Ion Channel-Targeting Toxins: Structural Mechanisms of Activation, Inhibition, and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
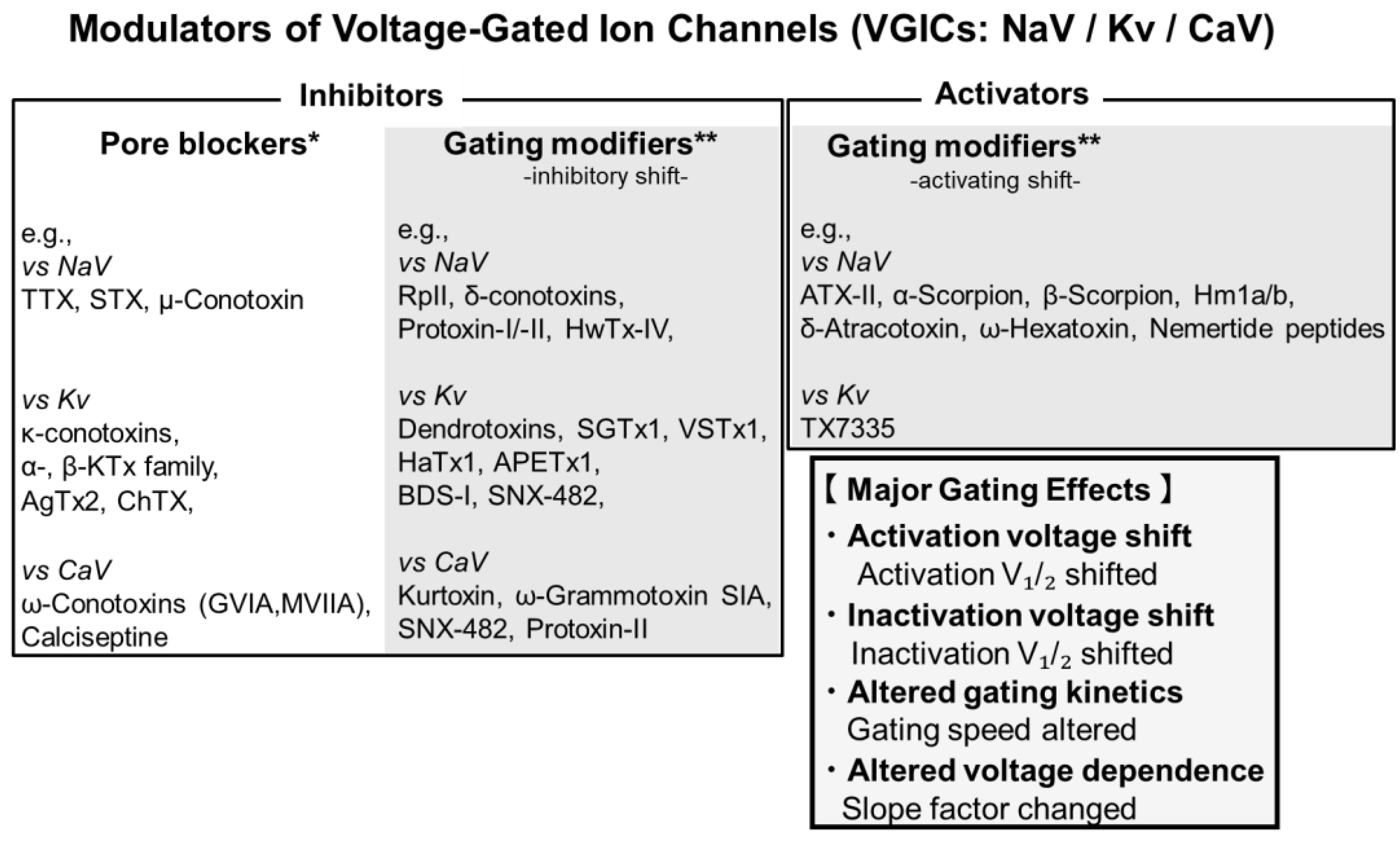
2. Classification of Ion Channel-Interacting Toxins
2.1. Toxins Targeting NaV
2.1.1. Pore-Targeting Inhibition of NaV Channels
2.1.2. Modulators of NaV Channel Gating
2.2. Toxins Targeting Kv
2.2.1. Pore-Targeting Inhibition of Kv
2.2.2. Modulators of Kv Channel Gating
2.3. Toxins Targeting CaV
2.3.1. Pore-Targeting Inhibition of CaV
2.3.2. Modulators of CaV Channel Gating
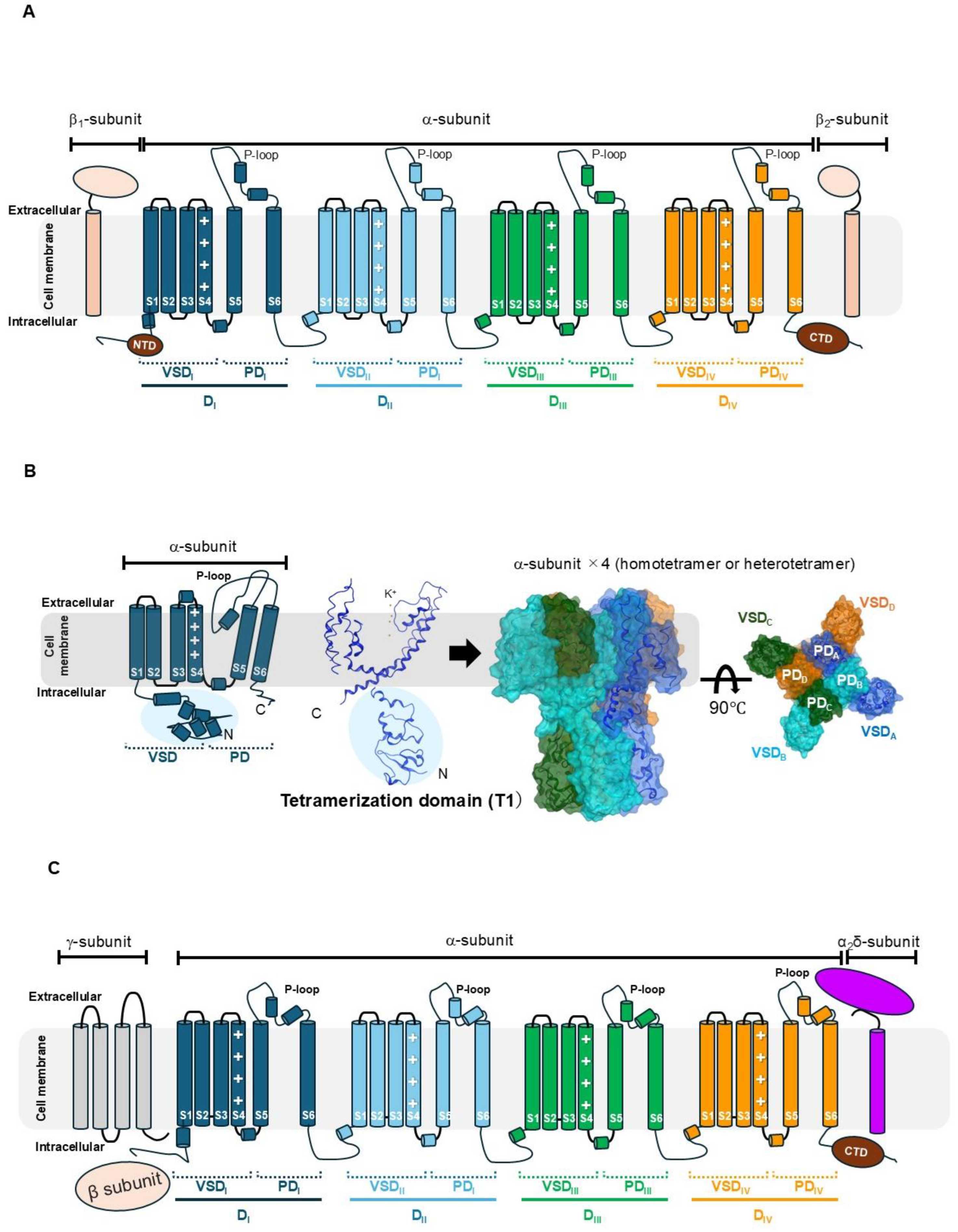
3. Structural Analysis of Toxin and Ion Channel Interactions
3.1. Structural Determinants of NaV–Toxin Interactions
3.1.1. NaV Channel Inhibitors: Pore Blockers and Gating-Modifying Toxins
3.1.2. NaV Channel Activators: Gating-Modifying Peptide Toxins
3.2. Structural Features and Interaction Details of Kv and Toxin
3.2.1. Kv Channel Inhibitors: Pore Blockers and Gating-Modifying Toxins
3.2.2. Kv Channel Activators: Gating-Modifying Peptide Toxins
3.3. Structural Features and Interaction Details of CaV and Toxin
4. Disease-Related Ion Channels and Drug Discovery Based on Toxin Studies
5. Bioengineering and Synthetic Modifications for Improved Pharmacological Properties
5.1. Medical Applications of Chemical Molecule Modulating Ion Channel
5.2. Degenerative Retinal Diseases
6. Therapeutic Strategies for Restoring Vision
6.1. Gene Therapy, Stem Cell Therapy, and Visual Prostheses
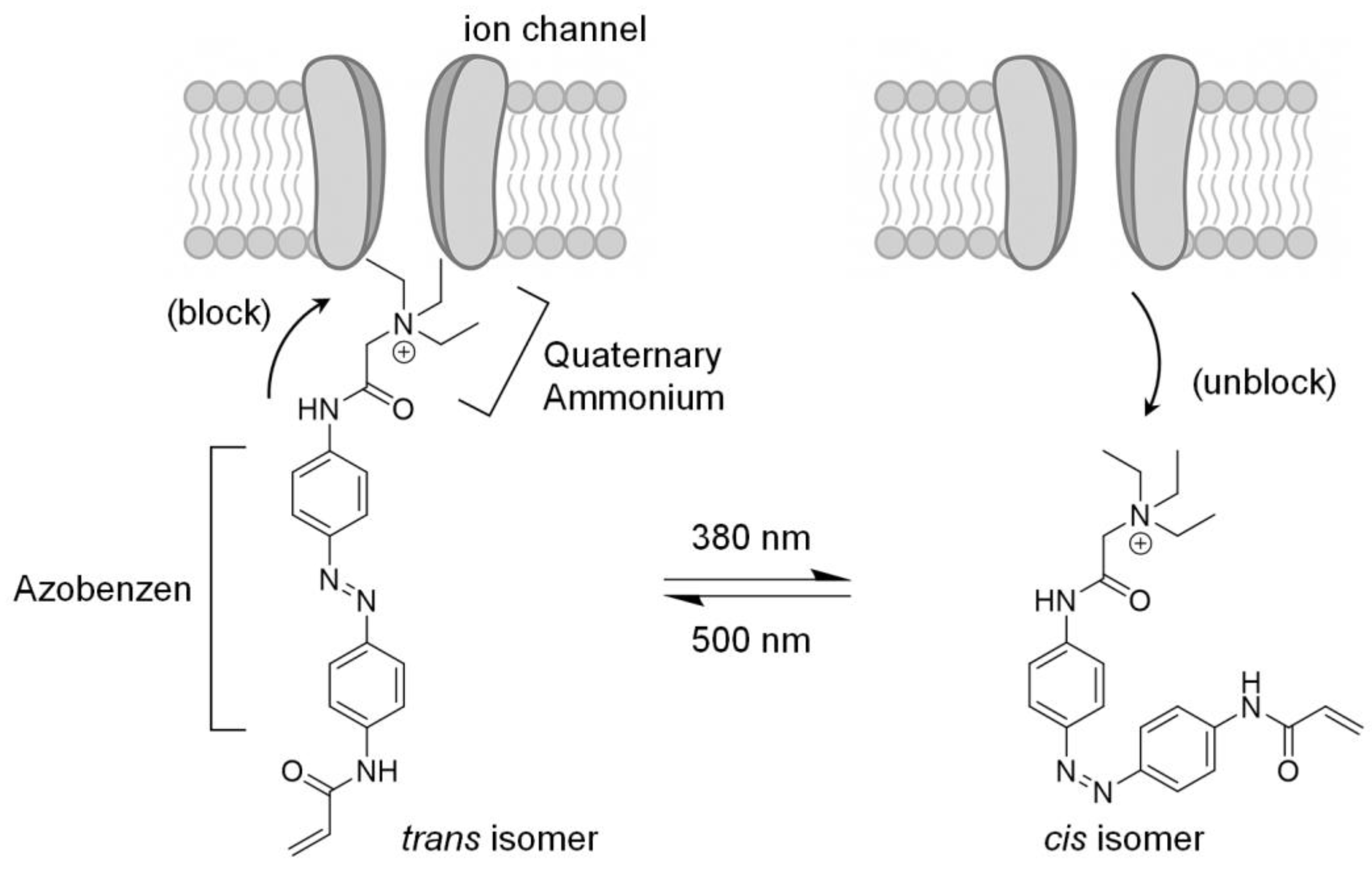
6.2. Photopharmacology Using a Chemical Photoswitch
6.3. Features of Chemical Photoswitches
6.4. First-Generation Chemical Photoswitch
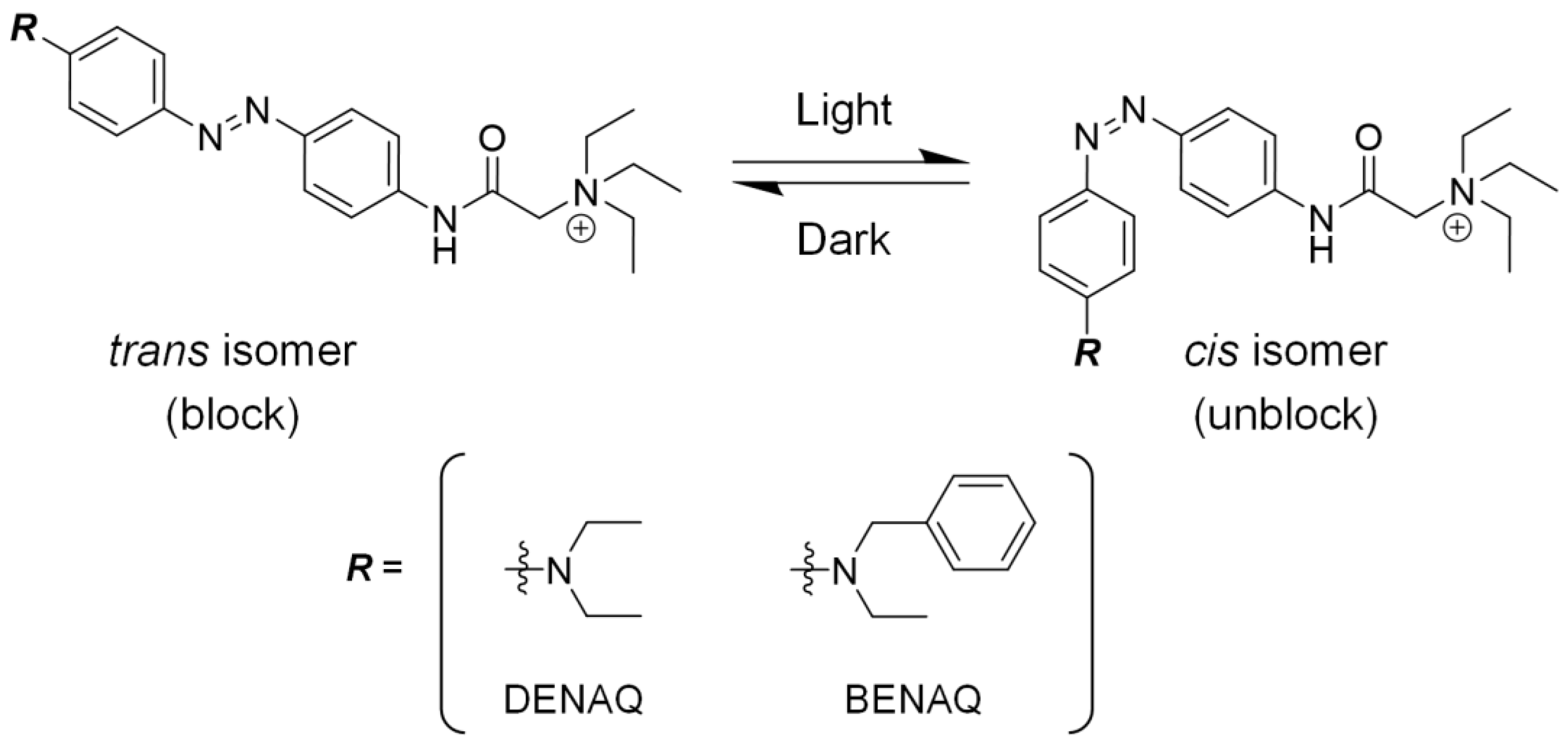
6.5. Second-Generation Chemical Photoswitches
6.6. Acceleration of Drug Development
7. Conclusions and Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VGIC | Voltage-gated ion channels |
| VSD | Voltage-sensing domain |
| NaV | Voltage-gated sodium channel |
| Kv | Voltage-gated potassium channel |
| CaV | Voltage-gated calcium channel |
| TTX | Tetrodotoxin |
| STX | Saxitoxin |
| NaTx | Sea anemone sodium channel toxins |
| ASIC | Acid-sensing ion channel |
| ICK | Inhibitory cystine knot fold |
| KTx | Potassium channel toxins |
| BK | Large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel |
| cryo-EM | Cryo-electron microscopy |
| EMDB | Electron Microscopy Data Bank |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| 3DEM | Three-dimensional electron microscopy |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| hERG | Human ether-à-go-go–related gene (Kv11.1) channel |
| RGC | Retinal ganglion cell |
| RP | Retinitis pigmentosa |
| AMD | Age-related macular degeneration |
| QA | Quaternary ammonium |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| AAQ | Acrylamide azobenzene quaternary ammonium |
| DENAQ | Diethyl aminoazobenzene quaternary ammonium |
| BENAQ | Benzyl ethyl aminoazobenzene quaternary ammonium |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| CSαβ | Cystine-stabilized α/β motif |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| AgTx2 | Agitoxin-2 |
| ChTX | Charybdotoxin |
| ATX-II | Anemonia toxin II |
| HwTx-IV | Huwentoxin-IV |
| ProTx | Protoxin |
| SNX-482 | Spider toxin from Hysterocrates gigas |
| ω-Conotoxin GVIA | Omega-conotoxin GVIA |
| ω-Conotoxin MVIIA | Omega-conotoxin MVIIA (Ziconotide) |
| ω-Conotoxin MVIIC | Omega-conotoxin MVIIC |
| ω-Agatoxin IVA | Omega-agatoxin IVA |
| APETx1 | Anthopleurin-like peptide toxin 1 |
| BDS-I | Blood Depressing Substance I |
| VSTx1 | Voltage-Sensor Toxin 1 |
| HaTx1 | Hanatoxin |
| Hm1 | Tarantula toxin from Heteroscodra maculata |
References
- Felipe, A.; Ferrer-Montiel, A. Membrane Channels in Health and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harraz, O.F.; Delpire, E. Recent Insights into Channelopathies. Physiol. Rev. 2024, 104, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto-Neves, D.; Jaggar, J.H. Physiological Functions and Pathological Involvement of Ion Channel Trafficking in the Vasculature. J. Physiol. 2024, 602, 3275–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuis, J.R.; Mueller, A.; Israel, M.R.; Vetter, I. The Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Activators. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.; Anselmi, C.; Kalia, J.; Jara-Oseguera, A.; Schwieters, C.D.; Krepkiy, D.; Lee, W.C.; Kim, E.-H.; Kim, J.I.; Faraldo-Gómez, J.D.; et al. Structural Insights into the Mechanism of Activation of the TRPV1 Channel by a Membrane-Bound Tarantula Toxin. Elife 2016, 5, e11273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, J.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Smith, J.J.; Chin, Y.K.Y.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Structural Basis for the Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels by Animal Toxins. Science 2018, 362, eaau2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, N.A.; Tabakmakher, V.M.; Yureva, D.A.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Kuzmenkov, A.I. Kalium 3.0 Is a Comprehensive Depository of Natural, Artificial, and Labeled Polypeptides Acting on Potassium Channels. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A.; Cestèle, S.; Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; Yu, F.H.; Konoki, K.; Scheuer, T. Voltage-Gated Ion Channels and Gating Modifier Toxins. Toxicon 2007, 49, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, J.; Milescu, M.; Salvatierra, J.; Wagner, J.; Klint, J.K.; King, G.F.; Olivera, B.M.; Bosmans, F. From Foe to Friend: Using Animal Toxins to Investigate Ion Channel Function. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, H.R. Marine Toxins Targeting Ion Channels. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 37–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariens, E.J. Affinity and Intrinsic Activity in the Theory of Competitive Inhibition. I. Problems and Theory. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1954, 99, 32–49. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, C.J. Ion Channels, Receptors, Agonists and Antagonists. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 21, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, R.P. A Modification of Receptor Theory. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1956, 11, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.W.; Leff, P. Operational Models of Pharmacological Agonism. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1983, 220, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, K.J.; MacKinnon, R. Hanatoxin Modifies the Gating of a Voltage-Dependent K+ Channel through Multiple Binding Sites. Neuron 1997, 18, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li-Smerin, Y.; Swartz, K.J. Gating Modifier Toxins Reveal a Conserved Structural Motif in Voltage-Gated Ca2+ and K+ Channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8585–8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J. Neurotoxins and Their Binding Areas on Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels at 60: Structure, Function and Pathophysiology: Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2577–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Snutch, T.P.; Striessnig, J. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and Structure-Function Relationships of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, J.J.; Tate, S.N.; Nobbs, M.; Romanos, M.A. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels as Therapeutic Targets. Drug Discov. Today 2000, 5, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, E.P.; Lehmann-Horn, F.; Rüdel, R. Overexcited or Inactive: Ion Channels in Muscle Disease. Cell 1995, 80, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, N.W.; Meisler, M.H. Evolution and Diversity of Mammalian Sodium Channel Genes. Genomics 1999, 57, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisler, M.H.; Hill, S.F.; Yu, W. Sodium Channelopathies in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 22, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegazza, M.; Cestèle, S.; Catterall, W.A. Sodium Channelopathies of Skeletal Muscle and Brain. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1633–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lera Ruiz, M.; Kraus, R.L. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Clinical Indications. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7093–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.F. Venoms as a Platform for Human Drugs: Translating Toxins into Therapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaeus, M.J.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Ing, C.; Ramanadane, K.; Pomès, R.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structures of Closed and Open States of a Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3051–E3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, J.; Olivera, B.M.; Bosmans, F. Animal Toxins Influence Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Function. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2014, 221, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yu, J.; Ye, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Lin, H.; Feng, J.; Deng, K. Conotoxins: Classification, Prediction, and Future Directions in Bioinformatics. Toxins 2025, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.A.; Tomaselli, G.F. Using the Deadly Mu-Conotoxins as Probes of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Toxicon 2004, 44, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.R.; Bulaj, G.; Norton, R.S. Structure and Function of μ-Conotoxins, Peptide-Based Sodium Channel Blockers with Analgesic Activity. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1677–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Yoshikami, D.; Azam, L.; Gajewiak, J.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G.; Zhang, M.-M. μ-Conotoxins That Differentially Block Sodium Channels NaV1.1 through 1.8 Identify Those Responsible for Action Potentials in Sciatic Nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10302–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monastyrnaya, M.M.; Kalina, R.S.; Kozlovskaya, E.P. The Sea Anemone Neurotoxins Modulating Sodium Channels: An Insight at Structure and Functional Activity after Four Decades of Investigation. Toxins 2022, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madio, B.; King, G.F.; Undheim, E.A.B. Sea Anemone Toxins: A Structural Overview. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.E.; Adnet, P.J.; Reyford, H.; Wieland, S.J.; Stewart, S.L.; Rosenberg, H. ATX II, a Sodium Channel Toxin, Sensitizes Skeletal Muscle to Halothane, Caffeine, and Ryanodine. Anesthesiology 1999, 90, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.-Y.; Cheng, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-A.; Chen, Y.-J. ATX-II-Induced Pulmonary Vein Arrhythmogenesis Related to Atrial Fibrillation and Long QT Syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cestèle, S.; Qu, Y.; Rogers, J.C.; Rochat, H.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A. Voltage Sensor-Trapping: Enhanced Activation of Sodium Channels by Beta-Scorpion Toxin Bound to the S3-S4 Loop in Domain II. Neuron 1998, 21, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.V.; Coronas, F.I.V.; Beirão, P.S.L. Voltage-Dependent Displacement of the Scorpion Toxin Ts3 from Sodium Channels and Its Implication on the Control of Inactivation: Scorpion Toxin and Sodium Channel Inactivation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jover, E.; Martin-Moutot, N.; Couraud, F.; Rochat, H. Scorpion Toxin: Specific Binding to Rat Synaptosomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1978, 85, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor, F.J.; Catterall, W.A. Site of Covalent Attachment of Alpha-Scorpion Toxin Derivatives in Domain I of the Sodium Channel Alpha Subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8742–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.C.; Qu, Y.; Tanada, T.N.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A. Molecular Determinants of High Affinity Binding of Alpha-Scorpion Toxin and Sea Anemone Toxin in the S3-S4 Extracellular Loop in Domain IV of the Na+ Channel Alpha Subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 15950–15962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leipold, E.; Hansel, A.; Borges, A.; Heinemann, S.H. Subtype Specificity of Scorpion Beta-Toxin Tz1 Interaction with Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels Is Determined by the Pore Loop of Domain 3. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klint, J.K.; Senff, S.; Rupasinghe, D.B.; Er, S.Y.; Herzig, V.; Nicholson, G.M.; King, G.F. Spider-Venom Peptides That Target Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Pharmacological Tools and Potential Therapeutic Leads. Toxicon 2012, 60, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosmans, F.; Swartz, K.J. Targeting Voltage Sensors in Sodium Channels with Spider Toxins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.C.; Lewis, R.J. Structure-Function and Therapeutic Potential of Spider Venom-Derived Cysteine Knot Peptides Targeting Sodium Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.-C.; Sun, F.-D.; Zhang, L.; Huang, B.; An, H.-L.; Rong, M.-Q.; Du, C.-W. General Mechanism of Spider Toxin Family I Acting on Sodium Channel Nav1.7. Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, G.M.; Walsh, R.; Little, M.J.; Tyler, M.I. Characterisation of the Effects of Robustoxin, the Lethal Neurotoxin from the Sydney Funnel-Web Spider Atrax Robustus, on Sodium Channel Activation and Inactivation. Pflugers Arch. 1998, 436, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alewood, D.; Birinyi-Strachan, L.C.; Pallaghy, P.K.; Norton, R.S.; Nicholson, G.M.; Alewood, P.F. Synthesis and Characterization of Delta-Atracotoxin-Ar1a, the Lethal Neurotoxin from Venom of the Sydney Funnel-Web Spider (Atrax Robustus). Biochemistry 2003, 42, 12933–12940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, W. Sodium Channel Inactivation: Molecular Determinants and Modulation. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 1271–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.Y.; Chin, Y.K.Y.; Ma, L.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Herzig, V.; King, G.F. A Selective NaV1.1 Activator with Potential for Treatment of Dravet Syndrome Epilepsy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 113991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, R.E.; Warren, V.A.; Kraus, R.L.; Hwang, J.C.; Liu, C.J.; Dai, G.; Brochu, R.M.; Kohler, M.G.; Gao, Y.-D.; Garsky, V.M.; et al. Two Tarantula Peptides Inhibit Activation of Multiple Sodium Channels. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 14734–14747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, L.; Montnach, J.; Oliveira-Mendes, B.; Khakh, K.; Thomas, B.; Lin, S.; Caumes, C.; Wesolowski, S.; Nicolas, S.; Servent, D.; et al. Synthetic Analogues of Huwentoxin-IV Spider Peptide with Altered Human NaV1.7/NaV1.6 Selectivity Ratios. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 798588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsson, E.; Andersson, H.S.; Strand, M.; Peigneur, S.; Eriksson, C.; Lodén, H.; Shariatgorji, M.; Andrén, P.E.; Lebbe, E.K.M.; Rosengren, K.J.; et al. Peptide Ion Channel Toxins from the Bootlace Worm, the Longest Animal on Earth. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsson, E.; Peigneur, S.; Andersson, H.S.; Laborde, Q.; Strand, M.; Tytgat, J.; Göransson, U. Functional Characterization of the Nemertide α Family of Peptide Toxins. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, N.M.; Weckhuysen, S.; Gorman, K.; King, M.D.; Lerche, H. Genetic Potassium Channel-Associated Epilepsies: Clinical Review of the Kv Family. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 24, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, J. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels and Genetic Epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1466075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, I.E.; Pajak, R.Z.; Harte, M.K.; Glazier, J.D.; Hager, R. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels as a Potential Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1449151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finol-Urdaneta, R.K.; Belovanovic, A.; Micic-Vicovac, M.; Kinsella, G.K.; McArthur, J.R.; Al-Sabi, A. Marine Toxins Targeting Kv1 Channels: Pharmacological Tools and Therapeutic Scaffolds. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, R.S.; Chandy, K.G. Venom-Derived Peptide Inhibitors of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouhat, S.; Andreotti, N.; Jouirou, B.; Sabatier, J.-M. Animal Toxins Acting on Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2503–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, H.; Castle, N.A.; Pardo, L.A. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels as Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 982–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, K.J.; Stocker, M.; Terlau, H.; Stühmer, W.; Jacobsen, R.; Walker, C.; Grilley, M.; Watkins, M.; Hillyard, D.R.; Gray, W.R.; et al. Kappa-Conotoxin PVIIA Is a Peptide Inhibiting the Shaker K+ Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, D.; Díaz-Franulic, I. Binding of κ-Conotoxin-PVIIA to Open and Closed Shaker K-Channels Are Differentially Affected by the Ionic Strength. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, L.C.; Viana, G.M.M.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Beraldo-Neto, E. Scorpion Peptides and Ion Channels: An Insightful Review of Mechanisms and Drug Development. Toxins 2023, 15, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerni, F.A.; Pucca, M.B.; Peigneur, S.; Cremonez, C.M.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Electrophysiological Characterization of Ts6 and Ts7, K+ Channel Toxins Isolated through an Improved Tityus Serrulatus Venom Purification Procedure. Toxins 2014, 6, 892–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, I.S.; Alano-da-Silva, N.M.; Ferreira, I.G.; Cerni, F.A.; Sachett, J.d.A.G.; Monteiro, W.M.; Pucca, M.B.; Arantes, E.C. Understanding the Complexity of Tityus Serrulatus Venom: A Focus on High Molecular Weight Components. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 30, e20230046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucca, M.B.; Bertolini, T.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Bonato, V.L.; Arantes, E.C. Immunosuppressive Evidence of Tityus Serrulatus Toxins Ts6 and Ts15: Insights of a Novel K(+) Channel Pattern in T Cells. Immunology 2016, 147, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.L.; Garcia-Calvo, M.; Hidalgo, P.; Lee, A.; MacKinnon, R. Purification and Characterization of Three Inhibitors of Voltage-Dependent K+ Channels from Leiurus Quinquestriatus Var. Hebraeus Venom. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 6834–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.A.L.; Roux, B. Modeling the Structure of Agitoxin in Complex with the Shaker K+ Channel: A Computational Approach Based on Experimental Distance Restraints Extracted from Thermodynamic Mutant Cycles. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 2595–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, R. Determination of the Subunit Stoichiometry of a Voltage-Activated Potassium Channel. Nature 1991, 350, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.S.; Miller, C. Interaction of Charybdotoxin with Permeant Ions inside the Pore of a K+ Channel. Neuron 1992, 9, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Chung, S.-H. Structural Basis of the Selective Block of Kv1.2 by Maurotoxin from Computer Simulations. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, E.; Sabatier, J.M.; Kharrat, R.; Meunier, S.; El Ayeb, M.; Van Rietschoten, J.; Darbon, H. Solution Structure of Maurotoxin, a Scorpion Toxin from Scorpio Maurus, with High Affinity for Voltage-gated Potassium Channels. Proteins 1997, 29, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benishin, C.G.; Sorensen, R.G.; Brown, W.E.; Krueger, B.K.; Blaustein, M.P. Four Polypeptide Components of Green Mamba Venom Selectively Block Certain Potassium Channels in Rat Brain Synaptosomes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 34, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L. Twenty Years of Dendrotoxins. Toxicon 2001, 39, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imredy, J.P.; MacKinnon, R. Energetic and Structural Interactions between Delta-Dendrotoxin and a Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 296, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruta, V.; Jiang, Y.; Lee, A.; Chen, J.; MacKinnon, R. Functional Analysis of an Archaebacterial Voltage-Dependent K+ Channel. Nature 2003, 422, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, L.R.; Milescu, M.; Li-Smerin, Y.; Mindell, J.A.; Kim, J.I.; Swartz, K.J. Voltage-Sensor Activation with a Tarantula Toxin as Cargo. Nature 2005, 436, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Kim, S.; Roh, S.H.; Endoh, H.; Kodera, Y.; Maeda, T.; Kohno, T.; Wang, J.M.; Swartz, K.J.; Kim, J.I. Solution Structure and Functional Characterization of SGTx1, a Modifier of Kv2.1 Channel Gating. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Eu, Y.-J.; Shin, S.Y.; Milescu, M.; Swartz, K.J.; Kim, J.I. Solution Structure and Lipid Membrane Partitioning of VSTx1, an Inhibitor of the KvAP Potassium Channel. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 6015–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; MacKinnon, R. Voltage-Dependent K+ Channel Gating and Voltage Sensor Toxin Sensitivity Depend on the Mechanical State of the Lipid Membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19276–19281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimm, T.; Bean, B.P. Inhibition of A-Type Potassium Current by the Peptide Toxin SNX-482. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 9182–9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diochot, S.; Loret, E.; Bruhn, T.; Béress, L.; Lazdunski, M. APETx1, a New Toxin from the Sea Anemone Anthopleura Elegantissima, Blocks Voltage-Gated Human Ether-a-Go-Go-Related Gene Potassium Channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Tseng, G.-N. Gating Charges in the Activation and Inactivation Processes of the HERG Channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 2004, 124, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagot, B.; Diochot, S.; Pimentel, C.; Lazdunski, M.; Darbon, H. Solution Structure of APETx1 from the Sea Anemone Anthopleura Elegantissima: A New Fold for an HERG Toxin. Proteins 2005, 59, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Shimomura, T.; Kubo, Y.; Oka, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Imai, S.; Yanase, N.; Akimoto, M.; Fukuda, M.; Yokogawa, M.; et al. Mechanism of HERG Inhibition by Gating-Modifier Toxin, APETx1, Deduced by Functional Characterization. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diochot, S.; Schweitz, H.; Béress, L.; Lazdunski, M. Sea Anemone Peptides with a Specific Blocking Activity against the Fast Inactivating Potassium Channel Kv3.4. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 6744–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, S.Y.M.; Thompson, D.; Wang, Z.; Fedida, D.; Robertson, B. Modulation of Kv3 Subfamily Potassium Currents by the Sea Anemone Toxin BDS: Significance for CNS and Biophysical Studies. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8735–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Torres, I.O.; Jin, T.B.; Cadene, M.; Chait, B.T.; Poget, S.F. Discovery and Characterisation of a Novel Toxin from Dendroaspis Angusticeps, Named Tx7335, That Activates the Potassium Channel KcsA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbig, K.L.; Lauerer, R.J.; Bahr, J.C.; Souza, I.A.; Myers, C.T.; Uysal, B.; Schwarz, N.; Gandini, M.A.; Huang, S.; Keren, B.; et al. De Novo Pathogenic Variants in CACNA1E Cause Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy with Contractures, Macrocephaly, and Dyskinesias. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophoff, R.A.; Terwindt, G.M.; Vergouwe, M.N.; van Eijk, R.; Oefner, P.J.; Hoffman, S.M.; Lamerdin, J.E.; Mohrenweiser, H.W.; Bulman, D.E.; Ferrari, M.; et al. Familial Hemiplegic Migraine and Episodic Ataxia Type-2 Are Caused by Mutations in the Ca2+ Channel Gene CACNL1A4. Cell 1996, 87, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Splawski, I.; Timothy, K.W.; Decher, N.; Kumar, P.; Sachse, F.B.; Beggs, A.H.; Sanguinetti, M.C.; Keating, M.T. Severe Arrhythmia Disorder Caused by Cardiac L-Type Calcium Channel Mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8089–8096, discussion 8086-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y. Current Updates on Arrhythmia within Timothy Syndrome: Genetics, Mechanisms and Therapeutics. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2023, 25, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M.; Miljanich, G.P.; Ramachandran, J.; Adams, M.E. Calcium Channel Diversity and Neurotransmitter Release: The Omega-Conotoxins and Omega-Agatoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994, 63, 823–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljanich, G.P. Ziconotide: Neuronal Calcium Channel Blocker for Treating Severe Chronic Pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro-Junior, E.L.; Kalina, R.; Gladkikh, I.; Leychenko, E.; Tytgat, J.; Peigneur, S. A Tale of Toxin Promiscuity: The Versatile Pharmacological Effects of Hcr 1b-2 Sea Anemone Peptide on Voltage-Gated Ion Channels. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferron, L.; Zamponi, G.W. A Tale of Two Calcium Channels: Structural Pharmacology of Cav2.1 and Cav3.2. Cell Res. 2024, 34, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Bae, C.; Lee, J.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, H.H.; Kohno, T.; Swartz, K.J.; Kim, J.I. Solution Structure of Kurtoxin: A Gating Modifier Selective for Cav3 Voltage-Gated Ca(2+) Channels. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1862–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidach, S.S.; Mintz, I.M. Kurtoxin, a Gating Modifier of Neuronal High- and Low-Threshold ca Channels. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2023–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, R.S.; Jaffe, H.; Cribbs, L.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Swartz, K.J. Inhibition of T-Type Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels by a New Scorpion Toxin. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, R.A.; Defeo, P.A.; Davison, M.D.; Young, J.; Herman, J.L.; Spreen, R.C.; Horn, M.B.; Mangano, T.J.; Keith, R.A. Isolation and Pharmacological Characterization of Omega-Grammotoxin SIA, a Novel Peptide Inhibitor of Neuronal Voltage-Sensitive Calcium Channel Responses. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 44, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, S.I.; Lampe, R.A.; Keith, R.A.; Bean, B.P. Voltage-Dependent Inhibition of N- and P-Type Calcium Channels by the Peptide Toxin Omega-Grammotoxin-SIA. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, K.; Park, E.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Takahashi, H.; Swartz, K.; Shimada, I. Solution Structure of Omega-Grammotoxin SIA, a Gating Modifier of P/Q and N-Type Ca(2+) Channel. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 321, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourinet, E.; Stotz, S.C.; Spaetgens, R.L.; Dayanithi, G.; Lemos, J.; Nargeot, J.; Zamponi, G.W. Interaction of SNX482 with Domains III and IV Inhibits Activation Gating of Alpha(1E) (Ca(V)2.3) Calcium Channels. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomb, R.; Szoke, B.; Palma, A.; Wang, G.; Chen, X.-h.; Hopkins, W.; Cong, R.; Miller, J.; Urge, L.; Tarczy-Hornoch, K.; et al. Selective Peptide Antagonist of the Class E Calcium Channel from the Venom of the Tarantula Hysterocrates Gigas. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 15353–15362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, B.T.; Blumenthal, K.M.; Smith, J.J.; Warren, V.A.; Smith, M.M. ProTx-I and ProTx-II: Gating Modifiers of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Toxicon 2007, 49, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalhofer, W.A.; Calhoun, J.; Burrows, R.; Bailey, T.; Kohler, M.G.; Weinglass, A.B.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; Garcia, M.L.; Koltzenburg, M.; Priest, B.T. ProTx-II, a Selective Inhibitor of NaV1.7 Sodium Channels, Blocks Action Potential Propagation in Nociceptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bladen, C.; Hamid, J.; Souza, I.A.; Zamponi, G.W. Block of T-Type Calcium Channels by Protoxins I and II. Mol. Brain 2014, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgerton, G.B.; Blumenthal, K.M.; Hanck, D.A. Evidence for Multiple Effects of ProTxII on Activation Gating in Na(V)1.5. Toxicon 2008, 52, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Liu, D.; Wu, K.; Lei, J.; Yan, N. Structures of Human Nav1.7 Channel in Complex with Auxiliary Subunits and Animal Toxins. Science 2019, 363, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payandeh, J.; Scheuer, T.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. The Crystal Structure of a Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel. Nature 2011, 475, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Yan, N. Structure of a Eukaryotic Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel at near-Atomic Resolution. Science 2017, 355, eaal4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, D.A.; Morais Cabral, J.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Kuo, A.; Gulbis, J.M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; MacKinnon, R. The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K+ Conduction and Selectivity. Science 1998, 280, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, Z.; Li, Z.; Yan, C.; Lu, S.; Dong, M.; Yan, N. Structure of the Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel Cav1.1 Complex. Science 2015, 350, aad2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, T.; Rohou, A.; Arthur, C.P.; Tzakoniati, F.; Wong, E.; Estevez, A.; Kugel, C.; Franke, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Structural Basis of Nav1.7 Inhibition by a Gating-Modifier Spider Toxin. Cell 2019, 176, 1238–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; MacKinnon, R. Structural Basis of Human KCNQ1 Modulation and Gating. Cell 2020, 180, 340–347.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, G.; Peng, W.; Shen, H.; Lei, J.; Yan, N. Structure of the Nav1.4-Β1 Complex from Electric Eel. Cell 2017, 170, 470–482.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, H.; Wu, K.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Lei, J.; et al. Structure of the Human Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Nav1.4 in Complex with Β1. Science 2018, 362, eaau2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Z. Structural Advances in Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 908867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Shi, H.; Tonggu, L.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Lenaeus, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Yoshioka, C.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structure of the Cardiac Sodium Channel. Cell 2020, 180, 122–134.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Pan, X.; Shen, H.; Yan, N. High-Resolution Structures of Human Nav1.7 Reveal Gating Modulation through α-π Helical Transition of S6IV. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Huang, J.; Jin, X.; Yan, N. Cryo-EM Structure of Human Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Nav1.6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2220578120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, B.; McCarthy, S.; Gonen, S. Structural Basis of Inhibition of Human NaV1.8 by the Tarantula Venom Peptide Protoxin-I. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisedchaisri, G.; Tonggu, L.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; McCord, E.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structural Basis for High-Affinity Trapping of the NaV1.7 Channel in Its Resting State by Tarantula Toxin. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 38–48.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, S.; Kuyucak, S. Molecular Dynamics Study of Binding of Μ-Conotoxin GIIIA to the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Na(v)1.4. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, T.R.; Aglieco, F.; Dib-Hajj, S.D. Critical Molecular Determinants of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Sensitivity to Mu-Conotoxins GIIIA/B. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, C.Y.; Chin, Y.K.-Y.; Walker, A.A.; Guo, S.; Blomster, L.V.; Ward, M.J.; Herzig, V.; Rokyta, D.R.; King, G.F. Venom Peptides with Dual Modulatory Activity on the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel NaV1.1 Provide Novel Leads for Development of Antiepileptic Drugs. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Huang, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, K.; Jin, X.; Huang, G.; Li, J.; Pan, X.; Yan, N. Structural Mapping of Nav1.7 Antagonists. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Molecular Properties of Voltage-Sensitive Sodium Channels. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1986, 55, 953–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Zou, X.; Cao, Z. Selective Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Peptide Toxins from Animal Venom: Pharmacological Probes and Analgesic Drug Development. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botte, M.; Huber, S.; Bucher, D.; Klint, J.K.; Rodríguez, D.; Tagmose, L.; Chami, M.; Cheng, R.; Hennig, M.; Abdul Rahman, W. Apo and Ligand-Bound High Resolution Cryo-EM Structures of the Human Kv3.1 Channel Reveal a Novel Binding Site for Positive Modulators. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, Y.P.; Morera, F.J.; Carvacho, I.; Latorre, R. A Marriage of Convenience: Beta-Subunits and Voltage-Dependent K+ Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24485–24489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lee, A.; Chen, J.; Ruta, V.; Cadene, M.; Chait, B.T.; MacKinnon, R. X-Ray Structure of a Voltage-Dependent K+ Channel. Nature 2003, 423, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.B.; Campbell, E.B.; Mackinnon, R. Crystal Structure of a Mammalian Voltage-Dependent Shaker Family K+ Channel. Science 2005, 309, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Theemsche, K.M.; Van de Sande, D.V.; Snyders, D.J.; Labro, A.J. Hydrophobic Drug/Toxin Binding Sites in Voltage-Dependent K+ and Na+ Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumino, A.; Sumikama, T.; Uchihashi, T.; Oiki, S. High-Speed AFM Reveals Accelerated Binding of Agitoxin-2 to a K+ Channel by Induced Fit. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax0495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Bian, S.; Rivetta, A.; Allen, K.; Sigworth, F.J. CryoEM Structures of Kv1.2 Potassium Channels, Conducting and Non-Conducting. eLife 2025, 12, RP89459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, S.; Cui, X.; Xu, H.; Qiu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, B.; Peng, C.; Liu, S.; et al. Molecular Insights into the Gating Mechanisms of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel CaV2.3. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage Gated Sodium and Calcium Channels: Discovery, Structure, Function, and Pharmacology. Channels 2023, 17, 2281714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichida, S.; Abe, J.; Yu-an, Z.; Minami, T.; Wada, T.; Yazawa, M.; Sohma, H. Structural Specificity for the Inhibitory Effect of Calmodulin on Specific 125I-Omega-Conotoxin GVIA Binding. Neurochem. Res. 2003, 28, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Gao, S.; Yan, N. Structural Biology of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. Channels 2023, 18, 2290807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Garcia, M.L. Therapeutic Potential of Venom Peptides. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Yao, X.; Yan, N. Structure of Human Cav2.2 Channel Blocked by the Painkiller Ziconotide. Nature 2021, 596, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmrich, V.; Gross, G. P/Q-Type Calcium Channel Modulators: P/Q-Type Calcium Channel Blockers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 741–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cong, Y.; Wu, T.; Wang, T.; Lou, X.; Yang, X.; Yan, N. Structural Basis for Different ω-Agatoxin IVA Sensitivities of the P-Type and Q-Type Cav2.1 Channels. Cell Res. 2024, 34, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yao, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, G.; Fan, X.; Xue, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Structural Basis for Human Cav1.2 Inhibition by Multiple Drugs and the Neurotoxin Calciseptine. Cell 2023, 186, 5363–5374.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGivern, J.G. Ziconotide: A Review of Its Pharmacology and Use in the Treatment of Pain. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, N.; Uta, D.; Ohashi, M.; Hoshino, R.; Baba, H. Omega-Conotoxin MVIIA Reduces Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibiting N-Type Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channels on Spinal Dorsal Horn. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1366829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarcha, E.J.; Olsen, C.M.; Probst, P.; Peckham, D.; Muñoz-Elías, E.J.; Kruger, J.G.; Iadonato, S.P. Safety and Pharmacodynamics of Dalazatide, a Kv1.3 Channel Inhibitor, in the Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis: A Randomized Phase 1b Trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yu, L.; Ji, Y.; Tao, J. Kv1.3 Channel as a Key Therapeutic Target for Neuroinflammatory Diseases: State of the Art and Beyond. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, R.; Kubeil, M.; Zarschler, K.; Chhabra, S.; Tajhya, R.B.; Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.W.; Bachmann, M.; Norton, R.S.; Stephan, H. Distribution and Kinetics of the Kv1.3-Blocking Peptide HsTX1[R14A] in Experimental Rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.H.; Huq, R.; Tanner, M.R.; Chhabra, S.; Khoo, K.K.; Estrada, R.; Dhawan, V.; Chauhan, S.; Pennington, M.W.; Beeton, C.; et al. A Potent and Kv1.3-Selective Analogue of the Scorpion Toxin HsTX1 as a Potential Therapeutic for Autoimmune Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigneur, S.; Orts, D.; Prieto da Silva, A.; Oguiura, N.; Boni-Mitake, M.; Brandt de Oliveira, E.; Zaharenko, A.J.; de Freitas, J.C.; Tytgat, J. 13. Crotamine Pharmacology Revisited: Novel Insights Based on the Inhibition of Kv Channels. Toxicon 2012, 60, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Back, S.K.; Choi, H.-W.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, H.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Suh, H.-W.; Na, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Analgesic Effect of Highly Reversible ω-Conotoxin FVIA on N Type Ca2+ Channels. Mol. Pain 2010, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeton, C.; Wulff, H.; Barbaria, J.; Clot-Faybesse, O.; Pennington, M.; Bernard, D.; Cahalan, M.D.; Chandy, K.G.; Béraud, E. Selective Blockade of T Lymphocyte K(+) Channels Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis, a Model for Multiple Sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13942–13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weuring, W.J.; Singh, S.; Volkers, L.; Rook, M.B.; van ’t Slot, R.H.; Bosma, M.; Inserra, M.; Vetter, I.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; Braun, K.P.J.; et al. NaV1.1 and NaV1.6 Selective Compounds Reduce the Behavior Phenotype and Epileptiform Activity in a Novel Zebrafish Model for Dravet Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0219106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.L.; Milligan, C.J.; Richardson, R.J.; Jancovski, N.; Grunnet, M.; Jacobson, L.H.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Mobli, M.; Chow, C.Y.; Herzig, V.; et al. Selective NaV1.1 Activation Rescues Dravet Syndrome Mice from Seizures and Premature Death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8077–E8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Di Iorio, E.; Barbaro, V.; Ponzin, D.; Sorrentino, F.S.; Parmeggiani, F. Retinitis Pigmentosa: Genes and Disease Mechanisms. Curr. Genomics 2011, 12, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, K.L.; DeAngelis, M.M. Epidemiology of Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Associations with Cardiovascular Disease Phenotypes and Lipid Factors. Eye Vis. 2016, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochitsky, I.; Kienzler, M.A.; Isacoff, E.; Kramer, R.H. Restoring Vision to the Blind with Chemical Photoswitches. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 10748–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drivas, T.G.; Bennett, J. The Bionic Retina: A Small Molecule with Big Potential for Visual Restoration. Neuron 2012, 75, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busskamp, V.; Picaud, S.; Sahel, J.A.; Roska, B. Optogenetic Therapy for Retinitis Pigmentosa. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Viswanathan, S.; Brodie, S.E.; Deng, W.-T.; Coleman, K.E.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Nirenberg, S. A Clinically Viable Approach to Restoring Visual Function Using Optogenetic Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 29, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, J.M.; da Cruz, L. A Review and Update on the Current Status of Stem Cell Therapy and the Retina. Br. Med. Bull. 2012, 102, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Chader, G.J.; Falabella, P.; Stefanini, F.; Rowland, T.; Clegg, D.O.; Kashani, A.H.; Hinton, D.R.; et al. Stem Cell Based Therapies for Age-Related Macular Degeneration: The Promises and the Challenges. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 48, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz, L.; Fynes, K.; Georgiadis, O.; Kerby, J.; Luo, Y.H.; Ahmado, A.; Vernon, A.; Daniels, J.T.; Nommiste, B.; Hasan, S.M.; et al. Phase 1 Clinical Study of an Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium Patch in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.A.; Drew-Bear, L.E.; Vega-Garces, M.; Betancourt-Belandria, H.; Arevalo, J.F. An Update on Visual Prosthesis. Int. J. Retina Vitreous 2023, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikado, T.; Kamei, M.; Sakaguchi, H.; Kanda, H.; Endo, T.; Hirota, M.; Morimoto, T.; Nishida, K.; Kishima, H.; Terasawa, Y.; et al. One-Year Outcome of 49-Channel Suprachoroidal-Transretinal Stimulation Prosthesis in Patients with Advanced Retinitis Pigmentosa. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 6147–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasawa, Y.; Tashiro, H.; Nakano, Y.; Ohta, J. Safety and Efficacy of Semichronic Suprachoroidal Transretinal Stimulation with Femtosecond Laser-Induced Porosity and Smooth-Surface Electrodes. Sens. Mater. 2018, 30, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, H.; Kuwabara, M.; Nakano, Y.; Terasawa, Y.; Osawa, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Doi, H.; Ohta, J. In Vitro and in Vivo Long-Term Electrochemical Properties of Electrodes with Femtosecond-Laser-Induced Porosity for Visual Prostheses Based on Suprachoroidal Transretinal Stimulation. Sens. Mater. 2018, 30, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Tashiro, H.; Terasawa, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Haruta, M.; Sasagawa, K.; Takehara, H.; Morimoto, T.; Fujikado, T.; Ohta, J. Effects of Long-Term in Vivo Stimulation on the Electrochemical Properties of a Porous Stimulation Electrode for a Suprachoroidal–Transretinal Stimulation (STS) Retinal Prosthesis. Sens. Mater. 2023, 35, 3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochitsky, I.; Kramer, R.H. Optopharmacological Tools for Restoring Visual Function in Degenerative Retinal Diseases. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 34, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochitsky, I.; Helft, Z.; Meseguer, V.; Fletcher, R.B.; Vessey, K.A.; Telias, M.; Denlinger, B.; Malis, J.; Fletcher, E.L.; Kramer, R.H. How Azobenzene Photoswitches Restore Visual Responses to the Blind Retina. Neuron 2016, 92, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, D.L.; Banghart, M.R.; Dunn, T.W.; Borges, K.; Wagenaar, D.A.; Gaudry, Q.; Karakossian, M.H.; Otis, T.S.; Kristan, W.B.; Trauner, D.; et al. Photochemical Control of Endogenous Ion Channels and Cellular Excitability. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourot, A.; Tochitsky, I.; Kramer, R.H. Light at the End of the Channel: Optical Manipulation of Intrinsic Neuronal Excitability with Chemical Photoswitches. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.W.; Rasband, M.N.; Meseguer, V.; Kramer, R.H.; Golding, N.L. Serotonin Modulates Spike Probability in the Axon Initial Segment through HCN Channels. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourot, A.; Kienzler, M.A.; Banghart, M.R.; Fehrentz, T.; Huber, F.M.E.; Stein, M.; Kramer, R.H.; Trauner, D. Tuning Photochromic Ion Channel Blockers. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochitsky, I.; Polosukhina, A.; Degtyar, V.E.; Gallerani, N.; Smith, C.M.; Friedman, A.; Van Gelder, R.N.; Trauner, D.; Kaufer, D.; Kramer, R.H. Restoring Visual Function to Blind Mice with a Photoswitch That Exploits Electrophysiological Remodeling of Retinal Ganglion Cells. Neuron 2014, 81, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochitsky, I.; Trautman, J.; Gallerani, N.; Malis, J.G.; Kramer, R.H. Restoring Visual Function to the Blind Retina with a Potent, Safe and Long-Lasting Photoswitch. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, R.J.; Daniels, E.; Barras, C.; Dwyer, A.; Strem, B.; Wykoff, C.C.; Van Gelder, R.N. Synthetic Phototransduction with a Light-Responsive Molecule (KIO-301) in Advanced Retinitis Pigmentosa: The ABACUS-1 Phase 1/2 Trial. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2024, 65, 407. [Google Scholar]
- Terlau, H.; Olivera, B.M. Conus Venoms: A Rich Source of Novel Ion Channel-Targeted Peptides. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A.; Lenaeus, M.J.; Gamal El-Din, T.M. Structure and Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Sodium and Calcium Channels. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remme, C.A. SCN5A Channelopathy: Arrhythmia, Cardiomyopathy, Epilepsy and Beyond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 378, 20220164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisedchaisri, G.; Gamal El-Din, T.M. Druggability of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels-Exploring Old and New Drug Receptor Sites. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 858348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahel, J.-A.; Boulanger-Scemama, E.; Pagot, C.; Arleo, A.; Galluppi, F.; Martel, J.N.; Esposti, S.D.; Delaux, A.; de Saint Aubert, J.-B.; de Montleau, C.; et al. Partial Recovery of Visual Function in a Blind Patient after Optogenetic Therapy. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, S.; Finol-Urdaneta, R.K.; Köpfer, D.; Markushina, A.; Song, J.; French, R.J.; Kopec, W.; de Groot, B.L.; Giacobassi, M.J.; Leavitt, L.S.; et al. Conotoxin ΚM-RIIIJ, a Tool Targeting Asymmetric Heteromeric Kv1 Channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Dudley, S.C., Jr.; Choudhary, G.; Pfahnl, A.; Oshima, Y.; Daly, J.W. The Structure of Zetekitoxin AB, a Saxitoxin Analog from the Panamanian Golden Frog Atelopus Zeteki: A Potent Sodium-Channel Blocker. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4346–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.R.; Denomme, N.; Hajare, H.S.; Du Bois, J. A Chemogenetic Ligand-Receptor Pair for Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Subtype-Selective Inhibition. bioRxiv 2025. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ion Channel | Toxin/Molecule | Mechanism | Disease/Pathophysiological Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaV2.2 (N-type) | ω-Conotoxin MVIIA (Ziconotide) | Pore blockade | Severe chronic pain, neuropathic pain |
| CaV2.2 | ω-Conotoxin CVID | Selective CaV2.2 inhibitor | Chronic and neuropathic pain |
| Kv1.3 | ShK/Dalazatide | Kv1.3 pore blocker | Autoimmune diseases (e.g., psoriasis) |
| Kv1.3 | HsTX1[R14A] | Selective Kv1.3 inhibitor | Autoimmune and inflammatory diseases |
| NaV1.1 | Hm1a/Hm1b | NaV1.1 activation | Dravet syndrome |
| NaV1.1 | AA43279 | NaV1.1 gating enhancer | Dravet syndrome |
| NaV1.7 | ProTx-II/HwTx-IV | NaV1.7 inhibition | Pain disorders |
| CaV1.2 | Calciseptine | L-type Ca2+ inhibition | Hypertension, arrhythmia |
| CaV2.1 | ω-Agatoxin IVA | P/Q-type Ca2+ inhibition | Episodic ataxia, FHM |
| hERG (Kv11.1) | APETx1 | hERG gating inhibition | Long QT syndrome |
| Kv/HCN (RGCs) | AAQ, DENAQ, BENAQ | Photoswitchable block of Kv and HCN channels in retinal ganglion cells | Retinal degenerative diseases |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aoki-Shioi, N.; Nomura, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Hirose, S. Ion Channel-Targeting Toxins: Structural Mechanisms of Activation, Inhibition, and Therapeutic Potential. Toxins 2025, 17, 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120579
Aoki-Shioi N, Nomura S, Tanaka Y, Hirose S. Ion Channel-Targeting Toxins: Structural Mechanisms of Activation, Inhibition, and Therapeutic Potential. Toxins. 2025; 17(12):579. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120579
Chicago/Turabian StyleAoki-Shioi, Narumi, Shuhei Nomura, Yasuyoshi Tanaka, and Shinichi Hirose. 2025. "Ion Channel-Targeting Toxins: Structural Mechanisms of Activation, Inhibition, and Therapeutic Potential" Toxins 17, no. 12: 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120579
APA StyleAoki-Shioi, N., Nomura, S., Tanaka, Y., & Hirose, S. (2025). Ion Channel-Targeting Toxins: Structural Mechanisms of Activation, Inhibition, and Therapeutic Potential. Toxins, 17(12), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120579





