Ustilaginoidin D Induces Acute Toxicity and Hepatotoxicity in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
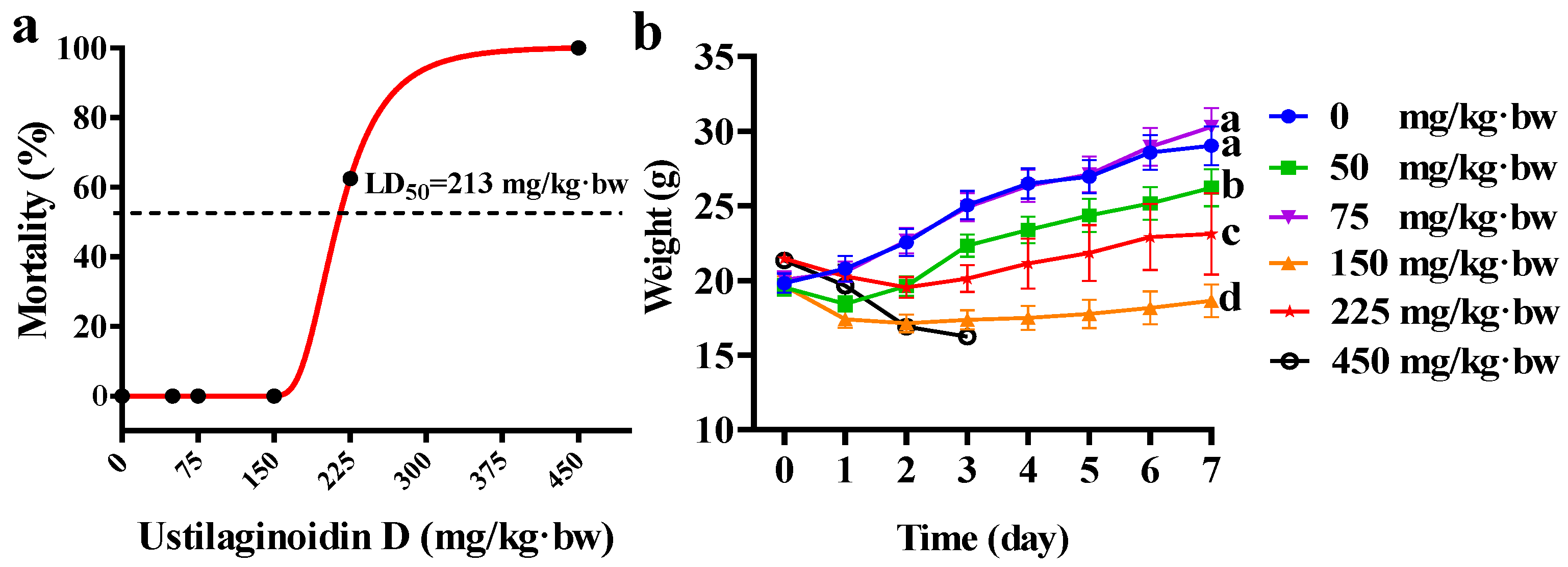
2.1. Acute Toxicity Induced by Ustilaginoidin D in Mice
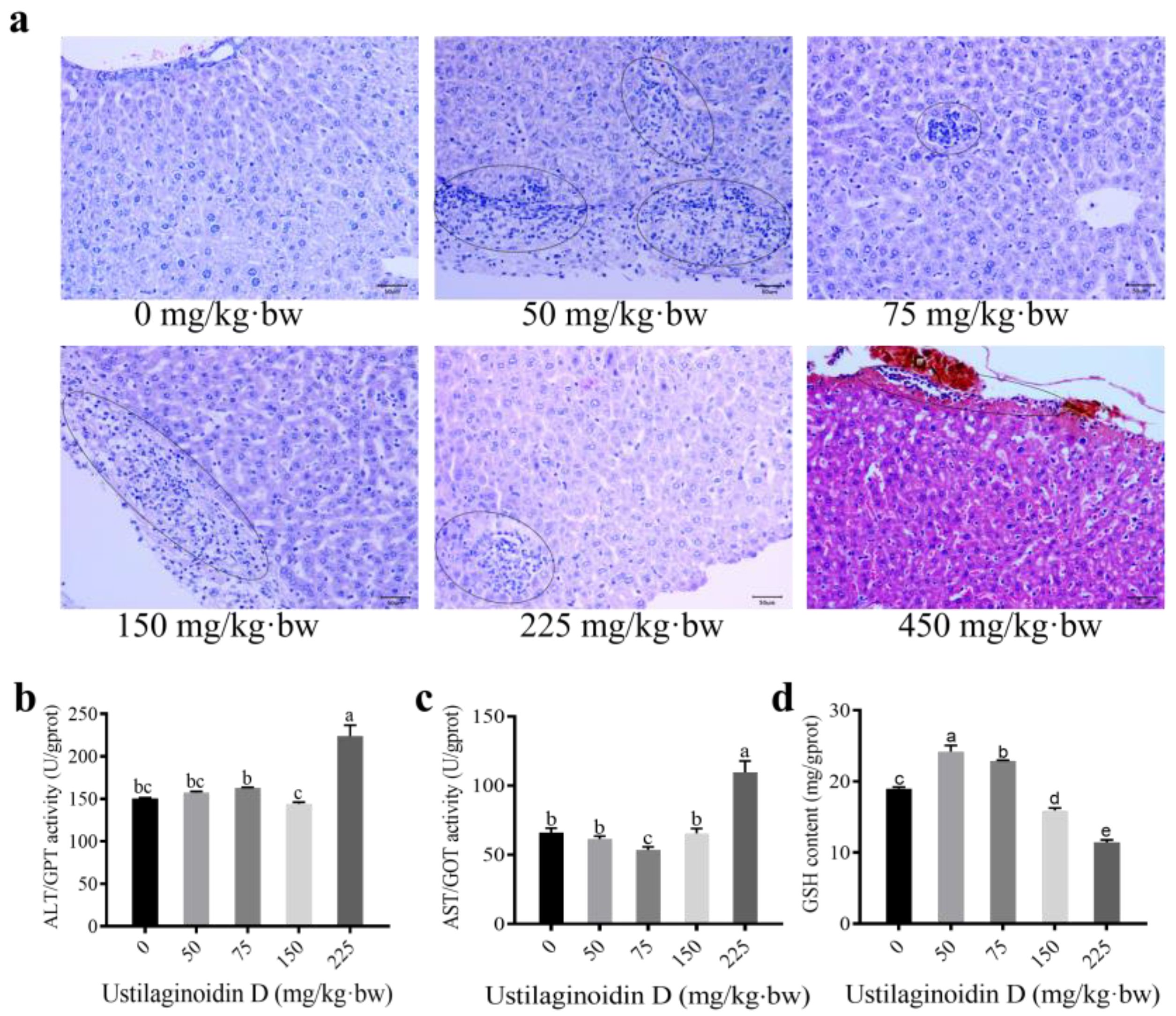
2.2. Treatment of Ustilaginoidin D Leads to Significant Hepatotoxicity in Mice
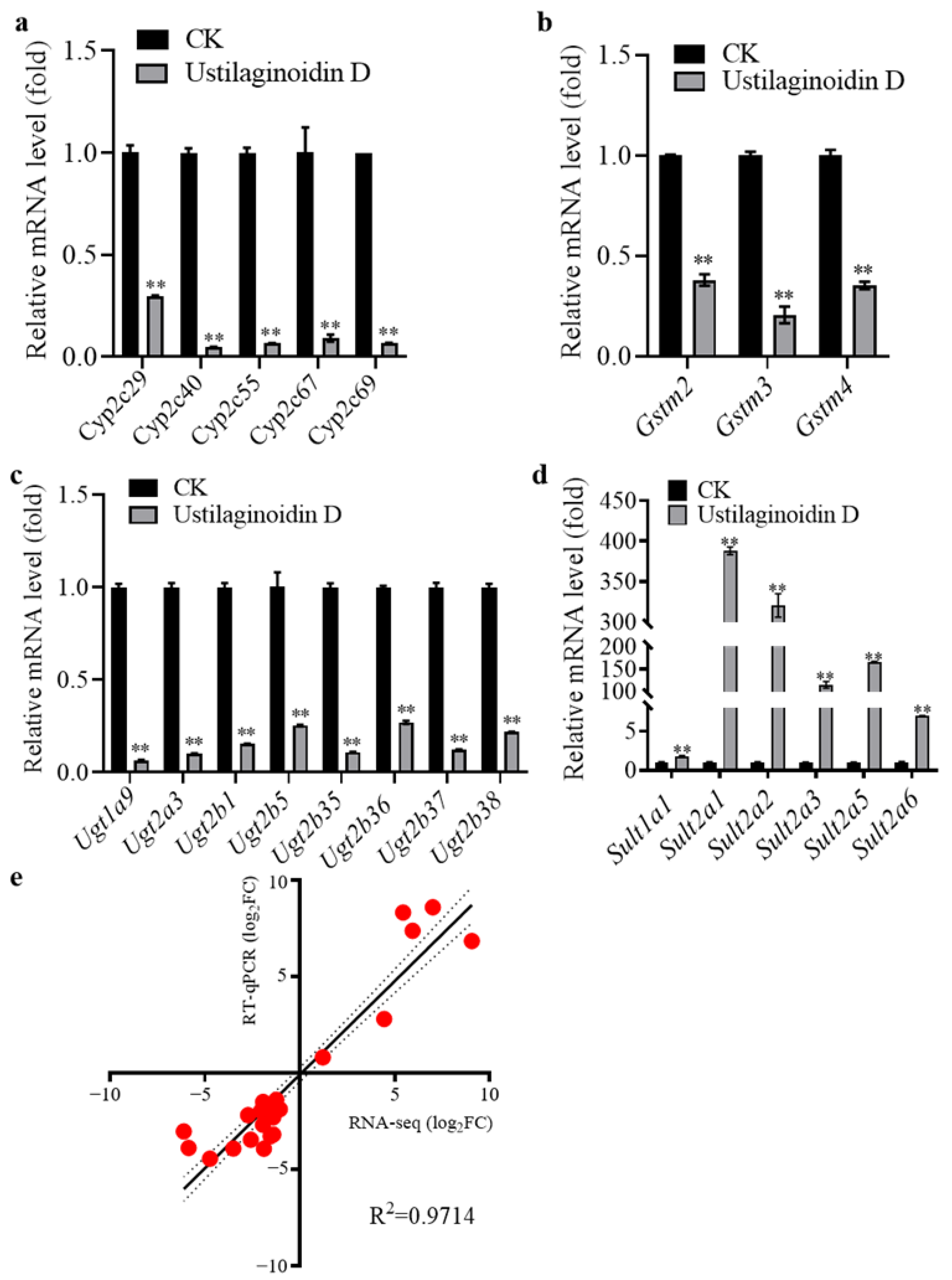
2.3. Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis to Evaluate the Impact of Ustilaginoidin D on the Mouse Liver Function
2.4. Validation of Differentially Expressed Genes by RT-qPCR
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Experimental Animals, Diets, and Housing Conditions
5.2. Chemicals, Reagents, Treatment and Dosing Protocols
5.3. Histopathological Evaluation of Mouse Liver Through Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining
5.4. Assessment of the Enzymatic Activities of ALT and AST and the Content of GSH in Mouse Livers
5.5. RNA-Seq Analysis
5.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
5.7. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooks, S.A.; Anders, M.M.; Yeater, K.M. Effect of furrow irrigation on the severity of false smut in susceptible rice varieties. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Fan, J.; Fang, A.; Li, Y.; Tariqjaveed, M.; Li, D.; Hu, D.; Wang, W. Ustilaginoidea virens: Insights into an emerging rice pathogen. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2020, 58, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Gong, Z.; Xu, P.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. The false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens requires rice stamens for false smut ball formation. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Fang, A.; Han, Y.; Yang, J.; Xue, M.; Bao, J.; Hu, D.; Zhou, B.; Sun, X.; et al. Specific adaptation of Ustilaginoidea virens in occupying host florets revealed by comparative and functional genomics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Infection processes of Ustilaginoidea virens during artificial inoculation of rice panicles. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 139, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, E.; Ashizawa, T.; Sonoda, R.; Tanaka, C. Villosiclava virens gen. nov., comb. nov., teleomorph of Ustilaginoidea virens, the causal agent of rice false smut. Mycotaxon 2008, 106, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Jin, J.; Hu, D.; Yong, M.; Xu, Y.; He, L. Elucidation of the infection process of Ustilaginoidea virens (teleomorph: Villosiclava virens) in rice spikelets. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Ominato, K.; Natori, S.; Tashiro, T.; Tsuruo, T. Cytotoxicity and antitumor activities of fungal bis (naphtho-gamma-pyrone) derivatives. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1988, 11, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Sekita, S.; Koyama, K.; Natori, S.; Takahashi, A. Effect of chaetochromin A, chaetochromin D and ustilaginoidin A, bis (naphtho-γ-pyrone) derivatives, on the mouse embryo limb bud and midbrain cells in culture. Congenit. Anom. 1987, 3, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, K.; Hisada, K.; Mori, S.; Nozawa, Y.; Koyama, K.; Natori, S. The impairing effect of chaetochromin a and related mycotoxins on mitochondrial respiration. JSM Mycotoxins. 2009, 1991, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Meng, J.; Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Han, Y.; Jiang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L.; et al. Determination of the absolute configurations of the stereogenic centers of ustilaginoidins by studying the biosynthetic monomers from a gene knockout mutant of Villosiclava virens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zou, J.; Li, D.; Zhao, D.; Li, W.; Sun, W. Ustilaginoidin D induces hepatotoxicity and behaviour aberrations in zebrafish larvae. Toxicology 2021, 456, 152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRae, A.C.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as tools for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, B.; Yan, K.; Sang, R.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Yu, M.; Liu, X.; Qiu, Q.; Zhang, X. Integrated network toxicology, molecular docking, and in vivo experiments to elucidate molecular mechanism of aflatoxin B1 hepatotoxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 275, 116278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Shen, J.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, M.; Ma, X. Pxr activation relieves deoxynivalenol-induced liver oxidative stress via Malat1 lncRNA m6A demethylation. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2308742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Jia, K.; Huang, L.; Liao, X.; Guo, X.; Lu, H. Hepatotoxicity of tricyclazole in zebrafish (danio rerio). Chemosphere 2019, 232, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Zou, L.; Deng, Y.; Meng, Y.; Liao, X.; Lu, H. Clethodim exposure induces developmental immunotoxicity and neurobehavioral dysfunction in zebrafish embryos. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, F.J. Cytochrome P450 humanised mice. Hum. Genomics. 2004, 1, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averill-Bates, D.A. The antioxidant glutathione. Vitam. Horm. 2023, 121, 109–141. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.I.; Izumiyama, N.; Ohtsubo, K.I.; Koiso, Y.; Iwasaki, S.; Sonoda, R.; Fujita, Y.; Yaegashi, H.; Sato, Z. “Lupinosis”-like lesions in mice caused by ustiloxin, produced by Ustilaginoieda virens: A morphological study. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Sinha, I.; Calcagnotto, A.; Trushin, N.; Haley, J.S.; Schell, T.D.; Richie, J.P.J. Oral supplementation with liposomal glutathione elevates body stores of glutathione and markers of immune function. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danridge, L.; Greer, B.; Sullivan, S.; Rutebuka, O.; DiVincenti, L.; Wolff, A. Humane endpoints, defined. Lab Anim. 2024, 53, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergnolle, N. Modulation of visceral pain and inflammation by protease-activated receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Manavathu, E.K.; Chandrasekar, P.H. Aspergillus flavus: An emerging non-fumigatus Aspergillus species of significance. Mycoses 2009, 52, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaike, S.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus flavus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloi, T.P.; Ziqubu, K.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Mabaso, N.H.; Ndlovu, Z. Aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity through mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation as central pathological mechanisms: A review of experimental evidence. Toxicology 2024, 509, 153983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, U.; Krishnamurthy, P. Detoxification functions of the liver; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, R.; Hu, J.; He, A. IGF-1 promotes multiple myeloma progression through PI3K/Akt-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Life Sci. 2020, 249, 117503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Hunter, K.; LeVoyer, T.; Roush, J.; Wise, P.; Michielli, R.A.; Shen, F.; Evans, A.A.; London, W.T.; Buetow, K.H. Susceptibility to aflatoxin B1-related primary hepatocellular carcinoma in mice and humans. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4594–4601. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, S.L.; Cai, Q.S.; Wang, J.S.; Hong, J.Y. Efficient activation of aflatoxin B1 by cytochrome P450 2A13, an enzyme predominantly expressed in human respiratory tract. Int. J. Cancer. 2006, 118, 2665–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lootens, O.; De Boevre, M.; Ning, J.; Gasthuys, E.; Van Bocxlaer, J.; De Saeger, S.; Vermeulen, A. Building a human physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for aflatoxin B1 to simulate interactions with drugs. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Armanious, M.; Bedair, R.W.; Amin, N.S.; El, T.H. When less is more: The association between the expression of polymorphic CYPs and AFB1-induced HCC. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 54, e14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vleet, T.R.; Watterson, T.L.; Klein, P.J.; Coulombe, R.J. Aflatoxin B1 alters the expression of p53 in cytochrome P450-expressing human lung cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 89, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieswijk, L.; Claessen, S.M.; Bekers, O.; van Herwijnen, M.; Theunissen, D.H.; Jennen, D.G.; de Kok, T.M.; Kleinjans, J.C.; van Breda, S.G. Aflatoxin B1 induces persistent epigenomic effects in primary human hepatocytes associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Toxicology. 2016, 350, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Kouznetsova, V.L.; Kesari, S.; Tsigelny, I.F. Synergism in actions of HBV with aflatoxin in cancer development. Toxicology 2023, 499, 153652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, N.; Karrow, N.A.; Krumm, C.S.; Qi, D.; Sun, L. Aflatoxin B1 metabolism: Regulation by phase I and II metabolizing enzymes and chemoprotective agents. Mutat. Res. /Rev. Mutat. Res. 2018, 778, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, C.S.; Oberlies, N.H.; Paine, M.F. Mechanisms underlying food–drug interactions: Inhibition of intestinal metabolism and transport. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 136, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, A.J.; Corridon, P.; Ullah, M.; Pfaffenberger, Z.J.; Xu, W.M.; Winfree, S.; Sandoval, R.H.; Hato, T.; Witzmann, F.A.; Mohallem, R.; et al. Sulfotransferase 1c2 increases mitochondrial respiration by converting mitochondrial membrane cholesterol to cholesterol sulfate. Biochemistry 2024, 63, 2310–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettrager, E.J.; Meehan, A.W.; Falany, C.N.; van Waardenburg, R.C.A.M. Sulfotransferase 4A1 activity facilitates sulfate-dependent cellular protection to oxidative stress. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, K.; Murphy, J.I.; Dhoot, G.K. SULF1/SULF2 reactivation during liver damage and tumour growth. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 146, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Packard, E.A.; Levin, M.G.; Judy, R.L.; Damrauer, S.M.; Day, S.M.; Ritchie, M.D.; Rader, D.J. A genome-first approach to rare variants in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy genes MYBPC3 and MYH7 in a medical biobank. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Vander, R.A.; Blair, C.A.; Kao, K.; Bremner, S.B.; Childers, M.C.; Pathak, D.; Heinrich, P.; Lee, D.; Chirikian, O.; et al. Incomplete-penetrant hypertrophic cardiomyopathy MYH7 G256E mutation causes hypercontractility and elevated mitochondrial respiration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2024, 121, e1976554175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.L.; Li, G.S.; Li, D.M.; Tang, D.; Huang, J.Z.; Feng, H.; He, R.Q.; Huang, Z.G.; Dang, Y.W.; Kong, J.L.; et al. The clinical significance of integrin subunit alpha V in cancers: From small cell lung. Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zang, J.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Sun, H.; Yang, L.; Cheng, J.; Wang, R.; Mao, H.; Xu, A.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of the multifaceted role of ITGAV in digestive system cancer progression and immune infiltration. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1480771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liska, D.J. The detoxification enzyme systems. Altern. Med. Rev. 1998, 3, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Hu, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, A.; et al. Time serial transcriptome reveals Cyp2c29 as a key gene in hepatocellular carcinoma development. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Ou, Q.; Shang, J. Expression and prognostic value of SULT1A2 in bladder cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Cui, F.; Sun, W. Towards understanding the biosynthetic pathway for ustilaginoidin mycotoxins in Ustilaginoidea virens. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 2629–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Duan, G.; Liu, L.; Long, Z.; Bai, X.; Ou, M.; Wang, P.; Jiang, D.; Li, D.; Sun, W. UvHOS3 -mediated histone deacetylation is essential for virulence and negatively regulates ustilaginoidin biosynthesis in Ustilaginoidea virens. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 25, e13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Duan, G.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Ou, M.; Bai, X.; Wang, P.; Zhao, D.; Nan, N.; et al. Histone deacetylase UvHST2 is a global regulator of secondary metabolism in Ustilaginoidea virens. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2023, 71, 13124–13136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin a induce a competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network of intestinal immunosuppression by whole-transcriptome analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Long-term polystyrene nanoplastic exposure disrupt hepatic lipid metabolism and cause atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardiff, R.D.; Miller, C.H.; Munn, R.J. Manual hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2014, 2014, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, H.; Yang, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, H. Astragaloside IV attenuate MI-induced myocardial fibrosis and cardiac remodeling by inhibiting ROS/caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. 2022, 21, 2309–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, T.A.; Wolfe, D. Tissue processing and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Methods Mol Biol. 2014, 1180, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Shi, Q.; Xiong, L.; Xin, G.; Yi, T.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, W. Transcriptome profiling of cells exposed to particular and intense electromagnetic radiation emitted by the "sg-iii" prototype laser facility. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, M.; Jia, Z.; Li, E.; Zhao, X.; Li, F.; Lin, R. Similar hepatotoxicity response induced by Rhizoma Paridis in zebrafish larvae, cell and rat. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 250, 112440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Han, Y.; Xiong, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, M. Lifestyle interventions for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A network meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.E.; El-Masry, S.A.; El Shebini, S.M.; Ahmed, N.H.; Mehanna, N.S.; Abdel Wahed, M.M.; Amine, D.; Hashish, A.; Selim, M.; Afify, M.A.S.; et al. Effect of weight loss program using prebiotics and probiotics on body composition, physique, and metabolic products: Longitudinal intervention study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Kaempferol ameliorates Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced neuronal ferroptosis by activating Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat Bioinforma Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Tesolato, S.E.; González-Gamo, D.; Barabash, A.; Claver, P.; de la Serna, S.C.; Domínguez-Serrano, I.; Dziakova, J.; de Juan, C.; Torres, A.J.; Iniesta, P. Expression analysis of hsa-miR-181a-5p, hsa-miR-143-3p, hsa-miR-132-3p and hsa-miR-23a-3p as biomarkers in colorectal Cancer-Relationship to the body mass index. Cancers 2023, 15, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Bai, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Dara, M.Z.N.; Liu, L.; Ou, M.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; et al. Ustilaginoidin D Induces Acute Toxicity and Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Toxins 2025, 17, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050250
Wang B, Bai X, Zhang M, Liu X, Dara MZN, Liu L, Ou M, Li D, Wang J, Liu L, et al. Ustilaginoidin D Induces Acute Toxicity and Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Toxins. 2025; 17(5):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050250
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bo, Xiaolong Bai, Min Zhang, Xiangxiang Liu, Muhammad Zulqar Nain Dara, Lingjing Liu, Mingming Ou, Dayong Li, Jiyang Wang, Ling Liu, and et al. 2025. "Ustilaginoidin D Induces Acute Toxicity and Hepatotoxicity in Mice" Toxins 17, no. 5: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050250
APA StyleWang, B., Bai, X., Zhang, M., Liu, X., Dara, M. Z. N., Liu, L., Ou, M., Li, D., Wang, J., Liu, L., & Sun, W. (2025). Ustilaginoidin D Induces Acute Toxicity and Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Toxins, 17(5), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050250




