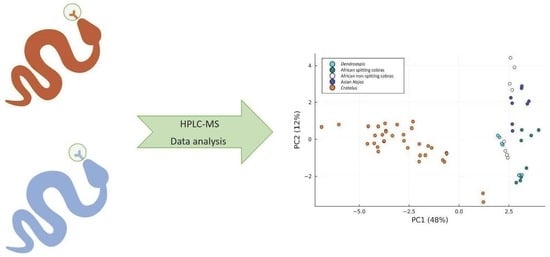
Metabolome-Based Classification of Snake Venoms by Bioinformatic Tools
Abstract
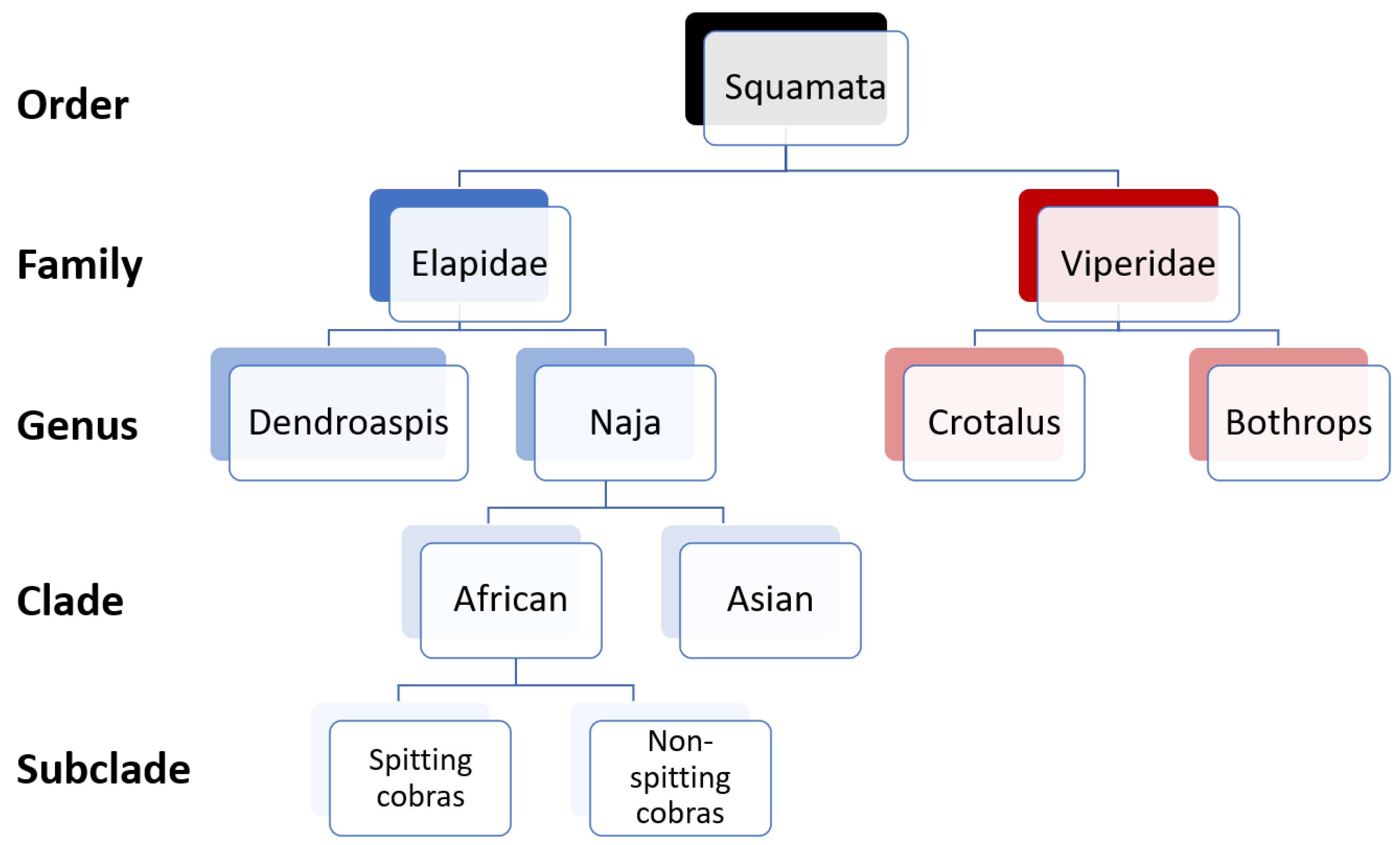
1. Introduction
2. Results
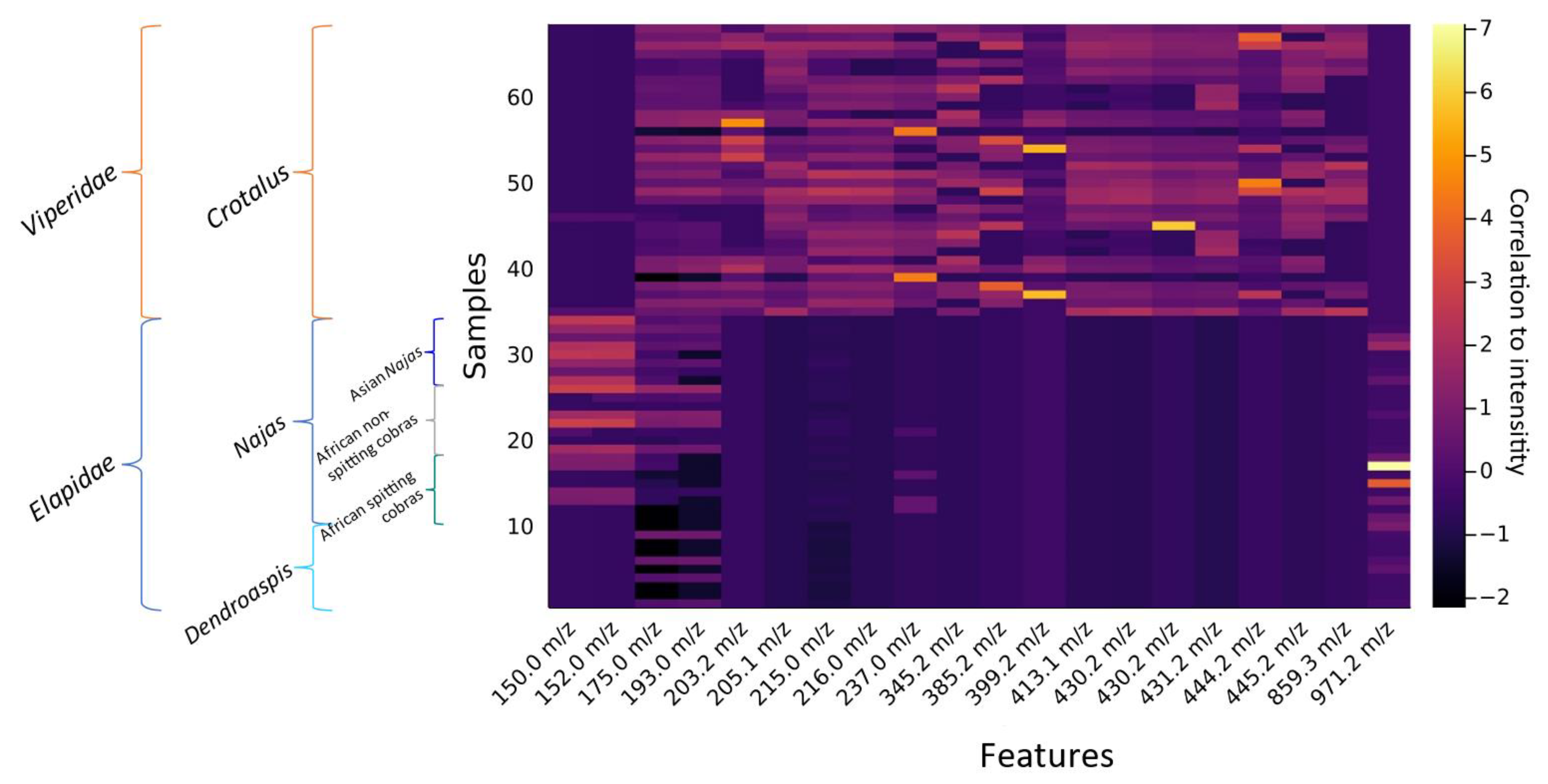
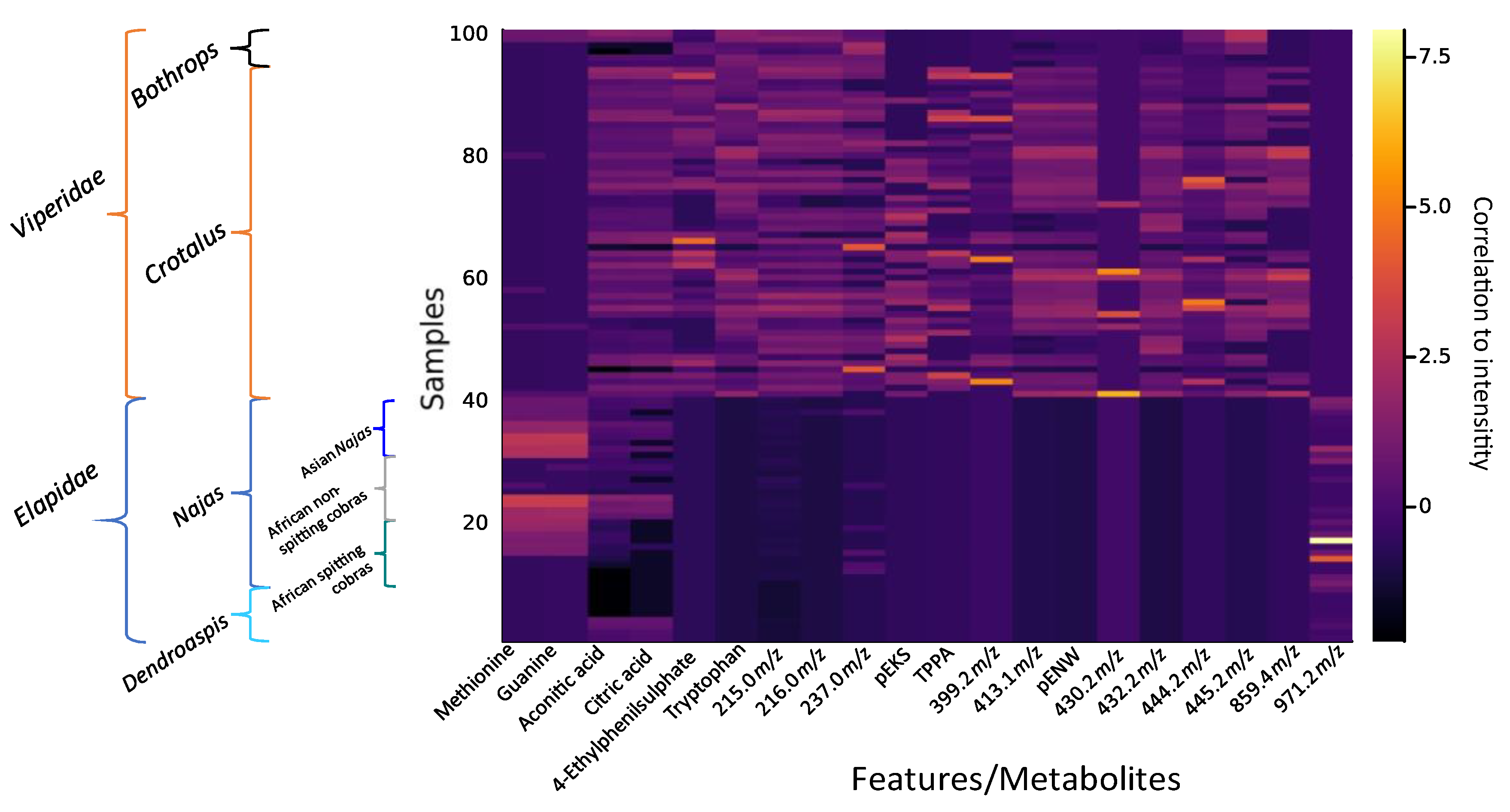
2.1. Feature Extraction
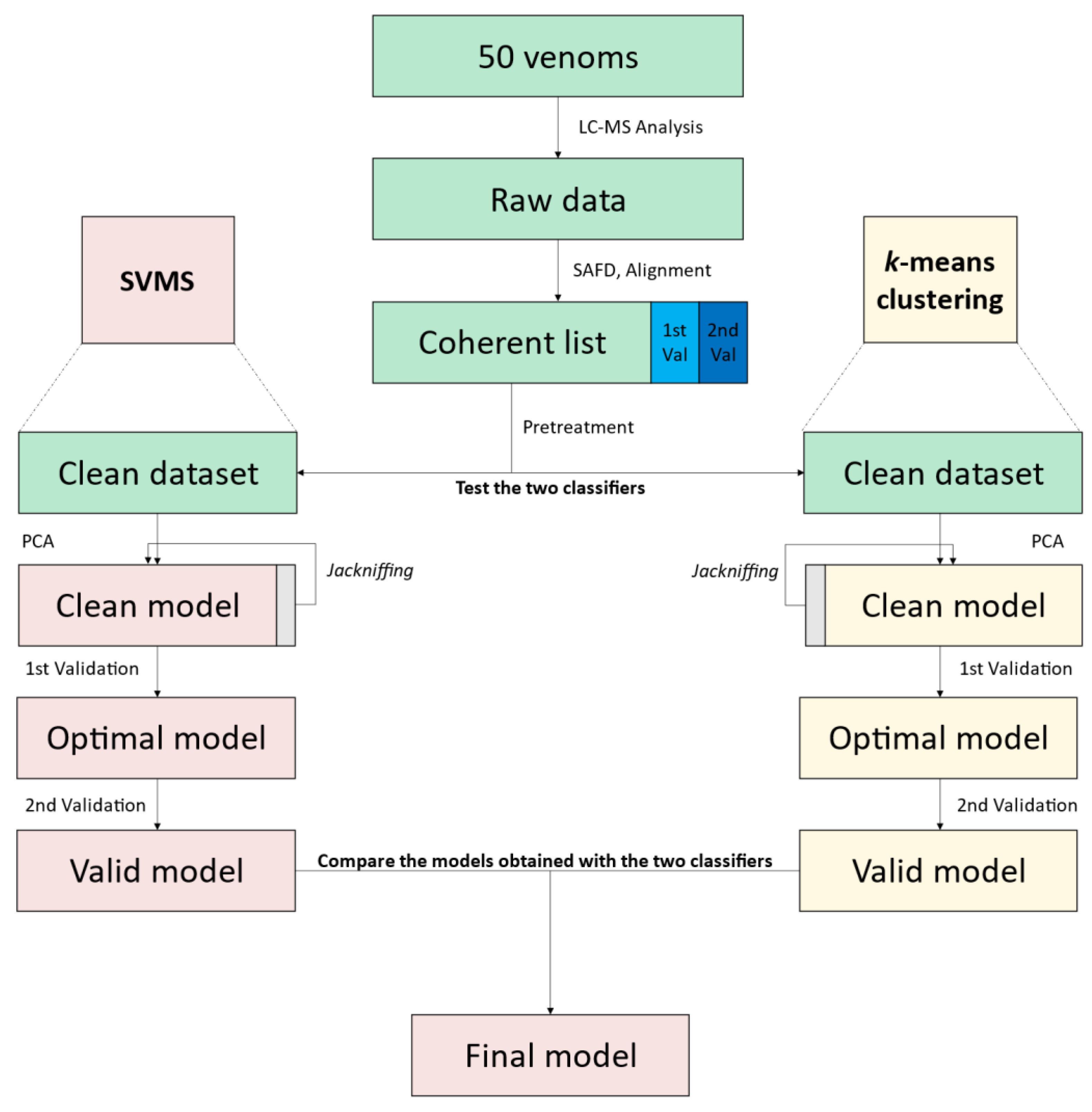
2.2. Model Building
2.3. Classification
2.4. Workflow
2.4.1. Model That Used k-Means Clustering
2.4.2. Model That Used Support Vector Machines
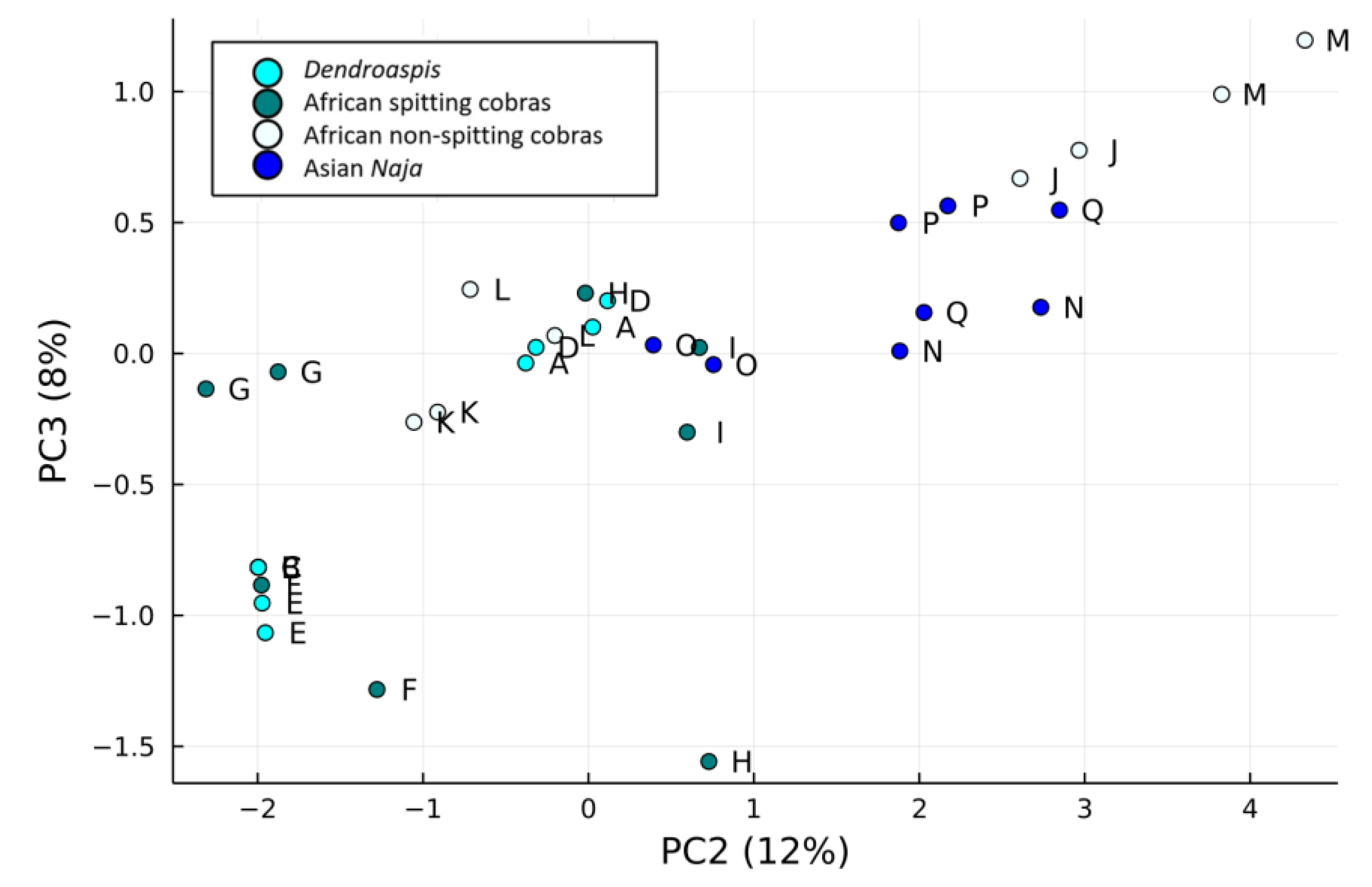
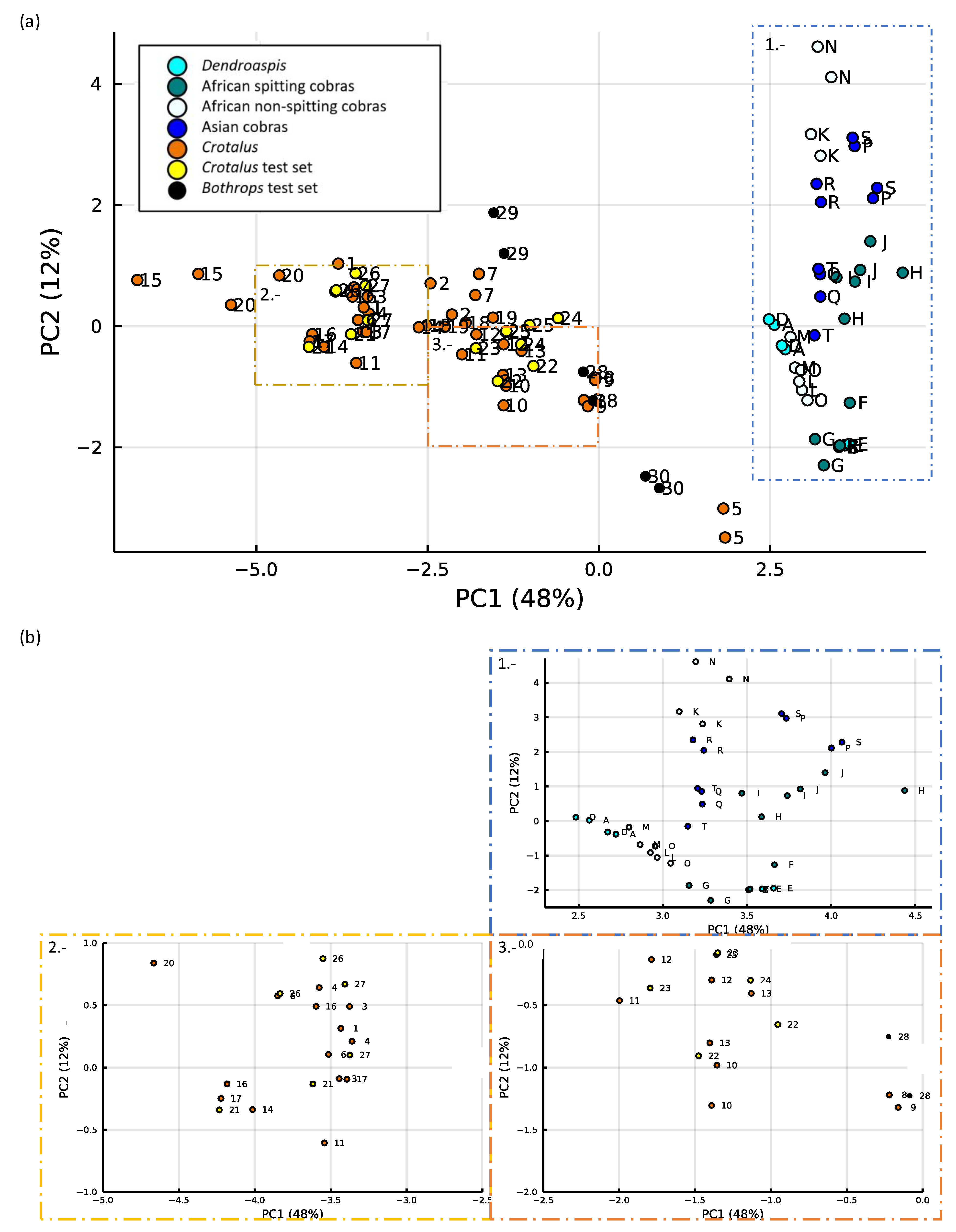
2.5. Results of PCA of the Small Molecules Found in Snake Venom
2.5.1. k-Means Clustering
2.5.2. Support Vector Machines
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemical and Biological Reagents
5.2. Analysis of Small Molecules
5.2.1. Separation
5.2.2. Detection
5.2.3. Data Processing
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hotez, P.J.; Aksoy, S.; Brindley, P.J.; Kamhawi, S. What constitutes a neglected tropical disease? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.-P. Snakebite envenomation turns again into a neglected tropical disease! J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohapatra, B.; Warrell, D.A.; Suraweera, W.; Bhatia, P.; Dhingra, N.; Jotkar, R.M.; Rodriguez, P.S.; Mishra, K.; Whitaker, R.; Jha, P.; et al. Snakebite Mortality in India: A Nationally Representative Mortality Survey. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Scheib, H.; van der Weerd, L.; Young, B.; McNaughtan, J.; Ramjan, S.F.R.; Vidal, N.; Poelmann, R.E.; Norman, J.A. Evolution of an Arsenal. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 215–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slagboom, J.; Kool, J.; Harrison, R.A.; Casewell, N.R. Haemotoxic snake venoms: Their functional activity, impact on snakebite victims and pharmaceutical promise. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Arrahman, A.; Xie, C.; Casewell, N.R.; Lewis, R.J.; Kool, J.; Cardoso, F.C. Multifunctional Toxins in Snake Venoms and Therapeutic Implications: From Pain to Hemorrhage and Necrosis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Briones, A.; Aird, S. Organic and Peptidyl Constituents of Snake Venoms: The Picture Is Vastly More Complex Than We Imagined. Toxins 2018, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, S.; Villar Briones, A.; Roy, M.; Mikheyev, A. Polyamines as Snake Toxins and Their Probable Pharmacological Functions in Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex cocktails: The evolutionary novelty of venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, D.A.; Savitzky, A.H.; Burghardt, G.M.; Nguyen, C.; Meinwald, J.; Schroeder, F.C.; Mori, A. Chemical defense of an A sian snake reflects local availability of toxic prey and hatchling diet. J. Zool. 2013, 289, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.-F.; Hung, C.-C.; Wu, S.-H.; Chiou, S.-H. Characterization of Three Endogenous Peptide Inhibitors for Multiple Metalloproteinases with Fibrinogenolytic Activity from the Venom of Taiwan Habu (Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 248, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Guidelines for the Prevention and Clinical Management of Snakebite in Africa; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Alape-Girón, A.; Sanz, L.; Escolano, J.; Flores-Díaz, M.; Madrigal, M.; Sasa, M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake Venomics of the Lancehead Pitviper Bothrops asper: Geographic, Individual, and Ontogenetic Variations. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3556–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, F.; Costa, T.; Baiwir, D.; De Pauw, E.; Quinton, L.; Sampaio, S. Proteopeptidomic, Functional and Immunoreactivity Characterization of Bothrops moojeni Snake Venom: Influence of Snake Gender on Venom Composition. Toxins 2018, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, I.S.; Cardoso, I.A.; de Castro Figueiredo Bordon, K.; Carone, S.E.I.; Boldrini-França, J.; Pucca, M.B.; Zoccal, K.F.; Faccioli, L.H.; Sampaio, S.V.; Rosa, J.C.; et al. Global proteomic and functional analysis of Crotalus durissus collilineatus individual venom variation and its impact on envenoming. J. Proteom. 2019, 191, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, Y.; Isbister, G.K.; Mirtschin, P.; Hodgson, W.C.; Konstantakopoulos, N. Validation of a cell-based assay to differentiate between the cytotoxic effects of elapid snake venoms. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2011, 63, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazandjian, T.D.; Petras, D.; Robinson, S.D.; Van Thiel, J.; Greene, H.W.; Arbuckle, K.; Barlow, A.; Carter, D.A.; Wouters, R.M.; Whiteley, G.; et al. Convergent evolution of pain-inducing defensive venom components in spitting cobras. Science 2022, 371, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. LIII. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quenouille, M.H. Approximate Tests of Correlation in Time-Series. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1949, 11, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, J. Some Methods for Classification and Analysis of Multivariate Observations. In Multivariate Observations; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 1967; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Boser, B.E.; Guyon, I.M.; Vapnik, V.N. A training algortihm for optimal margin classifiers. In Proceedings of the COLT ’92: Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–29 July 1992; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catell, R.B. The scree test for the number of factors. Multiva. Behav. Res. 1966, 1, 140–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfarouk, K.O.; Ahmed, S.B.M.; Elliott, R.L.; Benoit, A.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Ibrahim, M.E.; Orozco, J.D.P.; Cardone, R.A.; Reshkin, S.J.; Harguindey, S. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Dynamics in Cancer and Its Dependency on Intracellular pH. Metabolites 2020, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucl. Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisdorph, N.A.; Walmsley, S.; Reisdorph, R. A Perspective and Framework for Developing Sample Type Specific Databases for LC/MS-Based Clinical Metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odell, G.V.; Ferry, P.C.; Vick, L.M.; Fenton, A.W.; Decker, L.S.; Cowell, R.L.; Ownby, C.L.; Gutierrez, J.M. Citrate inhibition of snake venom proteases. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.; Madore, F. Role of citrate and other methods of anticoagulation in patients with severe liver failure requiring continuous renal replacement therapy. Clin. Kidney J. 2009, 2, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagides, N.; Jackson, T.; Ikonomopoulou, M.; Arbuckle, K.; Pretzler, R.; Yang, D.; Ali, S.A.; Koludarov, I.; Dobson, J.; Sanker, B.; et al. How the Cobra Got Its Flesh-Eating Venom: Cytotoxicity as a Defensive Innovation and Its Co-Evolution with Hooding, Aposematic Marking, and Spitting. Toxins 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, S.H.; Friis, R.U.W.; Petersen, S.D.; Martos-Esteban, A.; Lautsen, A.H. Snake Venomics Display: An online toolbox for visualization of snake venomics data. Toxicon 2018, 152, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, K.; Pitts, M.; Tongyoo, P.; Rojnuckarin, P.; Wilkinson, M. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases and Their Peptide Inhibitors from Myanmar Russell’s Viper Venom. Toxins 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, B.; Kaiser, I.I. Inhibition of metalloproteinases in Bothrops asper venom by endogenous peptides. Toxicon 1993, 31, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robeva, A.; Politi, V.; Shannon, J.D.; Bjarnason, J.B.; Fox, J.W. Synthetic and endogenous inhibitors of snake venom metalloproteinases. Biomed. Biochim. Acta 1991, 50, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Santis, M.C.; Porporato, P.E.; Martini, M.; Morandi, A. Signaling Pathways Regulating Redox Balance in Cancer Metabolism. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanipour, S.; O’Brien, J.W.; Reid, M.J.; Thomas, K.V. Self Adjusting Algorithm for the Nontargeted Feature Detection of High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Coupled with Liquid Chromatography Profile Data. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10800–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Qualitative Classification | Thresholds |
|---|---|
| Hard hits | (80, 100] % |
| Hits | (55, 80] % |
| Unsure | (45, 55] % |
| Miss | (20, 45] % |
| Hard miss | [0, 20] % |
| Feature | Metabolite | m/z-Value | Average Retention Time (min) | Confidence Level (MSI) | Mostly Seen in the Clade: |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Methionine (1) | 149.95 | 4.2 | 1 | Asian cobras |
| 2 | Guanine (1) | 151.95 | 4.4 | 2 | Asian cobras |
| 3 | Aconitic acid (1) | 175.02 | 5.3 | 2 | All but African spitting cobras |
| 4 | Citric acid (1) | 193.03 | 5.3 | 1 | All but African spitting cobras |
| 5 | 4-Ethylphenilsulphate (2) | 203.22 | 4.3 | 2 | Bothrops and Crotalus |
| 6 | Tryptophan (1) | 204.10 | 17.5 | 1 | Crotalus |
| 7 | Deoxyribose 5-monophosphate (2) | 215.02 | 5.1 | - | All but Dendroaspis |
| 8 | O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine (2) | 216.02 | 5.1 | - | Bothrops and Crotalus |
| 9 | [Unknown]Na+ | 237.00 | 4.9 | - | Bothrops and Crotalus |
| 10 | pEKS (tripeptide) (1) | 345.18 | 5.1 | 2 | Crotalus |
| 11 | TPPA (tetrapeptide) (1) | 385.21 | 5.2 | 2 | Crotalus |
| 12 | pERI (tripeptide) (1) | 399.24 | 13.2 | - | Crotalus |
| 13 | Unknown | 413.15 | 16.2 | - | Crotalus |
| 14 | pENW (tripeptide) (1) | 430.17 | 16.3 | 2 | Bothrops and Crotalus |
| 15 | Unknown | 430.27 | 16.3 | - | Crotalus |
| 16 | Unknown | 431.17 | 16.0 | - | Bothrops and Crotalus |
| 17 | Unknown | 444.20 | 16.2 | - | Bothrops and Crotalus |
| 18 | Unknown | 445.19 | 16.4 | - | Bothrops and Crotalus |
| 19 | Unknown | 859.34 | 16.1 | - | Crotalus |
| 20 | Unknown | 971.17 | 17.8 | - | African spitting cobras |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alonso, L.L.; Slagboom, J.; Casewell, N.R.; Samanipour, S.; Kool, J. Metabolome-Based Classification of Snake Venoms by Bioinformatic Tools. Toxins 2023, 15, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020161
Alonso LL, Slagboom J, Casewell NR, Samanipour S, Kool J. Metabolome-Based Classification of Snake Venoms by Bioinformatic Tools. Toxins. 2023; 15(2):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020161
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlonso, Luis L., Julien Slagboom, Nicholas R. Casewell, Saer Samanipour, and Jeroen Kool. 2023. "Metabolome-Based Classification of Snake Venoms by Bioinformatic Tools" Toxins 15, no. 2: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020161
APA StyleAlonso, L. L., Slagboom, J., Casewell, N. R., Samanipour, S., & Kool, J. (2023). Metabolome-Based Classification of Snake Venoms by Bioinformatic Tools. Toxins, 15(2), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020161