Purification and Mechanism of Microcystinase MlrC for Catalyzing Linearized Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxins Using Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
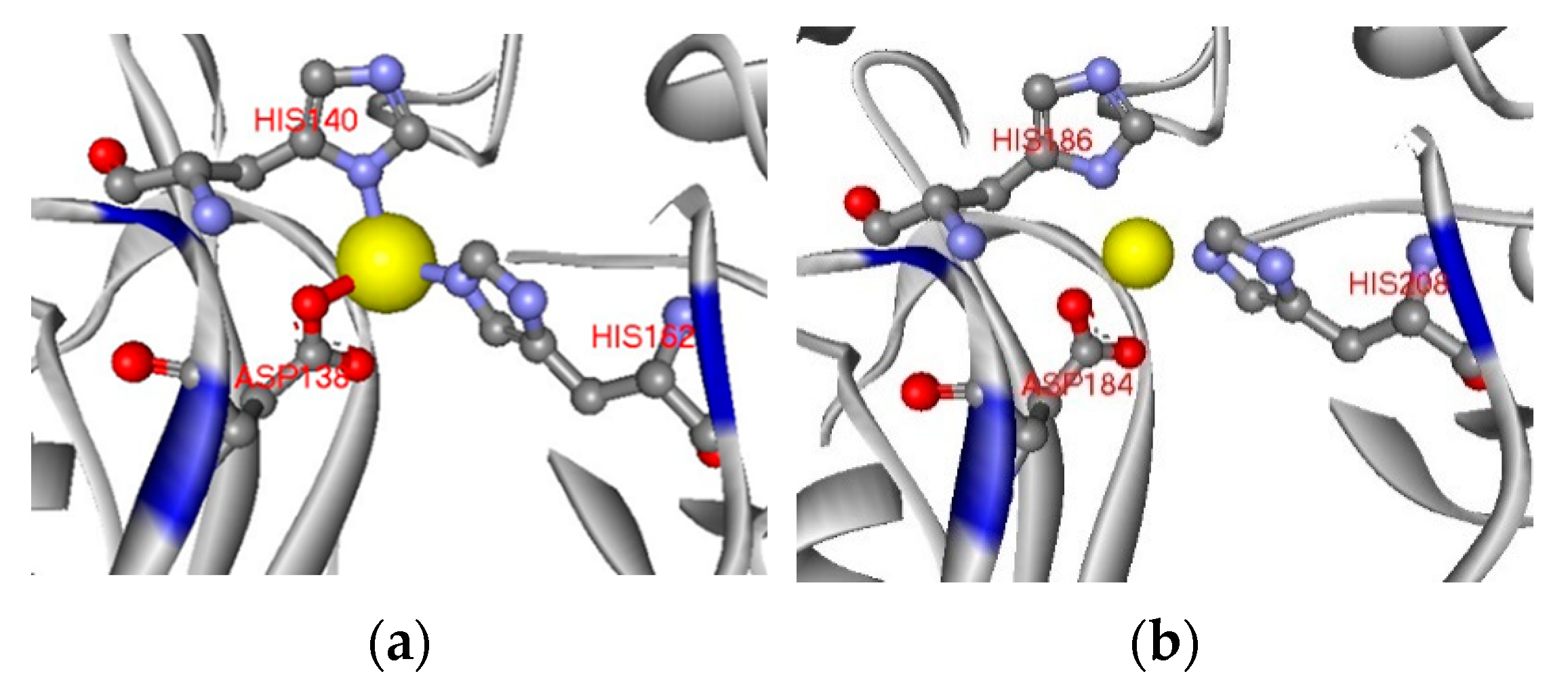
2.1. Homology Modeling of USTB-05-C
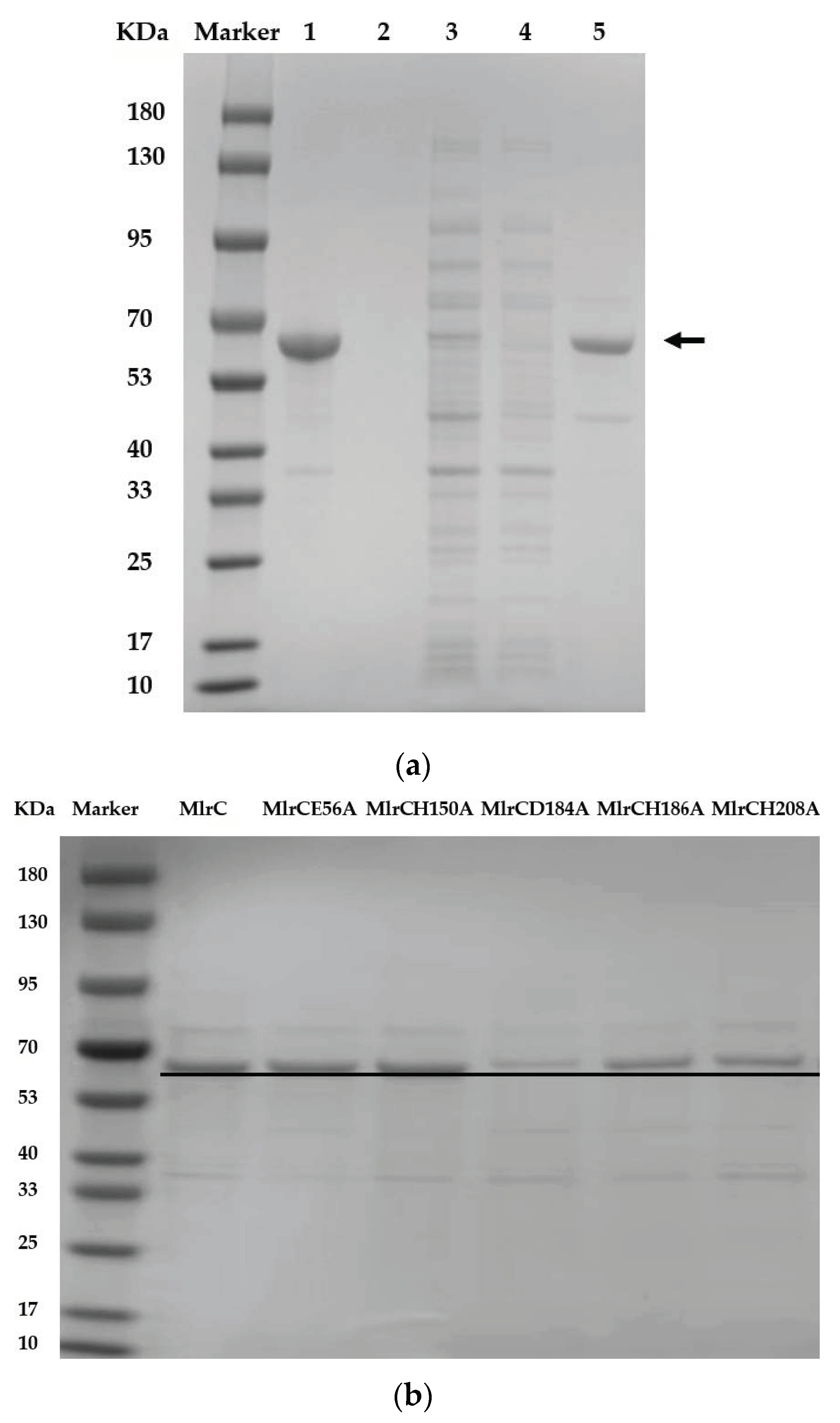
2.2. Purification of Recombinant USTB-05-C
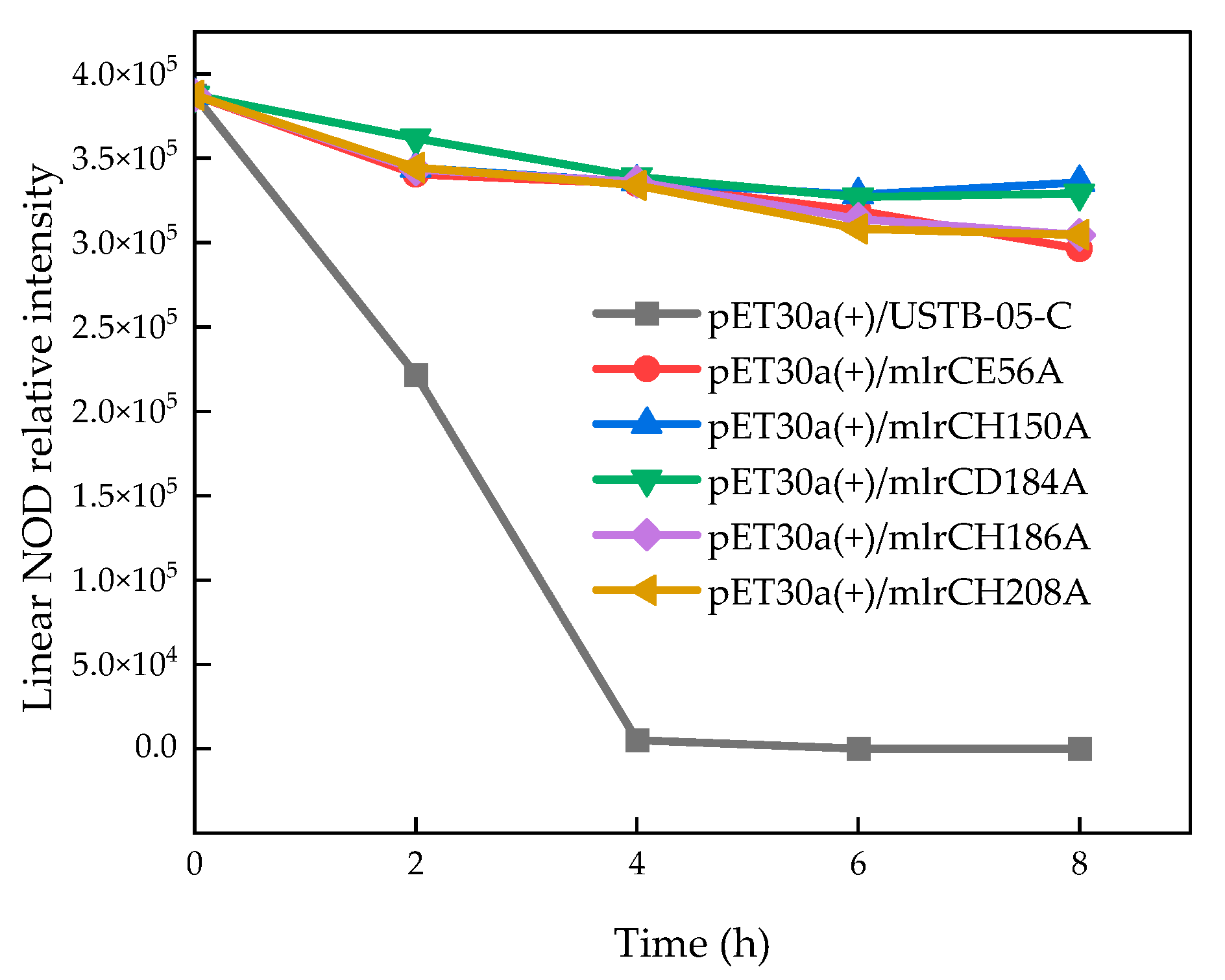
2.3. Enzyme Activity
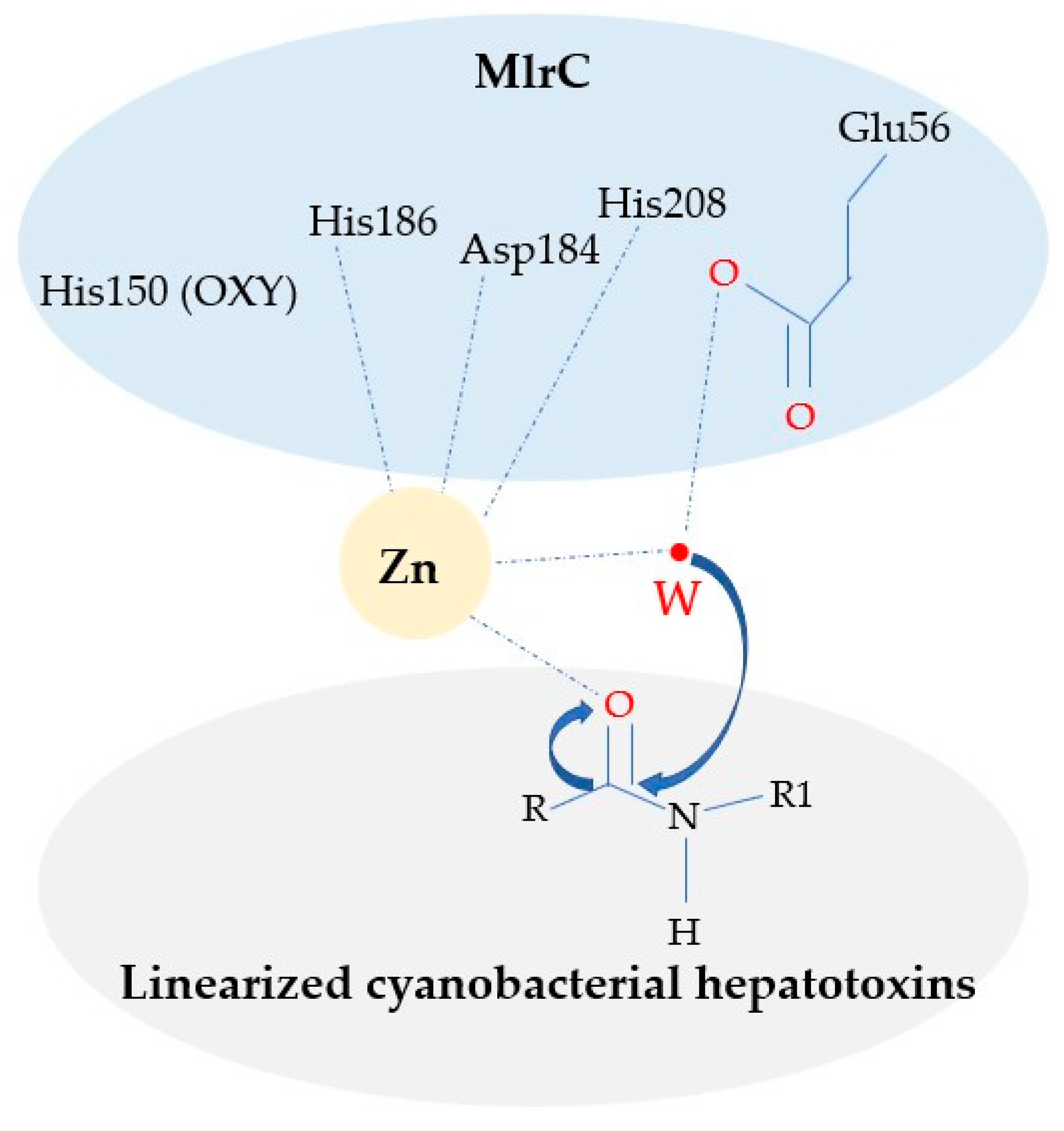
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Strain and Mutagenesis
5.2. Homology Modeling
5.3. Cloning and Expression of Mutant Recombinants
5.4. Purification of USTB-05-C
5.5. Determination of Enzyme Activity
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Qu, G.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Wang, T. Elimination of Microcystis aeruginosa in water via dielectric barrier discharge plasma: Efficacy, mechanism and toxin release. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Gao, L.; Zamyadi, A.; Glover, C.M.; Ma, N.; Wu, H.; Li, M. Multi-proxy approaches to investigate cyanobacteria invasion from a eutrophic lake into the circumjacent groundwater. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanchett, G.; Oliveira-Filho, E.C. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins: From impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human health to anticarcinogenic effects. Toxins 2013, 5, 1896–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harke, M.J.; Steffen, M.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Otten, T.G.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Wood, S.A.; Paerl, H.W. A review of the global ecology, genomics, and biogeography of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis spp. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, E.P.; Hardy, F.J.; Moore, B.C.; Bryan, M. A review of microcystin detections in Estuarine and Marine waters: Environmental implications and human health risk. Harmful Algae 2017, 61, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, L.; Mihali, T.; Moffitt, M.; Kellmann, R.; Neilan, B. On the Chemistry, Toxicology and Genetics of the Cyanobacterial Toxins, Microcystin, Nodularin, Saxitoxin and Cylindrospermopsin. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1650–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernoff, N.; Hill, D.; Lang, J.; Schmid, J.; Le, T.; Farthing, A.; Huang, H. The Comparative Toxicity of 10 Microcystin Congeners Administered Orally to Mice: Clinical Effects and Organ Toxicity. Toxins 2020, 12, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, F.; Feng, H.; Wei, J.; Massey, I.Y.; Liang, G.; Zhang, F.; Yin, L.; Kacew, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. A complete route for biodegradation of potentially carcinogenic cyanotoxin microcystin-LR in a novel indigenous bacterium. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Wei, J.; Huang, F.; Feng, H.; Peng, T.; Luo, J.; Yang, F. The detoxification activities and mechanisms of microcystinase towards MC-LR. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2022, 236, 113436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Xie, X.; Huang, F.; Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Han, T.; Massey, I.Y.; Liang, G.; Pu, Y.; Yang, F. Simultaneous Microcystis algicidal and microcystin synthesis inhibition by a red pigment prodigiosin. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, J.; Li, J. Functional and structural analyses for MlrC enzyme of Novosphingobium sp. THN1 in microcystin-biodegradation: Involving optimized heterologous expression, bioinformatics and site-directed mutagenesis. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Eschedor, J.T.; Patterson, G.M.; Moore, R.E. Toxicity and partial structure for a hepatotoxic peptide produced by Nodularia spumigena Mertens emend. Toxicon 1989, 27, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Toruńska, A.; Bolałek, J.; Pliński, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Biodegradation and sorption of nodularin (NOD) in finegrained sediments. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Chorus, I. Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater “seafood” and its consequences for public health: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullerjahn, G.S.; McKay, R.M.; Davis, T.W.; Baker, D.B.; Boyer, G.L.; D’Anglada, L.V.; Doucette, G.J.; Ho, J.C.; Irwin, E.G.; Kling, C.L.; et al. Global solutions to regional problems: Collecting global expertise to address the problem of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. A Lake Erie case study. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, A.M.; Anderson, E.J.; Beletsky, D.; Boland, S.; Bosch, N.S.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Chaffin, J.D.; Cho, K.; Confesor, R.; Daloglu, I.; et al. Record-setting algal bloom in Lake Erie caused by agricultural and meteorological trends consistent with expected future conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6448–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.; Li, J. Current research scenario for microcystins biodegradation-A review on fundamental knowledge, application prospects and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F. Importance of bacterial biodegradation and detoxification processes of microcystins for environmental health. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2018, 21, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Tang, T.; Monis, P.T.; Hoefel, D. Biodegradation of multiple cyanobacterial metabolites in drinking water supplies. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Asakawa, M.; Anzai, Y.; Sumino, T.; Harada, K. Degradation of microcystins using immobilized microorganism isolated in an eutrophic lake. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, J.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, X. Blood-brain barrier disruption and inflammation reaction in mice after chronic exposure to Microcystin-LR. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 689, 662–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Kotlarska, E.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Biodegradation of nodularin and other nonribosomal peptides by the Baltic bacteria. Inter. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2018, 134, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Riddles, P.; Jones, G.J.; Smith, W.; Blakeley, R.L. Characterisation of a gene cluster involved in bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin LR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 16, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, D.G.; Jones, G.J.; Blakeley, R.L.; Jones, A.; Negri, A.P.; Riddles, P. Enzymatic pathway for the bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin LR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4086–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, N.; Yang, F.; Yan, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Q.; Lv, L.; Wang, H. Pathway for Biodegrading Nodularin (NOD) by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Toxins 2016, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Lv, L.; Yin, C.; Liu, X.; Du, H.; Yan, H. Pathway for Biodegrading Microcystin-YR by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124425. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Fan, J.; Yan, H.; Ahmad, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Structural basis of microcystinase activity for biodegrading microcystin-LR. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, A.; Dong, Y.Y.; Pike, A.C.W.; Dong, L.; Shrestha, L.; Berridge, G.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Sansom, M.S.P.; Edwards, A.M.; Bountra, C.; et al. The Structural Basis of ZMPSTE24-Dependent Laminopathies. Science 2013, 339, 1604–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziga, D.; Zielinska, G.; Wladyka, B.; Bochenska, O.; Maksylewicz, A.; Strzalka, W.; Meriluoto, J. Characterization of Enzymatic Activity of MlrB and MlrC Proteins Involved in Bacterial Degradation of Cyanotoxins Microcystins. Toxins 2016, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ma, H.; Fan, J.; Yan, H.; Zhang, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Cloning and Expression of Genes for Biodegrading Nodularin by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Toxins 2019, 11, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormas, K.A.; Lymperopoulou, D.S. Cyanobacterial toxin degrading bacteria: Who are they? BioMed res. Int. 2013, 2013, 463894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashile, G.P.; Mpupa, A.; Dimpe, M.K.; Nomngongo, P.N. Magnetic activated carbon@ iron oxide@manganese oxide composite as an adsorbent for preconcentration of microcystin –LR in surface water, tap water, water and wastewater. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, U.; Weckesser, J. Elimination of microcystin peptide toxins from water by reverse osmosis. Environ. Toxicol. 1998, 13, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, B.C.; Rositano, J.; Burch, M.D. Destruction of cyanobacterial peptide hepatotoxins by chlorine and chloramine. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Yin, C.; Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Lv, L. Characterization of the second and third steps in the enzymatic pathway for microcystin-RR biodegradation by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Characterization of the first step involved in enzymatic pathway for microcystin-RR biodegraded by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Maseda, H.; Okano, K.; Kurashima, T.; Kawauchi, Y.; Xue, Q.; Utsumi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. Enzymatic pathway for biodegrading microcystin LR in Sphingopyxis sp. C-1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, S.; Kato, H.; Mizuno, M.; Tsuji, K.; Harada, K.-I. Bacterial Degradation of Microcystins and Nodularin. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Ma, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, H. Purification and activity of the first recombinant enzyme for biodegrading hepatotoxin by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Algal Res. 2020, 47, 101863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.; McCormick, A.J.; Fu, P.; Dziga, D. Microcystinase-a review of the natural occurrence, heterologous expression, and biotechnological application of MlrA. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, L.; Yan, M.; Li, J.; Hou, S.; Wan, J.; Feng, L. Simultaneous Microcystin Degradation and Microcystis aeruginosa Inhibition with the Single Enzyme Microcystinase A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8811–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Chen, J.; Yan, H. Biodegradation of Microcystin-RR by a New Isolated Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 18, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Q.; Teng, J.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Chen, S.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Fang, D.; Yan, H. Purification and Mechanism of Microcystinase MlrC for Catalyzing Linearized Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxins Using Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Toxins 2022, 14, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090602
Zou Q, Teng J, Wang K, Huang Y, Hu Q, Chen S, Xu Q, Zhang H, Fang D, Yan H. Purification and Mechanism of Microcystinase MlrC for Catalyzing Linearized Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxins Using Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Toxins. 2022; 14(9):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090602
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Qianwen, Junhui Teng, Kunyan Wang, Yiming Huang, Qingbei Hu, Sisi Chen, Qianqian Xu, Haiyang Zhang, Duyuan Fang, and Hai Yan. 2022. "Purification and Mechanism of Microcystinase MlrC for Catalyzing Linearized Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxins Using Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05" Toxins 14, no. 9: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090602
APA StyleZou, Q., Teng, J., Wang, K., Huang, Y., Hu, Q., Chen, S., Xu, Q., Zhang, H., Fang, D., & Yan, H. (2022). Purification and Mechanism of Microcystinase MlrC for Catalyzing Linearized Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxins Using Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Toxins, 14(9), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090602




