Characterization of a Family of Scorpion Toxins Modulating Ca2+-Activated Cl− Current in Vascular Myocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
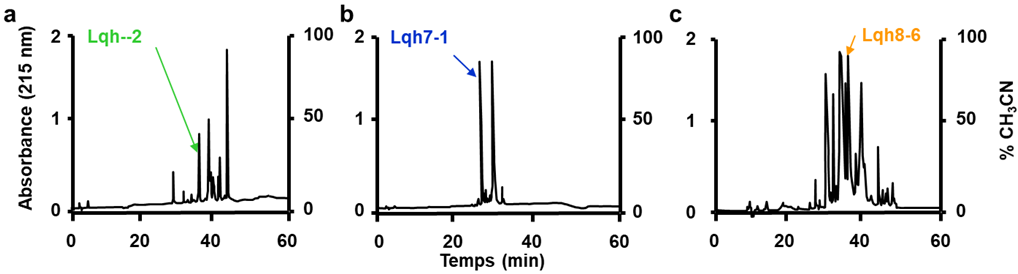
2.1. Purification and Characterization of Lqh Peptides
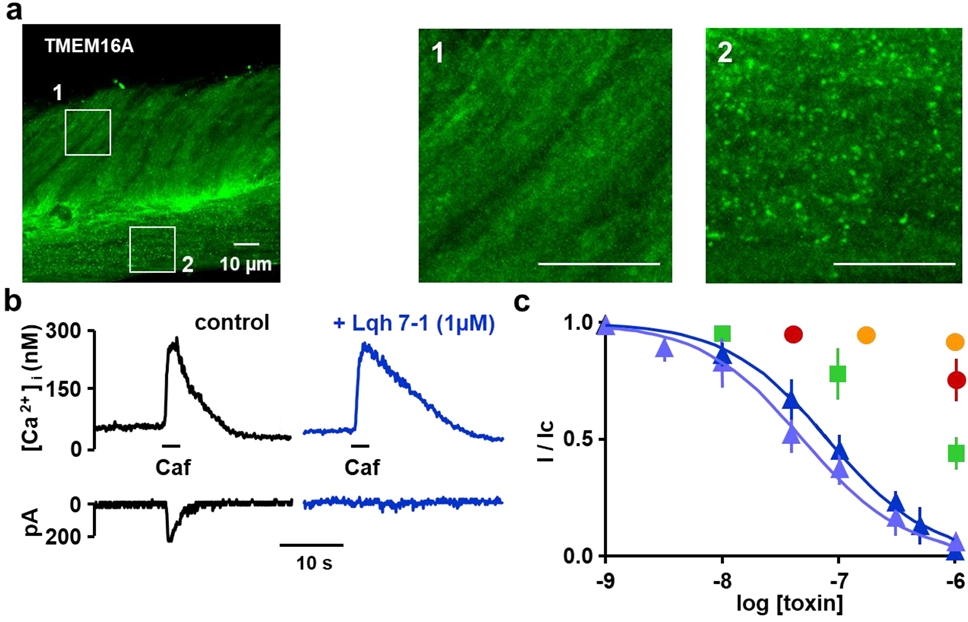
2.2. Expression of TMEM16A/Ano1 in Rat Portal Vein Smooth Muscle
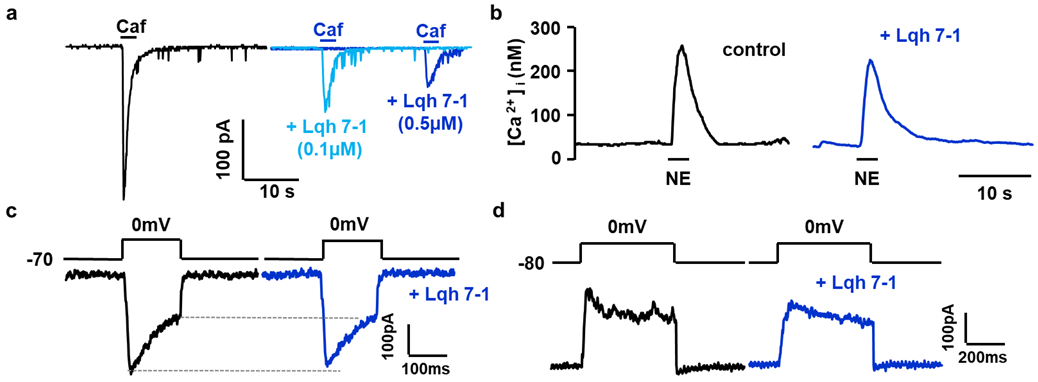
2.3. Inhibitory Effects on Calcium Activated Chloride Current Expressed in VSMC
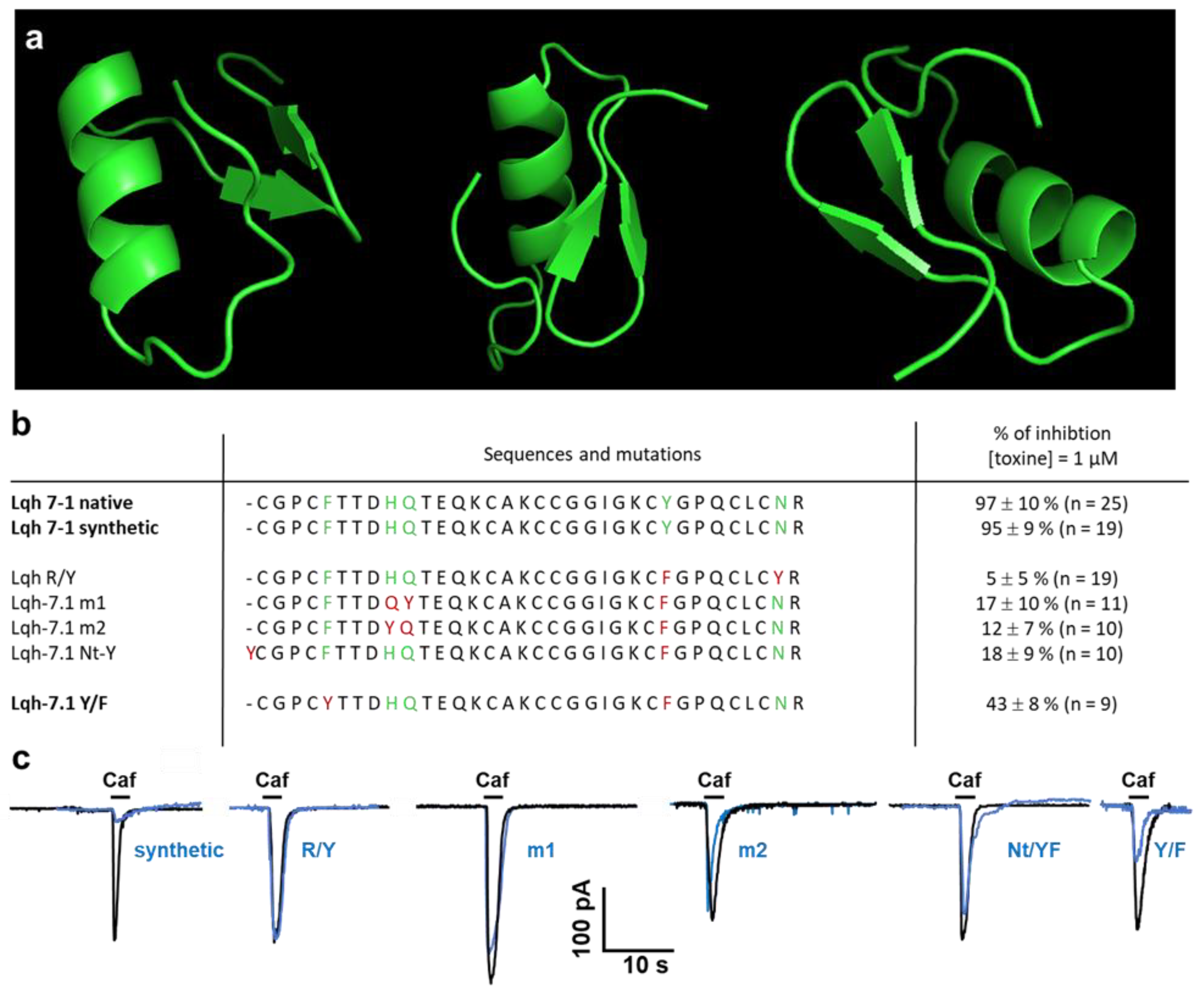
2.4. Specificity of Lqh 7.1 Peptide
2.5. Modeling of Lqh 7-1 Toxin
3. Discussion and Perspectives
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Purification of Lqh’s Peptides
4.2. Ion Spray Mass Spectroscopy
4.3. Determination of Lqh’s Sequences
4.4. Synthesis of Lqh 7-1
4.5. Circular Dichroism
4.6. Preparation of RNA and RT-PCR
4.7. Immnohistochemistry Coupled to Fluorescence
4.8. Animals
4.9. Cell Preparation
4.10. [Ca2+]i Measurements
4.11. Membrane Current and [Ca2+]i Measurements
4.12. Solutions
4.13. Chemicals and Drugs
4.14. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okada, Y.; Sato-Numata, K.; Sabirov, R.Z.; Numata, T. Cell Death Induction and Protection by Activation of Ubiquitously Expressed Anion/Cation Channels. Part 2: Functional and Molecular Properties of ASOR/PAC Channels and Their Roles in Cell Volume Dysregulation and Acidotoxic Cell Death. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, K. The Ca2+-activated chloride channel ANO1/TMEM16A: An emerging therapeutic target for epithelium-originated diseases? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1412–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stölting, G.; Fischer, M.; Fahlke, C. CLC channel function and dysfunction in health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hübner, C.A.; Schroeder, B.C.; Ehmke, H. Regulation of vascular tone and arterial blood pressure: Role of chloride transport in vascular smooth muscle. Pflug. Arch. 2015, 467, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, A.; Weir, N.; Robertson, C.; He, L.; Betsholtz, C.; Longden, T.A. The Ion Channel and GPCR Toolkit of Brain Capillary Pericytes. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020, 14, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilius, B.; Sehrer, J.; Viana, F.; De Greef, C.; Raeymaekers, L.; Eggermont, J.; Droogmans, G. Volume-activated Cl− currents in different mammalian non-excitable cell types. Pflug. Arch. 1994, 428, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, J.; Duan, D.; Janiak, R.; Kuenzli, K.; Horowitz, B.; Hume, J.R. Functional and molecular expression of volume-regulated chloride channels in canine vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Physiol. 1998, 507 Pt 3, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.T.; Conway, M.A.; Knot, H.J.; Brayden, J.E. Chloride channel blockers inhibit myogenic tone in rat cerebral arteries. J. Physiol. 1997, 502 Pt 2, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, A.; Pacaud, P.; Loirand, G.; Mironneau, C.; Mironneau, J. Pharmacological block of Ca2+-activated Cl− current in rat vascular smooth muscle cells in short-term primary culture. Pflug. Arch. 1991, 419, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, F.S.; Barna, T.J. Chloride ion currents contribute functionally to norepinephrine-induced vascular contraction. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, H151–H160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajanaphanich, M.; Schultz, C.; Rudolf, M.T.; Wasserman, M.; Enyedi, P.; Craxton, A.; Shears, S.B.; Tsien, R.Y.; Barrett, K.E.; Traynor-Kaplan, A. Long-term uncoupling of chloride secretion from intracellular calcium levels by Ins(3,4,5,6)P4. Nature 1994, 371, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismailov, I.I.; Fuller, C.M.; Berdiev, B.K.; Shlyonsky, V.G.; Benos, D.J.; Barrett, K.E. A biologic function for an «orphan» messenger: D-myo-inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate selectively blocks epithelial calcium-activated chloride channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10505–10509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilius, B.; Prenen, J.; Voets, T.; Eggermont, J.; Bruzik, K.S.; Shears, S.B.; Droogmans, G. Inhibition by inositoltetrakisphosphates of calcium- and volume-activated Cl- currents in macrovascular endothelial cells. Pflug. Arch. 1998, 435, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, B.C.; Cheng, T.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Expression cloning of TMEM16A as a calcium-activated chloride channel subunit. Cell 2008, 134, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.D.; Cho, H.; Koo, J.Y.; Tak, M.H.; Cho, Y.; Shim, W.-S.; Park, S.P.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.; Kim, B.-M.; et al. TMEM16A confers receptor-activated calcium-dependent chloride conductance. Nature 2008, 455, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, A.; Caci, E.; Ferrera, L.; Pedemonte, N.; Barsanti, C.; Sondo, E.; Pfeffer, U.; Ravazzolo, R.; Zegarra-Moran, O.; Galietta, L.J.V. TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with calcium-dependent chloride channel activity. Science 2008, 322, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matchkov, V.V.; Black Joergensen, H.; Kamaev, D.; Hoegh Jensen, A.; Beck, H.C.; Skryabin, B.V.; Aalkjaer, C. A paradoxical increase of force development in saphenous and tail arteries from heterozygous ANO1 knockout mice. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, H.; Zheng, L.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.-B.; Wang, G.-L.; Du, Y.-H.; Lv, X.-F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.-G.; et al. Downregulation of TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel contributes to cerebrovascular remodeling during hypertension by promoting basilar smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation 2012, 125, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.-L.; Sun, L.; Zheng, H.-Q.; Wang, G.-L.; Du, Y.-H.; Lv, X.-F.; Ma, M.-M.; Guan, Y.-Y. Smooth muscle-specific TMEM16A expression protects against angiotensin II-induced cerebrovascular remodeling via suppressing extracellular matrix deposition. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2019, 134, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaudeau, S.; Leprêtre, N.; Mironneau, J. Chloride and monovalent ion-selective cation currents activated by oxytocin in pregnant rat myometrial cells. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1994, 171, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, H.A.; Parkington, H.C. Single channel Cl− and K+ currents from cells of uterus not treated with enzymes. Pflug. Arch. 1987, 410, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Guo, S.; Wang, X.; Pang, C.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, Y.; An, H. Recent advances in TMEM16A: Structure, function, and disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 7856–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Xiu, R.; Jia, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yi, J. Cepharanthine, a novel selective ANO1 inhibitor with potential for lung adenocarcinoma therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 119132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochat, H.; Bernard, P.; Couraud, F. Scorpion toxins: Chemistry and mode of action. Adv. Cytopharmacol. 1979, 3, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Liu, S.-L.; Sun, P.-B.; Pan, H.; Tian, C.-L.; Zhang, L.-H. Peptide toxins and small-molecule blockers of BK channels. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Gallego, G.; Navia, M.A.; Reuben, J.P.; Katz, G.M.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; Garcia, M.L. Purification, sequence, and model structure of charybdotoxin, a potent selective inhibitor of calcium-activated potassium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 3329–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crest, M.; Jacquet, G.; Gola, M.; Zerrouk, H.; Benslimane, A.; Rochat, H.; Mansuelle, P.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F. Kaliotoxin, a novel peptidyl inhibitor of neuronal BK-type Ca2+-activated K+ channels characterized from Androctonus mauretanicus mauretanicus venom. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBin, J.A.; Maggio, J.E.; Strichartz, G.R. Purification and characterization of chlorotoxin, a chloride channel ligand from the venom of the scorpion. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 264 Pt 1, C361–C369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.; Burks, S.R.; Frank, J.A. Chlorotoxin—A Multimodal Imaging Platform for Targeting Glioma Tumors. Toxins 2018, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroceanu, L.; Gillespie, Y.; Khazaeli, M.B.; Sontheimer, H. Use of chlorotoxin for targeting of primary brain tumors. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4871–4879. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, D.L.; Vatanpour, H.; Harvey, A.L.; Boyot, P.; Pinkasfeld, S.; Doljansky, Y.; Bouet, F.; Ménez, A. Neuromuscular effects of some potassium channel blocking toxins from the venom of the scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus hebreus. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 1994, 32, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, A.; Beg, O.U.; Shafqat, J.; Zaidi, Z.H.; Jörnvall, H. Characterization of two different peptides from the venom of the scorpion Buthus sindicus. FEBS Lett. 1989, 257, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytgat, J.; Debont, T.; Rostoll, K.; Müller, G.J.; Verdonck, F.; Daenens, P.; van der Walt, J.J.; Possani, L.D. Purification and partial characterization of a «short» insectotoxin-like peptide from the venom of the scorpion Parabuthus schlechteri. FEBS Lett. 1998, 441, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Alam, M.; Abbasi, A.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Fry, B.G.; Kalbacher, H.; Voelter, W. Structure-Activity Relationship of Chlorotoxin-like Peptides. Toxins 2016, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loirand, G.; Pacaud, P.; Baron, A.; Mironneau, C.; Mironneau, J. Large conductance calcium-activated non-selective cation channel in smooth muscle cells isolated from rat portal vein. J. Physiol. 1991, 437, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, J.L.; Macrez-Leprêtre, N.; Mironneau, J. Angiotensin II-activated Ca2+ entry-induced release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores in rat portal vein myocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 118, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loirand, G.; Mironneau, C.; Mironneau, J.; Pacaud, P. Two types of calcium currents in single smooth muscle cells from rat portal vein. J. Physiol. 1989, 412, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, J.L.; Drobecq, H.; Sautiere, P.; Tartar, A.; Mironneau, J.; Qar, J.; Lavie, J.L.; Hugues, M. Purification of a new dimeric protein from Cliona vastifica sponge, which specifically blocks a non-L-type calcium channel in mouse duodenal myocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontems, F.; Gilquin, B.; Roumestand, C.; Ménez, A.; Toma, F. Analysis of side-chain organization on a refined model of charybdotoxin: Structural and functional implications. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 7756–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitri, C.; Sharma, H.; Corvol, H.; Tabary, O. TMEM16A/ANO1: Current Strategies and Novel Drug Approaches for Cystic Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, S.C.; Yang, H. Structure–Function of TMEM16 Ion Channels and Lipid Scramblases. In Ion Channels in Biophysics and Physiology; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Zhou, L., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, S.; Prendergast, C.; Arrowsmith, S. Calcium-Activated Chloride Channels in Myometrial and Vascular Smooth Muscle. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 751008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsdale, R.L.; Pipatpolkai, T.; Agostinelli, E.; Russell, A.J.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Tammaro, P. An outer-pore gate modulates the pharmacology of the TMEM16A channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023572118. Available online: http://www.pnas.org/content/118/34/e2023572118 (accessed on 13 December 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, M.C.; Silva, I.A.; Figueira, M.F.; Amaral, M.D.; Lopes-Pacheco, M. Pharmacological Modulation of Ion Channels for the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 13, 693–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, C.; Wei, L.; Tytgat, J.; Droogmans, G.; Nilius, B. Chlorotoxin does not inhibit volume-regulated, calcium-activated and cyclic AMP-activated chloride channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesús-Pérez, J.J.; Cruz-Rangel, S.; Espino-Saldaña, Á.E.; Martínez-Torres, A.; Qu, Z.; Hartzell, H.C.; Corral-Fernandez, N.E.; Pérez-Cornejo, P.; Arreola, J. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, cholesterol, and fatty acids modulate the calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A (ANO1). Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, C.M.; Acheson, K.E.; Rorsman, N.J.G.; Jongkind, R.C.; Tammaro, P. Contrasting effects of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate on cloned TMEM16A and TMEM16B channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2984–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.J.; Voit-Ostricki, L.; Lovas, S.; Watts, C.R. Effects of Selective Substitution of Cysteine Residues on the Conformational Properties of Chlorotoxin Explored by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardevet, L.; Rani, D.; Aziz, T.A.E.; Bazin, I.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Fadl, M.; Brambilla, E.; De Waard, M. Chlorotoxin: A Helpful Natural Scorpion Peptide to Diagnose Glioma and Fight Tumor Invasion. Toxins 2015, 7, 1079–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, C.G.; Walker, D.G.; Miller, D.M.; Butte, P.; Morrison, B.; Kittle, D.S.; Hansen, S.J.; Nufer, K.L.; Byrnes-Blake, K.A.; Yamada, M.; et al. Phase 1 Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Fluorescence Imaging Study of Tozuleristide (BLZ-100) in Adults with Newly Diagnosed or Recurrent Gliomas. Neurosurgery 2019, 85, E641–E649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamelak, A.N.; Rosenfeld, S.; Bucholz, R.; Raubitschek, A.; Nabors, L.B.; Fiveash, J.B.; Shen, S.; Khazaeli, M.B.; Colcher, D.; Liu, A.; et al. Phase I Single-Dose Study of Intracavitary-Administered Iodine-131-TM-601 in Adults With Recurrent High-Grade Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 24, 3644–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Starr, R.; Chang, W.-C.; Aguilar, B.; Alizadeh, D.; Wright, S.L.; Yang, X.; Brito, A.; Sarkissian, A.; Ostberg, J.R.; et al. Chlorotoxin-directed CAR T cells for specific and effective targeting of glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiseh, M.; Gabikian, P.; Bahrami, S.-B.; Veiseh, O.; Zhang, M.; Hackman, R.C.; Ravanpay, A.C.; Stroud, M.R.; Kusuma, Y.; Hansen, S.J.; et al. Tumor paint: A chlorotoxin:Cy5.5 bioconjugate for intraoperative visualization of cancer foci. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6882–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulley, S.; Neeb, Z.P.; Burris, S.K.; Bannister, J.P.; Thomas-Gatewood, C.M.; Jangsangthong, W.; Jaggar, J.H. TMEM16A/ANO1 channels contribute to the myogenic response in cerebral arteries. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, N.; Ilkan, Z.; Pearson, C.L.; Pfeiffer, T.; Singhal, P.; Rock, J.R.; Sethi, H.; Gill, D.; Attwell, D.; Tammaro, P. The Ca2+-gated channel TMEM16A amplifies capillary pericyte contraction and reduces cerebral blood flow after ischemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cil, O.; Chen, X.; Askew Page, H.R.; Baldwin, S.N.; Jordan, M.C.; Myat Thwe, P.; Anderson, M.O.; Haggie, P.M.; Greenwood, I.A.; Roos, K.P.; et al. A small molecule inhibitor of the chloride channel TMEM16A blocks vascular smooth muscle contraction and lowers blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoury, B.; Tamuleviciute, A.; Tammaro, P. TMEM16A/anoctamin 1 protein mediates calcium-activated chloride currents in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. J. Physiol. 2010, 588 Pt 13, 2305–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Huang, C.; Ma, M.; Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, G.; Du, Y.; et al. TMEM16A inhibits angiotensin II-induced basilar artery smooth muscle cell migration in a WNK1-dependent manner. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3994–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.-M.; Gao, M.; Guo, K.-M.; Wang, M.; Li, X.-Y.; Zeng, X.-L.; Sun, L.; Lv, X.-F.; Du, Y.-H.; Wang, G.-L.; et al. TMEM16A Contributes to Endothelial Dysfunction by Facilitating Nox2 NADPH Oxidase–Derived Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in Hypertension. Hypertension 2017, 69, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Liu, S.; Liang, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, T.; Luo, S.; Gao, K.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Bai, L.; et al. Ca2+-activated Cl− channel TMEM16A inhibition by cholesterol promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 29, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-L.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.-S.; Cheng, L.-M.; Liu, W.-L.; Chen, X.-F.; Li, Y.-J.; Guan, Y.-Y.; Zeng, X.; Du, Y.-H. Blockade of TMEM16A protects against renal fibrosis by reducing intracellular Cl- concentration. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 179, 3043–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.G.; Kwon, O.; Hwang, E.M.; Kim, H.W.; Park, J.Y. Conditional deletion of TMEM16A in cholinergic neurons of the medial habenula induces anhedonic-like behavior in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 426, 113841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sautière, P.; Cestèle, S.; Kopeyan, C.; Martinage, A.; Drobecq, H.; Doljansky, Y.; Gordon, D. New toxins acting on sodium channels from the scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus suggest a clue to mammalian vs. insect selectivity. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert, M.; Laine, B.; Helbecque, N.; Mornon, J.P.; Hénichart, J.P.; Sautière, P. Conformational study of the chromosomal protein MC1 from the archaebacterium Methanosarcina barkeri. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1038, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flahaut, C.; Mizon, C.; Aumercier-Maes, P.; Colson, P.; Bailly, C.; Sautiere, P.; Mizon, J. Disulphide bonds assignment in the inter-alpha-inhibitor heavy chains--structural and functional implications. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 255, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.J.; Hill, C.S.; Martin, S.R.; Thomas, J.O. Alpha-helix in the carboxy-terminal domains of histones H1 and H5. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ano2 | Ano3 | Ano4 | Ano6 | Ano7 | Ano8 | Ano9 | Ano10 | Cftr |
| 0.007 | 0.0007 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.07 | 0.003 |
| Clcn1 | Clcn2 | Clcn3 | Clcn4 | Clcn5 | Clcn6 | Clcn7 | Clcnka | Clcnkb |
| 0 | 0.005 | 0 | 0 | 0.0002 | 0.02 | 0.002 | 0.0004 | 0.001 |
| Slc12a1 | Slc12a2 | Slc12a4 | Slc12a5 | Slc12a6 | Slc12a7 | Slc12a9 | Sema3g | Sadd45a |
| 0.001 | 0.126 | 0.044 | 0.0001 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0 | 0.057 | 0.154 |
| Lrrc8a | Lrrc8b | Lrrc8c | Lrrc8d | Lrrc8e | Ttyh1 | Ttyh2 | Ttyh3 | Tmem206 |
| 0.065 | 0.045 | 0.020 | 0.028 | 0 | 0.077 | 0 | 0.019 | 0.004 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morel, J.-L.; Mokrzycki, N.; Lippens, G.; Drobecq, H.; Sautière, P.; Hugues, M. Characterization of a Family of Scorpion Toxins Modulating Ca2+-Activated Cl− Current in Vascular Myocytes. Toxins 2022, 14, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110780
Morel J-L, Mokrzycki N, Lippens G, Drobecq H, Sautière P, Hugues M. Characterization of a Family of Scorpion Toxins Modulating Ca2+-Activated Cl− Current in Vascular Myocytes. Toxins. 2022; 14(11):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110780
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorel, Jean-Luc, Nathalie Mokrzycki, Guy Lippens, Hervé Drobecq, Pierre Sautière, and Michel Hugues. 2022. "Characterization of a Family of Scorpion Toxins Modulating Ca2+-Activated Cl− Current in Vascular Myocytes" Toxins 14, no. 11: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110780
APA StyleMorel, J.-L., Mokrzycki, N., Lippens, G., Drobecq, H., Sautière, P., & Hugues, M. (2022). Characterization of a Family of Scorpion Toxins Modulating Ca2+-Activated Cl− Current in Vascular Myocytes. Toxins, 14(11), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110780





