Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Alaskan Butter Clams: Does Cleaning Make Them Safe to Eat?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
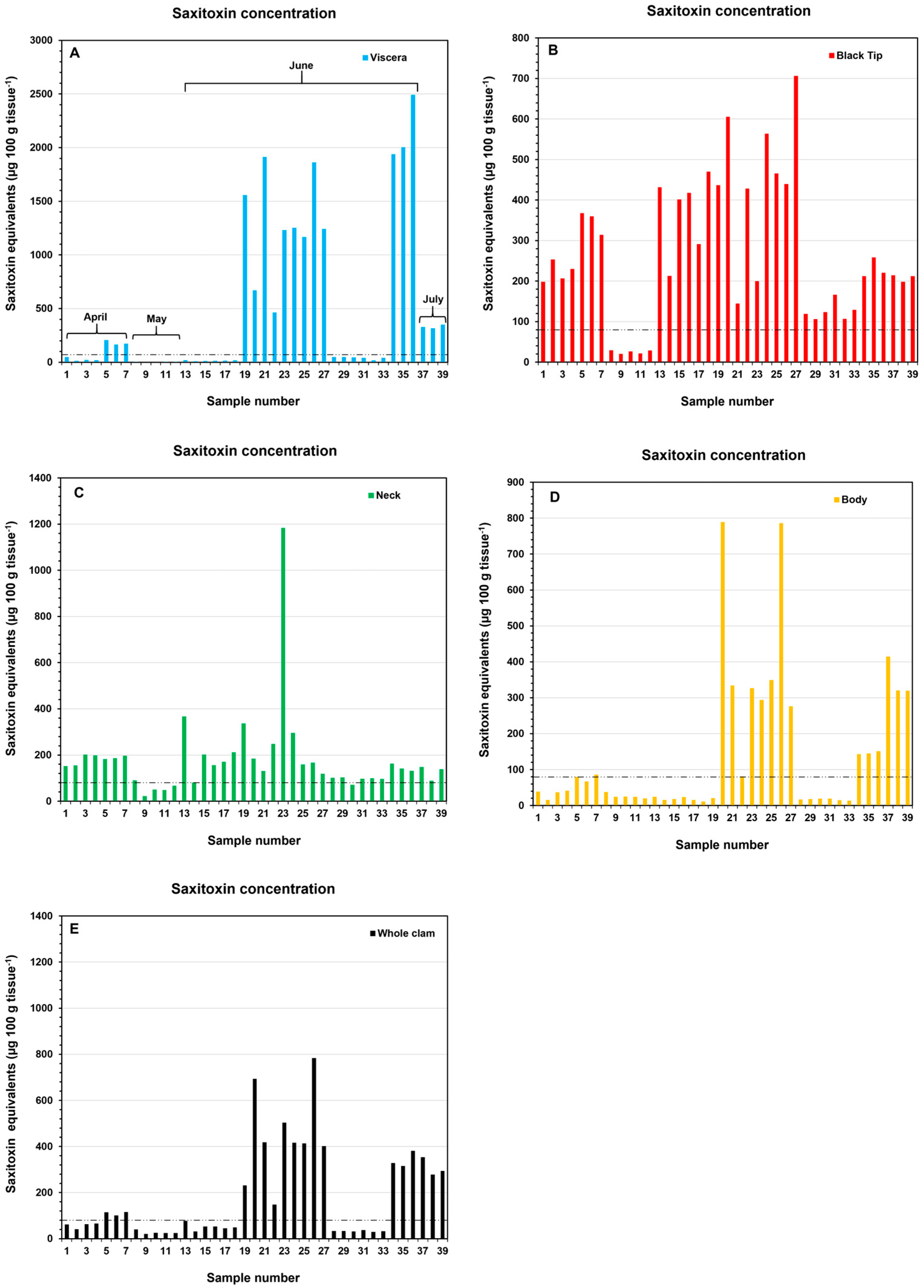
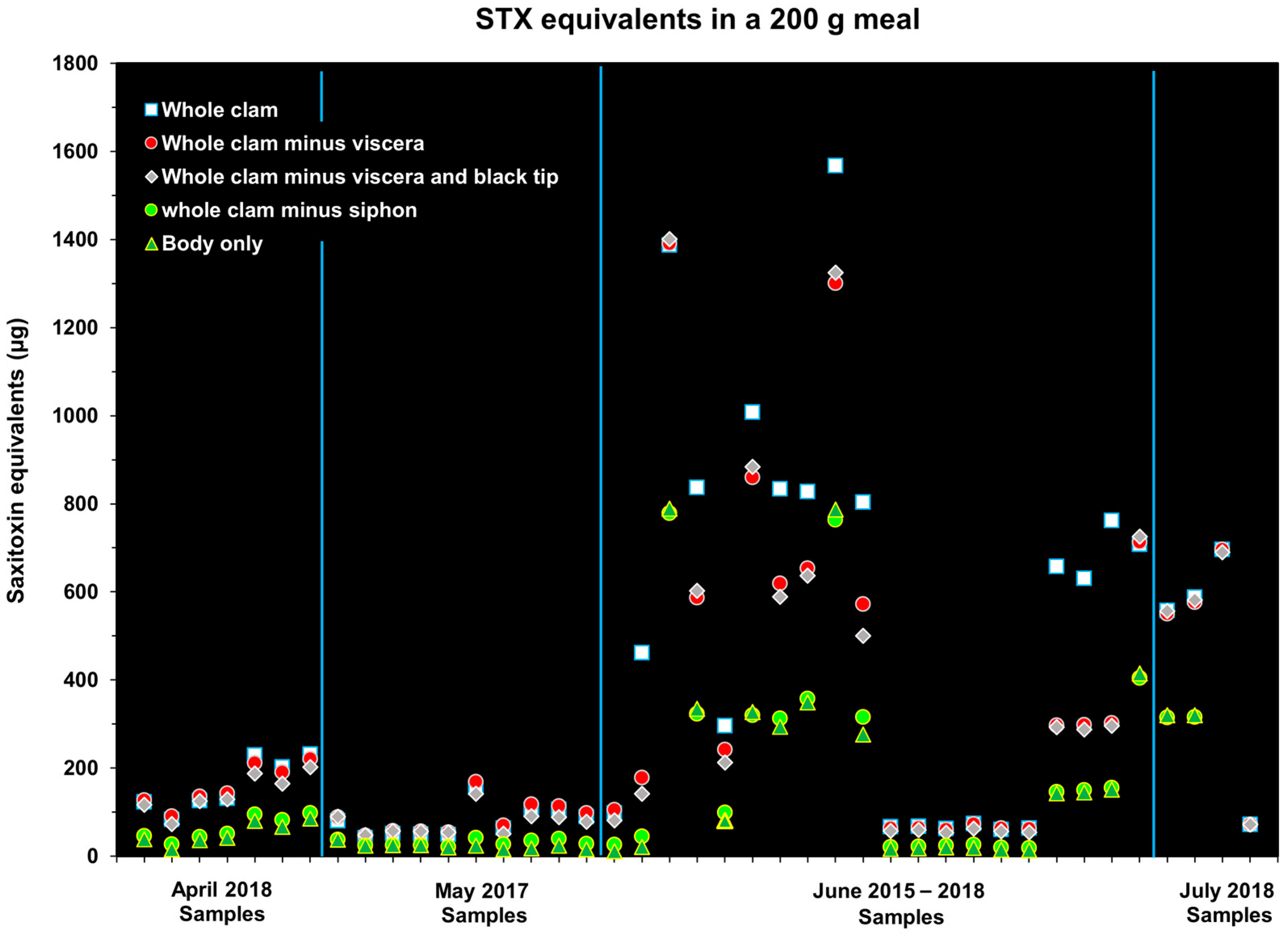
2.1. Effects of Removing Various Tissues, or Combination of Tissues, on Toxin Concentrations in Alaskan Butter Clams
2.2. Impact of Siphon Removal on Toxin Concentration in Southeast Alaska Butter Clams
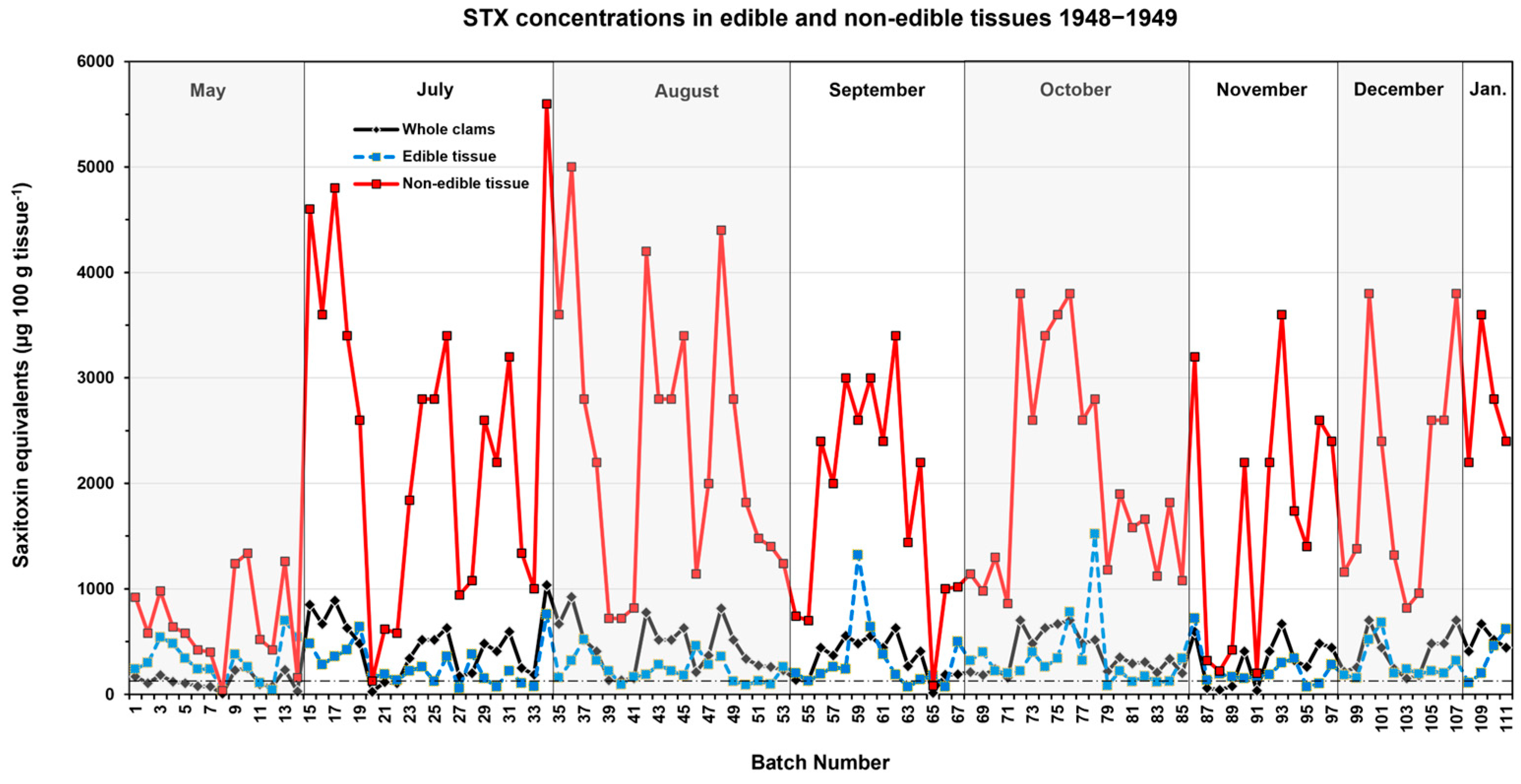
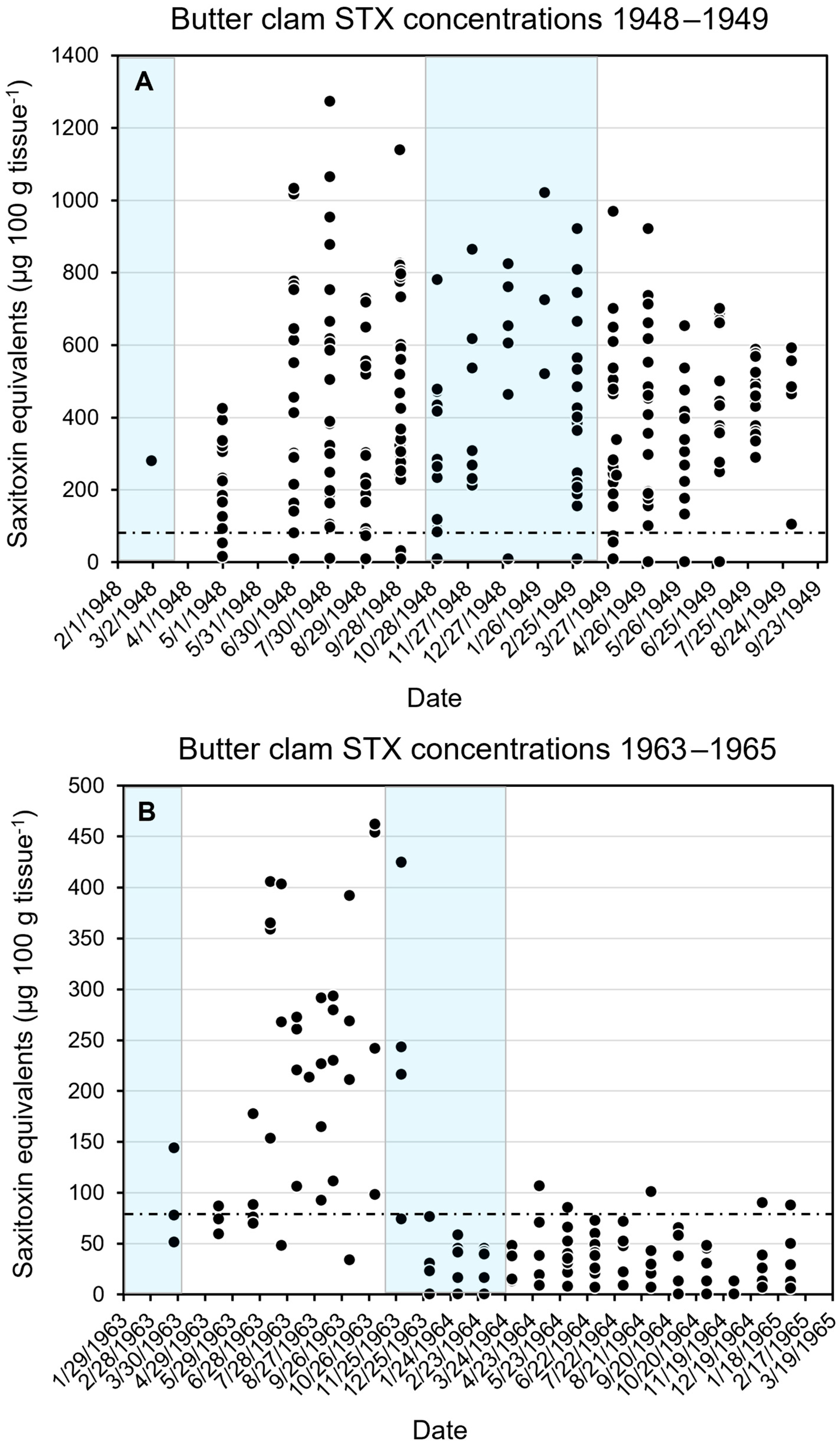
2.3. Seasonal Changes in Butter Clam STX Concentrations
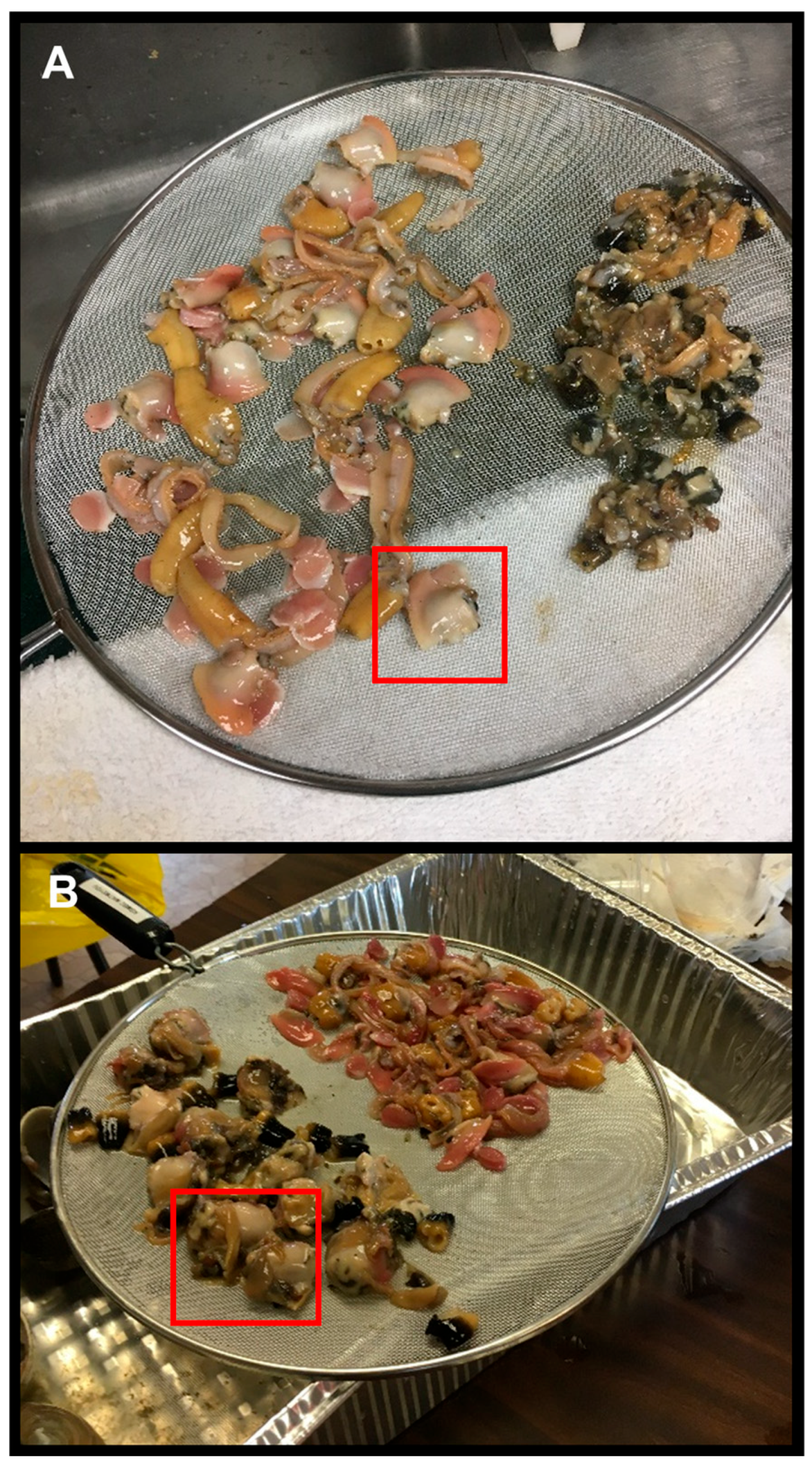
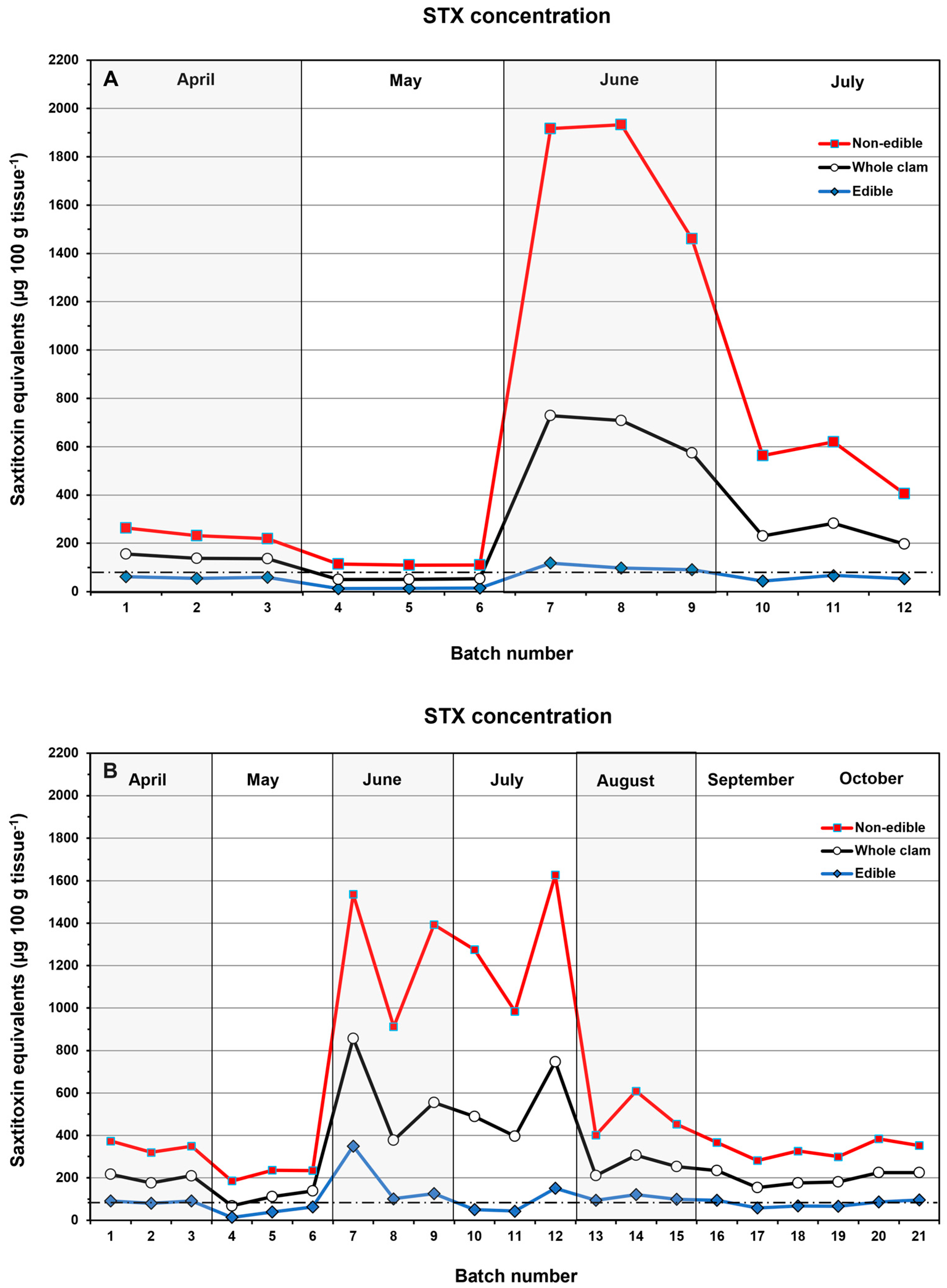
2.4. Comparison of Two Cleaning Methods Practiced by Alaskan Native Communities
2.5. Risk Associated with Consuming Meal Contaminated by Saxitoxins
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Butter Clam Collection
5.2. Saxitoxin Analysis
5.3. Determining STX–eq Concentrations in Edible and Non–Edible Tissues
5.4. Seasonal Changes in Saxitoxin Concentrations in Butter Clams
5.5. Estimates of PSP Risk Based on the Amount of Toxin Consumed in an Average–Sized Meal
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Hallmann, N.; Burchell, M.; Schöne, B.R.; Irvine, G.V.; Maxwell, D. High–resolution sclerochronological analysis of the bivalve mollusk Saxidomus gigantea from Alaska and British Columbia: Techniques for revealing environmental archives and archaeological seasonality. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnlein, H.; Humphries, M. Traditional Animal Foods of Indigenous Peoples of Northern North America the Contributions of Wildlife Diversity to the Subsistence and Nutrition of Indigenous Cultures; Centre for Indigenous Peoples’ Nutrition and Environment, McGill University: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Toniello, G.; Lepofsky, D.; Lertzman–Lepofsky, G.; Salomon, A.K.; Rowell, K. 11,500 y of human–clam relationships provide long–term context for intertidal management in the Salish Sea, British Columbia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22106–22114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, L.; Miller, A.; Kosatsky, T. Changing trends in paralytic shellfish poisonings reflect increasing sea surface temperatures and practices of indigenous and recreational harvesters in British Columbia, Canada. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumway, S.E. A review of the effects of algal blooms on shellfish and aquaculture. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 1990, 21, 65–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, K.G. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Update―Alaska, 1993–2021. Bulletin No. 5. Available online: https://epi.alaska.gov/bulletins/docs/b2022_05.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Ansdell, V. Food Poisoning from Marine Toxins. Available online: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/environmental–hazards–risks/food–poisoning–from–marine–toxins (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Tester, P.A.; Matweyou, J.; Himelbloom, B.; Wright, B.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Litaker, R.W. Saxitoxin and the cold war. In Harmful Algae 2018—From Ecosystems to Socioecosystems: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae: Nantes, France, 2020; pp. 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.S.; Magnusson, H.W. Seasonal Variations in Toxicity of Butter Clams from Selected Alaskan Beaches; United States Deparment of the Interior Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1950; p. 24. Available online: https://spo.nmfs.noaa.gov/sites/default/files/legacy-pdfs/SSRF53.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Kibler, S.R.; Litaker, R.W.; Matweyou, J.A.; Hardison, D.R.; Wright, B.A.; Tester, P.A. Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in butter clams (Saxidomus gigantea) from the Kodiak Archipelago, Alaska. Harmful Algae 2022, 111, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SEATOR. Southeast Alaska Tribal Ocean Research. Available online: http://seator.org/ (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- McConnell, J. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP): Knik Tribe’s Natural Resources Department. Available online: https://www.kniktribe.org/alaska-knik-tribe-paralytic-shellfish-poisoning (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Neal, R.A. Fluctuations in the Levels of Paralytic Shellfish Toxin in Four Species of Lamellibranch Mollusks Near Ketchikan, Alaska, 1963–1965. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 1967; 149p. [Google Scholar]
- Tester, P.A.; Wright, B.; Litaker, R.W.; McKinney, P.; Holland, W.C.; Kibler, S.R.; Vandersea, M.W. Saxitoxin in Alaskan Commercial Crab Species. PLoS ONE 2025, in press.
- Wekell, J.C.; Hurst, J.; Lefebvre, K. The Origin of the Regulatory Limits for PSP and ASP Toxins in Shellfish. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 927–930. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285809374 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- EFSA. European Food Safety Authority. Marine biotoxins in shellfish—Saxitoxin group. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, S.C.; Webb, N.G.; Boundy, M.J.; Harwood, D.T.; Munday, J.S.; Sprosen, J.M.; Somchit, C.; Broadhurst, R.B. A sub–acute dosing study of saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin mixtures in mice suggests that the current paralytic shellfish toxin regulatory limit is fit for purpose. Toxins 2023, 15, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnich, N.; Thébault, A. Dose–response modelling of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) in humans. Toxins 2018, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbard, J.; Naubert, J. Paralytic shellfish poisoning on the Canadian Atlantic coast. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1948, 38, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarren, E.F.; Schafer, M.L.; Campbell, J.E.; Lewis, K.H.; Jensen, E.T.; Schantz, E.J. Public health significance of paralytic shellfish poison. In Advances in Food Research; Chichester, C.O., Mrak, E.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1961; Volume 10, pp. 135–179. [Google Scholar]
- Redwood, D.G.; Day, G.M.; Beans, J.A.; Hiratsuka, V.Y.; Nash, S.H.; Howard, B.V.; Umans, J.G.; Koller, K.R. Alaska native traditional food and harvesting activity patterns over 10 years of follow–up. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2019, 3, nzz114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASEHL. Alaska State Environmental Health Laboratory. Sample Submission Manual. 2020. Available online: https://dec.alaska.gov/eh/lab/ (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- Kobayashi, M. An Analytical Method of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins Using a Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/sites/shimadzu.com.an/files/pim/pim_document_file/applications/application_note/16803/an_01–00364–en.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Lawrence, J.F.; Niedzwiadek, B.; Menard, C. Quantitative determination of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in shellfish using prechromatographic oxidation and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1714–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben–Gigirey, B.; Rodríguez–Velasco, M.L.; Otero, A.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. A comparative study for PSP toxins quantification by using MBA and HPLC official methods in shellfish. Toxicon 2012, 60, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, D.T.; Boundy, M.; Selwood, A.I.; van Ginkel, R.; MacKenzie, L.; McNabb, P.S. Refinement and implementation of the Lawrence method (AOAC 2005.06) in a commercial laboratory: Assay performance during an Alexandrium catenella bloom event. Harmful Algae 2013, 24, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Norton, D.M.; Hatfield, R.G.; Morris, S.; Reese, A.R.; Algoet, M.; Lees, D.N. Refinement and Extension of AOAC Method 2005.06 to Include Additional Toxins in Mussels: Single–Laboratory Validation. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 92, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, K.D.; Sayler, G.S. An overview on the marine neurotoxin, saxitoxin: Genetics, molecular targets, methods of detection and ecological functions. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 991–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. CDC Body Measurements. National Centers for Health Statistics. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/body–measurements.htm (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- SnapCalorie. Butter Clam. Available online: https://www.snapcalorie.com/nutrition/butter_clam_nutrition.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).



| Month | Mean | SD | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| May | 22 | 20 | 15 |
| July | 57 | 23 | 19 |
| August | 60 | 18 | 19 |
| September | 48 | 27 | 14 |
| October | 53 | 18 | 17 |
| November | 45 | 28 | 13 |
| December | 52 | 14 | 10 |
| January | 59 | 21 | 4 |
| Overall | 49 | 24 | 111 |
| Average–Sized Man (90.6 kg) (µg STX–eq. Ingested) | Average–Sized Woman (78 kg) (µg STX–eq. Ingested) | Probability of No Symptoms | Probability of Mild Symptoms | Probability of Moderate Symptoms | Probability of Severe Symptoms | Probability of Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 91 | 78 | 88.67% | 9.22% | 1.57% | 0.53% | 0.00% |
| 906 | 775 | 45.49% | 30.66% | 12.99% | 10.59% | 0.27% |
| 9060 | 7750 | 7.55% | 19.50% | 19.43% | 46.37% | 7.15% |
| 90,600 | 77,500 | 0.30% | 2.40% | 5.30% | 47.70% | 44.30% |
| 906,000 | 775,000 | 0.00% | 0.05% | 0.26% | 11.59% | 88.10% |
| Tissues Retained as Edible | Tissues Discarded as Non–Edible |
|---|---|
| Whole clams (includes viscera, black tip at the end of the siphon, siphon neck, and body of the clam) | |
| Black tip, neck, body | Viscera |
| Siphon neck, clam body | Viscera, black tip |
| Clam body | Viscera, black tip, siphon neck |
| Viscera, clam body | Black tip, siphon neck |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Litaker, R.W.; Matweyou, J.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; Tester, P.A. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Alaskan Butter Clams: Does Cleaning Make Them Safe to Eat? Toxins 2025, 17, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060271
Litaker RW, Matweyou JA, Kibler SR, Hardison DR, Holland WC, Tester PA. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Alaskan Butter Clams: Does Cleaning Make Them Safe to Eat? Toxins. 2025; 17(6):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060271
Chicago/Turabian StyleLitaker, R. Wayne, Julie A. Matweyou, Steven R. Kibler, D. Ransom Hardison, William C. Holland, and Patricia A. Tester. 2025. "Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Alaskan Butter Clams: Does Cleaning Make Them Safe to Eat?" Toxins 17, no. 6: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060271
APA StyleLitaker, R. W., Matweyou, J. A., Kibler, S. R., Hardison, D. R., Holland, W. C., & Tester, P. A. (2025). Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Alaskan Butter Clams: Does Cleaning Make Them Safe to Eat? Toxins, 17(6), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060271





