Differential Effects of Marimastat and Prinomastat on the Metalloprotease Activity of Various Snake Venoms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
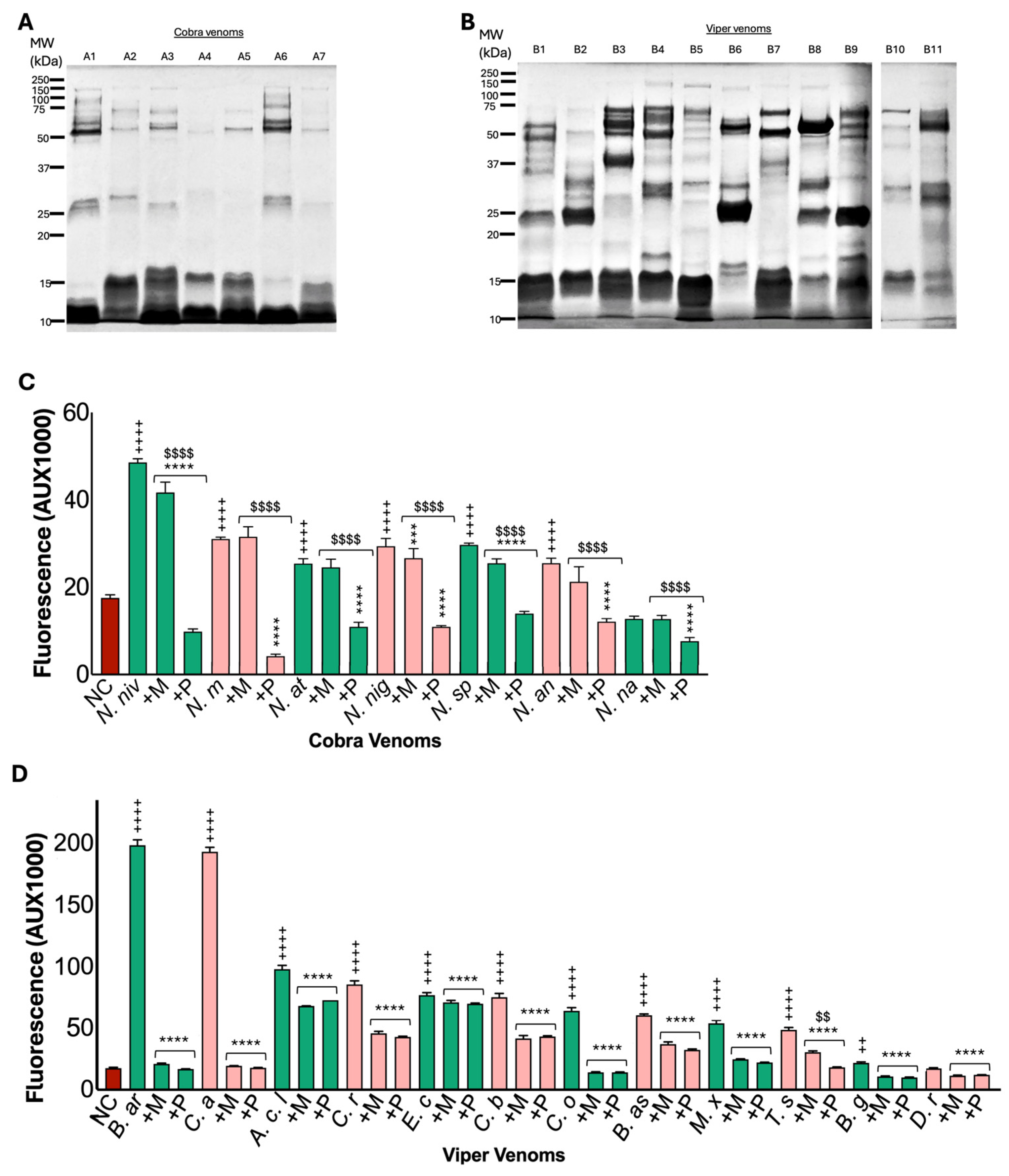
2.1. Viper and Elapid Venoms Exhibit Distinct Protein Profiles
2.2. Most Cobra and Viper Venoms Exhibit Metalloprotease Activity
2.3. Marimastat Does Not Effectively Inhibit the Metalloprotease Activities of Cobra Venoms
2.4. Viper Venoms Exhibit Greater Proteolytic Activities than Cobra Venoms
2.5. Selective Cobra and All Viper Venoms Exhibit Fibrinogenolytic Activities
2.6. Marimastat and Prinomastat Show Significant Affinities Toward the Venom Metalloproteases
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venoms Used
4.2. Metalloprotease Assay
4.3. Fibrinogenolytic Assay
4.4. SDS-PAGE
4.5. Caseinolytic Assay
4.6. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, H.F.; Layfield, H.J.; Vallance, T.; Patel, K.; Bicknell, A.B.; Trim, S.A.; Vaiyapuri, S. The Urgent Need to Develop Novel Strategies for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Snakebites. Toxins 2019, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite Envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offor, B.C.; Muller, B.; Piater, L.A. A Review of the Proteomic Profiling of African Viperidae and Elapidae Snake Venoms and Their Antivenom Neutralisation. Toxins 2022, 14, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaoba, O.T.; Dos Santos, P.K.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S.; Ferreira de Souza, D.H. Snake Venom Metalloproteases (SVMPs): A Structure–Function Update. Toxicon X 2020, 7, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preciado, L.M.; Pereañez, J.A. Low Molecular Mass Natural and Synthetic Inhibitors of Snake Venom Metalloproteases. Toxin Rev. 2017, 37, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layfield, H.J.; Williams, H.F.; Ravishankar, D.; Mehmi, A.; Sonavane, M.; Salim, A.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Lakshminarayanan, K.; Vallance, T.M.; Bicknell, A.B.; et al. Repurposing Cancer Drugs Batimastat and Marimastat to Inhibit the Activity of a Group I Metalloprotease from the Venom of the Western Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox). Toxins 2020, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Wong, K.Y.; Huang, L.K.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H.; Wu, W.G. Snake Venomics and Antivenomics of Cape Cobra (Naja nivea) from South Africa: Insights into Venom Toxicity and Cross-Neutralization Activity. Toxins 2022, 14, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, D.A. Snake Bite. Lancet 2010, 375, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramhall, S.R.; Hallissey, M.T.; Whiting, J.; Scholefield, J.; Tierney, G.; Stuart, R.C.; Hawkins, R.E.; McCulloch, P.; Maughan, T.; Brown, P.D.; et al. Marimastat as Maintenance Therapy for Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Randomised Trial. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scatena, R. Prinomastat, a Hydroxamate-Based Matrix Metalloprotease Inhibitor: A Novel Pharmacological Approach for Tissue Remodelling-Related Diseases. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, K.R.; Collier, M.; Paradiso, L.; Stuart-Smith, J.; Dixon, M.; Clendeninn, N.; Yeun, G.; Alberti, D.; Binger, K.; Wilding, G. Phase I and Pharmacokinetic Study of Prinomastat, a Matrix Metalloprotease Inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albulescu, L.-O.; Xie, C.; Ainsworth, S.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Dawson, C.A.; Softley, R.; Bartlett, K.E.; Harrison, R.A.; Kool, J.; et al. A Therapeutic Combination of Two Small Molecule Toxin Inhibitors Provides Broad Preclinical Efficacy Against Viper Snakebite. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, K.; Treschow, A.F.; Auf dem Keller, U.; Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Laustsen, A.H.; Workman, C.T. Protease Activity Profiling of Snake Venoms Using High-Throughput Peptide Screening. Toxins 2019, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, H.S.; McCann, P.P. Matrix Metalloprotease Inhibition as a Novel Anticancer Strategy: A Review with Special Focus on Batimastat and Marimastat. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 75, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.S.; Rucavado, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Peptidomimetic Hydroxamate Metalloprotease Inhibitors Abrogate Local and Systemic Toxicity Induced by Echis ocellatus (Saw-Scaled) Snake Venom. Toxicon 2017, 132, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudresha, G.V.; Khochare, S.; Casewell, N.R.; Sunagar, K. Preclinical Evaluation of Small Molecule Inhibitors as Early Intervention Therapeutics Against Russell’s Viper Envenoming in India. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.; Mendes, B.; Patiño, R.S.P.; Pico, J.; Laines, J.; Terán, M.; Mogollón, N.G.S.; Zaruma-Torres, F.; Caldeira, C.A.d.S.; da Silva, S.L. Assessing the Stability of Historical and Desiccated Snake Venoms from a Medically Important Ecuadorian Collection. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 230, 108702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Hernández-Guzmán, U.; Quesada-Bernat, S.; Sanz, L.; Rokyta, D.R.; Storey, D.; Albulescu, L.O.; Wüster, W.; Smith, C.F.; et al. Venom Complexity in a Pitviper Produced by Facultative Parthenogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Park, J.E.; Park, J.W.; Lee, J.S. Purification and Biochemical Characterization of a Fibrin(ogen)olytic Metalloprotease from Macrovipera mauritanica Snake Venom Which Induces Vascular Permeability. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, A.C.; Pereañez, J.A.; Núñez, V.; Benjumea, D.M.; Fernandez, M.; Rucavado, A.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J. Isolation and Biological Characterization of Batx-I, a Weak Hemorrhagic and Fibrinogenolytic PI Metalloprotease from Colombian Bothrops atrox Venom. Toxicon 2010, 56, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Harrison, R.A.; Bicknell, A.B.; Gibbins, J.M.; Hutchinson, G. Purification and Functional Characterisation of Rhinocerase, a Novel Serine Protease from the Venom of Bitis gabonica rhinoceros. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, K.; Fischer, H.; Meier, J. Thrombin-Like Snake Venom Proteinases. Toxicon 1982, 20, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, S.; Markland, F.S., Jr. Snake Venom Fibrin(ogen)olytic Enzymes. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1021–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.M.; Maroun, R.C. Snake Venom Serine Proteinases: Sequence Homology vs. Substrate Specificity—A Paradox to Be Solved. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1115–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackessy, S.P. Thrombin-Like Enzymes in Snake Venoms. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; Mackessy, S.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 519–557. [Google Scholar]
- Bittenbinder, M.A.; Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Op den Brouw, B.; Naude, A.; Vonk, F.J.; Fry, B.G. Differential Destructive (Non-Clotting) Fibrinogenolytic Activity in Afro-Asian Elapid Snake Venoms and the Links to Defensive Hooding Behavior. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 60, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megale, Â.A.A.; Magnoli, F.C.; Kuniyoshi, A.K.; Iwai, L.K.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Portaro, F.C.V.; da Silva, W.D. Kn-Ba: A Novel Serine Protease Isolated from Bitis arietans Snake Venom with Fibrinogenolytic and Kinin-Releasing Activities. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıkan, H.; Alpagut Keskin, N.; Çiçek, K. Electrophoretic Characterization of Venom Proteins of Montivipera xanthina (Gray, 1849) (Ophidia: Viperidae). Basic Appl. Herpetol. 2017, 31, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kini, R.M.; Koh, C.Y. Metalloproteases Affecting Blood Coagulation, Fibrinolysis and Platelet Aggregation from Snake Venoms: Definition and Nomenclature of Interaction Sites. Toxins 2016, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, T.; Araki, S.; Mori, H.; Takeda, S. Crystal Structures of Catrocollastatin/VAP2B Reveal a Dynamic, Modular Architecture of ADAM/Adamalysin/Reprolysin Family Proteins. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2416–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.H.; Goh, K.S.; Davamani, F.; Wu, P.L.; Huang, Y.W.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Wu, W.G.; Chen, C.J. Structures of Two Elapid Snake Venom Metalloproteases with Distinct Activities Highlight the Disulfide Patterns in the D Domain of ADAMalysin Family Proteins. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 169, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and Ligand Preparation: Parameters, Protocols, and Influence on Virtual Screening Enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein–Ligand Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.P.; Pincus, D.L.; Rapp, C.S.; Day, T.J.; Honig, B.; Shaw, D.E.; Friesner, R.A. A Hierarchical Approach to All-Atom Protein Loop Prediction. Proteins 2004, 55, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, K.; Chow, E.; Xu, H.; Dror, R.; Eastwood, M.; Gregersen, B.; Klepeis, J.; Kolossváry, I.; Moraes, M.; Sacerdoti, F.; et al. Molecular Dynamics—Scalable Algorithms for Molecular Dynamics Simulations on Commodity Clusters. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing (SC ’06), Tampa, FL, USA, 11–17 November 2006; p. 84. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Wu, C.; Ghoreishi, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Damm, W.; Ross, G.A.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Russell, E.; Von Bargen, C.D.; et al. OPLS4: Improving Force Field Accuracy on Challenging Regimes of Chemical Space. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khatibi, M.; Almeida, J.R.; Gilabadi, S.; Ramírez, D.; Valenzuela-Hormazábal, P.; Patel, K.; Vaiyapuri, S. Differential Effects of Marimastat and Prinomastat on the Metalloprotease Activity of Various Snake Venoms. Toxins 2025, 17, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120571
Khatibi M, Almeida JR, Gilabadi S, Ramírez D, Valenzuela-Hormazábal P, Patel K, Vaiyapuri S. Differential Effects of Marimastat and Prinomastat on the Metalloprotease Activity of Various Snake Venoms. Toxins. 2025; 17(12):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120571
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhatibi, Mahtab, José R. Almeida, Soheil Gilabadi, David Ramírez, Paulina Valenzuela-Hormazábal, Ketan Patel, and Sakthivel Vaiyapuri. 2025. "Differential Effects of Marimastat and Prinomastat on the Metalloprotease Activity of Various Snake Venoms" Toxins 17, no. 12: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120571
APA StyleKhatibi, M., Almeida, J. R., Gilabadi, S., Ramírez, D., Valenzuela-Hormazábal, P., Patel, K., & Vaiyapuri, S. (2025). Differential Effects of Marimastat and Prinomastat on the Metalloprotease Activity of Various Snake Venoms. Toxins, 17(12), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120571







