Structural and Energetic Evidence Supports the Non-Covalent Phosphate Cyclization by the Class II Phospholipase D from Loxosceles intermedia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
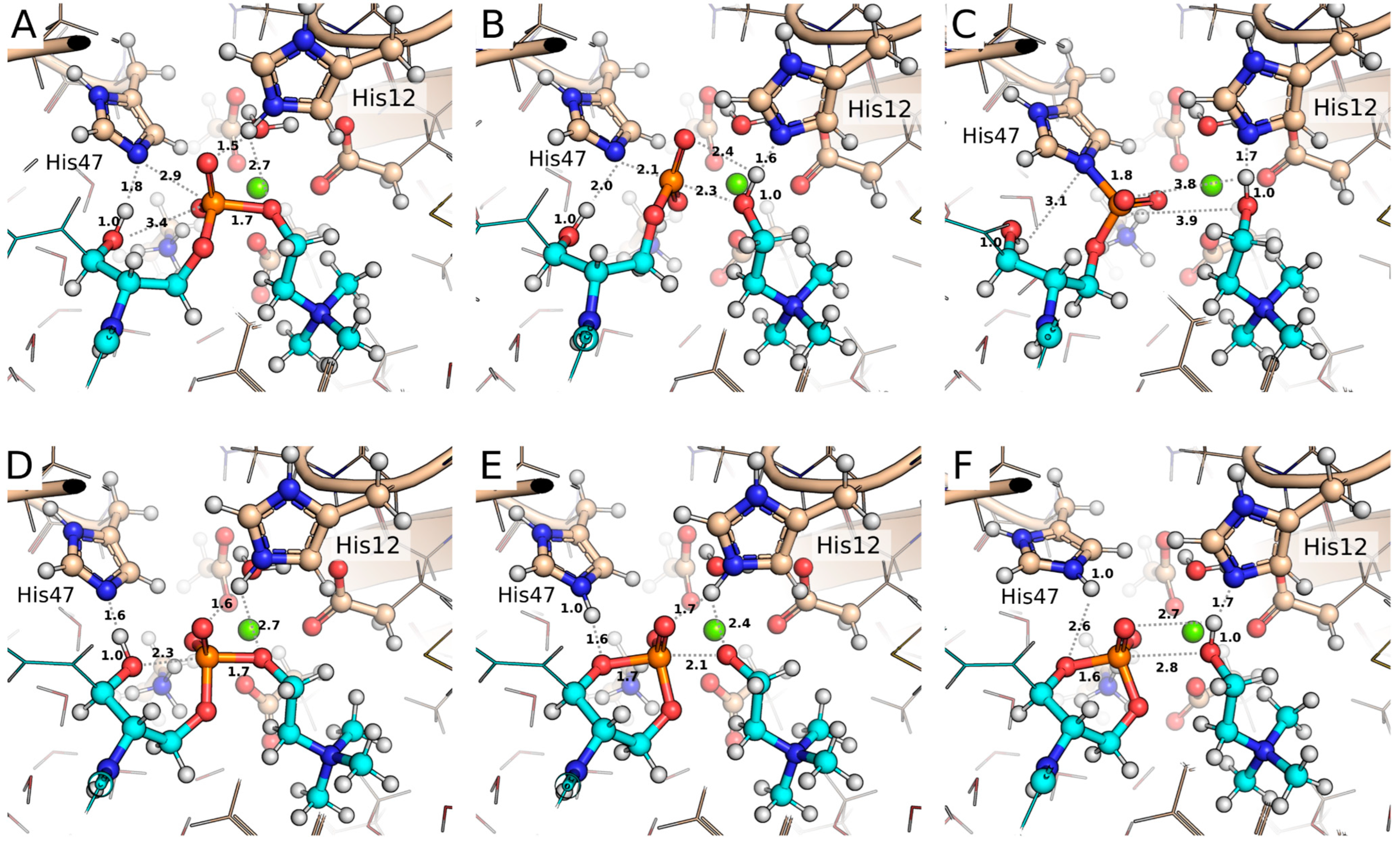
2.1. Crystallographic Evidence for the Cyclic Phosphate Bound at the PLD Active Site
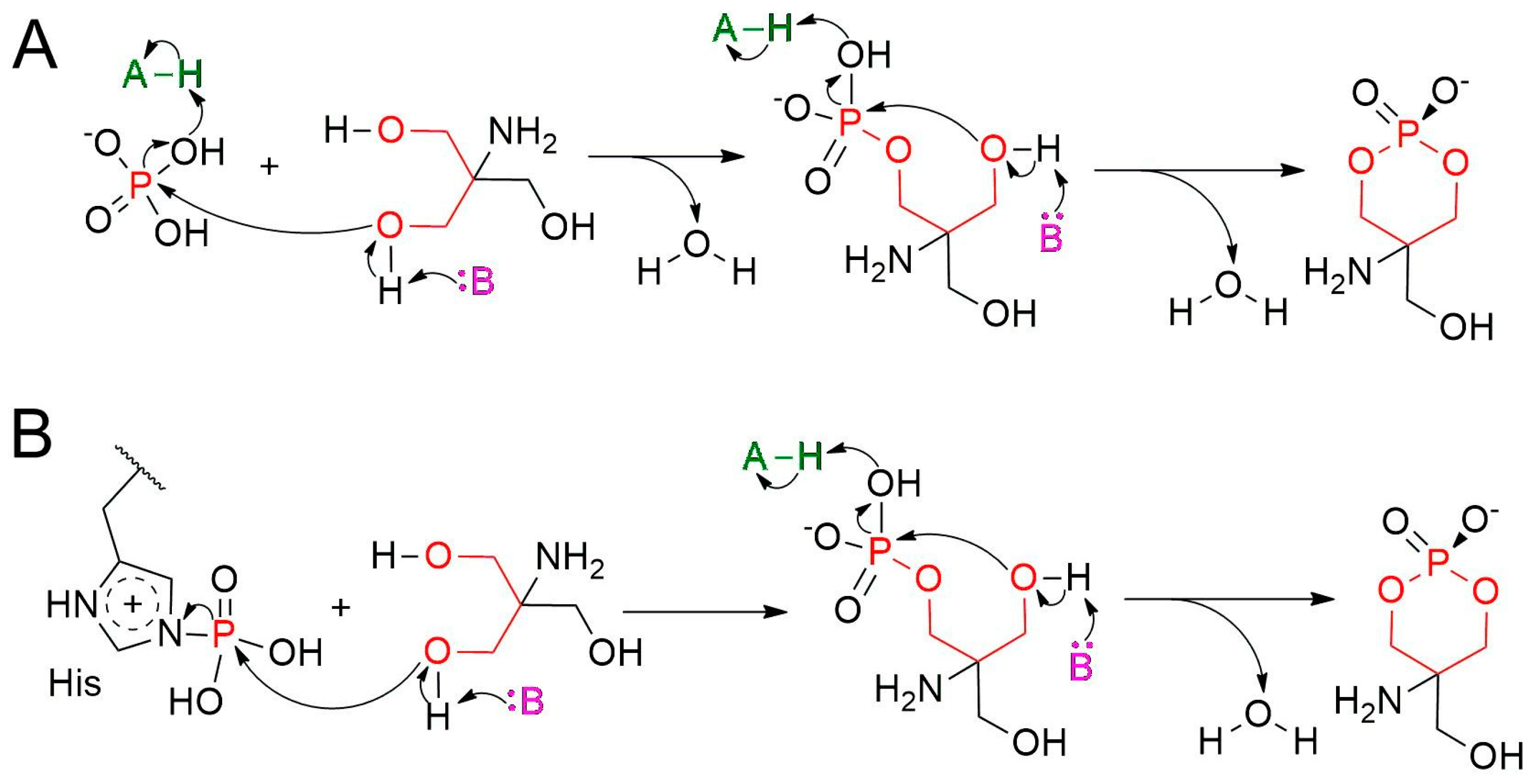
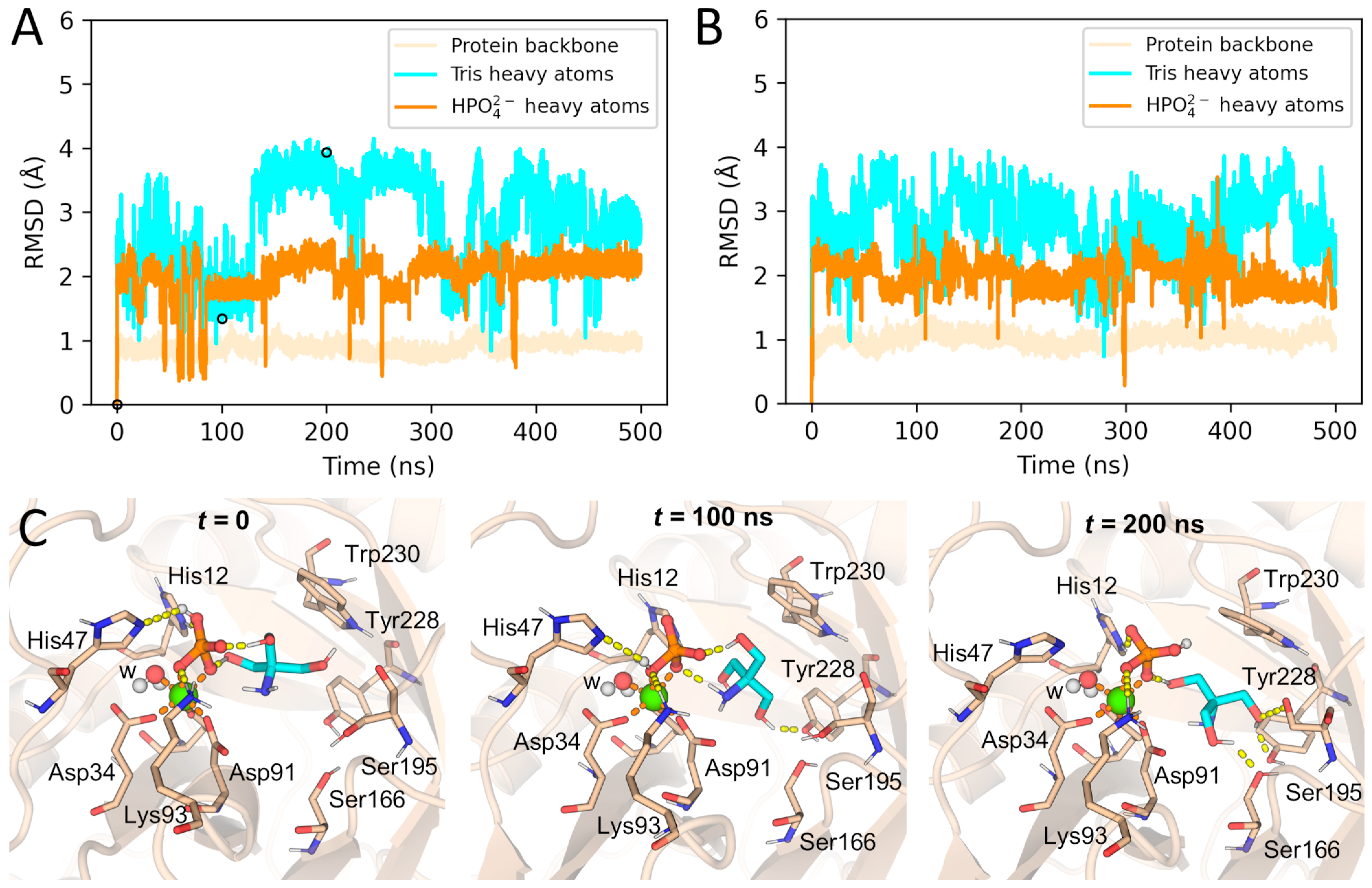
2.2. Formation of ACP at the Active Site
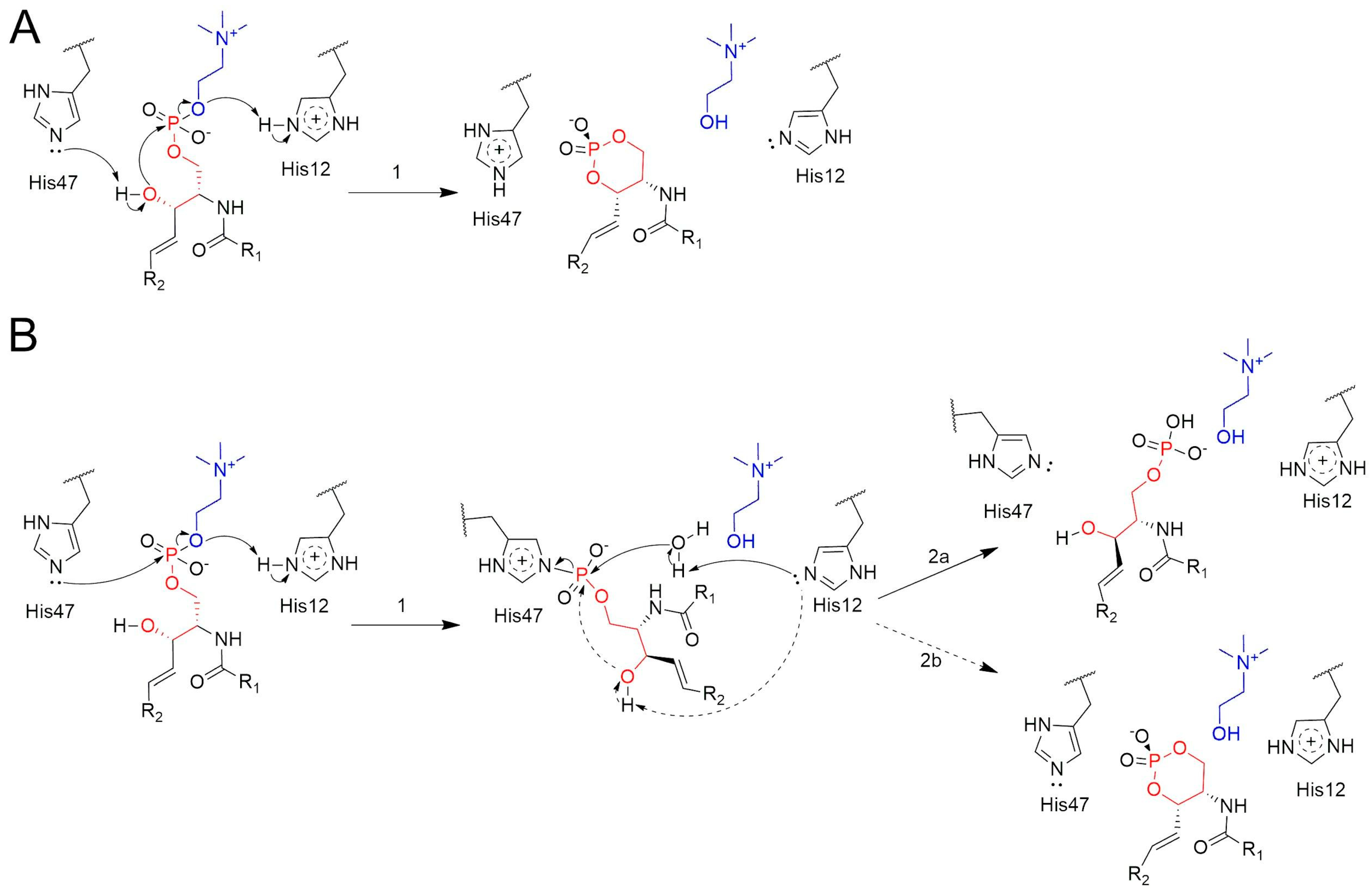
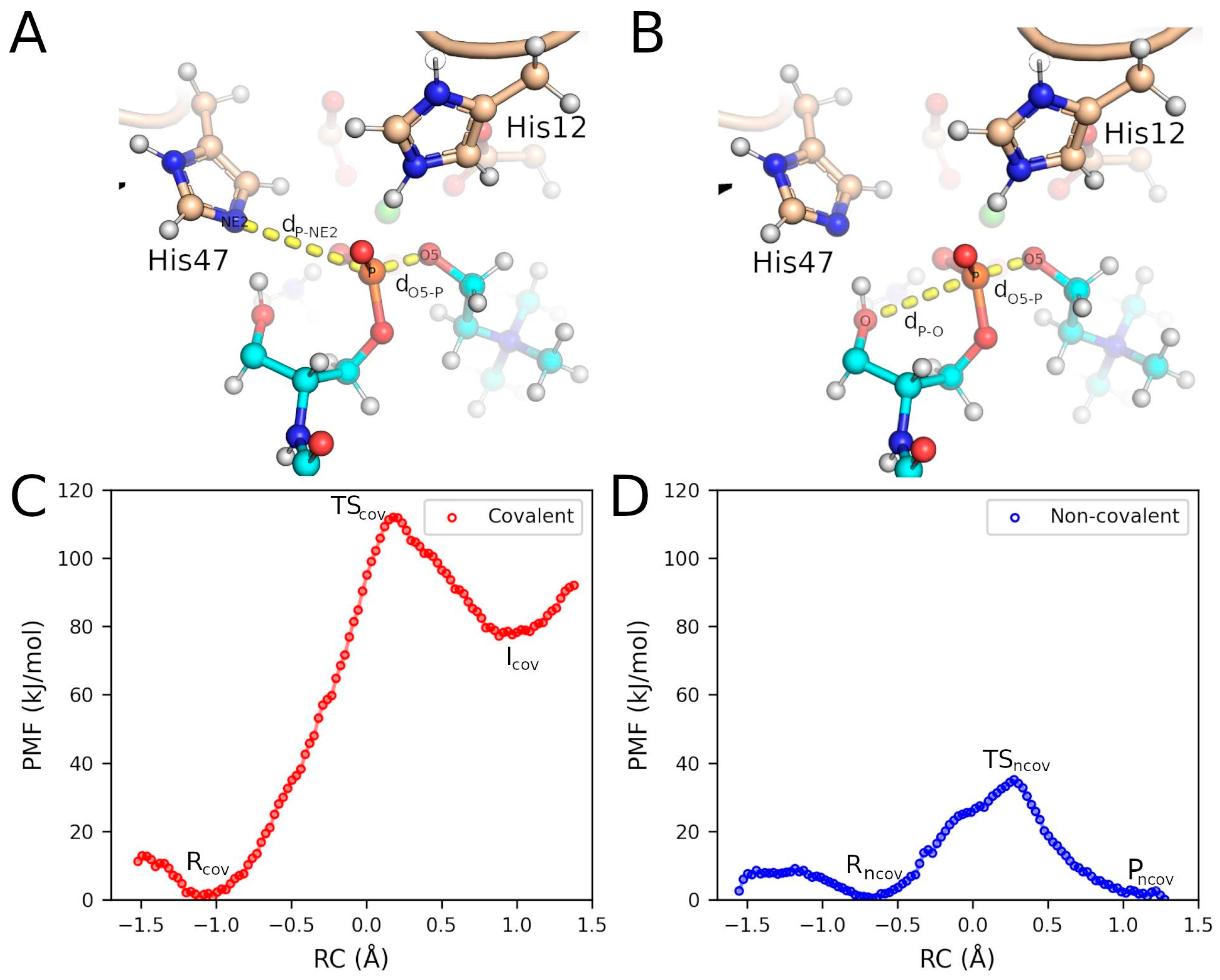
2.3. QM/MM Calculations Support the Non-Covalent Mechanism
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Refinement of the PDB 3RLH Crystal Structure
5.2. Ligand Parametrization for MD Simulations
5.3. MD Simulation Setup
5.4. Alchemical Free Energy Calculations
5.5. QM/MM Simulations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selvy, P.E.; Lavieri, R.R.; Lindsley, C.W.; Brown, H.A. Phospholipase D: Enzymology, Functionality, and Chemical Modulation. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6064–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, E.A.; Billington, S.J.; Carlson, P.; McGee, D.J.; Jost, B.H. Phospholipase D Promotes Arcanobacterium Haemolyticum Adhesion via Lipid Raft Remodeling and Host Cell Death Following Bacterial Invasion. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambourgi, D.V.; Paixão-Cavalcante, D.; Gonçalves de Andrade, R.M.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.d.F.; Magnoli, F.C.; Paul Morgan, B.; van den Berg, C.W. Loxosceles Sphingomyelinase Induces Complement-Dependent Dermonecrosis, Neutrophil Infiltration, and Endogenous Gelatinase Expression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambourgi, D.V.; Gonçalves-de-Andrade, R.M.; van den Berg, C.W. Loxoscelism: From Basic Research to the Proposal of New Therapies. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, M.A.; Okamoto, C.K.; Gonçalves-de-Andrade, R.M.; van den Berg, C.W.; Tambourgi, D.V. Sphingomyelinase D from Loxosceles laeta Venom Induces the Expression of MMP7 in Human Keratinocytes: Contribution to Dermonecrosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, C.R.; Fan, H.W. Clinical Picture and Laboratorial Evaluation in Human Loxoscelism. Toxicon 2011, 58, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladão, R.; Neto, O.B.S.; de Oliveira Gonzaga, M.; Pimenta, D.C.; Lopes, A.R. Digestive Enzymes and Sphingomyelinase D in Spiders without Venom (Uloboridae). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Díaz, M.; Monturiol-Gross, L.; Naylor, C.; Alape-Girón, A.; Flieger, A. Bacterial Sphingomyelinases and Phospholipases as Virulence Factors. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 597–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, A.L.; Bird, P.; Nisbet, I.T. Cloning, Nucleotide Sequence, and Expression in Escherichia Coli of the Phospholipase D Gene from Corynebacterium Pseudotuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKean, S.C.; Davies, J.K.; Moore, R.J. Expression of Phospholipase D, the Major Virulence Factor of Corynebacterium Pseudotuberculosis, Is Regulated by Multiple Environmental Factors and Plays a Role in Macrophage Death. Microbiology 2007, 153, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, W.A.; Songer, J.G. Arcanobacterium Haemolyticum Phospholipase D Is Genetically and Functionally Similar to Corynebacterium Pseudotuberculosis Phospholipase D. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4310–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias-Lopes, C.; Neshich, I.A.P.; Neshich, G.; Ortega, J.M.; Granier, C.; Chávez-Olortegui, C.; Molina, F.; Felicori, L. Identification of New Sphingomyelinases D in Pathogenic Fungi and Other Pathogenic Organisms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liscovitch, M.; Czarny, M.; Fiucci, G.; Tang, X. Phospholipase D: Molecular and Cell Biology of a Novel Gene Family. Biochem. J. 2000, 345, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.T.; Freitas Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.; de Andrade, S.A.; Gabdoulkhakov, A.; Betzel, C.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Arni, R.K. Structural Insights into the Catalytic Mechanism of Sphingomyelinases D and Evolutionary Relationship to Glycerophosphodiester Phosphodiesterases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, M.H.J.; Binford, G.J. Evolutionary Dynamics of Origin and Loss in the Deep History of Phospholipase D Toxin Genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arán-Sekul, T.; Perčić-Sarmiento, I.; Valencia, V.; Olivero, N.; Rojas, J.M.; Araya, J.E.; Taucare-Ríos, A.; Catalán, A. Toxicological Characterization and Phospholipase D Activity of the Venom of the Spider Sicarius thomisoides. Toxins 2020, 12, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, L.J.; Barrett, J.T.; Campbell, B.J. Red Blood Cell Lysis Induced by the Venom of the Brown Recluse Spider: The Role of Sphingomyelinase D. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1978, 187, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binford, G.J.; Bodner, M.R.; Cordes, M.H.J.; Baldwin, K.L.; Rynerson, M.R.; Burns, S.N.; Zobel-Thropp, P.A. Molecular Evolution, Functional Variation, and Proposed Nomenclature of the Gene Family That Includes Sphingomyelinase D in Sicariid Spider Venoms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajoie, D.M.; Roberts, S.A.; Zobel-Thropp, P.A.; Delahaye, J.L.; Bandarian, V.; Binford, G.J.; Cordes, M.H.J. Variable Substrate Preference among Phospholipase D Toxins from Sicariid Spiders. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 10994–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.T.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Arni, R.K. Structural Basis for Metal Ion Coordination and the Catalytic Mechanism of Sphingomyelinases D. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13658–13664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambourgi, D.V.; Magnoli, F.C.; van den Berg, C.W.; Morgan, B.P.; de Araujo, P.S.; Alves, E.W.; Da Silva, W.D. Sphingomyelinases in the Venom of the Spider Loxosceles intermedia Are Responsible for Both Dermonecrosis and Complement-Dependent Hemolysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, I.G.; Ordoñez, M.; Presa, N.; Gomez-Larrauri, A.; Simón, J.; Trueba, M.; Gomez-Muñoz, A. Sphingomyelinase D/Ceramide 1-Phosphate in Cell Survival and Inflammation. Toxins 2015, 7, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurpiewski, G.; Forrester, L.J.; Barrett, J.T.; Campbell, B.J. Platelet Aggregation and Sphingomyelinase D Activity of a Purified Toxin from the Venom of Loxosceles reclusa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 1981, 678, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lynch, K.R. Brown Recluse Spider (Loxosceles reclusa) Venom Phospholipase D (PLD) Generates Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA). Biochem. J. 2005, 391, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiros, I.; McSweeney, S.; Hough, E. The Reaction Mechanism of Phospholipase D from Streptomyces sp. Strain PMF. Snapshots along the Reaction Pathway Reveal a Pentacoordinate Reaction Intermediate and an Unexpected Final Product. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 339, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, D.M.; Zobel-Thropp, P.A.; Kumirov, V.K.; Bandarian, V.; Binford, G.J.; Cordes, M.H.J. Phospholipase D Toxins of Brown Spider Venom Convert Lysophosphatidylcholine and Sphingomyelin to Cyclic Phosphates. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, D.M.; Cordes, M.H.J. Spider, Bacterial and Fungal Phospholipase D Toxins Make Cyclic Phosphate Products. Toxicon 2015, 108, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polli, N.L.C.; Baldissera, A.; de Oliveira Leite, I.; Gonzalez, J.E.H.; Gismene, C.; Mariutti, R.B.; Matsubara, F.H.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Arni, R.K.; Veiga, S.S.; et al. Chapter 15—Brown Spider Venom Phospholipases D: From Molecular Biology and Structural Analyses to Potential Vaccine and Serum Therapy Applications. In Phospholipases in Physiology and Pathology; Chakraborti, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 263–286. ISBN 978-0-323-95687-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves-Moreira, D.; Gremski, L.H.; de Moraes, F.R.; Vuitika, L.; Wille, A.C.M.; Hernández González, J.E.; Chaim, O.M.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Arni, R.K.; Veiga, S.S. Brown Spider Venom Phospholipase-D Activity upon Different Lipid Substrates. Toxins 2023, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Giuseppe, P.O.; Ullah, A.; Silva, D.T.; Gremski, L.H.; Wille, A.C.M.; Chaves Moreira, D.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Chaim, O.M.; Murakami, M.T.; Veiga, S.S.; et al. Structure of a Novel Class II Phospholipase D: Catalytic Cleft Is Modified by a Disulphide Bridge. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmayr, H.; Merrill, A.H. A Brief Overview of the Toxic Sphingomyelinase Ds of Brown Recluse Spider Venom and Other Organisms and Simple Methods to Detect Production of Its Signature Cyclic Ceramide Phosphate. Mol. Pharmacol. 2024, 105, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergelius, C.; Niinivehmas, S.; Maula, T.; Kurita, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Katsumura, S.; Pentikäinen, O.T.; Slotte, J.P. Structure-Activity Relationship of Sphingomyelin Analogs with Sphingomyelinase from Bacillus cereus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.3r1; Schrodinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2010.
- Agirre, J.; Atanasova, M.; Bagdonas, H.; Ballard, C.B.; Baslé, A.; Beilsten-Edmands, J.; Borges, R.J.; Brown, D.G.; Burgos-Mármol, J.J.; Berrisford, J.M.; et al. The CCP4 Suite: Integrative Software for Macromolecular Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2023, 79, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and Development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.J.; Headd, J.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Prisant, M.G.; Videau, L.L.; Deis, L.N.; Verma, V.; Keedy, D.A.; Hintze, B.J.; Chen, V.B.; et al. MolProbity: More and Better Reference Data for Improved All-Atom Structure Validation. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández González, J.E.; Hernández Alvarez, L.; Pascutti, P.G.; Valiente, P.A. Predicting Binding Modes of Reversible Peptide-Based Inhibitors of Falcipain-2 Consistent with Structure-Activity Relationships. Proteins 2017, 85, 1666–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Ben-Shalom, I.Y.; Berryman, J.T.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Cisneros, G.A.; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; et al. Amber; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Belfon, K.A.A.; Raguette, L.; Huang, H.; Migues, A.N.; Bickel, J.; Wang, Y.; Pincay, J.; Wu, Q.; et al. ff19SB: Amino-Acid-Specific Protein Backbone Parameters Trained against Quantum Mechanics Energy Surfaces in Solution. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2020, 16, 528–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boresch, S.; Tettinger, F.; Leitgeb, M.; Karplus, M. Absolute Binding Free Energies: A Quantitative Approach for Their Calculation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 9535–9551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimovich, P.V.; Shirts, M.R.; Mobley, D.L. Guidelines for the Analysis of Free Energy Calculations. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2015, 29, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doudou, S.; Burton, N.A.; Henchman, R.H. Standard Free Energy of Binding from a One-Dimensional Potential of Mean Force. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, M.J. pDynamo3 Molecular Modeling and Simulation Program. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 5849–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachega, J.F.R.; Timmers, L.F.S.M.; Assirati, L.; Bachega, L.R.; Field, M.J.; Wymore, T. GTKDynamo: A PyMOL Plug-in for QC/MM Hybrid Potential Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannwarth, C.; Ehlert, S.; Grimme, S. GFN2-xTB—An Accurate and Broadly Parametrized Self-Consistent Tight-Binding Quantum Chemical Method with Multipole Electrostatics and Density-Dependent Dispersion Contributions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 1652–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Refinement | 3RLH | 3RLH (Reprocessed) |
|---|---|---|
| Rfactor | 17.2 | 16.7 |
| Rfree | 21.4 | 19.7 |
| RMSD bond distances (Å) | 0.023 | 0.0185 |
| RMSD bond angles (°) | 1.930 | 1.57 |
| Ramachandran outliers (%) | 0 | 0 |
| Ramachandran favored (%) | 99.3 | 98.9 |
| Waters molecules | 184 | 190 |
| Ligands | Mg2+, PGE a, PEG b and EDO c | Mg2+, PGE a, PEG b, EDO c and ACP d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gismene, C.; Ruggiero Bachega, J.F.; Doherty, D.Z.; Veiga, S.S.; Arni, R.K.; Hernández González, J.E. Structural and Energetic Evidence Supports the Non-Covalent Phosphate Cyclization by the Class II Phospholipase D from Loxosceles intermedia. Toxins 2025, 17, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030111
Gismene C, Ruggiero Bachega JF, Doherty DZ, Veiga SS, Arni RK, Hernández González JE. Structural and Energetic Evidence Supports the Non-Covalent Phosphate Cyclization by the Class II Phospholipase D from Loxosceles intermedia. Toxins. 2025; 17(3):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030111
Chicago/Turabian StyleGismene, Carolina, José Fernando Ruggiero Bachega, Daniel Z. Doherty, Silvio Sanches Veiga, Raghuvir K. Arni, and Jorge Enrique Hernández González. 2025. "Structural and Energetic Evidence Supports the Non-Covalent Phosphate Cyclization by the Class II Phospholipase D from Loxosceles intermedia" Toxins 17, no. 3: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030111
APA StyleGismene, C., Ruggiero Bachega, J. F., Doherty, D. Z., Veiga, S. S., Arni, R. K., & Hernández González, J. E. (2025). Structural and Energetic Evidence Supports the Non-Covalent Phosphate Cyclization by the Class II Phospholipase D from Loxosceles intermedia. Toxins, 17(3), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030111






