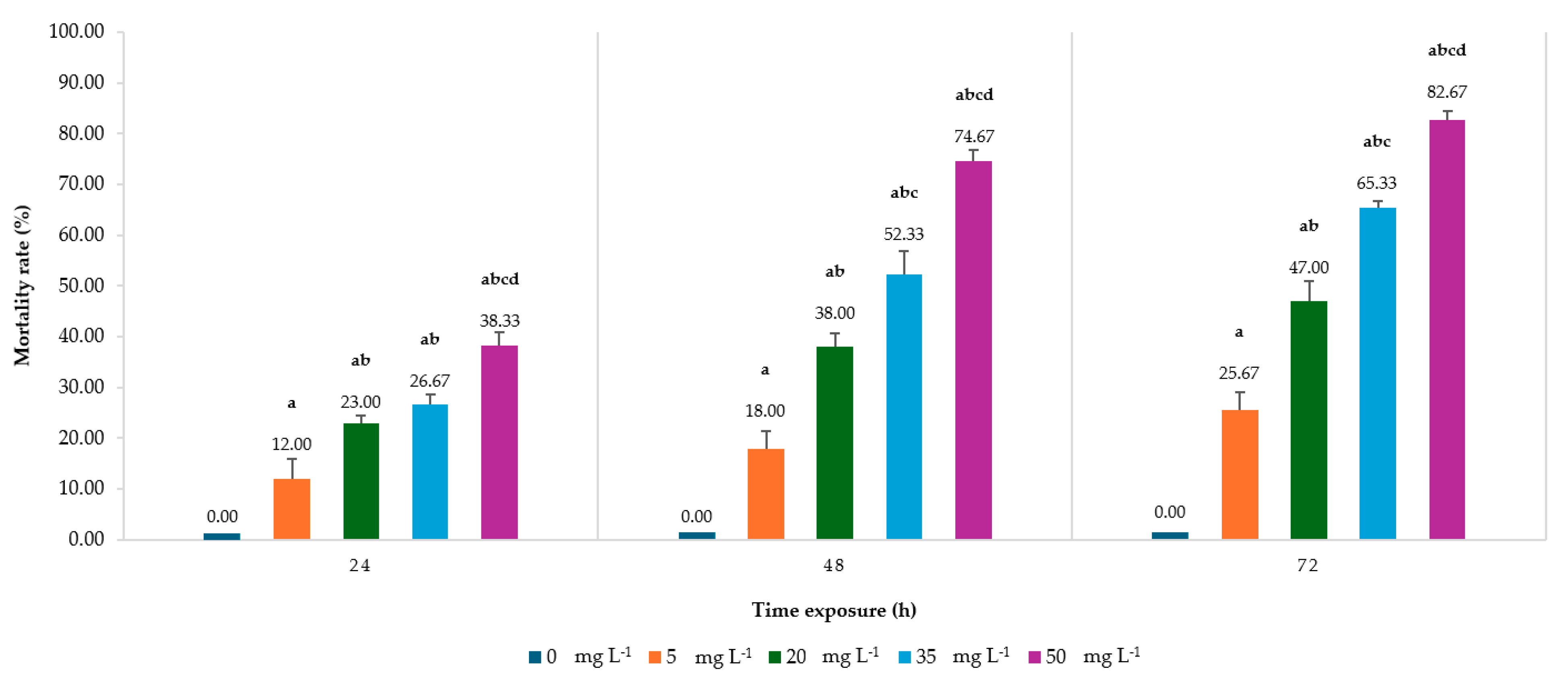
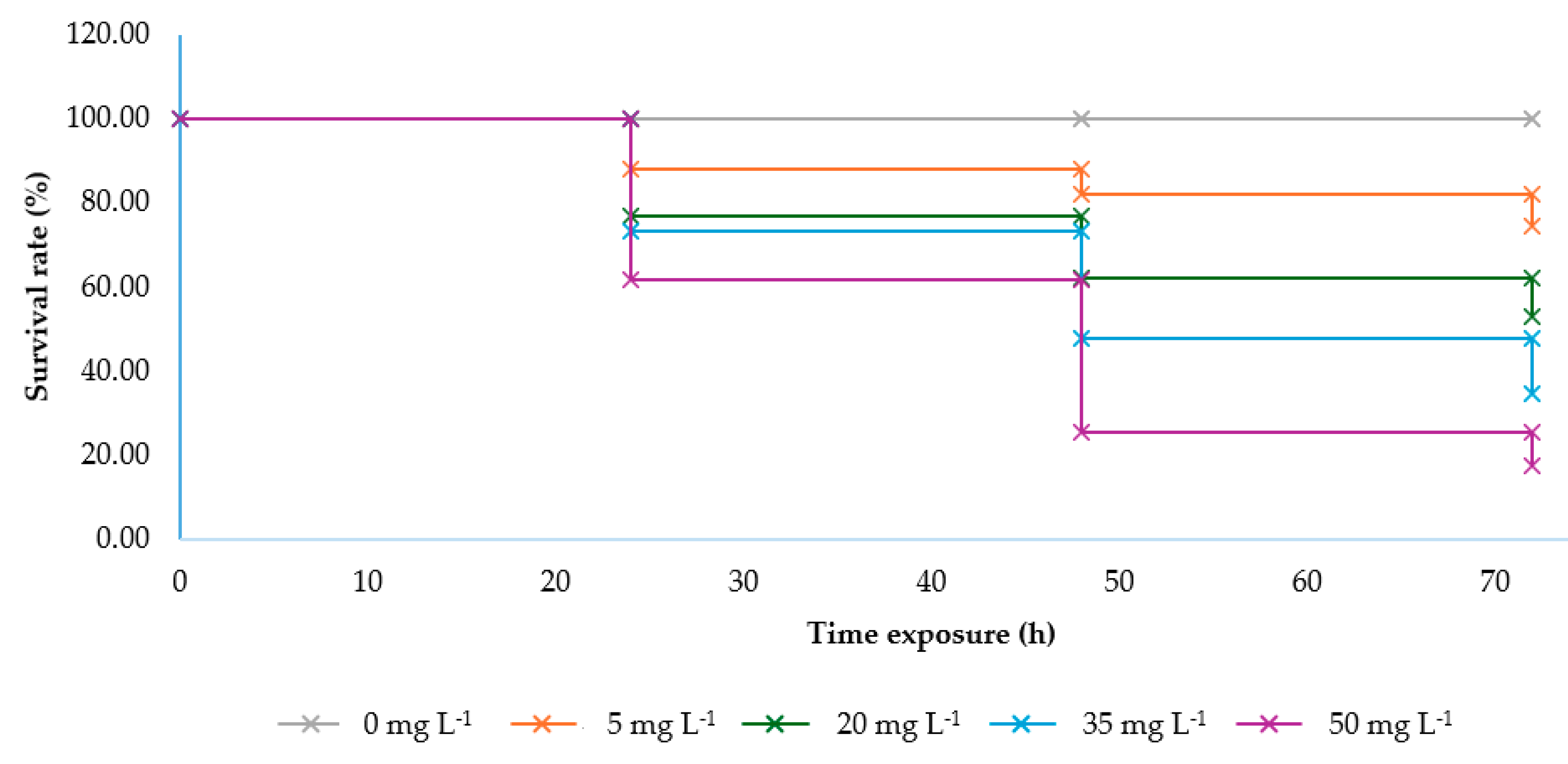
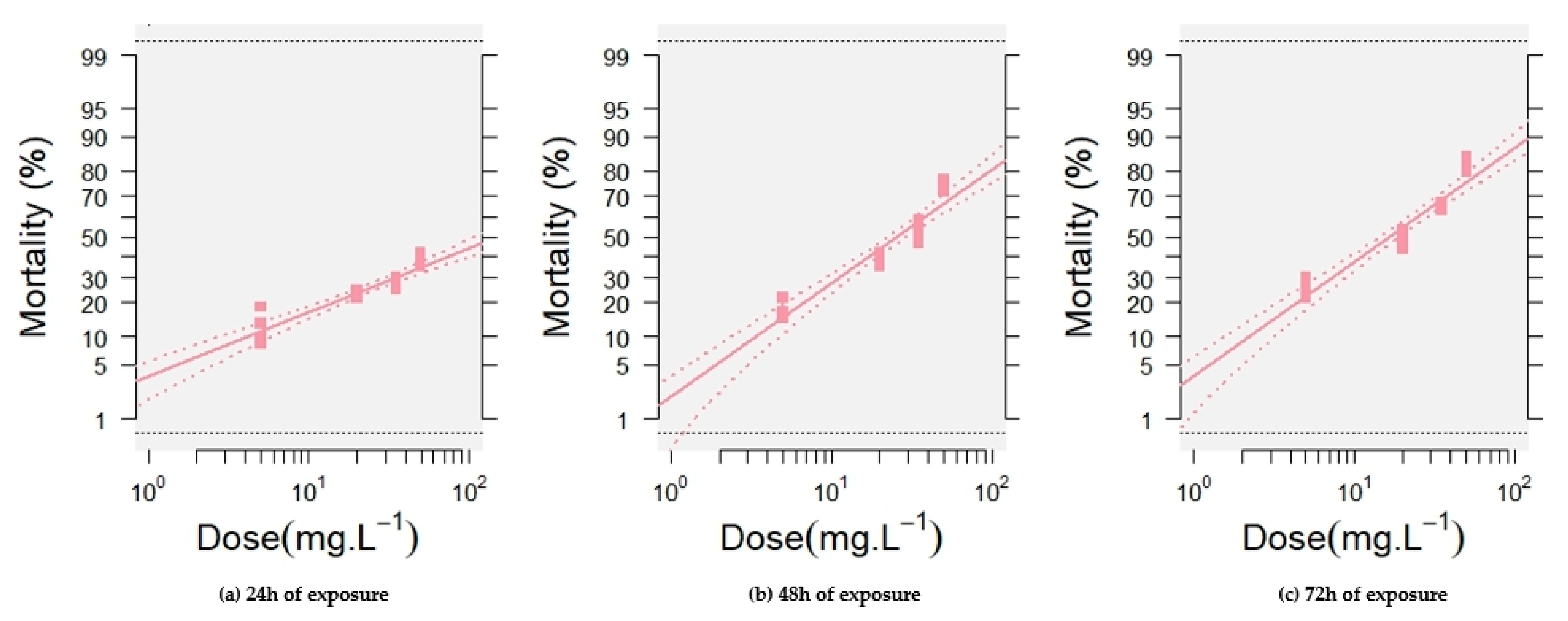

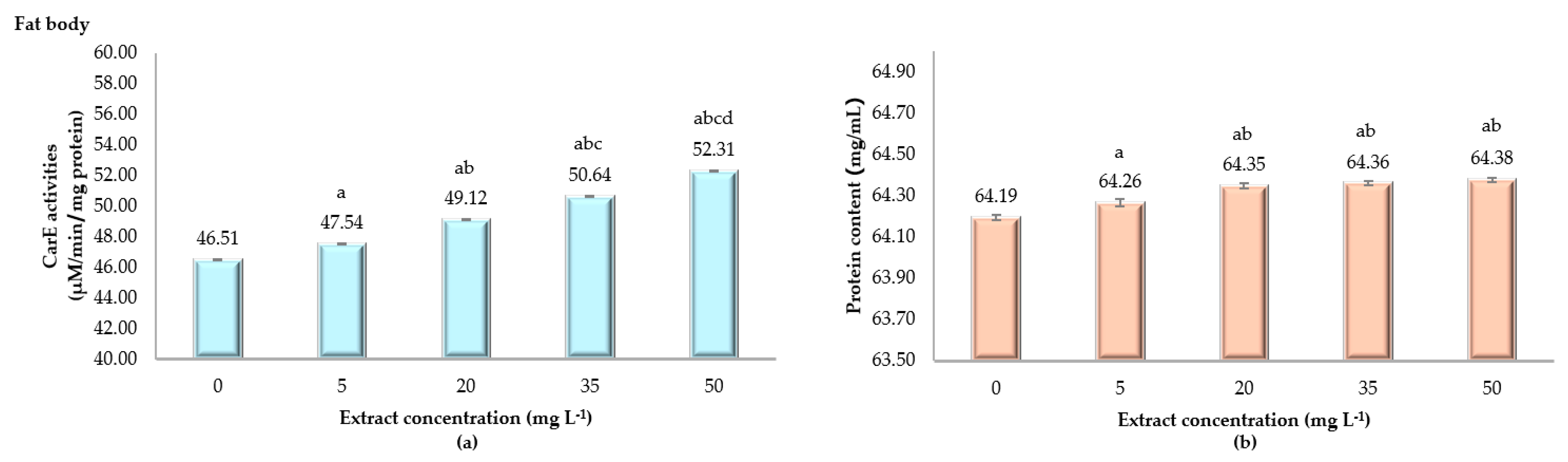

| Time Exposure (h) | Slope ± SE | Intercept ± SE | Toxicity Value of ANSE (mg L−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC10 (CI) | LC50 (CI) | LC90 (CI) | |||
| 24 | 0.82 ± 0.12 | (−1.79) ± 0.16 | 4.11 (1.50–24.00) | 149.00 (25.00–3370.00) | 5403.00 (423.00–476,627.00) |
| 48 | 1.46 ± 0.13 | (−2.05) ± 0.18 | 3.36 (1.69–9.06) | 25.00 (9.37–108.00) | 193.00 (52.00–1296.00) |
| 72 | 1.46 ± 0.12 | (−1.78) ± 0.16 | 2.20 (1.25–4.82) | 17.00 (7.09–54.00) | 125.00 (40.00–610.00) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rattanapan, A.; Phannasri, C.; Phannasri, C.; Sujayanont, P.; Sagulsawasdipan, K. Toxicodynamic Assessment of Aqueous Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) Seed Extract on Mortality and Carboxylesterase Activity in Key Organs of Bombyx mori L. Larvae. Toxins 2025, 17, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060304
Rattanapan A, Phannasri C, Phannasri C, Sujayanont P, Sagulsawasdipan K. Toxicodynamic Assessment of Aqueous Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) Seed Extract on Mortality and Carboxylesterase Activity in Key Organs of Bombyx mori L. Larvae. Toxins. 2025; 17(6):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060304
Chicago/Turabian StyleRattanapan, Ajin, Chuthep Phannasri, Chawiwan Phannasri, Patcharawan Sujayanont, and Kattinat Sagulsawasdipan. 2025. "Toxicodynamic Assessment of Aqueous Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) Seed Extract on Mortality and Carboxylesterase Activity in Key Organs of Bombyx mori L. Larvae" Toxins 17, no. 6: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060304
APA StyleRattanapan, A., Phannasri, C., Phannasri, C., Sujayanont, P., & Sagulsawasdipan, K. (2025). Toxicodynamic Assessment of Aqueous Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) Seed Extract on Mortality and Carboxylesterase Activity in Key Organs of Bombyx mori L. Larvae. Toxins, 17(6), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060304





