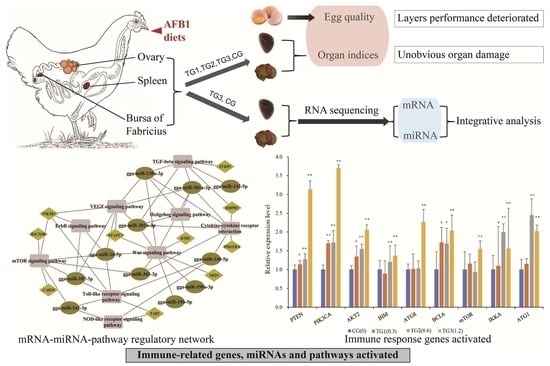
Integrated Transcriptome Analysis Reveals mRNA–miRNA Pathway Crosstalk in Roman Laying Hens’ Immune Organs Induced by AFB1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Egg Quality Was Adversely Affected by Dietary AFB1
2.2. Transcriptional Profiles of the Chicken Immune Organs
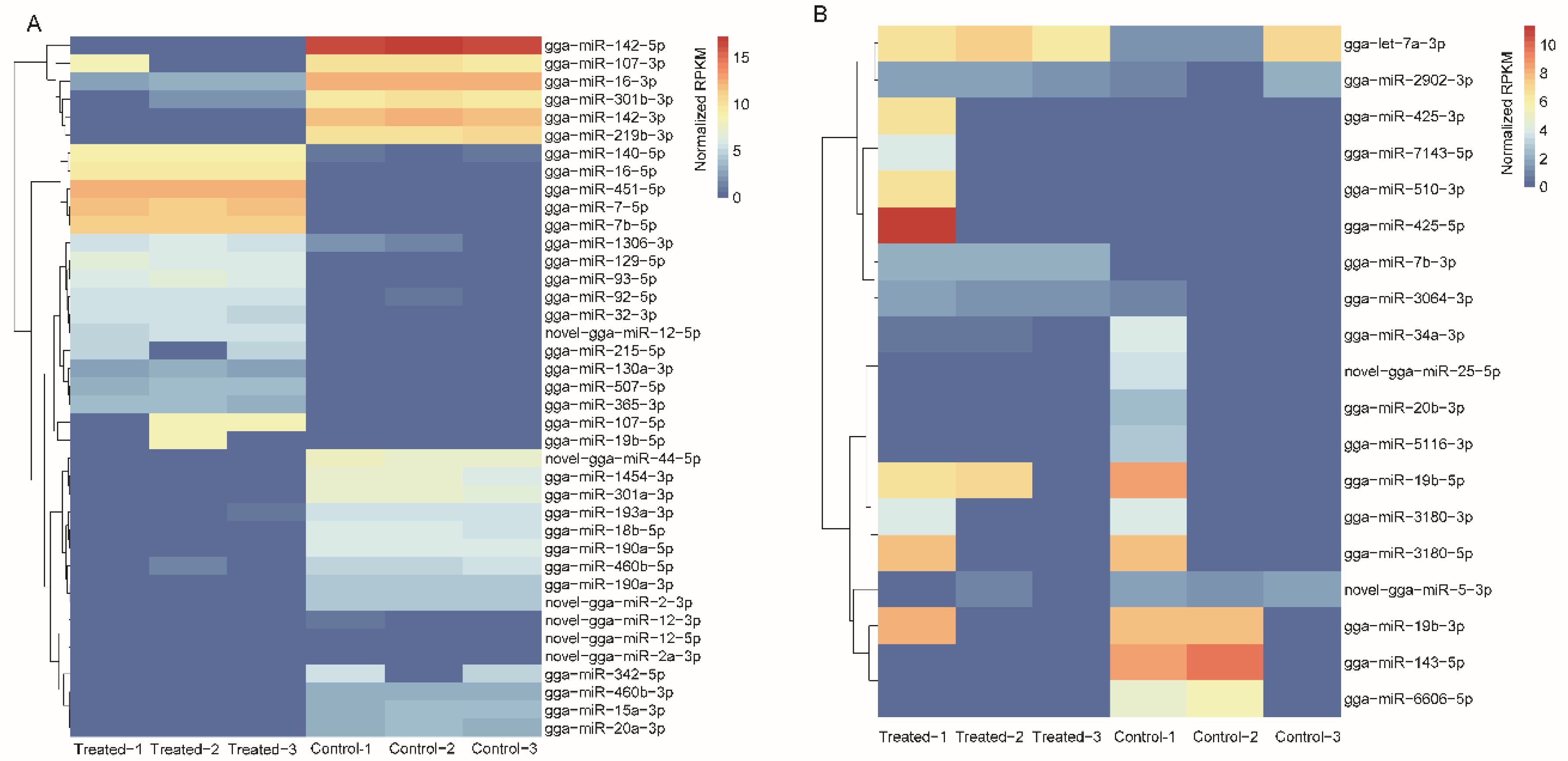
2.3. Transcriptional Response to AFB1 Consumption
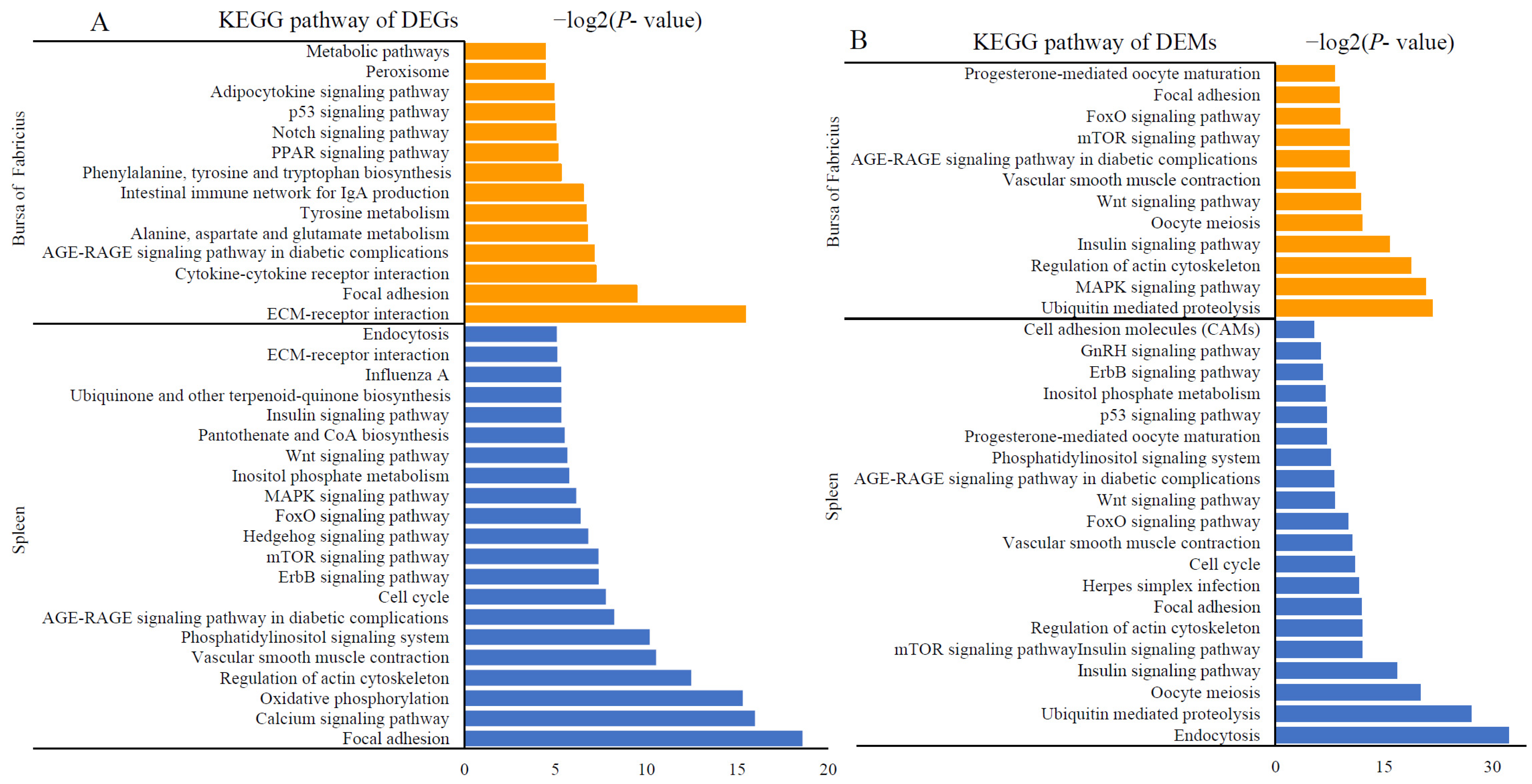
2.4. Activation of Immune- and Metabolism-Related Pathways after AFB1 Consumption
2.5. Integrated Analysis of DEGs and DEMs
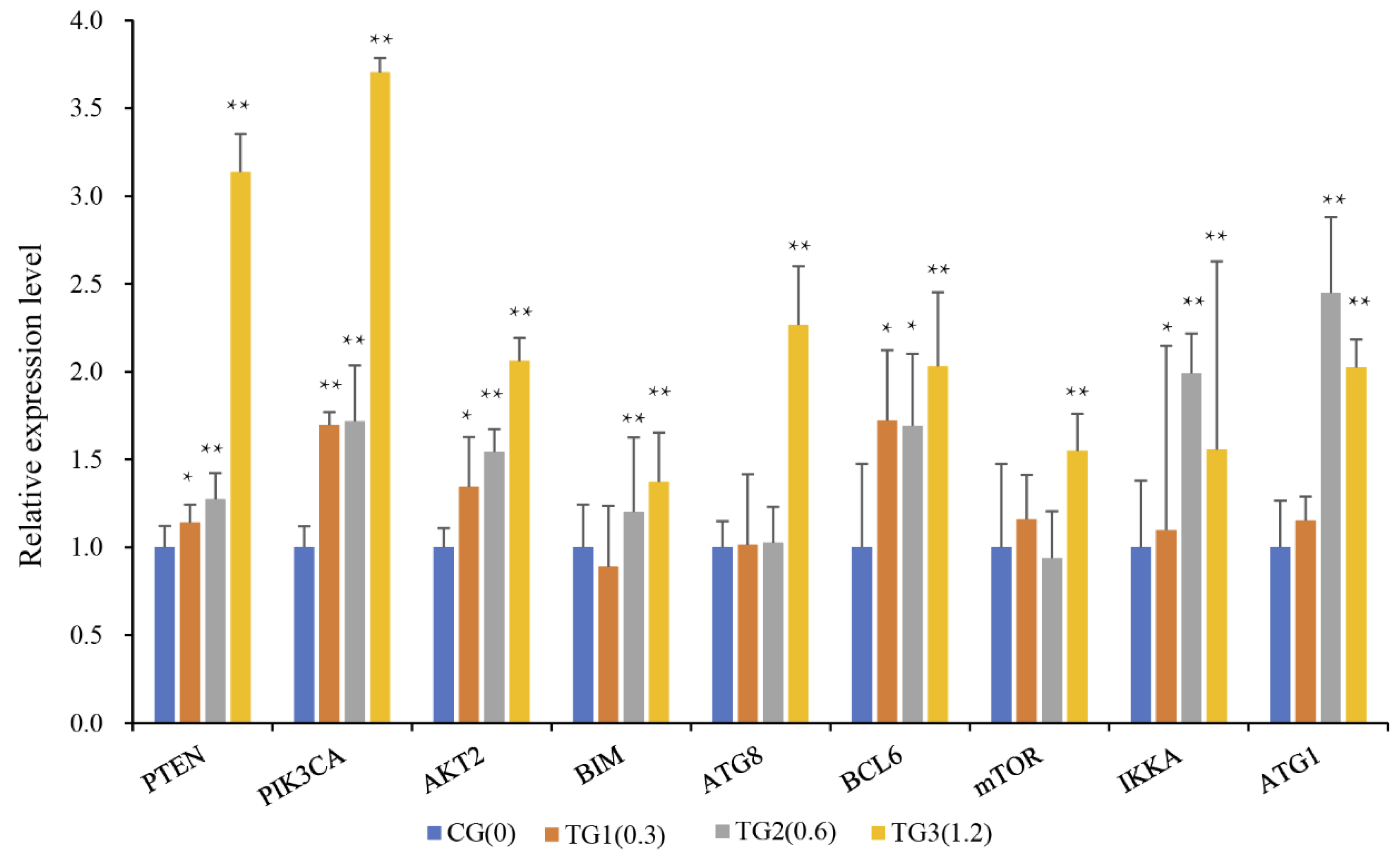
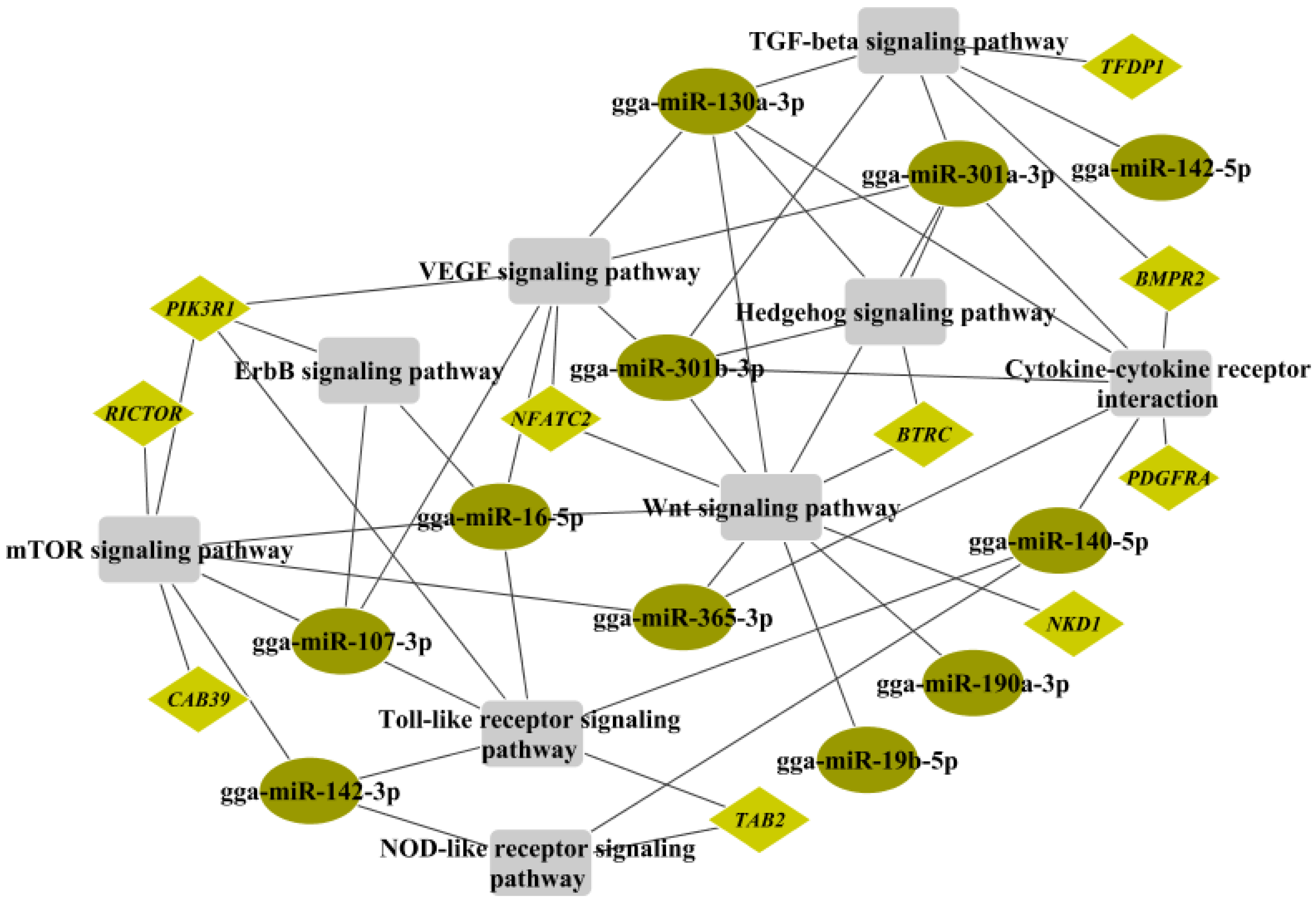
2.6. Crosstalk between miRNA–mRNA and Pathways in Cancer Progression and Immune Response
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals, Diets, and Sampling
5.2. Measurements of Egg Quality and Organ Indices
5.3. RNA Isolation and Sequencing
5.4. Transcriptomic Data Analysis
5.5. mRNA–miRNA Target Association Analysis
5.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR of Genes Associated with Interacting Pathways
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, W.; Yu, P.; Yang, K.; Cao, D. Aflatoxin B1: Metabolism, toxicology, and its involvement in oxidative stress and cancer development. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2022, 32, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauletto, M.; Tolosi, R.; Giantin, M.; Guerra, G.; Barbarossa, A.; Zaghini, A.; Dacasto, M. Insights into Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity in Cattle: An In Vitro Whole-Transcriptomic Approach. Toxins 2020, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, A.W.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E.; Bohm, J. Aflatoxin B1 in Affecting Broiler’s Performance, Immunity, and Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review of History and Contemporary Issues. Toxins 2011, 3, 566–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrar, M.; Anjum, F.M.; Butt, M.S.; Pasha, I.; Randhawa, M.A.; Saeed, F.; Waqas, K. Aflatoxins: Biosynthesis, occurrence, toxicity, and remedies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A.B.; Engin, A. DNA damage checkpoint response to aflatoxin B1. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 65, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, P.; Wang, Y.; Viallet, J.; Jilkova, Z.M. The Chicken Embryo Model: A Novel and Relevant Model for Immune-Based Studies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 791081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratcliffe, M.J. Antibodies, immunoglobulin genes and the bursa of Fabricius in chicken B cell development. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, W.T.; Tjoelker, L.W.; Thompson, C.B. Avian B-cell development: Generation of an immunoglobulin repertoire by gene conversion. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1991, 9, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masteller, E.L.; Thompson, C.B. B Cell Development in the Chicken. Poult. Sci. 1994, 73, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriaco, E.; Píñera, P.P.; Díaz-Esnal, B.; Laurà, R. Age-related changes in the avian primary lymphoid organs (thymus and bursa of Fabricius). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 62, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, I.; Vervelde, L. Structure of the avian lymphoid system. In Avian Immunology; Davison, F., Kaspers, B., Schat, K.A., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2008; pp. 13–50. [Google Scholar]
- Madej, J.P.; Chrząstek, K.; Piasecki, T.; Wieliczko, A. New insight into the structure, development, functions and popular disorders of bursa Fabricii. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2013, 42, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, J. L’involution physiologique de la bourse de Fabricius et ses relations avec 1’apparition de la maturite sexuelle. C. R. Soc. Biol. 1913, 75, 638–648. [Google Scholar]
- Jolly, J. La bourse de Fabricius. Et les organes lymphoepitheliaux. Arch. D’anat. Micro. 1914, 22, 316–546. [Google Scholar]
- Schauder, W.; Martin, F. Lehrbuch der Anatomie der Haustiere. Anat. Hausvogel 1923, 4, 339–398. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, G. Normal Growth of the Bursa of Fabricius in Chickens-Sciencedirect. Poult. Sci. 1956, 35, 843–851. [Google Scholar]
- Rawal, S.; Kim, J.E.; Coulombe, R., Jr. Aflatoxin B1 in poultry: Toxicology, metabolism and prevention. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, K.; Bai, S.; Ding, X.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, J.; Fang, J.; Chen, K. Histological Lesions, Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis and T Cell Subsets Changes of Spleen in Chicken Fed Aflatoxin-contaminated Corn. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8567–8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological Properties and Their Involvement in Cancer Development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Shu, G.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; et al. Protective role of sodium selenite on histopathological lesions, decreased T-cell subsets and increased apoptosis of thymus in broilers intoxicated with aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Chen, Z.; Geng, Y.; Lai, W.; Tang, L.; et al. Effects of Dietary Selenium on Histopathological Changes and T Cells of Spleen in Broilers Exposed to Aflatoxin B1. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yuan, S.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Wang, F.; Cui, H.; Fang, J. Effects of sodium selenite on the decreased percentage of T cell subsets, contents of serum IL-2 and IFN-gamma induced by aflatoxin B1 in broilers. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guan, K.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, F.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ouyang, P.; Su, G.; et al. Effects of aflatoxin B1 on the cell cycle distribution of splenocytes in chickens. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2019, 32, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabourin, P.J.; Price, J.A.; Casbohm, S.L.; Perry, M.R.; Tuttle, R.S.; Rogers, J.V.; Rowell, K.S.; Estep, J.E.; Sabourin, C.L. Evaluation of Acute Immunotoxicity of Aerosolized Aflatoxin B1 in Female C57BL/6N Mice. J. Immunotoxicol. 2006, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, K.M.; Mendoza, K.M.; Coulombe, J.R.A. Altered Gene Response to Aflatoxin B1 in the Spleens of Susceptible and Resistant Turkeys. Toxins 2019, 11, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.G.; Zhao, L.H.; Wei, H.; Duan, G.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ji, C. Effects of Lipoic Acid on Immune Function, the Antioxidant Defense System, and Inflammation-Related Genes Expression of Broiler Chickens Fed Aflatoxin Contaminated Diets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5649–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalvi, R.R. An overview of aflatoxicosis of poultry: Its characteristics, prevention and reduction. Vet. Res. Commun. 1986, 10, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Fink-Gremmels, J.; Li, D.; Tong, X.; Tang, J.; Nan, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. An overview of aflatoxin B1 biotransformation and aflatoxin M1 secretion in lactating dairy cows. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, A.; Yu, R.C.; Chou, C.C.; Liu, J.R.; Cheng, K.C. Protective and Detoxifying Effects Conferred by Dietary Selenium and Curcumin against AFB1-Mediated Toxicity in Livestock: A Review. Toxins 2018, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.; Oğuz, H.; Demet, O.; Donmez, H.; Boydak, M.; Sur, E. Efficacy of polyvinylpolypyrrolidone in reducing the immunotoxicity of aflatoxin in growing broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2000, 41, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, A.W.; Ghareeb, K.; Abd-El-Fattah, A.A.M.; Twaruzek, M.; Böhm, J. Gross intestinal adaptations in relation to broiler performance during chronic aflatoxin exposure. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaya, S.R.; Vijayalakshmi, Y.; Sejian, V. Exploration of plant products and phytochemicals against aflatoxin toxicity in broiler chicken production: Present status. Toxicon 2021, 200, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Mishra, S.K.; Wang, T.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Fan, X.; Zeng, B.; Yang, M.; et al. AFB1 Induced Transcriptional Regulation Related to Apoptosis and Lipid Metabolism in Liver of Chicken. Toxins 2020, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zou, M.; Sun, Y.; Peng, X. gga-miR-451 Negatively Regulates Mycoplasma gallisepticum (HS Strain)-Induced Inflammatory Cytokine Production via Targeting YWHAZ. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- YZhao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zou, M.; Peng, X. Transcriptional Regulation of gga-miR-451 by AhR:Arnt in Mycoplasma gallisepticum (HS Strain) Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gao, W.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. MicroRNA transcriptome analysis in chicken kidneys in response to differing virulent infectious bronchitis virus infections. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3397–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, H.; Zheng, S.J. Epigenetic Upregulation of Chicken MicroRNA-16-5p Expression in DF-1 Cells following Infection with Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV) Enhances IBDV-Induced Apoptosis and Viral Replication. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01724-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zou, M.; Fu, Y.; Peng, X. Upregulated gga-miR-16-5p Inhibits the Proliferation Cycle and Promotes the Apoptosis of MG-Infected DF-1 Cells by Repressing PIK3R1-Mediated the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB Pathway to Exert Anti-Inflammatory Effect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, D.-R.; Yang, G.; Li, G.; Chang, C. Preclinical studies using miR-32-5p to suppress clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis via altering the miR-32-5p/TR4/HGF/Met signaling. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, M.; Qu, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, T.; Wen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Qian, J.; Pan, Q.X.; Wang, J.Y.; Xia, X.X.; Wang, X.L.; Zhu, Y.M.; Wang, Y.S. gga-miR-142-5p attenuates IRF7 signaling and promotes replication of IBDV by directly targeting the chMDA5’s 3’ untranslated region. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 221, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, M.; Deng, G.; Peng, X. gga-miR-142-3p negatively regulates Mycoplasma gallisepticum (HS strain)-induced inflammatory cytokine production via the NF-κB and MAPK signaling by targeting TAB2. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Liu, S.; Cao, Y.; Chao, G.; Wang, P.; Pan, H. Downregulation of ZC3H13 by miR-362-3p/miR-425-5p is associated with a poor prognosis and adverse outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging 2022, 14, 2304–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhan, T.; Lu, X.; Liao, T.; Guo, L.; et al. Gga-miR-19b-3p Inhibits Newcastle Disease Virus Replication by Suppressing Inflammatory Response via Targeting RNF11 and ZMYND11. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Luo, D.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-C.; Zhou, L.; Yang, T.-X.; Tang, C.; Shen, H.; Wang, K.-J. MiR 3180-5p promotes proliferation in human bladder smooth muscle cell by targeting PODN under hydrodynamic pressure. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudlsperger, C.; Bian, Y.; Contag Wise, S.; Burnett, J.; Coupar, J.; Yang, X.; Zhen, C.; Van Waes, C. TGF-β and NF-κB signal pathway cross-talk is mediated through TAK1 and SMAD7 in a subset of head and neck cancers. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1449–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Rheins, M.; Winter, A. The Significance of the Bursa of Fabricius of Chickens in Antibody Production: 3. Resistance to Salmonella Typhimurium Infection. Poult. Sci. 1959, 38, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Gou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Fan, Q.; Ding, F.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, S. Effects of Dietary Iron Level on Growth Performance, Immune Organ Indices and Meat Quality in Chinese Yellow Broilers. Animals 2020, 10, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, H.; Adam, F.A.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. Insights into the chicken bursa of fabricius response to Newcastle disease virus at 48 and 72 hours post-infection through RNA-seq. Veter. Microbiol. 2019, 236, 108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Han, B.; You, Z.; Qu, L.; Liu, C.; Song, J.; Lian, L.; Yang, N. Gga-miR-219b targeting BCL11B suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of Marek’s disease tumor cell MSB1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gen, L.; Pan, S.; Chen, J.; Zhu, W.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of differential expression microRNAs in the spleen between Beijing fatty chickens and Leghorns chickens. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2016, 49, 754–764. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.X.; Song, W.; Chen, Z.H.; Wei, J.H.; Liao, Y.J.; Lei, J.; Hu, M.; Chen, G.Z.; Liao, B.; Lu, J.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of a microRNA signature in stage II colon cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, R.; Viegas, S. Mycotoxin Exposure and Related Diseases. Toxins 2020, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos Pereira, C.; Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O. Prevalent Mycotoxins in Animal Feed: Occurrence and Analytical Methods. Toxins 2019, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasoli, M.; Yeap, S.K.; Tan, S.W.; Roohani, K.; Kristeen-Teo, Y.W.; Alitheen, N.B.; Rahaman, Y.A.; Aini, I.; Bejo, M.H.; Kaiser, P.; et al. Differential modulation of immune response and cytokine profiles in the bursae and spleen of chickens infected with very virulent infectious bursal disease virus. BMC Veter. Res. 2015, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Fan, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, W.; Qiao, X.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of differentially expressed mRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in chicken bursae of Fabricius during infection with very virulent infectious bursal disease virus. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorkquist, A. Toll Like Receptor and Clusters of Differentiation RNA Expression Levels in the Bursa of Fabricius of Broiler Chickens Challenged with Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. Min. 2003, 46, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Gu, C.; Wang, H.; Feng, J.; Bao, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S. Influence of Huangqin Decoction on the immune function and fecal microbiome of chicks after experimental infection with Escherichia coli O78. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Q.; Szodoray, P.; Zeher, M. Toll-Like Receptor Pathways in Autoimmune Diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Ding, M.; Guo, Y.; Su, A.; Zhai, M.; Tian, Y.; Li, K.; Sun, G.; Jiang, R.; Han, R.; et al. Use of transcriptomic analysis to identify microRNAs related to the effect of stress on thymus immune function in a chicken stress model. Res. Veter. Sci. 2021, 140, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.L.; Gerth, A.J.; Ranger, A.M.; Glimcher, L.H. NFATc1 and NFATc2 Together Control Both T and B Cell Activation and Differentiation. Immunity 2001, 14, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Heib, V.; Klein, M.; Doener, F.; Bopp, T.; Taube, C.; Radsak, M.; Schild, H.; Schmitt, E.; Stassen, M. Impaired Mast Cell-Driven Immune Responses in Mice Lacking the Transcription Factor NFATc2. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 6136–6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, K.M.; Mendoza, K.M.; Coulombe, J.R.A. Differential Transcriptome Responses to Aflatoxin B1 in the Cecal Tonsil of Susceptible and Resistant Turkeys. Toxins 2019, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NRC. Nutrition Requirements of Poultry, 9th ed.; National Academy Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso-Moreira, M.; Halbert, J.; Valloton, D.; Velten, B.; Chen, C.; Shao, Y.; Liechti, A.; Ascenção, K.; Rummel, C.; Ovchinnikova, S.; et al. Gene expression across mammalian organ development. Nature 2019, 571, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | CG (0) | TG1 (0.3) | TG2 (0.6) | TG3 (1.2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egg weight (g) | 52.37 ± 2.46 | 53.16 ± 2.40 | 52.6 ± 2.99 | 52.45 ± 3.81 |
| Yolk percentage | 0.26 ± 0.01 c | 0.27 ± 0.02 a | 0.26 ± 0.02 b | 0.28 ± 0.02 a |
| Albumen percentage | 0.61 ± 0.02 b | 0.61 ± 0.02 a | 0.61 ± 0.02 a | 0.60 ± 0.02 a |
| Albumen height (mm) | 5.65 ± 1.03 b | 5.90 ± 0.91 b | 5.26 ± 1.06 b | 6.09 ± 0.74 ac |
| Eggshell percentage | 6.56 ± 0.70 | 6.53 ± 0.68 | 6.66 ± 0.59 | 6.47 ± 0.46 |
| Shell thickness of blunt end (mm) | 0.37 ± 0.05 | 0.37 ± 0.04 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 0.36 ± 0.04 |
| Shell thickness of equator (mm) | 0.37 ± 0.04 a | 0.36 ± 0.04 a | 0.36 ± 0.03 ab | 0.29 ± 0.15 b |
| Shell thickness of sharp end (mm) | 0.36 ± 0.06 | 0.38 ± 0.04 | 0.38 ± 0.04 | 0.38 ± 0.02 |
| Shell strength (kg) | 4.49 ± 0.80 b | 6.13 ± 9.23 a | 6.64 ± 11.61 ab | 3.72 ± 0.95 ab |
| Shape index | 1.30 ± 0.03 a | 1.29 ± 0.03 b | 1.29 ± 0.04 b | 1.26 ± 0.03 c |
| Egg length (cm) | 54.01 ± 1.12 a | 53.76 ± 1.22 b | 53.79 ± 1.34 b | 52.4 ± 1.36 c |
| Egg width (cm) | 41.45 ± 0.74 | 41.83 ± 0.59 | 41.59 ± 0.95 | 41.5 ± 1.43 |
| Tissue | Sample | Raw Reads (Mb) | Clean Reads (Mb) | Effective Rate (%) | Clean Reads (Gb) | Raw Reads (Gb) | Map Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spleen | TG-3 | 60.67 | 53.60 | 88.35 | 9.10 | 8.04 | 87.84 |
| TG-2 | 48.00 | 42.87 | 89.31 | 7.20 | 6.43 | 88.24 | |
| TG-1 | 55.13 | 53.63 | 97.27 | 8.27 | 8.04 | 86.74 | |
| CG-3 | 59.44 | 57.26 | 96.33 | 8.92 | 8.39 | 88.43 | |
| CG-2 | 50.75 | 50.15 | 98.82 | 7.61 | 7.47 | 88.23 | |
| CG-1 | 55.22 | 54.56 | 98.80 | 8.28 | 8.13 | 87.71 | |
| Bursa of Fabricius | TG-3 | 65.22 | 64.55 | 98.97 | 9.78 | 9.62 | 90.10 |
| TG-2 | 58.05 | 57.38 | 98.85 | 8.71 | 8.55 | 87.50 | |
| TG-1 | 61.71 | 61.11 | 99.03 | 9.26 | 9.10 | 90.02 | |
| CG-3 | 63.54 | 62.84 | 98.90 | 9.53 | 9.36 | 91.25 | |
| CG-2 | 63.15 | 62.36 | 98.75 | 9.47 | 9.29 | 89.88 | |
| CG-1 | 68.41 | 67.70 | 98.96 | 10.26 | 10.09 | 90.07 |
| Tissue | Sample | Raw Reads (Mb) | Clean Reads (Mb) | Effective Rate (%) | Raw Base (Gb) | Clean Base (Gb) | Map Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spleen | TG-3 | 12.75 | 10.71 | 84.03 | 0.64 | 0.54 | 74.70 |
| TG-2 | 15.53 | 12.86 | 82.78 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 76.00 | |
| TG-1 | 10.55 | 8.49 | 80.46 | 0.53 | 0.42 | 74.80 | |
| CG-3 | 12.84 | 11.21 | 87.29 | 0.64 | 0.25 | 82.80 | |
| CG-2 | 14.12 | 12.53 | 88.75 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 78.60 | |
| CG-1 | 13.25 | 11.56 | 87.24 | 0.66 | 0.25 | 81.00 | |
| Bursa of Fabricius | TG-3 | 16.27 | 13.52 | 83.10 | 0.81 | 0.68 | 69.30 |
| TG-2 | 9.46 | 7.72 | 81.60 | 0.47 | 0.39 | 73.70 | |
| TG-1 | 8.82 | 7.42 | 84.07 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 74.90 | |
| CG-3 | 16.29 | 13.75 | 84.40 | 0.81 | 0.69 | 70.70 | |
| CG-2 | 14.52 | 11.74 | 80.88 | 0.73 | 0.59 | 75.00 | |
| CG-1 | 14.16 | 12.11 | 85.52 | 0.71 | 0.61 | 74.30 |
| miRNA | LogFC | p-Value | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spleen | gga-miR-451-5p | −6.71 | 1.38 × 10−13 | [34,35] |
| gga-miR-7b-5p | −6.57 | 1.79 × 10−12 | [36] | |
| gga-miR-16-5p | −6.30 | 1.39 × 10−10 | [37,38,39] | |
| gga-miR-32-5p | −6.21 | 5.18 × 10−10 | [39,40] | |
| gga-miR-1454-3p | 5.76 | 1.78 × 10−7 | [36] | |
| gga-miR-301a-3p | 5.79 | 1.40 × 10−7 | [33] | |
| novel-gga-miR-44-5p | 5.87 | 5.79 × 10−8 | - | |
| gga-miR-219b-3p | 6.32 | 2.07 × 10−10 | [33] | |
| gga-miR-142-3p | 6.57 | 4.55 × 10−12 | [41,42] | |
| gga-miR-142-5p | 7.03 | 3.88 × 10−16 | [41,42] | |
| Bursa of Fabricius | gga-miR-425-5p | −4.97 | 6.46 × 10−4 | [43] |
| gga-miR-19b-5p | −4.65 | 3.57 × 10−4 | [44] | |
| gga-miR-3180-5p | −4.43 | 4.95 × 10−3 | [45] | |
| gga-miR-425-3p | −4.24 | 8.73 × 10−3 | [46] | |
| gga-miR-510-3p | −4.20 | 9.92 × 10−3 | - | |
| gga-miR-5116-3p | 3.69 | 1.97 × 10−2 | - | |
| novel-gga-miR-5-3p | 3.70 | 1.92 × 10−2 | - | |
| novel-gga-miR-25-5p | 3.98 | 9.19 × 10−3 | - | |
| gga-miR-143-5p | 5.15 | 7.00 × 10−5 | [40] | |
| gga-miR-6606-5p | 5.40 | 1.34 × 10−5 | [41] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, M.; Su, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Li, F. Integrated Transcriptome Analysis Reveals mRNA–miRNA Pathway Crosstalk in Roman Laying Hens’ Immune Organs Induced by AFB1. Toxins 2022, 14, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110808
Xu Z, Liu Q, Liu X, Yang M, Su Y, Wang T, Li D, Li F. Integrated Transcriptome Analysis Reveals mRNA–miRNA Pathway Crosstalk in Roman Laying Hens’ Immune Organs Induced by AFB1. Toxins. 2022; 14(11):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110808
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhongxian, Qian Liu, Xueqin Liu, Maosen Yang, Yuan Su, Tao Wang, Diyan Li, and Feng Li. 2022. "Integrated Transcriptome Analysis Reveals mRNA–miRNA Pathway Crosstalk in Roman Laying Hens’ Immune Organs Induced by AFB1" Toxins 14, no. 11: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110808
APA StyleXu, Z., Liu, Q., Liu, X., Yang, M., Su, Y., Wang, T., Li, D., & Li, F. (2022). Integrated Transcriptome Analysis Reveals mRNA–miRNA Pathway Crosstalk in Roman Laying Hens’ Immune Organs Induced by AFB1. Toxins, 14(11), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110808