RIPpore: A Novel Host-Derived Method for the Identification of Ricin Intoxication through Oxford Nanopore Direct RNA Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Ricin Purification and Cytotoxicity Assay in Cell Culture
2.2. 28s Ribosomal RNA-Targeted Oligo Design
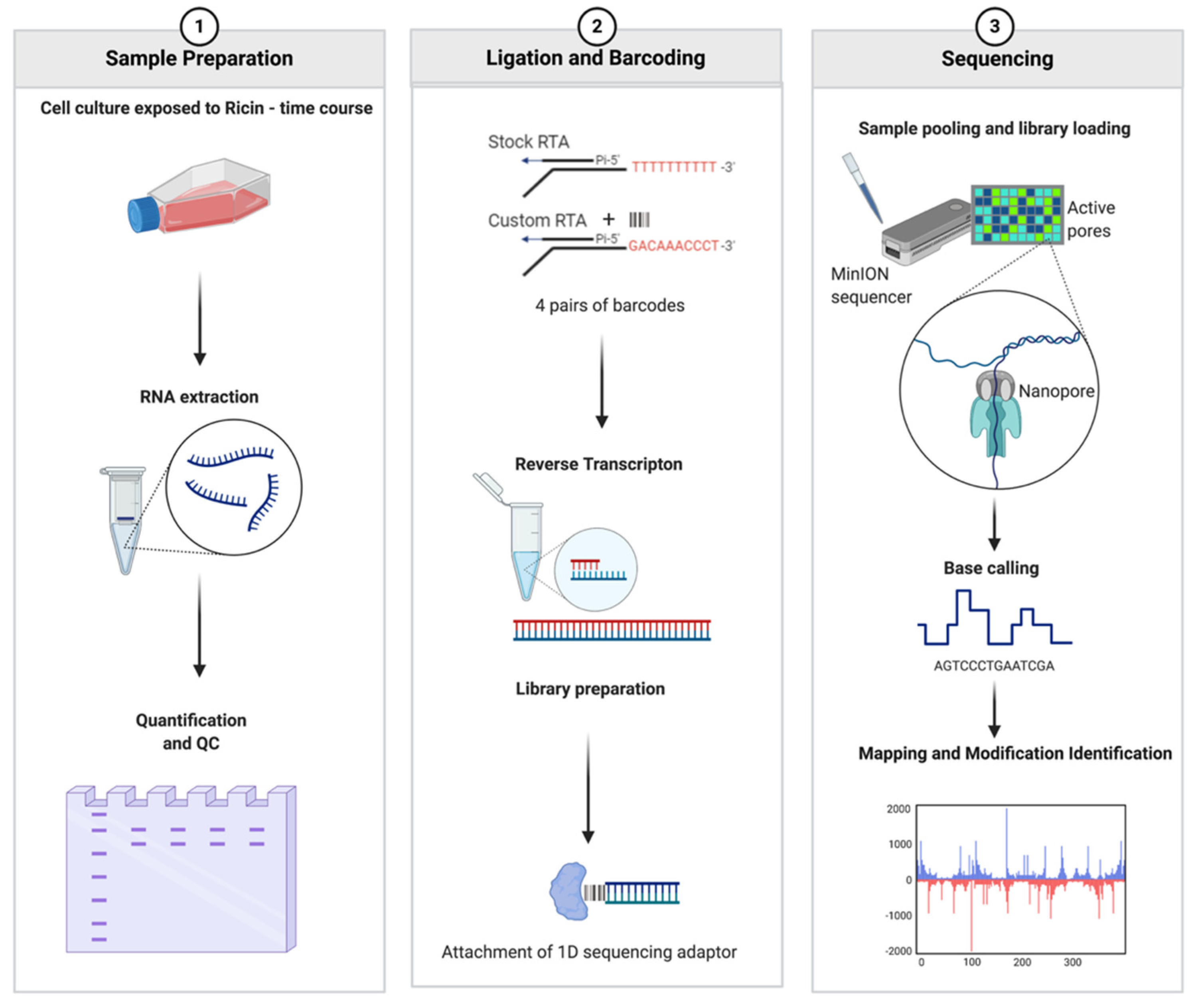
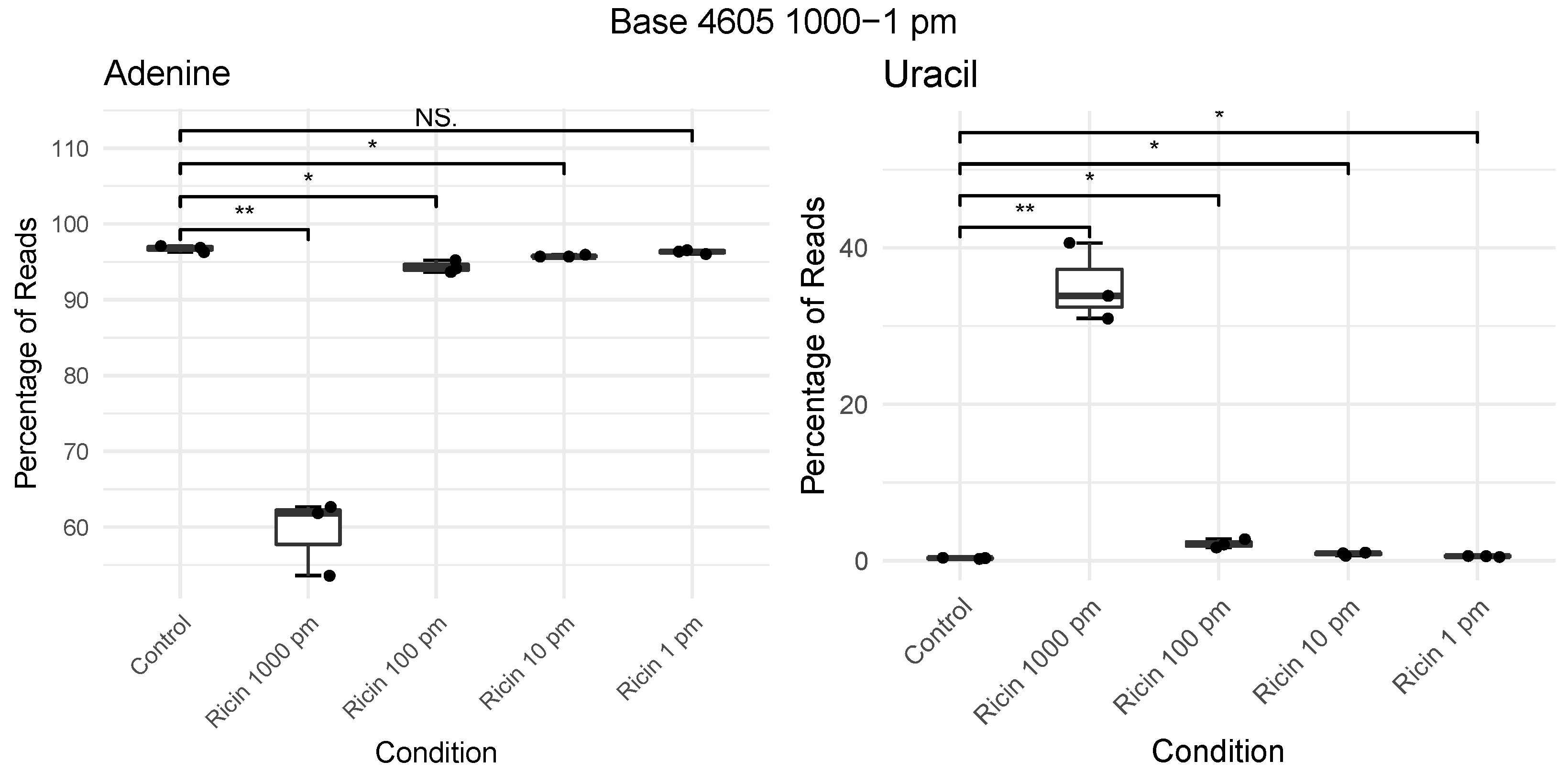
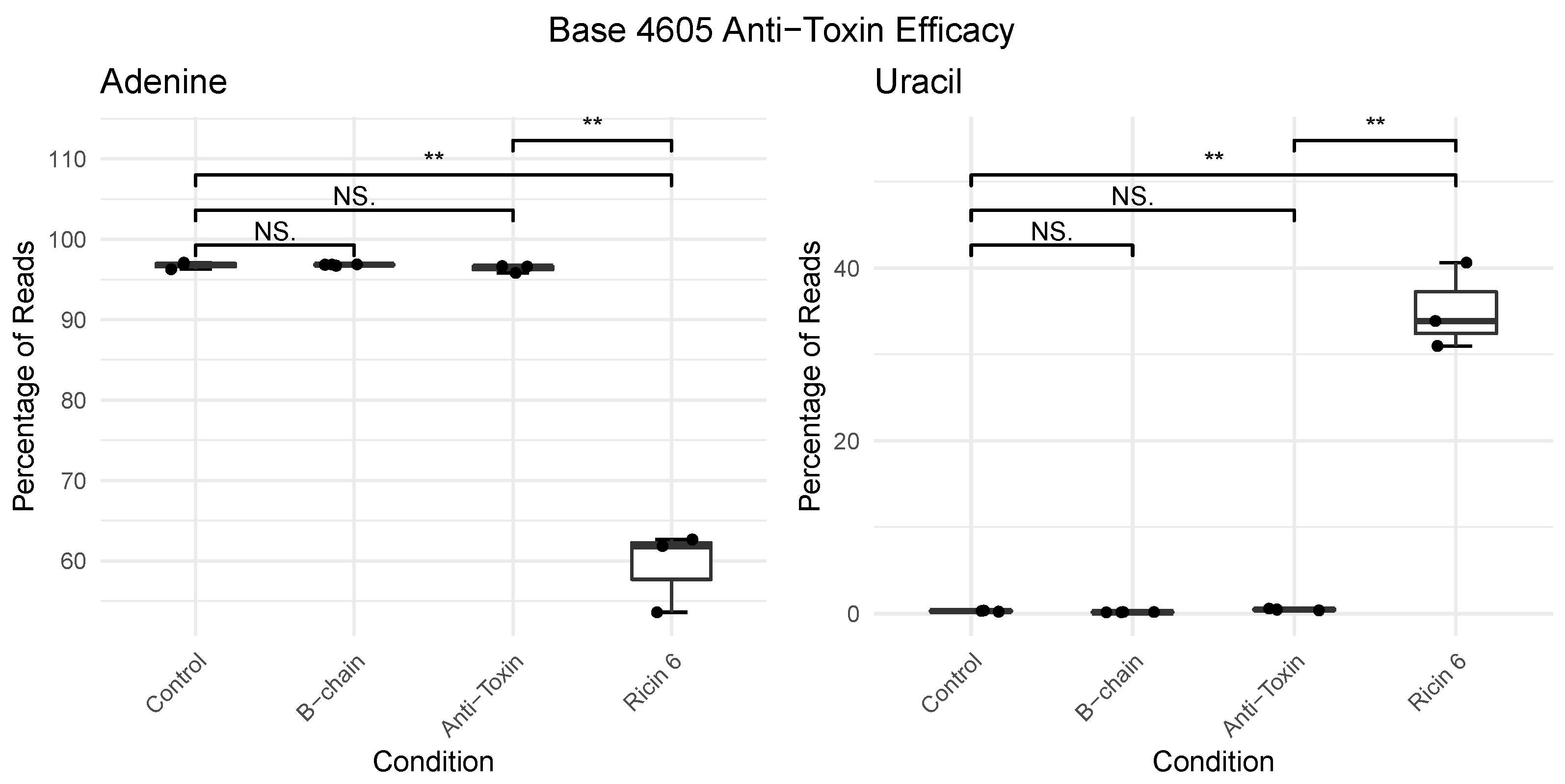
2.3. Development of RIPpore: A Tool for Measuring Depurination
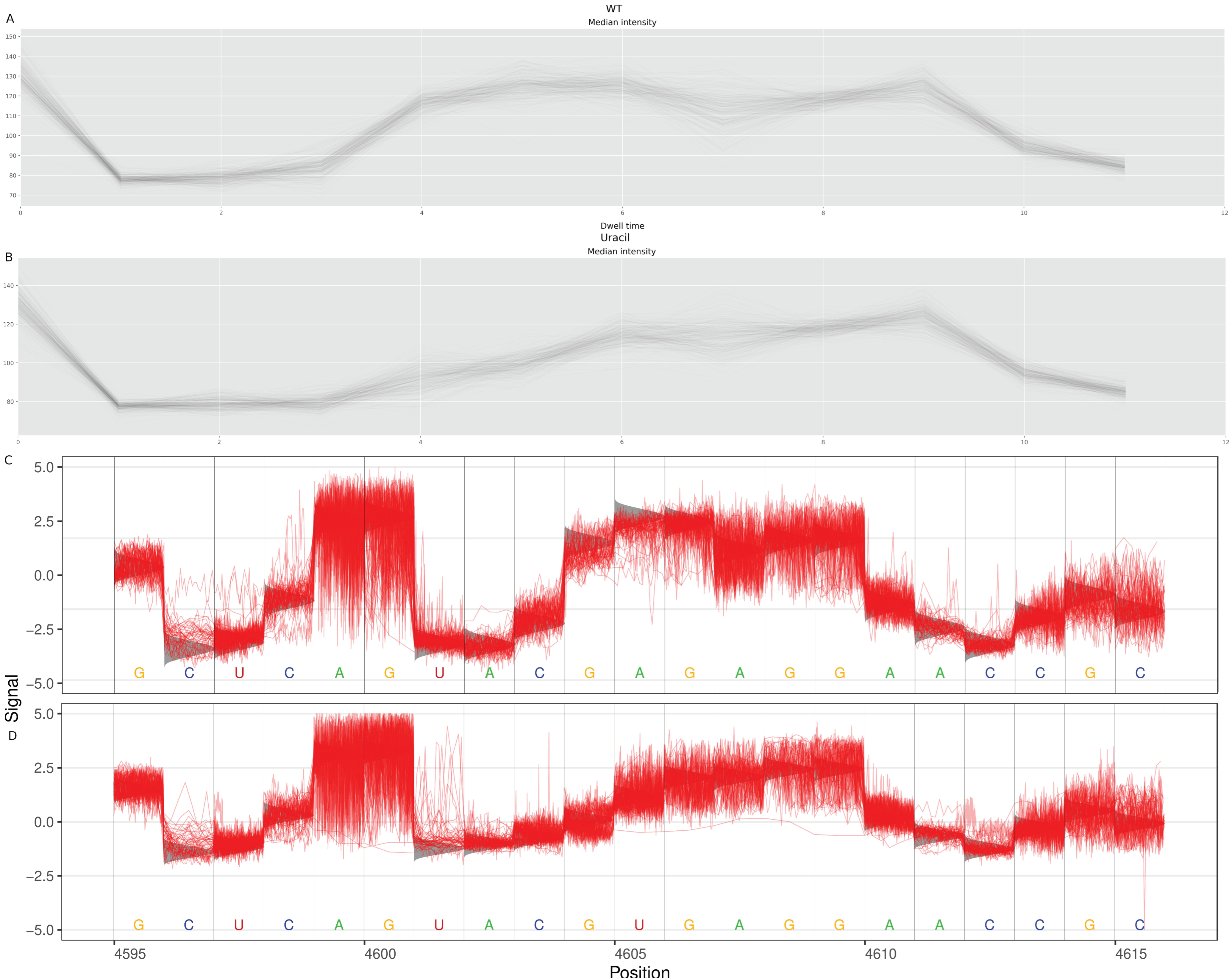
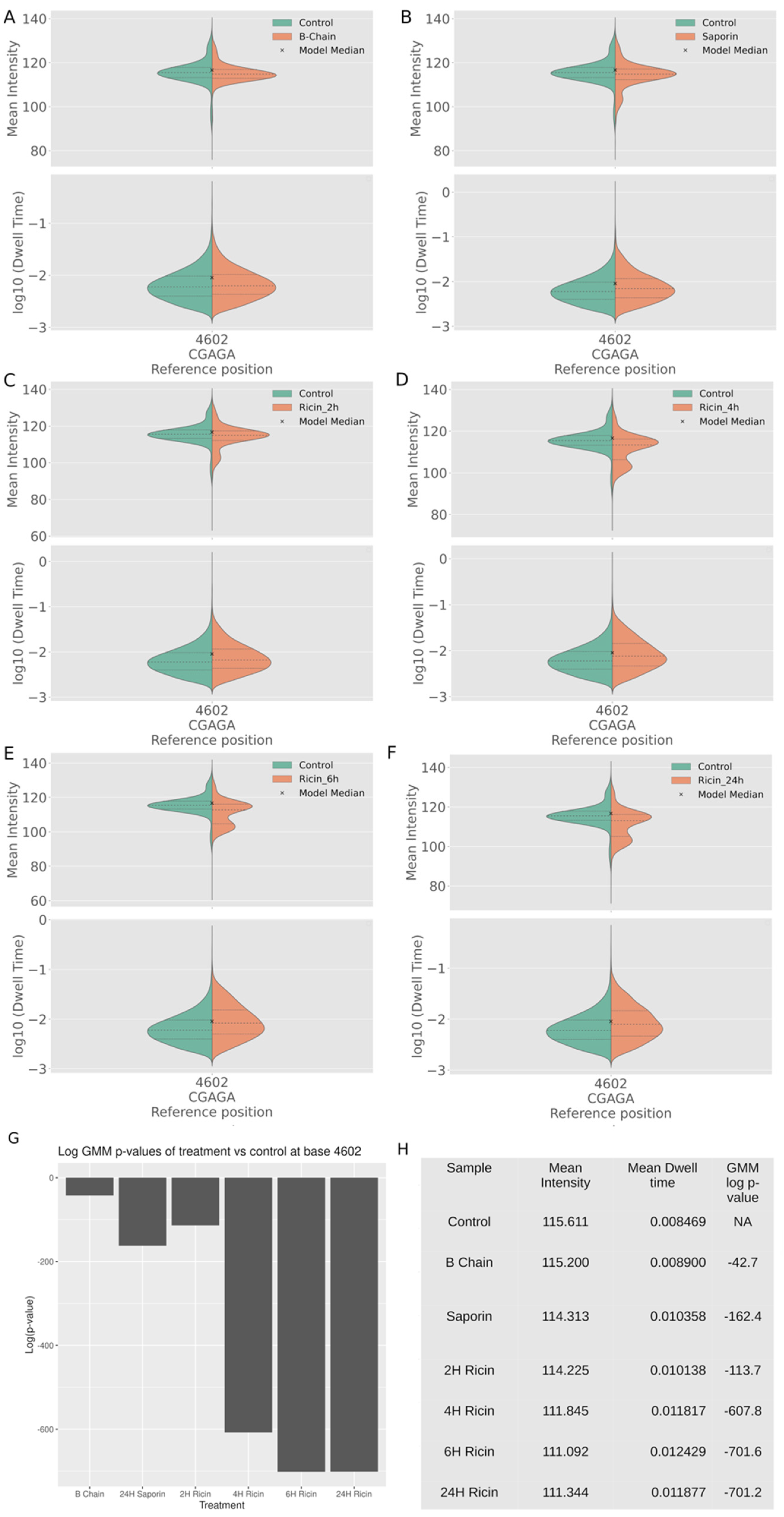
2.4. Charge Intensity Analysis of the Ricin Loop Shows a Shift Caused by Depurination
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ricin Extraction
4.2. Assessment of Ricin Purification
4.3. Cell Line
4.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
4.5. Antitoxin-Based Ricin Neutralisation
4.6. RIP Exposure
4.7. RIP Disposal
4.8. RNA Extraction
4.9. Quantifying RNA Content
4.10. Targeted Direct RNA Oligos A and B with and without Barcodes
| Standard ONT oligos | Oligo A: 5′-/5PHOS/GGCTTCTTCTTGCTCTTAGGTAGTAGGTTC-3′ Oligo B: 5′-GAGGCGAGCGGTCAATTTTCCTAAGAGCAAGAAGAAGCCGACAAACCCT-3′ |
| Deeplexicon 1 | OligoA1: 5′-/5Phos/GGCTTCTTCTTGCTCTTAGGTAGTAGGTTC-3′ OligoB1: 5′-GAGGCGAGCGGTCAATTTTCCTAAGAGCAAGAAGAAGCCGACAAACCCT-3′ |
| Deeplexicon 3 | OligoA2: 5′-/5Phos/GTGATTCTCGTCTTTCTGCGTAGTAGGTTC-3′ OligoB2: 5′-GAGGCGAGCGGTCAATTTTCGCAGAAAGACGAGAATCACGACAAACCCT-3′ |
| Deeplexicon 2 | OligoA3: 5′-/5Phos/GTACTTTTCTCTTTGCGCGGTAGTAGGTTC-3′ OligoB3: 5′-GAGGCGAGCGGTCAATTTTCCGCGCAAAGAGAAAAGTACGACAAACCCT-3′ |
| Deeplexicon 4 | OligoA4: 5′-/5Phos/GGTCTTCGCTCGGTCTTATTTAGTAGGTTC-3′ OligoB4: 5′-GAGGCGAGCGGTCAATTTTAATAAGACCGAGCGAAGACCGACAAACCCT-3′ |
| Poreplex 1 | Oligo A: 5′-/5Phos/CCTCCCCTAAAAACGAGCCGCATTTGCGTAGTAGGTTC-3′ Oligo B: 5′-GAGGCGAGCGGTCAATTTTCGCAAATGCGGCTCGTTTTTAGGGGAGG GACAAACCCT-3′ |
| Poreplex 2 | Oligo A: 5′-/5Phos/CCTCGTCGGTTCTAGGCATCGCGTATGCTAGTAGGTTC-3′ Oligo B: 5′-GAGGCGAGCGGTCAATTTTGCATACGCGATGCCTAGAACCGACGAGG GACAAACCCT-3′ |
| Poreplex 3 | Oligo A: 5′-/5Phos/CCTCCCACTTTCACACGCACTAACCAGGTAGTAGGTTC-3′ Oligo B: 5′-GAGGCGAGCGGTCAATTTTCCTGGTTAGTGCGTGTGAAAGTGGGAGG GACAAACCCT-3′ |
| Poreplex 4 | Oligo A: 5′-/5Phos/CCTCCTTCAGAAGAGGGTCGCTTCTACCTAGTAGGTTC-3′ Oligo B: 5′-GAGGCGAGCGGTCAATTTTGGTAGAAGCGACCCTCTTCTGAAGGAGG GACAAACCCT-3′ |
4.11. Oxford Nanopore Library Preparation
4.12. Oxford Nanopore Sequencing
4.13. Demultiplexing
4.14. Quantification of Depurination
- Concatenate all fastqs in fastq_pass per sample;
- Map concatenated fastqs to NR_003287.4 using: minimap2 -ax splice -uf -k14 ref.fa reads.fq > aln.sam minimap2 [25] version 2.17-r941;
- Sort and index sam file using Samtools Samtools [26] version 1.9;
- Run rippore.py to calculate per base nucleotide counts. By default, use base 4605; if using a different 28s rRNA reference to NCBI: NR_003287.4, provide the correct base with -b option. rippore.py -s sample.sam. RIPpore can be found at https://gitlab.com/yryan/rippore, accessed on 6 August 2021.
4.15. Statistical Analysis
4.16. Raw Signal Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Virgilio, M.; Lombardi, A.; Caliandro, R.; Fabbrini, M.S. Ribosome-inactivating proteins: From plant defense to tumor attack. Toxins 2010, 2, 2699–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirpe, F.; Gilabert-Oriol, R. Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins: An Overview. In Plant Toxins; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Carlini, C.R., Ligabue-Braun, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Worbs, S.; Köhler, K.; Pauly, D.; Avondet, M.A.; Schaer, M.; Dorner, M.B.; Dorner, B.G. Ricinus communis intoxications in human and veterinary medicine—A summary of real cases. Toxins 2011, 3, 1332–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradberry, S. Ricin and abrin. Medicine 2012, 40, 80–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, A.; Polito, L.; Scicchitano, V.; Orrico, C.; Pasquinelli, G.; Musiani, S.; Santi, S.; Riccio, M.; Bortolotti, M.; Battelli, M.G. Endocytosis and intracellular localisation of type 1 ribosome-inactivating protein saporin-s6. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Saporin-S6: A useful tool in cancer therapy. Toxins 2013, 5, 1698–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, T.; Nyberg, B. Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 3610–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratigopoulou, M.; van Dam, T.P.; Guikema, J.E.J. Base Excision Repair in the Immune System: Small DNA Lesions with Big Consequences. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, E.; Saeed, M.; Zahid, M.; Cassada, D.; Snow, D.; Miljkovic, M.; Rogan, E. Mechanism of DNA depurination by carcinogens in relation to cancer initiation. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobst, K.A.; Klenov, A.; Neller, K.C.M.; Hudak, K.A. Modified Nucleic Acids in Biology and Medicine; Jurga, S., Erdmann, V.A., Barciszewski, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 273–297. [Google Scholar]
- Karran, R.A.; Hudak, K.A. Depurination of Brome mosaic virus RNA3 inhibits its packaging into virus particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7209–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, M.J.; Jolliffe, N.A.; Marsden, C.J.; Pateman, C.S.C.; Smith, D.C.; Spooner, R.A.; Watson, P.D.; Roberts, L.M. Ricin Mechanisms of cytotoxicity. Toxicol. Rev. 2003, 22, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.L.; Shields, K.A.; Chong, D.C. Detection and quantification of ricin-mediated 28S ribosomal depurination by digital droplet PCR. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 563, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, M.M.; Ruzicka, J.A.; Taylor, E.W.; Hall, A.R. Detecting DNA Depurination with Solid-State Nanopores. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stoiber, M.; Quick, J.; Egan, R.; Eun Lee, J.; Celniker, S.; Neely, R.K.; Loman, N.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Brown, J. De novo Identification of DNA Modifications Enabled by Genome-Guided Nanopore Signal Processing. bioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxford Nanopore. Sequencing Short Fragments with Nanopore Technology. 2022. Available online: https://nanoporetech.com/applications/short-fragment-mode (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Audi, J.; Belson, M.; Patel, M.; Schier, J.; Osterloh, J. Ricin poisoning: A comprehensive review. JAMA 2005, 294, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlakić, M. The ribosomal subunit assembly line. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thullier, P.; Griffiths, G. Broad recognition of ricin toxins prepared from a range of Ricinus cultivars using immunochromatographic tests. Clin. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchrieser, J.; Dufloo, J.; Hubert, M.; Monel, B.; Planas, D.; Rajah, M.M.; Planchais, C.; Porrot, F.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Van der Werf, S.; et al. Syncytia formation by SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, S.J.C.; Griffiths, G.D.; Jenner, D.C.; Gwyther, R.J.; Stahl, F.M.; Cork, L.J.; Holley, J.L.; Green, A.C.; Clark, G.C. Production, Characterisation and Testing of an Ovine Antitoxin against Ricin; Efficacy, Potency and Mechanisms of Action. Toxins 2017, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, A.; Hassan, H.H.; Sedelnikova, S.; Niranjan, D.; Hautbergue, G.; Abbas, S.A.; Partridge, L.; Rice, D.; Binz, T.; Davletov, B. Two complementary approaches for intracellular delivery of exogenous enzymes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/hyeshik/poreplex (accessed on 16 June 2022).
- Smith, M.A.; Ersavas, T.; Ferguson, J.M.; Liu, H.; Lucas, M.C.; Begik, O.; Bojarski, L.; Barton, K.; Novoa, E.M. Molecular barcoding of native RNAs using nanopore sequencing and deep learning. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leger, A.; Amaral, P.P.; Pandolfini, L.; Capitanchik, C.; Capraro, F.; Barbieri, I.; Migliori, V.; Luscombe, N.M.; Enright, A.J.; Tzelepis, K.; et al. RNA modifications detection by comparative Nanopore direct RNA sequencing. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Exposure | Min | Max | Median | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.21 | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.06 |
| B-Chain | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.001 |
| Anti Toxin | 0.38 | 0.60 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.11 |
| Saporin | 7.55 | 16.97 | 8.52 | 11.02 | 5.18 |
| Ricin 2 h | 9.18 | 15.34 | 11.65 | 12.04 | 3.13 |
| Ricin 4 h | 24.77 | 29.71 | 26.48 | 25.98 | 3.40 |
| Ricin 6 h | 26.54 | 35.06 | 30.66 | 30.76 | 4.26 |
| Ricin 24 h | 19.78 | 39.64 | 23.81 | 27.74 | 10.50 |
| Ricin 100 pm | 1.68 | 2.75 | 2.07 | 2.17 | 0.54 |
| Ricin 10 pm | 0.64 | 1.04 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.21 |
| Ricin 1 pm | 0.46 | 0.61 | 0.58 | 0.55 | 0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryan, Y.; Harrison, A.; Trivett, H.; Hartley, C.; David, J.; Clark, G.C.; Hiscox, J.A. RIPpore: A Novel Host-Derived Method for the Identification of Ricin Intoxication through Oxford Nanopore Direct RNA Sequencing. Toxins 2022, 14, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070470
Ryan Y, Harrison A, Trivett H, Hartley C, David J, Clark GC, Hiscox JA. RIPpore: A Novel Host-Derived Method for the Identification of Ricin Intoxication through Oxford Nanopore Direct RNA Sequencing. Toxins. 2022; 14(7):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070470
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyan, Yan, Abbie Harrison, Hannah Trivett, Catherine Hartley, Jonathan David, Graeme C. Clark, and Julian A. Hiscox. 2022. "RIPpore: A Novel Host-Derived Method for the Identification of Ricin Intoxication through Oxford Nanopore Direct RNA Sequencing" Toxins 14, no. 7: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070470
APA StyleRyan, Y., Harrison, A., Trivett, H., Hartley, C., David, J., Clark, G. C., & Hiscox, J. A. (2022). RIPpore: A Novel Host-Derived Method for the Identification of Ricin Intoxication through Oxford Nanopore Direct RNA Sequencing. Toxins, 14(7), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070470






