An Experimental Model of Acute Pulmonary Damage Induced by the Phospholipase A2-Rich Venom of the Snake Pseudechis papuanus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
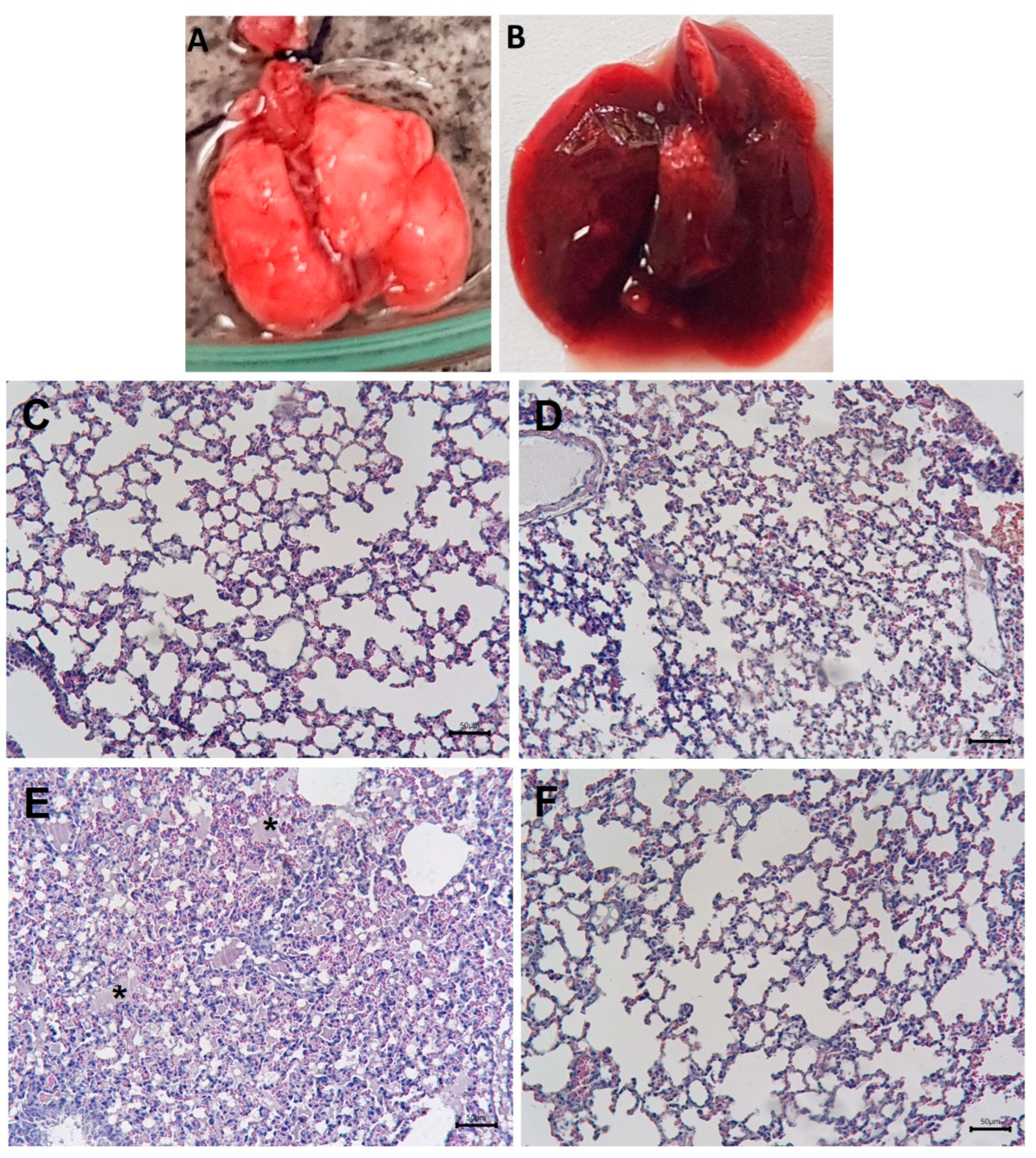
2.1. Macroscopic and Histological Alterations in the Lungs and Inhibition by Varespladib
2.2. Effect of Venom on Lung Surfactant Factor
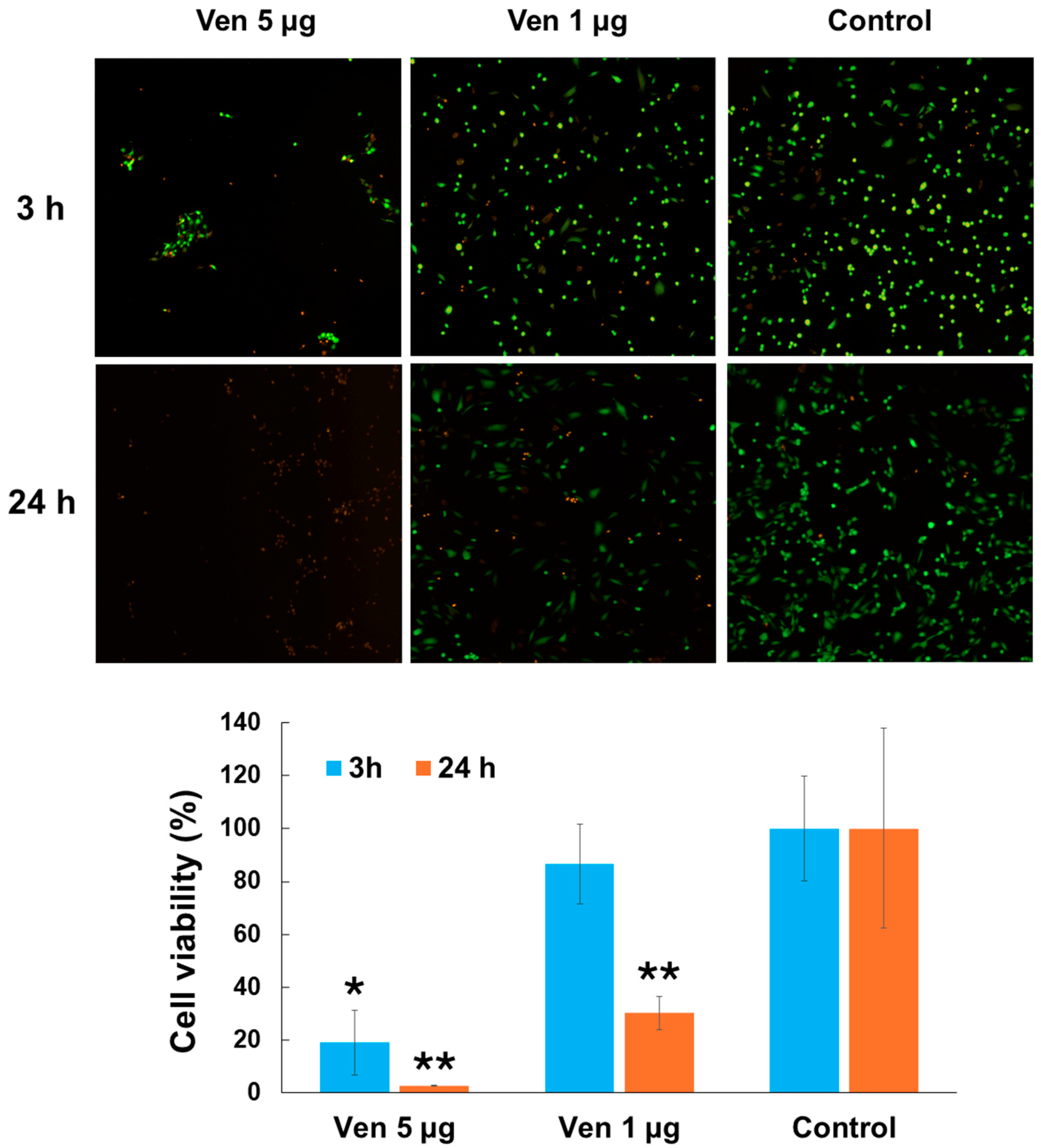
2.3. Cytotoxic Effect of Venom on Endothelial Cells
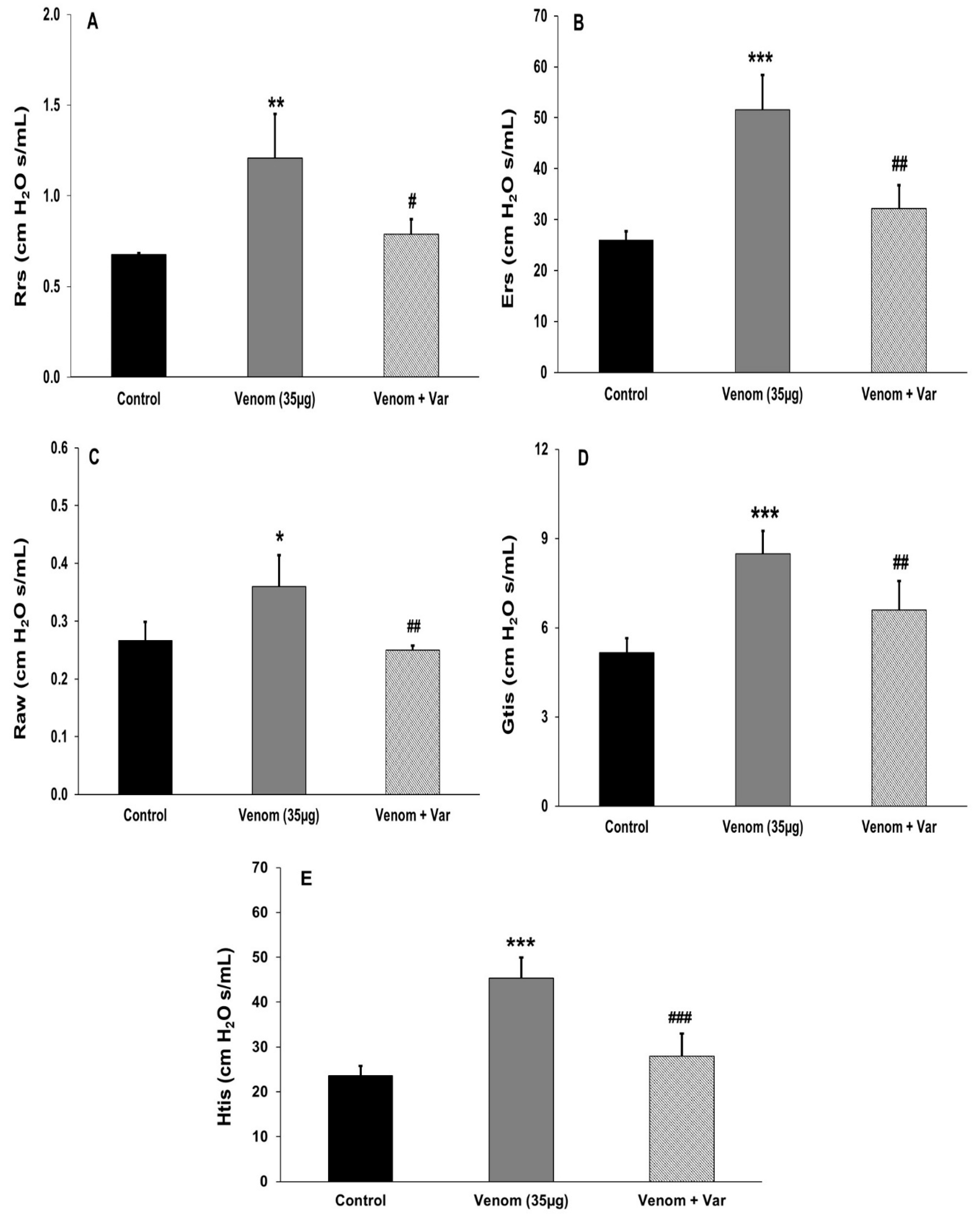
2.4. Effect of Venom on Pulmonary Mechanics
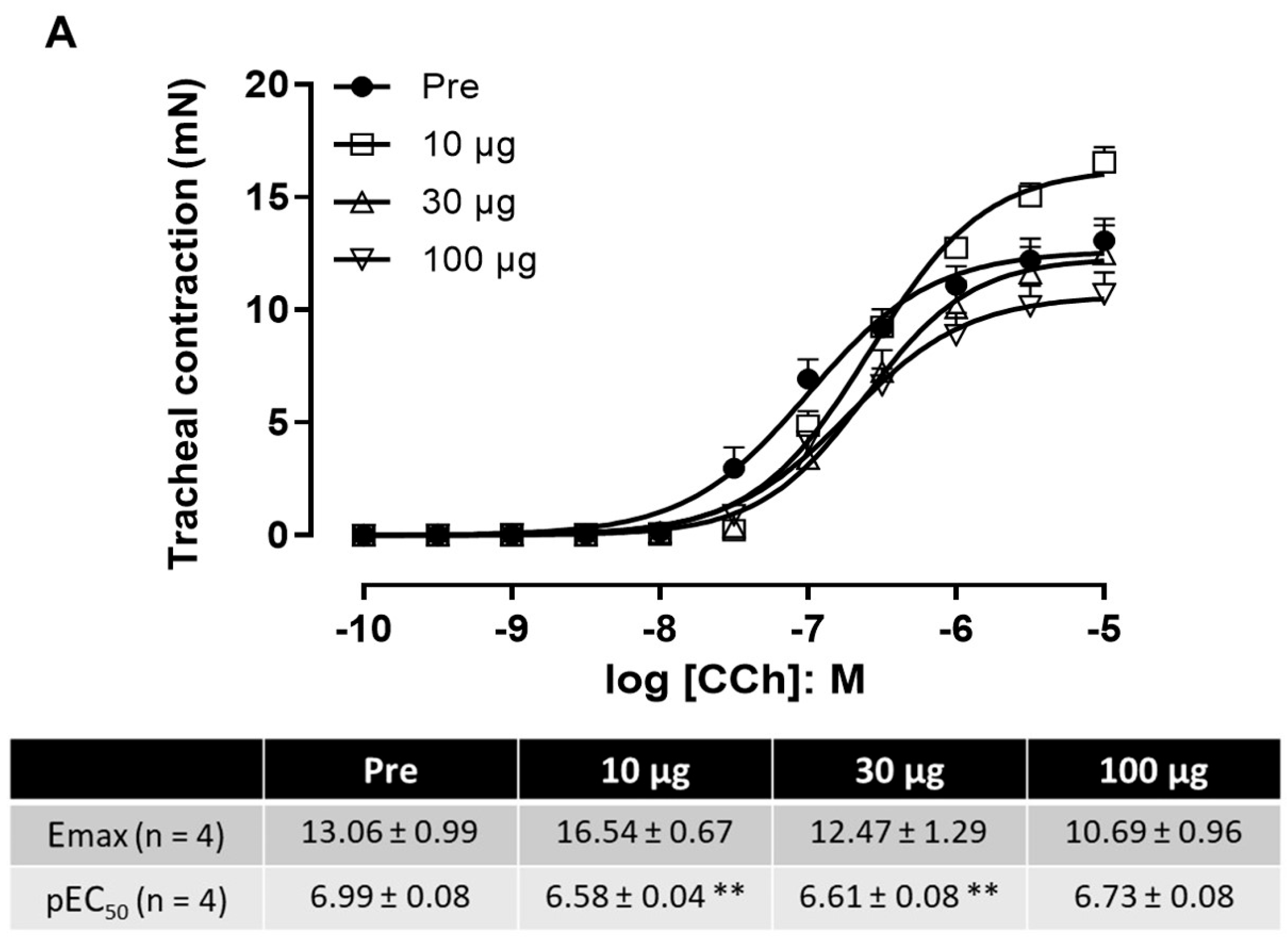
2.5. Effect of Venom on Tracheal and Bronchial Reactivity
2.6. Effect of Venom on Exhaled NO
2.7. Effect of Venom on Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Activity (ACE)
2.8. Analyses of BALF
2.8.1. Inflammatory Cells
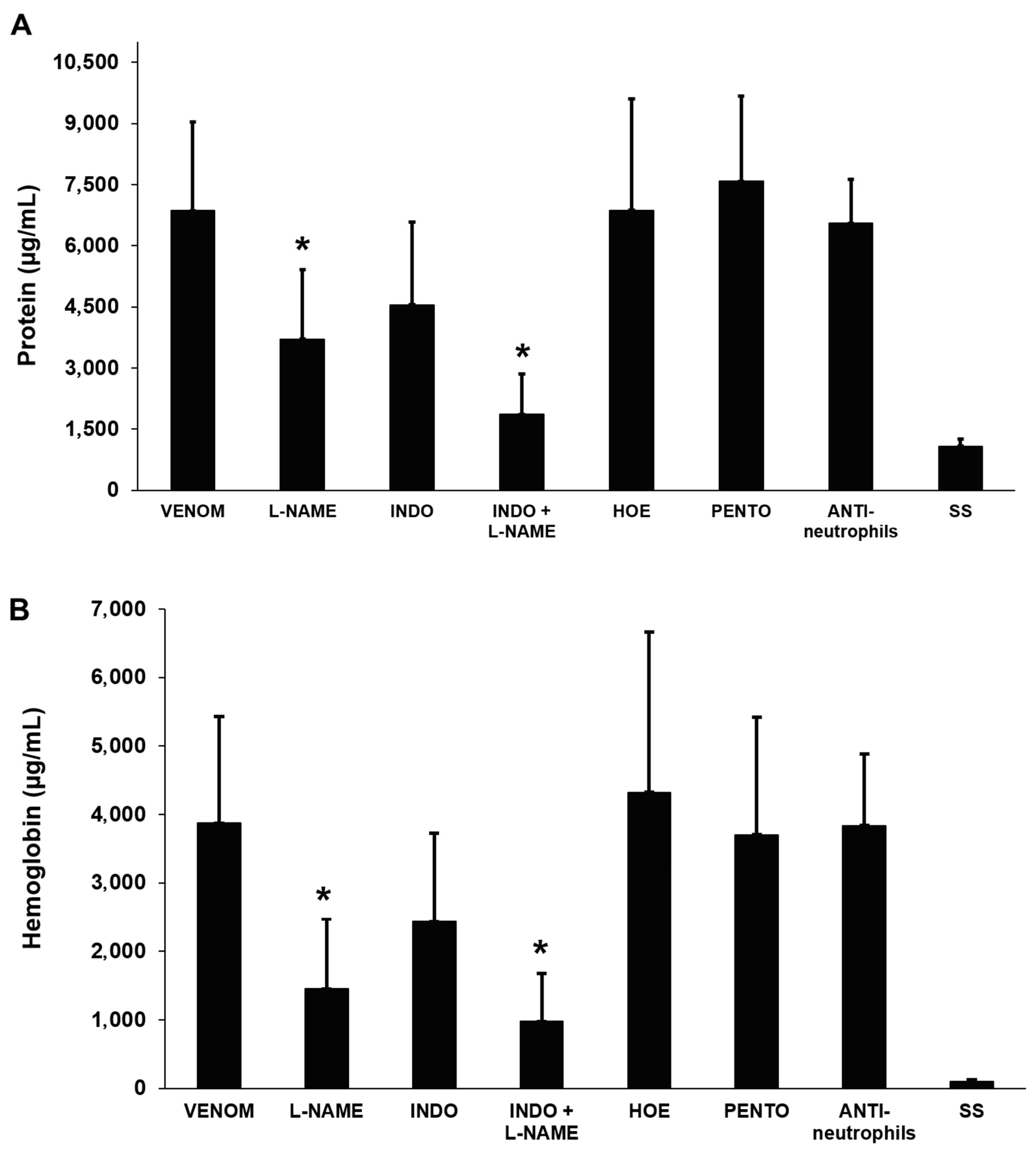
2.8.2. Total Protein and Hemoglobin Concentration
2.9. Effects of Anti-Inflammatory Agents on Venom-Induced Pulmonary Edema
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venom
4.2. Animal Ethics Approvals
4.3. Histological Analyses
4.4. Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) Activity and Inhibition by Varespladib
4.5. Effect of Venom on Lung-Derived Surfactant Factor
4.6. Cytotoxic Effect of Venom on Endothelial Cells
4.7. Effects of Venom on Pulmonary Mechanics
4.8. Effect of Venom on Tracheal and Bronchial Reactivity
4.9. Quantification of Exhaled Nitric Oxide (NO)
4.10. Effect of Venom on Pulmonary Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Activity
4.11. Analysis of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF)
4.11.1. Total Cell Counts in BALF
4.11.2. Quantification of Total Protein and Hemoglobin in BALF
4.12. Effect of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on the Venom-Induced Pulmonary Edema
4.13. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite Envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrell, D.A. Snake Bite. Lancet 2010, 375, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Ownby, C.L. Skeletal Muscle Degeneration Induced by Venom Phospholipases A2: Insights into the Mechanisms of Local and Systemic Myotoxicity. Toxicon 2003, 42, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.B. Myotoxic Phospholipases A2 and the Regeneration of Skeletal Muscles. Toxicon 2003, 42, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, D.; Besnard, A.; Latil, M.; Jouvion, G.; Briand, D.; Thépenier, C.; Pascal, Q.; Guguin, A.; Gayraud-Morel, B.; Cavaillon, J.M.; et al. Comparative Study of Injury Models for Studying Muscle Regeneration in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.; Moreira, V.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Venoms. In Inflammation—From Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms to the Clinic; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 99–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, L.A.; França, F.O.S.; Barbaro, K.C.; Nunes, J.R.; Cardoso, J.L.C. Pulmonary Haemorrhage Causing Rapid Death after Bothrops jararacussu Snakebite: A Case Report. Toxicon 2003, 42, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palangasinghe, D.R.; Weerakkody, R.M.; Dalpatadu, C.G.; Gnanathasan, C.A. A Fatal Outcome Due to Pulmonary Hemorrhage Following Russell’s Viper Bite. Saudi Med. J. 2015, 36, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.J.; Fernández, L.L.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Simón, D.S.; Ceballos, Z.; Aguilar, L.F.; Sierra, M. Case Report: Hemothorax in Envenomation by the Viperid Snake Bothrops asper. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A.; Fox, J.W.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Key Events in Microvascular Damage Induced by Snake Venom Hemorrhagic Metalloproteinases. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1781–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J. Snake Venoms and Coagulopathy. Toxicon 2005, 45, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, K.S.O.; Boechem, N.T.; Do Nascimento, S.M.; Murakami, Y.L.B.; Barboza, A.P.B.; Melo, P.A.; Castro, P.; De Moraes, V.L.G.; Rocco, P.R.M.; Zin, W.A. Pulmonary Mechanics and Lung Histology in Acute Lung Injury Induced by Bothrops jararaca Venom. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2004, 139, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escalante, T.; Núñez, J.; Moura Da Silva, A.M.; Rucavado, A.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Pulmonary Hemorrhage Induced by Jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca Snake Venom. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 193, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.C.; Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Basement Membrane Degradation and Inflammation Play a Role in the Pulmonary Hemorrhage Induced by a P-III Snake Venom Metalloproteinase. Toxicon 2021, 197, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, B.; Veerabasappa Gowda, T. Molecular Mechanism of Lung Hemorrhage Induction by VRV-PL-VIIIa from Russell’s Viper (Vipera russelli) Venom. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1129–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.L.; Wei, J.F.; Li, T.; Qiao, L.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Huang, T.; He, S.H. Purification, Characterization and Potent Lung Lesion Activity of an L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Agkistrodon blomhoffii ussurensis Snake Venom. Toxicon 2007, 50, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, P.N.; Amorim, C.F.; Paneque Peres, A.C.; Silva, C.A.M.; Zamuner, S.R.; Ribeiro, W.; Cogo, J.C.; Vieira, R.P.; Dolhnikoff, M.; de Oliveira, L.V.F. Pulmonary Mechanic and Lung Histology Injury Induced by Crotalus durissus terrificus Snake Venom. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Alam, J.M.; Abbasi, A.; Zaidi, Z.H.; Stoeva, S.; Voelter, W. Sea Snake Hydrophis cyanocinctus Venom. II. Histopathological Changes, Induced by a Myotoxic Phospholipase A2 (PLA2-H1). Toxicon 2000, 38, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cher, C.D.N.; Armugam, A.; Lachumanan, R.; Coghlan, M.W.; Jeyaseelan, K. Pulmonary Inflammation and Edema Induced by Phospholipase A2: Global Gene Analysis and Effects on Aquaporins and Na+/K+-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31352–31360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaquin, S.; Bayat, S.; Arab, O.; Mourier, G.; Lorne, E.; Kamel, S.; Dupont, H.; Ducancel, F.; Mahjoub, Y. Respiratory Effects of Sarafotoxins from the Venom of Different Atractaspis Genus Snake Species. Toxins 2016, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla, D.; Bande, B.W.; Welton, R.E.; Paiva, O.K.; Sanz, L.; Segura, Á.; Wright, C.E.; Calvete, J.J.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Williams, D.J. Proteomics and Antivenomics of Papuan Black Snake (Pseudechis papuanus) Venom with Analysis of Its Toxicological Profile and the Preclinical Efficacy of Australian Antivenoms. J. Proteom. 2017, 150, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, J.; Cipriani, V.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Arbuckle, K.; Debono, J.; Dashevsky, D.; Panagides, N.; Ikonomopoulou, M.P.; Koludarov, I.; Li, B.; et al. Proteomic and Functional Variation within Black Snake Venoms (Elapidae: Pseudechis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 205, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, G.D.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Wilkinson, M.C.; Lowe, G.M.; Theakston, R.D.G. Characterisation of a Purified Phospholipase A2 from the Venom of the Papuan Black Snake (Pseudechis papuanus). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1250, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Križaj, I. Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 Toxins. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, L.D.J.; Ware, L.B. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Causes, Pathophysiology, and Phenotypes. Lancet 2022, 400, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitsiouli, E.; Nakos, G.; Lekka, M.E. Phospholipase A2 Subclasses in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letsiou, E.; Htwe, Y.M.; Dudek, S.M. Secretory Phospholipase A2 Enzymes in Acute Lung Injury. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeds, M.C.; Grier, B.L.; Suckling, B.N.; Safta, A.M.; Long, D.L.; Waite, B.M.; Morris, P.E.; Hite, R.D. Secretory Phospholipase A2 Mediated Depletion of Phosphatidylglycerol in Early Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 343, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsiouli, E.; Tenopoulou, M.; Papadopoulos, S.; Lekka, M.E. Phospholipases A2 as Biomarkers in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Biomed. J. 2021, 44, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeffner, F.; Bolon, B.; Davis, I.C. Mouse Models of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 1074–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastarache, J.A.; Blackwell, T.S. Development of Animal Models for the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. DMM Dis. Models Mech. 2009, 2, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Effect of the Metalloproteinase Inhibitor Batimastat in the Systemic Toxicity Induced by Bothrops asper Snake Venom: Understanding the Role of Metalloproteinases in Envenomation. Toxicon 2004, 43, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Gunawardena, P.; Weilgama, D.; Maduwage, K.; Gawarammana, I. Comparative In-Vivo Toxicity of Venoms from South Asian Hump-Nosed Pit Vipers (Viperidae: Crotalinae: Hypnale). BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, C.; Rucavado, A.; Warrell, D.A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Systemic Effects Induced by the Venom of the Snake Bothrops caribbaeus in a Murine Model. Toxicon 2013, 63, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahloul, M.; Chaari, A.; Dammak, H.; Samet, M.; Chtara, K.; Chelly, H.; Ben Hamida, C.; Kallel, H.; Bouaziz, M. Pulmonary Edema Following Scorpion Envenomation: Mechanisms, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis and Treatment. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 162, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbister, G.K.; Bawaskar, H.S. Scorpion Envenomation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.B.; Akella, A. Non-Cardiogenic Mechanisms for the Pulmonary Edema Induced by Scorpion Venom. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 157, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, F.O.; Benvenuti, L.A.; Fan, H.W.; Dos Santos, D.R.; Hain, S.H.; Picchi-Martins, F.R.; Cardoso, J.L.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Theakston, R.D.; Warrell, D.A. Severe and Fatal Mass Attacks by “Killer” Bees (Africanized Honey Bees—Apis mellifera scutellata) in Brazil: Clinicopathological Studies with Measurement of Serum Venom Concentrations. Q. J. Med. 1994, 87, 269–282. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7938407/ (accessed on 8 April 2025). [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, J.S.; Riciopo, P.M.; Pereira, A.F.M.; Jeronimo, B.C.; Angstmam, D.G.; Pôssas, F.C.; de Andrade Filho, A.; Cerni, F.A.; Pucca, M.B.; Ferreira Junior, R.S. Clinical Complications in Envenoming by Apis Honeybee Stings: Insights into Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Pharmacological Interventions. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1437413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumtecho, S.; Suteparuk, S.; Sitprija, V. Pulmonary Involvement from Animal Toxins: The Cellular Mechanisms. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 29, e20230026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.R.; Carter, R.W.; Matteo, I.A.; Samuel, S.P.; Rao, S.; Fry, B.G.; Bickler, P.E. Varespladib in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming: Development History and Preclinical Evidence Supporting Advancement to Clinical Trials in Patients Bitten by Venomous Snakes. Toxins 2022, 14, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan-Socha, S.; Zuk, J.; Plutecka, H.; Jakiela, B.; Mlicka-Kowalczyk, E.; Krzyzanowski, B.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Zareba, L.; Bazan, J.G.; Musial, J. Blocking of A1β1 and A2β1 Adhesion Molecules Inhibits Eosinophil Migration through Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cell Monolayer. Postepy. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2014, 68, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, Y.; Murakami, E.; Uchiya, K.I.; Nonogaki, T.; Nikai, T. Okinalysin, a Novel P-I Metalloproteinase from Ovophis okinavensis: Biological Properties and Effect on Vascular Endothelial Cells. Toxins 2014, 6, 2594–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakamura, M.; Hatanaka, Y.; Kayanoki, Y.; Tatsumi, H.; Taniguchi, N. Induction of Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Endothelial Cells Treated with Snake Venom: Implication of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species and Protective Effects of Glutathione and Superoxide Dismutases. J. Biochem. 1997, 122, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.G.; Bao, Y.; Serrano, S.M.T.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Fox, J.W. Use of Microarrays for Investigating the Subtoxic Effects of Snake Venoms: Insights into Venom-Induced Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Toxicon 2003, 41, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, E.A.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Tomlins, S. Immediate Early Inflammatory Gene Responses of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells to Hemorrhagic Venom. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 60, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.R.T.; Aissa, A.F.; Ribeiro, D.L.; Costa, T.R.; Ferreira, R.S.; Sampaio, S.V.; Antunes, L.M.G. Cytotoxic, Genotoxic, and Oxidative Stress-Inducing Effect of an L-Amino Acid Oxidase Isolated from Bothrops jararacussu Venom in a Co-Culture Model of HepG2 and HUVEC Cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, E.; Cirilo, A.; Reyes, A.; Barrientos, M.; Galan, J.; Sánchez, E.E.; Suntravat, M. Snake Venom Cysteine-Rich Secretory Protein from Mojave Rattlesnake Venom (Css-CRiSP) Induces Acute Inflammatory Responses on Different Experimental Models. Toxicon X 2024, 21, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittenbinder, M.A.; Bonanini, F.; Kurek, D.; Vulto, P.; Kool, J.; Vonk, F.J. Using Organ-on-a-Chip Technology to Study Haemorrhagic Activities of Snake Venoms on Endothelial Tubules. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.Q.; Santos, L.C.; Teixeira, S.C.; Correia, T.M.L.; Andrade, L.O.S.B.; Gimenes, S.N.C.; Colombini, M.; Marques, L.M.; Jiménez-Charris, E.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; et al. Antiangiogenic Properties of BthMP, a P–I Metalloproteinase from Bothrops moojeni Snake Venom by VEGF Pathway in Endothelial Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 706, 149748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Chang, C. Isolation and Characterization of a Toxic Phospholipase A2 from the Venom of the Taiwan Habu (Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus). Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 1994, 19, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque Modesto, J.C.; Spencer, P.J.; Fritzen, M.; Valença, R.C.; Oliva, M.L.V.; da Silva, M.B.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M.; Guarnieri, M.C. BE-I-PLA2, a Novel Acidic Phospholipase A2 from Bothrops erythromelas Venom: Isolation, Cloning and Characterization as Potent Anti-Platelet and Inductor of Prostaglandin I2 Release by Endothelial Cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J.M.; Attoub, S.; Arafat, H.; Mechkarska, M.; Casewell, N.R.; Harrison, R.A.; Calvete, J.J. Cytotoxic Activities of [Ser49]Phospholipase A2 from the Venom of the Saw-Scaled Vipers Echis ocellatus, Echis pyramidum Leakeyi, Echis carinatus sochureki, and Echis coloratus. Toxicon 2013, 71, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polloni, L.; Azevedo, F.V.P.V.; Teixeira, S.C.; Moura, E.; Costa, T.R.; Gimenes, S.N.C.; Correia, L.I.V.; Freitas, V.; Yoneyama, K.A.G.; Rodrigues, R.S.; et al. Antiangiogenic Effects of Phospholipase A2 Lys49 BnSP-7 from Bothrops pauloensis Snake Venom on Endothelial Cells: An in Vitro and Ex Vivo Approach. Toxicol. In Vitro 2021, 72, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.C.; Oliveira, V.Q.; Teixeira, S.C.; Correia, T.M.L.; Andrade, L.O.S.B.; Polloni, L.; Marques, L.M.; Clissa, P.B.; Baldo, C.; Ferro, E.A.V.; et al. PLA2-MjTX-II from Bothrops moojeni Snake Venom Exhibits Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenic Effects on Human Lung Cancer Cells. Toxicon 2024, 243, 107742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo Cordeiro Eulálio, M.; de Lima, A.M.; Brant, R.S.C.; Francisco, A.F.; Santana, H.M.; Paloschi, M.V.; da Silva Setúbal, S.; da Silva, C.P.; Silva, M.D.S.; Boeno, C.N.; et al. Characterization of a Novel Acidic Phospholipase A2 Isolated from the Venom of Bothrops mattogrossensis: From Purification to Structural Modeling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Sun, L.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xianzheng, W.; Liao, Y.; Tong, X.; Shan, J. Potential Therapeutic Applications of Pulmonary Surfactant Lipids in the Host Defence Against Respiratory Viral Infections. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 730022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autilio, C.; Pérez-Gil, J. Understanding the Principle Biophysics Concepts of Pulmonary Surfactant in Health and Disease. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2019, 104, F443–F451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Rehder, K.J.; Turner, D.A. Adjunctive Treatments in Pediatric Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2014, 8, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiguti, A.S.; Laing, G.D.; Lowe, G.M.; Zuzel, M.; Warrell, D.A.; Theakston, R.D.G. Biological Properties of the Venom of the Papuan Black Snake (Pseudechis papuanus): Presence of a Phospholipase A2 Platelet Inhibitor. Toxicon 1994, 32, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalloo, D.; Trevett, A.; Black, J.; Mapao, J.; Naraqi, S.; Owens, D.; Hutton, R.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Warrell, D.A. Neurotoxicity and Haemostatic Disturbances in Patients Envenomed by the Papuan Black Snake (Pseudechis papuanus). Toxicon 1994, 32, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.; Fry, B.G.; Hodgson, W.C. Neurotoxic Effects of Venoms from Seven Species of Australasian Black Snakes (Pseudechis): Efficacy of Black and Tiger Snake Antivenoms. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2005, 32, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruppu, S.; Reeve, S.; Smith, A.I.; Hodgson, W.C. Isolation and Pharmacological Characterisation of Papuantoxin-1, a Postsynaptic Neurotoxin from the Venom of the Papuan Black Snake (Pseudechis papuanus). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastarache, J.A.; Roberts, L.J.; Ware, L.B. Thinking Outside the Cell: How Cell-Free Hemoglobin Can Potentiate Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L231–L232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janz, D.R.; Ware, L.B. The Role of Red Blood Cells and Cell-Free Hemoglobin in the Pathogenesis of ARDS. J. Intensive Care 2015, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegan, J.E.; Bastarache, J.A.; Ware, L.B. Toxic Effects of Cell-Free Hemoglobin on the Microvascular Endothelium: Implications for Pulmonary and Nonpulmonary Organ Dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L429–L439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, G.U.; Kohler, G.; Headley, S.; Tolley, E.; Stentz, F.; Postlethwaite, A. Inflammatory Cytokines in the BAL of Patients with ARDS. Persistent Elevation over Time Predicts Poor Outcome. Chest 1995, 108, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, J.; Soehnlein, O. Contribution of Neutrophils to Acute Lung Injury. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, Y.; Kurdowska, A.; Allen, T.C. Acute Lung Injury: A Clinical and Molecular Review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rex, D.A.B.; Vaid, N.; Deepak, K.; Dagamajalu, S.; Prasad, T.S.K. A Comprehensive Review on Current Understanding of Bradykinin in COVID-19 and Inflammatory Diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 9915–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, S.J.; Evans, T.W. Measurement of Endogenous Nitric Oxide in the Lungs of Patients with the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, R. Oxygen Radicals, Nitric Oxide, and Peroxynitrite: Redox Pathways in Molecular Medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5839–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.M.; Carvajal, I.M.; Fredenburgh, L.E.; Liu, X.; Porrata, Y.; Cullivan, M.L.; Haley, K.J.; Sonna, L.A.; De Sanctis, G.T.; Ingenito, E.P.; et al. Nitric Oxide Synthase-2 down-Regulates Surfactant Protein-B Expression and Enhances Endotoxin-Induced Lung Injury in Mice. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1276–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikawa, K.; Nishina, K.; Takao, Y.; Obara, H. ONO-1714, a Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor, Attenuates Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rabbits. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 97, 1751–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.I.; Chu, S.J.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.I.; Hsu, K. Effects of an Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor on Phorbol Myristate Acetate-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2003, 30, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddei, S.; Bortolotto, L. Unraveling the Pivotal Role of Bradykinin in ACE Inhibitor Activity. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2016, 16, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, M.; Mackessy, S.P. An Aqueous Endpoint Assay of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantos, Z.; Adamicza, A.; Govaerts, E.; Daroczy, B. Mechanical Impedances of Lungs and Chest Wall in the Cat. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 73, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, J.D.; Neves, L.P.; Olivo, C.R.; Duran, A.; Almeida, F.M.; Arantes, P.M.M.; Prado, C.M.; Leick, E.A.; Tanaka, A.S.; Martins, M.A.; et al. A Treatment with a Protease Inhibitor Recombinant from the Cattle Tick (Rhipicephalus boophilus microplus) Ameliorates Emphysema in Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, P.L.; Lovell-Smith, C.J. Optimized Assay for Serum Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Activity. Clin. Chem. 1981, 27, 2048–2052. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6273013/ (accessed on 8 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Cushman, D.W.; Cheung, H.S. Spectrophotometric Assay and Properties of the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme of Rabbit Lung. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1971, 20, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kampen, E.J.; Zijlstra, W.G. Determination of Hemoglobin and Its Derivatives. Adv. Clin. Chem. 1965, 8, 141–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solano, D.; Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T.; Tavares, E.B.G.; Bezerra, S.K.M.; Olivo, C.R.; Leick, E.A.; Rojas Moscoso, J.A.; Dias, L.; Tibério, I.d.F.L.C.; et al. An Experimental Model of Acute Pulmonary Damage Induced by the Phospholipase A2-Rich Venom of the Snake Pseudechis papuanus. Toxins 2025, 17, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060302
Solano D, Rucavado A, Escalante T, Tavares EBG, Bezerra SKM, Olivo CR, Leick EA, Rojas Moscoso JA, Dias L, Tibério IdFLC, et al. An Experimental Model of Acute Pulmonary Damage Induced by the Phospholipase A2-Rich Venom of the Snake Pseudechis papuanus. Toxins. 2025; 17(6):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060302
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolano, Daniela, Alexandra Rucavado, Teresa Escalante, Edith Bastos Gandra Tavares, Suellen Karoline Moreira Bezerra, Clarice Rosa Olivo, Edna Aparecida Leick, Julio Alejandro Rojas Moscoso, Lourdes Dias, Iolanda de Fátima Lopes Calvo Tibério, and et al. 2025. "An Experimental Model of Acute Pulmonary Damage Induced by the Phospholipase A2-Rich Venom of the Snake Pseudechis papuanus" Toxins 17, no. 6: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060302
APA StyleSolano, D., Rucavado, A., Escalante, T., Tavares, E. B. G., Bezerra, S. K. M., Olivo, C. R., Leick, E. A., Rojas Moscoso, J. A., Dias, L., Tibério, I. d. F. L. C., Hyslop, S., & Gutiérrez, J. M. (2025). An Experimental Model of Acute Pulmonary Damage Induced by the Phospholipase A2-Rich Venom of the Snake Pseudechis papuanus. Toxins, 17(6), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060302







