Bitiscetin-3, a Novel C-Type Lectin-like Protein Cloned from the Venom Gland of the Viper Bitis arietans, Induces Platelet Agglutination and Inhibits Binding of Von Willebrand Factor to Collagen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Construction of cDNA and a Library of cDNA-Containing Vectors
2.3. Primers
2.4. PCR and Sequencing
2.5. GenBank Accession Numbers of Bitiscetin-3α and -β
2.6. Sequence Comparisons
2.7. Recombinant Expression of cDNA
2.8. Purification of Recombinant Protein
2.9. Platelet Agglutination Assay
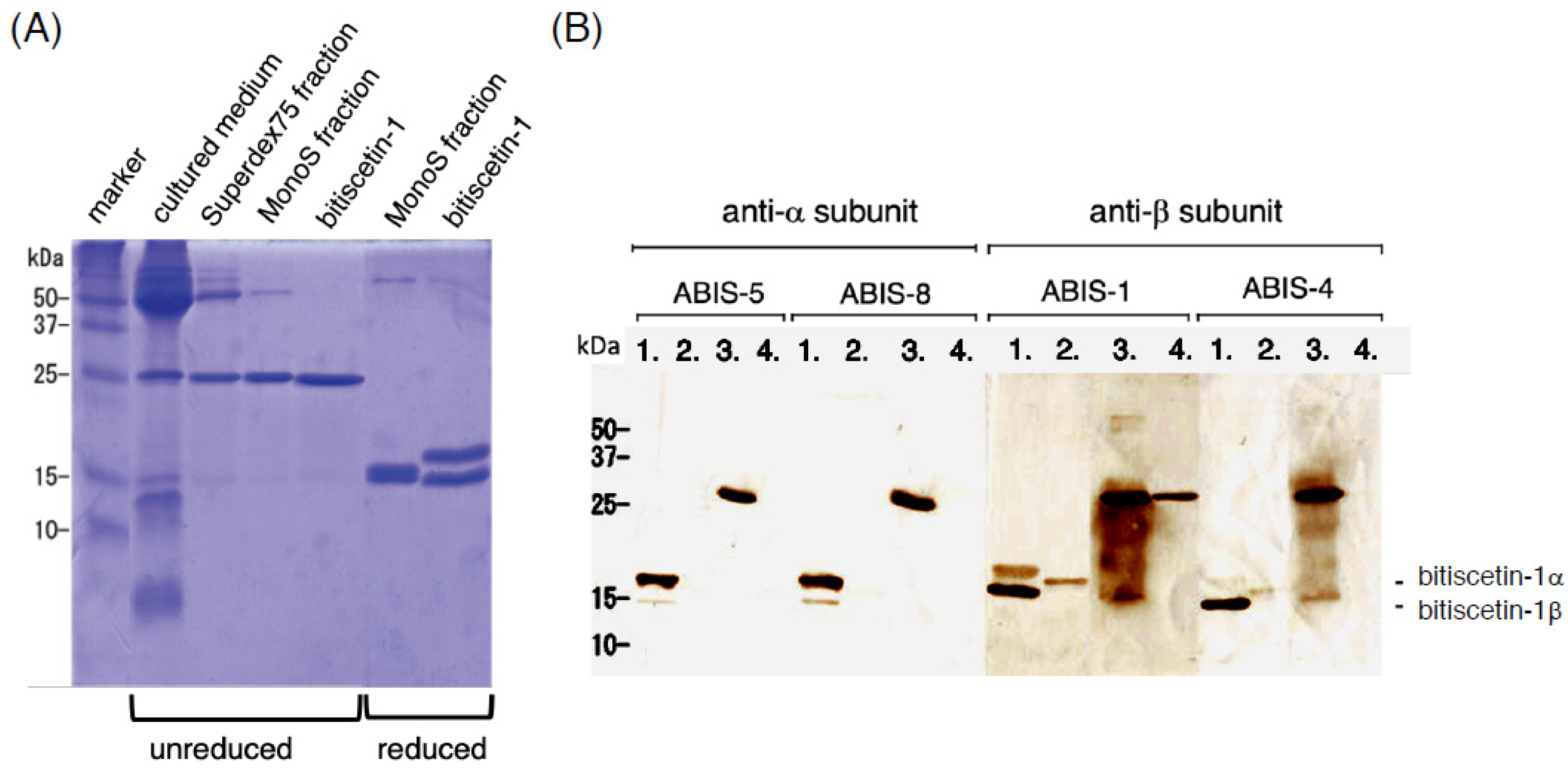
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay (ELISA) for Analyzing the Effect of rBit-3 on Binding of GPIb to VWF
2.12. ELISA for Analyzing the Effect of rBit-3 on Binding of Bitiscetin-1 to VWF
2.13. ELISA for Evaluating the Effect of rBit-3 on VWF-to-Collagen Binding
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. cDNA Cloning of a Novel Bitiscetin
3.2. Bitiscetin-1β cDNA Could Not Be Detected
3.3. The Bitiscetin-3α and -3β Amino Acid Sequences
3.4. Recombinant Expression of Bitiscetin-3
3.5. rBit-3 Induces Platelet Agglutination in Platelet-Rich Plasma, Which Can Be Blocked by Anti-VWF mAb NMC-4
3.6. rBit-3 Can Induce Agglutination of Washed Platelets, but Does So More Efficiently after the Addition of VWF
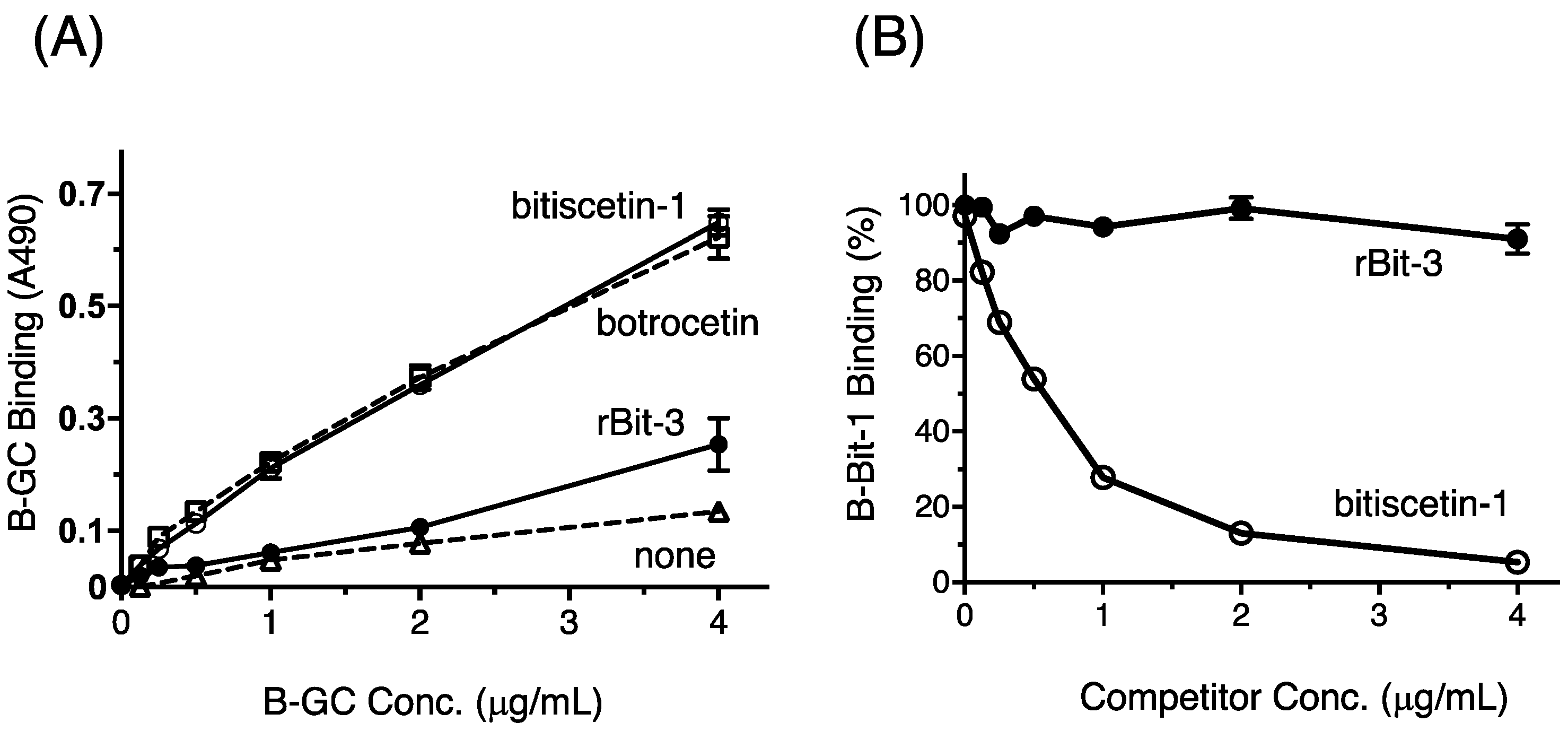
3.7. rBit-3 Enhances Binding between GPIb and VWF, but Not as Efficient as Bitiscetin-1 or Botrocetin
3.8. rBit-3 Does Not Compete with Bitiscetin-1 for Binding to VWF
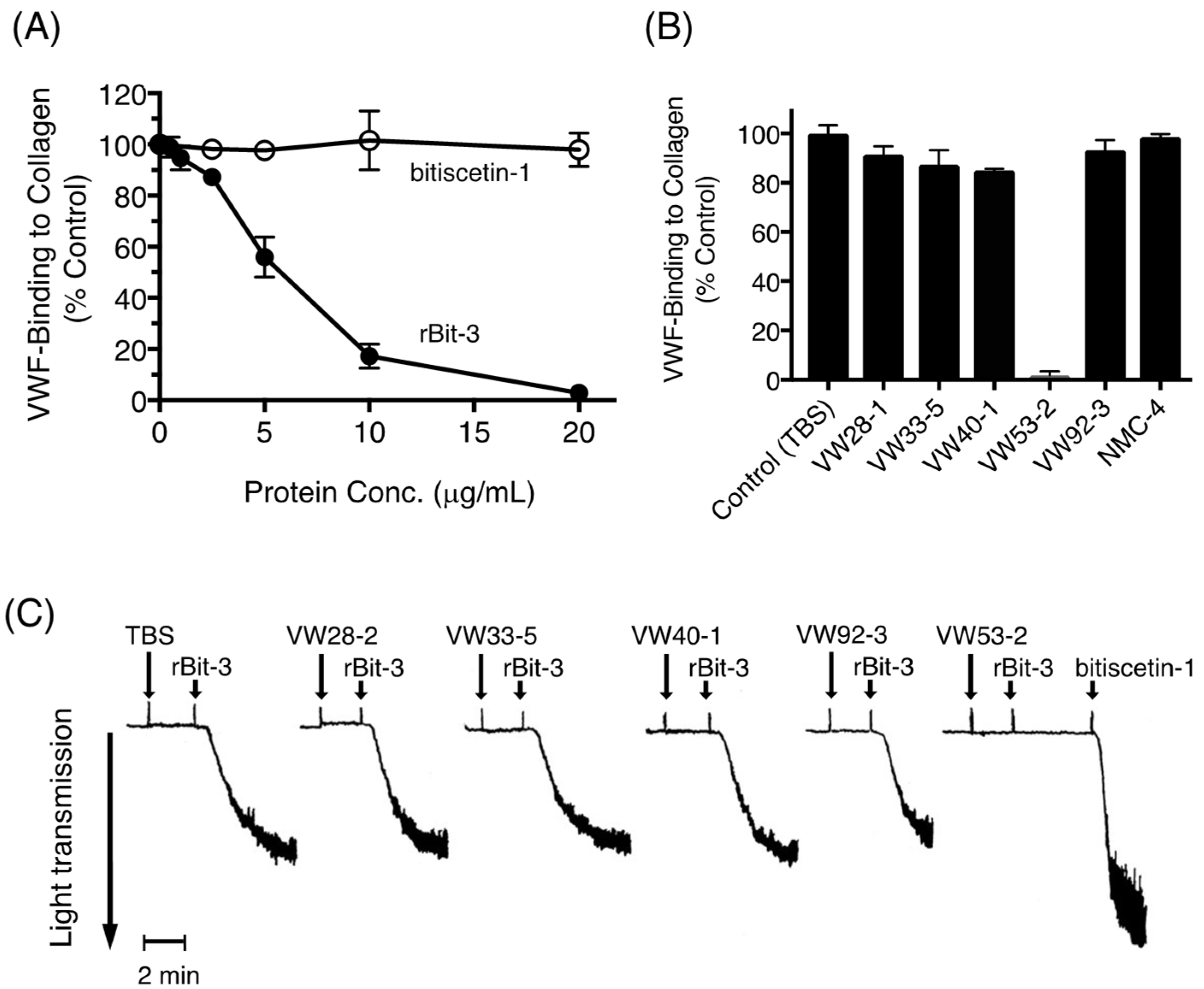
3.9. Effects of rBit-3 on the Collagen-VWF Interaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kini, R.M. Toxins for decoding interface selectivity in nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, N.; Williams, V. Practical applications of snake venom toxins in haemostasis. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemetson, K.J.; Morita, T.; Kini, R.M. Classification and nomenclature of snake venom C-type lectins and related proteins. Toxicon 2009, 54, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, F.S.; Kettner, C.; Schiffman, S.; Shaw, E.; Bajwa, S.S.; Reddy, K.N.; Kirakossian, H.; Patkos, G.B.; Theodor, I.; Pirkle, H. Kallikrein-like activity of crotalase, a snake venom enzyme that clots fibrinogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.C.; Ianzer, D.; Guerreiro, J.R.; Serrano, S.M. Bradykinin-potentiating peptides: Beyond captopril. Toxicon 2012, 59, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péterfi, O.; Boda, F.; Szabó, Z.; Ferencz, E.; Bába, L. Hypotensive Snake Venom Components—A Mini-Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T. Structures and functions of snake venom CLPs (C-type lectin-like proteins) with anticoagulant-, procoagulant-, and platelet-modulating activities. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeyewickrema, L.C.; Berndt, M.C.; Andrews, R.K. Snake venom probes of platelet adhesion receptors and their ligands. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Hamako, J.; Titani, K. Structure and function of snake venom proteins affecting platelet plug formation. Toxins 2010, 2, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.J.; Chung, C.H.; Huang, T.F. From Discovery of Snake Venom Disintegrins to A Safer Therapeutic Antithrombotic Agent. Toxins 2019, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Long, C.; Li, H.; Mwangi, J.; Lu, Q.; Lai, R.; Shen, C. Snake C-Type Lectins Potentially Contribute to the Prey Immobilization in Protobothrops mucrosquamatus and Trimeresurus stejnegeri Venoms. Toxins 2020, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed Abd El-Aziz, T.; Garcia Soares, A.; Stockand, J.D. Snake Venoms in Drug Discovery: Valuable Therapeutic Tools for Life Saving. Toxins 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelensky, A.N.; Gready, J.E. The C-type lectin-like domain superfamily. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 6179–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eble, J.A. Structurally Robust and Functionally Highly Versatile-C-Type Lectin (-Related) Proteins in Snake Venoms. Toxins 2019, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkhous, K.M.; Smith, S.V.; Read, M.S. Botrocetin and von Willebrand factor. In Hemostasis and Animal Venoms; Pirkle, H., Markland, F.S., Jr., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 377–398. [Google Scholar]
- Usami, Y.; Fujimura, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Ozeki, Y.; Nishio, K.; Fukui, H.; Titani, K. Primary structure of two-chain botrocetin, a von Willebrand factor modulator purified from the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamako, J.; Matsui, T.; Suzuki, M.; Ito, M.; Makita, K.; Fujimura, Y.; Ozeki, Y.; Titani, K. Purification and characterization of bitiscetin, a novel von Willebrand factor modulator protein from Bitis arietans snake venom. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 226, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadler, J.E. von Willebrand factor: Two sides of a coin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenting, P.J.; Christophe, O.D.; Denis, C.V. von Willebrand factor biosynthesis, secretion, and clearance: Connecting the far ends. Blood 2015, 125, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Meyer, D.; Sadler, J.E. Localization of von willebrand factor-binding sites for platelet glycoprotein Ib and botrocetin by charged-to-alanine scanning mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 11044–11049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Hamako, J.; Matsushita, T.; Nakayama, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Titani, K. Binding site on human von Willebrand factor of bitiscetin, a snake venom-derived platelet aggregation inducer. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 7939–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, M.S.; Shermer, R.W.; Brinkhous, K.M. Venom coagglutinin: An activator of platelet aggregation dependent on von Willebrand factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 4514–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkhous, K.M.; Reddick, R.L.; Read, M.S.; Nichols, T.C.; Bellinger, D.A.; Griggs, T.R. von Willebrand factor and animal models: Contributions to gene therapy, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, and coronary artery thrombosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1991, 66, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maita, N.; Nishio, K.; Nishimoto, E.; Matsui, T.; Shikamoto, Y.; Morita, T.; Sadler, J.E.; Mizuno, H. Crystal structure of von Willebrand factor A1 domain complexed with snake venom, bitiscetin: Insight into glycoprotein Ibalpha binding mechanism induced by snake venom proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 37777–37781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K.; Doggett, T.; Laurenzi, I.J.; Liddington, R.C.; Diacovo, T.G. The snake venom protein botrocetin acts as a biological brace to promote dysfunctional platelet aggregation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obert, B.; Houllier, A.; Meyer, D.; Girma, J.P. Conformational changes in the A3 domain of von Willebrand factor modulate the interaction of the A1 domain with platelet glycoprotein Ib. Blood 1999, 93, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obert, B.; Romijn, R.A.; Houllier, A.; Huizinga, E.G.; Girma, J.P. Characterization of bitiscetin-2, a second form of bitiscetin from the venom of Bitis arietans: Comparison of its binding site with the collagen-binding site on the von Willebrand factor A3-domain. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopek, M.W.; Girma, J.P.; Fujikawa, K.; Davie, E.W.; Titani, K. Human von Willebrand factor: A multivalent protein composed of identical subunits. Biochemistry 1986, 25, 3146–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, Y.; Usami, Y.; Titani, K.; Niinomi, K.; Nishio, K.; Takase, T.; Yoshioka, A.; Fukui, H. Studies on anti-von Willebrand factor (vWF) monoclonal antibody NMC-4, which inhibits both ristocetin- and botrocetin-induced vWF binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib. Blood 1991, 77, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.M. A method for making alignments of related protein sequences that share very little similarity; shark interleukin 2 as an example. Immunogenetics 2021, 73, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korber, B. HIV Signature and Sequence Variation Analysis. In Computational Analysis of HIV Molecular Sequences; Rodrigo, A.G., Learn, G.H., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Hamako, J.; Suzuki, M.; Hayashi, N.; Ito, M.; Makita, K.; Fujimura, Y.; Ozeki, Y.; Titani, K. Complete amino acid sequence of bitiscetin, a novel von Willebrand factor modulator protein, purified from snake venom of Bitis arietans. Res. Commun. Biochem. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 1, 271–284. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, M.; Hamako, J.; Sakurai, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Titani, K.; Matsui, T. Complete amino acid sequence of kaouthiagin, a novel cobra venom metalloproteinase with two disintegrin-like sequences. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 4503–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Hori, A.; Hamako, J.; Matsushita, F.; Ozeki, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Hayakawa, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimura, Y. Mutant botrocetin-2 inhibits von Willebrand factor-induced platelet agglutination. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.A.; Oliver, J.; Hasson, S.S.; Bharati, K.; Theakston, R.D. Novel sequences encoding venom C-type lectins are conserved in phylogenetically and geographically distinct Echis and Bitis viper species. Gene 2003, 315, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, G.; Logan, R.A.; Leung, K.Y.; Newberry, F.J.; Rowley, P.D.; Dunbar, J.P.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Casewell, N.R.; Harrison, R.A. Stabilising the Integrity of Snake Venom mRNA Stored under Tropical Field Conditions Expands Research Horizons. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, T.P.; Woods, K.R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 3824–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Delaney, M.K.; O’Brien, K.A.; Du, X. Signaling during platelet adhesion and activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Kunishima, S.; Hamako, J.; Katayama, M.; Kamiya, T.; Naoe, T.; Ozeki, Y.; Fujimura, Y.; Titani, K. Interaction of von Willebrand factor with the extracellular matrix and glycocalicin under static conditions. J. Biochem. 1997, 121, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romijn, R.A.; Westein, E.; Bouma, B.; Schiphorst, M.E.; Sixma, J.J.; Lenting, P.J.; Huizinga, E.G. Mapping the collagen-binding site in the von Willebrand factor-A3 domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 15035–15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daltry, J.C.; Wuster, W.; Thorpe, R.S. Diet and snake venom evolution. Nature 1996, 379, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, E.L.; Arbuckle, K. Coevolution of Snake Venom Toxic Activities and Diet: Evidence that Ecological Generalism Favours Toxicological Diversity. Toxins 2019, 11, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizinga, E.G.; Martijn van der Plas, R.; Kroon, J.; Sixma, J.J.; Gros, P. Crystal structure of the A3 domain of human von Willebrand factor: Implications for collagen binding. Structure 1997, 5, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brondijk, T.H.; Bihan, D.; Farndale, R.W.; Huizinga, E.G. Implications for collagen I chain registry from the structure of the collagen von Willebrand factor A3 domain complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5253–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Lin, J.; Cruz, M.A.; Dong, J.F.; Zhu, C. Force-induced cleavage of single VWFA1A2A3 tridomains by ADAMTS-13. Blood 2010, 115, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.T.; de Groot, R.; Xiang, Y.; Luken, B.M.; Lane, D.A. Unraveling the scissile bond: How ADAMTS13 recognizes and cleaves von Willebrand factor. Blood 2011, 118, 3212–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Fujimura, Y.; Kokubo, T.; Imamura, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Handa, M.; Suzuki, M.; Matsui, T.; Titani, K.; Yoshioka, A. The cDNA cloning and molecular characterization of a snake venom platelet glycoprotein Ib-binding protein, mamushigin, from Agkistrodon halys blomhoffii venom. Thromb. Haemost. 1998, 79, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, E.; Fujimura, Y.; Miura, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Fukui, H.; Narita, N.; Usami, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Titani, K. Alboaggregin-B and botrocetin, two snake venom proteins with highly homologous amino acid sequences but totally distinct functions on von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 191, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Usami, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Miura, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Makita, K.; Taniuchi, Y.; Hirano, K.; Titani, K. Complete amino acid sequence and identification of the platelet glycoprotein Ib-binding site of jararaca GPIb-BP, a snake venom protein isolated from Bothrops jararaca. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10635–10639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nashimoto, Y.; Matsushita, F.; Dijkstra, J.M.; Nakamura, Y.; Akiyama, H.; Hamako, J.; Morita, T.; Araki, S.; Matsui, T. Bitiscetin-3, a Novel C-Type Lectin-like Protein Cloned from the Venom Gland of the Viper Bitis arietans, Induces Platelet Agglutination and Inhibits Binding of Von Willebrand Factor to Collagen. Toxins 2022, 14, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040236
Nashimoto Y, Matsushita F, Dijkstra JM, Nakamura Y, Akiyama H, Hamako J, Morita T, Araki S, Matsui T. Bitiscetin-3, a Novel C-Type Lectin-like Protein Cloned from the Venom Gland of the Viper Bitis arietans, Induces Platelet Agglutination and Inhibits Binding of Von Willebrand Factor to Collagen. Toxins. 2022; 14(4):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040236
Chicago/Turabian StyleNashimoto, Youhei, Fumio Matsushita, Johannes M. Dijkstra, Yuta Nakamura, Hidehiko Akiyama, Jiharu Hamako, Takashi Morita, Satohiko Araki, and Taei Matsui. 2022. "Bitiscetin-3, a Novel C-Type Lectin-like Protein Cloned from the Venom Gland of the Viper Bitis arietans, Induces Platelet Agglutination and Inhibits Binding of Von Willebrand Factor to Collagen" Toxins 14, no. 4: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040236
APA StyleNashimoto, Y., Matsushita, F., Dijkstra, J. M., Nakamura, Y., Akiyama, H., Hamako, J., Morita, T., Araki, S., & Matsui, T. (2022). Bitiscetin-3, a Novel C-Type Lectin-like Protein Cloned from the Venom Gland of the Viper Bitis arietans, Induces Platelet Agglutination and Inhibits Binding of Von Willebrand Factor to Collagen. Toxins, 14(4), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040236




