The Clot Thickens: Differential Coagulotoxic and Cardiotoxic Activities of Anguimorpha Lizard Venoms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
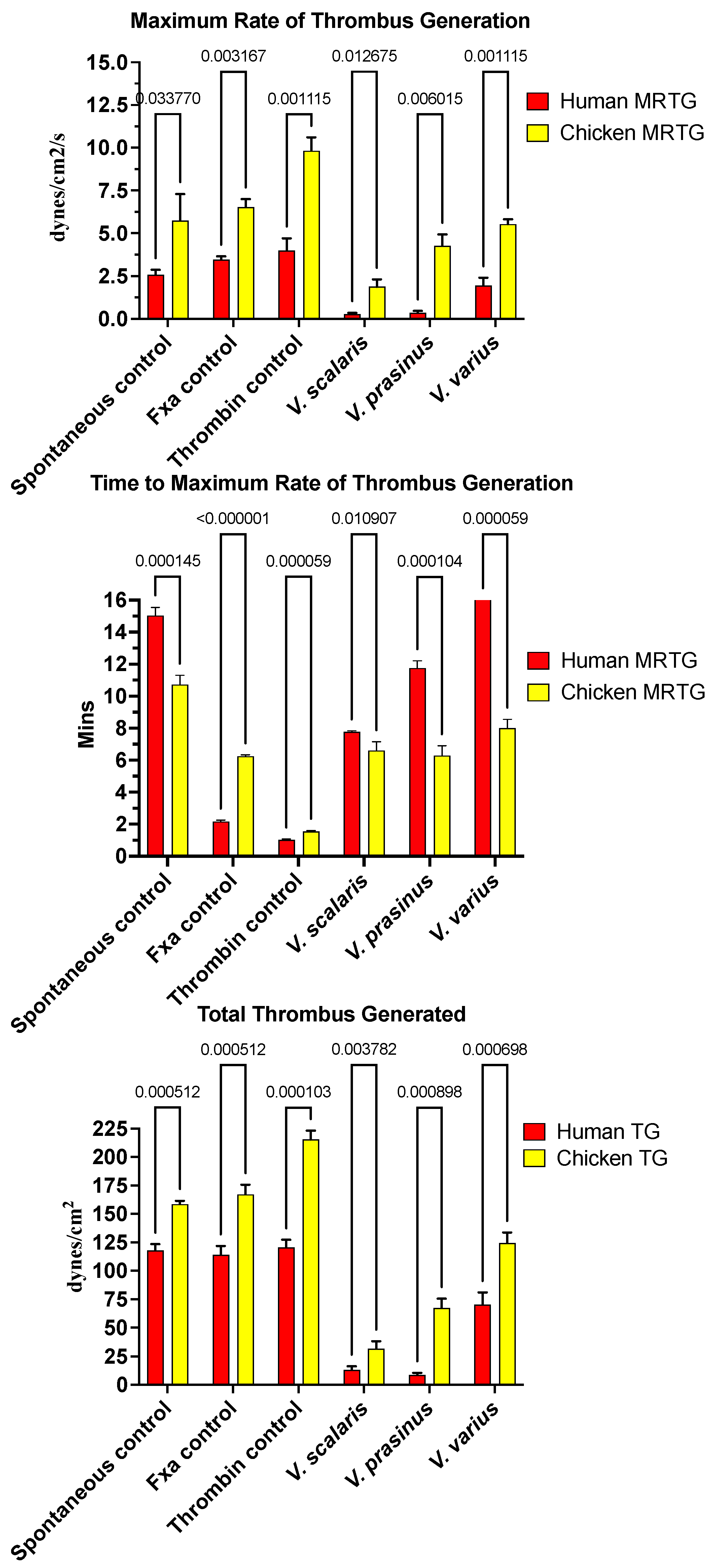
2.1. Anticoagulant Effects of Varanus Venoms
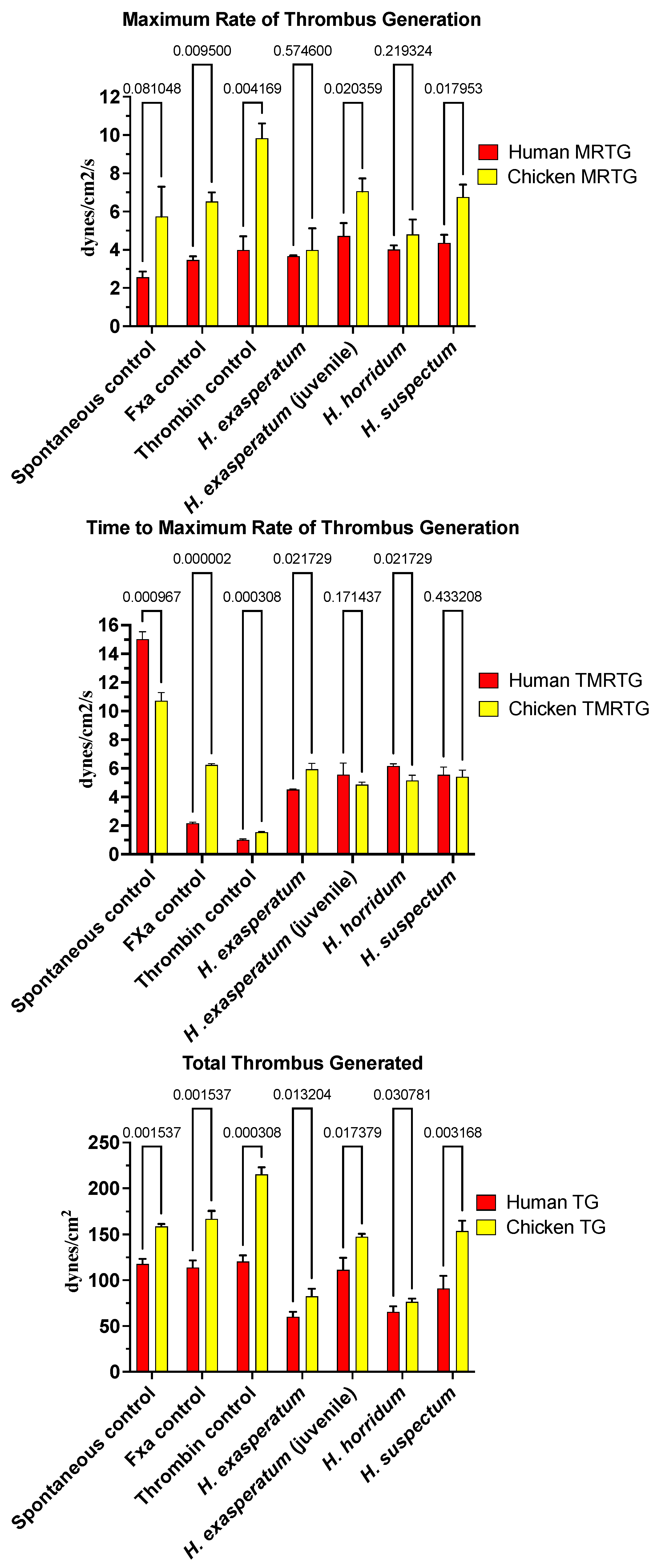
2.2. Procoagulant Effects of Heloderma Venoms
2.3. Cardiovascular System Effects of Heloderma and Varanus Venoms
3. Discussion
3.1. Varanus Venom Anticoagulation
3.2. Heloderma Venoms’ Procoagulation
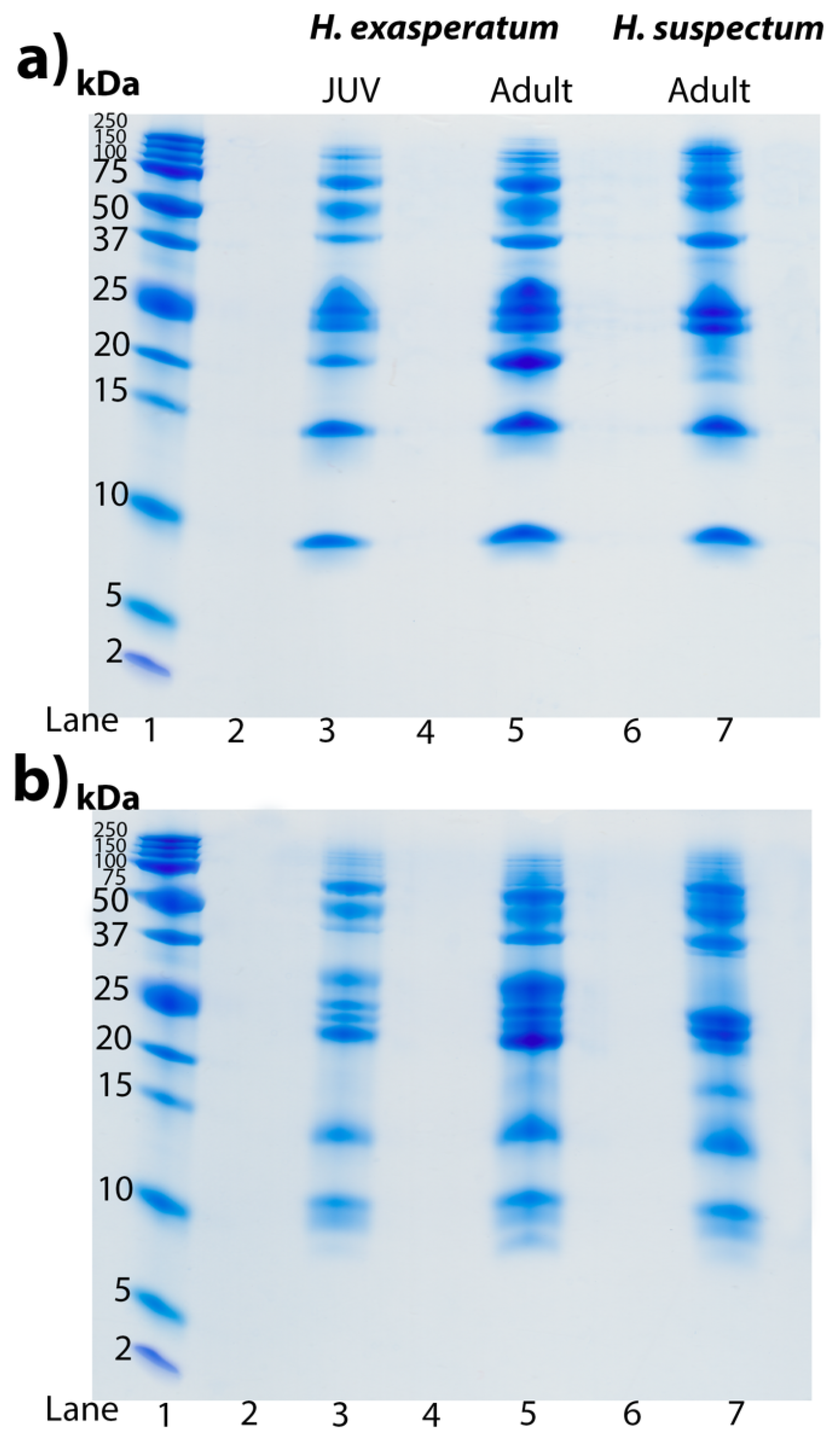
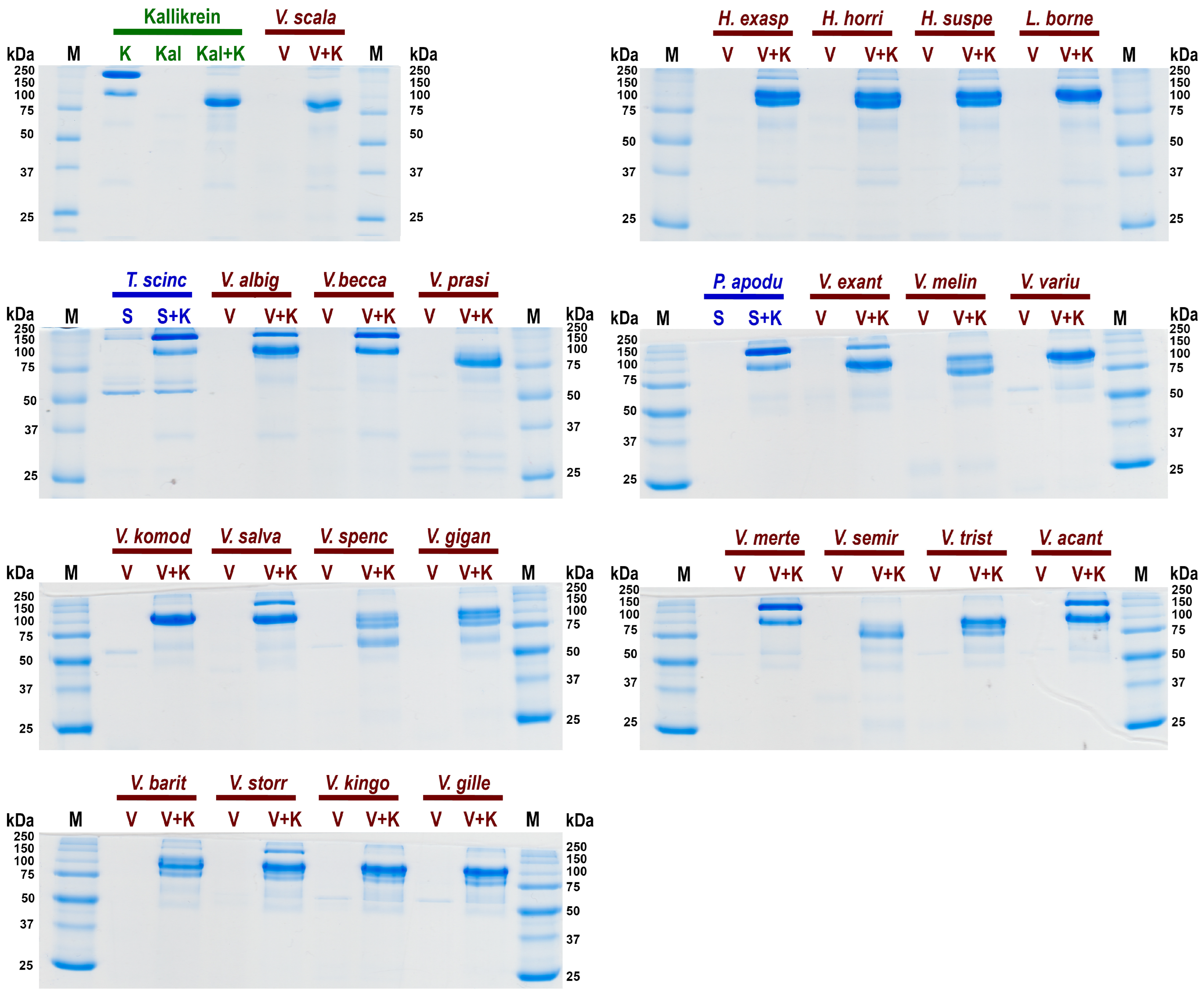
3.3. Kininogen Cleavage by Heloderma and Varanoid Venoms
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Sample Acquisition and Stocks
5.2. Plasma
5.3. Thromboelastography
5.4. Coagulation Factor Inhibition
5.5. Clotting Factor Activation Assays
5.6. Tricine Gels
5.7. Kininogen Gels
5.8. Statistical Analyses and Figure Production
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alagón, A.; Possani, L.D.; Smart, J.; Schleuning, W.D. Helodermatine, a kallikrein-like, hypotensive enzyme from the venom of Heloderma horridum horridum (Mexican beaded lizard). J. Exp. Med. 1986, 164, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Hay, C.; Violette, A.; Fourmy, R.; Cochran, C.; Fry, B.G. Varanid lizard venoms disrupt the clotting ability of human fibrinogen through destructive cleavage. Toxins 2019, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, J.S.; Harris, R.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Huynh, T.; Hodgson, W.C.; Bosmans, F.; Fourmy, R.; Violette, A.; Fry, B.G. The dragon’s paralysing spell: Evidence of sodium and calcium ion channel binding neurotoxins in helodermatid and varanid lizard venoms. Toxins 2021, 13, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Vidal, N.; Norman, J.A.; Vonk, F.J.; Scheib, H.; Ramjan, S.F.; Kuruppu, S.; Fung, K.; Hedges, S.B.; Richardson, M.K.; et al. Early evolution of the venom system in lizards and snakes. Nature 2006, 439, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Winter, K.; Norman, J.A.; Roelants, K.; Nabuurs, R.J.; van Osch, M.J.; Teeuwisse, W.M.; van der Weerd, L.; McNaughtan, J.E.; Kwok, H.F.; et al. Functional and structural diversification of the Anguimorpha lizard venom system. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2369–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Wroe, S.; Teeuwisse, W.; van Osch, M.J.; Moreno, K.; Ingle, J.; McHenry, C.; Ferrara, T.; Clausen, P.; Scheib, H.; et al. A central role for venom in predation by Varanus komodoensis (Komodo Dragon) and the extinct giant Varanus (Megalania) priscus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8969–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendon, R.A.; Tu, A.T. Biochemical characterization of the lizard toxin gilatoxin. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 3517–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koludarov, I.; Jackson, T.N.; Sunagar, K.; Nouwens, A.; Hendrikx, I.; Fry, B.G. Fossilized venom: The unusually conserved venom profiles of Heloderma species (beaded lizards and gila monsters). Toxins 2014, 6, 3582–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koludarov, I.; Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.; Jackson, T.N.; Ruder, T.; Whitehead, D.; Saucedo, A.C.; Mora, G.R.; Alagon, A.C.; King, G.; et al. Structural and molecular diversification of the Anguimorpha lizard mandibular venom gland system in the arboreal species Abronia graminea. J. Mol. Evol. 2012, 75, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.F.; Chiang, H.S. Effect on human platelet aggregation of phospholipase A2 purified from Heloderma horridum (beaded lizard) venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1211, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koludarov, I.; Jackson, T.N.; Brouw, B.O.D.; Dobson, J.; Dashevsky, D.; Arbuckle, K.; Clemente, C.J.; Stockdale, E.J.; Cochran, C.; Debono, J.; et al. Enter the dragon: The dynamic and multifunctional evolution of anguimorpha lizard venoms. Toxins 2017, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebs, D. Some studies on biochemistry of venom gland of Heloderma horridum. Toxicon 1968, 5, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebs, D. Purification and properties of a kinin-liberating enzyme from the venom of the scaly lizard Heloderma suspectum. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmakol. 1968, 264, 280–281. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, A.T.; Murdock, D.S. Protein nature and some enzymatic properties of the lizard Heloderma suspectum suspectum (Gila monster) venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1967, 22, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebs, D. Purification and properties of a kinin liberating enzyme from venom of Heloderma suspectum. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Fur Pharmakol. 1969, 264, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebs, D. Isolation and properties of kallikrein from venom of gila monster (Heloderma suspectum). Hoppe-Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 1969, 350, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alagón, A.C.; Maldonado, M.E.A.; Julia, J.Z.; Sanchez, C.R.; Possani, L.D. Venom from 2 subspecies of Heloderma horridum (Mexican Beaded Lizard)—General characterization and purification of n-benzoyl-l-arginine ethyl-ester hydrolase. Toxicon 1982, 20, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebs, D. Biochemistry of Heloderma venom. Toxicon 1970, 8, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Nikai, T.; Imai, K.; Komori, Y.; Sugihara, H. Isolation and characterization of arginine ester hydrolase from Heloderma horridum (beaded lizard) venom. Int. J. Biochem. 1992, 24, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Nikai, T.; Imai, K.; Sugihara, H.; Tu, A.T. Isolation and characterization of horridum toxin with arginine ester hydrolase activity from Heloderma horridum (beaded lizard) venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1988, 264, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.A. Hypotension, myocardial infarction, and coagulopathy following gila monster bite. J. Emerg. Med. 1989, 7, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, A.T. Lethal toxins of lizard venoms that possess kallikrein-like activity. In Natural and Selected Synthetic Toxins; Acs Symposium Series; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; Volume 745, pp. 283–301. [Google Scholar]
- Utaisincharoen, P.; Mackessy, S.P.; Miller, R.A.; Tu, A.T. Complete primary structure and biochemical properties of gilatoxin, a serine protease with kallikrein-like and angiotensin-degrading activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 21975–21983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Winter, K.; Hodgson, W.C.; Griesman, L.; Kwok, H.F.; Scanlon, D.; Karas, J.; Shaw, C.; Wong, L.; et al. Novel venom proteins produced by differential domain-expression strategies in beaded lizards and gila monsters (genus Heloderma). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P.; Amri, K. Severe Heloderma spp. envenomation: A review of the literature. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, H.; Tejero-Trujeque, R.; Dhital, S.K. Septic arthritis due to a Savannah Monitor lizard bite: A case report. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2008, 33, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikrant, S.; Verma, B.S. Monitor lizard bite-induced acute kidney injury—A case report. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 444–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.; Weinstein, S.A. Reply to Vikrant and Verma about “Monitor Lizard Envenoming”. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, K.; Chippaux, J.P. Report of a severe Heloderma suspectum envenomation. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R.; Brooks, D.; Ruha, A.M.; Shirazi, F.; Chase, P.; Boesen, K.; Walter, F. Gila monster (Heloderma suspectum) envenomation: Descriptive analysis of calls to United States Poison Centers with focus on Arizona cases. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, F.E.; Bogert, C.M. Gila monster—Its biology, venom and bite—A review. Toxicon 1981, 19, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimple, P.D.; Tomassoni, A.J.; Otten, E.J.; Bahner, D. Report on envenomation by a Gila monster (Heloderma suspectum) with a discussion of venom apparatus, clinical findings, and treatment. Wilderness Environ. Med. 1997, 8, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducey, S.D.; Cooper, J.S.; Wadman, M.C. Bitten by a Dragon. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2016, 27, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopyev, O.; Makeev, V.M.; Kudryavtsev, S.V.; Makarov, A.N. Case of intoxification from a bite of Varanus griseus. Izy. Akad. Turkm. SSR 1987, 87, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Zima, Y.A. On the Toxicity of the Bite of the Caspian Desert Monitor Lizard (Varanus griseus caspius). Biawak 2019, 13, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, B.G. From genome to “venome”: Molecular origin and evolution of the snake venom proteome inferred from phylogenetic analysis of toxin sequences and related body proteins. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Richards, R.; Earl, S.; Cousin, X.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Weise, C.; Sunagar, K. Lesser-known or putative reptile toxins. In Venomous Reptiles & Their Toxins; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 364–407. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, B.G.; Wuster, W.; Kini, R.M.; Brusic, V.; Khan, A.; Venkataraman, D.; Rooney, A.P. Molecular evolution and phylogeny of elapid snake venom three-finger toxins. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 57, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.; Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Reeks, T.; Fry, B.G. Three-finger toxins (3FTxs). In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 215–227. [Google Scholar]
- Earl, S.; Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Fry, B.G. Factor Va enzymes. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Trabi, M.; Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Fry, B.G. Factor Xa enzymes. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zdenek, C.N.; Hay, C.; Arbuckle, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Bos, M.H.A.; Op den Brouw, B.; Debono, J.; Allen, L.; Dunstan, N.; Morley, T.; et al. Coagulotoxic effects by brown snake (Pseudonaja) and taipan (Oxyuranus) venoms, and the efficacy of a new antivenom. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 58, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanggaard, K.W.; Dyrlund, T.F.; Thomsen, L.R.; Nielsen, T.A.; Brondum, L.; Wang, T.; Thogersen, I.B.; Enghild, J.J. Characterization of the gila monster (Heloderma suspectum suspectum) venom proteome. J. Proteom. 2015, 117, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.K.; Booth, W.J.; Gorman, J.J.; Castaldi, P.A.; Berndt, M.C. Purification of botrocetin from Bothrops jararaca venom. Analysis of the botrocetin-mediated interaction between von Willebrand factor and the human platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 8317–8326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, F.T.; Eble, J.A. The collagen-binding integrin alpha2beta1 is a novel interaction partner of the Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom protein flavocetin-A. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, F.T.; Fry, B.G.; Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Eble, J.A.; Reeks, T.; Clemetson, K.J. Lectin proteins. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 299–311. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, H.M.; Tans, G.; Yukelson, L.Y.; Janssen-Claessen, T.W.; Bertina, R.M.; Hemker, H.C.; Rosing, J. Protein C activation by an activator purified from the venom of Agkistrodon halys halys. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 1993, 4, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Banerjee, Y.; Mizuguchi, J.; Iwanaga, S.; Kini, R.M. Hemextin AB complex, a unique anticoagulant protein complex from Hemachatus haemachatus (African Ringhals cobra) venom that inhibits clot initiation and factor VIIa activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42601–42611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbouche, R.; Marrakchi, N.; Mansuelle, P.; Krifi, M.; Fenouillet, E.; Rochat, H.; el Ayeb, M. Novel anti-platelet aggregation polypeptides from Vipera lebetina venom: Isolation and characterization. FEBS Lett. 1996, 392, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbouche, R.; Marrakchi, N.; Mabrouk, K.; Krifi, M.N.; Van Rietschoten, J.; Fenouillet, E.; El Ayeb, M.; Rochat, H. Anti-platelet activity of the peptides composing the Lebetin 1 family, a new class of inhibitors of platelet aggregation. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittenbinder, M.A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Op den Brouw, B.; Youngman, N.J.; Dobson, J.S.; Naude, A.; Vonk, F.J.; Fry, B.G. Coagulotoxic cobras: Clinical implications of strong anticoagulant actions of african spitting Naja venoms that are not neutralised by antivenom but are by LY315920 (Varespladib). Toxins 2018, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, L.; Alagón, A.; Fry, B.G.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Sunagar, K.; Chippaux, J.P. Signs, symptoms and treatment of envenomation. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 32–60. [Google Scholar]
- Braud, S.; Bon, C.; Wisner, A. Snake venom proteins acting on hemostasis. Biochimie 2000, 82, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Monleon, D.; Esteve, V.; Celda, B.; Juarez, P.; Sanz, L. Snake venom disintegrins: Evolution of structure and function. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Sanz, L. Snake venomics of Bitis gabonica gabonica. Protein family composition, subunit organization of venom toxins, and characterization of dimeric disintegrins bitisgabonin-1 and bitisgabonin-2. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Sunagar, K.; Takacs, Z.; Calvete, J.J.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Fry, B.G. Snake venom metalloprotease enzymes. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 347–363. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.Q.; Jin, Y.; Wu, J.B.; Zhou, X.D.; Lu, Q.M.; Wang, W.Y.; Xiong, Y.L. A new protein structure of P-II class snake venom metalloproteinases: It comprises metalloproteinase and disintegrin domains. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Carvalho, L.P.; Chan, M.Y.; Kini, R.M.; Kang, T.S. Fasxiator, a novel factor XIa inhibitor from snake venom, and its site-specific mutagenesis to improve potency and selectivity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, G.; Subburaju, S.; Kini, R.M. Purification, characterization, and amino acid sequence determination of acanthins, potent inhibitors of platelet aggregation from Acanthophis antarcticus (common death adder) venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 354, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque Modesto, J.C.; Spencer, P.J.; Fritzen, M.; Valenca, R.C.; Oliva, M.L.; da Silva, M.B.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M.; Guarnieri, M.C. BE-I-PLA2, a novel acidic phospholipase A2 from Bothrops erythromelas venom: Isolation, cloning and characterization as potent anti-platelet and inductor of prostaglandin I2 release by endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria, L.; Antunes, E.; Bon, C.; de Araujo, A.L. Pharmacological characterization of the rat paw edema induced by Bothrops lanceolatus (Fer de lance) venom. Toxicon 2001, 39, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.Y.; Navdaev, A.; Clemetson, J.M.; Magnenat, E.; Wells, T.N.; Clemetson, K.J. Bilinexin, a snake C-type lectin from Agkistrodon bilineatus venom agglutinates platelets via GPIb and alpha2beta1. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.W.; Serrano, S.M.T. Structural considerations of the snake venom metalloproteinases, key members of the M12 reprolysin family of metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2005, 45, 969–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Takacs, Z.; Reeks, T.; Sunagar, K. C-type natriuretic peptides. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 318–326. [Google Scholar]
- Fuly, A.L.; Francischetti, I.M.; Zingali, R.B.; Carlini, C.R. Partial purification and some physicochemical properties of phospholipases A2 from the venom of the bushmaster snake (Lachesis muta). Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1993, 26, 459–463. [Google Scholar]
- Fuly, A.L.; Machado, O.L.; Alves, E.W.; Carlini, C.R. Mechanism of inhibitory action on platelet activation of a phospholipase A2 isolated from Lachesis muta (Bushmaster) snake venom. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 78, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, V.M.; Kini, R.M. Exactin: A specific inhibitor of Factor X activation by extrinsic tenase complex from the venom of Hemachatus haemachatus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamako, J.; Matsui, T.; Suzuki, M.; Ito, M.; Makita, K.; Fujimura, Y.; Ozeki, Y.; Titani, K. Purification and characterization of bitiscetin, a novel von Willebrand factor modulator protein from Bitis arietans snake venom. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 226, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, M.Z.; Wang, Q.C.; Liu, G.F. Effects of an acidic phospholipase A2 purified from Ophiophagus hannah (king cobra) venom on rat heart. Toxicon 1993, 31, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Z.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Pathological changes induced by an acidic phospholipase A2 from Ophiophagus hannah venom on heart and skeletal muscle of mice after systemic injection. Toxicon 1996, 34, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Nikai, T.; Sugihara, H.; Ownby, C.L. Hemorrhagic toxin from the venom of Agkistrodon bilineatus (common cantil). Int. J. Biochem. 1989, 21, 667–673. [Google Scholar]
- Kerns, R.T.; Kini, R.M.; Stefansson, S.; Evans, H.J. Targeting of venom phospholipases: The strongly anticoagulant phospholipase A(2) from Naja nigricollis venom binds to coagulation factor Xa to inhibit the prothrombinase complex. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 369, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M.; Evans, H.J. Correlation between the enzymatic activity, anticoagulant and antiplatelet effects of phospholipase A2 isoenzymes from Naja nigricollis venom. Thromb. Haemost. 1988, 60, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Kini, R.M. Structure-function relationships and mechanism of anticoagulant phospholipase A2 enzymes from snake venoms. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1147–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisiel, W.; Kondo, S.; Smith, K.J.; McMullen, B.A.; Smith, L.F. Characterization of a protein C activator from Agkistrodon contortrix contortrix venom. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 12607–12613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, A.E.; Bashkov, G.V.; Bobruskin, I.D.; Romanova, E.P.; Makarov, V.A.; Strukova, S.M. Protein C activator from the venom of Agkistrodon blomhoffi ussuriensis retards thrombus formation in the arterio-venous shunt in rats. Thromb. Res. 1993, 70, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Williams, J.A.; Deadman, J.J.; Salmon, G.P.; Kakkar, V.V.; Wilkinson, J.M.; Baruch, D.; Authi, K.S.; Rahman, S. Preferential antagonism of the interactions of the integrin alpha IIb beta 3 with immobilized glycoprotein ligands by snake-venom RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) proteins. Evidence supporting a functional role for the amino acid residues flanking the tripeptide RGD in determining the inhibitory properties of snake-venom RGD proteins. Biochem. J. 1994, 304 Pt 3, 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Clemetson, J.M.; Clemetson, K.J. Snake venoms and hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkiewicz, C.; Vijay-Kumar, S.; McLane, M.A.; Niewiarowski, S. Significance of RGD loop and C-terminal domain of echistatin for recognition of alphaIIb beta3 and alpha(v) beta3 integrins and expression of ligand-induced binding site. Blood 1997, 90, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkiewicz, C.; Calvete, J.J.; Marcinkiewicz, M.M.; Raida, M.; Vijay-Kumar, S.; Huang, Z.; Lobb, R.R.; Niewiarowski, S. EC3, a novel heterodimeric disintegrin from Echis carinatus venom, inhibits alpha4 and alpha5 integrins in an RGD-independent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 12468–12473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinkiewicz, C.; Calvete, J.J.; Vijay-Kumar, S.; Marcinkiewicz, M.M.; Raida, M.; Schick, P.; Lobb, R.R.; Niewiarowski, S. Structural and functional characterization of EMF10, a heterodimeric disintegrin from Eristocophis macmahoni venom that selectively inhibits alpha 5 beta 1 integrin. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 13302–13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkiewicz, C.; Lobb, R.R.; Marcinkiewicz, M.M.; Daniel, J.L.; Smith, J.B.; Dangelmaier, C.; Weinreb, P.H.; Beacham, D.A.; Niewiarowski, S. Isolation and characterization of EMS16, a C-lectin type protein from Echis multisquamatus venom, a potent and selective inhibitor of the alpha2beta1 integrin. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 9859–9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrakchi, N.; Zingali, R.B.; Karoui, H.; Bon, C.; el Ayeb, M. Cerastocytin, a new thrombin-like platelet activator from the venom of the Tunisian viper Cerastes cerastes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1244, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, R.S.; Dennis, M.S.; Louie, A.; Shuster, M.; Mulkerrin, M.G.; Lazarus, R.A. Mambin, a potent glycoprotein IIb-IIIa antagonist and platelet aggregation inhibitor structurally related to the short neurotoxins. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 4766–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, R.Q.; Zingali, R.B. Inhibition of prothrombin activation by bothrojaracin, a C-type lectin from Bothrops jararaca venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 382, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.Q. Targeting exosites on blood coagulation proteases. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2005, 77, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Muanpasitporn, C.; Rojnuckarin, P. Expression and characterization of a recombinant fibrinogenolytic serine protease from green pit viper (Trimeresurus albolabris) venom. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.K.; Kalita, B.; Thakur, R. Two acidic, anticoagulant PLA2 isoenzymes purified from the venom of monocled cobra Naja kaouthia exhibit different potency to inhibit thrombin and factor Xa via phospholipids independent, non-enzymatic mechanism. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagaki, T.; Kazim, A.L.; Kisiel, W. Isolation and characterization of a protein C activator from tropical moccasin venom. Thromb. Res. 1990, 58, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewiarowski, S.; Kirby, E.P.; Brudzynski, T.M.; Stocker, K. Thrombocytin, a serine protease from Bothrops atrox venom. 2. Interaction with platelets and plasma-clotting factors. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 3570–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikai, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Komori, Y.; Masuda, K.; Fox, J.W.; Sugihara, H. Primary structure and functional characterization of bilitoxin-1, a novel dimeric P-II snake venom metalloproteinase from Agkistrodon bilineatus venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 378, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, S.; Fujimura, Y.; Miura, S.; Ozaki, Y.; Usami, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Titani, K.; Yoshida, E.; Sugimoto, M.; Yoshioka, A.; et al. Purification and characterization of bothrombin, a fibrinogen-clotting serine protease from the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, D.; Horii, K.; Mizuno, H.; Morita, T. Characterization and preliminary crystallographic studies of EMS16, an antagonist of collagen receptor (GPIa/IIa) from the venom of Echis multisquamatus. J. Biochem. 2003, 134, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Carvalho, A.L.; Guimaraes, P.R.; Abreu, P.A.; Dutra, D.L.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Ho, P.L.; Castro, H.C.; Zingali, R.B. Identification and characterization of a new member of snake venom thrombin inhibitors from Bothrops insularis using a proteomic approach. Toxicon 2008, 51, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshikawa, K.; Terada, S. Ussuristatin 2, a novel KGD-bearing disintegrin from Agkistrodon ussuriensis venom. J. Biochem. 1999, 125, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulion, B.; Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Arbuckle, K.; Lister, C.; Coimbra, F.C.P.; Op den Brouw, B.; Debono, J.; Rogalski, A.; Violette, A.; et al. Factor X activating Atractaspis snake venoms and the relative coagulotoxicity neutralising efficacy of African antivenoms. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 288, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Kim, H.; Chung, K.; Kim, D.S.; Yun, Y. Expression and characterization of a novel plasminogen activator from Agkistrodon halys venom. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Lu, W.; Kirby, E.P. Alboaggregin-B: A new platelet agonist that binds to platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 11529–11536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Lu, W.; Beviglia, L.; Niewiarowski, S.; Kirby, E.P. Echicetin: A snake venom protein that inhibits binding of von Willebrand factor and alboaggregins to platelet glycoprotein Ib. Blood 1993, 81, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Holt, J.C.; Niewiarowski, S. Isolation, characterization and amino acid sequence of echicetin beta subunit, a specific inhibitor of von Willebrand factor and thrombin interaction with glycoprotein Ib. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 205, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Emig, F.A.; Mao, A.; Lu, W.; Kirby, E.P.; Niewiarowski, S.; Kowalska, M.A. Interaction of echicetin with a high affinity thrombin binding site on platelet glycoprotein GPIb. Thromb. Haemost. 1995, 74, 954–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucavado, A.; Soto, M.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Theakston, R.D.; Fox, J.W.; Escalante, T.; Gutierrez, J.M. Characterization of aspercetin, a platelet aggregating component from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper which induces thrombocytopenia and potentiates metalloproteinase-induced hemorrhage. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 85, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rucavado, A.; Soto, M.; Escalante, T.; Loria, G.D.; Arni, R.; Gutierrez, J.M. Thrombocytopenia and platelet hypoaggregation induced by Bothrops asper snake venom. Toxins involved and their contribution to metalloproteinase-induced pulmonary hemorrhage. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Magalhes, A.; Mandelbaum, F.R.; Diniz, C.R. Purification and characterization of the hemorrhagic factor II from the venom of the Bushmaster snake (Lachesis muta muta). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1074, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Santos, C.I.; Magalhaes, A.; Diniz, C.R.; Figueiredo, S.; Gilroy, J.; Richardson, M. Isolation of a proteinase with plasminogen-activating activity from Lachesis muta muta (bushmaster) snake venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 378, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.L.; Sano-Martins, I.S. Platelet dysfunction during Bothrops jararaca snake envenomation in rabbits. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 92, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarray, S.; Delamarre, E.; Marvaldi, J.; El Ayeb, M.; Marrakchi, N.; Luis, J. Lebectin and lebecetin, two C-type lectins from snake venom, inhibit alpha5beta1 and alphaV-containing integrins. Matrix Biol. 2007, 26, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarborough, R.M.; Rose, J.W.; Hsu, M.A.; Phillips, D.R.; Fried, V.A.; Campbell, A.M.; Nannizzi, L.; Charo, I.F. Barbourin. A GPIIb-IIIa-specific integrin antagonist from the venom of Sistrurus m. barbouri. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 9359–9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.M.; Mentele, R.; Sampaio, C.A.; Fink, E. Purification, characterization, and amino acid sequence of a serine proteinase, PA-BJ, with platelet-aggregating activity from the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 7186–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.M.; Wang, D.; Shannon, J.D.; Pinto, A.F.; Polanowska-Grabowska, R.K.; Fox, J.W. Interaction of the cysteine-rich domain of snake venom metalloproteinases with the A1 domain of von Willebrand factor promotes site-specific proteolysis of von Willebrand factor and inhibition of von Willebrand factor-mediated platelet aggregation. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 3611–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, K.L. Purification and preliminary characterisation of praelongin phospholipases, antiplatelet agents from the snake venom of Acanthophis praelongus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1379, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subburaju, S.; Kini, R.M. Isolation and purification of superbins I and II from Austrelaps superbus (copperhead) snake venom and their anticoagulant and antiplatelet effects. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunagar, K.; Tsai, I.H.; Lomonte, B.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Fry, B.G. Group II Phospholipase A2 Enzymes. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Reeks, T.; Fry, B.G. Group I Phospholipase A2 Enzymes. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 324–327. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, N.H.; Fry, B.G.; Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Reeks, T.; Fung, S.Y. L-amino acid oxidase enzymes. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Titani, K.; Sakai, Y.; Kaku, S.; Hisamichi, N.; Satoh, N.; Takenaka, T.; et al. Flavocetin-A and -B, two high molecular mass glycoprotein Ib binding proteins with high affinity purified from Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom, inhibit platelet aggregation at high shear stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1244, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikha, M.; De Clerck, Y.A.; Markland, F.S. Contortrostatin, a snake venom disintegrin, inhibits beta 1 integrin-mediated human metastatic melanoma cell adhesion and blocks experimental metastasis. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 4993–4998. [Google Scholar]
- Usami, Y.; Fujimura, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Ozeki, Y.; Nishio, K.; Fukui, H.; Titani, K. Primary structure of two-chain botrocetin, a von Willebrand factor modulator purified from the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usami, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Yoshida, E.; Sakurai, Y.; Hirano, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Titani, K. Primary structure of alboaggregin-B purified from the venom of Trimeresurus albolabris. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 219, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Harrison, R.A.; Bicknell, A.B.; Gibbins, J.M.; Hutchinson, G. Purification and functional characterisation of rhinocerase, a novel serine protease from the venom of Bitis gabonica rhinoceros. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Sunagar, K.; Gibbins, J.M.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Reeks, T.; Fry, B.G. Kallikrein Enzymes In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 267–280. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, G.; Zhao, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Giese, R.W.; Peng, S. Bioassay-directed purification of an acidic phospholipase A(2) from Agkistrodon halys pallas venom. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicka-Patynowski, I.; Niewiarowski, S.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Calvete, J.J.; Marcinkiewicz, M.M.; McLane, M.A. Structural requirements of echistatin for the recognition of alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(5)beta(1) integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37809–37814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Gu, L.; Wang, Q.; Shu, Y.; Lin, Z. Preliminary crystallographic study of an acidic phospholipase A2 from Ophiophagus hannah (king cobra). Acta Crystallographica. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2002, 58, 1836–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngman, N.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dobson, J.S.; Bittenbinder, M.A.; Gillett, A.; Hamilton, B.; Dunstan, N.; Allen, L.; Veary, A.; Veary, E.; et al. Mud in the blood: Novel potent anticoagulant coagulotoxicity in the venoms of the Australian elapid snake genus Denisonia (mud adders) and relative antivenom efficacy. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 302, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdenek, C.N.; Youngman, N.J.; Hay, C.; Dobson, J.; Dunstan, N.; Allen, L.; Milanovic, L.; Fry, B.G. Anticoagulant activity of black snake (Elapidae: Pseudechis) venoms: Potency, mechanisms, and antivenom efficacy. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 330, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wisner, A.; Xiong, Y.; Bon, C. A novel plasminogen activator from snake venom. Purification, characterization, and molecular cloning. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 10246–10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingali, R.B.; Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Guillin, M.C.; Bon, C. Bothrojaracin, a new thrombin inhibitor isolated from Bothrops jararaca venom: Characterization and mechanism of thrombin inhibition. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 10794–10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingali, R.B.; Bianconi, M.L.; Monteiro, R.Q. Interaction of bothrojaracin with prothrombin. Haemostasis 2001, 31, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingali, R.B.; Ferreira, M.S.; Assafim, M.; Frattani, F.S.; Monteiro, R.Q. Bothrojaracin, a Bothrops jararaca snake venom-derived (pro)thrombin inhibitor, as an anti-thrombotic molecule. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005, 34, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, V.G.; Frank, N. The kallikrein-like activity of Heloderma venom is inhibited by carbon monoxide. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2019, 47, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebs, D.; Lomonte, B.; Fernandez, J.; Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Mahlow, K.; Muller, J.; Kohler, G.; Zollweg, M. The earless monitor lizard Lanthanotus borneensis—A venomous animal? Toxicon 2021, 189, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponczek, M.B.; Gailani, D.; Doolittle, R.F. Evolution of the contact phase of vertebrate blood coagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Okumura, Y.; Ohdachi, S.D.; Oba, Y.; Yoshikuni, M.; Kido, H.; Uemura, D. Blarina toxin, a mammalian lethal venom from the short-tailed shrew Blarina brevicauda: Isolation and characterization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7542–7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debono, J.; Bos, M.H.A.; Frank, N.; Fry, B. Clinical implications of differential antivenom efficacy in neutralising coagulotoxicity produced by venoms from species within the arboreal viperid snake genus Trimeresurus. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 316, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debono, J.; Bos, M.H.A.; Nouwens, A.; Ge, L.; Frank, N.; Kwok, H.F.; Fry, B.G. Habu coagulotoxicity: Clinical implications of the functional diversification of Protobothrops snake venoms upon blood clotting factors. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 55, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, A.; Koludarov, I.; Mikheyev, A.S. Co-option of the same ancestral gene family gave rise to mammalian and reptilian toxins. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debono, J.; Bos, M.H.A.; Coimbra, F.; Ge, L.; Frank, N.; Kwok, H.F.; Fry, B.G. Basal but divergent: Clinical implications of differential coagulotoxicity in a clade of Asian vipers. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 58, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, J.; Bos, M.H.A.; Do, M.S.; Fry, B.G. Clinical implications of coagulotoxic variations in Mamushi (Viperidae: Gloydius) snake venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 225, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneci, L.; Zdenek, C.N.; Bourke, L.A.; Cochran, C.; Sanchez, E.E.; Neri-Castro, E.; Benard-Valle, M.; Alagon, A.; Frank, N.; Fry, B.G. A symphony of destruction: Dynamic differential fibrinogenolytic toxicity by rattlesnake (Crotalus and Sistrurus) venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 245, 109034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, F. Diet of a large carnivorous lizard, Varanus varius. Wildl. Res. 2001, 28, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, D.C.; Jones, A.A. Varanus varius (lace monitor, common goanna): Diet. Herpetol. Bull. 2012, 40, 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, M.E.; Douglas, M.R.; Schuett, G.W.; Beck, D.D.; Sullivan, B.K. Conservation phylogenetics of helodermatid lizards using multiple molecular markers and a supertree approach. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 55, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, N.J.; Chowdhury, A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Coster, K.; Sundman, E.; Braun, R.; Fry, B.G. Utilising venom activity to infer dietary composition of the Kenyan horned viper (Bitis worthingtoni). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2021, 240, 108921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngman, N.J.; Debono, J.; Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Harris, R.J.; Op den Brouw, B.; Coimbra, F.C.P.; Naude, A.; Coster, K.; Sundman, E.; et al. Venomous Landmines: Clinical Implications of Extreme Coagulotoxic Diversification and Differential Neutralization by Antivenom of Venoms within the Viperid Snake Genus Bitis. Toxins 2019, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, V.; Debono, J.; Goldenberg, J.; Jackson, T.N.; Arbuckle, K.; Dobson, J.; Koludarov, I.; Li, B.; Hay, C.; Dunstan, N. Correlation between ontogenetic dietary shifts and venom variation in Australian brown snakes (Pseudonaja). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 197, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, T.N.; Koludarov, I.; Ali, S.A.; Dobson, J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dashevsky, D.; Op den Brouw, B.; Masci, P.P.; Nouwens, A.; Josh, P.; et al. Rapid Radiations and the Race to Redundancy: An Investigation of the Evolution of Australian Elapid Snake Venoms. Toxins 2016, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, D.D. Biology of Gila Monsters and Beaded Lizards; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2005; p. 212. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Lozano, J.L.; de Sousa, M.V.; Ricart, C.A.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Flores Sanchez, E.; Muniz, E.G.; Buhrnheim, P.F.; Morhy, L. Ontogenetic variation of metalloproteinases and plasma coagulant activity in venoms of wild Bothrops atrox specimens from Amazonian rain forest. Toxicon 2002, 40, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackessy, S.P. Fibrinogenolytic proteases from the venoms of juvenile and adult northern Pacific rattlesnakes (Crotalus viridis oreganus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Comp. Biochem. 1993, 106, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneci, L.; Zdenek, C.N.; Chowdhury, A.; Rodrigues, C.F.B.; Neri-Castro, E.; Benard-Valle, M.; Alagon, A.; Fry, B.G. A Clot Twist: Extreme Variation in Coagulotoxicity Mechanisms in Mexican Neotropical Rattlesnake Venoms. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 612846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, D.D. Ecology and behavior of the gila monster in southwestern Utah. J. Herpetol. 1990, 24, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.D.; Lowe, C.H. Ecology of the beaded lizard, Heloderma horridum, in a tropical dry forest in jalisco, mexico. J. Herpetol. 1991, 25, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, Y.; Nikai, T.; Sugihara, H. Purification and characterization of a lethal toxin from the venom of Heloderma horridum horridum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 154, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdenek, C.N.; Chowdhury, A.; Haw, G.Y.H.; Violette, A.; Fourmy, R.; Christ, T.; Vonk, F.J.; Fry, B.G. Taxon-selective venom variation in adult and neonate Daboia russelii (Russell’s Viper), and antivenom efficacy. Toxicon 2022, 205, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, I.G.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Portik, D.M.; Weijola, V.; Welton, L.; Donnellan, S.C.; Keogh, J.S. Phylogenomics of monitor lizards and the role of competition in dictating body size disparity. Syst. Biol. 2021, 70, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Champagne, D.E.; Scheib, H.; Tyndall, J.D.; King, G.F.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Norman, J.A.; Lewis, R.J.; Norton, R.S.; et al. The toxicogenomic multiverse: Convergent recruitment of proteins into animal venoms. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Reeks, T.; Kwok, H.F. B-type natriuretic peptides. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 312–317. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Dashevsky, D.; Rokyta, D.; Ghezellou, P.; Fathinia, B.; Shi, Q.; Richardson, M.K.; Fry, B.G. Dynamic genetic differentiation drives the widespread structural and functional convergent evolution of snake venom proteinaceous toxins. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, H.F.; Chen, T.; O’Rourke, M.; Ivanyi, C.; Hirst, D.; Shaw, C. Helokinestatin: A new bradykinin B-2 receptor antagonist decapeptide from lizard venom. Peptides 2008, 29, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.; Kwok, H.; Ivanyi, C.; Shaw, C. The structure of helokinestatin-5 and its biosynthetic precursor from Gila monster (Heloderma suspectum) venom: Evidence for helokinestatin antagonism of bradykinin-induced relaxation of rat tail artery smooth muscle. Peptides 2010, 31, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundemar, L.; Högestätt, E.D. Vascular effects of helodermin, helospectin I and helospectin II: A comparison with vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). Br. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 99, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konturek, S.J.; Yanaihara, N.; Pawlik, W.; Jaworek, J.; Szewczyk, K. Comparison of helodermin, VIP and PHI in pancreatic secretion and blood flow in dogs. Regul. Pept. 1989, 24, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruse, S.; Yasui, A.; Kishida, S.; Kadowaki, M.; Hoshino, M.; Ozaki, T.; Robberecht, P.; Christophe, J.; Yanaihara, C.; Yanaihara, N. Helodermin has a VIP-like effect upon canine blood flow. Peptides 1986, 7, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, N.; Williams, V. Practical applications of snake venom toxins in haemostasis. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Lewin, M.R.; Carter, R.W.; Casewell, N.R.; Fry, B.G. Keel venom: Rhabdophis subminiatus (Red-Necked Keelback) venom pathophysiologically affects diverse blood clotting pathways. Toxicon 2022, 218, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.; Youngman, N.J.; Neri-Castro, E.; Guadarrama-Martinez, A.; Lewin, M.R.; Carter, R.; Frank, N.; Fry, B.G. Differential antivenom and small-molecule inhibition of novel coagulotoxic variations in Atropoides, Cerrophidion, Metlapilcoatlus, and Porthidium American viperid snake venoms. Toxins 2022, 14, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagaki, T.; Lin, P.; Kisiel, W. Activation of human factor VII by the prothrombin activator from the venom of Oxyuranus scutellatus (Taipan snake). Thromb. Res. 1992, 65, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Factor Inhibition | Methodology Details |
|---|---|
| FIXa | Step 1: 50 μL venom + 50 μL 0.025 M calcium + 25 μL OK buffer + 50 μL PPL + 25 μL Factor IXa (15 μg/mL) (HTI cat. #HCXIA-0160) Step 2: 120 s incubation at 37 °C Step 3: Addition of 75 μL human plasma |
| FXIa | Step 1: 50 μL venom + 50 μL 0.025 M calcium + 25 μL OK buffer + 50 μL PPL + 25 μL Factor XIa (15 μg/mL) (Haemonetics Technologies Incorporated (HTI) cat. #HCXIA-0160) Step 2: 120 s incubation at 37 °C Step 3: Addition of 75 μL human plasma |
| FXa | Step 1: 50 μL venom + 50 μL 0.025 M calcium + 25 μL OK buffer + 50 μL PPL + 25 μL Factor Xa Step 2: 120 s incubation at 37 °C Step 3: Addition of 75 μL human plasma |
| Thrombin | Step 1: 50 μL venom + 50 μL 0.025 M calcium + 25 μL OK buffer + 50 μL PPL + 25 μL thrombin (Stago Liquid Fib kit cat. #00611) Step 2: 120 s incubation at 37 °C Step 3: Addition of 75 μL human plasma |
| Human Zymogen Activation Assays | Methodology Details |
|---|---|
| Blank wells | 20 μL of enzyme buffer without calcium (150 mM NaCl, and 50 mM Tri-HCl (pH 7.3) + 10 μL PPL |
| FVII, FIX, FX, FXI, FXII, Prothrombin control wells | 10 μL of enzyme buffer without calcium (150 mM NaCl, and 50 mM Tri-HCl (pH 7.3) + 10 μL phospholipid (PPL) + 10 μL (10 μg/mL FVII or FIX, FX, FXI, FXII) or 1 μg/mL prothrombin. |
| FVIIa, FIXa, FXIa, FXIIa, Thrombin control wells | 10 μL of enzyme buffer without calcium (150 mM NaCl, and 50 mM Tri-HCl (pH 7.3) + 10 μL PPL + 10 μL (10 μg/mL FVIIa or FIXa, FXa, FXIa)(replaced with 10 μL kaolin (5 mg of kaolin/mL for FXIIa control) or 1 μg/mL Thrombin). |
| Venom control wells | 10 μL of enzyme buffer without calcium (150 mM NaCl, and 50 mM Tri-HCl (pH 7.3) + 10 μL PPL + 10 μL venom (50 μg/mL). |
| Venom + zymogen wells | 10 μL zymogen (10 μg/mL FVII or FIX, FX, FXI, FXII or 1 μg/mL prothrombin) + 10 μL PPL + 10 μL venom (50 μg/mL) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobson, J.; Chowdhury, A.; Tai-A-Pin, J.; van der Ploeg, H.; Gillett, A.; Fry, B.G. The Clot Thickens: Differential Coagulotoxic and Cardiotoxic Activities of Anguimorpha Lizard Venoms. Toxins 2024, 16, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16060283
Dobson J, Chowdhury A, Tai-A-Pin J, van der Ploeg H, Gillett A, Fry BG. The Clot Thickens: Differential Coagulotoxic and Cardiotoxic Activities of Anguimorpha Lizard Venoms. Toxins. 2024; 16(6):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16060283
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobson, James, Abhinandan Chowdhury, Jeremie Tai-A-Pin, Harold van der Ploeg, Amber Gillett, and Bryan G. Fry. 2024. "The Clot Thickens: Differential Coagulotoxic and Cardiotoxic Activities of Anguimorpha Lizard Venoms" Toxins 16, no. 6: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16060283
APA StyleDobson, J., Chowdhury, A., Tai-A-Pin, J., van der Ploeg, H., Gillett, A., & Fry, B. G. (2024). The Clot Thickens: Differential Coagulotoxic and Cardiotoxic Activities of Anguimorpha Lizard Venoms. Toxins, 16(6), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16060283






