Deepening the Whole Transcriptomics of Bovine Liver Cells Exposed to AFB1: A Spotlight on Toll-like Receptor 2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
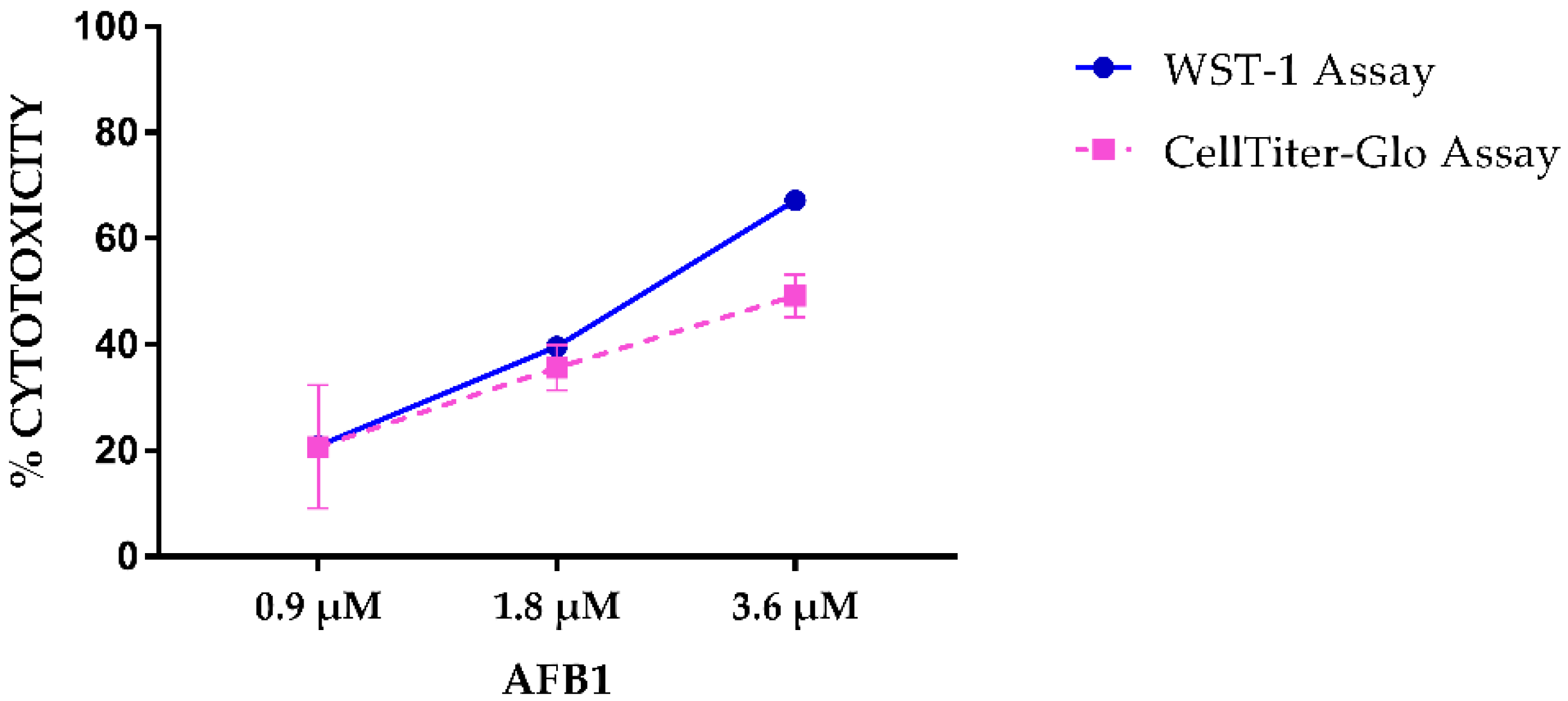
2.1. AFB1 Cytotoxicity
2.2. LC-MS/MS Quantification of AFB1, AFM1 and AFL
2.3. Quantitation of Apoptosis and Necrosis by Annexin V and Propidium Iodide
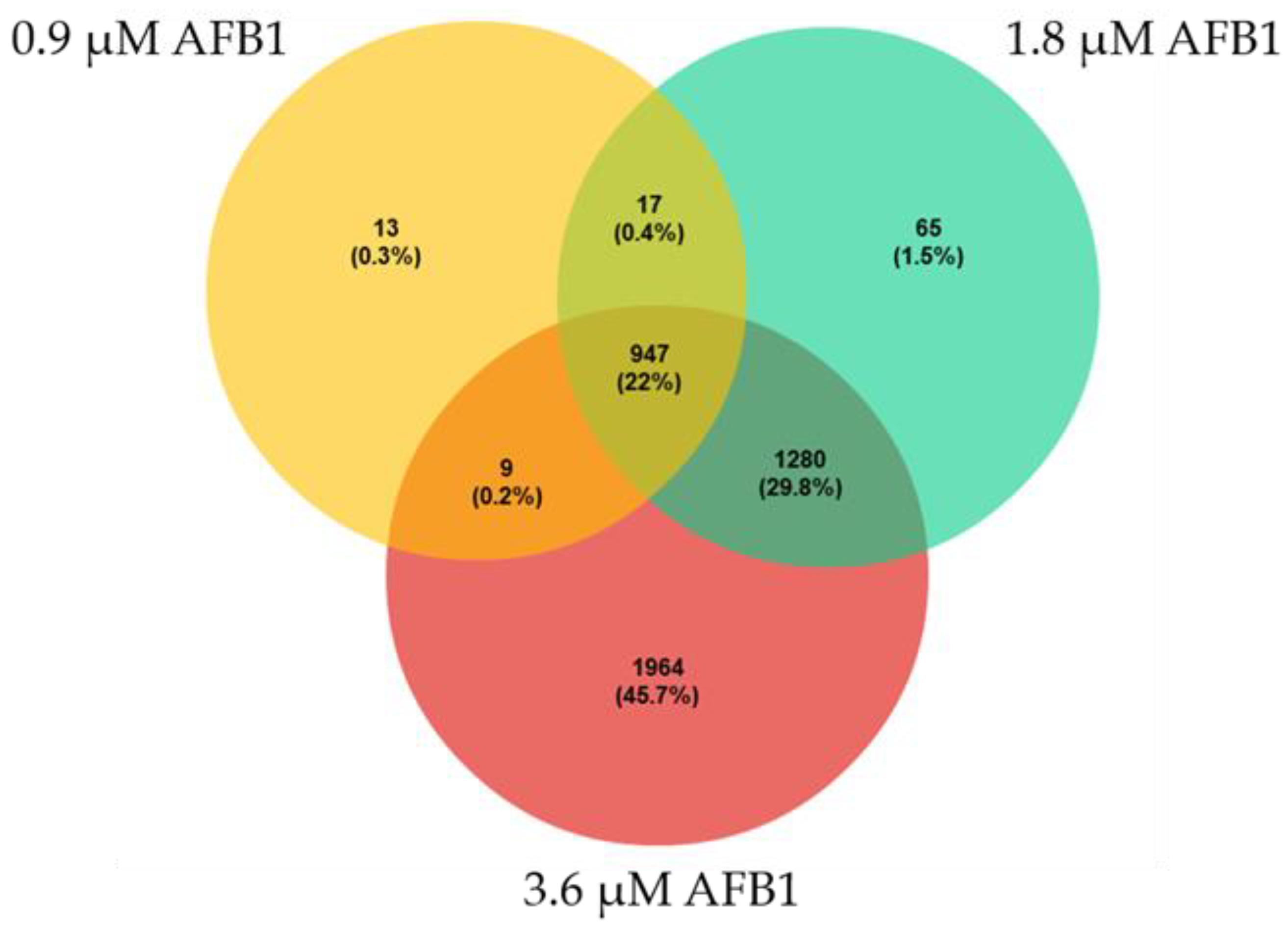
2.4. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Functional and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
2.6. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
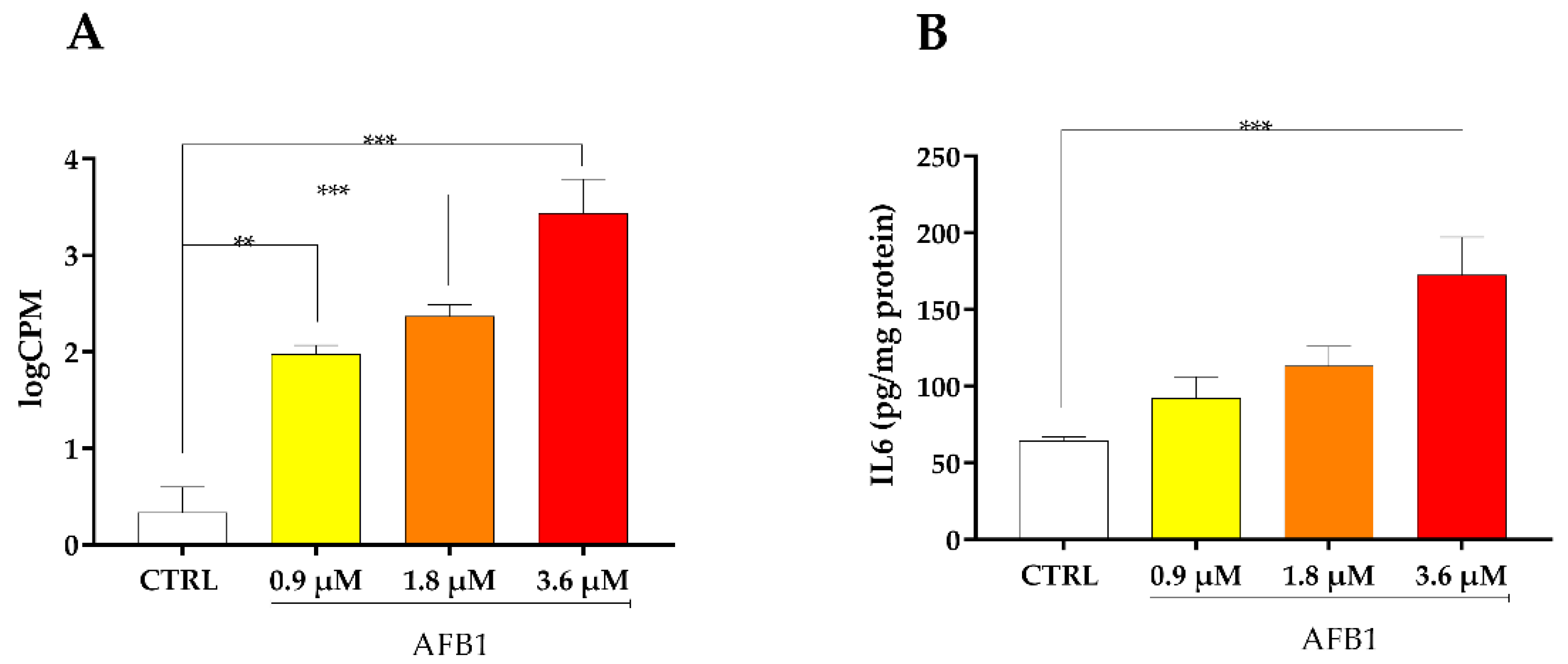
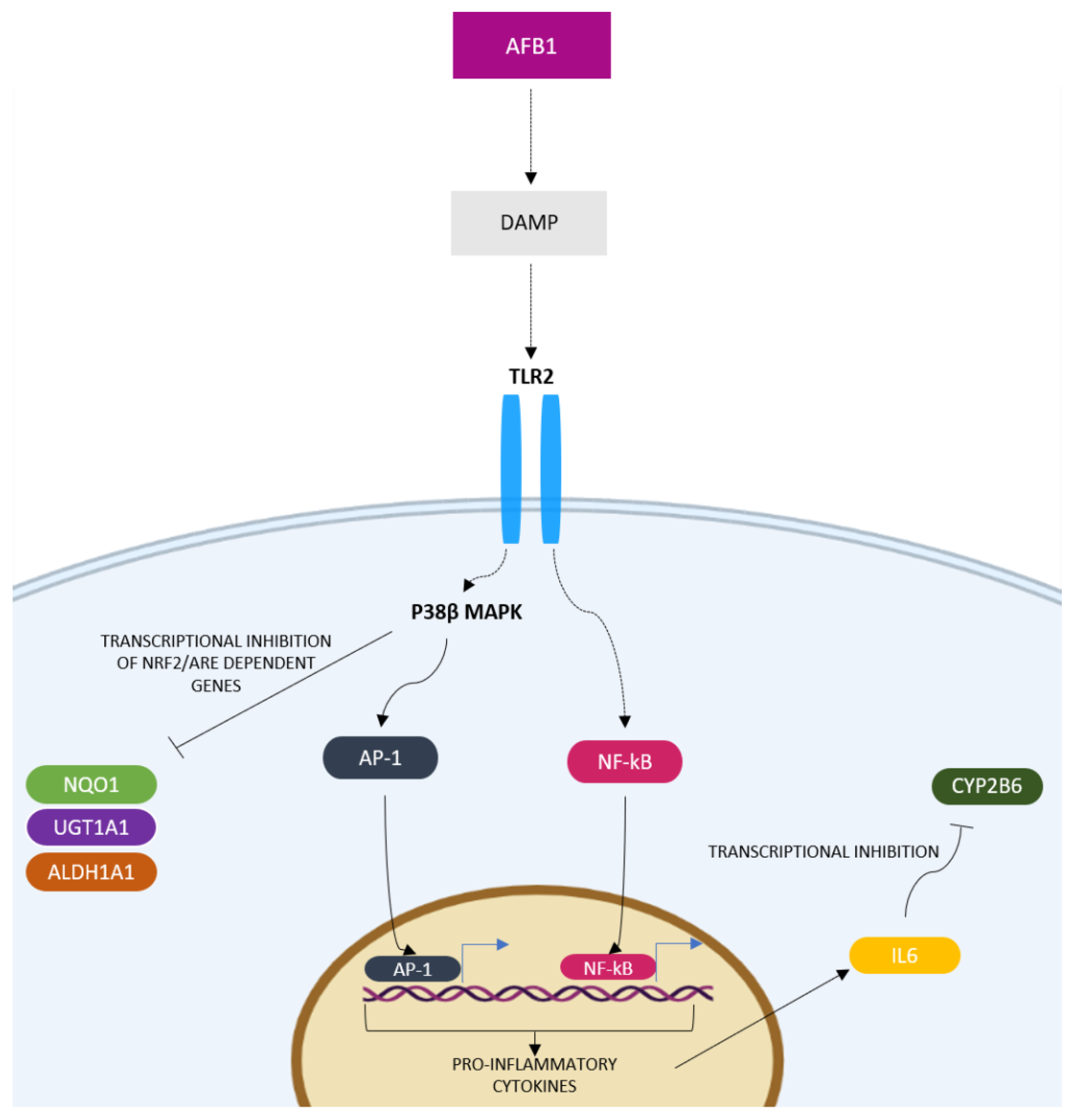
2.7. Inflammatory Response Signaling Pathway
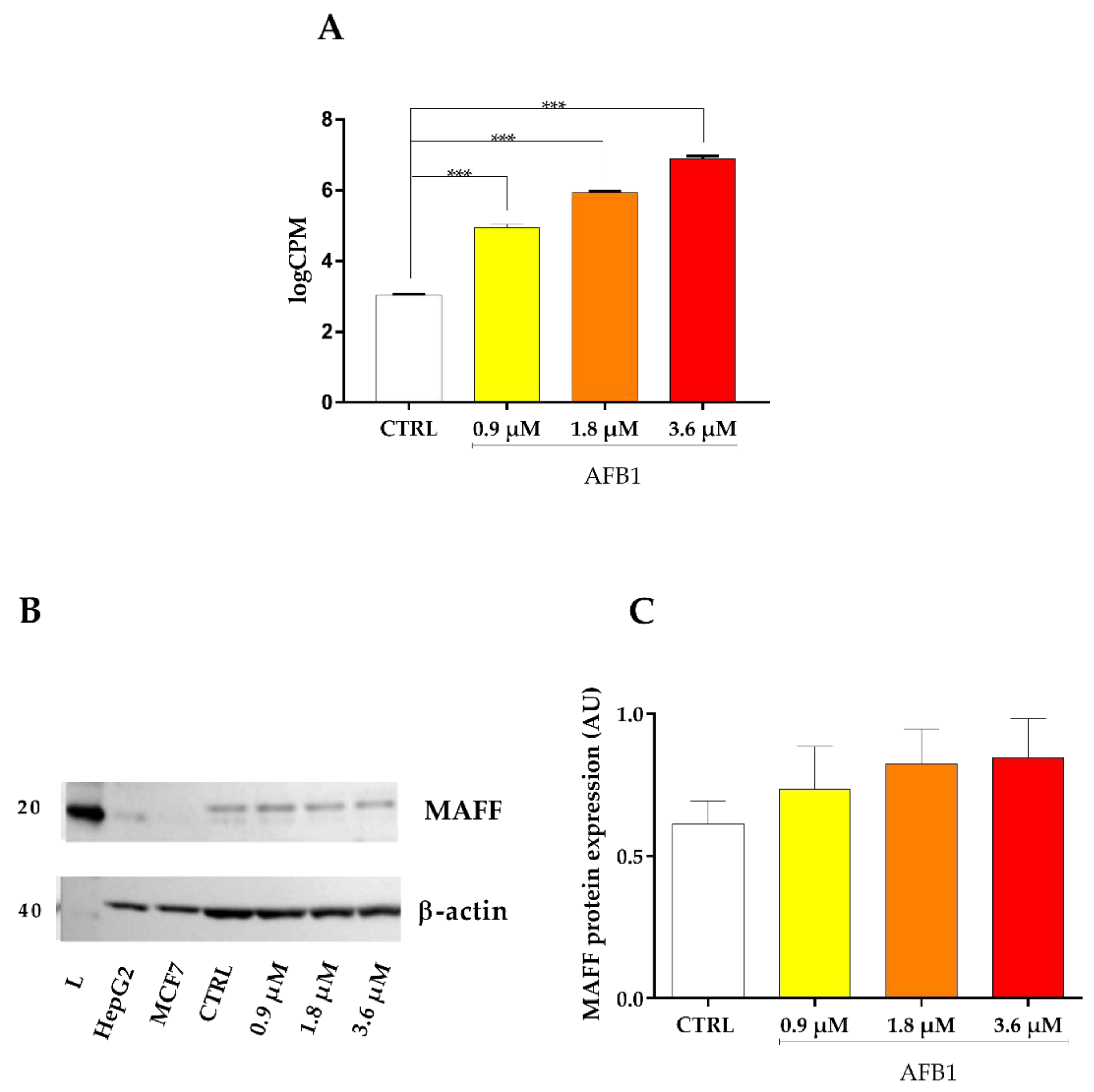
2.8. Oxidative Stress Signaling Cascade
3. Discussion
3.1. AFB1 Biotranformation
3.2. AFB1 Cytotoxicity and Mechanism of Cell Death
3.3. AFB1 Effects on BFH12 Cell Transcriptome
3.3.1. AFB1-Mediated Induction of Inflammatory Response
3.3.2. AFB1-Mediated Induction of Oxidative Stress
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals and Reagents
5.2. Cell Culture
5.3. AFB1 Cytotoxicity
5.4. Cells Incubation for Gene Expression Analysis, Post-Translational and Analytical Investigations
5.5. LC-MS/MS Quantification of AFB1, AFM1 and AFL
5.6. Total RNA Extraction and RNA-seq Analysis
5.7. PPI Network Analysis
5.8. Flow Cytometry
5.9. Protein Isolation and Immunoblotting
5.10. Interleukin 6 Detection by ELISA
5.11. CYP2B6 and NQO1 Enzymatic Activity
5.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahato, D.K.; Lee, K.E.; Kamle, M.; Devi, S.; Dewangan, K.N.; Kumar, P.; Kang, S.G. Aflatoxins in Food and Feed: An Overview on Prevalence, Detection and Control Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Effects on Public Health of an Increase of the Levels for Aflatoxin Total from 4 Μg/Kg to 10 Μg/Kg for Tree Nuts Other than Almonds, Hazelnuts and Pistachios—Statement of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y. Mycotoxins as Human Carcinogens—The IARC Monographs Classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.J.; Dobson, A.D.W. Mycotoxin Production by Aspergillus, Fusarium and Penicillium Species. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 43, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battilani, P.; Toscano, P.; Van Der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Moretti, A.; Camardo Leggieri, M.; Brera, C.; Rortais, A.; Goumperis, T.; Robinson, T. Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Maize in Europe Increases Due to Climate Change. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Vermeulen, L.C.; Gavai, A.K.; Liu, C. Climate Change Impacts on Aflatoxin B1 in Maize and Aflatoxin M1 in Milk: A Case Study of Maize Grown in Eastern Europe and Imported to the Netherlands. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambrone, J.J.; Diener, U.L.; Davis, N.D.; Panangala, V.S.; Hoerr, F.J. Effects of Aflatoxin on Young Turkeys and Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 1985, 64, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, I.; Chauhan, S.S. Studies on Production Performance and Toxin Residues in Tissues and Eggs of Layer Chickens Fed on Diets with Various Concentrations of Aflatoxin AFB1. Br. Poult. Sci. 2007, 48, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Brake, J.; Hamilton, P.B.; Hagler, W.M.; Nesheim, S. Dietary Exposure of Broiler Breeders to Aflatoxin Results in Immune Dysfunction in Progeny Chicks. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, I.P.; Marin, D.E.; Bouhet, S.; Pinton, P.; Taranu, I.; Accensi, F. Immunotoxicological Risk of Mycotoxins for Domestic Animals. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.S.; Brasel, J.M. Toxicity, Metabolism, and Impact of Mycotoxins on Humans and Animals. Toxicology 2001, 167, 101–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, W.O.; Richard, J.L.; Osweiler, G.D.; Trampel, D.W. Clinical and Pathologic Changes in Acute Bovine Aflatoxicosis: Rumen Motility and Tissue and Fluid Concentrations of Aflatoxins B1 and M1. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1986, 47, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, N.Y.; Karrow, N.A.; Krumm, C.S.; Qi, D.S.; Sun, L.H. Aflatoxin B1 Metabolism: Regulation by Phase I and II Metabolizing Enzymes and Chemoprotective Agents. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2018, 778, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, L.L.; Massey, T.E. Aflatoxin B1-Induced DNA Damage and Its Repair. Cancer Lett. 2006, 241, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohnal, V.; Wu, Q.; Kuča, K. Metabolism of Aflatoxins: Key Enzymes and Interindividual as Well as Interspecies Differences. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, S.; Coulombe, R.A. Metabolism of Aflatoxin B1 in Turkey Liver Microsomes: The Relative Roles of Cytochromes P450 1A5 and 3A37. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 254, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, K.M.; Mendoza, K.M.; Abrahante, J.E.; Coulombe, R.A. Comparative Response of the Hepatic Transcriptomes of Domesticated and Wild Turkey to Aflatoxin B1. Toxins 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgioushy, M.M.; Elgaml, S.A.; El-Adl, M.M.; Hegazy, A.M.; Hashish, E.A. Aflatoxicosis in Cattle: Clinical Findings and Biochemical Alterations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 35526–35534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, S.; Tanveer Munir, M.; Ali Shah, M.; Shahzad, M.; Ahmad Khan, R.; Sohoo, M.-R.; Ullah Khan, A.; Ameen, K.; Rafia-Munir, A.; Saleem, F.; et al. Outbreak of Aflatoxicosis on a Local Cattle Farm in Pakistan. Veterinaria 2015, 3, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Peles, F.; Sipos, P.; Győri, Z.; Pfliegler, W.P.; Giacometti, F.; Serraino, A.; Pagliuca, G.; Gazzotti, T.; Pócsi, I. Adverse Effects, Transformation and Channeling of Aflatoxins Into Food Raw Materials in Livestock. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshelli, M.; Qader, M.M.; Jambi, E.J.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Rateb, M.E. Current Status and Future Opportunities of Omics Tools in Mycotoxin Research. Toxins 2018, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.Y.; Qi, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Gu, C.Q.; Song, W.J.; Krumm, C.S.; Sun, L.H.; Qi, D.S. Response of the Hepatic Transcriptome to Aflatoxin B1 in Ducklings. Toxicon 2016, 111, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monson, M.S.; Settlage, R.E.; McMahon, K.W.; Mendoza, K.M.; Rawal, S.; El-Nezami, H.S.; Coulombe, R.A.; Reed, K.M. Response of the Hepatic Transcriptome to Aflatoxin B1 in Domestic Turkey (Meleagris gallopavo). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauletto, M.; Tolosi, R.; Giantin, M.; Guerra, G.; Barbarossa, A.; Zaghini, A.; Dacasto, M. Insights into Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity in Cattle: An in Vitro Whole-Transcriptomic Approach. Toxins 2020, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Nyamagoud, S.B.; SreeHarsha, N.; Mishra, A.; Gubbiyappa, S.K.; Singh, Y. Sitagliptin protects liver against aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity through upregulating Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 pathway. BioFactors 2019, 46, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Huang, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; He, X.; Xu, W.; Huang, K. Proteomics Reveals the Alleviation of Zinc towards Aflatoxin B1-Induced Cytotoxicity in Human Hepatocyes (HepG2 Cells). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Zhan, D.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, W.H.; He, C.Y.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, Z.N. Aflatoxin B1 Enhances Pyroptosis of Hepatocytes and Activation of Kupffer Cells to Promote Liver Inflammatory Injury via Dephosphorylation of Cyclooxygenase-2: An in Vitro, Ex Vivo and in Vivo Study. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3305–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubblefield, R.D.; Pier, A.C.; Richard, J.L.; Shotwell, O.L. Fate of Aflatoxins in Tissues, Fluids, and Excrements from Cows Dosed Orally with Aflatoxin B1. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1983, 44, 1750–1752. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Lv, Y.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y.; Xu, W. Zinc Inhibits Aflatoxin B1-Induced Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity in Human Hepatocytes (HepG2 Cells). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 92, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Che, C.; Korolchuk, V.I.; Gan, F.; Pan, C.; Huang, K. Selenomethionine Alleviates AFB1-Induced Damage in Primary Chicken Hepatocytes by Inhibiting CYP450 1A5 Expression via Upregulated SelW Expression. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.P. Metabolism Comparative Cytotoxicity Assay (MCCA) and Cytotoxic Metabolic Pathway Identification Assay (CMPIA) with Cryopreserved Human Hepatocytes for the Evaluation of Metabolism-Based Cytotoxicity in Vitro: Proof-of-Concept Study with Aflatoxin B1. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 179, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Hong, M.W.; Park, T.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.J. Transcriptomic Alterations Induced by Aflatoxin B1 and Ochratoxin A in LMH Cell Line. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5265–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajewski, M.; Walczak-Drzewiecka, A.; Sałkowska, A.; Dastych, J. Aflatoxins Upregulate CYP3A4 MRNA Expression in a Process That Involves the PXR Transcription Factor. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 205, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’arcy, M.S. Cell Death: A Review of the Major Forms of Apoptosis, Necrosis and Autophagy. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallach, D.; Kang, T.B.; Dillon, C.P.; Green, D.R. Programmed Necrosis in Inflammation: Toward Identification of the Effector Molecules. Science 2016, 352, aaf2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughal, M.J.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, J. Aflatoxin B1 Invokes Apoptosis via Death Receptor Pathway in Hepatocytes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8239–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Mughal, M.J.; Fang, J.; Peng, X. The Protective Role of Selenium Against AFB1-Induced Liver Apoptosis by Death Receptor Pathway in Broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 191, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mishra, S.K.; Wang, T.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Fan, X.; Zeng, B.; Yang, M.; et al. AFB1 Induced Transcriptional Regulation Related to Apoptosis and Lipid Metabolism in Liver of Chicken. Toxins 2020, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, I.; Hermenean, A.; Bulgaru, C.; Pistol, G.C.; Ciceu, A.; Grosu, I.A.; Marin, D.E. Diet Containing Grape Seed Meal By-Product Counteracts AFB1 Toxicity in Liver of Pig after Weaning. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 110899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wei, H.; Ji, C.; Zhang, J. Molecular Mechanisms of Lipoic Acid Protection against Aflatoxin B1-Induced Liver Oxidative Damage and Inflammatory Responses in Broilers. Toxins 2015, 7, 5435–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, G.; Gao, L.; Niu, C.; Xu, J.; Li, S. Lactobacillus Plantarum C88 Protects against Aflatoxin B1-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibition of NF-ΚB-Mediated Inflammatory Responses and Excessive Apoptosis. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murarolli, R.A. Effects of Aflatoxin B1 (AFB 1) on Hepatic Gene Expression in Pigs and Turkeys; University of Missouri: Columbia, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, F.; Giordano, A.; Barbarisi, M.; Barbarisi, A. From Cell-ECM Interactions to Tissue Engineering. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 199, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanos, N.K.; Theocharis, A.D.; Neill, T.; Iozzo, R.V. Matrix Modeling and Remodeling: A Biological Interplay Regulating Tissue Homeostasis and Diseases. Matrix Biol. 2019, 75–76, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumailley, M. The Laminin Family. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2013, 7, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, M.; Braunstein, G.; Koeffler, H.P. LAMC2 as a Therapeutic Target for Cancers. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcourt, U.; Alcaraz, L.B.; Exposito, J.-Y.; Lethias, C.; Bartholin, L. Cell Adhesion & Migration Tenascin-X: Beyond the Architectural Function. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liot, S.; Aubert, A.; Hervieu, V.; El Kholti, N.; Schalkwijk, J.; Verrier, B.; Valcourt, U.; Lambert, E. Loss of Tenascin-X Expression during Tumor Progression: A New Pan-Cancer Marker. Matrix Biol. Plus 2020, 6–7, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R. Basement Membranes: Structure, Assembly and Role in Tumour Angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanjore, H.; Kalluri, R. The Role of Type IV Collagen and Basement Membranes in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Iyama, K.I.; Ishikawa, N.; Egami, H.; Nakao, M.; Sado, Y.; Ninomiya, Y.; Baba, H. Loss of Expression of Type IV Collagen α5 and α6 Chains in Colorectal Cancer Associated with the Hypermethylation of Their Promoter Region. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komuro, I.; Kurihara, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Takaku, F.; Yazaki, Y. Endothelin Stimulates C-Fos and c-Myc Expression and Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. FEBS Lett. 1988, 238, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram, A.; Razandi, M.; Hu, R.M.; Levin, E.R. Vasoactive Peptides Modulate Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor Production and Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 17097–17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Loizidou, M.; Dashwood, M.; Savage, F.; Sheard, C.; Taylor, I. Stimulation of Colorectal Cancer Cell Line Growth by ET-1 and Its Inhibition by ETA Antagonists. Gut 2000, 47, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, K.; Nihei, Z. Expression of Endothelin-1 Immunoreactivity in Breast Cancer. Surg. Oncol. 1995, 4, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Fujita, M.; Nagai, K.; Kako, M.; Furue, H.; Haku, E.; Osamura, Y.; Yamaji, T. Production and Secretion of Endothelin by Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.F.; Luo, J.S. S100A4 Expression Is Closely Linked to Genesis and Progression of Glioma by Regulating Proliferation, Apoptosis, Migration and Invasion. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 2883–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lipkin, M.; Newmark, H. Effect of Added Dietary Calcium on Colonic Epithelial-Cell Proliferation in Subjects at High Risk for Familial Colonic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 1381–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galione, A.; Evans, A.M.; Ma, J.; Parrington, J.; Arredouani, A.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, M.X. The Acid Test: The Discovery of Two-Pore Channels (TPCs) as NAADP-Gated Endolysosomal Ca2+ Release Channels. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2009, 458, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolesi, G.E.; Shi, C.; Elbaum, L.; Jollimore, C.; Rozenberg, G.; Barnes, S.; Kelly, M.E. The Ca2+ Channel Antagonists Mibefradil and Pimozide Inhibit Cell Growth via Different Cytotoxic Mechanisms. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 62, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.N.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, C.F.; Sun, Z.; Lai, M.D.; Lin, Y.C. Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels: Novel Targets for Cancer Therapy. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2059–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Shi, W.; Lv, P.; Meng, W.; Mao, G.; Gong, C.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. Critical Role of Caveolin-1 in Aflatoxin B1-Induced Hepatotoxicity via the Regulation of Oxidation and Autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, L.; He, X.; Huang, K.; Xu, W. Single-Cell Sequencing Reveals Novel Mechanisms of Aflatoxin B1-Induced Hepatotoxicity in S Phase-Arrested L02 Cells. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2020, 36, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwata, K.; Shibutani, M.; Hayashi, H.; Shimamoto, K.; Hayashi, S.M.; Suzuki, K.; Mitsumori, K. Concomitant Apoptosis and Regeneration of Liver Cells as a Mechanism of Liver-Tumor Promotion by β-Naphthoflavone Involving TNFα-Signaling Due to Oxidative Cellular Stress in Rats. Toxicology 2011, 283, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josse, R.; Dumont, J.; Fautrel, A.; Robin, M.-A.; Guillouzo, A. Identification of Early Target Genes of Aflatoxin B1 in Human Hepatocytes, Inter-Individual Variability and Comparison with Other Genotoxic Compounds. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opferman, J.T.; Kothari, A. Anti-Apoptotic BCL-2 Family Members in Development. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 25, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.S.; Fornace, A.J. Death and Decoy Receptors and P53-Mediated Apoptosis. Leukemia 2000, 14, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macé, K.; Aguilar, F.; Wang, J.-S.; Vautravers, P.; Gómez-Lechón, M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Groopman, J.; Harris, C.C.; Pfeifer, A.M. Aflatoxin B1-induced DNA adduct formation and p53 mutations in CYP450-expressing human liver cell lines. Carcinogenesis 1997, 18, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Code, E.L.; Crespi, C.L.; Penman, B.W.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Chang, T.K.H.; Waxman, D.J. Human cytochrome P4502B6: Interindividual hepatic expression, substrate specificity, and role in procarcinogen activation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1997, 25, 985–993. [Google Scholar]
- Guerre, P.; Pineau, T.; Costet, P.; Burgat, V.; Galtier, P. Effects of AFB1 on CYP 1A1, 1A2 and 3A6 MRNA, and P450 Expression in Primary Culture of Rabbit Hepatocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 2000, 111, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, V.S.; Valdehita, A.; Navas, J.M.; Rubinstein, H.R.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L. Effects of Aflatoxin B1, Fumonisin B1 and Their Mixture on the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Cytochrome P450 1A Induction. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 75, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed-Boussema, I.; Pascussi, J.M.; Maurel, P.; Bacha, H.; Hassen, W. Effect of Aflatoxin B1 on Nuclear Receptors PXR, CAR, and AhR and Their Target Cytochromes P450 MRNA Expression in Primary Cultures of Human Hepatocytes. Int. J. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Shoeb, M.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Zhang, M.; Ramana, K.V.; Srivastava, S.K.; Vasiliou, V.; Ansari, N.H. Molecular Cloning and Oxidative Modification of Human Lens ALDH1A1: Implication in Impaired Detoxification of Lipid Aldehydes. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2009, 72, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosialou, E.; Ekström, G.; Adang, A.E.P.; Morgenstern, R. Evidence That Rat Liver Microsomal Glutathione Transferase Is Responsible for Glutathione-Dependent Protection against Lipid Peroxidation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993, 45, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Pulford, D.J. The Glut Athione S-Transferase Supergene Family: Regulation of GST and the Contribution of the Lsoenzymes to Cancer Chemoprotection and Drug Resistance Part I. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 30, 445–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattes, W.B.; Daniels, K.K.; Summan, M.; Xu, Z.A.; Mendrick, D.L. Xenobiotica the Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems Tissue and Species Distribution of the Glutathione Pathway Transcriptome. Xenobiotica 2006, 36, 1081–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukey, R.H.; Strassburg, C.P. Human Udp-Glucuronosyltransferases: Metabolism, Expression, and Disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol 2000, 40, 581–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, S.; Spalenza, V.; Dellafiora, L.; Badino, P.; Barbarossa, A.; Dall’Asta, C.; Nebbia, C.; Girolami, F. Modulation of Aflatoxin B1 Cytotoxicity and Aflatoxin M1 Synthesis by Natural Antioxidants in a Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cell Line. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 57, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanioka, N.; Nonaka, Y.; Saito, K.; Negishi, T.; Okamoto, K.; Kataoka, H.; Narimatsu, S. Effect of Aflatoxin B1 on UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase MRNA Expression in HepG2 Cells. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrick, B.A.; Phadke, D.P.; Auerbach, S.S.; Mav, D.; Stiegelmeyer, S.M.; Shah, R.R.; Tice, R.R. RNA-Seq Profiling Reveals Novel Hepatic Gene Expression Pattern in Aflatoxin B1 Treated Rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Nrf2-ARE Signaling in Cellular Protection: Mechanism of Action and the Regulatory Mechanisms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Inflammation 2010: New Adventures of an Old Flame. Cell 2010, 140, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zayat, S.R.; Sibaii, H.; Mannaa, F.A. Toll-like Receptors Activation, Signaling, and Targeting: An Overview. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A.; Medzhitov, R. Innate Immune Recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubartelli, A.; Lotze, M.T. Inside, Outside, Upside down: Damage-Associated Molecular-Pattern Molecules (DAMPs) and Redox. Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, X.Z.; Malinin, N.L.; Merkulova, A.A.; Tischenko, M.; Kerr, B.A.; Borden, E.C.; Podrez, E.A.; Salomon, R.G.; Byzova, T.V. Oxidative Stress Induces Angiogenesis by Activating TLR2 with Novel Endogenous Ligands. Nature 2010, 467, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadl, A.; Sharma, P.R.; Chen, W.; Agrawal, R.; Meher, A.K.; Rudraiah, S.; Grubbs, N.; Sharma, R.; Leitinger, N. Oxidized Phospholipid-Induced Inflammation Is Mediated by Toll-like Receptor 2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvandi, A.M.; Mehrzad, J.; Saleh-Moghaddam, M. Biologically Relevant Doses of Mixed Aflatoxins B and G Up-Regulate MyD88, TLR2, TLR4 and CD14 Transcripts in Human PBMCs. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2013, 35, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Mehrzad, J.; Mahmoudi, M.; Schneider, M. Environmentally Relevant Level of Aflatoxin B1 Dysregulates Human Dendritic Cells through Signaling on Key Toll-like Receptors. Int. J. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, R.; Xia, S.; Wei, G.; Ishfaq, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Protective Role of Curcumin on Aflatoxin B1-Induced TLR4/RIPK Pathway Mediated-Necroptosis and Inflammation in Chicken Liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrzad, J.; Milani, M.; Mahmoudi, M. Naturally Occurring Level of Mixed Aflatoxins B and G Stimulate Toll-like Receptor-4 in Bovine Mononuclear Cells. Vet. Q. 2013, 33, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases in Organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-ΚB: A Key Role in Inflammatory Diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansell, A.; Jenkins, B.J. Dangerous Liaisons between Interleukin-6 Cytokine and Toll-like Receptor Families: A Potent Combination in Inflammation and Cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipp, M.C.; Acco, A. Involvement of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Inflammation and Cancer: A Review. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickmann, L.J.; Patel, S.K.; Rock, D.A.; Wienkers, L.C.; Slatter, J.G. Effects of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and an Anti-IL-6 Monoclonal Antibody on Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes in Human Hepatocyte Culture. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2011, 39, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, A.E.; Morgan, E.T. Gene-Specific Effects of Inflammatory Cytokines on Cytochrome P450 2C, 2B6 and 3A4 MRNA Levels in Human Hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, K.; Janefeldt, A.; Andersson, L.; Berke, Z.; Grime, K.; Andersson, T.B. Heparg Cells as Human-Relevant in Vitro Model to Study the Effects of Inflammatory Stimuli on Cytochrome P450 Isoenzymes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Kaya, E.; Kisacam, M.A. The Effect on Oxidative Stress of Aflatoxin and Protective Effect of Lycopene on Aflatoxin Damage. Aflatoxin-Control Anal. Detect. Health Risks 2017, 30, 67–90. [Google Scholar]
- Benkerroum, N. Chronic and Acute Toxicities of Aflatoxins: Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, C.; Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. Transcriptional Regulation by Nrf2. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.-Q.; You, K.S.; Oh, S.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Silencing of NRF2 Reduces the Expression of ALDH1A1 and ALDH3A1 and Sensitizes to 5-FU in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Otsuki, A.; Keleku-Lukwete, N.; Yamamoto, M. Overview of Redox Regulation by Keap1–Nrf2 System in Toxicology and Cancer. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2016, 1, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Wei, X.; Niu, C.; Jia, M.; Li, Q.; Meng, D. Bach1: Function, Regulation, and Involvement in Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1347969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuoka, F.; Yamamoto, M. Small Maf Proteins (MafF, MafG, MafK): History, Structure and Function. Gene 2016, 586, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vipin, A.V.; Raksha Rao, K.; Kurrey, N.K.; Anu Appaiah, K.A.; Venkateswaran, G. Protective Effects of Phenolics Rich Extract of Ginger against Aflatoxin B1-Induced Oxidative Stress and Hepatotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Muhammad, I.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, X. Sensitivity of Arbor Acres Broilers and Chemoprevention of Aflatoxin B1-Induced Liver Injury by Curcumin, a Natural Potent Inducer of Phase-II Enzymes and Nrf2. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 59, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, M.; Cao, K.; Jin, S.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Curcumin Mitigates Aflatoxin B1-Induced Liver Injury via Regulating the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 161, 112823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Jin, S.; Feng, X. Dietary Resveratrol Alleviates AFB1-Induced Ileum Damage in Ducks via the Nrf2 and NF-ΚB/NLRP3 Signaling Pathways and CYP1A1/2 Expressions. Agriculture 2022, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Talalay, P. NAD(P)H:Quinone Acceptor Oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), a Multifunctional Antioxidant Enzyme and Exceptionally Versatile Cytoprotector. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 501, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Mandlekar, S.; Lei, W.; Fahl, W.E.; Tan, T.H.; Kong, A.N.T. P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Negatively Regulates the Induction of Phase II Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes That Detoxify Carcinogens. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 2322–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yueh, M.-F.; Tukey, R.H. Nrf2-Keap1 Signaling Pathway Regulates Human UGT1A1 Expression in Vitro and in Transgenic UGT1 Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8749–8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleich, A.; Kaiser, B.; Schumann, J.; Fuhrmann, H. Establishment and Characterisation of a Novel Bovine SV40 Large T-Antigen-Transduced Foetal Hepatocyte-Derived Cell Line. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.—Anim. 2016, 52, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. ClusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes among Gene Clusters. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Interpreting Genome-Wide Expression Profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauletto, M.; Giantin, M.; Tolosi, R.; Bassan, I.; Barbarossa, A.; Zaghini, A.; Dacasto, M. Curcumin Mitigates Afb1-Induced Hepatic Toxicity by Triggering Cattle Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: A Whole Transcriptomic In Vitro Study. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zancanella, V.; Giantin, M.; Lopparelli, R.M.; Nebbia, C.; Dacasto, M. Constitutive Expression and Phenobarbital Modulation of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes and Related Nuclear Receptors in Cattle Liver and Extra-Hepatic Tissues. Xenobiotica 2012, 42, 1096–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauletto, M.; Giantin, M.; Tolosi, R.; Bassan, I.; Barbarossa, A.; Zaghini, A.; Dacasto, M. Discovering the Protective Effects of Resveratrol on Aflatoxin B1-Induced Toxicity: A Whole Transcriptomic Study in a Bovine Hepatocyte Cell Line. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| AFB1 (μM) | AFM1 (μM) | AFL (μM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 0.9 μM | 0.800 ± 0.037 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.054 ± 0.004 |
| AFB1 1.8 μM | 1.170 ± 0.057 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.074 ± 0.014 |
| AFB1 3.6 μM | 2.812 ± 0.183 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.165 ± 0.020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iori, S.; Pauletto, M.; Bassan, I.; Bonsembiante, F.; Gelain, M.E.; Bardhi, A.; Barbarossa, A.; Zaghini, A.; Dacasto, M.; Giantin, M. Deepening the Whole Transcriptomics of Bovine Liver Cells Exposed to AFB1: A Spotlight on Toll-like Receptor 2. Toxins 2022, 14, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070504
Iori S, Pauletto M, Bassan I, Bonsembiante F, Gelain ME, Bardhi A, Barbarossa A, Zaghini A, Dacasto M, Giantin M. Deepening the Whole Transcriptomics of Bovine Liver Cells Exposed to AFB1: A Spotlight on Toll-like Receptor 2. Toxins. 2022; 14(7):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070504
Chicago/Turabian StyleIori, Silvia, Marianna Pauletto, Irene Bassan, Federico Bonsembiante, Maria Elena Gelain, Anisa Bardhi, Andrea Barbarossa, Anna Zaghini, Mauro Dacasto, and Mery Giantin. 2022. "Deepening the Whole Transcriptomics of Bovine Liver Cells Exposed to AFB1: A Spotlight on Toll-like Receptor 2" Toxins 14, no. 7: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070504
APA StyleIori, S., Pauletto, M., Bassan, I., Bonsembiante, F., Gelain, M. E., Bardhi, A., Barbarossa, A., Zaghini, A., Dacasto, M., & Giantin, M. (2022). Deepening the Whole Transcriptomics of Bovine Liver Cells Exposed to AFB1: A Spotlight on Toll-like Receptor 2. Toxins, 14(7), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070504







