Distinct Metabolic States Are Observed in Hypoglycemia Induced in Mice by Ricin Toxin or by Fasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
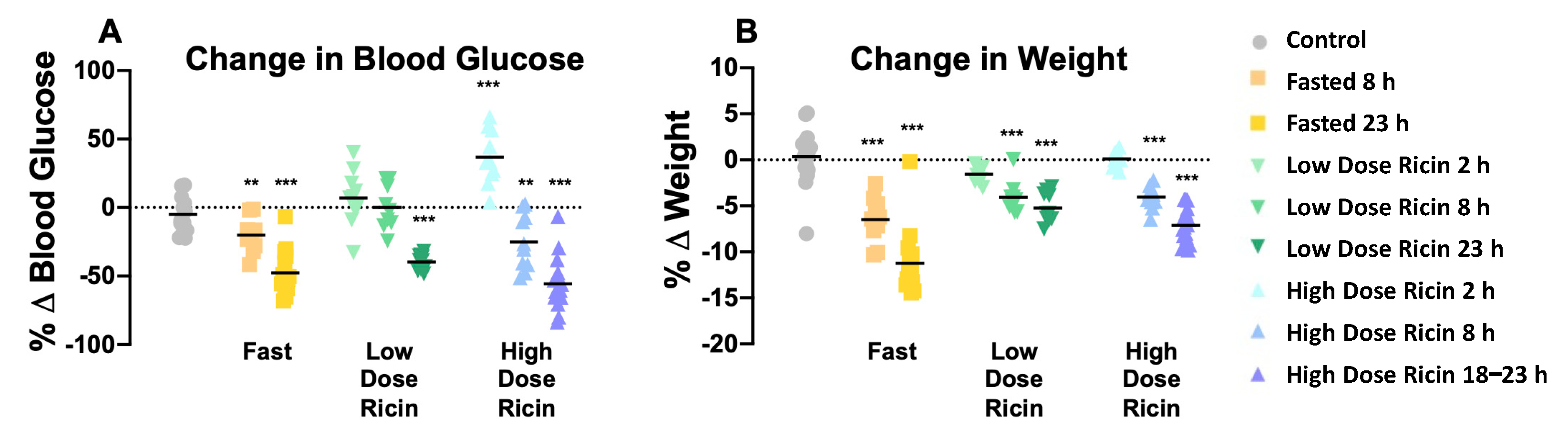
2.1. The Effect of Ricin Treatment and Fasting on Weight Loss and Blood Glucose Concentration
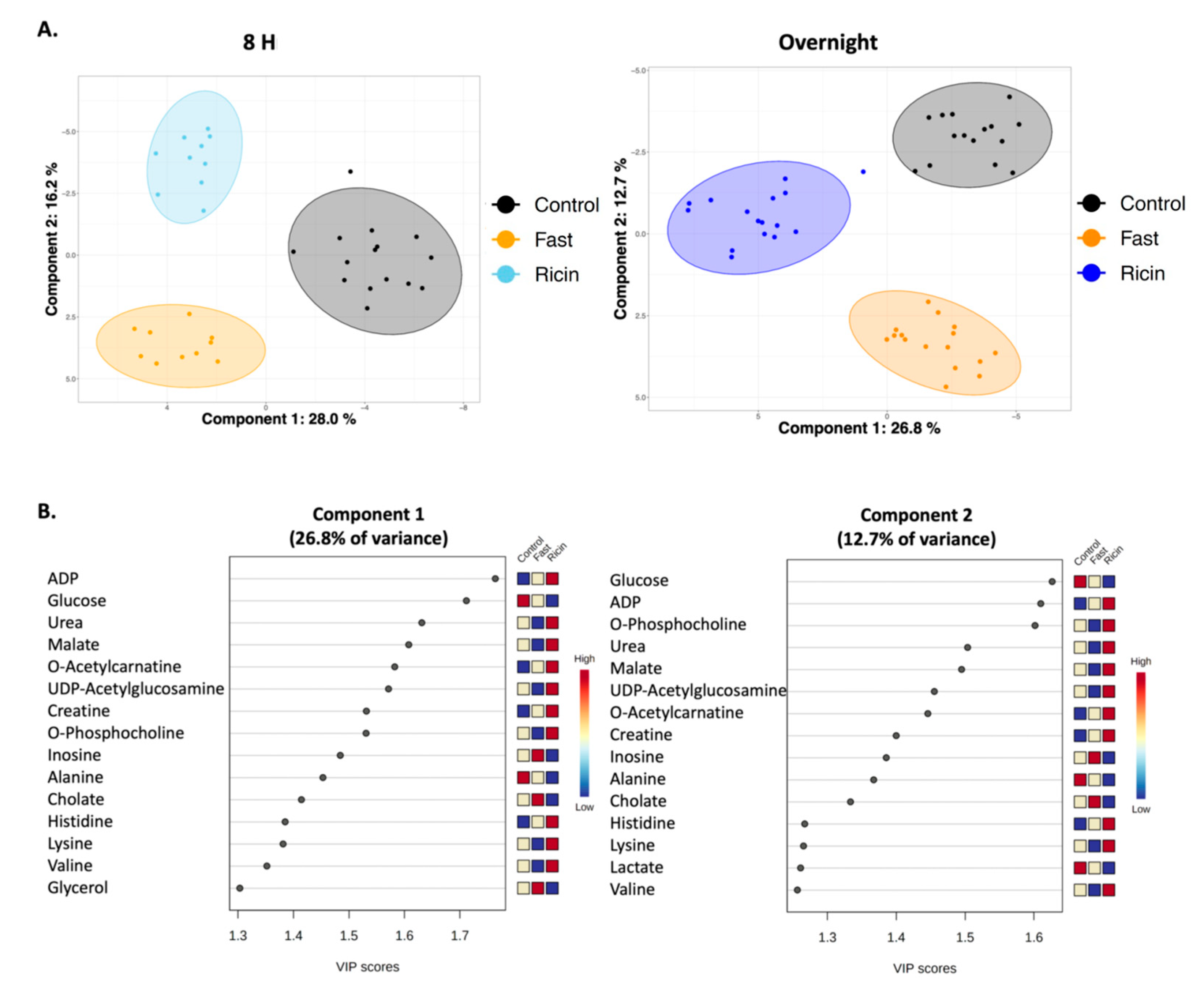
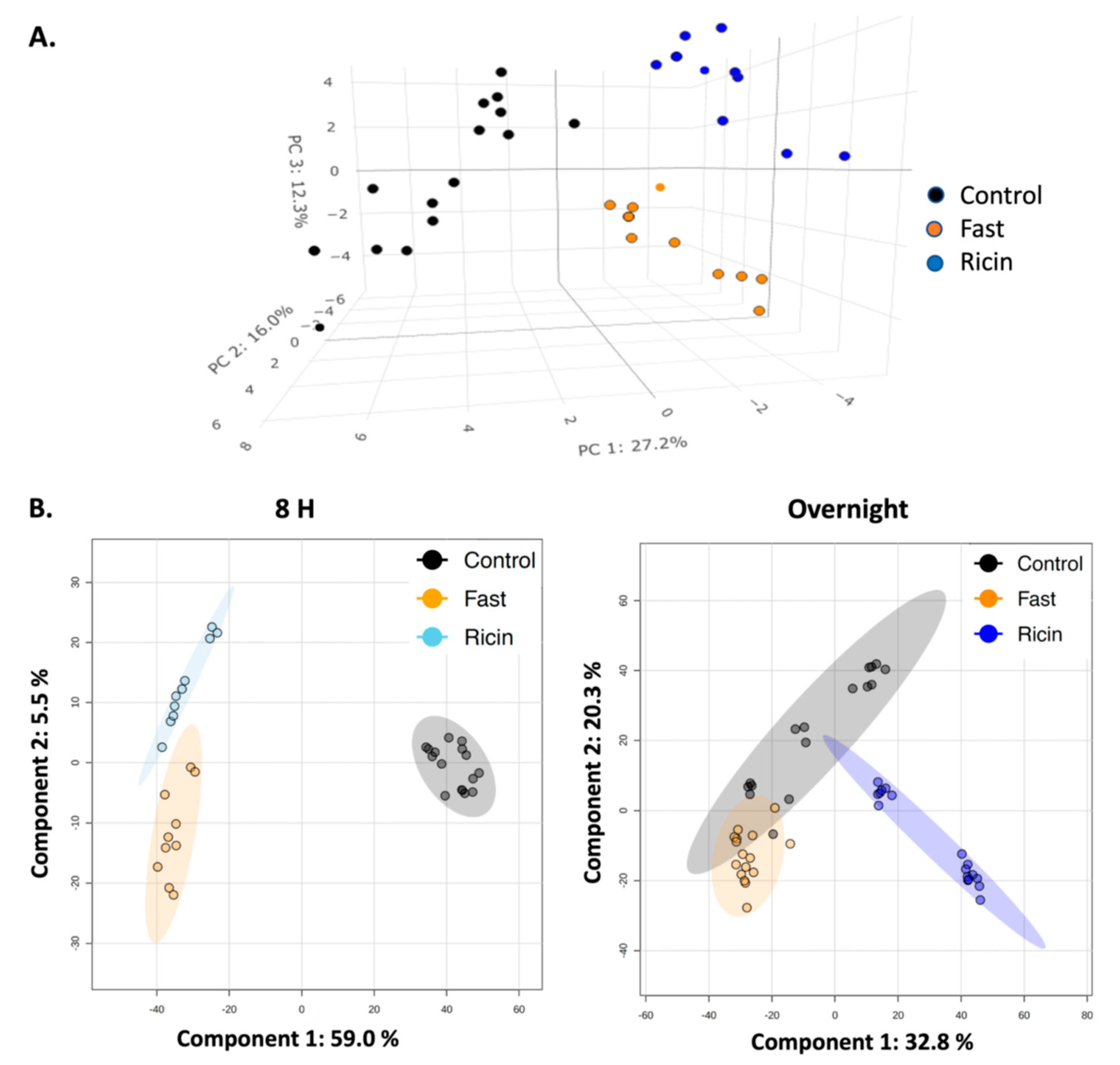
2.2. Analyses of Hepatic Metabolites in Hypoglycemia Induced by Ricin Administration or by Fasting
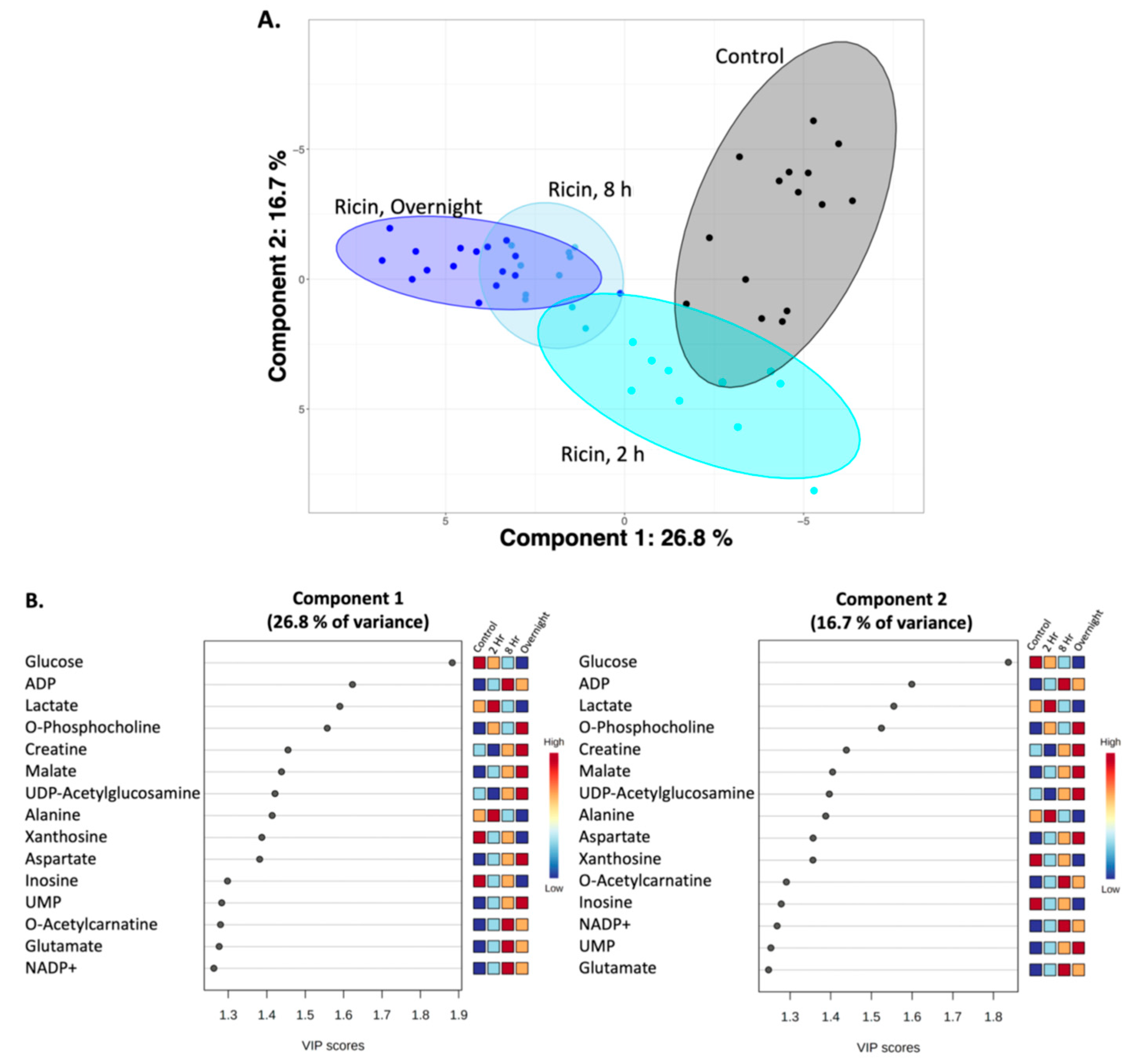
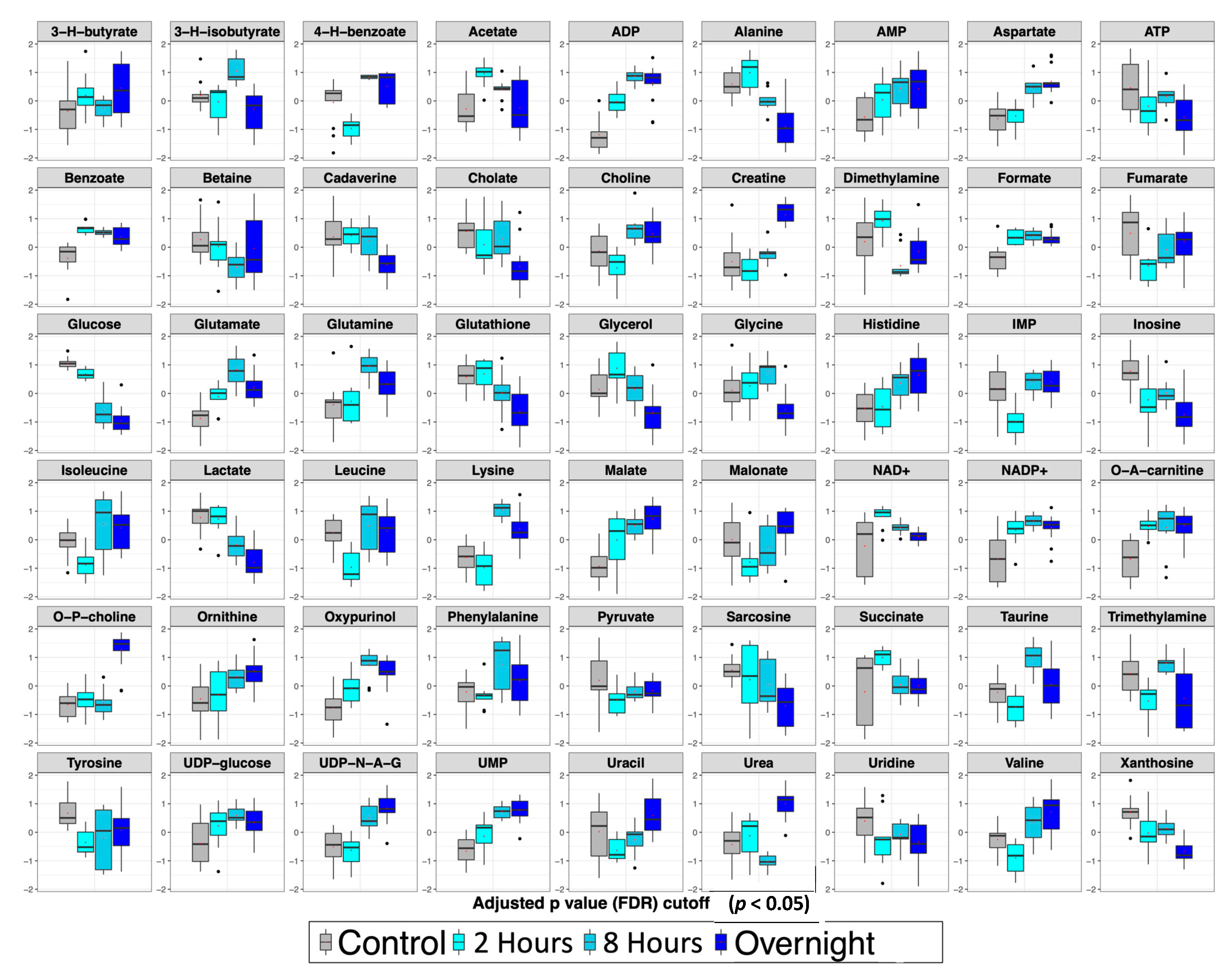
2.3. Temporal Analysis of Metabolic Changes Following Ricin Administration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Handling
4.2. Metabolite Extraction for NMR Analysis
4.3. H-NMR Analyses
4.4. Statistical Analysis of the Metabolite NMR Data
4.5. Metabolite Extraction for LC-MS Analysis
4.6. LC-MS Analyses
4.7. Statistical Analysis of Mass Spectrometry Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Deurs, B.; Tønnessen, T.I.; Petersen, O.W.; Sandvig, K.; Olsnes, S. Routing of internalized ricin and ricin conjugates to the Golgi complex. J. Cell Biol. 1986, 102, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandvig, K.; van Deurs, B. Entry of ricin and Shiga toxin into cells: Molecular mechanisms and medical perspectives. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5943–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, M.J.; Jolliffe, N.A.; Marsden, C.J.; Pateman, C.S.; Smith, D.C.; Spooner, R.A.; Watson, P.D.; Roberts, L.M. Ricin. Mechanisms of cytotoxicity. Toxicol. Rev. 2003, 22, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvig, K.; Skotland, T.; van Deurs, B.; Klokk, T.I. Retrograde transport of protein toxins through the Golgi apparatus. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 140, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, R.A.; Lord, J.M. Ricin Trafficking in Cells. Toxins 2015, 7, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa-Rogozińska, N.; Sominka, H.; Nowakowska-Gołacka, J.; Sandvig, K.; Słomińska-Wojewódzka, M. Intracellular Transport and Cytotoxicity of the Protein Toxin Ricin. Toxins 2019, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grela, P.; Szajwaj, M.; Horbowicz-Drożdżal, P.; Tchórzewski, M. How Ricin Damages the Ribosome. Toxins 2019, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandvig, K.; Kavaliauskiene, S.; Skotland, T. The Protein Toxins Ricin and Shiga Toxin as Tools to Explore Cellular Mechanisms of Internalization and Intracellular Transport. Toxins 2021, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradberry, S.M.; Dickers, K.J.; Rice, P.; Griffiths, G.D.; Vale, J.A. Ricin poisoning. Toxicol. Rev. 2003, 22, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audi, J.; Belson, M.; Patel, M.; Schier, J.; Osterloh, J. Ricin poisoning: A comprehensive review. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005, 294, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schep, L.J.; Temple, W.A.; Butt, G.A.; Beasley, M.D. Ricin as a weapon of mass terror—Separating fact from fiction. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, G.D. Understanding ricin from a defensive viewpoint. Toxins 2011, 3, 1373–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.H.; Smallshaw, J.E.; Song, K.; Berry, J.; Vitetta, E.S. Passive and active vaccination strategies to prevent ricin poisoning. Toxins 2011, 3, 1163–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.D. Bioterrorism: Toxins as weapons. J. Pharm. Pract. 2012, 25, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.H.; Bhaskaran, M.; Brey, R.N.; Didier, P.J.; Doyle-Meyers, L.A.; Roy, C.J. Clinical and Pathological Findings Associated with Aerosol Exposure of Macaques to Ricin Toxin. Toxins 2015, 7, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, M.; Didier, P.J.; Sivasubramani, S.K.; Doyle, L.A.; Holley, J.; Roy, C.J. Pathology of Lethal and Sublethal Doses of Aerosolized Ricin in Rhesus Macaques. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 42, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddaloni, M.; Cooke, C.; Wilkinson, R.; Stout, A.V.; Eng, L.; Pincus, S.H. Immunological characteristics associated with protective efficacy of antibodies to ricin. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6221–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, S.; Das, A.; Song, K.; Maresh, G.; Corti, M.; Berry, J. Role of Fc in Antibody-Mediated Protection from Ricin Toxin. Toxins 2014, 6, 1512–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Mize, R.R.; Marrero, L.; Corti, M.; Kirk, J.M.; Pincus, S.H. Antibody to Ricin A Chain Hinders Intracellular Routing of Toxin and Protects Cells Even after Toxin Has Been Internalized. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.H.; McClure, J. Soluble CD4 enhances the efficacy of immunotoxins directed against gp41 of the human immunodeficiency virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.H.; Fang, H.; Wilkinson, R.A.; Marcotte, T.K.; Robinson, J.E.; Olson, W.C. In vivo efficacy of anti-gp41, but not anti-gp120, immunotoxins in a mouse model of HIV infection. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 2236–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, S.H.; Song, K.; Maresh, G.A.; Frank, A.; Worthylake, D.; Chung, H.K.; Polacino, P.; Hamer, D.H.; Coyne, C.P.; Rosenblum, M.G.; et al. Design and In Vivo Characterization of Immunoconjugates Targeting HIV gp160. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01360-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, S.H.; Eng, L.; Cooke, C.L.; Maddaloni, M. Identification of hypoglycemia in mice as a surrogate marker of ricin toxicosis. Comp. Med. 2002, 52, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roche, J.; Stone, M.; Gross, L.; Lindner, M.; Seaner, R.; Pincus, S.; Obrig, T. Post-exposure targeting of specific epitopes on ricin toxin abrogates toxin-induced hypoglycemia, hepatic injury, and lethality in a mouse model. Lab. Investig. 2008, 88, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, L.M.; O'Hara, J.; Brey, R.N.; Mantis, N.J. A Monoclonal Immunoglobulin G Antibody Directed against an Immunodominant Linear Epitope on the Ricin A Chain Confers Systemic and Mucosal Immunity to Ricin. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flexner, S. The histological changes produced by ricin and abrin intoxications. J. Exp. Med. 1897, 2, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.; Korcheva, V.; Jacoby, D.B.; Magun, B. Intrapulmonary delivery of ricin at high dosage triggers a systemic inflammatory response and glomerular damage. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, J.M.; Aslam, R.U.; Mantis, N.J. Evidence for widespread epithelial damage and coincident production of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in a murine model of intestinal ricin intoxication. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindauer, M.L.; Wong, J.; Iwakura, Y.; Magun, B.E. Pulmonary inflammation triggered by ricin toxin requires macrophages and IL-1 signaling. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.; Wilkinson, L.J.; Griffiths, G.D. Inflammatory gene expression in response to sub-lethal ricin exposure in Balb/c mice. Toxicology 2009, 264, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapoznikov, A.; Gal, Y.; Evgy, Y.; Aftalion, M.; Katalan, S.; Sabo, T.; Kronman, C.; Falach, R. Intramuscular Exposure to a Lethal Dose of Ricin Toxin Leads to Endothelial Glycocalyx Shedding and Microvascular Flow Abnormality in Mice and Swine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falach, R.; Goldvaser, M.; Halpern, P.; Rosner, A.; Sapoznikov, A.; Gal, Y.; Goren, O.; Sabo, T.; Kronman, C.; Katalan, S. Pathophysiological profile of awake and anesthetized pigs following systemic exposure to the highly lethal ricin toxin. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 60, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapoznikov, A.; Rosner, A.; Falach, R.; Gal, Y.; Aftalion, M.; Evgy, Y.; Israeli, O.; Sabo, T.; Kronman, C. Intramuscular Ricin Poisoning of Mice Leads to Widespread Damage in the Heart, Spleen, and Bone Marrow. Toxins 2019, 11, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.H. Tissue changes in alimentary canal of mouse induced by ricin poisoning. J. Physiol. 1957, 135, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro, M.; Mitarai, M.; Harada, H.; Sekine, I.; Nishimori, N.; Kikutani, M. Biochemical studies on oral toxicity of ricin. I. Ricin administered orally can impair sugar absorption by rat small intestine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 3222–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, I.; Kawase, Y.; Nishimori, I.; Mitarai, M.; Harada, H.; Ishiguro, M.; Kikutani, M. Pathological study on mucosal changes in small intestine of rat by oral administration of ricin. I. Microscopical evaluations. Pathol. Int. 1986, 36, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, C.J.; Song, K.; Sivasubramani, S.K.; Gardner, D.J.; Pincus, S.H. Animal models of ricin toxicosis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 357, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, S.J.; Padgen, D.B.; Knight, S.; Gwyther, R.J.; Holley, J.L.; Clark, G.C.; Green, A.C. Establishment of a Novel Oral Murine Model of Ricin Intoxication and Efficacy Assessment of Ovine Ricin Antitoxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamor, M.; Gharbi, E.; Bouzid, S.; Chakroun-Walha, O.; Rekik, N. Ricin poisoning after oral ingestion of castor beans: A case report and literature review. Afr. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 10, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.H.; Kyro, A.; Maresh, G.A.; Peters, T.; Kempa, J.; Marcotte, T.; Gao, Z.; Ye, J.; Copié, V.; Song, K. Parenteral exposure of mice to ricin toxin induces fatal hypoglycemia by suppressing hepatic glucose-6-phosphatase expression. Toxins 2022, 14, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G. Multivariate outliers and decompositions of mahalanobis distance. Commun Stat.-Theory Methods 2000, 29, 1511–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittah, N.E.; Vella, A. Management of endocrine disease: Pathogenesis and management of hypoglycemia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 177, R37–R47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryer, P.E. Hypoglycemia is the limiting factor in the management of diabetes. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 1999, 15, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chajek-Shaul, T.; Barash, V.; Weidenfeld, J.; Friedman, G.; Ziv, E.; Shohami, E.; Shiloni, E. Lethal hypoglycemia and hypothermia induced by administration of low doses of tumor necrosis factor to adrenalectomized rats. Metab. Clin. Exp. 1990, 39, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cabo, R.; Mattson, M.P. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.P.; Weiss, S.B. The function of cytidine coenzymes in the biosynthesis of phospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 222, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibellini, F.; Smith, T.K. The Kennedy pathway—De novo synthesis of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallampalli, R.K.; Ryan, A.J.; Salome, R.G.; Jackowski, S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits expression of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9699–9708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozawa, O.; Suzuki, A.; Kaida, T.; Tokuda, H.; Uematsu, T. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha autoregulates interleukin-6 synthesis via activation of protein kinase C. Function of sphingosine 1-phosphate and phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25099–25104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Wang, Q.; Su, Y.; Xuan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Qian, Y.; Lash, G.E. Identification and functional analyses of differentially expressed metabolites in early stage endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatham, J.C.; Zhang, J.; Wende, A.R. Role of O-Linked N-Acetylglucosamine Protein Modification in Cellular (Patho)Physiology. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 427–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhman, A.R.; Kuhn, K.; Alaaeddine, N.; Lotz, M. N-Acetylglucosamine Prevents IL-1β-Mediated Activation of Human Chondrocytes. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5155–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, D.F.; Wamsley, J.J.; Kumar, M.; Li, D.; Gray, L.G.; Hart, G.W.; Jones, D.R.; Mayo, M.W. Modification of RelA by O-linked N-acetylglucosamine links glucose metabolism to NF-κB acetylation and transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16888–16893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousf, S.; Sardesai, D.M.; Mathew, A.B.; Khandelwal, R.; Acharya, J.D.; Sharma, S.; Chugh, J. Metabolic signatures suggest o-phosphocholine to UDP-N-acetylglucosamine ratio as a potential biomarker for high-glucose and/or palmitate exposure in pancreatic β-cells. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Nava, R.; Alarcón-Aguilar, F.J.; Giacoman-Martínez, A.; Blancas-Flores, G.; Aguayo-Cerón, K.A.; Ballinas-Verdugo, M.A.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; Huang, F.; Villafaña-Rauda, S.; Almanza-Pérez, J.C. Glycine is a competitive antagonist of the TNF receptor mediating the expression of inflammatory cytokines in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancas-Flores, G.; Alarcón-Aguilar, F.J.; García-Macedo, R.; Almanza-Pérez, J.C.; Flores-Sáenz, J.L.; Román-Ramos, R.; Ventura-Gallegos, J.L.; Kumate, J.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Cruz, M. Glycine suppresses TNF-alpha-induced activation of NF-κB in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 689, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvir, A.; Dagan, Z.; Mizrachi, A.; Eisenkraft, A. Lessons from a suicide attempt by intra-abdominal ricin injection. Am. J. Disaster Med. 2021, 16, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, R.V.; Goodchild, S.A.; Winder, C.L.; Southam, A.D.; Weber, R.J.M.; Stahl, F.M.; Docx, C.; Patel, V.; Green, A.C.; Viant, M.R.; et al. Multiple metabolic pathways are predictive of ricin intoxication in a rat model. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Numata, K.; Ito, T.; Takagi, K.; Matsukawa, A. Innate immune response in Th1- and Th2-dominant mouse strains. Shock 2004, 22, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, A.; Brian, P.; Tripet, B.P.; Eilers, B.J.; Tegman, M.; Thompson, D.; Copié, V.; Burkhead, J.L. Copper modulates sex-specific fructose hepatoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NALFD) Wistar rat models. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 78, 108316–108327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goksuluk, S.K.D.; Zararsiz, G. MVN: An R Package for Assessing Multivariate Normality. R J. 2014, 6, 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt, A.J.; Hess, A.M. Filtering for increased power for microarray data analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kempa, J.; O’Shea-Stone, G.; Moss, C.E.; Peters, T.; Marcotte, T.K.; Tripet, B.; Eilers, B.; Bothner, B.; Copié, V.; Pincus, S.H. Distinct Metabolic States Are Observed in Hypoglycemia Induced in Mice by Ricin Toxin or by Fasting. Toxins 2022, 14, 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120815
Kempa J, O’Shea-Stone G, Moss CE, Peters T, Marcotte TK, Tripet B, Eilers B, Bothner B, Copié V, Pincus SH. Distinct Metabolic States Are Observed in Hypoglycemia Induced in Mice by Ricin Toxin or by Fasting. Toxins. 2022; 14(12):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120815
Chicago/Turabian StyleKempa, Jacob, Galen O’Shea-Stone, Corinne E. Moss, Tami Peters, Tamera K. Marcotte, Brian Tripet, Brian Eilers, Brian Bothner, Valérie Copié, and Seth H. Pincus. 2022. "Distinct Metabolic States Are Observed in Hypoglycemia Induced in Mice by Ricin Toxin or by Fasting" Toxins 14, no. 12: 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120815
APA StyleKempa, J., O’Shea-Stone, G., Moss, C. E., Peters, T., Marcotte, T. K., Tripet, B., Eilers, B., Bothner, B., Copié, V., & Pincus, S. H. (2022). Distinct Metabolic States Are Observed in Hypoglycemia Induced in Mice by Ricin Toxin or by Fasting. Toxins, 14(12), 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120815









