Cvill6 and Cvill7: Potent and Selective Peptide Blockers of Kv1.2 Ion Channel Isolated from Mexican Scorpion Centruroides villegasi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
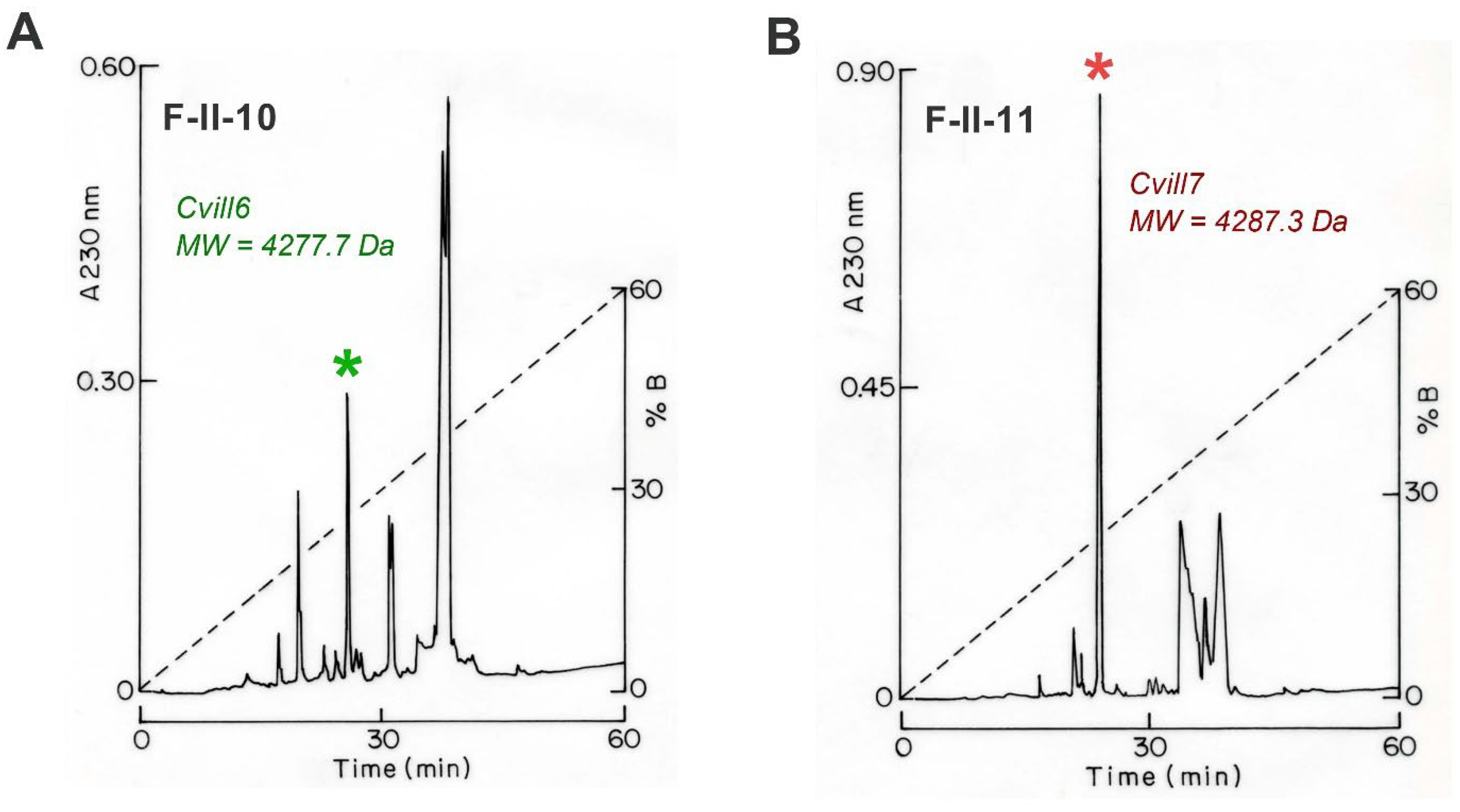
2.1. Purification and Primary Sequence Determination of Cvill Peptides
2.2. Comparative Sequence Analysis and Prediction of Structural Features of Cvill Peptides
2.3. Effect of Cvill Peptides on Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels
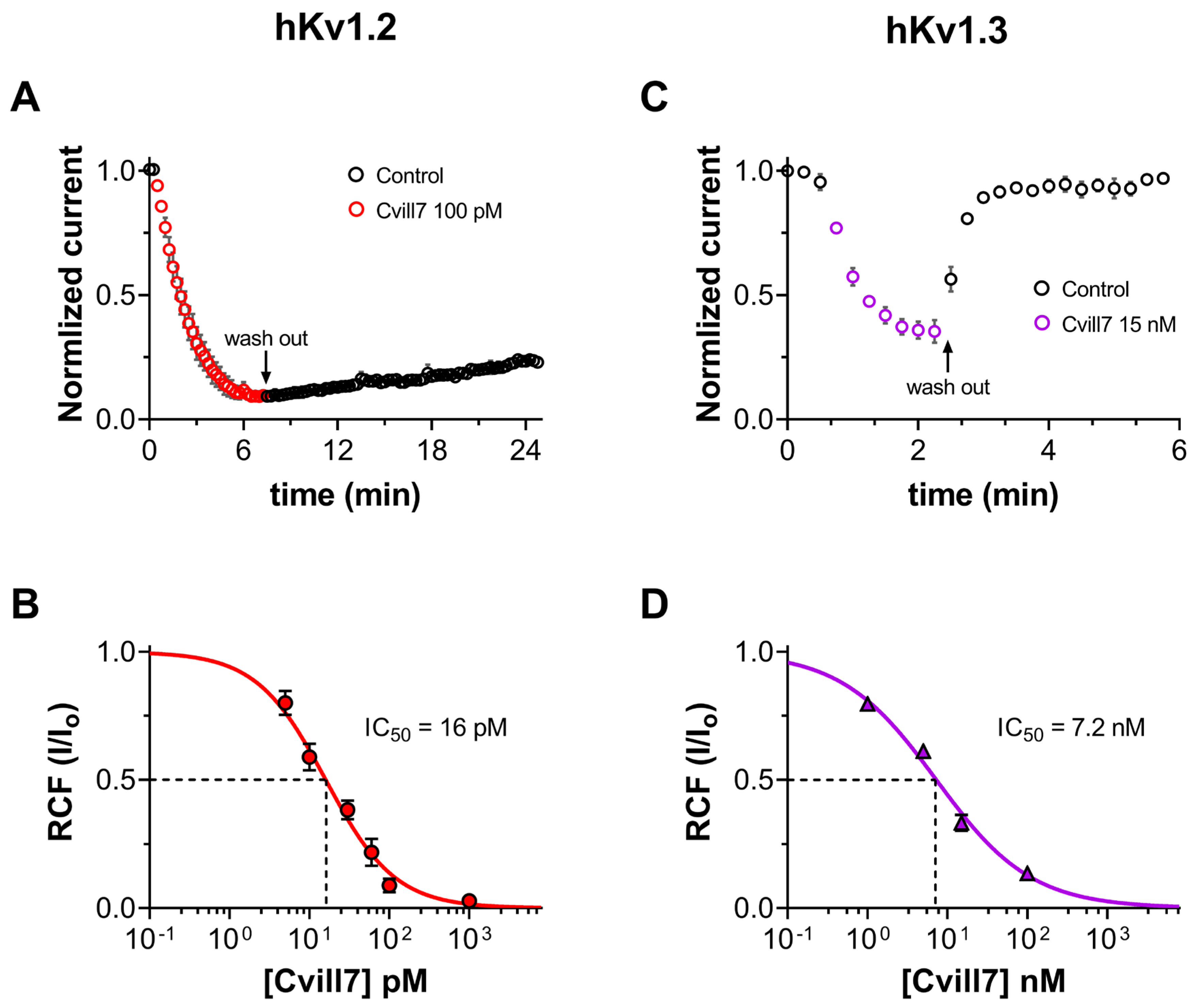
2.4. Cvill7 Selectively Inhibits Kv1.2 over Kv1.3 with Low-Picomolar Affinity
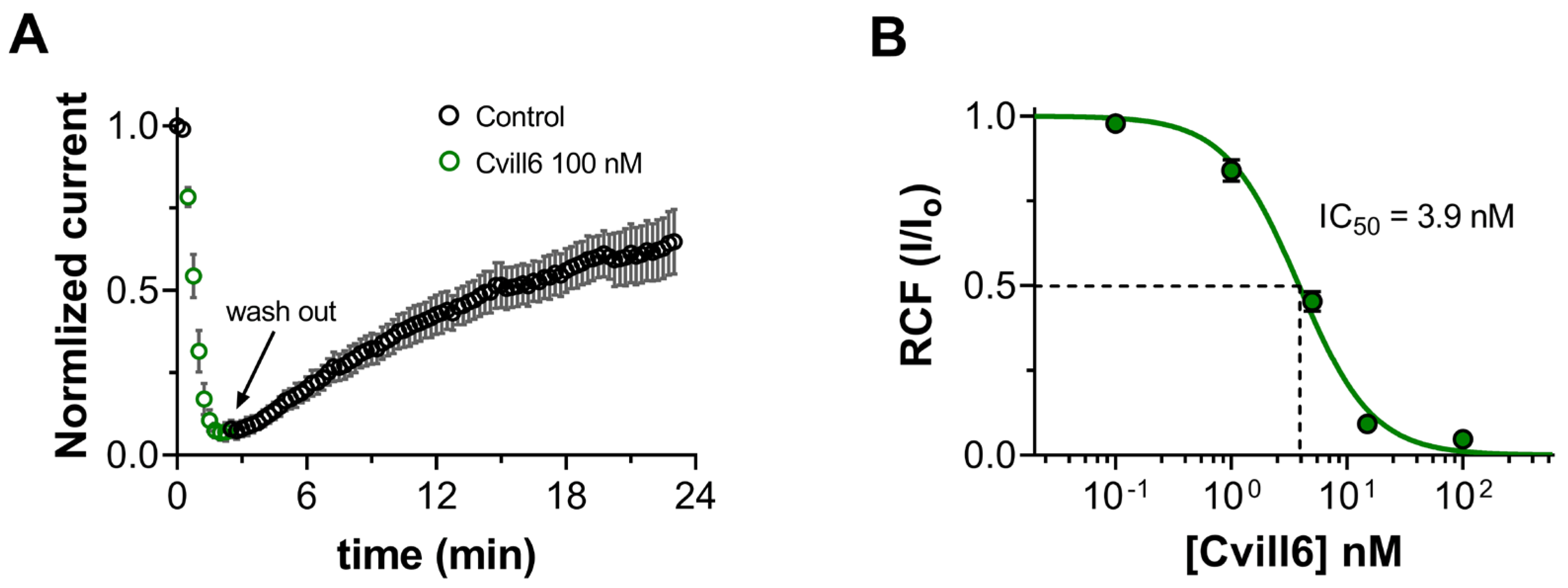
2.5. Cvill6 Inhibits Kv1.2 with Nanomolar Affinity
2.6. Activity of Cvill6 and Cvill7 Toxins on Ca2+-Activated Potassium Channels
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Toxin Purification and Primary Sequence Determination
5.2. Alignment of Primary Sequences with Known Toxins
5.3. Modeling of Cvill Peptides
5.4. Electrophysiology
5.4.1. Cells and Heterologous Expression of Ion Channels
5.4.2. Solutions
5.4.3. Current Recording Conditions
5.4.4. Data Analysis and Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stillwell, W. An Introduction to Biological Membranes: From Bilayers to Rafts; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gutman, G.A.; Chandy, K.G.; Grissmer, S.; Lazdunski, M.; Mckinnon, D.; Pardo, L.A.; Robertson, G.A.; Rudy, B.; Sanguinetti, M.C.; Stühmer, W. International Union of Pharmacology. LIII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of voltage-gated potassium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 473–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, A.D.; Gutman, G.A.; Aldrich, R.; Chandy, K.G.; Grissmer, S.; Wulff, H. International Union of Pharmacology. LII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of calcium-activated potassium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Q.; Purhonen, P.; Hebert, H. Structure of potassium channels. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3677–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hille, B. Ionic channels in excitable membranes. Current problems and biophysical approaches. Biophys. J. 1978, 22, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, W.A.; Amarillo, Y.; Chiu, J.; Chow, A.; Lau, D.; McCormack, T.; Morena, H.; Nadal, M.S.; Ozaita, A.; Pountney, D. Molecular diversity of K+ channels. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 868, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, L.; Qiu, T.; Cao, Z.; Kang, T. Potassium channels: Structures, diseases, and modulators. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 83, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, H.; Castle, N.A.; Pardo, L.A. Voltage-gated potassium channels as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 982–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, K.A.; Svalastoga, P.; Martinez, A.; Glennon, J.C.; Haavik, J. Potassium channels in behavioral brain disorders. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential: A narrative review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 152, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kunkel, D.; Schwartzkroin, P.; Tempel, B. Localization of Kv1. 1 and Kv1. 2, two K channel proteins, to synaptic terminals, somata, and dendrites in the mouse brain. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 4588–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, J.S.; Rhodes, K.J. Localization of voltage-gated ion channels in mammalian brain. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, J.S. Subcellular localization of K+ channels in mammalian brain neurons: Remarkable precision in the midst of extraordinary complexity. Neuron 2015, 85, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.C.; Jan, L.Y. The distribution and targeting of neuronal voltage-gated ion channels. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, J. Voltage-gated potassium channels and genetic epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1466075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrbe, S.; Hedrich, U.B.; Riesch, E.; Djémié, T.; Müller, S.; Møller, R.S.; Maher, B.; Hernandez-Hernandez, L.; Synofzik, M.; Caglayan, H.S. De novo loss-or gain-of-function mutations in KCNA2 cause epileptic encephalopathy. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mínguez-Viñas, T.; Prakash, V.; Wang, K.; Lindström, S.H.; Pozzi, S.; Scott, S.A.; Spiteri, E.; Stevenson, D.A.; Ashley, E.A.; Gunnarsson, C. Two epilepsy-associated variants in KCNA2 (KV1. 2) at position H310 oppositely affect channel functional expression. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 5367–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driedger, J.H.; Schröter, J.; Jüngling, J.; Biskup, S.; Klotz, K.A.; Bast, T.; Dietel, T.; Korenke, C.; Christoph, S.; Brennenstuhl, H. Refining genotypes and phenotypes in KCNA2-related neurological disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2824. [Google Scholar]
- Masnada, S.; Hedrich, U.B.; Gardella, E.; Schubert, J.; Kaiwar, C.; Klee, E.W.; Lanpher, B.C.; Gavrilova, R.H.; Synofzik, M.; Bast, T. Clinical spectrum and genotype–phenotype associations of KCNA2-related encephalopathies. Brain 2017, 140, 2337–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, M.A.; Bellows, S.T.; Li, M.; Carroll, R.; Micallef, S.; Carvill, G.L.; Myers, C.T.; Howell, K.B.; Maljevic, S.; Lerche, H. Dominant KCNA2 mutation causes episodic ataxia and pharmacoresponsive epilepsy. Neurology 2016, 87, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, S.; Coimbra, R. Ataxia and myoclonic epilepsy due to a heterozygous new mutation in KCNA2: Proposal for a new channelopathy. Clin. Genet. 2015, 87, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, U.B.; Lauxmann, S.; Wolff, M.; Synofzik, M.; Bast, T.; Binelli, A.; Serratosa, J.M.; Martínez-Ulloa, P.; Allen, N.M.; King, M.D. 4-Aminopyridine is a promising treatment option for patients with gain-of-function KCNA2-encephalopathy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaaz4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrici, P.; Conte, E.; Blunck, R.; Stregapede, F.; Liantonio, A.; Tosi, M.; D’Adamo, M.C.; De Luca, A.; Brankovic, V.; Zanni, G. A novel KCNA2 variant in a patient with non-progressive congenital ataxia and epilepsy: Functional characterization and sensitivity to 4-aminopyridine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McTague, A.; Cross, J.H. Treatment of epileptic encephalopathies. CNS Drugs 2013, 27, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, K.; Yokogawa, M.; Osawa, M. Peptide toxins targeting KV channels. Pharmacol. Potassium Channels 2021, 267, 481–505. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, L.C.; Viana, G.M.M.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Beraldo-Neto, E. Scorpion peptides and ion channels: An insightful review of mechanisms and drug development. Toxins 2023, 15, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Zeng, D.-Y.; Hu, Y.-T.; He, Y.-W.; Pan, N.; Ding, J.-P.; Cao, Z.-J.; Liu, M.-L.; Li, W.-X.; Yi, H. Structural and functional diversity of acidic scorpion potassium channel toxins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmenkov, A.; Grishin, E.; Vassilevski, A. Diversity of potassium channel ligands: Focus on scorpion toxins. Biochemistry 2015, 80, 1764–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, S.; Andreotti, N.; Jouirou, B.; Sabatier, J.-M. Animal toxins acting on voltage-gated potassium channels. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2503–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, N.A.; Tabakmakher, V.M.; Yureva, D.A.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Kuzmenkov, A.I. Kalium 3.0 is a comprehensive depository of natural, artificial, and labeled polypeptides acting on potassium channels. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyar, J.; Withka, J.M.; Rizzi, J.P.; Singleton, D.H.; Andrews, G.C.; Lin, W.; Boyd, J.; Hanson, D.C.; Simon, M.; Dethlefs, B. Topology of the pore-region of a K+ channel revealed by the NMR-derived structures of scorpion toxins. Neuron 1995, 15, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, S.; Mosbah, A.; Visan, V.; Wulff, H.; Delepierre, M.; Darbon, H.; Grissmer, S.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.-M. The functional dyad of scorpion toxin Pi1 is not itself a prerequisite for toxin binding to the voltage-gated Kv1. 2 potassium channels. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.; Kreusch, A.; Pfaffinger, P.J. Towards the three-dimensional structure of voltage-gated potassium channels. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartok, A.; Toth, A.; Somodi, S.; Szanto, T.G.; Hajdu, P.; Panyi, G.; Varga, Z. Margatoxin is a non-selective inhibitor of human Kv1. 3 K+ channels. Toxicon 2014, 87, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Calvo, M.; Leonard, R.; Novick, J.; Stevens, S.; Schmalhofer, W.; Kaczorowski, G.; Garcia, M. Purification, characterization, and biosynthesis of margatoxin, a component of Centruroides margaritatus venom that selectively inhibits voltage-dependent potassium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 18866–18874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, M.U.; Tajti, G.; Gaspar, A.; Szanto, T.G.; Borrego, J.; Panyi, G. Optimization of Pichia pastoris expression system for high-level production of margatoxin. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 733610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschak, A.; Bugianesi, R.M.; Mitterdorfer, J.r.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; Garcia, M.L.; Knaus, H.-G. Subunit Composition of Brain Voltage-gated Potassium Channels Determined by Hongotoxin-1, a Novel Peptide Derived fromCentruroides limbatus Venom. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 2639–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Santillán, E.; Possani, L.D. North American scorpion species of public health importance with a reappraisal of historical epidemiology. Acta Trop. 2018, 187, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldazo-Monsivaiz, J.G.; Ponce-Saavedra, J.; Flores-Moreno, M. Una especie nueva de alacrán del género Centruroides de importancia médica (Scorpiones: Buthidae) del estado de Guerrero, México. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2013, 84, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Francke, O.F.; Ureta, C.; Possani, L.D. Scorpions from Mexico: From species diversity to venom complexity. Toxins 2015, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño-Umbarila, L.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Romero-Moreno, J.A.; Delgado-Prudencio, G.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Becerril, B.; Possani, L.D. Toxic Peptides from the Mexican Scorpion Centruroides villegasi: Chemical Structure and Evaluation of Recognition by Human Single-Chain Antibodies. Toxins 2024, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño-Umbarila, L.; Romero-Moreno, J.A.; Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B. State of the art on the development of a recombinant antivenom against Mexican scorpion stings. Toxicon 2025, 257, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Vidal, J.; Carcamo-Noriega, E.; Pastor, N.; Zamudio-Zuñiga, F.; Guerrero-Vargas, J.A.; Castaño, S.; Possani, L.D.; Restano-Cassulini, R. Colombian scorpion Centruroides margaritatus: Purification and characterization of a gamma potassium toxin with full-block activity on the hERG1 channel. Toxins 2021, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, C.; Román-González, S.; Salas-Castillo, S.; Zamudio, F.; Gómez-Lagunas, F.; Possani, L. Proteomic analysis of the venom from the scorpion Tityus stigmurus: Biochemical and physiological comparison with other Tityus species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Prudencio, G.; Becerril, B.; Possani, L.D.; Ortiz, E. New proposal for the systematic nomenclature of scorpion peptides. Toxicon 2025, 253, 108192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.; Miller, C. Mechanism of charybdotoxin block of a voltage-gated K+ channel. Biophys. J. 1993, 65, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Qasim, A.; Sophanpanichkul, P.; Dai, H.; Nayak, M.; Sher, I.; Chill, J.; Goldstein, S.A. Selective block of human Kv1. 1 channels and an epilepsy-associated gain-of-function mutation by AETX-K peptide. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e23381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Bartok, A.; Zamudio-Zuñiga, F.; Balajthy, A.; Becerril, B.; Panyi, G.; Possani, L.D. Isolation, chemical and functional characterization of several new K+-channel blocking peptides from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides tecomanus. Toxicon 2016, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grissmer, S.; Nguyen, A.N.; Aiyar, J.; Hanson, D.C.; Mather, R.J.; Gutman, G.A.; Karmilowicz, M.J.; Auperin, D.D.; Chandy, K.G. Pharmacological characterization of five cloned voltage-gated K+ channels, types Kv1. 1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.5, and 3.1, stably expressed in mammalian cell lines. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 45, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, M.U.; Gurrola-Briones, G.; Romero-Imbachi, M.R.; Borrego, J.; Carcamo-Noriega, E.; Beltrán-Vidal, J.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Shakeel, K.; Possani, L.D.; Panyi, G. Characterization and chemical synthesis of Cm39 (α-KTx 4.8): A scorpion toxin that inhibits voltage-gated K+ channel KV1. 2 and small-and intermediate-conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ channels KCa2. 2 and KCa3. 1. Toxins 2023, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, S.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M. Contribution of the functional dyad of animal toxins acting on voltage-gated Kv1-type channels. J. Pept. Sci. Off. Publ. Eur. Pept. Soc. 2005, 11, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, K.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Naseem, M.U.; Becerril, B.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Delgado-Prudencio, G.; Possani, L.D.; Panyi, G. Of Seven New K+ Channel Inhibitor Peptides of Centruroides Bonito, α-KTx 2.24 Has a Picomolar Affinity for Kv1. 2. Toxins 2023, 15, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, B.; Ramirez, A.; Gurrola, G.; Nobile, M.; Prestipino, G.; Possani, L. Novel K+-channel-blocking toxins from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides limpidus limpidus Karsch. Biochem. J. 1994, 304, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Somodi, S.; Fernández, J.A.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Becerril, B.; Varga, Z.; Panyi, G.; Gáspár, R.; Possani, L.D. Novel α-KTx peptides from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides elegans selectively blockade Kv1. 3 over IKCa1 K+ channels of T cells. Toxicon 2005, 46, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Velázquez, L.L.; Quintero-Hernández, V.; Romero-Gutiérrez, M.T.; Coronas, F.I.; Possani, L.D. Mass fingerprinting of the venom and transcriptome of venom gland of scorpion Centruroides tecomanus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Lee, A.; Campbell, E.; MacKinnon, R. Structure of a pore-blocking toxin in complex with a eukaryotic voltage-dependent K+ channel. eLife 2013, 2, e00594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, M.U.; Carcamo-Noriega, E.; Beltrán-Vidal, J.; Borrego, J.; Szanto, T.G.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Delgado-Prudencio, G.; Possani, L.D.; Panyi, G. Cm28, a scorpion toxin having a unique primary structure, inhibits KV1. 2 and KV1. 3 with high affinity. J. Gen. Physiol. 2022, 154, e202213146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, P.; Fernández-Mariño, A.I.; Khanra, N.; He, C.; Paquette, A.J.; Wang, B.; Huang, R.; Smider, V.V.; Rice, W.J.; Swartz, K.J. Structures of the T cell potassium channel Kv1. 3 with immunoglobulin modulators. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajloun, Z.; Carlier, E.; Lecomte, C.; Geib, S.; Di Luccio, E.; Bichet, D.; Mabrouk, K.; Rochat, H.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M. Chemical synthesis and characterization of Pi1, a scorpion toxin from Pandinus imperator active on K+ channels. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5149–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCoursey, T.E.; Chandy, K.G.; Gupta, S.; Cahalan, M.D. Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: A role in mitogenesis? Nature 1984, 307, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.B.; Campbell, E.B.; MacKinnon, R. Voltage sensor of Kv1. 2: Structural basis of electromechanical coupling. Science 2005, 309, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimigean, C.M.; Allen, T.W. Origins of ion selectivity in potassium channels from the perspective of channel block. J. Gen. Physiol. 2011, 137, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Bian, S.; Rivetta, A.; Allen, K.; Sigworth, F.J. CryoEM structures of Kv1. 2 potassium channels, conducting and non-conducting. eLife 2025, 12, RP89459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Ni, F.; Ma, J. Structure of the full-length Shaker potassium channel Kv1. 2 by normal-mode-based X-ray crystallographic refinement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11352–11357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Barek, S.; Mosbah, A.; Sandoz, G.; Fajloun, Z.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Rochat, H.; Sampieri, F.; Guijarro, J.I.; Mansuelle, P.; Delepierre, M. Synthesis and characterization of Pi4, a scorpion toxin from Pandinus imperator that acts on K+ channels. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 3583–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, J.I.; M’Barek, S.; Gómez-Lagunas, F.; Garnier, D.; Rochat, H.; Sabatier, J.M.; Possani, L.D.; Delepierre, M. Solution structure of Pi4, a short four-disulfide-bridged scorpion toxin specific of potassium channels. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stühmer, W.; Ruppersberg, J.P.; Schröter, K.; Sakmann, B.; Stocker, M.; Giese, K.; Perschke, A.; Baumann, A.; Pongs, O. Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3235–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeule, M.; Regina, A.; Che, C.; Poirier, J.; Nguyen, T.; Gabathuler, R.; Castaigne, J.-P.; Beliveau, R. Identification and design of peptides as a new drug delivery system for the brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 324, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oller-Salvia, B.; Sánchez-Navarro, M.; Giralt, E.; Teixidó, M. Blood–brain barrier shuttle peptides: An emerging paradigm for brain delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4690–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adessi, C.; Soto, C. Strategies to improve stability and bioavailability of peptide drugs. Front. Med. Chem. Online 2004, 1, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraku, S.; Zmasek, C.M.; Nishimura, O.; Katoh, K. aLeaves facilitates on-demand exploration of metazoan gene family trees on MAFFT sequence alignment server with enhanced interactivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W22–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamill, O.P.; Marty, A.; Neher, E.; Sakmann, B.; Sigworth, F.J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch. 1981, 391, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezazadeh, S.; Kurata, H.T.; Claydon, T.W.; Kehl, S.J.; Fedida, D. An activation gating switch in Kv1. 2 is localized to a threonine residue in the S2-S3 linker. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 4173–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Toxins | Channel | kon (nM−1s−1) | koff (s−1) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cvill7 | Kv1.2 | 4 | ||
| Kv1.3 | 3 | |||
| Cvill6 | Kv1.2 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shakeel, K.; Naseem, M.U.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Possani, L.D.; Panyi, G. Cvill6 and Cvill7: Potent and Selective Peptide Blockers of Kv1.2 Ion Channel Isolated from Mexican Scorpion Centruroides villegasi. Toxins 2025, 17, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060279
Shakeel K, Naseem MU, Olamendi-Portugal T, Zamudio FZ, Possani LD, Panyi G. Cvill6 and Cvill7: Potent and Selective Peptide Blockers of Kv1.2 Ion Channel Isolated from Mexican Scorpion Centruroides villegasi. Toxins. 2025; 17(6):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060279
Chicago/Turabian StyleShakeel, Kashmala, Muhammad Umair Naseem, Timoteo Olamendi-Portugal, Fernando Z. Zamudio, Lourival Domingos Possani, and Gyorgy Panyi. 2025. "Cvill6 and Cvill7: Potent and Selective Peptide Blockers of Kv1.2 Ion Channel Isolated from Mexican Scorpion Centruroides villegasi" Toxins 17, no. 6: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060279
APA StyleShakeel, K., Naseem, M. U., Olamendi-Portugal, T., Zamudio, F. Z., Possani, L. D., & Panyi, G. (2025). Cvill6 and Cvill7: Potent and Selective Peptide Blockers of Kv1.2 Ion Channel Isolated from Mexican Scorpion Centruroides villegasi. Toxins, 17(6), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060279








